AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.7: Optical Isomerism + 3.3.8: Aldehydes and Ketones
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the general formula of aldehydes and ketones? (1)
CnH2nO
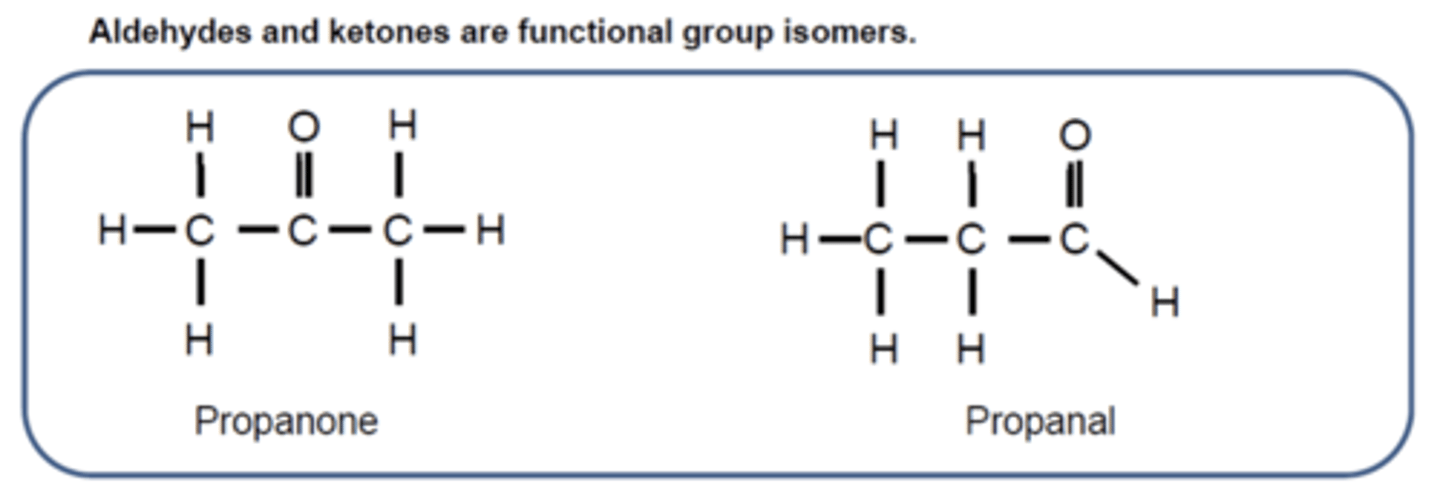
How do aldehydes and ketones differ in the placement of the C=O functional group? (2)
- Ketones have the C=O group in the middle of the carbon chain.
- Aldehydes have the C=O group at the end of the carbon chain
What are aldehydes and ketones classified as in terms of isomerism? (1)
They are functional group isomers of each other
How can aldehydes and ketones be distinguished in oxidation reactions? (2)
- Aldehydes are further oxidised to carboxylic acids.
- Ketones are not easily oxidised using potassium dichromate(VI).
Why can't potassium dichromate(VI) distinguish between primary and secondary alcohols? (1)
Both show the orange to green colour change during oxidation
Draw and label the structural formulas of propanone and propanal, and explain their functional group isomerism. (2)
What is the observation when aldehydes react with Tollens' reagent? (1)
A silver mirror is formed
What is the observation when ketones react with Tollens' reagent? (1)
No observable change
What is the observation when aldehydes react with Fehling's solution? (1)
A brick-red precipitate is formed.
What is the observation when ketones react with Fehling's solution? (1)
No observable change
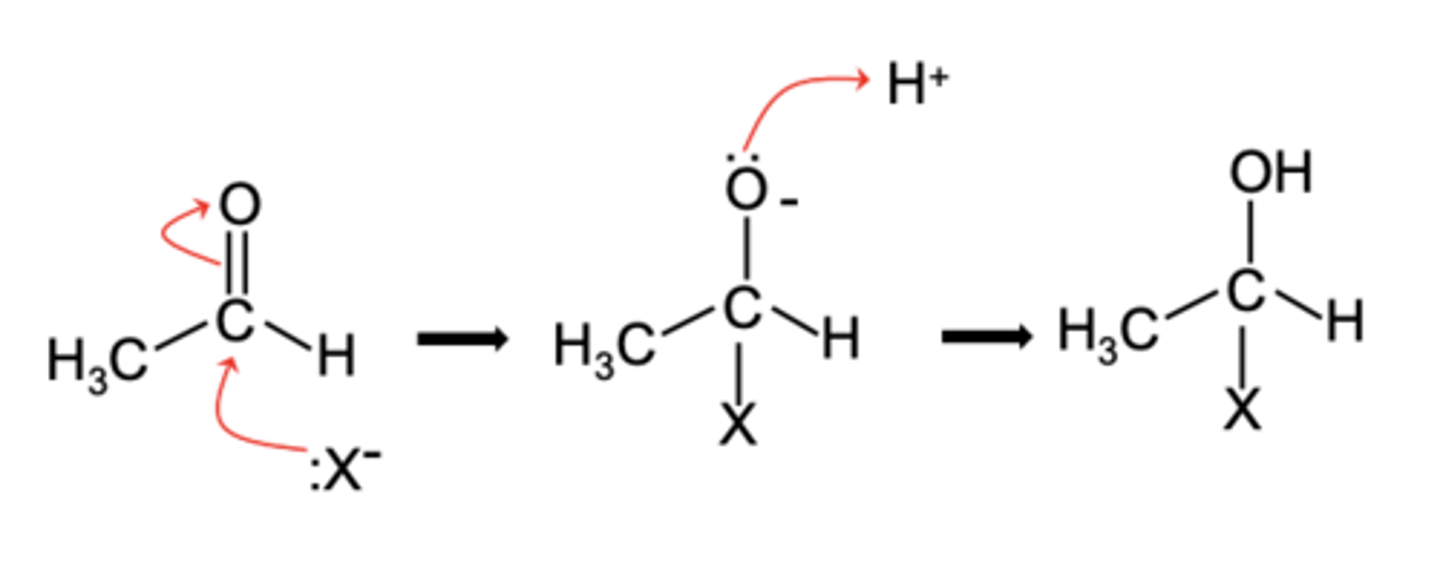
Draw a general mechanism for nucleophilic addition of aldehydes and ketones (3)
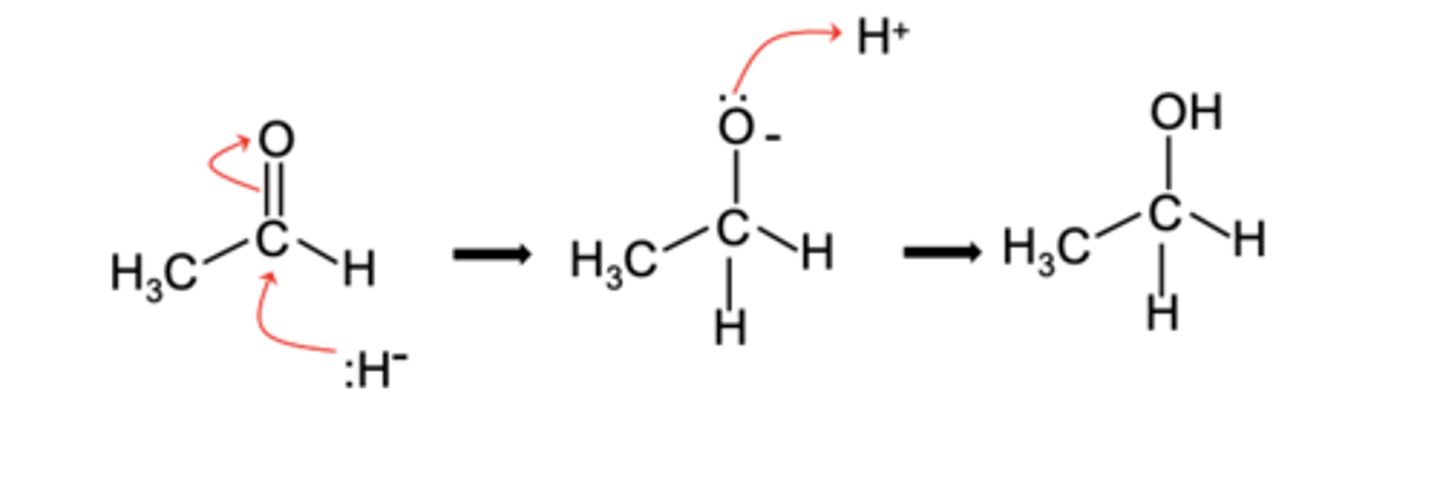
What is the role of sodium tetrahydridoborate (NaBH4) in reduction reactions? (2)
- NaBH4 acts as a reducing agent
- Providing hydride (H⁻) ions to reduce aldehydes and ketones to alcohols
What are aldehydes reduced to in the presence of a reducing agent? (1)
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols
Write the equation for the reduction of ethanal to ethanol. (1)
CH3CHO + 2[H] → CH3CH2OH
What are ketones reduced to in the presence of a reducing agent? (1)
Ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols
Write the equation for the reduction of propanone to propan-2-ol. (1)
CH3COCH3 + 2[H] → CH3CH(OH)CH3
Draw and label the nucleophilic addition mechanism for ethanal reacting with NaBH4
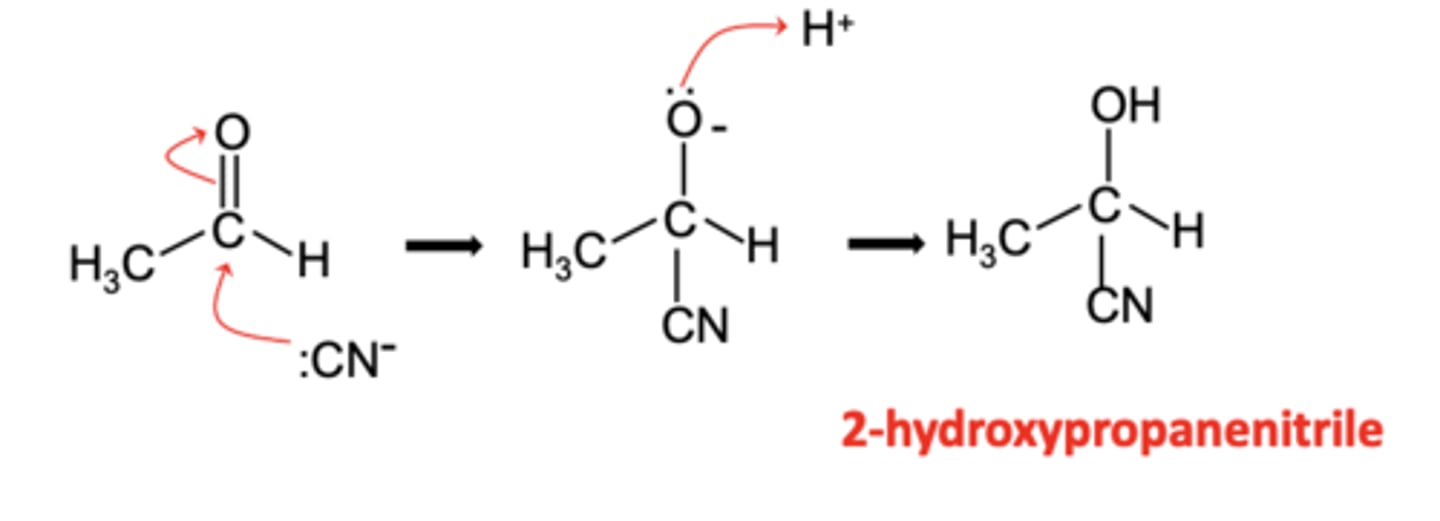
What happens when aldehydes and ketones react with potassium cyanide (KCN) and dilute HCl? (2)
- Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition with KCN
- Forming an alcohol with a nitrile functional group
Write the overall equation for the reaction of ethanal with KCN and dilute HCl. (1)
CH3CHO + KCN + HCl → CH3CH(OH)CN + KCl
Write the ionic equation for the nucleophilic addition reaction of ethanal with KCN. (1)
CH3CHO + CN⁻ + H⁺ → CH3CH(OH)CN
Draw and label the mechanism for the reaction of ethanal with KCN and dilute HCl (2)
What is a racemic mixture? (2)
- A racemic mixture contains equal amounts of each enantiomer
- Is optically inactive, and rotates a plane of polarized light equally in opposite directions
Why are racemic mixtures optically inactive? (2)
- They are optically inactive
- Because the rotations of the plane of polarised light by the enantiomers cancel each other out
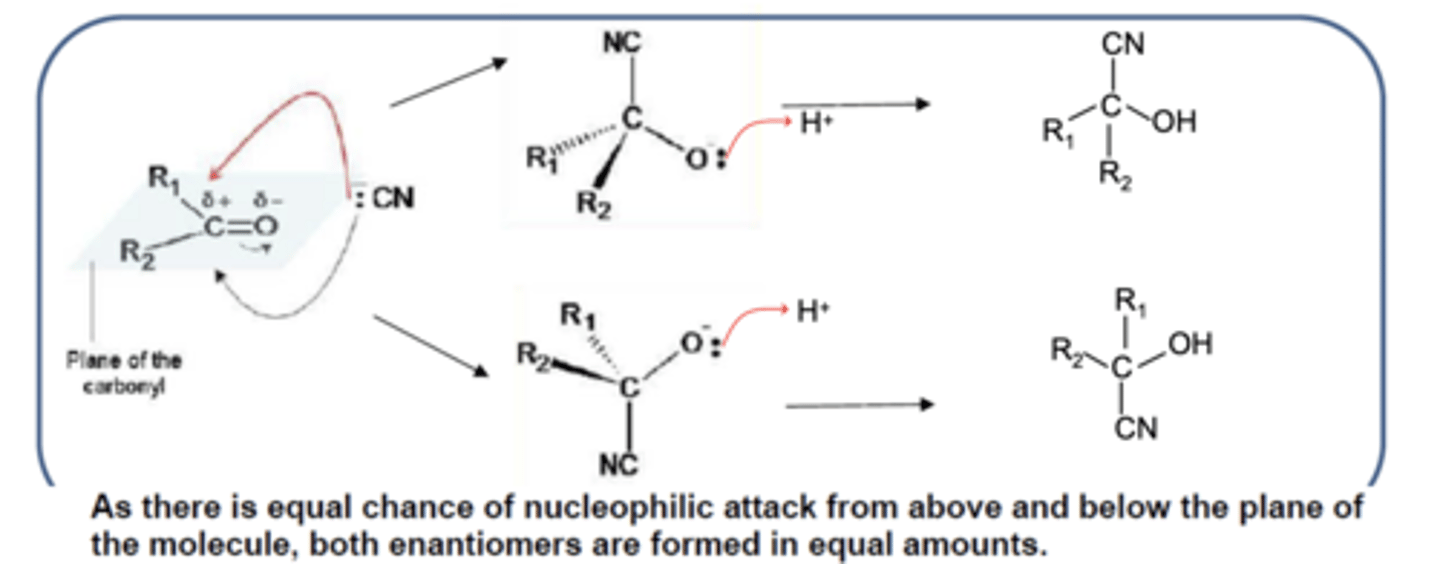
Draw and label the mechanism for nucleophilic addition resulting in the formation of an optical isomer from a carbonyl compound. (2)
What is the reagent and catalyst used in the catalytic hydrogenation of nitriles? (1)
Hydrogen (H2) and a nickel catalyst
What functional group is formed by the catalytic hydrogenation of nitriles? (1)
A primary amine (-CH2NH2) group
Write the reaction for the hydrogenation of CH3CN to form ethylamine (CH3CH2NH2). (1)
CH3CN + 4[H] → CH3CH2NH2
Why is the catalytic hydrogenation of nitriles important in synthesis? (2)
- It turns nitriles into more reactive amine groups
- Allowing further reactions in synthesis routes
How is a hydroxy group named in a molecule containing both a hydroxy group and a nitrile group? (2)
- The hydroxy group is named using the "hydroxy-" prefix
- The nitrile group uses the "-nitrile" suffix
Name the hydroxy-nitrile with the structure: CH3—CH2—CH(OH)—C≡N. (1)
2-hydroxybutanenitrile
Name the hydroxy-nitrile with the structure: CH3—CH2—C(OH)(CH3)—C≡N. (1)
2-hydroxy-2-methylbutanenitrile