CM22009 - Machine Learning
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Supervised Learning
A machine learning technique where an algorithm learns from a labelled dataset to make predictions or classifications on new, unseen data. The algorithm is trained on input-output pairs, where each input has a correct output label, similar to how a student learns from an example with a provided answer.
Unsupervised Learning
A type of machine learning that uses algorithms to find patterns and relationships in unlabelled data without any prior guidance or “ground truth”. Unlike supervised learning, which uses labelled data, unsupervised learning algorithms must discover hidden structures and insights on their own. Common tasks include clustering, association and dimensionality reduction
Reinforcement Learning
A machine learning paradigm where an agent learns to make optimal decisions in an environment through trial and error. It learns by taking actions, receiving rewards or penalties for those actions, and then adjusting its behaviour to maximise its cumulative reward over time
Supervised Learning Model Examples
Rainfall Forecasting, Object Detection, Classifying Fraudulent Transactions
Unsupervised Learning Examples
Customer Segmentation, Anomaly Detection
Reinforcement Learning Examples
Personalised Learning, Traffic Control, Gaming AI
Linear Regression Formula
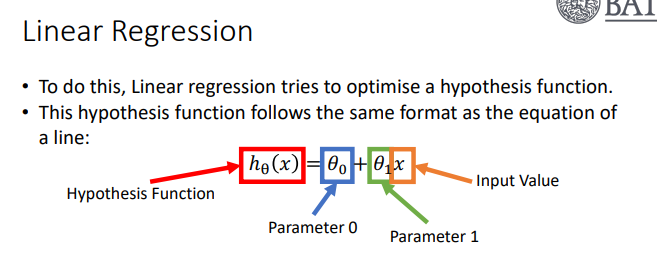
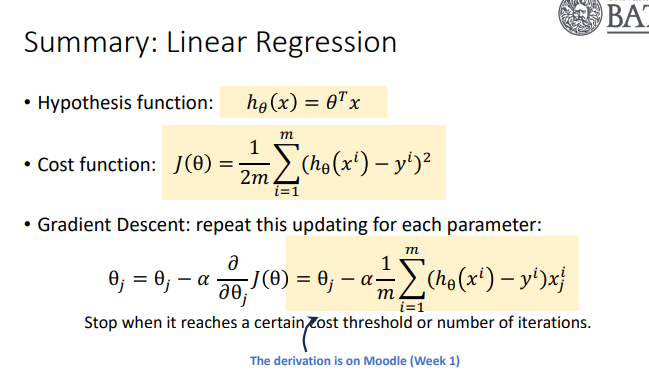
Linear Regression: Hypothesis Function, Cost Function, Gradient Descent Formula
Regression Problem
Using statistical and machine learning methods to predict a continuous numerical value (the dependent variable) based on one or more other variables (the independent variables)
Classification Problem
A type of supervised learning in machine learning where the goal is to predict a class label for a given input, meaning the output is a category rather than a continuous value
Types of Classification
Binary, Multi-class, Multi-label
Binary Classification
Classification between two classes (e.g. is this email spam or ham)
Multi-Class Classification
Classification between more than two classes, each input corresponds to one class (e.g. is this picture a dog, cat or goat)
Multi-Label Classification
Classification tasks where an input may have multiple classes associated with it (e.g. what colour does this image contain)
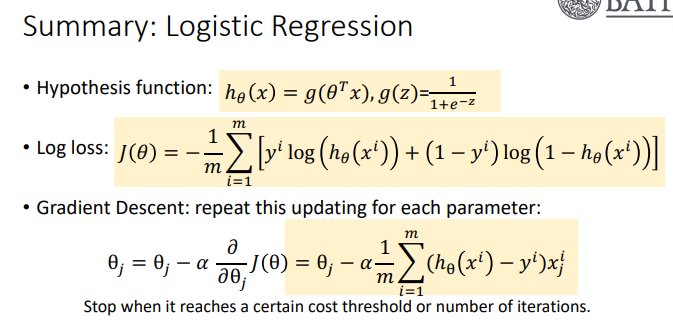
Logistic Regressions
A statistical method used to model the probability of a binary outcome based on one or more predictor variables
Logistic Regression: Hypothesis Function, Log Loss, Gradient Descent
K-Nearest Neighbour (KNN) Algorithm
A machine learning method used for classification and regression that works by finding the “k” nearest data points to a new, unknown data point
Advantages of KNN
Intuitive and easy to implement, No “training” needed, Adaptable
Disadvantages of KNN
Computationally expensive at the testing stage, Must hold training data in memory, Curse of Dimensionality (More points become equidistant in higher dimensions)
KNN Classification Examples
Recommendation System, Medical Diagnosis (finding similar patient cases)
KNN Regression Examples
House Price Prediction, Stock Price Forecasting
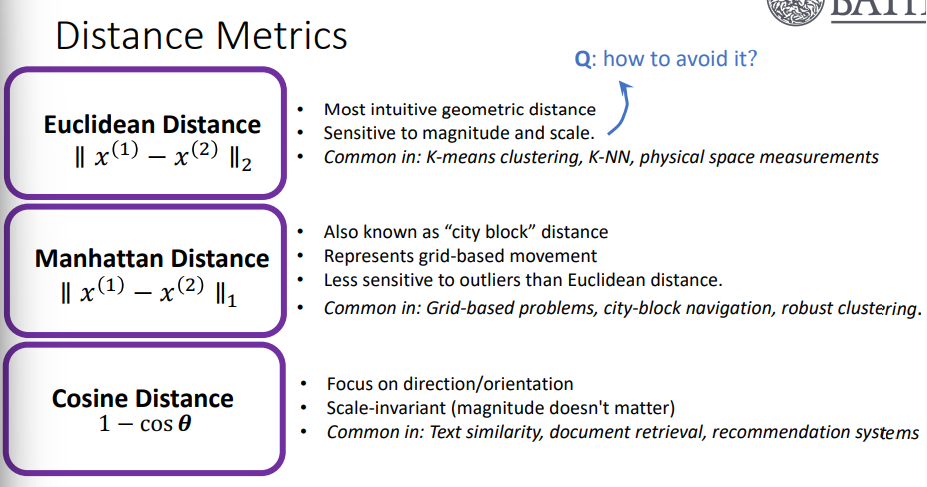
Distance Metrics
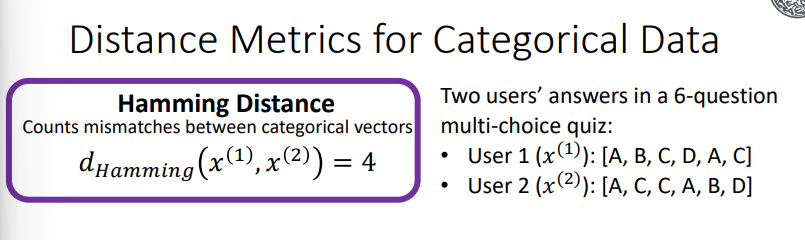
Hamming Distance
Counts mismatches between categorical vectors
Jaccard Distance
Why use Hamming Distance
Data is ordered and vectors are of the same length, You care about position-by-position mismatches (e.g. DNA sequence, multi-choice answers)
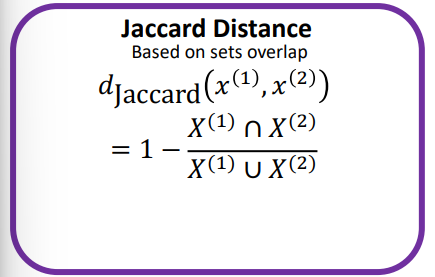
Jaccard Distance
Data is set-like (unordered categories, tags, items), You care about overlap vs total unique items (e.g. customer segmentation, shopping baskets, keywords/tags in documents)
Bias
Measures how far off, on average, a model’s predictions are from the ground truth values
Variance
Measures how much a model’s predictions change with different training datasets
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
When choosing the best model to fit your data you must strike a balance between high bias (prone to underfitting by missing important patterns) and high variance (prone to overfitting by capturing noise)