OB Exam 2 Chapter 12: nursing management during pregnancy
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Pre-conception care
prior to conception
interconception care
between pregnancies
goal of Preconception and Interconception Care
Prevent adverse pregnancy outcomes
focus of Preconception and Interconception Care
General health status of both partners
Preconception and Interconception Care: areas addressed
-Reproductive planning
-Physical exam
-Personal and family history
-Lab screening
-Nutritional status/weight/exercise
-Vaccines (flu, rubella, varicella, DPT)
-Assess teratogen exposure
-Folic acid intake of 400 - 800 mcg/day (per risk profile)
-Others
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: accutane
-Serious birth defects
-for current use not prior use
-especially teens and early 20's
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: alcohol misuse
Fetal alcohol syndrome.
NO safe time for alcohol in pregnancy
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: Antiepileptic meds. (Valporic acid)
Teratogenic
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: Diabetes (preconception)
3-fold increase in birth defects in those with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes if not well managed
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: folic acid deficiency
Associated with NTD's (neural tube defects)
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: HIV/AIDS
Antiretroviral treatment (significantly reduces risk to baby)
**catch early
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: STI's
-Chlamydia and Gonorrhea .. Associated with ectopic pregnancy and infertility
-Other STI's may be associated with intellectual and physical disabilities
risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: smoking
Preterm birth and LBW
greatest risk from environmental factors
-Embryo is at greatest risk from environmental factors between day 17 and day 56 after conception
-The nurse's role as advocate and educator is paramount
Importance of Adequate Glycemic Control
Should be addressed preconception and interconception
Incidence of diabetes in pregnancy has been increasing related to increased obesity
A1C
-Measures average blood glucose level over past 3 months
-Should be lower than 6.5% prenatally
-Should be lower than 6-7% in pregnancy
-Elevated levels are associated with congenital anomalies, pre-eclampsia, macrosomia
**if she enters pregnancy with DM already, otherwise A1C not used a lot bc its measured over months
recommendations for adequate glycemic control
Self monitoring of fasting and post prandial blood glucose levels
ADA targets for women with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes
-Fasting: Below 95 mg/dL
-1 hour postprandial: Below 140 mg/dL
-2 hour postprandial: Below 120 mg/dL
Treatment Recommendations for Gestational Diabetes
-Gestational Diabetes: Manifests for first time during pregnancy **while pregnant, not bc she is pregnant
-First treatment: Diet control
-Second treatment: Insulin (does not cross the placenta)
-Third treatment: Oral hypoglycemic
Components Specific to a Prenatal Visit
Due date determination
Abdominal/uterine assessment
Fetal development
Pelvic adequacy
Screening tests
Scheduling future prenatal visits
gravid
"The state of being pregnant"
gravida
-Total number of times a woman has been pregnant, regardless of the outcome
-Inclusive of multiple infants born
para
"Number of times a woman has given birth to a fetus of at least 20 weeks' gestation (viable or not) with multiple births counting as one birth event."
due date determination at first prenatal visit
-Naegele's Rule:
-First day of LMP - 3 months + 7 days = EDD/EDB
-Accurate determination of gestational age is vitally important.
prematurity
"Globally, prematurity is the leading cause of mortality in children less than 5 years of age."
GTPAL
-TPAL=para
-Method utilized for calculating a woman's obstetric history
G
Gravity: Total number of pregnancies. Include the current pregnancy (Think "Gravid/Gravida")
T
Term: Term births. Delivered between 38- and 42-weeks gestation
P
Preterm: Preterm births. Pregnancy ending > 20 weeks but prior to completion of the 37th week of gestation
A
Abortion: Pregnancies ending prior to 20 weeks or viability (spontaneous or elective/therapeutic)
L
Living: Currently living children to whom the woman has given birth
The First Prenatal Visit: Abdominal Assessment
Striae
Linea nigra
Muscle tone (effects of progesterone)
The First Prenatal Visit: Uterine Assessment (fundal height)
-Top of pubic bone to top of uterus (fundus)
-Patient lies on her back with knees slightly flexed
-Correlates well with weeks of gestation between 22 and 36 weeks (+/- 2 cm)
accuracy with fundal height
-More accurate: Same examiner each time (not realistic)
-Less accurate: later in pregnancy
-Inaccurate: Maternal obesity, Uterine fibroids,
Hydramnios
weeks and where the fundal height is
12 weeks: At the symphysis pubis
16 weeks: Midway between symphysis and umbilicus
20 weeks: At the umbilicus
36 weeks: Just below the xiphoid
Estimating gestational age during pregnancy
-Most accurate: Ultrasound
-Other methods: Maternal recall of LMP (use of Naegele's Rule)
-Fundal height measurement: After 20 weeks' gestation
Estimating gestational age after delivery
Dubowitz scoring (term/pre-term) **look at lanugo and creases on feet
The First Prenatal Visit: Fetal Development assessed via
-Quickening (between 16 and 22 weeks gestation)
-FHR (Doppler, 10-12 weeks)
-U/S (gestational sac at 4-5 weeks
fetal heartbeat at 6-7 weeks)
quickening
Mom's first experience of feeling fetal movement (subjective)
The First Prenatal Visit: Pelvic Adequacy/Pelvimetry
-Not a determinate for vaginal birth
-diagonal conjugate
-true (obstetric) conjugate
-ischial tuberosity diameter
diagonal conjugate
-Most useful in estimating pelvic size
-Fetal head passes through here first
-Should be 11.5 cm or greater
-false pelvis directs the baby into the true pelvis
-Distance between anterior surface of sacral prominence and anterior surface of symphysis pubis.
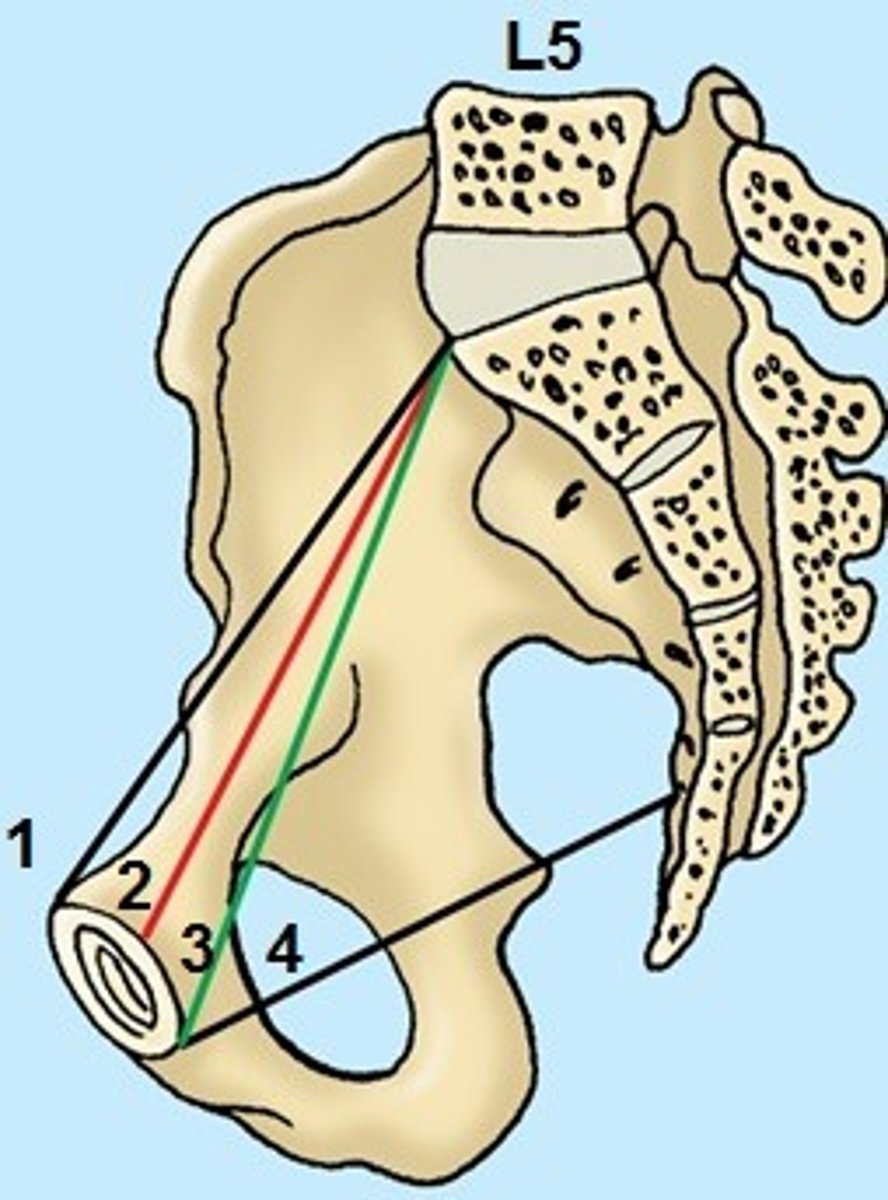
true (obstetric) conjugate
-Estimated measurement (cannot be directly measured)
-Subtract 1-2 cm from diagonal conjugate
-Should be at least 10 cm for a vaginal delivery
-Smallest front to back diameter through which fetal head must pass
-Distance from anterior surface of sacral prominence to posterior surface of symphysis pubis
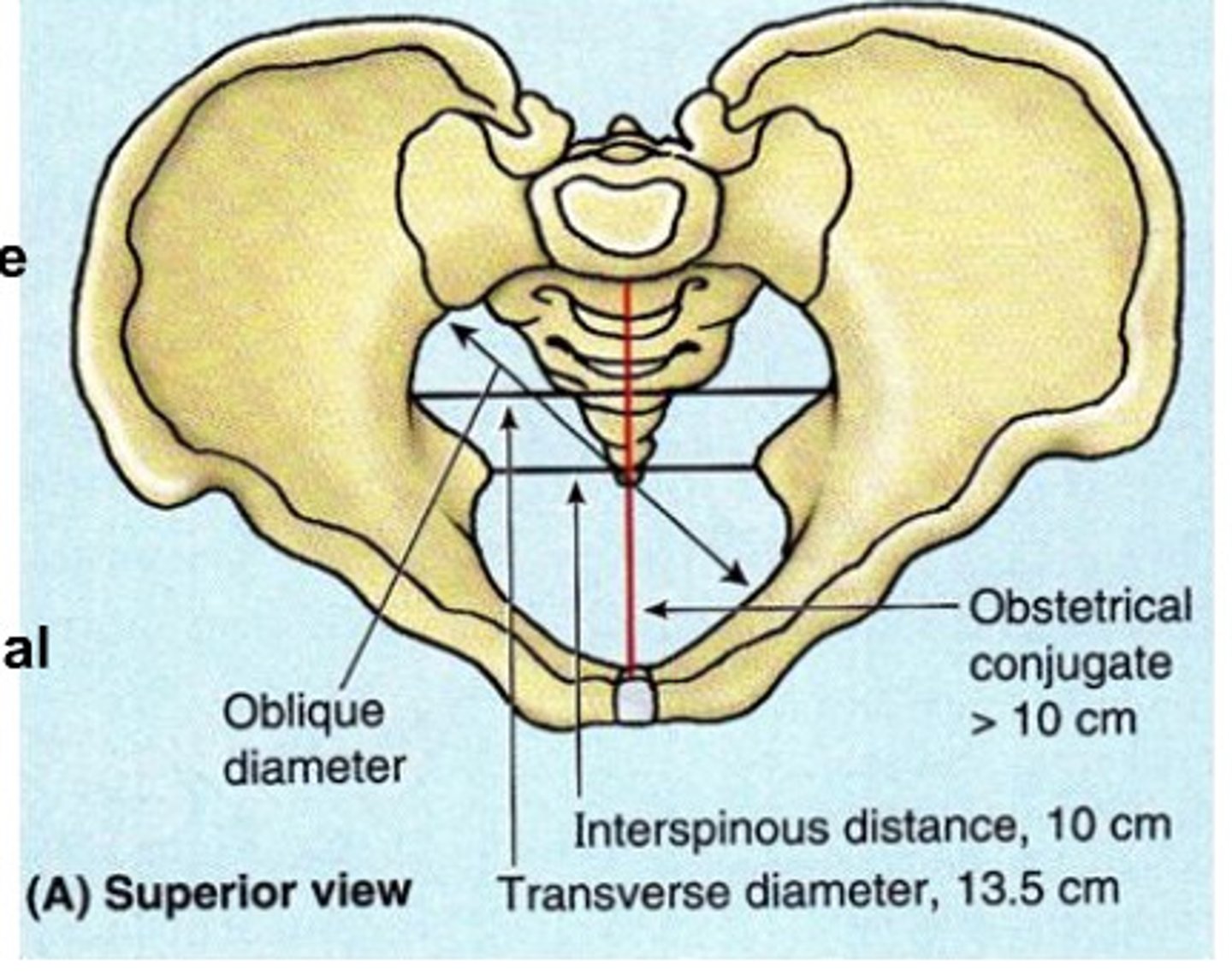
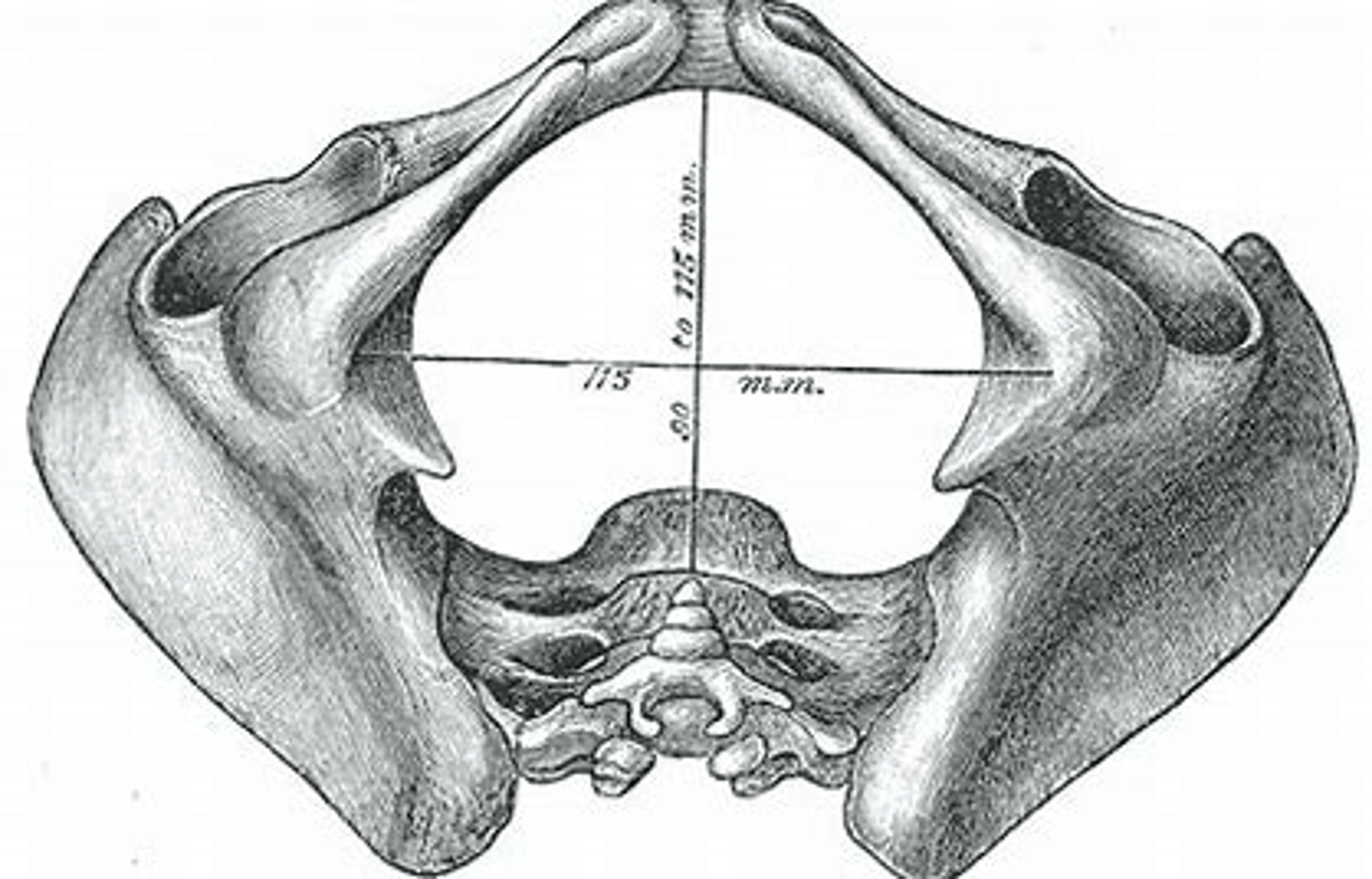
ischial tuberosity diameter
-Measured externally
-Adequate = 10.5 cm or greater (for passage of fetal head)
The First Prenatal Visit: Screening Tests
-Pap (if indicated; cervical cells)
-CBC: Hgb. (12-14 g) and Hct. (42% +/- 5%)
-HIV screening
-Rubella titer
-ABO and Rh typing
-Urine culture (also done at each visit; to make sure no UTI)
-Hep B screen
-STI testing (syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea):
Repeat at future visits if necessary **beginning of pregnancy and before delivery
The First Prenatal Visit: Scheduling Future Prenatal Visits
-First 28 weeks: every 4 weeks
-29 -36 weeks: every 2 weeks
-37 weeks - delivery: every week
Future Prenatal Visits: Assessments
-Weight and B/P
-Urine sample: Check for protein, glucose, ketones and nitrites
-Fundal height measurement: Assess fetal growth
-Quickening/fetal movement: Assess fetal well-being
-FHR: Normal = 110 - 160 beats per minute (bpm)
Future Prenatal Visits: Determining Fetal Movement (quickening)
-Mother's first perception of fetal movement (subjective)
-Multiparous earlier than nulliparous
Monitoring fetal activity at home: teach mom
-how (varied methods)
-length of time it takes to record 10 fetal movements (if > 2 hours... call HCP)
-purpose
-same time each day
-report any decrease in fetal activity/movement **after you feel it, it should be felt everyday
Screening for Gestational Diabetes
-24-28 weeks gestation
-1 hour OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test)
-Desired value = < 140 mg/dL
-If > 140 mg/dL a 3-hour diagnostic OGTT is done
**not before 20 weeks, doesn't show up in the 1st trimester
Edema (periorbital, hands, face, pretibial)
-29 - 36 weeks gestation
-gestational HTN, in 3rd trimester
-dependent, ankles feet
RhoGAM administration
-28 weeks gestation
-Rh-negative moms
-not given early in pregnancy
GBS
-37 - 40 weeks gestation
-risk factor at delivery so must be tested early
Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
-37 - 40 weeks gestation
-test at beginning of pregnancy and close to delivery
fetal position
-37 - 40 weeks gestation ... Leopolds
-closest to the Due date so baby should be settled in
Nursing Management for the Common Discomforts of Pregnancy: important points
-Identify the discomfort
-When in pregnancy (trimester) does it typically occur .. begin and end
-Recommendations for relief of symptoms (Health Promotion)
-When would we be concerned?
first trimester common discomfort
•Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP)
•Urinary frequency
•Fatigue: progesterone
•Breast tenderness: hormones, tends to end by the first trimester
•Constipation: decreased peristalsis from progesterone
•Nasal stuffiness, bleeding gums, and epistaxis: from estrogen
•Ptyalism: excessive saliva
•Food cravings
•Leukorrhea: increased vaginal discharge **DM at risk for yeast infection
Discomforts can begin in or be associated with one trimester though may continue through or re- occur in successive trimesters
:)
second trimester eases
-Ending of NVP
-Ending of breast tenderness
-Urinary frequency eases
-Fatigue eases
-Other first trimester discomforts may continue
second trimester discomforts
-Backache
-Leg cramps: charlie horses, dorsiflex to relieve
-Varicosities: support hose, but not knee-high
-Hemorrhoids: internal/external, use witch hazel, tucks, preparation H
-Flatulence and bloating: progesterone and diet, teach to walk every day
third trimester occurrences
-Urinary frequency returns
-Fatigue increases
-Other first and second trimester discomforts may continue
third trimester new onset discomforts
-Shortness of breath and Dyspnea: baby pressing up on diaphragm
-Pyrosis: progesterone and baby pushing up
-Dependent edema
-Braxton Hicks (for some, these begin in the 2nd trimester): from stretching of the uterus, no regular interval, recommend fluids/sit/stand/warm shower...whereas real labor this won't help bc its a hormone issue (low prog, high oxytocin)
Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP) causes
Multifactorial (hormones, metabolism, emotions, low B-6, others)
Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP) begins
5th week after LMP (2nd - 3rd week of pregnancy)
Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP) peaks
8-12 weeks
Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP) ends
16-18 weeks
Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy (NVP) treatment
-Frequent, small meals (snacks, carbs)
-B-6 (foods, vits.)
-Non-med.: Ginger, acupressure, wristbands
-Meds: (HCP consult)
Diclegis: (doxylamine pyridoxine .. A combination antihistamine and B-6)
Benadryl
Dramamine
Urinary frequency or incontinence cause
pressure on bladder
Urinary frequency or incontinence trimesters experienced
1st trimester (uterus ... 2 oz to 2 lbs.)
3rd trimester (uterine contents)
Urinary frequency or incontinence teach
Reduce fluids prior to bedtime
S/S of infection
fatigue cause
trimester dependent
-1st trimester (hormones, metabolic demands, psychosocial factors)
-**** 2nd trimester = highest energy (usually)
-3rd trimester (physical changes and discomforts)
teach about fatigue
Rest often, use pillows
Left side (preferred)
breast tenderness (cause/trimester/teach)
-Hormones (estrogen/progesterone)
-Trimester: First
-Teach: Supportive bra (even when sleeping)
ptyalism (what/cause/trimester/teach)
-What is it: Excessive secretion of saliva
-Cause: Unknown
-Trimester: 1st (begins), 2nd and 3rd (continues)
-Treat/teach: hard candy, gum, no real treatment
food cravings (cause/trimester/teach)
-Cause: Unknown
-Trimester: 1st (begins), 2nd and 3rd (continues)
-Teach: Moderation
constipation causes
Hormones (progesterone)**slows things down
Increased uterine size (pressure)
Increased water reabsorption
Calcium and Iron in PNV **iron is constipating
constipation trimesters
First (begins)
Second and third (continues)
teaching about constipation
-Diet (fiber and fluids)
-Physical activity: walk everyday
-Maintain normal bowel patterns
-Adequate fluids/water, warm fluids to stimulate the bowel
-Reduce refined carbs and cheese: in moderation
-Consider a bulk-forming laxative (Metamucil) per HCP: stretches bowel for BM
Nasal stuffiness, Bleeding gums and Epistaxis (estrogen) cause and trimesters
-edema of nasal mucosa from estrogen
-1st (begins), 2nd and 3rd (continues)
Nasal stuffiness, Bleeding gums and Epistaxis (estrogen) teaching points
Stay hydrated
Cool mist humidifier
No nasal decongestants/sprays
nosebleed teach
Tilt head slightly forward
Pinch nose (10-15 minutes)
Apply ice to bridge of nose (vasoconstriction)
bleeding gums teach
Soft toothbrush
Warm saline mouthwash
Good dental care
leukorrhea (what/cause)
What is it: Increased vaginal discharge
Cause: Estrogen (hyperplasia of the mucosa)
leukorrhea trimester
1st (begins), 2nd and 3rd (continues)
teach with leukorrhea
S/S of yeast infection (increased risk)
Cotton undergarments
Good hygiene
**soap and water only, no bubble bath sprays or deodorants
backache (cause/trimester)
Cause: Uterine size, spinal curvature, relaxed pelvic structures
Trimester: 2nd (begins) 3rd (continues)
backache teach
Heat, ice, massage
Posture, body mechanics, support shoes
Exercises .... Pelvic tilt
Tylenol (per HCP) **last resort
leg cramps (cause/trimester)
Cause: increased strain, muscle fatigue
Trimester: 2nd (begins) 3rd (continues)
leg cramps teach
Adequate Ca++ and PO4-, fluids
Dorsiflex foot
Elevate
Warmth, moisture on muscles
Support hose, low shoes
Varicosities of Vulva and Legs (cause/trimester/teach)
-Cause: Slowed venous return (gravid uterus)
-Trimester: 2nd (begins) 3rd (continues)
-Teach: Elevate legs, no crossing legs
Support hose (no knee-highs)
hemorrhoids (what/cause)
-What is it: Varicosities of the rectum (may be internal or external)
-Cause: Pressure (gravid uterus)
hemorrhoids teach
-How to prevent constipation
-Avoid prolonged sitting/standing
hemorrhoids treat
Preparation H
Anusol
Witch hazel or cool compresses
flatulence and bloating (cause/trimester)
-Cause: Decreased GI motility (progesterone, pressure from gravid uterus)
-Trimester: 2nd (begins) 3rd (continues)
flatulence and bloating teach
-Avoid gas-producing foods (beans, cabbage, onions) and foods with high white sugar content
-Reduce intake of carbonation, cheese
air swallowing (eat slowly)
-Action daily exercise, adequate fluids,
mints
Shortness of Breath and Dyspnea (cause/trimester)
Cause: hemodynamic changes, gravid uterus
Trimester: 3rd (usually)
SOB and dyspnea teach
Position changes
HOB up
Left side
Stretch (arms up, deep breaths)
Small meals
Relieved some after lightening (baby "drops")
Heartburn (Gastroesophageal reflux, Pyrosis) and Indigestion (causes/trimester)
-Causes: Progesterone (relaxes cardiac sphincter)
-Gravid uterus (displaces stomach, slows emptying)
-Trimester: 3rd (usually... could occur earlier)
Heartburn (Gastroesophageal reflux, Pyrosis) and Indigestion teach
-Avoid caffeine, alcohol, chocolate, citrus, spearmint/peppermint, spicy/greasy food
eating before bed
-Limit gas-producing or fatty foods
air swallowing (fast eating, gum chewing)
-Do eat slowly, small meals, upright after eating
dependent edema (where/cause)
-Where: legs/feet, face, periorbital area
-Cause: Slowed venous return (gravid uterus)
Increased fluid volume in pregnancy (6-8 liters)
Increased capillary permeability
-3rd trimester
dependent edema tx
Elevate feet/legs above heart
Support stockings (no knee highs)
Walk
Left side
Fluids (water)
Monitor sodium, sugar, fatty foods