2.3 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Wireless frequencies
Can be 2.4GHz or 5GHz, sometimes both.
Channels
Grouped by frequencies, and numbered by the IEEE; non-overlapping channels are ideal.
Regulations for 802.11 networks
Implemented in most countries, and typically concerns energy use, spectrum use, and power output.
2.4GHz vs 5GHz frequency usage
5GHz provides many more 20MHz channels to transmit data and less interference.
Bluetooth
Operates in wireless peripheral devices like headsets and speakers, using unlicensed ISM band at 2.4GHz.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
Termed for the range around Bluetooth devices, which is less than 10 meters of operation.
802.11a
The first wireless standard released in 1999, operating exclusively in the 5GHz range with speeds of 54 Mbit/s and a smaller range compared to 802.11b.
802.11b
Released in 1999, operates in the 2.4GHz range with a throughput of 11 Mbit/s, has a longer range than 802.11a, but introduces frequency conflict with other devices.
802.11g
Released in 2003, operates at 2.4GHz with speeds of 54 Mbit/s, backward-compatible with 802.11b, but shares the same frequency conflicts.
802.11n (Wi-Fi 4)
Released in 2009, can operate at both 2.4GHz and 5GHz with a maximum throughput of 600 Mbit/s using MIMO technology.
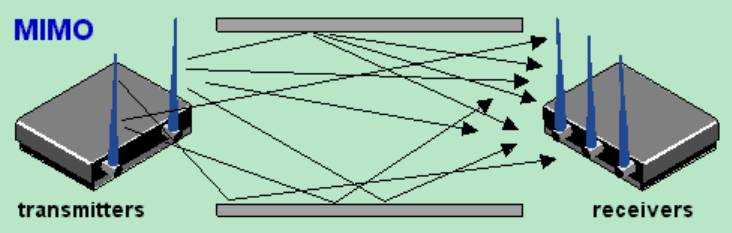
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)
Wireless technology that uses multiple antennas as both transmitters and receivers, boosting data transmission capabilities.
802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5)
Released in 2014, operates exclusively in the 5GHz range with a maximum throughput of 6936 Mbit/s and includes multi-user MIMO capabilities.
802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6)
Released in 2021, operates on both 5GHz and 2.4GHz with a maximum throughput of 9608 Mbit/s, introduces OFDMA for efficient connections in dense environments.
OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)
A technology introduced in Wi-Fi 6 that allows multiple users to share the same channel efficiently by dividing it into smaller sub-channels, enhancing network performance in crowded areas.
Long-range fixed wireless
Technique to extend 802.11 signals over large distances using directional antennas; requires compliance with local regulations.
Near-field communication (NFC)
Uses RFID signals for short-distance communication and authentication, commonly used for online payments and identification.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID)
Uses radio waves to identify tags embedded in objects for tracking purposes, featuring bi-directional communication and various tag formats.