Week 2: Activities of Daily Living and Comfort Care
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Define functional ability
The mental, social, physical, and emotional capacity to perform daily activities necessary for living
Is functional ability on a continuum, if so what does the continuum represent?
Yes, the continuum ranges from full function to lack of function, and varies from person to person, and at different points in time
List the early identification factors that affect function
Developmental stages
Physical (E.g. A patient with a wheelchair has an environment with only stairs and no ramps)
Psychological
Disease
Social and cultural factors
Physical environment
Age
Cognitive function
Level of depression
A sudden onset of functional decline is often indicative of what?
Acute illness or worsening chronic disease
What are activities of daily living?
The necessary and basic tasks a person has to perform on their own to live independently
List the 12 activities of daily living (ADL's) (according to roper-logan-tierney model of nursing)
Maintaining a safe environment (E.g. cleaning)
Breathing
Communication
Mobilizing
Eating and drinking
Toileting/eliminating
Personal cleansing and dressing
Maintaining body temperature
Working and playing
Sleeping
Expressing sexuality
Dying
What are instrumental activities of daily living (IADL's)?
These are complex activities necessary for independent living in the community
List the instrumental activities of daily living (IADL's)
Managing finances, banking and paying bills
Shopping and preparing meals
Managing medications
Use communication devices (i.e. phone)
Maintaining environment and personal items (cleaning, laundry)
Organizing and/or getting to and from place
How can ADL's be assessed?
Subjective and objective data from the patient, family, or observer
Identification of difficulties with the underlying reasons for the deficit
Perceptions, values, and goals are highly important (E.g. ask what they think would help, what they want to achieve)
What assessment tools are used to asses ADL's
Functional Independence Measure (FIM)
Katz Index of Activities of Daily Living
InterRAi (RAI-HC)
What is the Functional Independence Measure (FIM)?
A tool used by a healthcare practitioner to assess and grade the functional status of a person based on the level of assistance the person requires, and can be used to identify progress
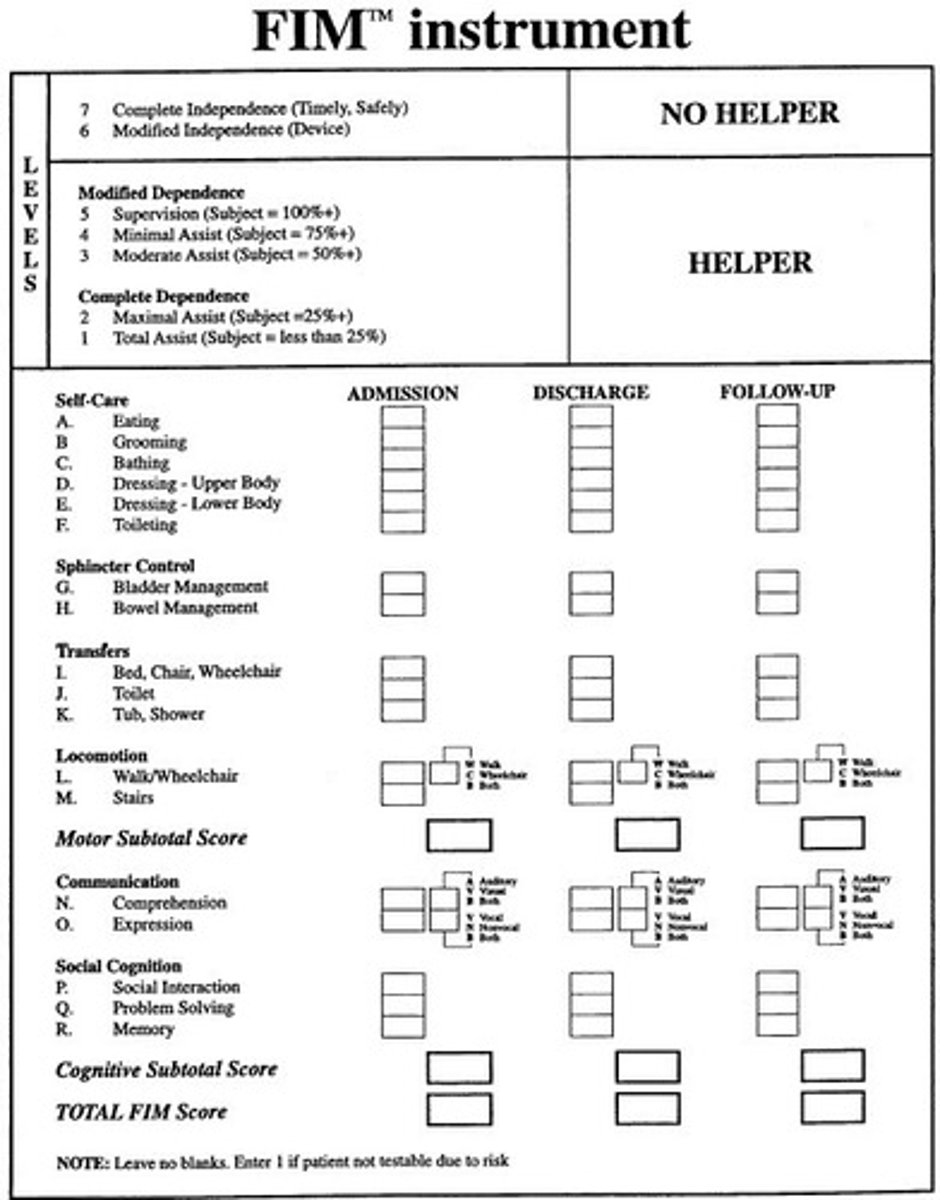
How is the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) scored?
Scored from 1-7, with 7 being complete independence, and 1 being complete dependence
The higher the score, the more independent the patient is on that task
When/where is Functional Independence Measure (FIMTM) used
Rehabilitation settings
What ADL categories are assessed in the Functional Independence Measure (FIM)?
Self-care (Eating, grooming, bathing, dressing upper and lower, toileting)
Sphincter control (Bladder, bowel)
Transfers (bed/chair/wheelchair, toilet, tub/shower)
Locomotion (Walk/wheelchair, stairs)
Communication (Comprehension, expression)
Social cognition (Social interaction, problem solving, memory)
MOA of the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living?
Assess functional status, and the client's ability to perform ADL's independently
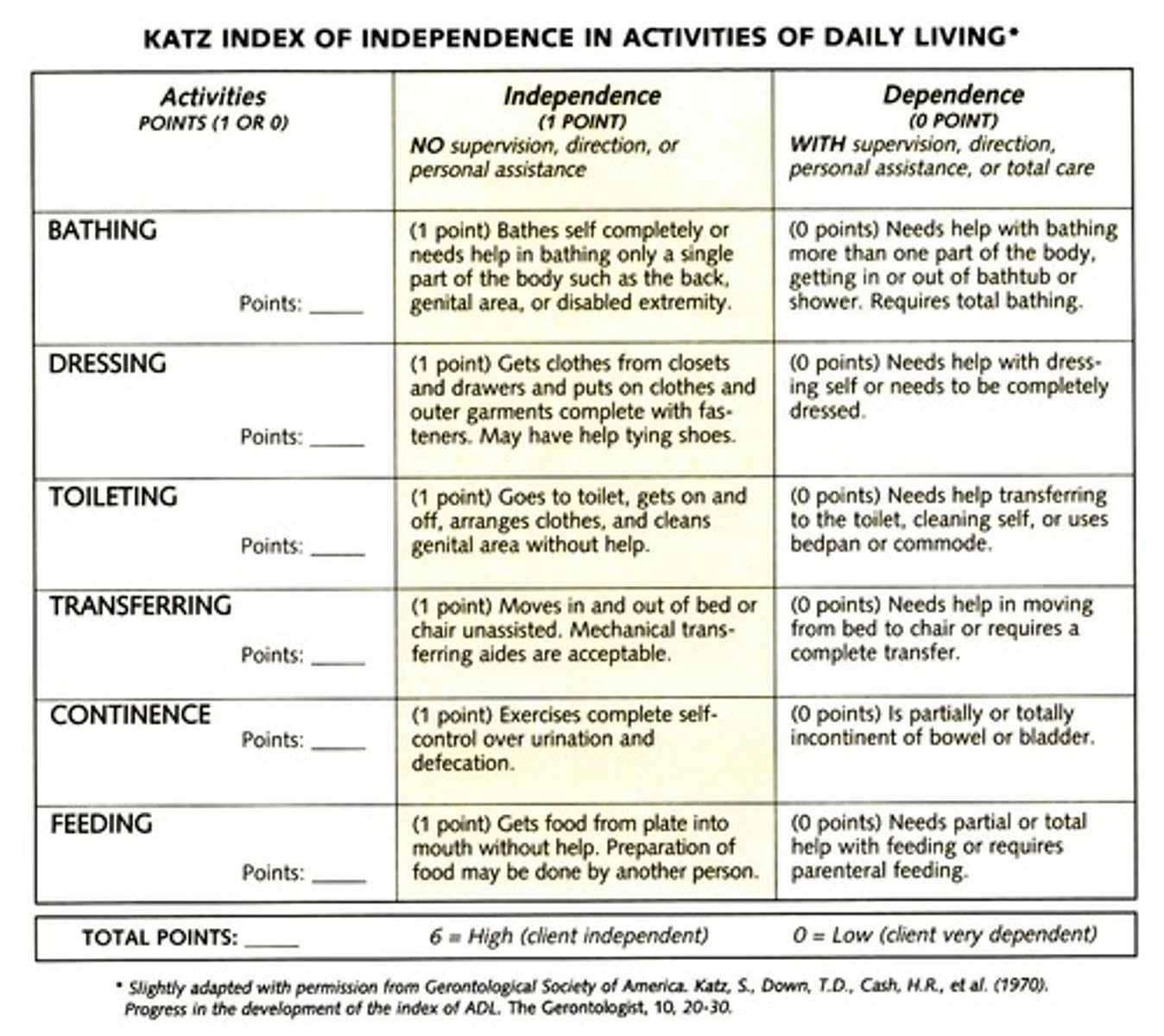
How is the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living scored?
Each category is either receives a score of 1 or 0:
1 point = Independent
0 point = Dependent
What ADL categories are assessed in the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living?
Bathing
Dressing
Toileting
Transferring
Continence
Feeding
What does a score of 6 represent on the Katz Index test?
6 points = Highly independent
MOA of the InterRAI?
Used in home and continuing care settings to develop and determine the right care in the right place
What categories are assessed in a interRAI?
ADL functioning
Communication/hearing
Depression
Environment/home safety
Health conditions
IADL
Self performance
Mental functions
Nutrition/hydration
Physical abilities
Reliance on healthcare services
Social functioning
Strengths
Continence
Dental status
Disease diagnosis
Falls
Medication use
Informal (family) support services
Mood and behavior
Pain
Preventative health measures
Skin conditions
Socio-demographic/background information
Vision
What are assistive devices?
Devices that help ease patients and caregivers
List the types of assistive devices
Crutches
Wheelchair
Walker
Cane
Transfer belt
MOA of crutches
An assistive device used for partial or non weight bearing ambulation. Patients require good balance, cardiovascular reserve, and strong upper body strength

Where should the weight be supported when using crutches?
The weight of the crutch should be on the wrist not the under arms (armpits)
MOA of wheelchairs
An assistive device that offers full support but requires patients to tolerate a seated position

MOA of walkers
An assistive device that offers more support than cane or crutches and can come in various forms such as: No wheels, two wheels, and four wheels

MOA of a cane
An assistive device that aids with balance and support, and relieves pressure on weight bearing joints
Should a cane be used on the affected or unaffected side?
Unaffected side
MOA of a transfer belt
Used to safely mobilize, and transfer patients, by wrapping it around the patient middle to hang on to their center of gravity
When ambulating a patient with a gait belt and they don't use an assistive device, should you stand on their stronger or weaker side when ambulating?
Stronger side
1 multiple choice option
When ambulating a patient with a gait belt and they use an assistive device, should you stand on their stronger or weaker side when ambulating?
Weaker side
1 multiple choice option
What should you do when the patient becomes dizzy/light headed when ambulating with a gait belt?
Immediately return them to the bed or guide them to a chair, whichever is closer
What should you do when the patient begins to fall when ambulating with a gait belt?
Gently ease the patient to the floor by holding firmly onto the gait belt. Stand with your feet apart to create a broad base of support and extend your leg as the patient slides gently to the floor. As the patient is sliding down bend your knees to ease them down gradually
What is the Alberta Aids to Daily Living Program (AADL)?
A program used to helps Albertans stay independent in their communities by paying for basic medical equipment and supplies
Alberta Aids to Daily Living Program (AADL) is a _________ program
Cost share
What does it mean for the Alberta Aids to Daily Living Program (AADL) to operate as a cost-sharing program?
Individuals or families contribute 25% of the benefit cost, up to a maximum of $500 per year. Those receiving income assistance are exempt from cost-sharing
Who is eligible for the Alberta Aids to Daily Living Program (AADL)?
Alberta residents with a valid AHCIP card, and those that require assistance because of a long term disability, chronic illness, or terminal illness
What is required to request access to the Alberta Aids to Daily Living Program (AADL)?
A clinical assessment by a healthcare professional to determine needs (AADL authorizer)
Define fundamental care (Basic care)
Actions a nurse takes to respect and focus on a person's essential needs to ensure their physical and psychosocial wellbeing
How are fundamental care (Basic care) need met?
Developing a positive and trusting relationship with the person being cared for as well as their family/carers
How does nursing contribute to the patient's journey?
Effective execution of basic needs in a way that is competent, respectful, personal and empathetic
What are the core relationship values in the fundamentals of care framework?
Trust
Focus
Anticipate
Know
Evaluate
How do you prepare to shave a male patient? (Taken from Films On Demand)
Assess medical history and lab values to assess bleeding risk
Assess facial hair (Broken skin, reddened areas)
Put the head of the bed up
Put on clean gloves
Place a towel over the patients chest and shoulder
How do you shave a male patient with a disable razor? (Taken from Films On Demand)
Soak a wash cloth in a basin with temperature appropriate water. Ring out the wash cloth and place it over the patients face for several seconds
Use soap or shaving cream (patient preference)
Apply a layer of shaving cream 1/4 inch thick and smooth evenly over the face
Hold the razor in your dominant hand at a 45 degree angle to the skin
With your non-dominate hand pull the skin taut
Shave with long firm strokes in the direction of the hair growth, and short strokes around the chin and lips
Dip the razor in the water basin as shaving cream accumulates
Change the water in the basin and throughly rinse and dry the patients face with a new wash cloth
Pat on after shave (patient preference)
Where should you dispose of a used razor?
The sharps container