Hearing
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Discuss the functional anatomy of the external ear.
The external ear includes the pinna and external auditory canal; it collects sound waves and funnels them toward the tympanic membrane, helping with sound localization.
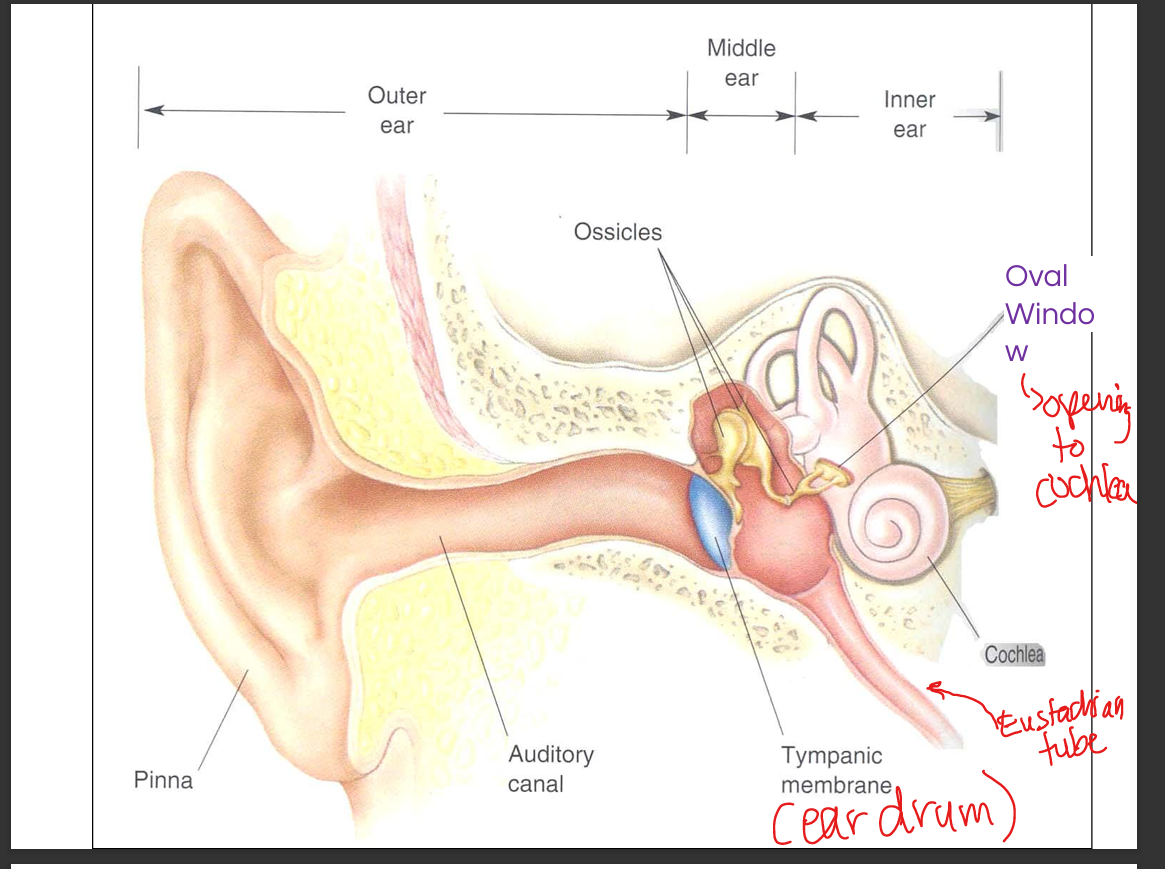

Discuss the functional anatomy of the middle ear.
The middle ear contains the tympanic membrane and ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes); it amplifies sound via lever action and area difference before transmitting vibrations to the oval window.
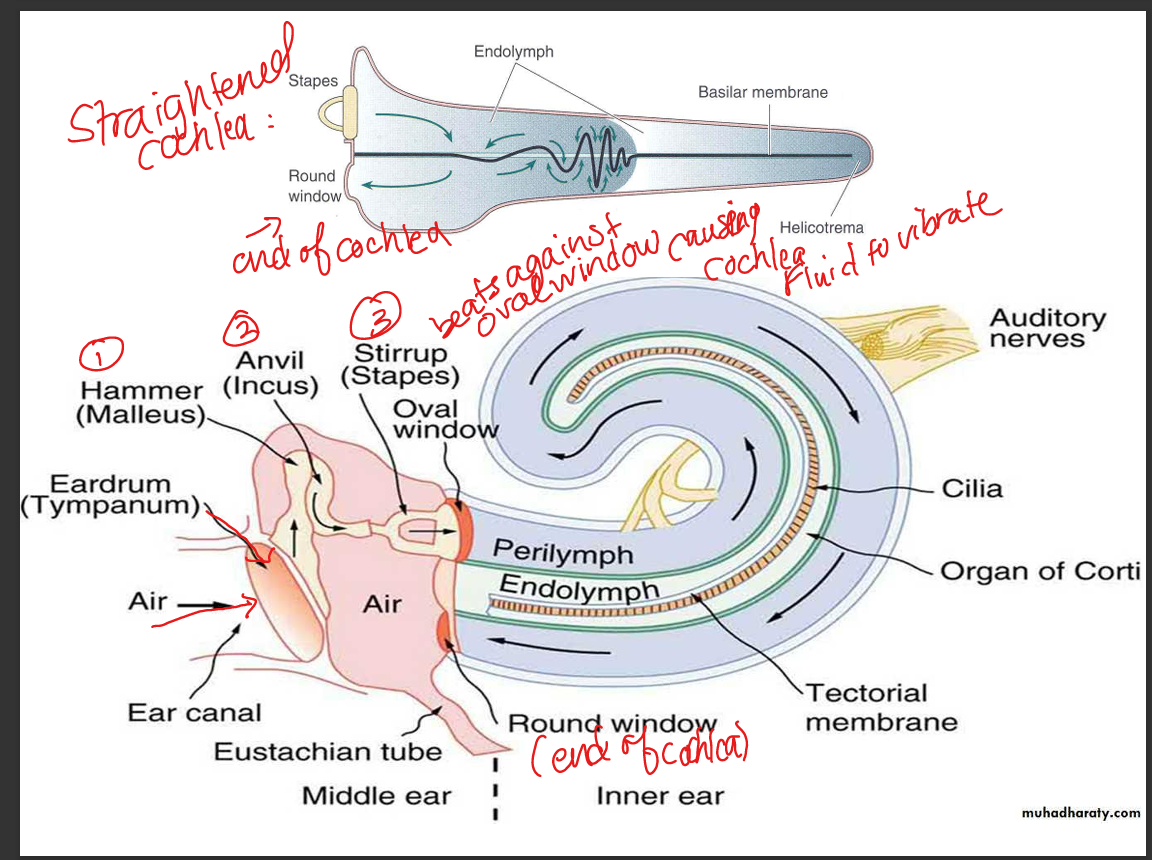

Discuss the functional anatomy of the inner ear.
The inner ear contains the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals; the cochlea converts mechanical vibrations(that vibrate fluid) into neural signals via hair cells in the Organ of Corti.
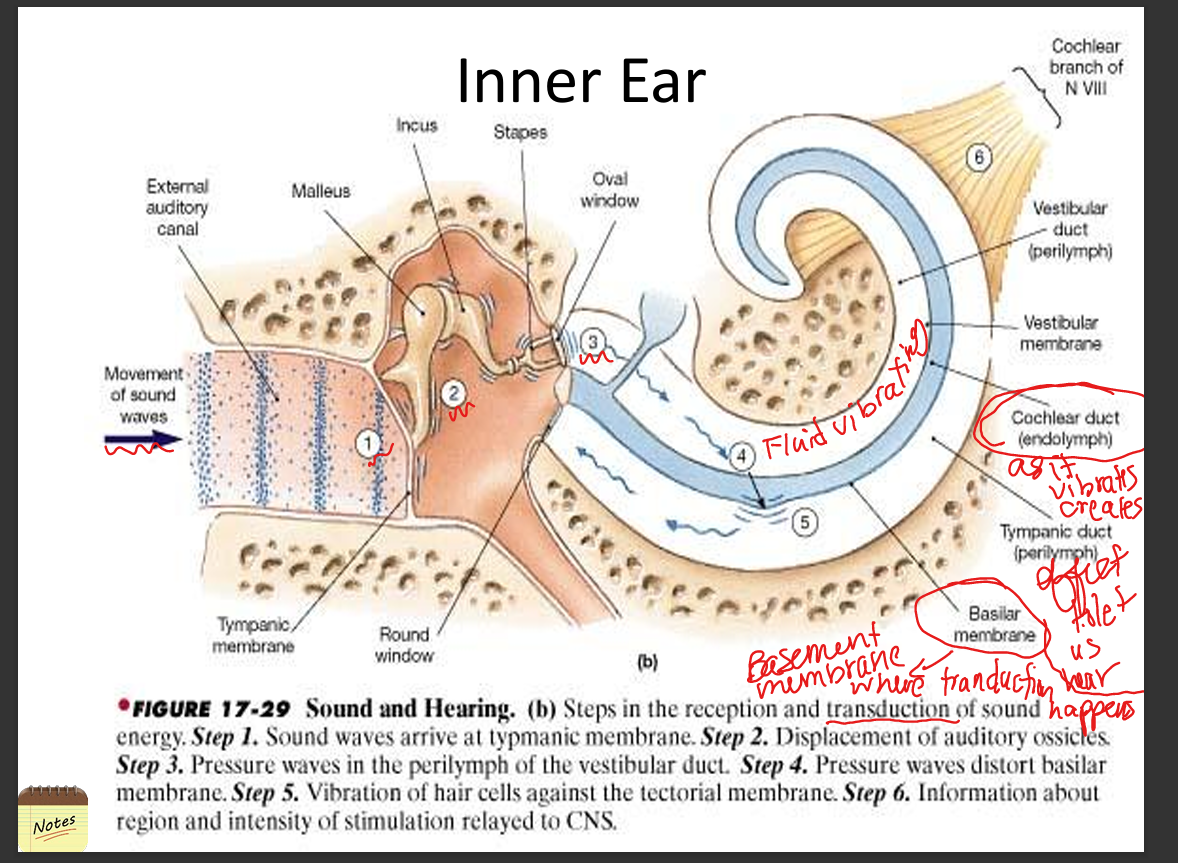

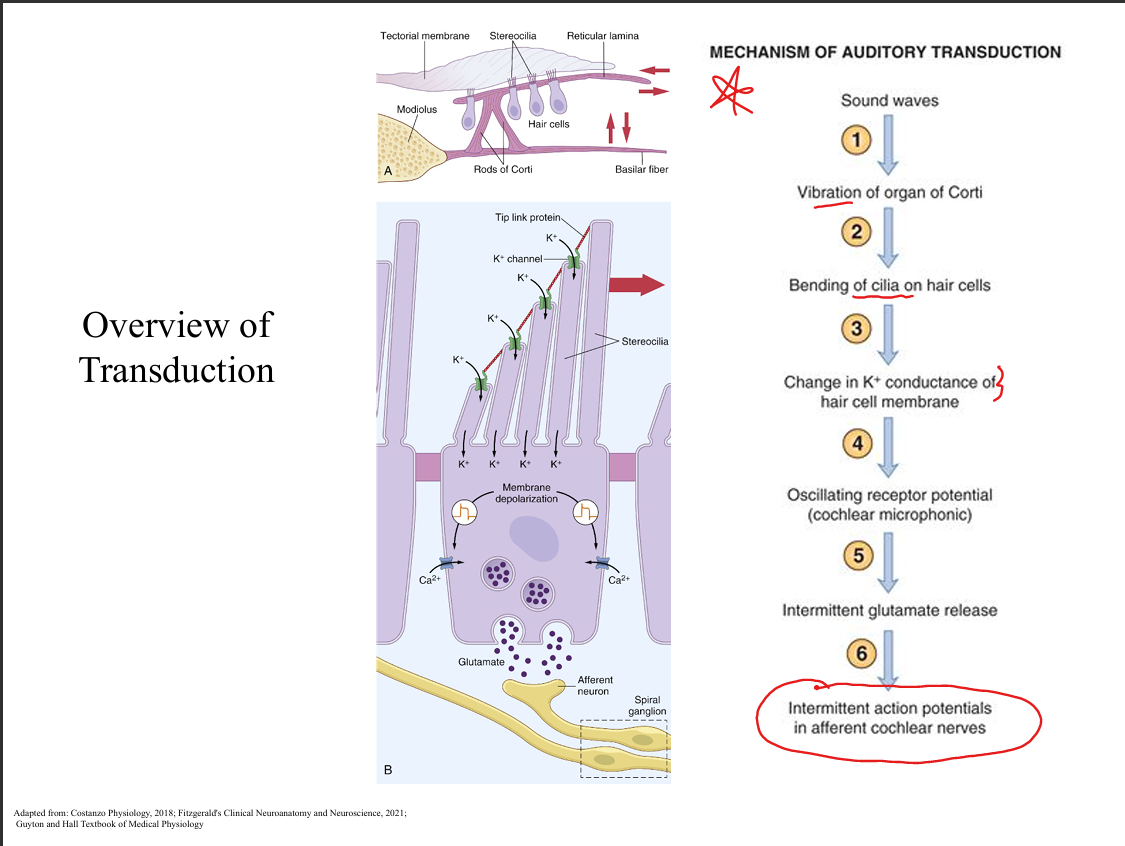
Explain how pressure waves in air are processed by the cochlea.
Sound waves vibrate the tympanic membrane → ossicles → oval window → perilymph in scala vestibuli → basilar membrane displacement → hair cell transduction → auditory nerve firing.
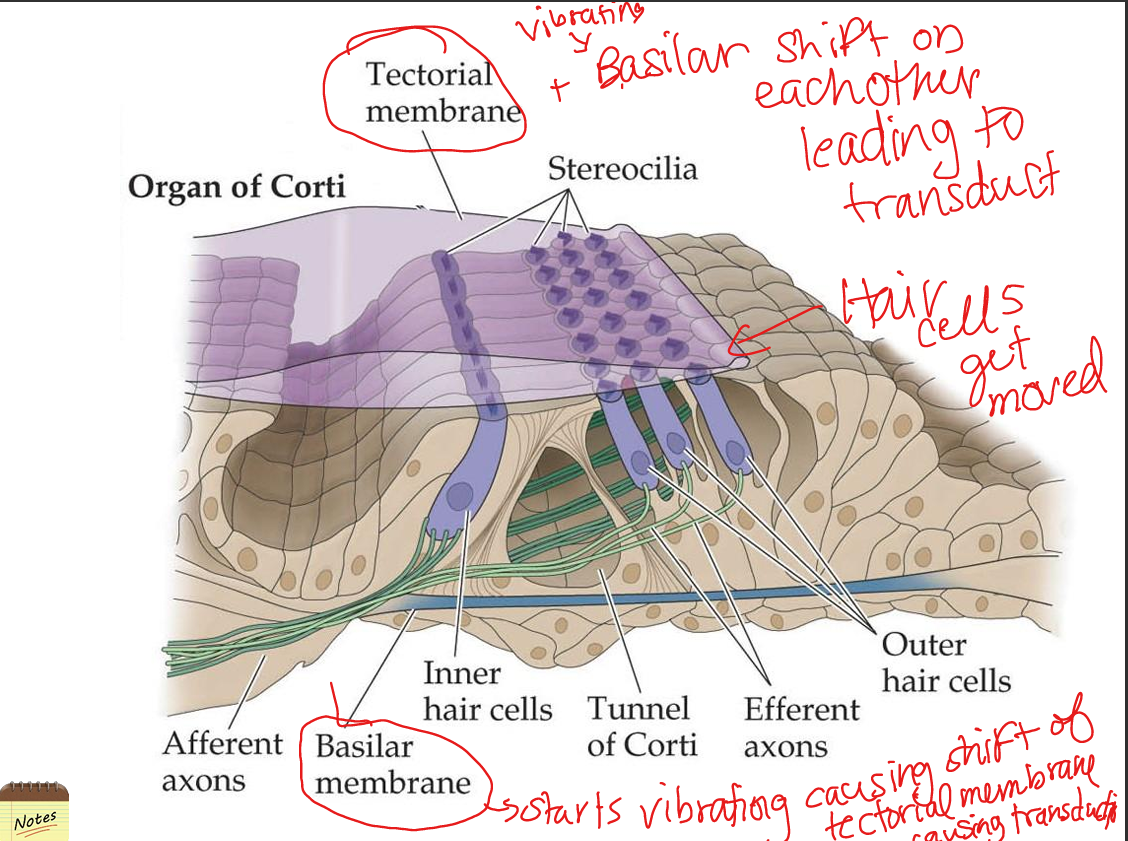

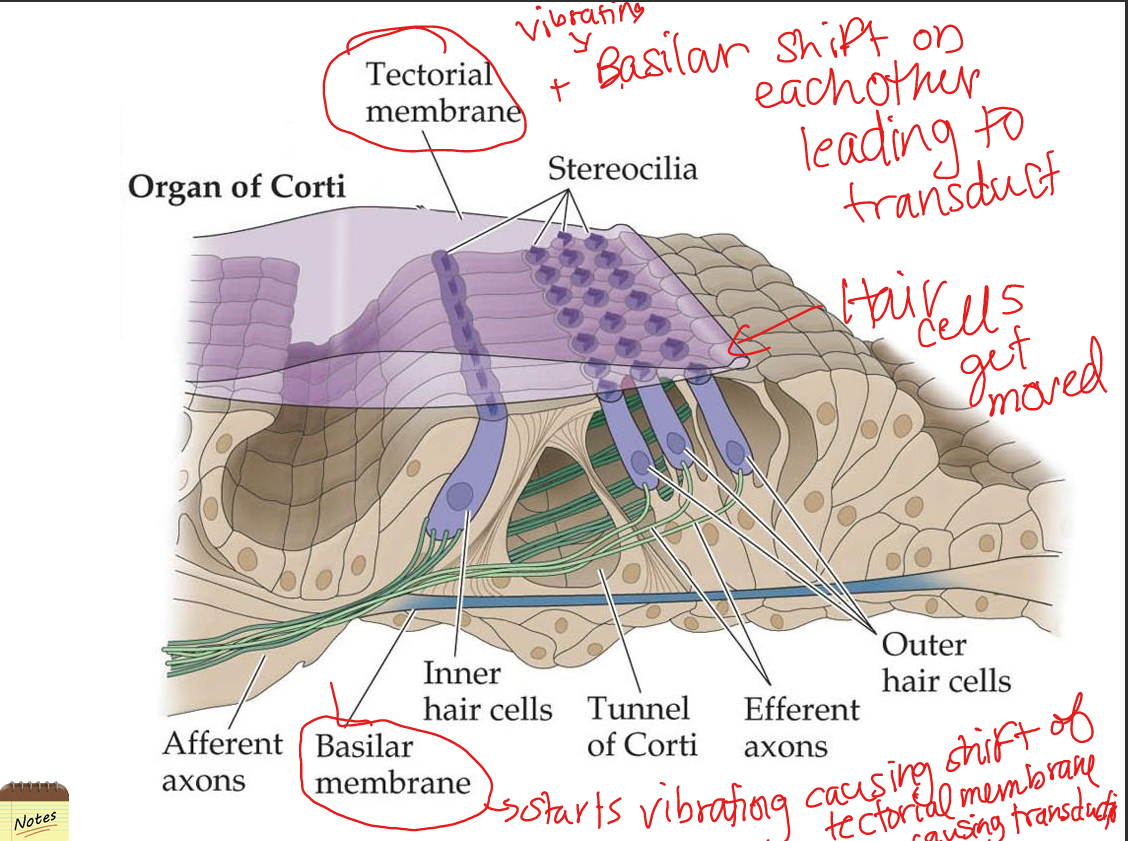
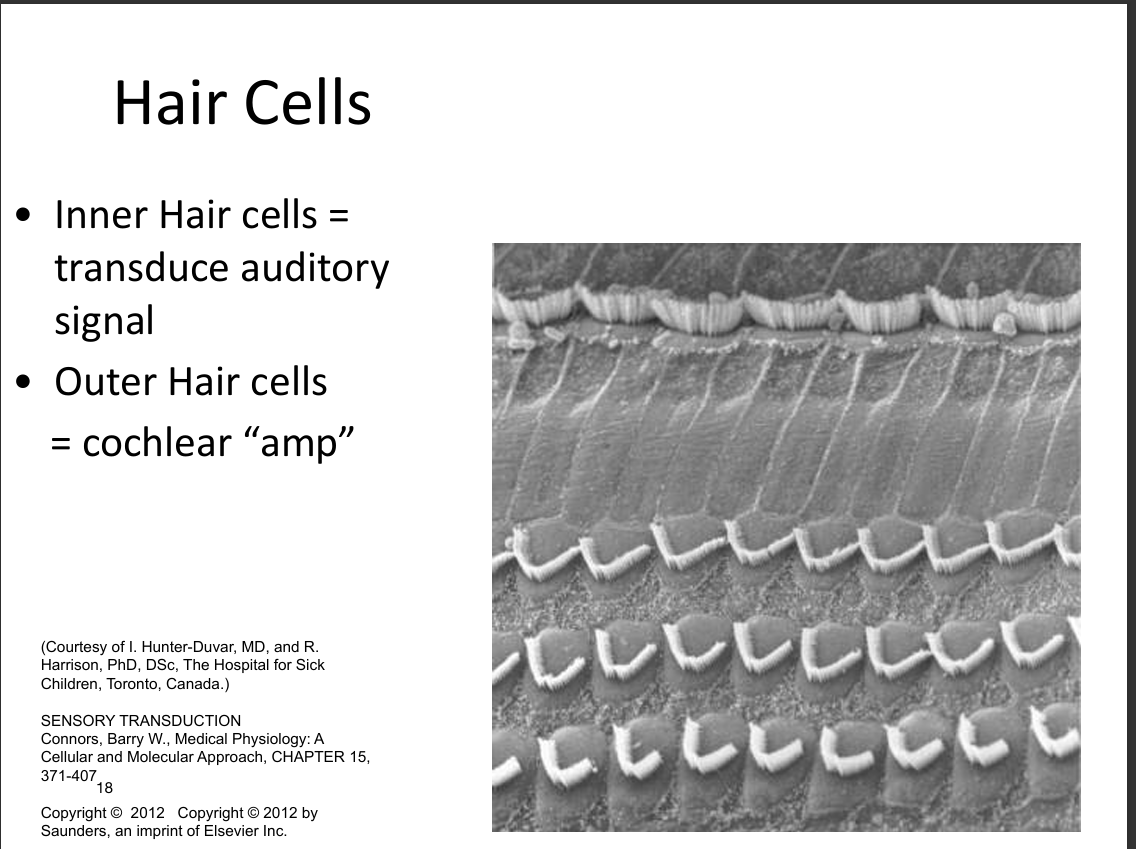
Compare inner and outer hair cells.
Inner hair cells transduce sound into neural signals; outer hair cells amplify and fine‑tune basilar membrane vibrations via electromotility.

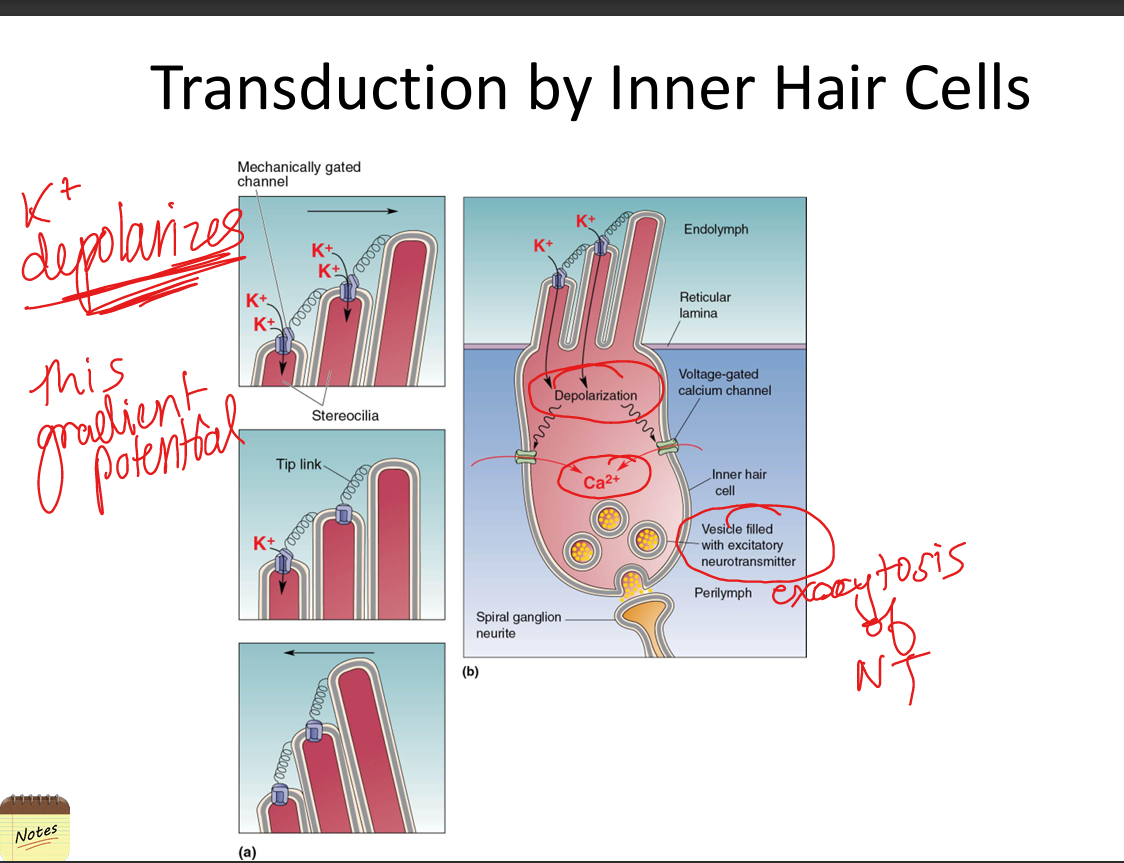
Explain how transduction of sound occurs.
Bending of stereocilia opens mechanically gated K+ channels (due to high‑K+ endolymph), causing depolarization → Ca2+ influx → glutamate release onto spiral ganglion neurons.

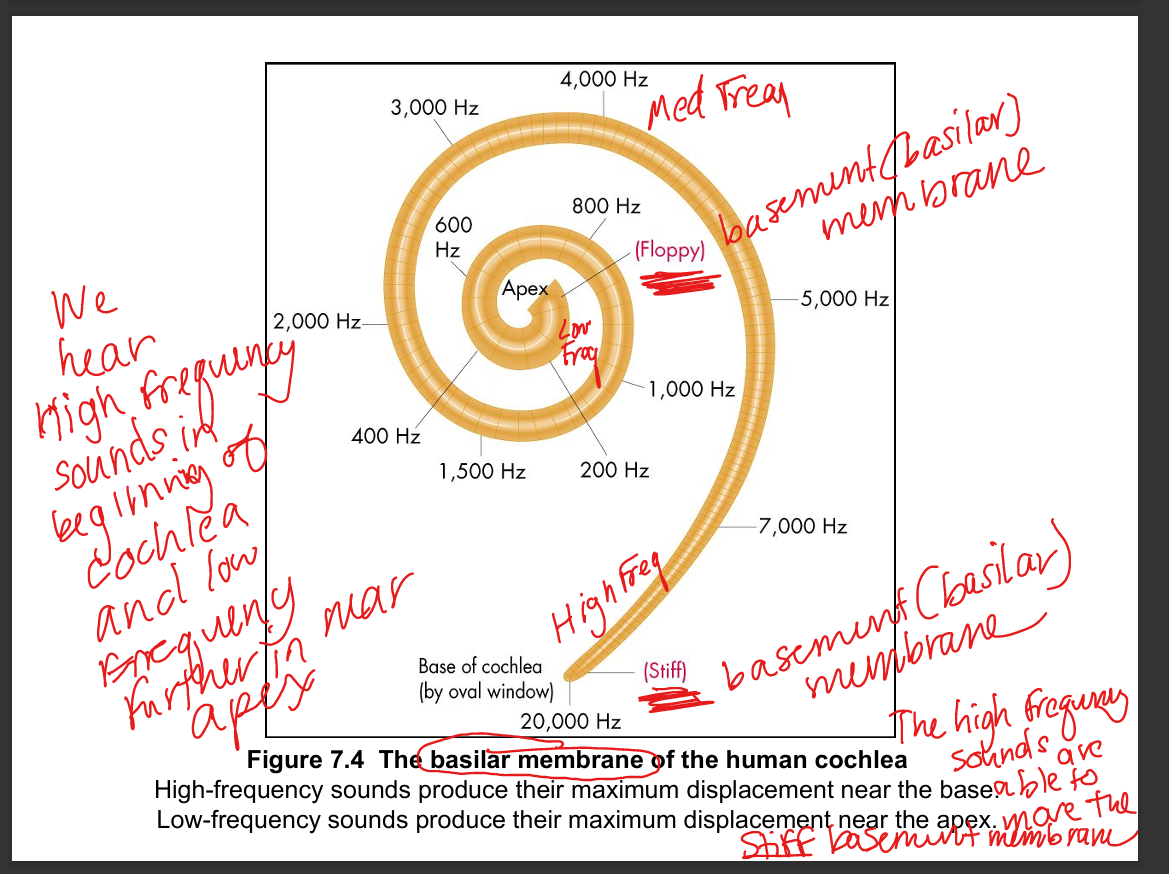
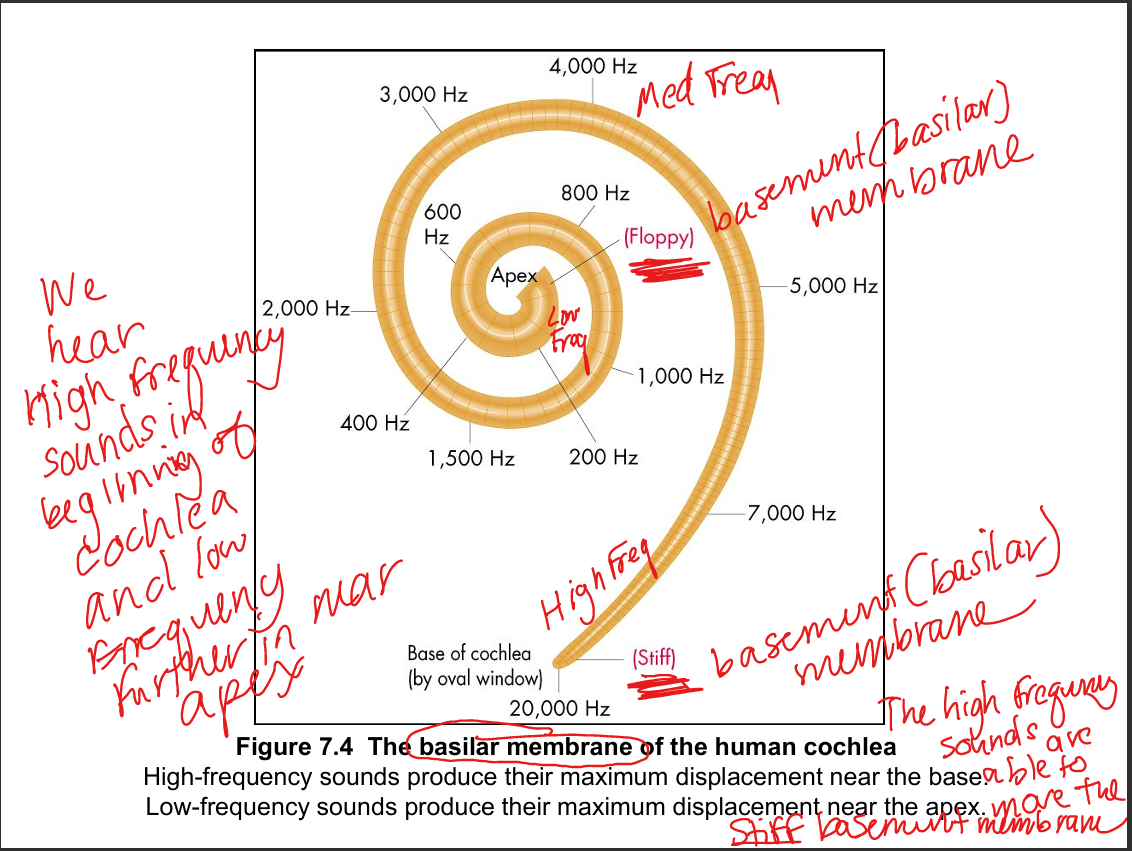
Explain how sound frequencies assort along the basilar membrane.
High frequencies peak at the stiff, narrow base; low frequencies peak at the wide, floppy apex — creating a tonotopic map.

Outline the auditory pathway.
Organ of Corti → spiral ganglion → cochlear nerve → cochlear nuclei → superior olivary complex(intensity+timing) → lateral lemniscus → inferior colliculus(localization + body integration) → medial geniculate nucleus → primary auditory cortex.
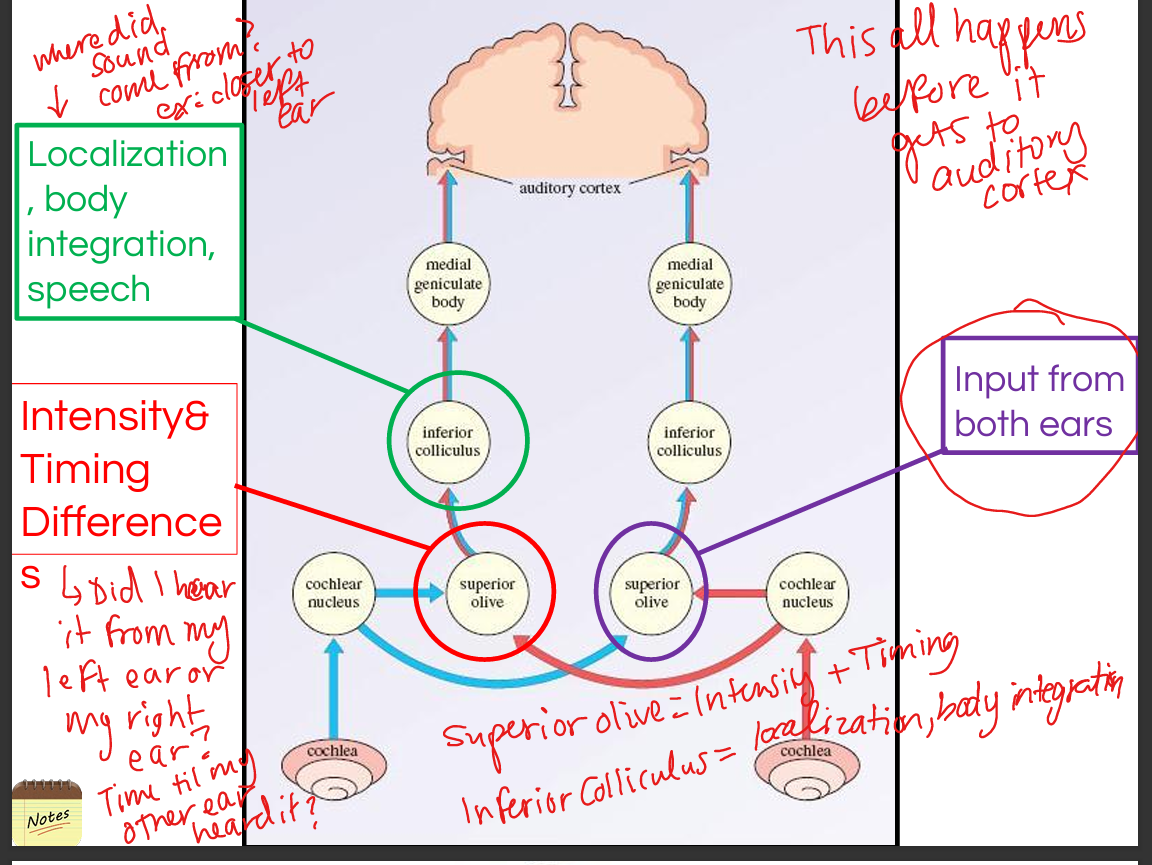
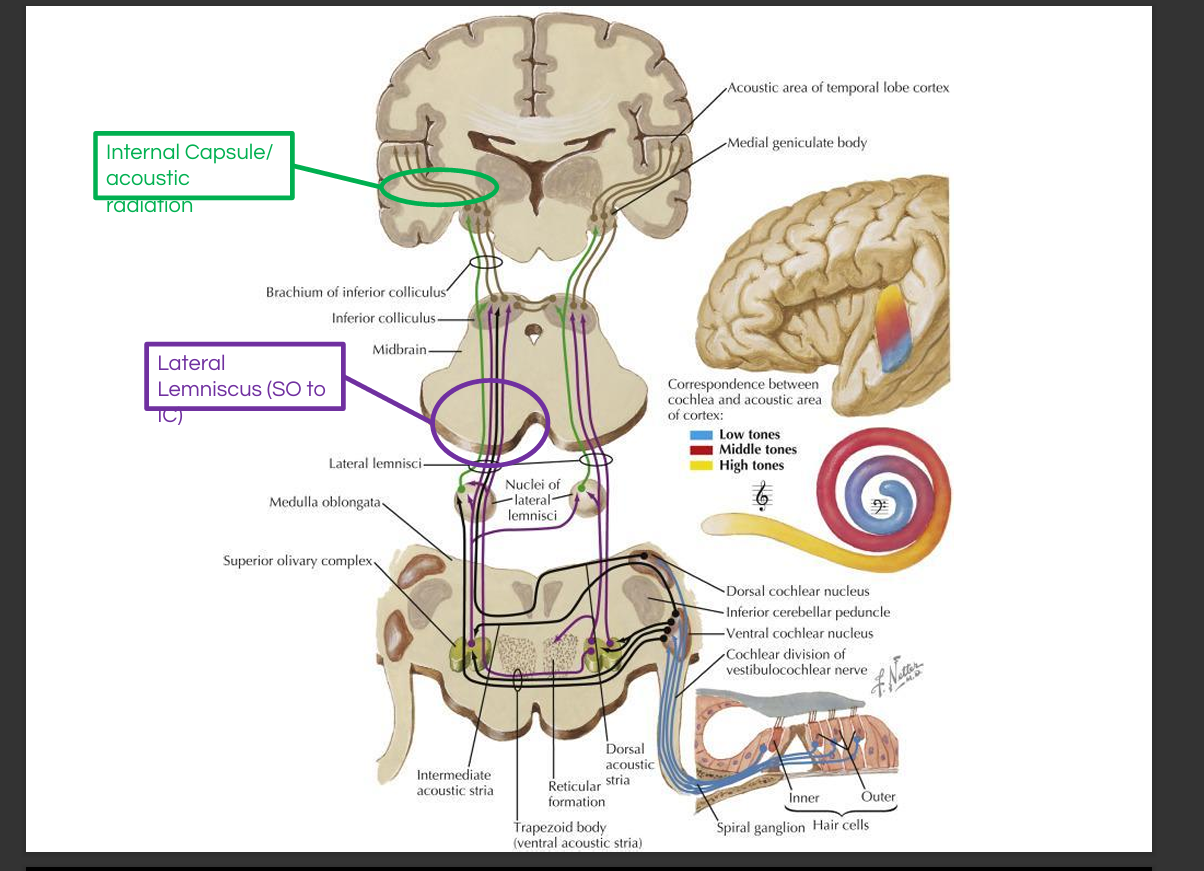

Describe the role of the superior olivary complex.
It computes sound localization using interaural time differences (medial SOC) and interaural intensity differences (lateral SOC).

Describe the role of the inferior colliculus.
It integrates spatial auditory information and contributes to reflexive orientation toward sound.

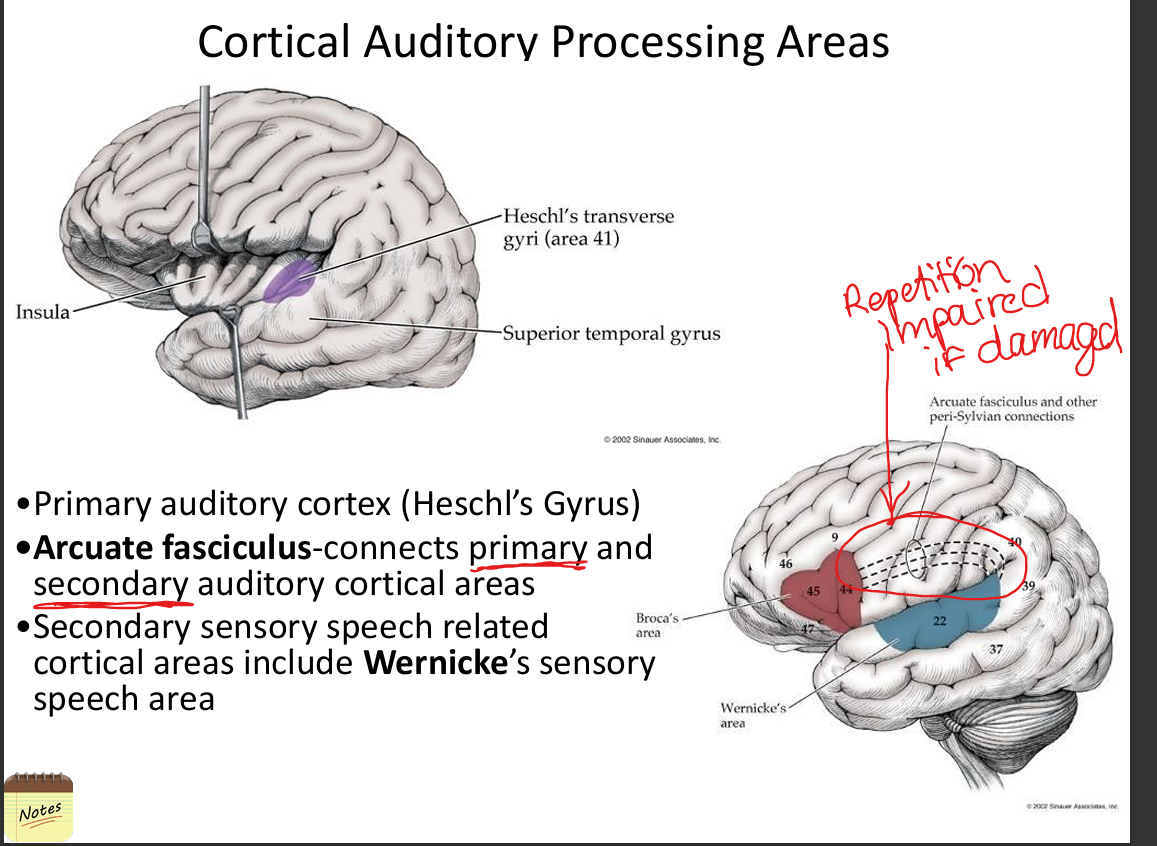
Describe the role of auditory cortex.
Primary auditory cortex (Heschl’s gyrus) processes pitch and tonotopy; secondary areas process speech, music, and temporal patterns.

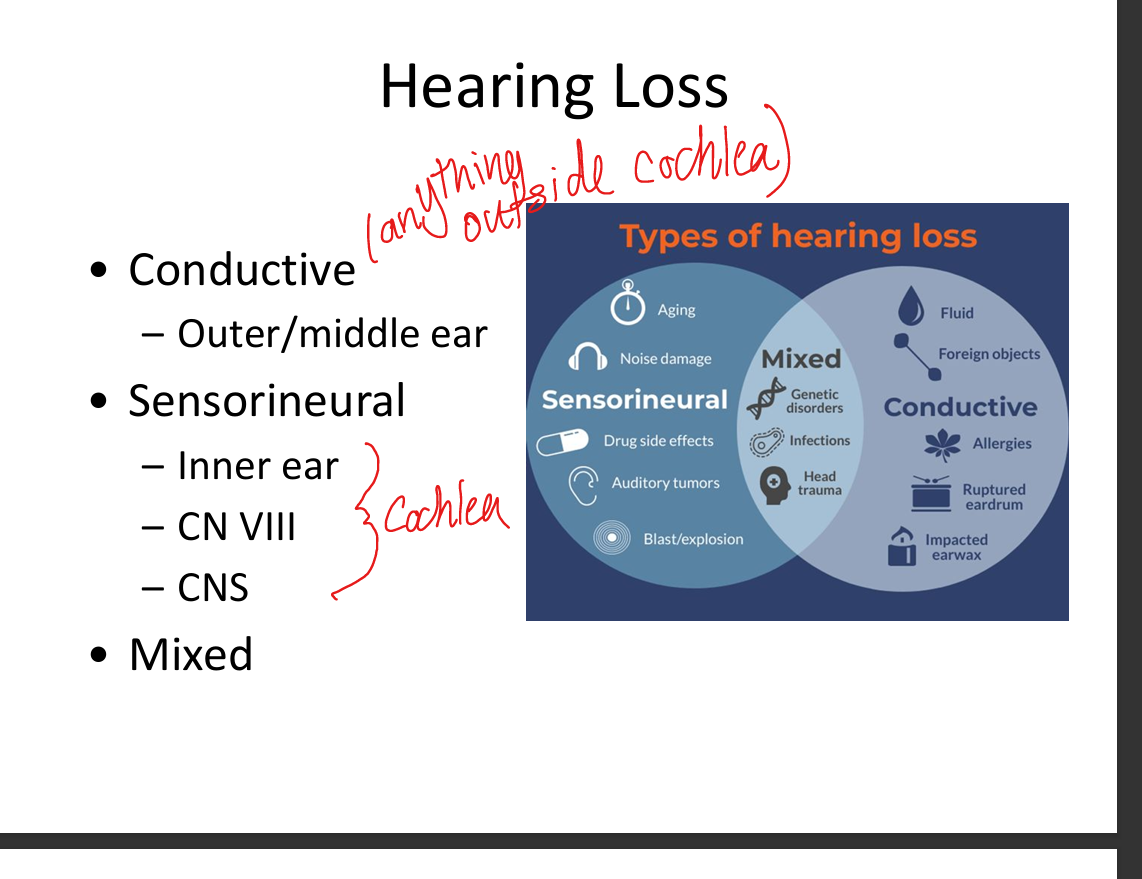
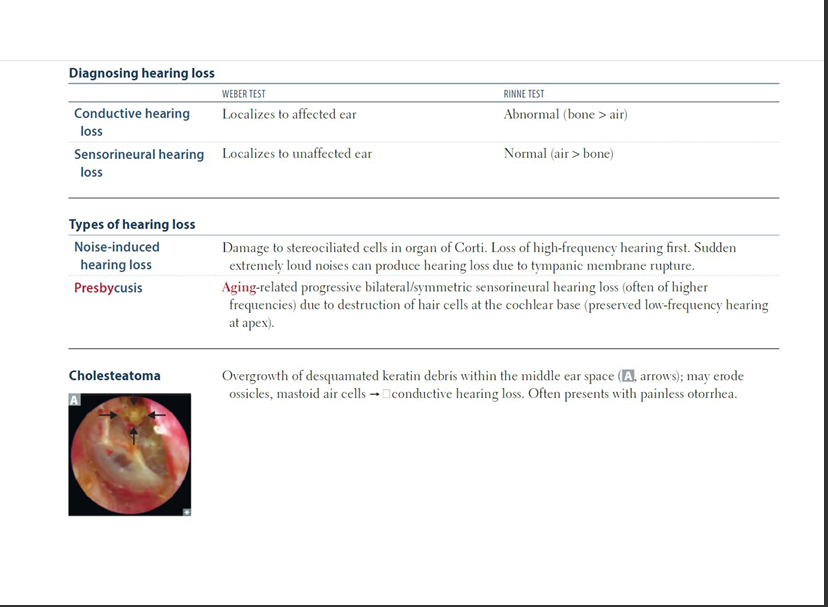
Compare conduction vs sensorineural deafness.
Conduction deafness affects outer/middle ear sound transmission; sensorineural deafness affects inner ear hair cells or CN VIII.

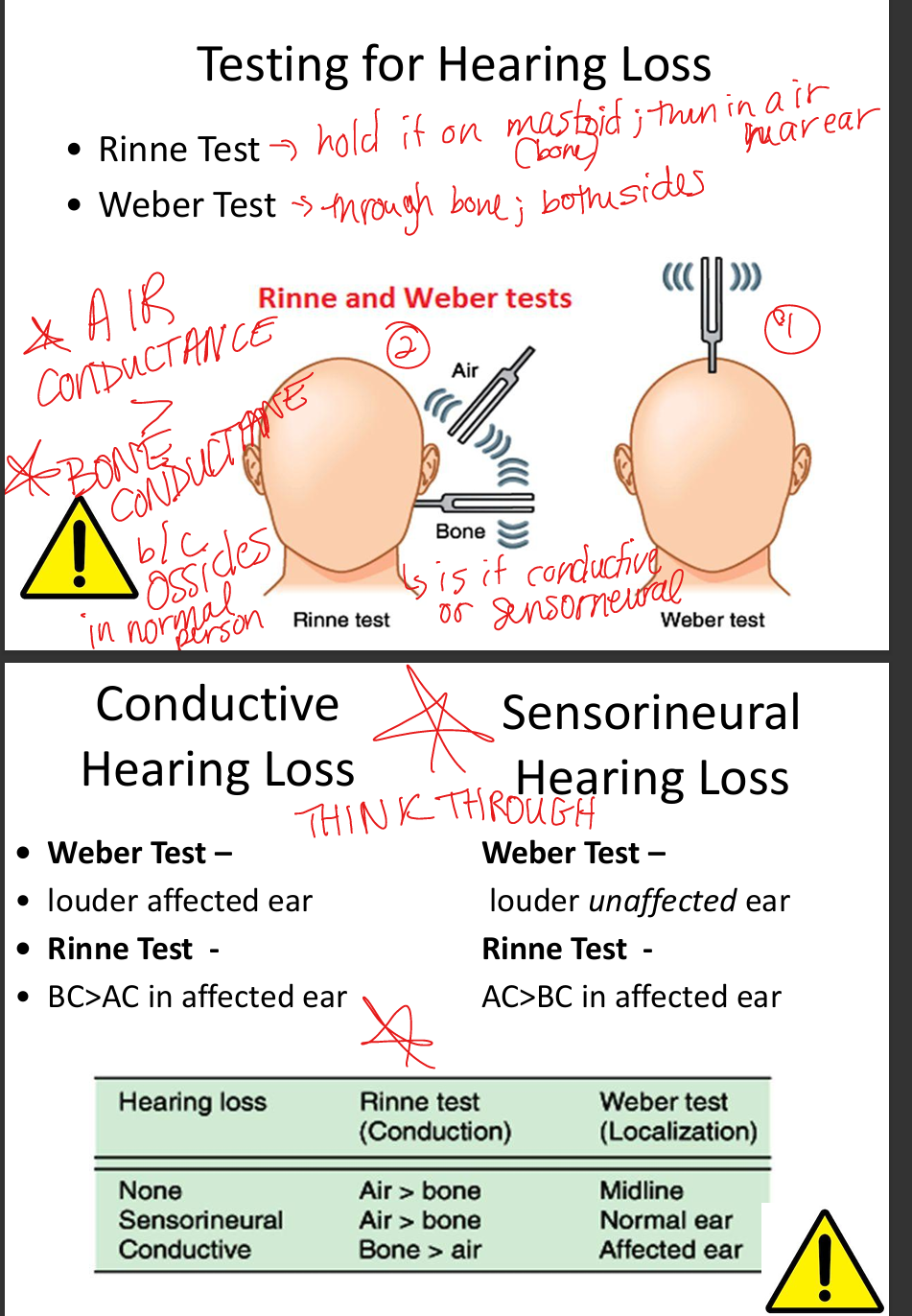
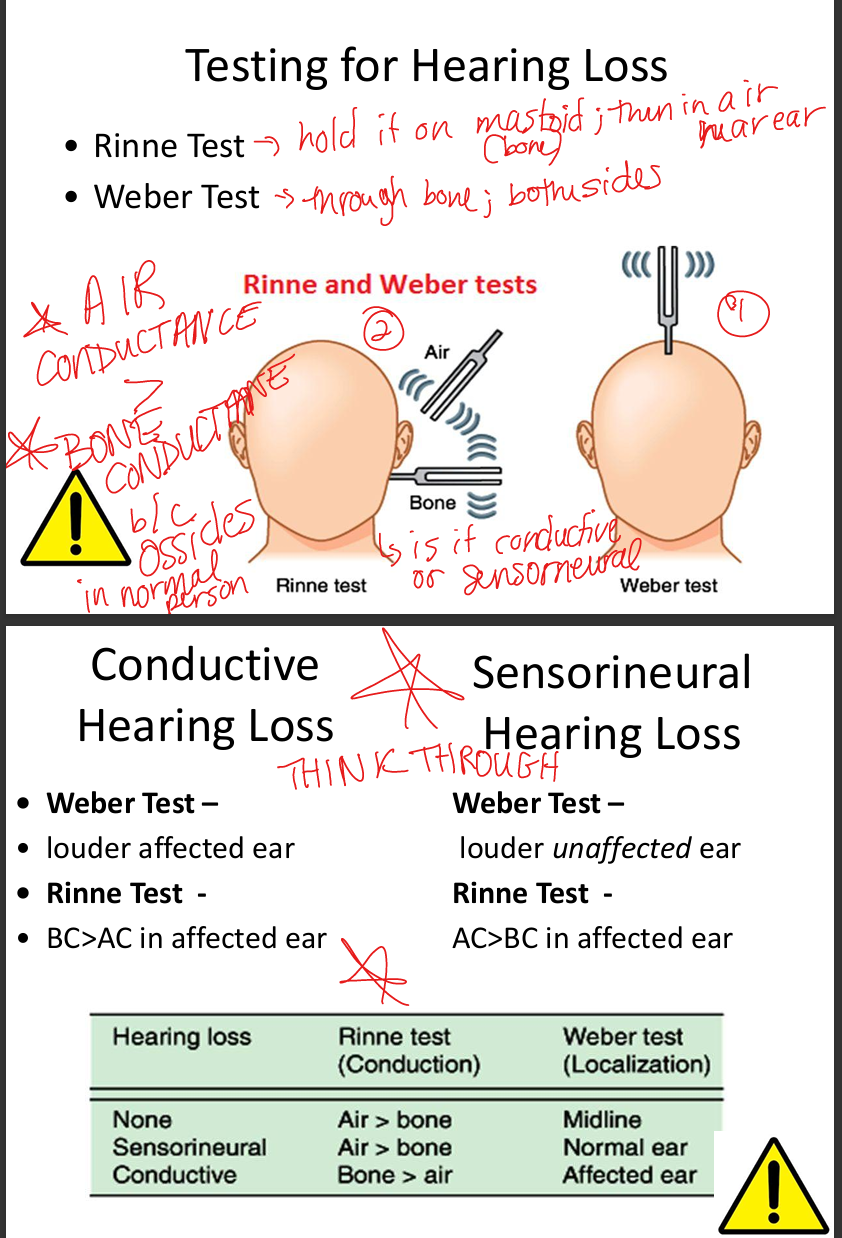
Describe clinical tests for conduction vs sensorineural deafness.
Weber: lateralizes to affected ear in conductive loss, to unaffected ear in Sensorineural Hearing Loss.
Rinne: Air Conduction>Bone Conduction =normal/SNHL; Bone Conduction>Air Conduction=conductive.

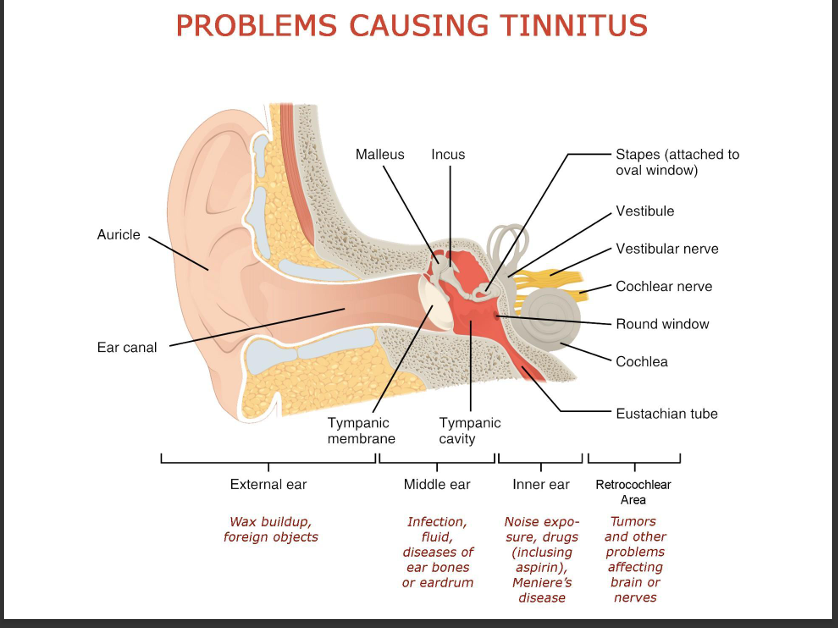
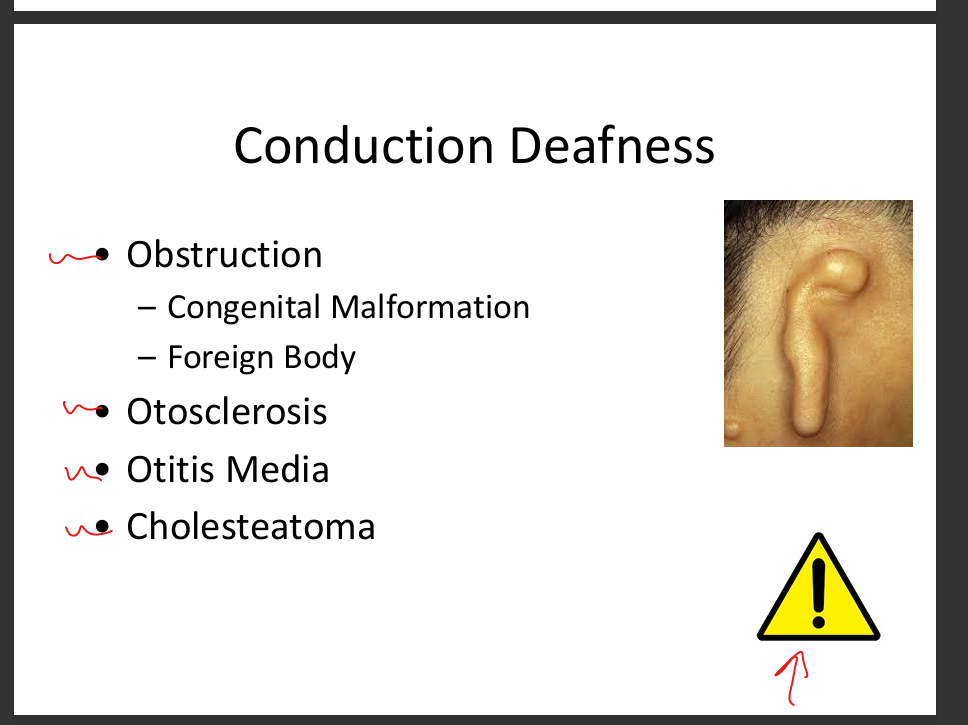
List common conductive hearing pathologies.
Otitis media(ear infection), otosclerosis(abnormal bone growth build up), cholesteatoma, Tympanic membrane perforation, obstruction

List common sensorineural hearing pathologies.
Presbycusis(loss of high frequency sounds), noise‑induced hair cell loss, Meniere’s disease, vestibular schwannoma, ototoxic drugs (aminoglycosides, loop diuretics).


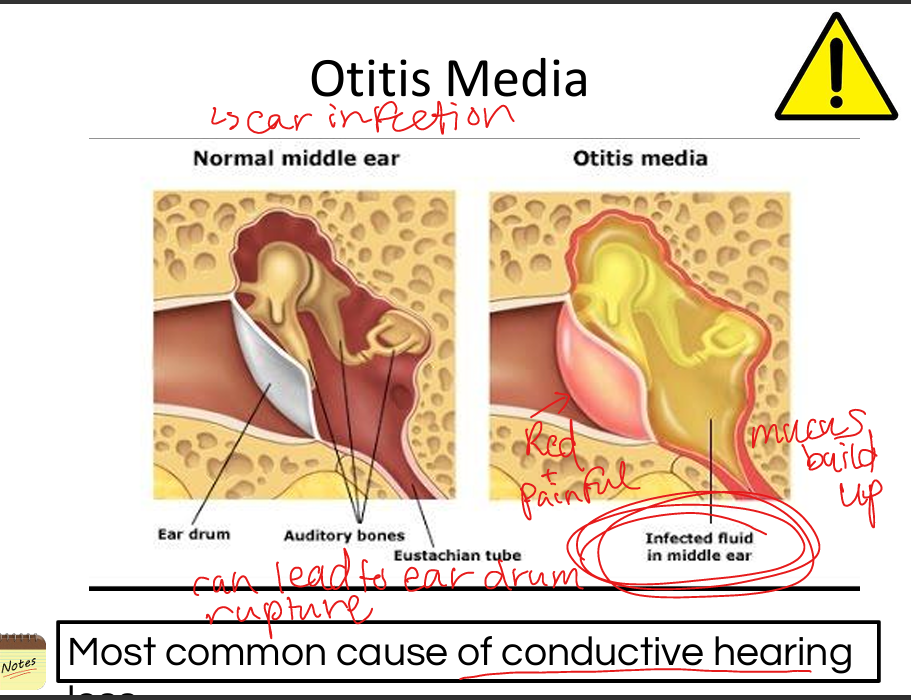
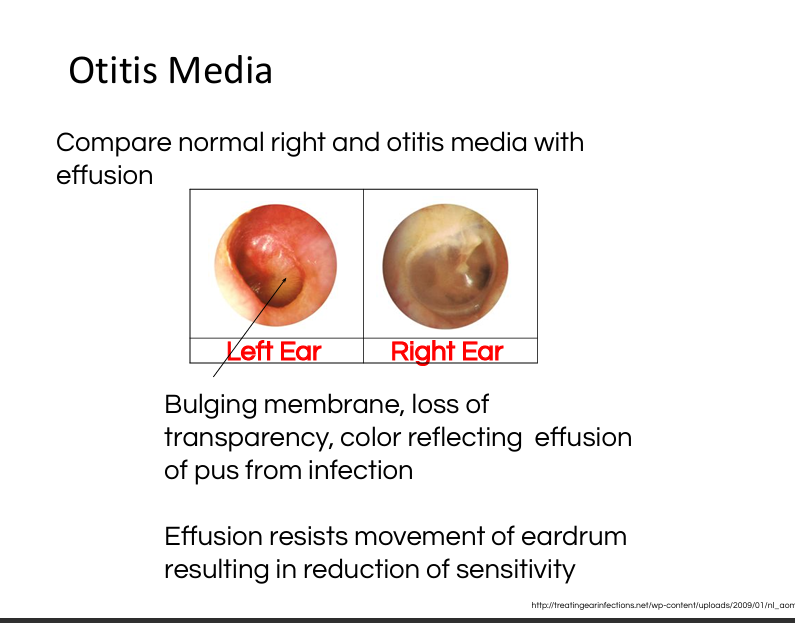
Explain otitis media.
Middle ear infection causing fluid buildup, reduced Tympanic membrane mobility, conductive hearing loss; diagnosed via otoscopy.

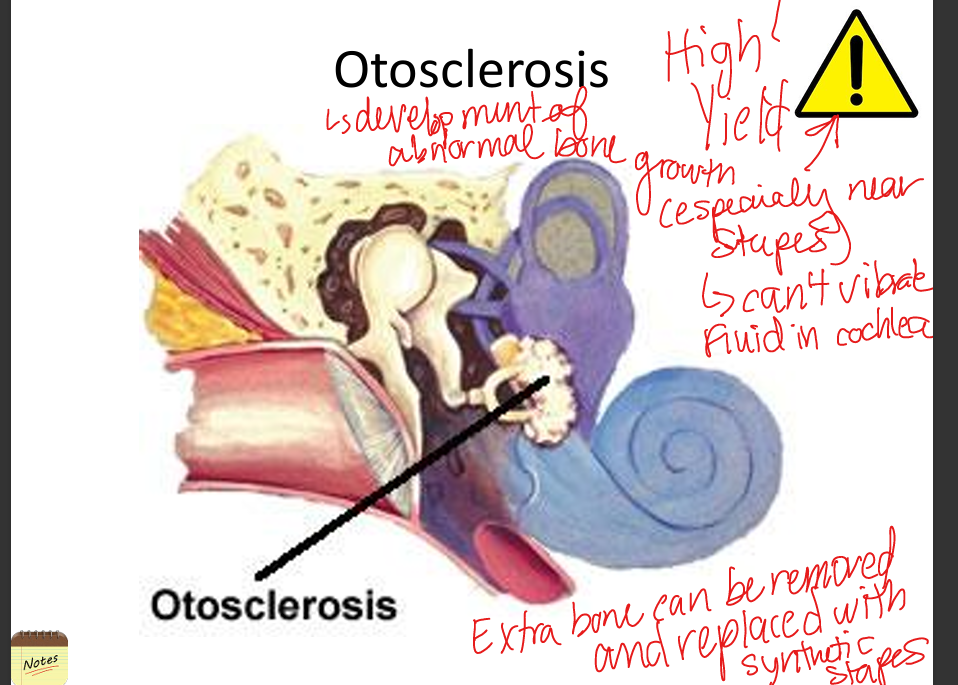
Explain otosclerosis.
Abnormal bone growth around stapes footplate causing fixation and conductive hearing loss; treated with stapedectomy.

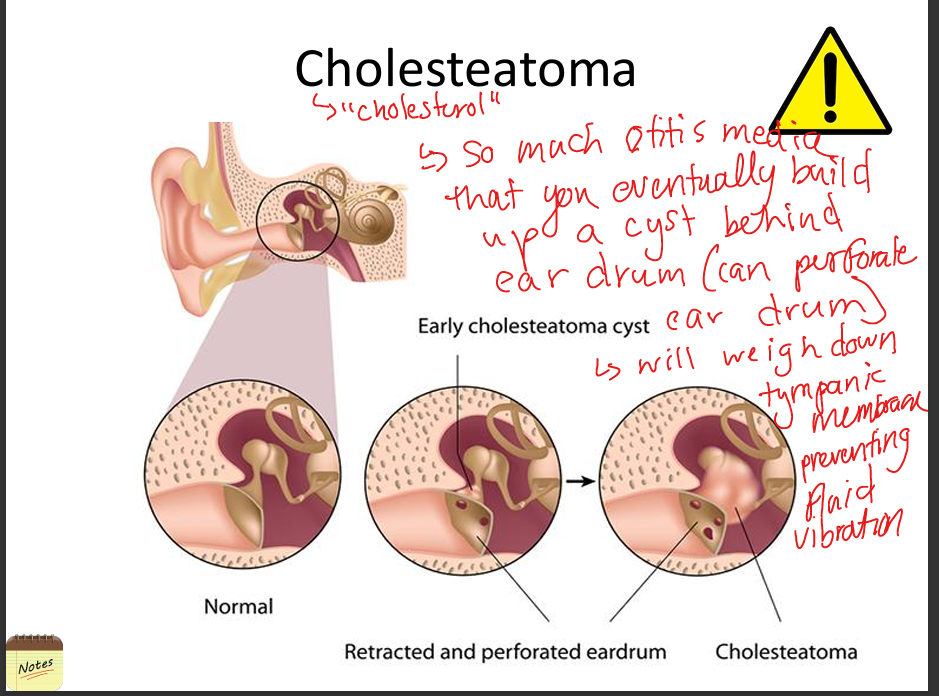
Explain cholesteatoma.
Benign keratinizing cyst in middle ear that erodes ossicles; causes conductive hearing loss and requires surgical removal.

Explain presbycusis.
Age‑related bilateral high‑frequency sensorineural hearing loss due to hair cell degeneration at cochlear base.

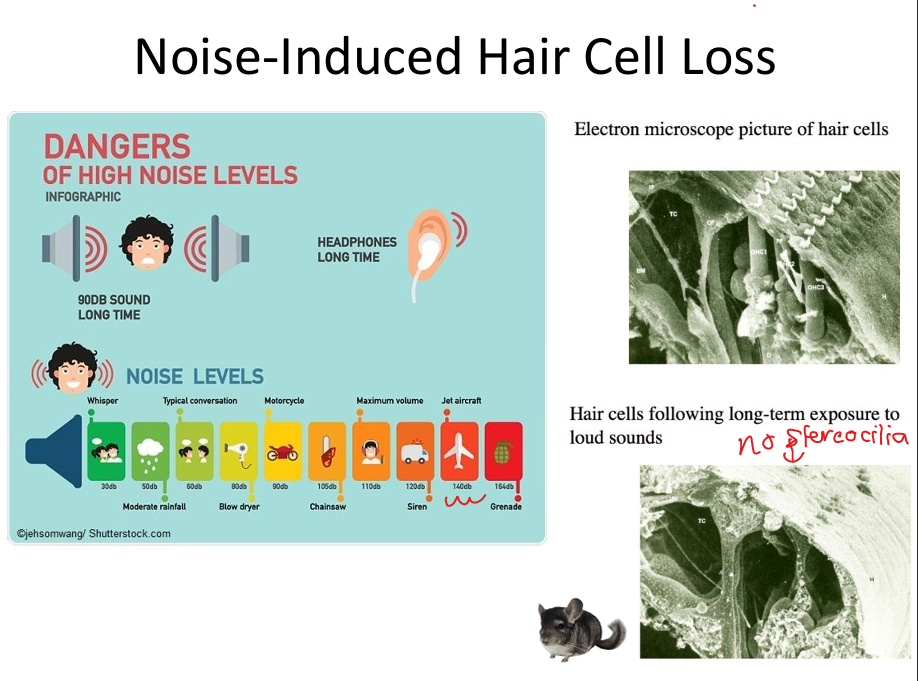
Explain noise‑induced hearing loss.
Prolonged loud sound damages outer hair cells; high frequencies lost first; irreversible.

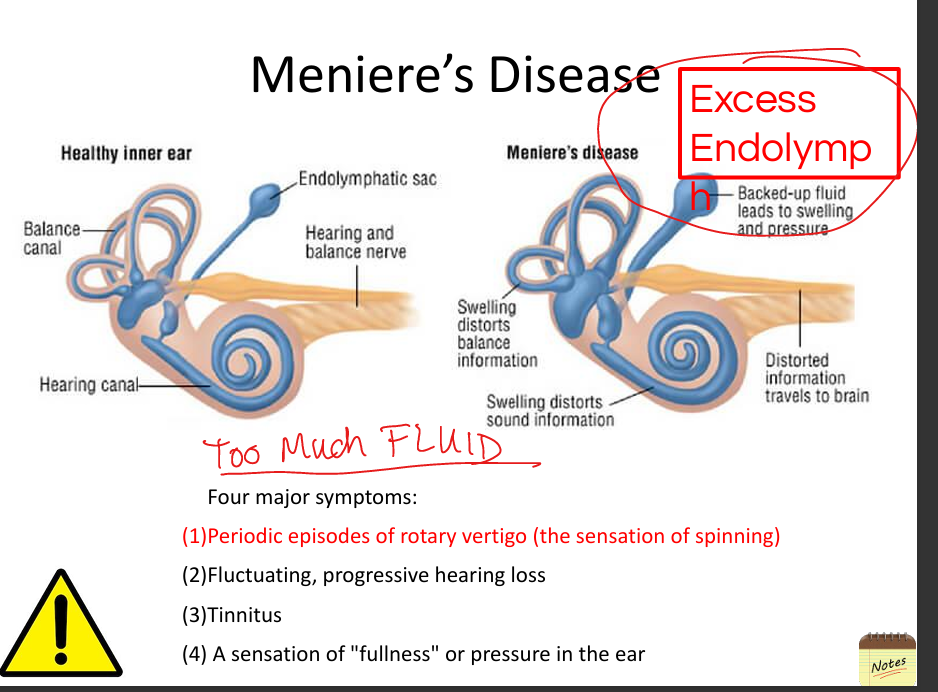
Explain Meniere’s disease.
Excess endolymph causes episodic vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and ear fullness.
(Men have too much fluid)

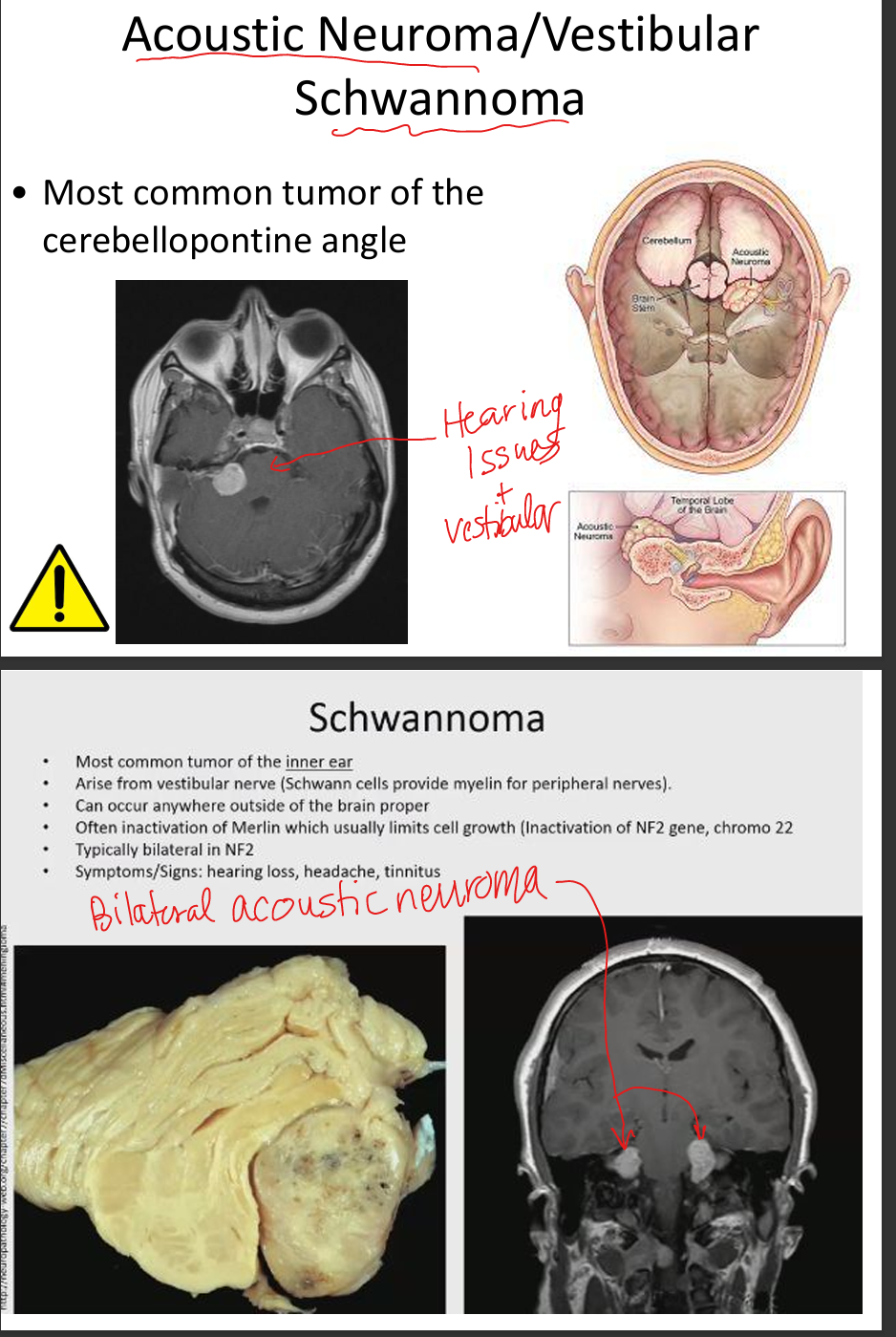
Explain vestibular schwannoma.
Benign tumor of CN VIII Schwann cells causing unilateral SNHL, tinnitus, imbalance; diagnosed with MRI.

Describe Rinne test interpretation.
AC>BC = normal or SNHL; BC>AC = conductive loss.
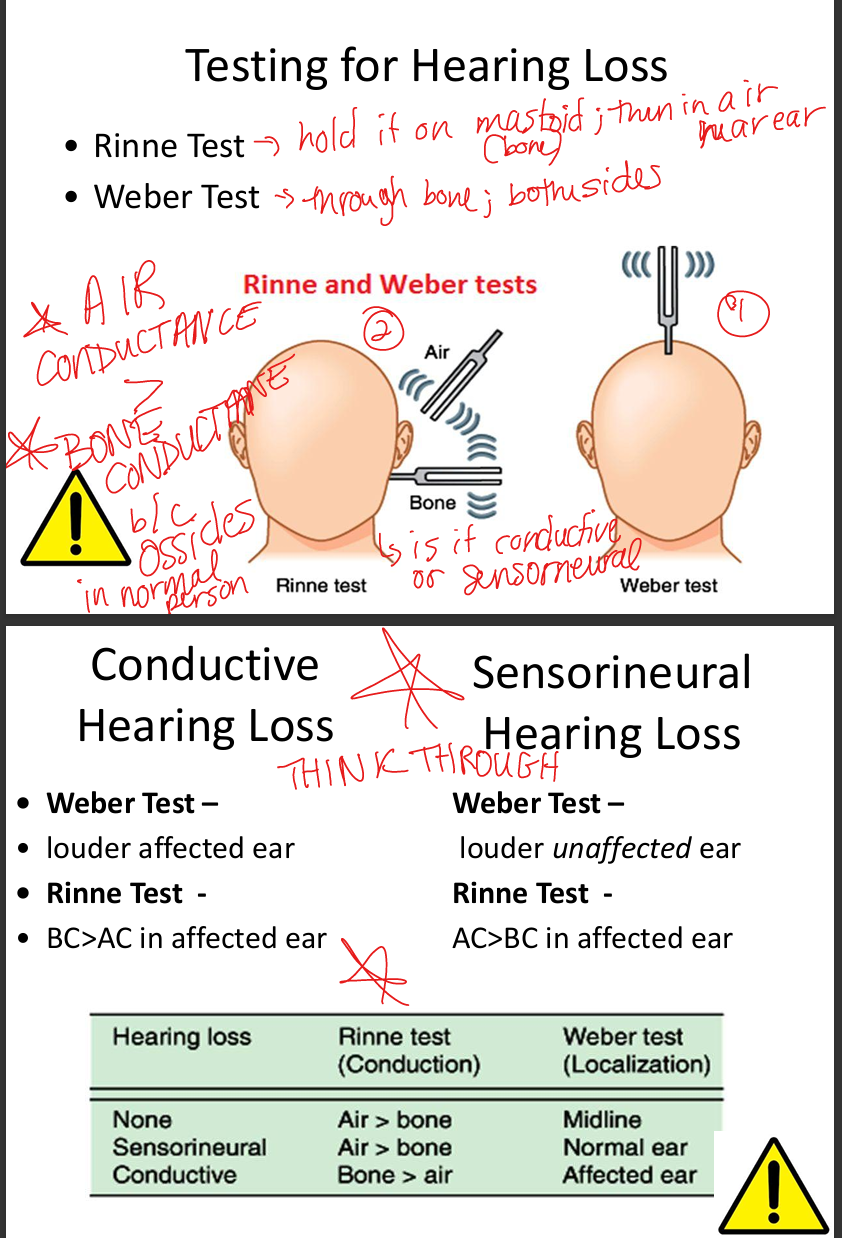

Describe Weber test interpretation.
Lateralizes to affected ear in conductive loss; to unaffected ear in SNHL.

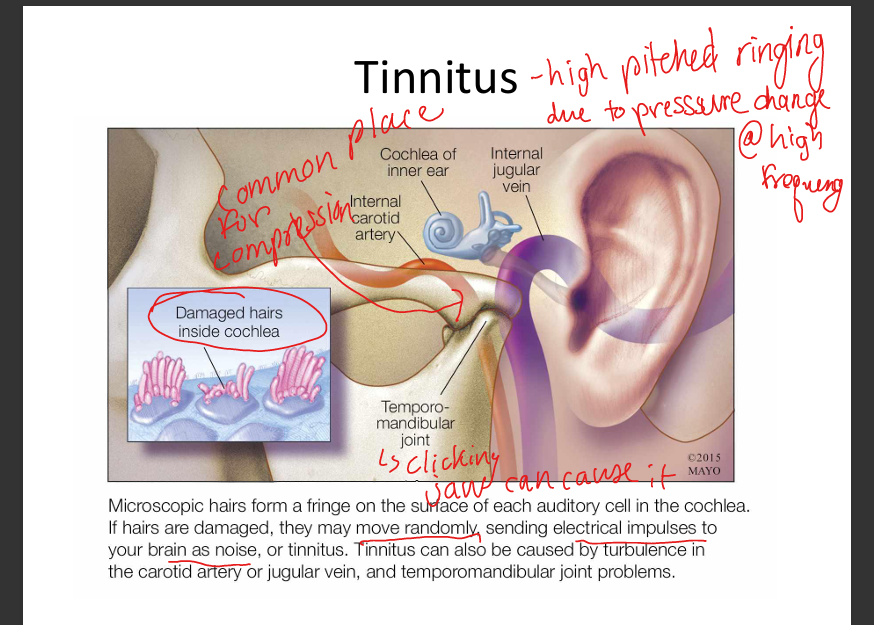
What is tinnitus? What can cause it?
High pitched ringing due to pressure change at high frequency. Causes: Foreign objects, infection, fluid, hair cell damage, turbulance in internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein, or temporomandibular joint porblems.