1.7 nucleic acids
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what makes up the genetic material of living organisms
DNA
what are the monomer subunits called in DNA
nucleotides
what is built up of many nucleotides but differ from DNA because they have different pentose sugars and bases
RNA
what do nucleotides consist of
pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
DNA bases
A,G,C,T
RNA bases
A,G,C,U
what forms the backbone of DNA molecules
the sugar and phosphate groups being identical all the way along the chain
what forms the genetic code
the sequence of bases in the chain varying
what gives DNA a large capacity for storing genetic information
different organisms having different lengths and any base sequence
why is DNA universal
because the genetic code carried in the sequence of bases that make a DNA molecule is similar across all forms of life
adenine pairs with thymine and needs how many hydrogen bonds
2
cytosine always pairs with guanine and needs how many hydrogen bonds
3
what is the pairing of bases in DNA and RNA called
complementary base pairing
the 2 DNA chains run in opposite directions meaning it is…
antiparallel
what is the basic material of inheritance
DNA
where is DNA contained
the nucleus in eukaryotes and the cytoplasm of prokaryotes
what is a nucleotide
the basic chemical unit of a nucleic acid
→ an organic base combined with pentose sugar and phosphate
compare and contrast DNA and RNA
DNA
contains deoxyribose
A,G,C,T
double-stranded
RNA
contains ribose
A,G,C,U
single-stranded
the process in which the genome’s DNA is copied in cells is called what
DNA replication
when a cell divides and the genetic code is passed on to the daughter cells, what is it called
DNA replication
what is the enzyme called that unzips the DNA molecule when going through DNA replication
helicase
each of 2 partner strands of DNA acting as a template for a new strand
semi-conservative replication
be able to draw what it looks like lil bro
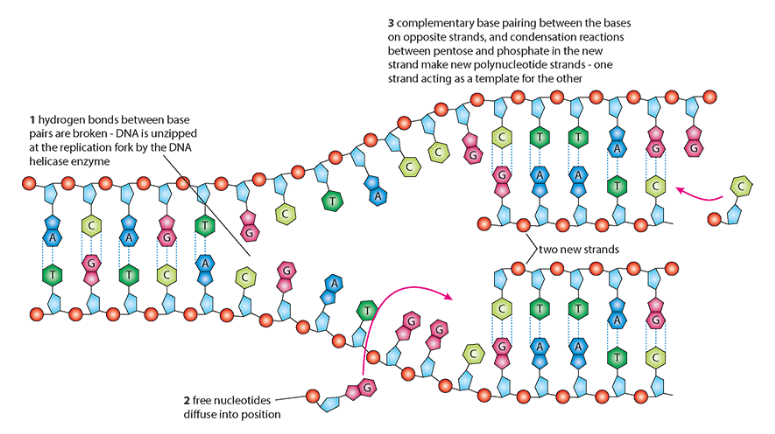
what is complementary base pairing also crucial for
gene expression
what does nucleosome refer to
a part of a eukaryotic chromosome, made of DNA wrapped around histone molecules and held in place by another histone protein
where is DNA found in eukaryotes
the nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane
what are the 3 key functions of histones
packaging of DNA
gene regulation
supercoiling DNA during cell division
a nitrogenous base such as cytosine, thymine, or uracil found in nucleic acids
pyrimidines
a nitrogenous base such as adenine or guanine found in nucleic acids
purines
the 4 DNA bases fall into 2 chemical groups. What are they
pyrimidines and purines
what ensures that the strands of DNA are always the same distance apart
the pairing of pyrimidine with a purine