Microbiology Study Guide Chapter 7 & 8
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Bonds with equal sharing of electrons (same atoms & carbon/hydrogen atoms)
Intermolecular forces involving a partially positive hydrogen atom bonded to a Partially negative atom.
Vanderwaals interaction-temporary and weak
Greed for electrons ( Ability of an element to hold electron next to it.)
An unchangeable property of each element.
Extreme difference - Ionic bond
Moderate difference - Polar Covalent (partial charges, use delta symbol for charge)
Small Difference - NonPolar Covalent
Organic vs Inorganic
Organic- contains carbon and hydrogen
Inorganic- does NOT contain carbon and hydrogen
Most abundant elements in living things
Hydrogen,Oxygen,Nitrogen,Carbon
Phosphorus,Sulfur
Low atomic mass
capable of forming strong bonds
Can be found in our body
Calcium, Iron, Zinc, Copper, Potassium Sodium, Magnesium
Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements.
-Structural connect differently
-Cis-Trans cis is same side trans is opposite sides
-Enantiomers- non-superimposible mirror images
A chemical reaction that builds polymers by removing water and creating a covalent bond.
A reaction that breaks down polymers by adding water to break a bond.
Peptide,Polypeptide,Protein
Protein polymers composed of many amino acid subunits.
Have a job. Can find sulfur
Carbohydrate polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits.
Store sugars.
DNA & RNA
Nucleic Acid polymers composed of many nucleotide subunits.(ribose, nitrogenous base, phosphate group)
Sub units not monomer or polymers.
Hydrophobic molecules including fats, oils, and phospholipids.
FattyAcid and Glycerol → Triglyceride
Organic Molecules
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Monosaccharides (carbohydrate)
1 sugar 1 monomer of carbohydrates
Simple sugars
Can name general shape based on carbons (EX: Triose,Pentose,Hexose)
Disaccharides (carbohydrate)
Glycosidic Bond
MALTOSE = Glucose Glucoe
LACTOSE = Glucose Galactose
SUCROSE = Frucose Glucose
Polysaccharides (carbohydrate)
Structural Polysaccharides
Modified glucose (NAG,NAM) (OH group replaced by —, no amino group, no double bonds.
Fatty Acids (lipid)
Saturated - we can’t add anymore hydrogen , no double bond
Unsaturated 1 or more double bonds
Monounsaturated 1 double bond
Polyunsaturated 2 double bonds
Triglycerides (lipid)
3 fatty acids on a glycerol backbone
This is how we store fatty acids
Phospholipid (lipid)
Has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic “tails”
Has a phosphate group
Biological Membranes
Steroids (lipid)
Sterols(has hydroxyl group)
Chelestrol
Ergosterol
Cholesterol (steroid(lipid))
Vital molecule in cells
increases temp stabilize membranes, pre cursor for other steroids
Amino Acids (Proteins)
Peptide Bonds
Dehydration synthesis from an amino acid
Conjugated Proteins
Add Things
Glycoproteins
Lipoproteins
Protein Structure
Primary
Primary sequence of amino acids
Secondary
Hydrogen bonding is using backbone of amino acid (ncc)
Alpha Felix and Beta Sheets
Tertiary
R group interactions
Electrostatic attraction, hydrophobic interactions metal ion coordination
(-+- or +-+)
Folding is essentially about charge
Quaternary
Multiple peptides
Denaturation
Heat
Anabolic
building up a molecule require energy
Catabolic
Breaking down a molecule
Gibbs Free Energy
The energy in a molecule that COULD be released.
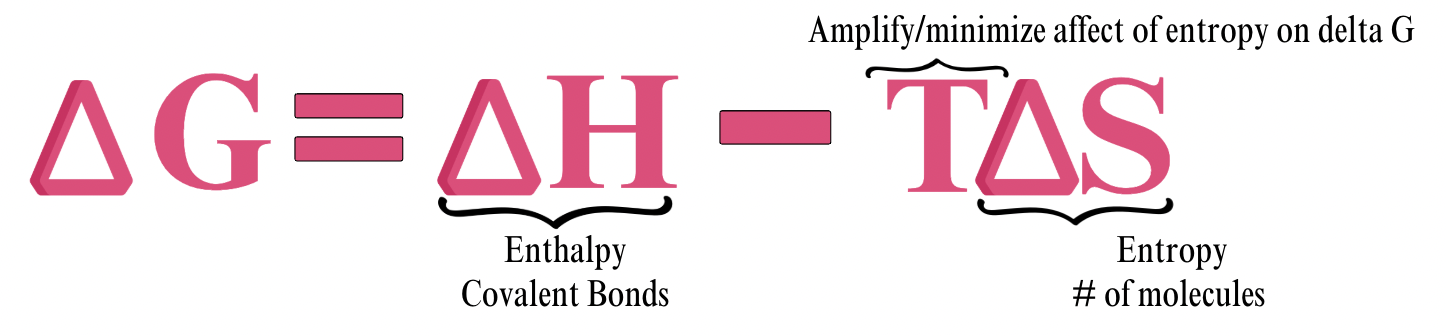

Enthalpy
Related to heat
About equal to the number of covalent bonds (more energy)
Entropy
About equal to number of molecules “the more you have the more chaos” (less energy)
Exergonic
EXITING ENERGY.
Spontaneous.
Gives energy
(High energy to low energy)
Endergonic
ENTERING ENERGY
NonSpontaneous.
Requests energy
(Low energy to high energy)
Carbon Sources (pptx. table)
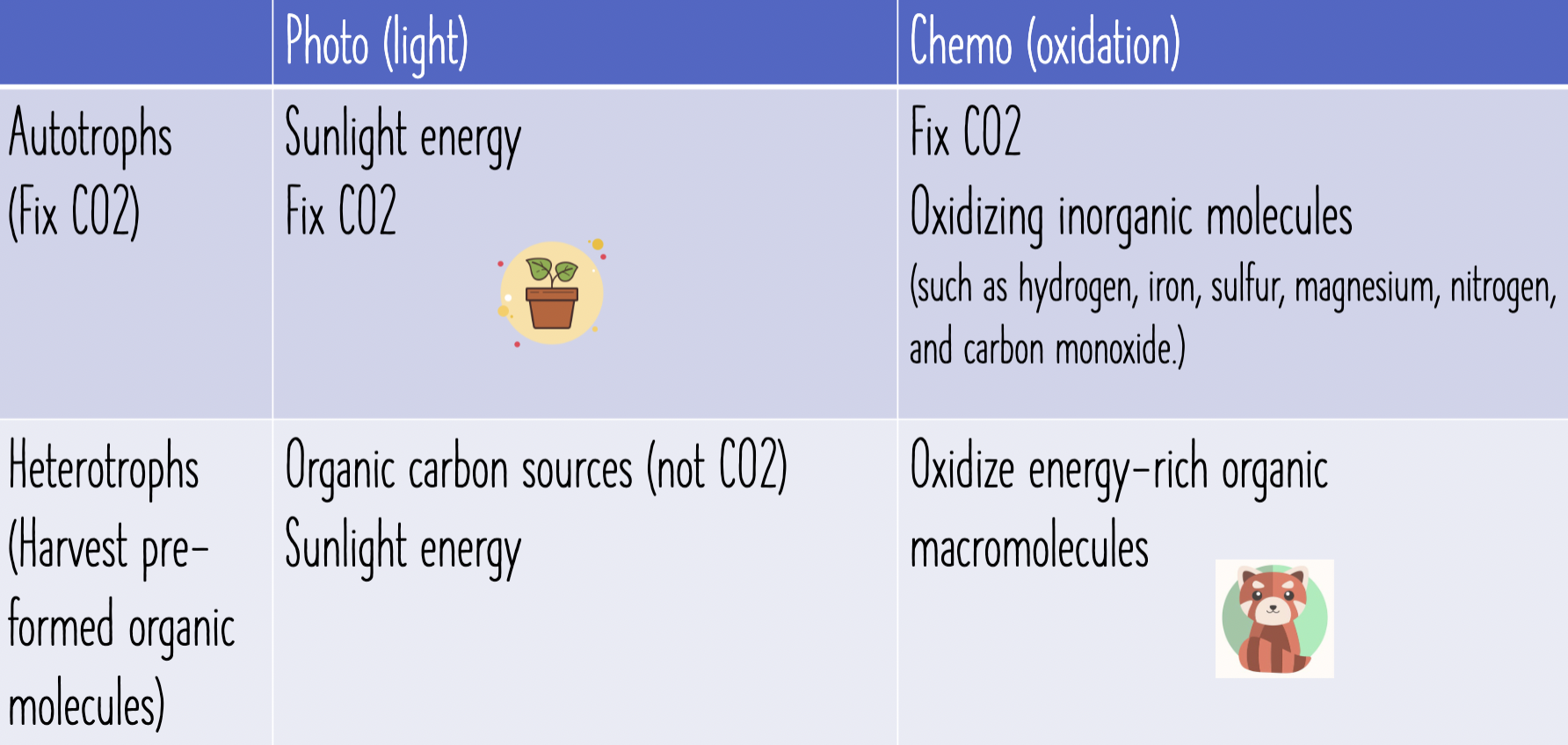

Autotrophs
Fix CO2
Heterotrophs
Harvest preformedorganic molecules
Redox Reactions
Exchanging electrons from a reducing agent to an oxidizing agent
-Incremental energy harvesting prevents explosion
‘OIL RIG’ Oxidation is losing Reduction is gaining
NAD+,NADP+,FAD electron carriers
Modified nucleotides
Engage in moving electrons as “Intermediate holders”
ATP
Energy currency & Energy states
Couples endergonic and exergonic reactions
Bonds store a lot of energy
Enzymes (Biocatalysts)
Cofactor and Coenzymes (organic/Vitamins bond near active site)
Activation energy go down providing shortcut for reaction to happen
DO NOT change amount of energy available, DO NOT change deltaG, DO NOT provide energy
Inhibition (enzymes)
Competitive Inhibitors
Active site is taken
Allosteric Modification
A change in shape
Inhibition altered active site
Activation active site not altered
Feedback Inhibition
Changing the process because of the outcome
Catabolic reaction that breaks down glucose into pyruvate.
DOES NOT USE OXYGEN
2 ATP > 4 ATP> 2 ATP & 2 NADH
Pyruvate oxidation (happens twice)
A transition reaction
NO ATP is produced
1 NADH produced PER pyruvate
Citric Acid Cycle / Kreb’s Cycle (happens twice)
Takes 2 things (Acetyl CoA & combines to one)
1 ATP produced
3 NADH produced
1 FADH2 produced
Cellular Respiration
A process taht breaks down food to produce energy for cells
EX: breaking down glucose to produce ATP
Can fail when no final electron acceptor is available. Genetic reasons: no genes for ETC proteins or cytric acid cycle enzymes.
Carbon Dioxide CO2
Is the most oxidized from of carbon
EMP Pathway-
Used by most microbes/animals
Entner-Doudoroff (ED) Pathway-
Along with EMP or alone depending on bacteria
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)-
Synthesis of nucleotides/amino acids
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
NADH > Protein Complex > Energy given off during transportation and then used to pump hydrogen into inter membrane space.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration
Use oxygen to complete
Anaerobic Respiration
Does not use oxygen but still…
The movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, generating ATP.
Uses hydrogen ions as a source of energy
Lost energy stored as a concentration gradient
Proton motive force drive ATP production ,nutrient transport, flagella rotation.
Oxidative Phosphorylation-
Energy in concentration gradients
An anaerobic process that converts pyruvate into other compounds, such as lactic acid or ethanol. (Deals with overload of NADH and Pyruvate)
Does not go through the process aerobic and anaerobic go through
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Acid decreases ph and increases acidity in environment causing denaturing of nearby proteins.
Pyruvate accepts an electron chamging to lactic acid
Homolactic
Produces lactic acid
Heterolactic
Produces more than just lactic acid
Alcohol Fermentation
2 Steps =release CO2 and Convert the rest to a hydroxyl group
Pyruvate changes to ethanol
Other Fermentaton Pathways
organisms are related to pathways and end products.
It is possible to differentiate microbes based on what and how they ferment.
Lipid Catabolism
Break ester bonds to get fatty acid off
Lipases,Phospholipases, beta oxidation
Lipases
Breaks down lipids
Phospholipases
Breaks down phospholipids
Beta oxidation
Breaks off 2 carbons at a time turn into acetyl-CoA
Produces FDH2,NADH,Acetyl-CoA
Protein Catabolism
How we break down proteins
Proteases, Deaminases
Proteases (extracellular & intracellular)
Extracellular > Break down proteins into smaller fragments
Intracellular > Breakdown proteins into amino acids
Deaminase
removes amino group and uses left overs
Light reactions
Provide energy (ATP) and electrons (NADPH)
Oxygenic
Oxygen producing
Anoxygenic
produces something other than oxygen (like sulfur or sulfate ions)
The Calvin Cycle (Dark Reaction)
You need ATP, High energy electrons, and Carbon for this reaction.
There are other alternative CO2 Fixation Pathways*
Carbon Fixation
Connecting of the CO2 and then breaking into 2 3carbon molecules
(CO2 is connecting to an organic form of carbon)
Reduction Oxidation
Passing electrons from NADPH
Regeneration of RuBP
Regenerates 3 5carbon molecules using energy(ATP)
Carbon Cycle
l
Carbon Fixation
make organic carbon molecules
Methanogenisis
Methanogens- CO2 to make methane (CH4)(Bad)
Methanotrophs- oxidize methane into CO2 (Good)
Respiration
Organic carbon molecules turned back into CO2
Why is Carbon(CO2) needed?
Used to create other carbonaceous molecules
Autotrophs fix carbon
Heterotrophs steal carbon
Nitrogen Cycle
Ammonification
Nitrogenous waste turned into ammonium
Nitrification
Takes ammonia turns it into Nitrite which is then turned into Nitrates
Denitrification
Turns nitrate and turns it into N2(g)
Nitrogen fixation
Bacteria incorporate N2(g)
Assimilation
makes nitrogenous compounds
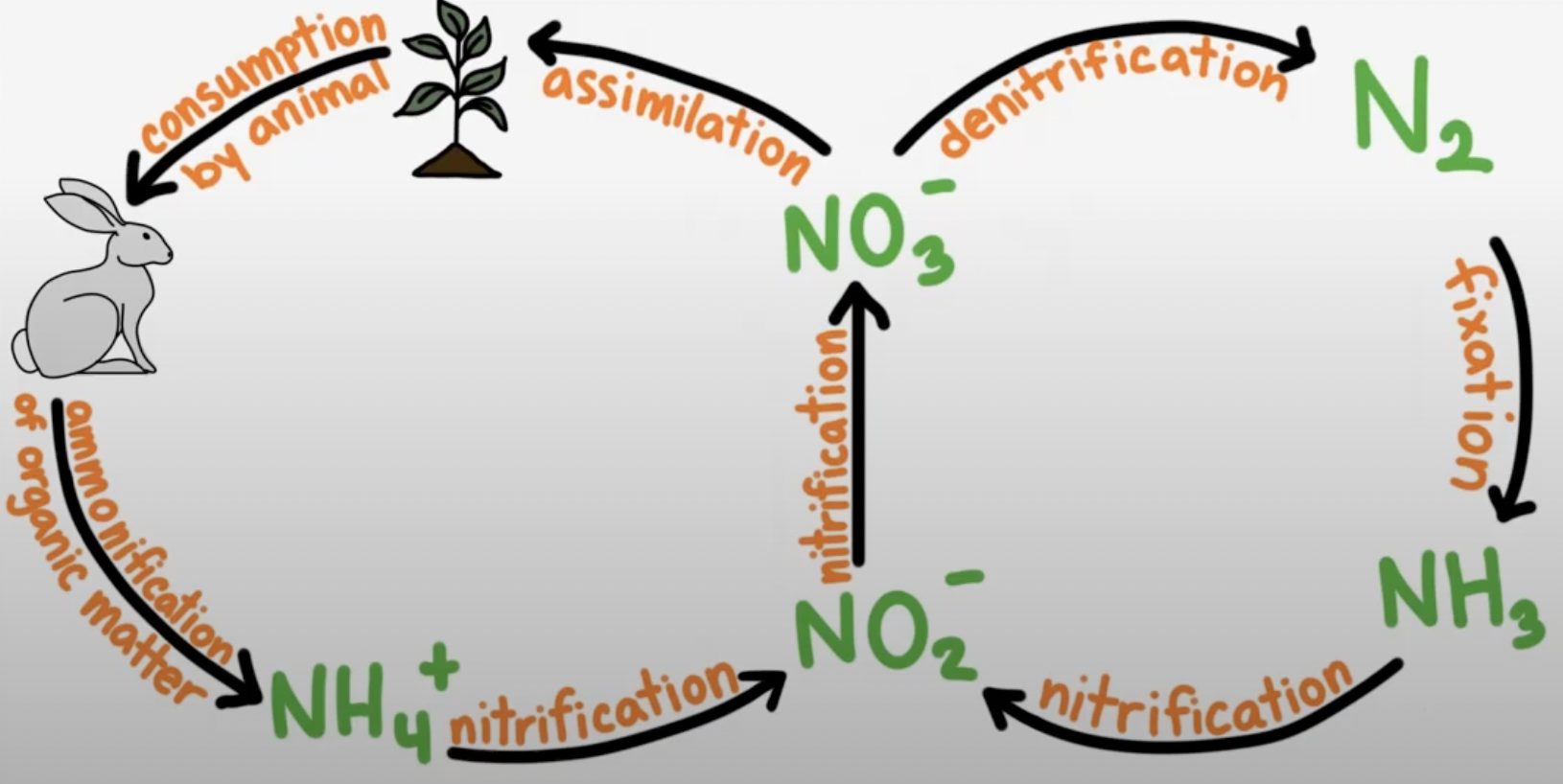
Why is Nitrogen (N2(g)) needed?
Accessing Nitrogen is hard
Bacteria can alter nitrogen for themselves and indirectly help other organisms (break it down into organic molecules.
Plants/phytoplankton can’t incorporate atmospheric nitrogen gas
Ammonia/Ammonium aren’t easily used
Eutrophication
Man made fertilizers release nitrogen and phosphorus via runoff
Nutrient runoff > Algae Growth > Death of Aquatic Algae > Anaerobic/ inhospitable environment
Sulfur Cycle
Fungi & Bacteria: convert organic sulfur in detritus > Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria and chemoautotrophs
Hydrogen Sulfide(electron donor)>sulfate
Leads to stratification of hydrogen sulfide in soil
Deeper= more anaerobic=more hydrogen
Why is Sulfur Needed?
Cysteine & methionine
Vitamin Synthesis (CoA)
Many plants and bacteria can use sulfate as a sulfur source
Different organisms use different pathways to produce different products
Different organisms use different pathways to produce different products