9 - ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES AND AUTONOMIC NERVES (BRS) 2026
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
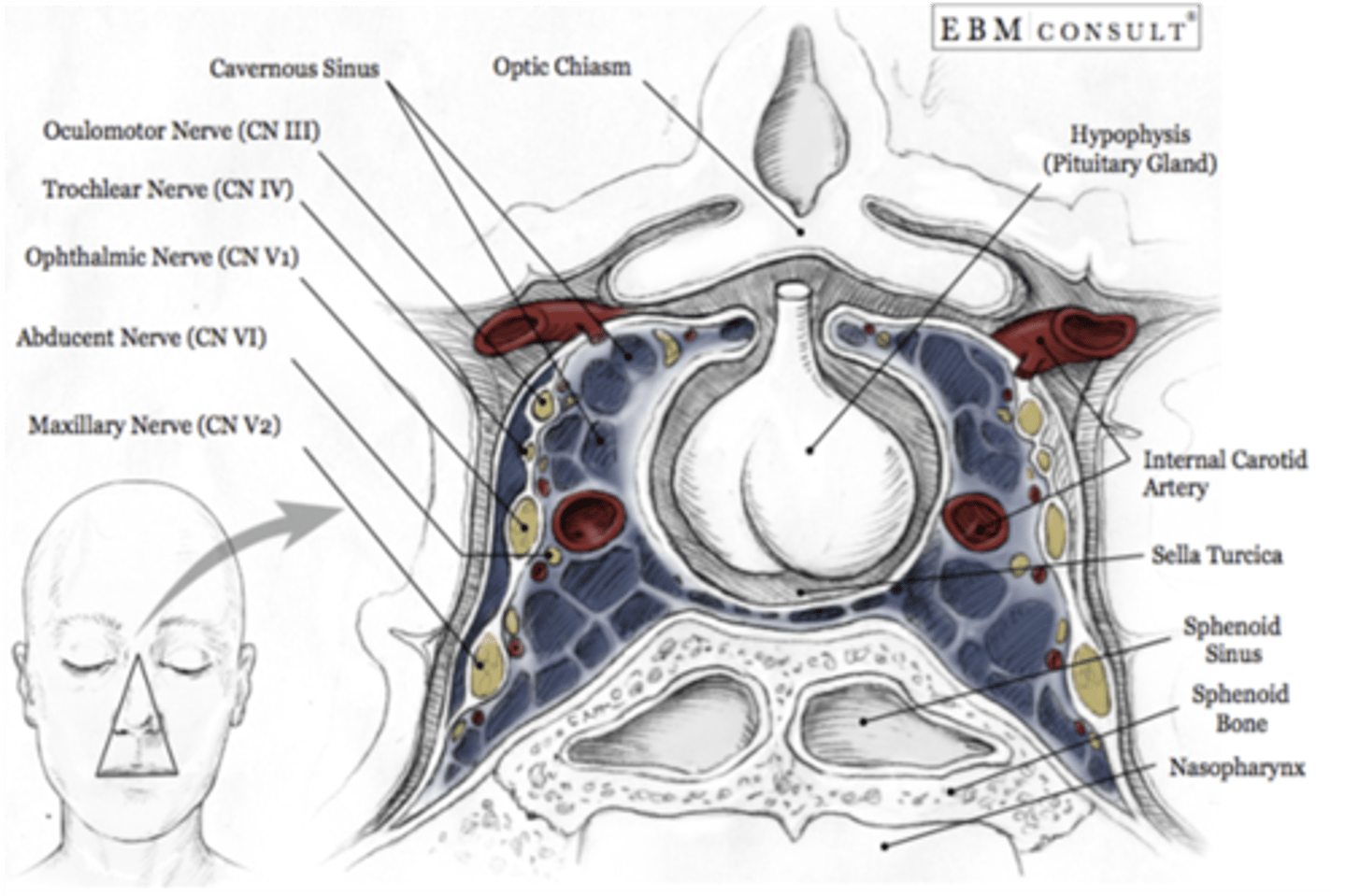
Cavernous sinus thrombosis can damage what three cranial nerves?
CN III, IV and VI
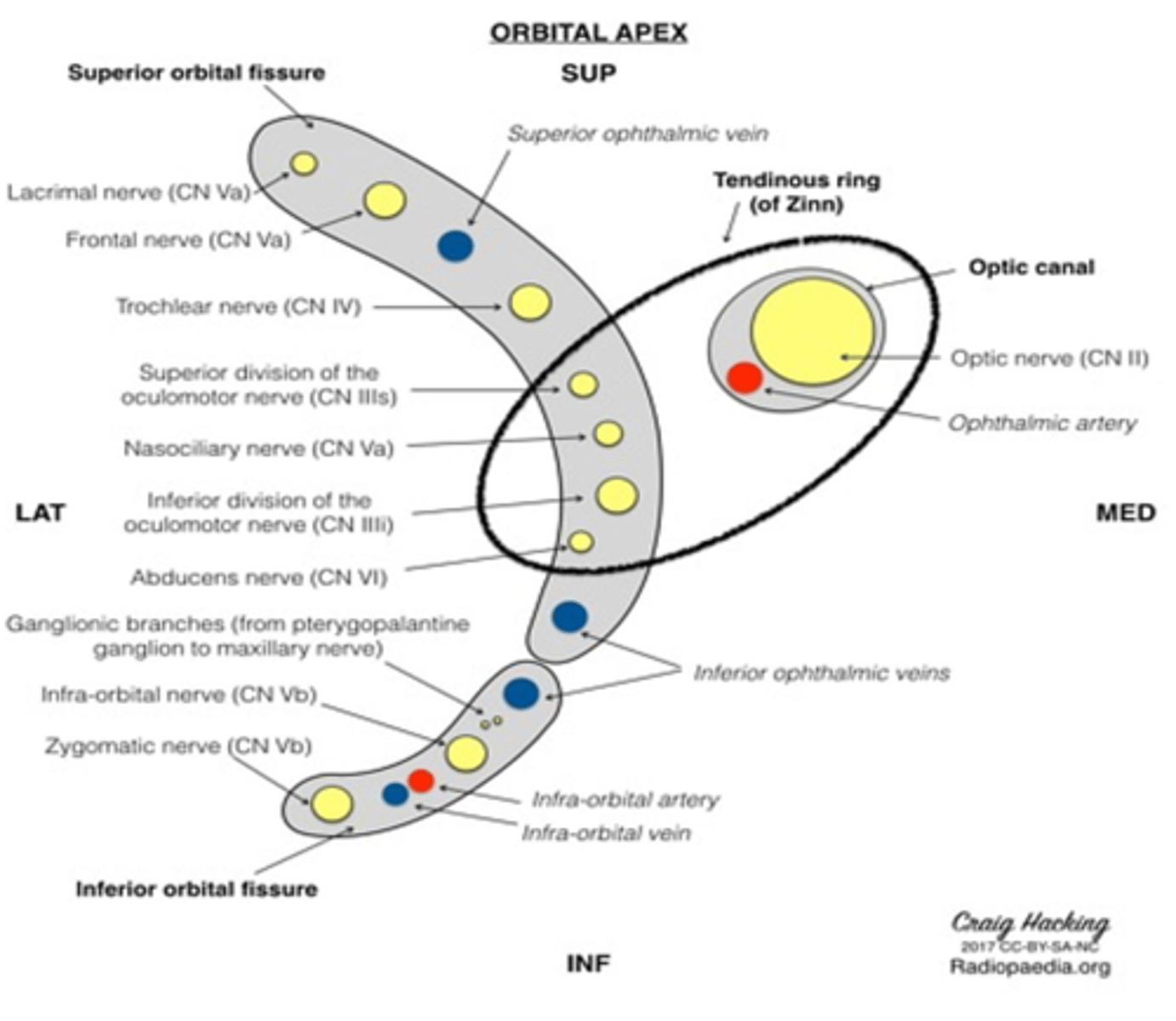
Optic canal tumors can lead to damage of what two structures?
Optic nerve
Ophthalmic artery
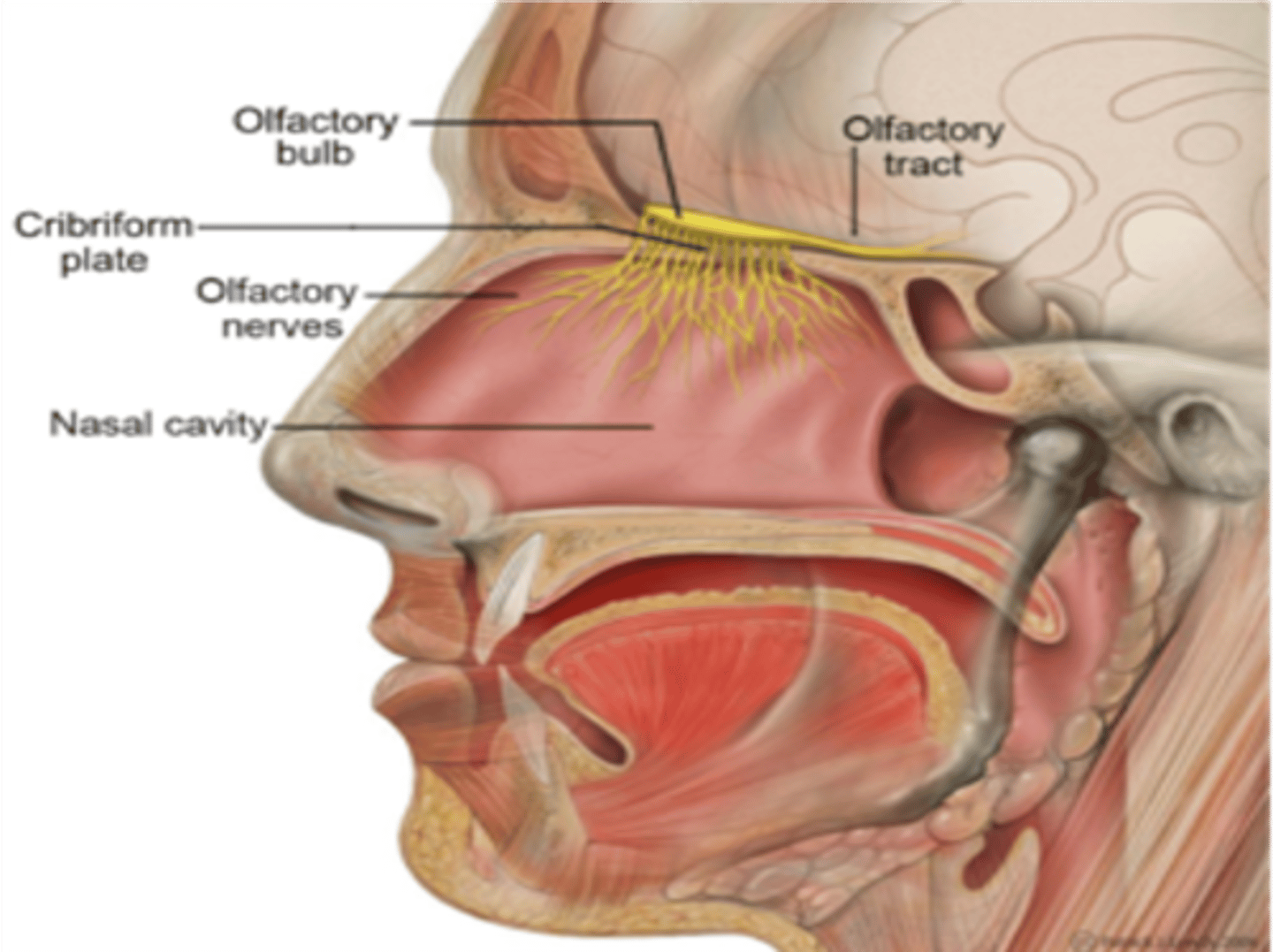
Lesion of the olfactory nerve leads to loss of smell, a condition also known as?
Anosmia
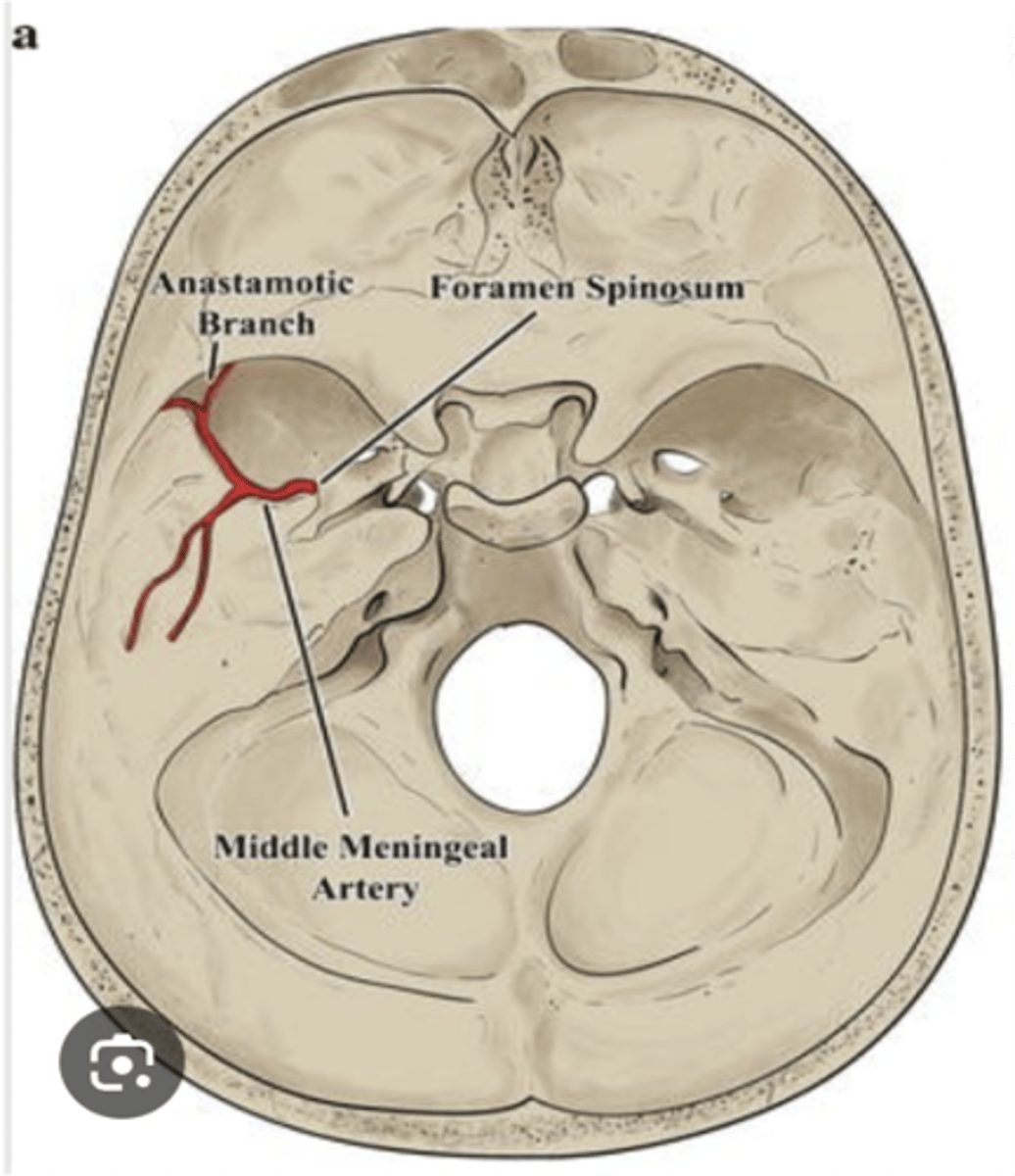
What artery passes through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
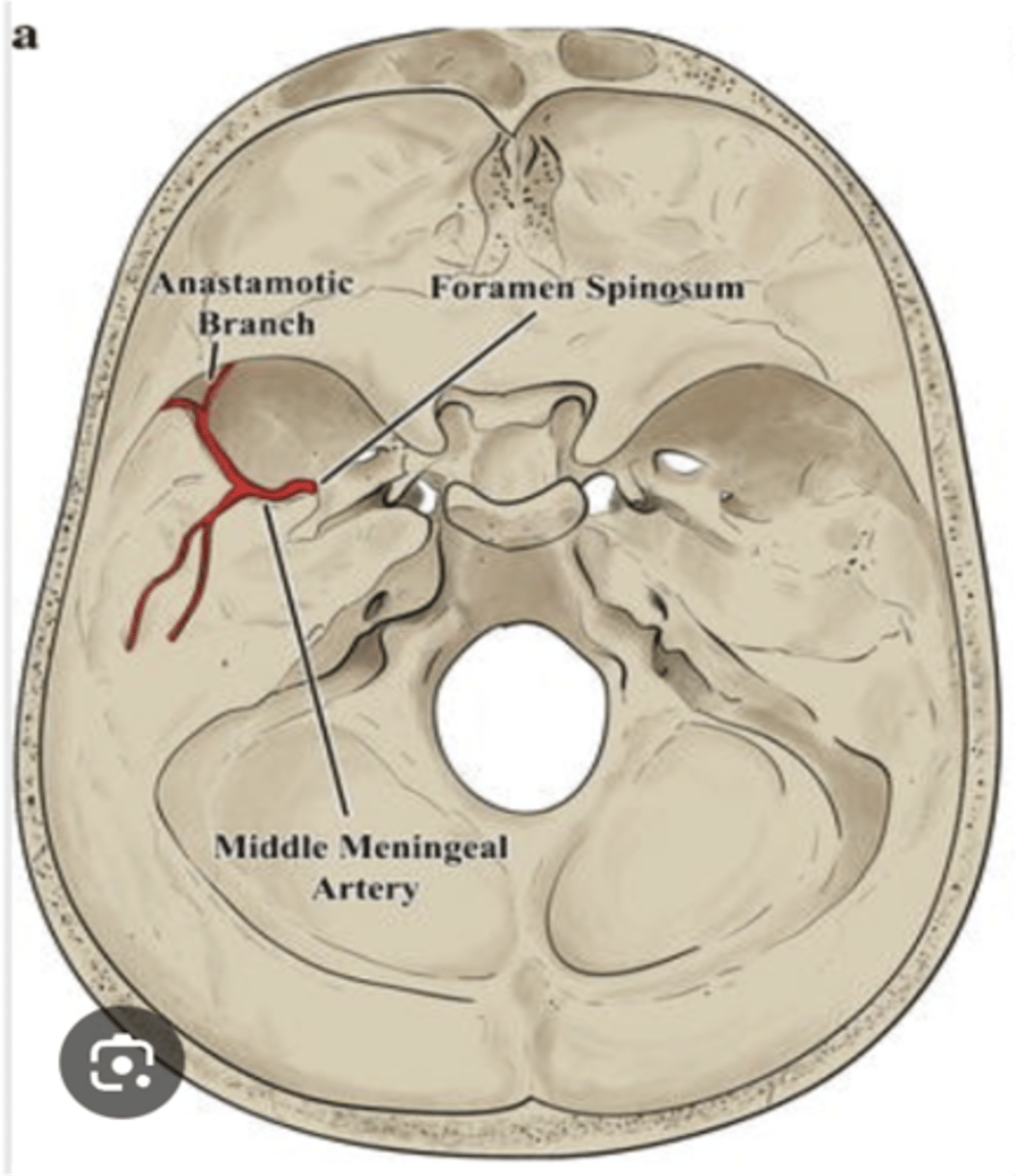
The middle meningeal artery passes through what foramen?
Foramen spinosum
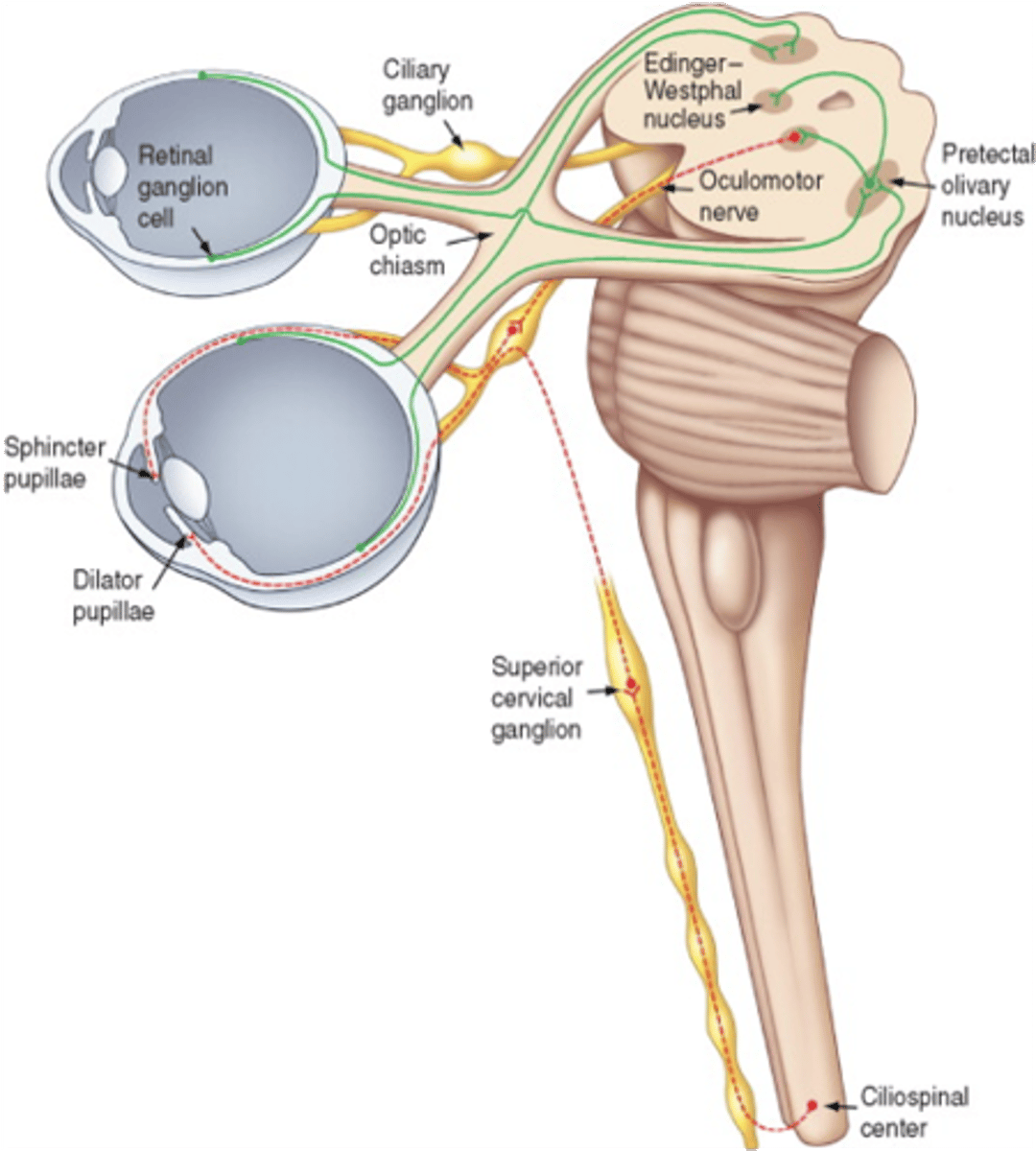
Dilation of pupil can be due to paralysis of what muscle?
Sphincter pupillae
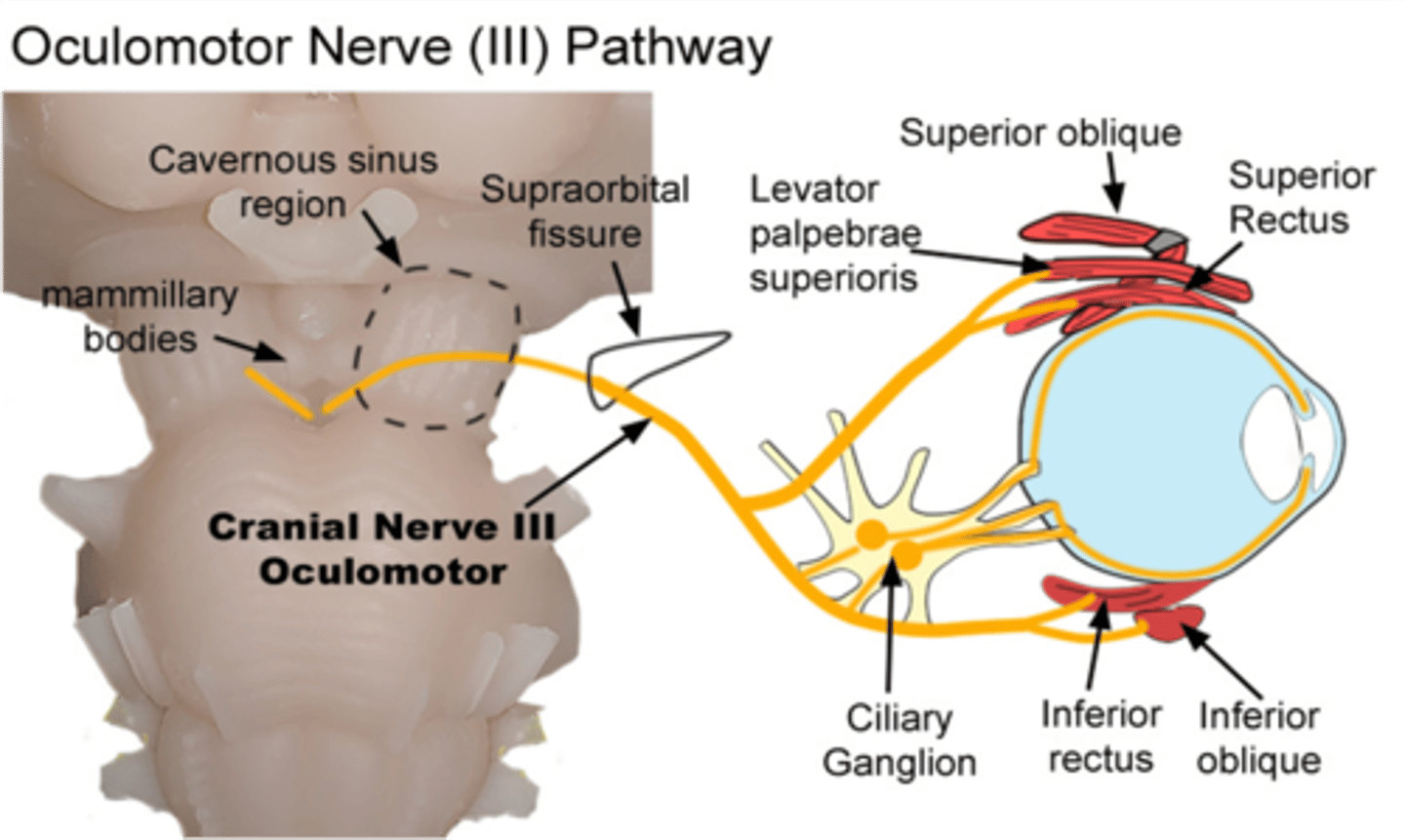
Ptosis in cranial nerve III lesion is due to the paralysis of what muscle?
Levator palpebrae superioris

What is the afferent limb of the pupillary light reflex?
Optic nerve (CN II)
What muscle is paralyzed with injury to the trochlear nerve?
Superior oblique muscle

Loss of accommodation in oculomotor nerve palsy is due to paralysis of what muscles?
Ciliary muscles
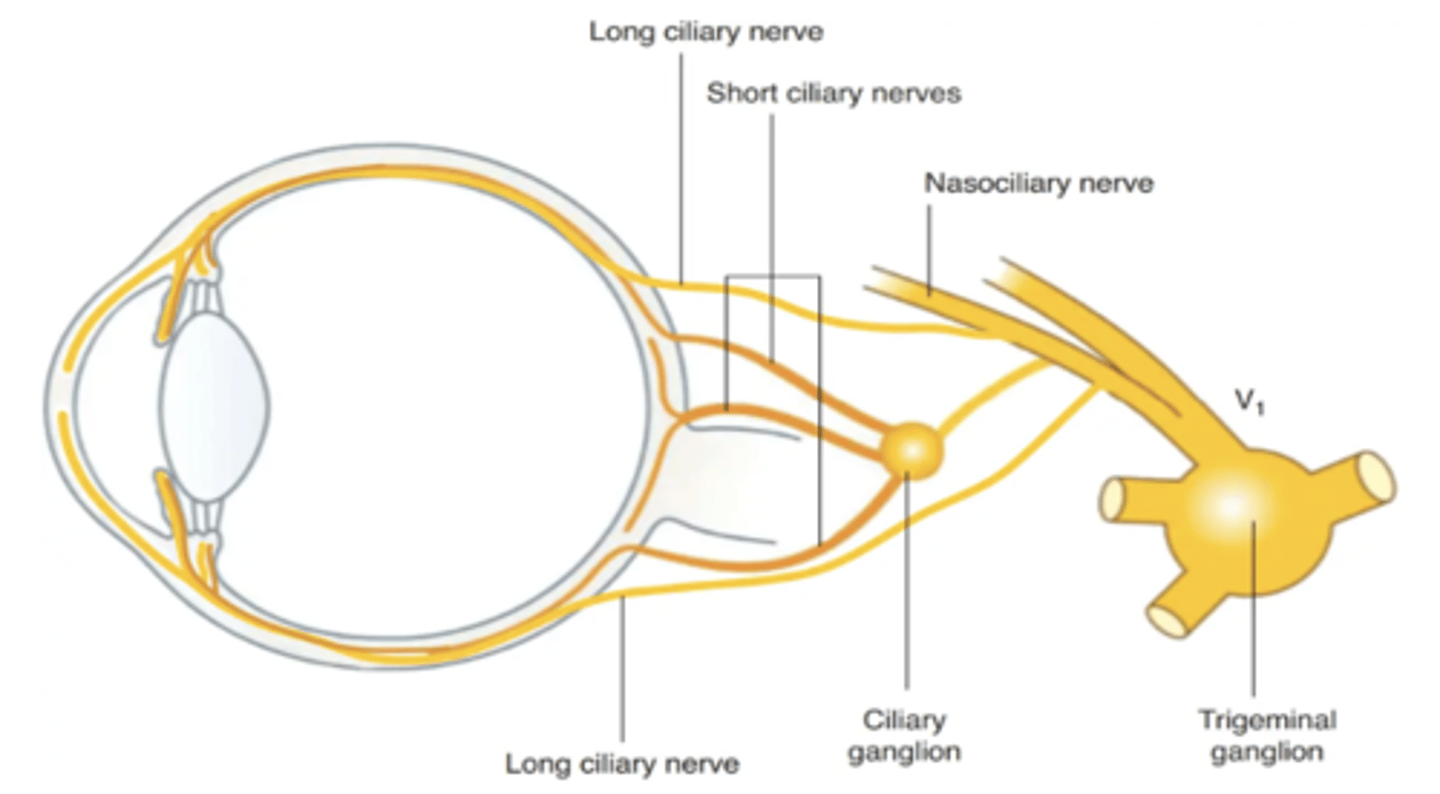
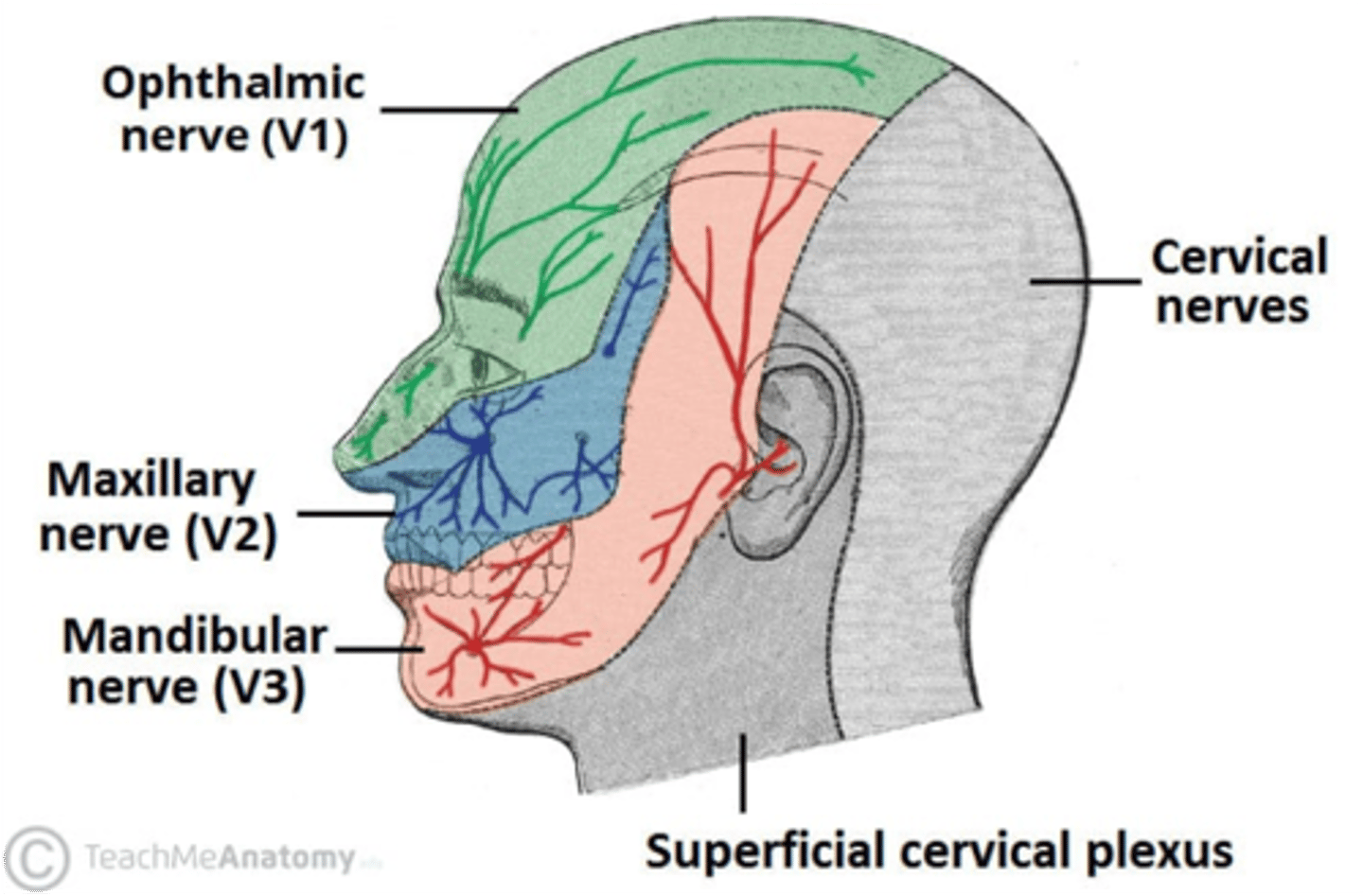
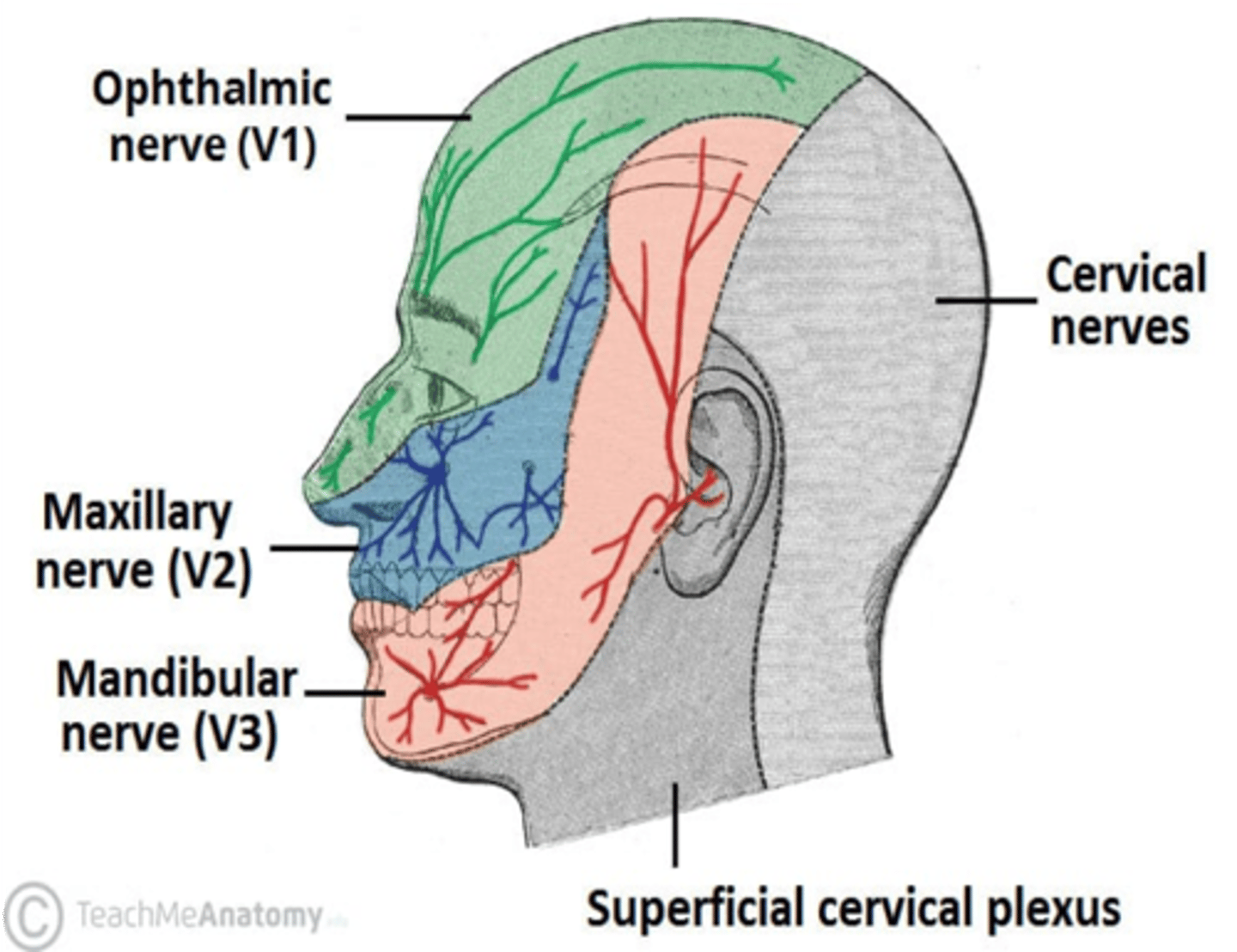
Loss of sensation on the face above the upper eyelid points to a lesion of what nerve?
Ophthalmic division of CN V
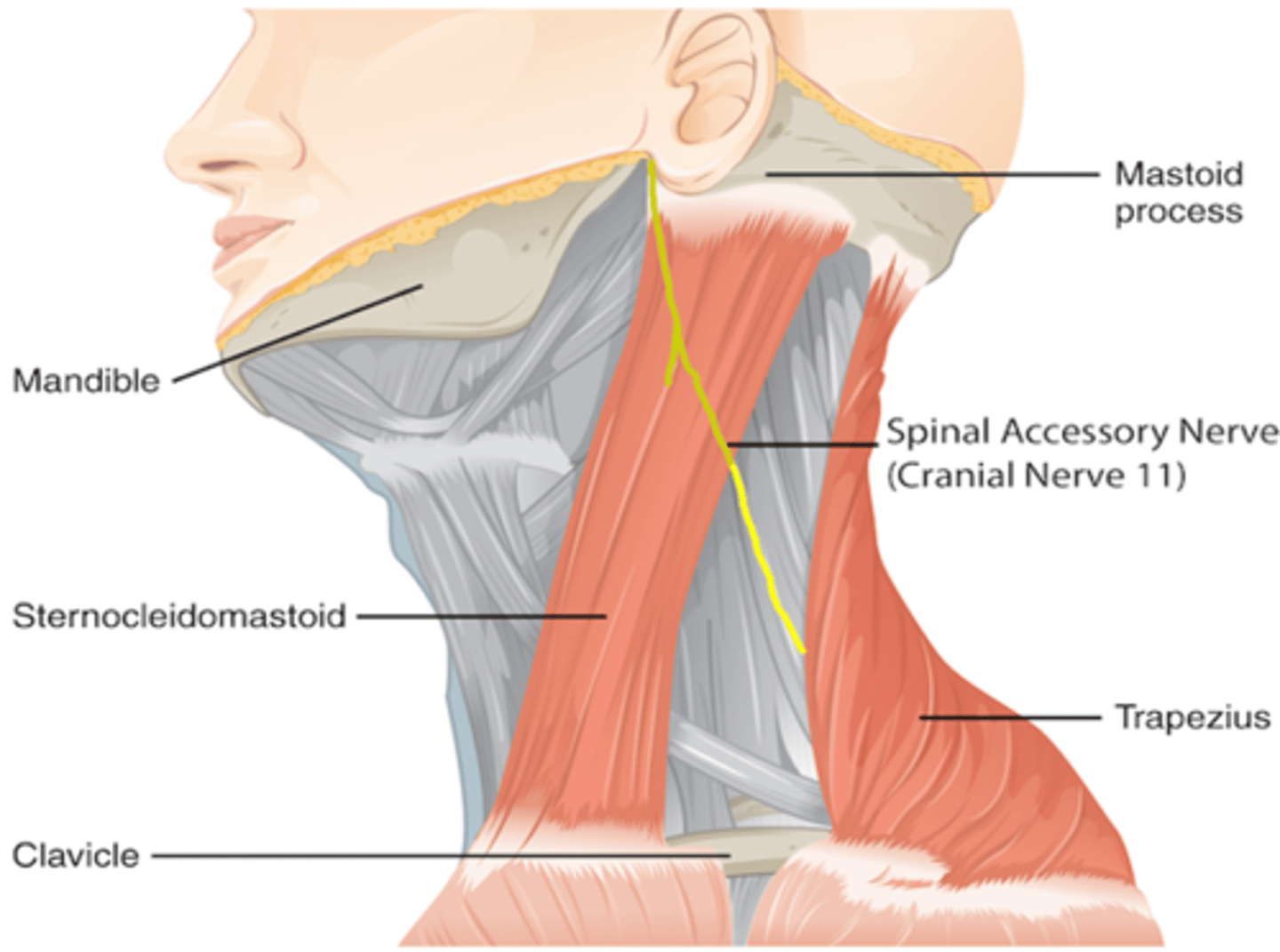
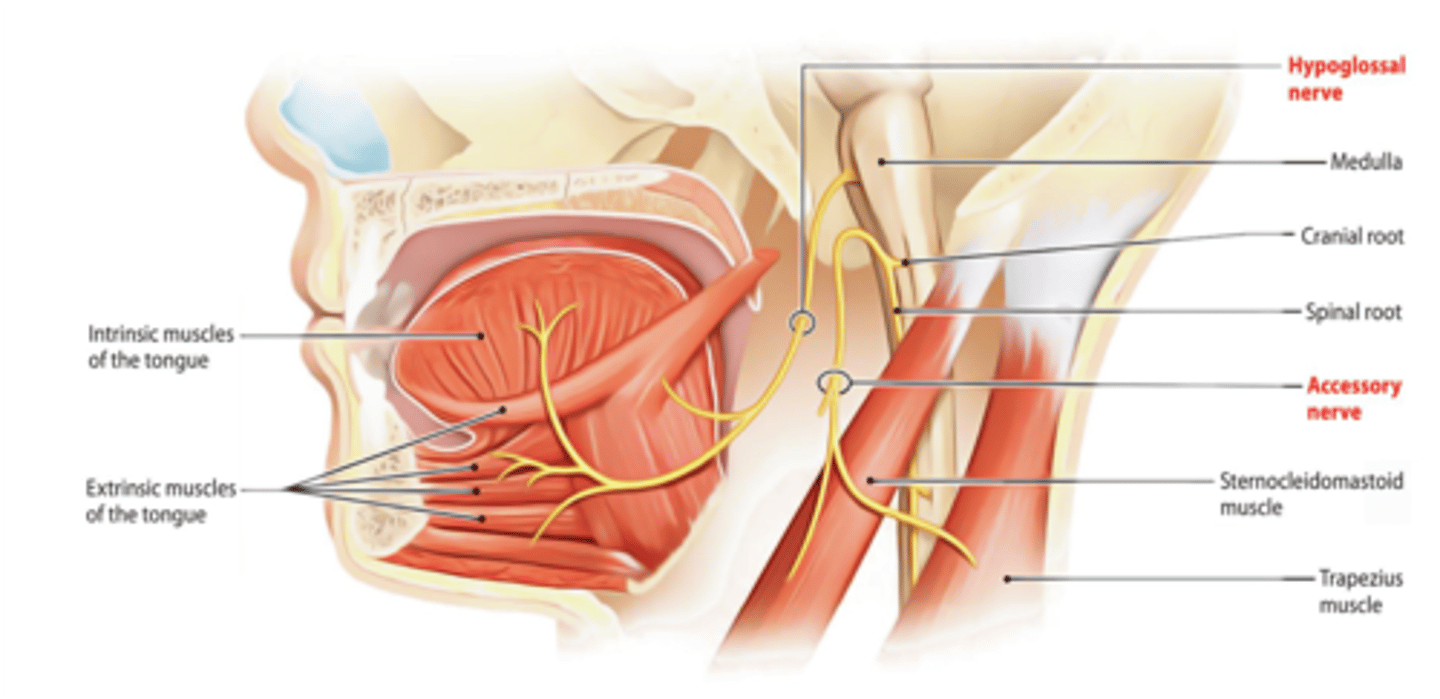
What are the 2 muscles innervated by the spinal accessory nerve?
Trapezius muscle
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
The trigeminal nerve supplies motor fibers to what group of muscles?
Muscles of mastication
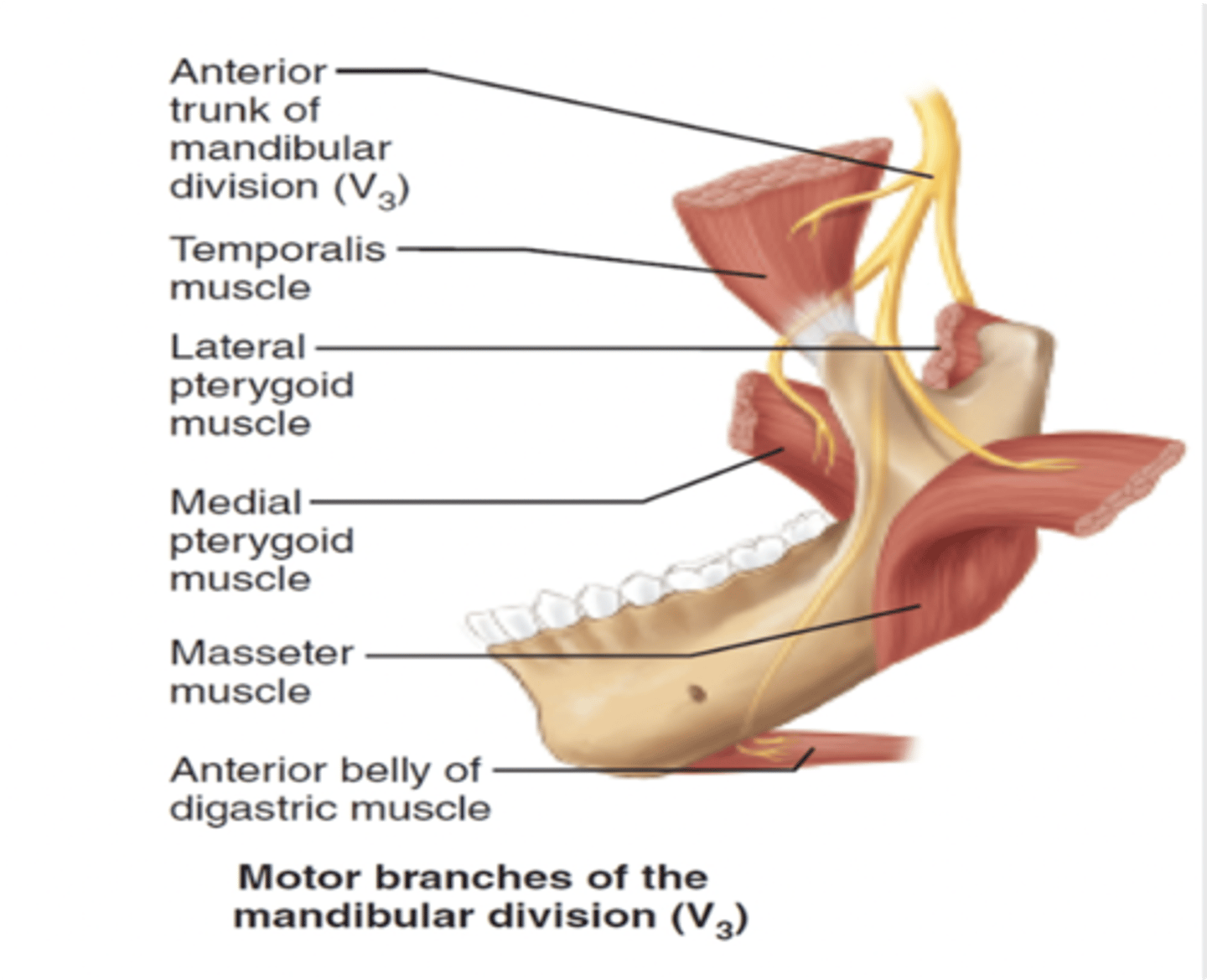
What cranial nerve carries general sensory fibers for the face?
Trigeminal nerve
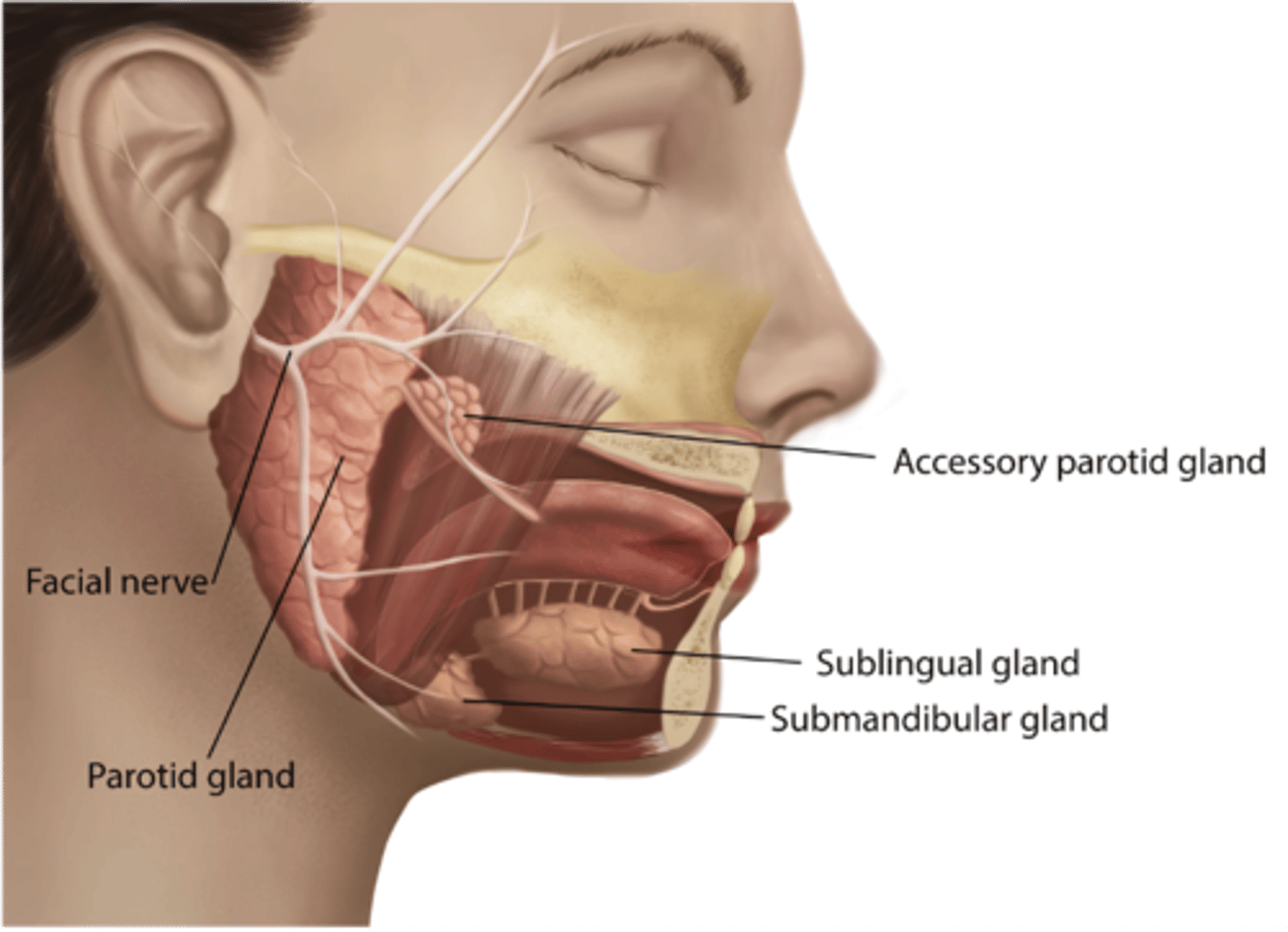
The facial nerve carries secretomotor fibers to what 4 glands?
Lacrimal
Submandibular
Sublingual
Nasal
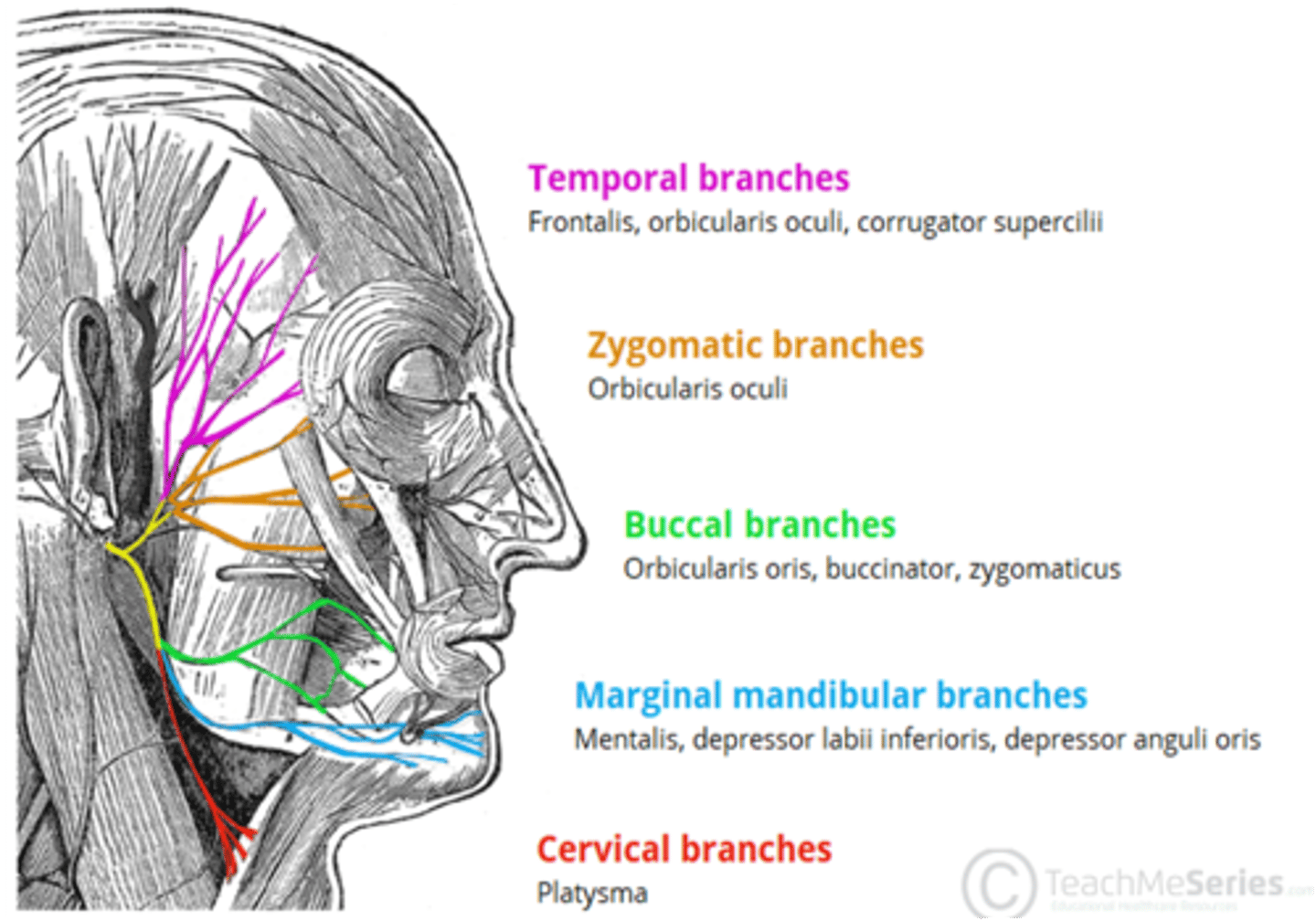
What cranial nerve provides motor fibers to the muscles of facial expression?
Cranial nerve VII (Facial nerve)
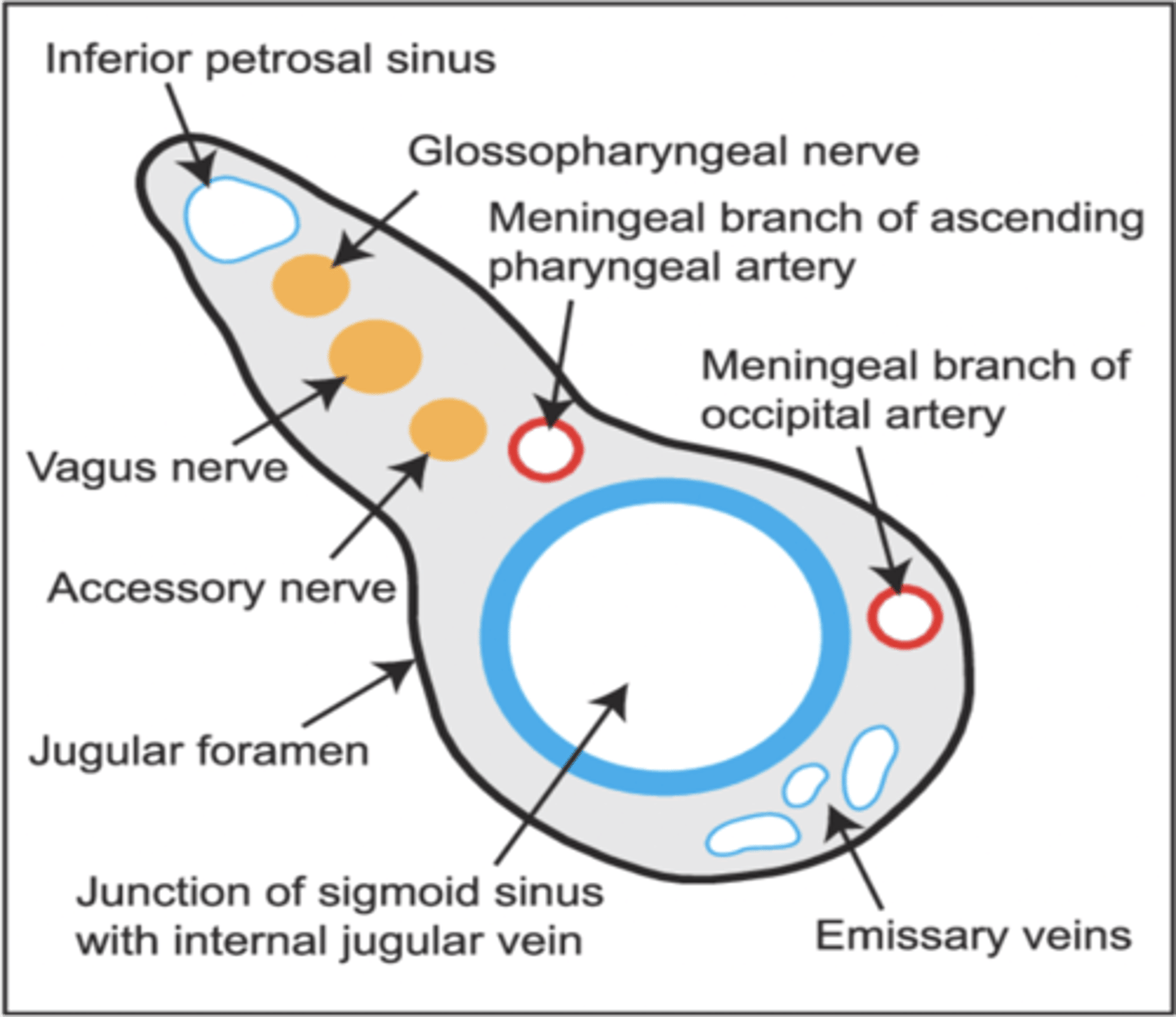
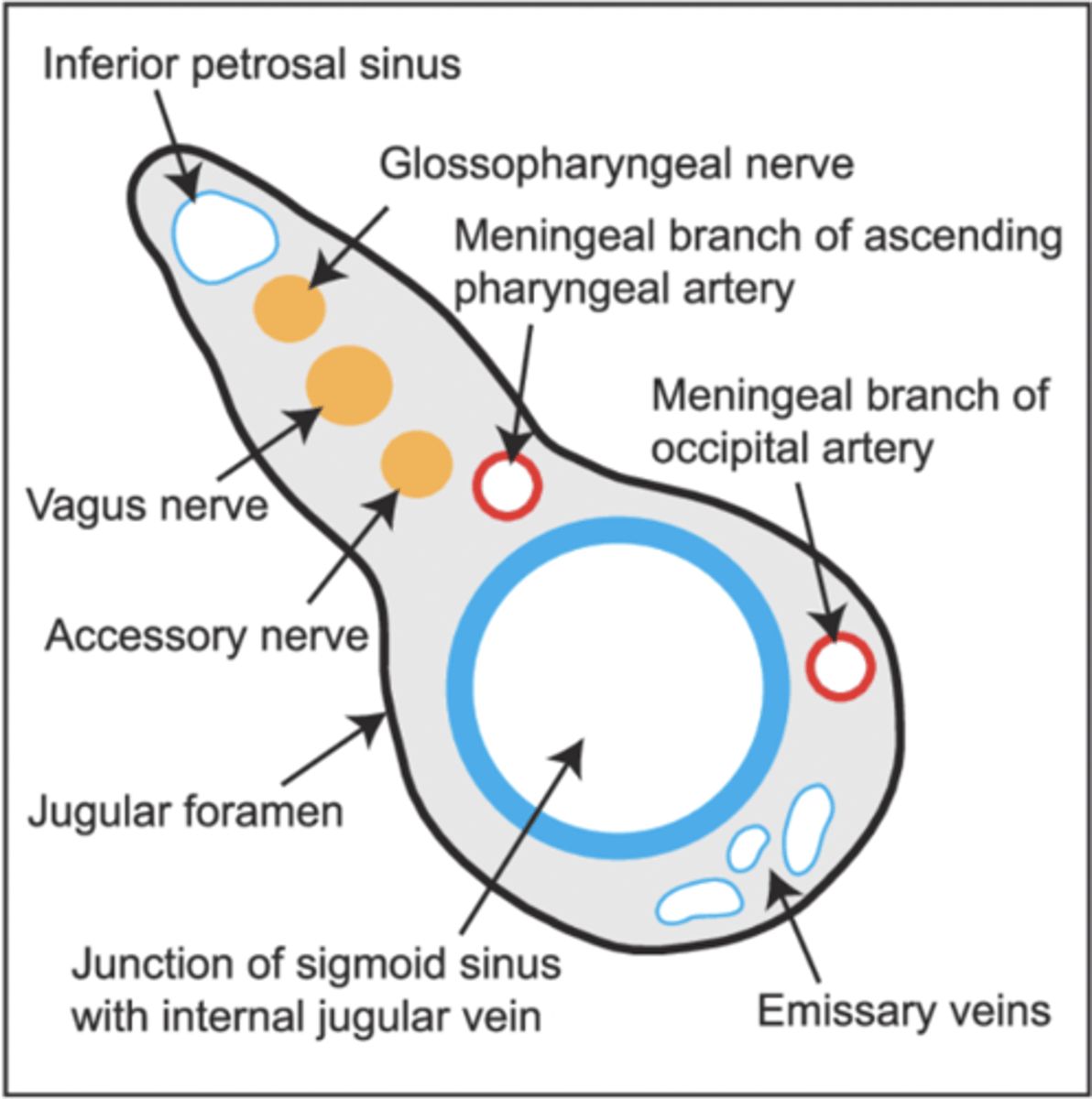
What foramen transmits cranial nerves IX, X, XI and the internal jugular vein?
Jugular foramen
Cranial nerve VI passes through what foramen?
Superior orbital fissure
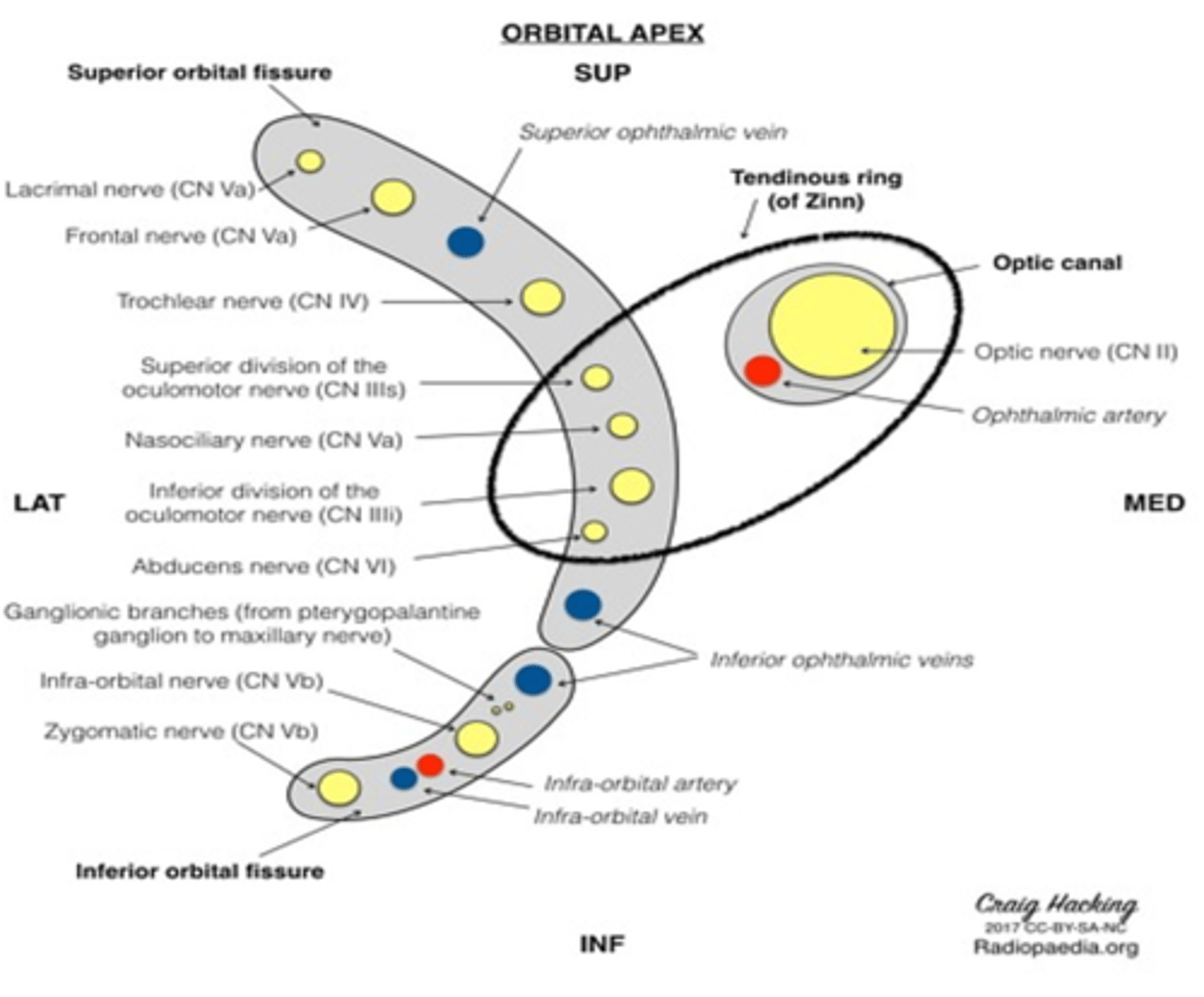
What cranial nerves pass through the internal auditory meatus?
Cranial nerves VII and VIII
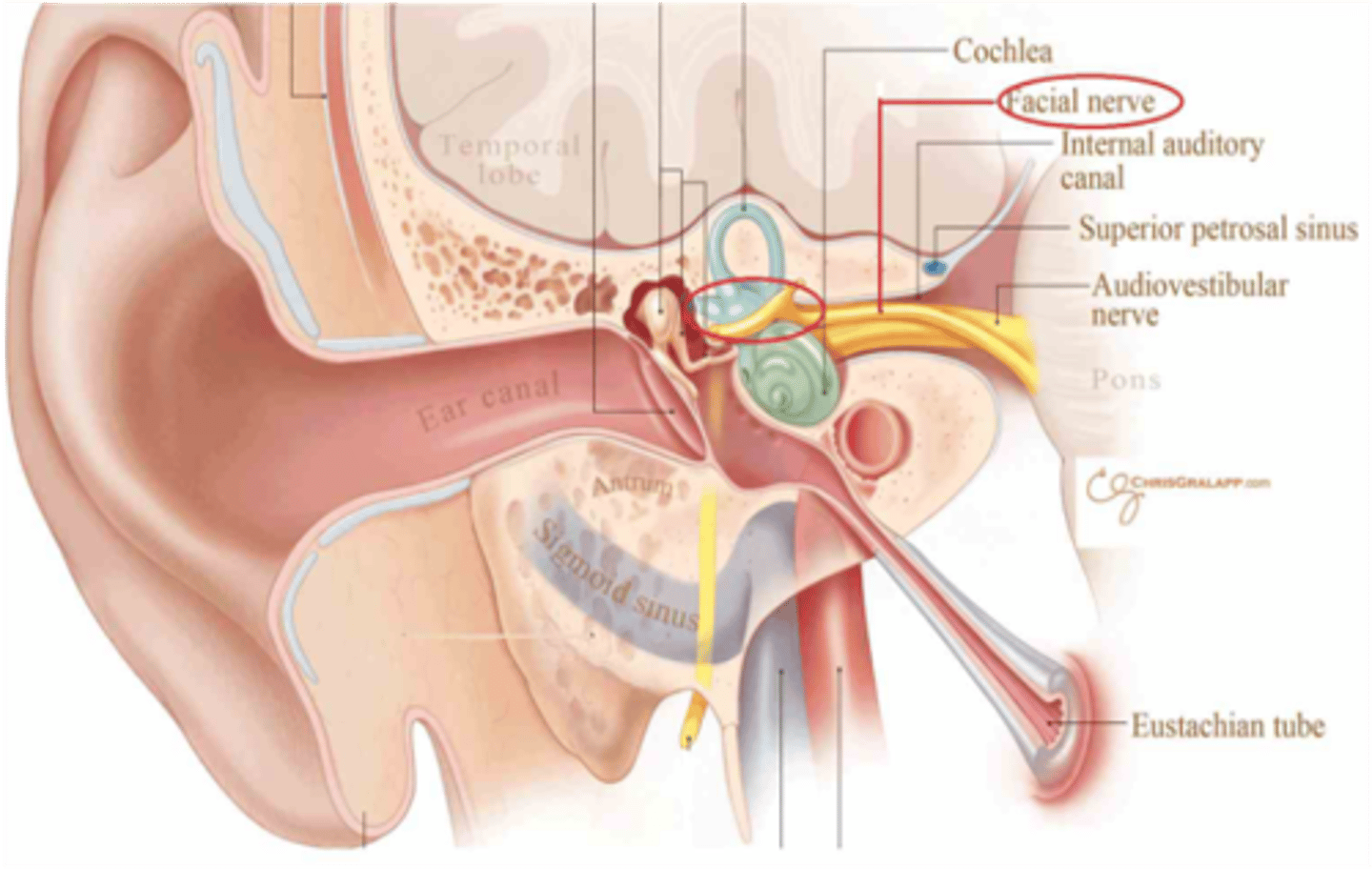
Cranial nerves VII and VIII pass through what foramen in the skull?
Internal auditory meatus
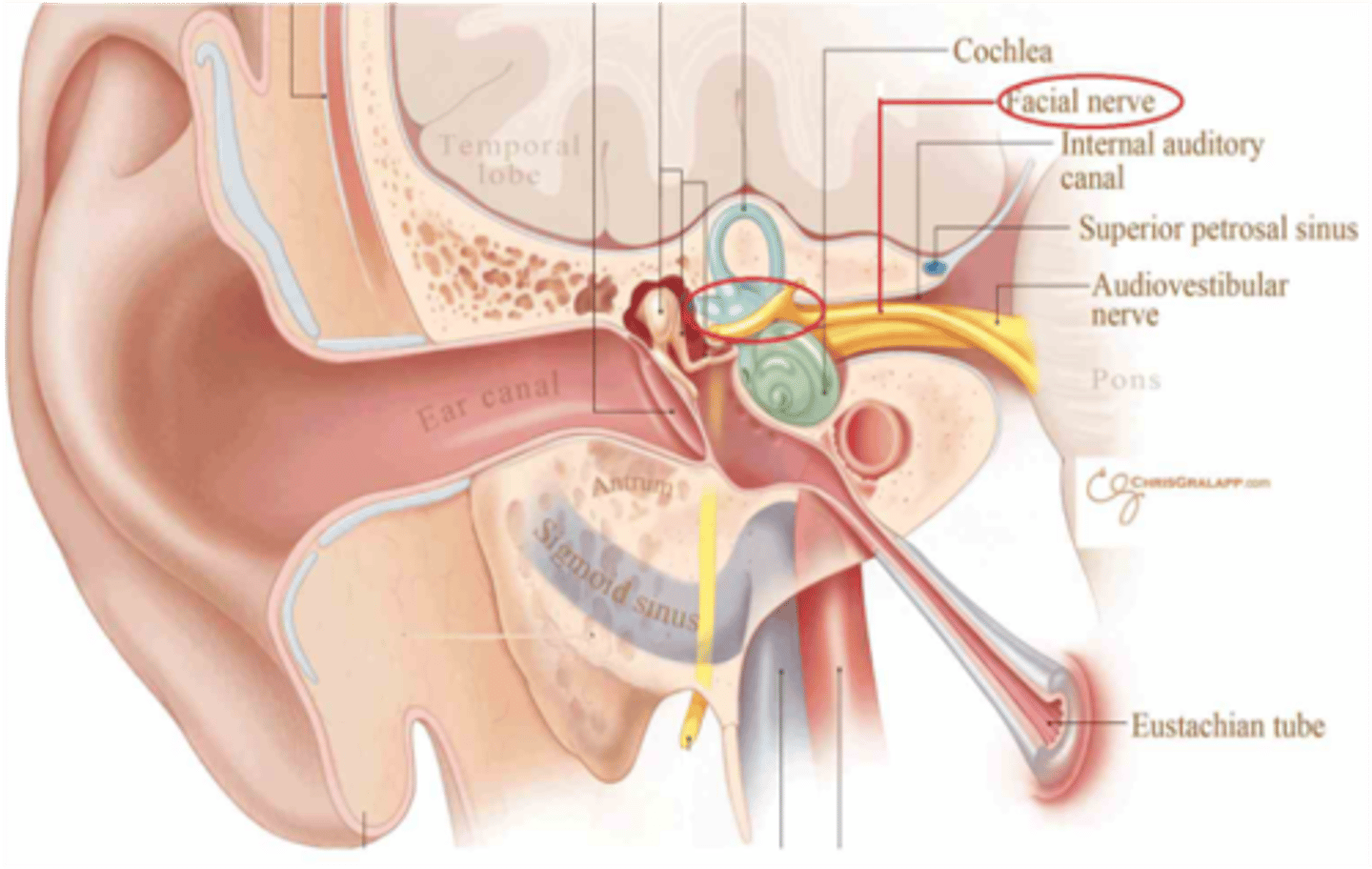
Cranial nerve XII passes through what foramen?
Hypoglossal canal
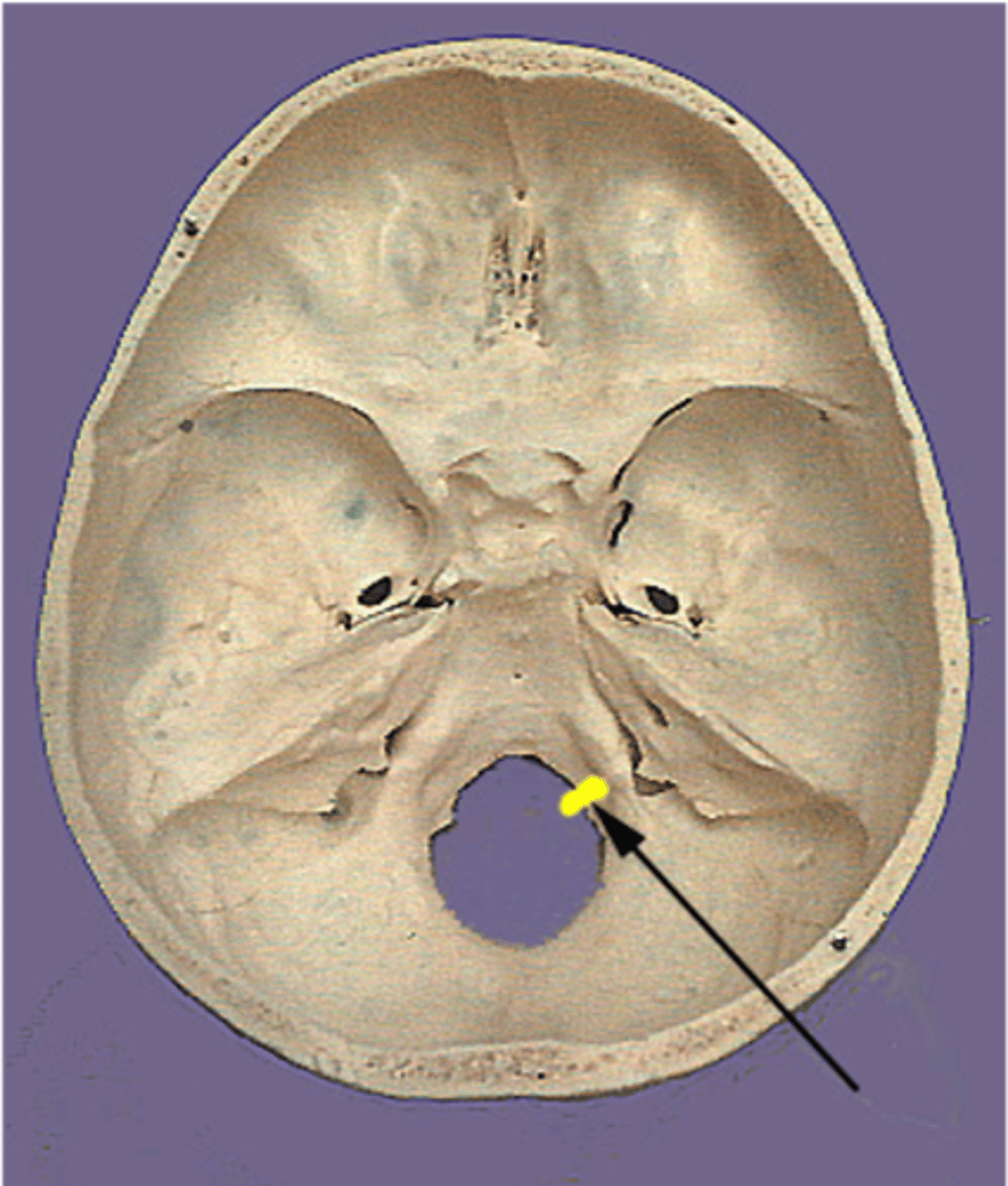
What structures pass through the jugular foramen?
Cranial nerves IX, X, XI and internal jugular vein
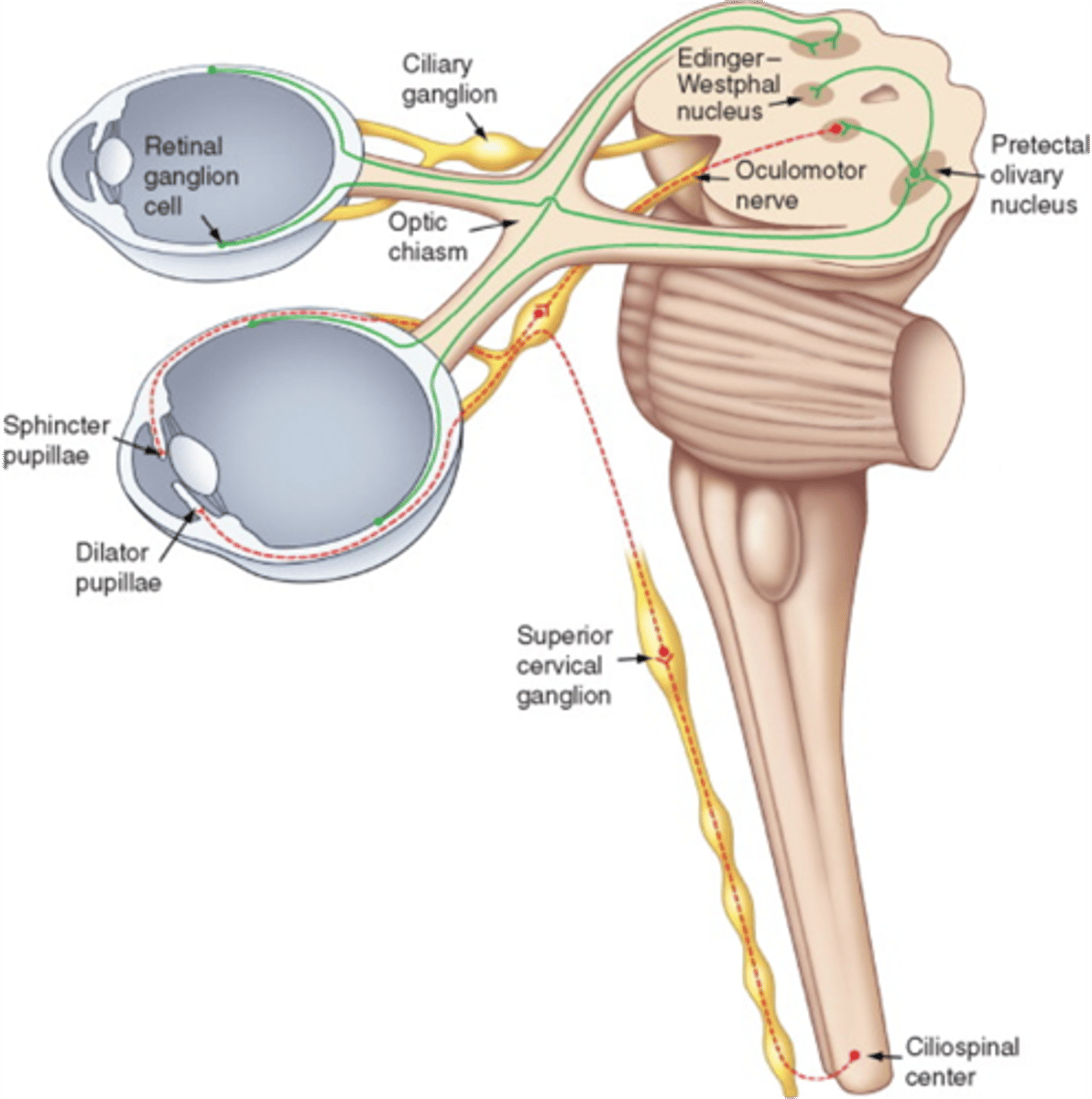
A constricted pupil is an expected finding in a lesion in the cervical region due to paralysis of what muscle?
Dilator pupillae
Injury to cranial nerve IX causes paralysis of what muscle?
Stylopharyngeus muscle
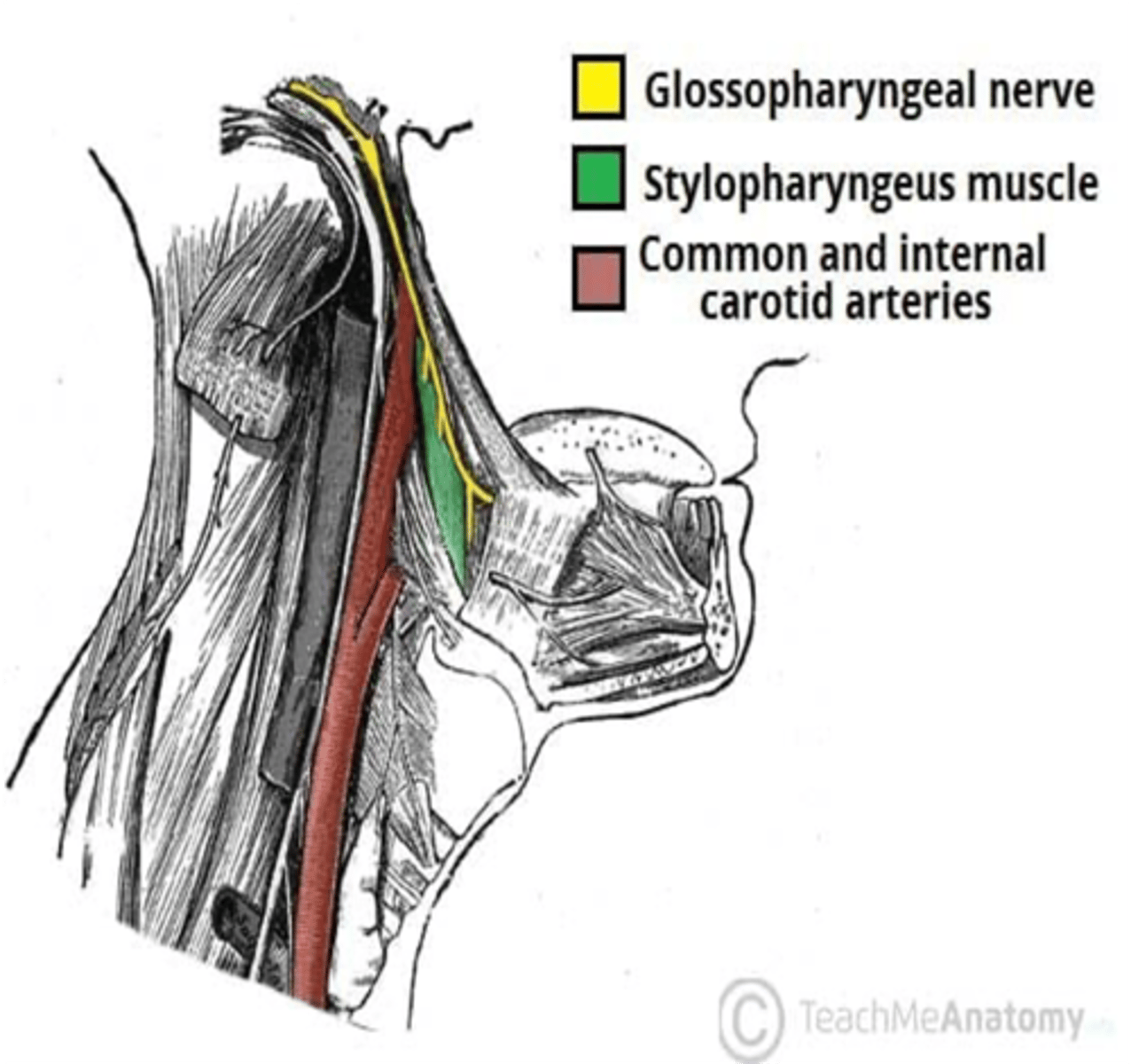
The stylopharyngeus muscle is innervated by what cranial nerve?
Glossopharyngeal nerve
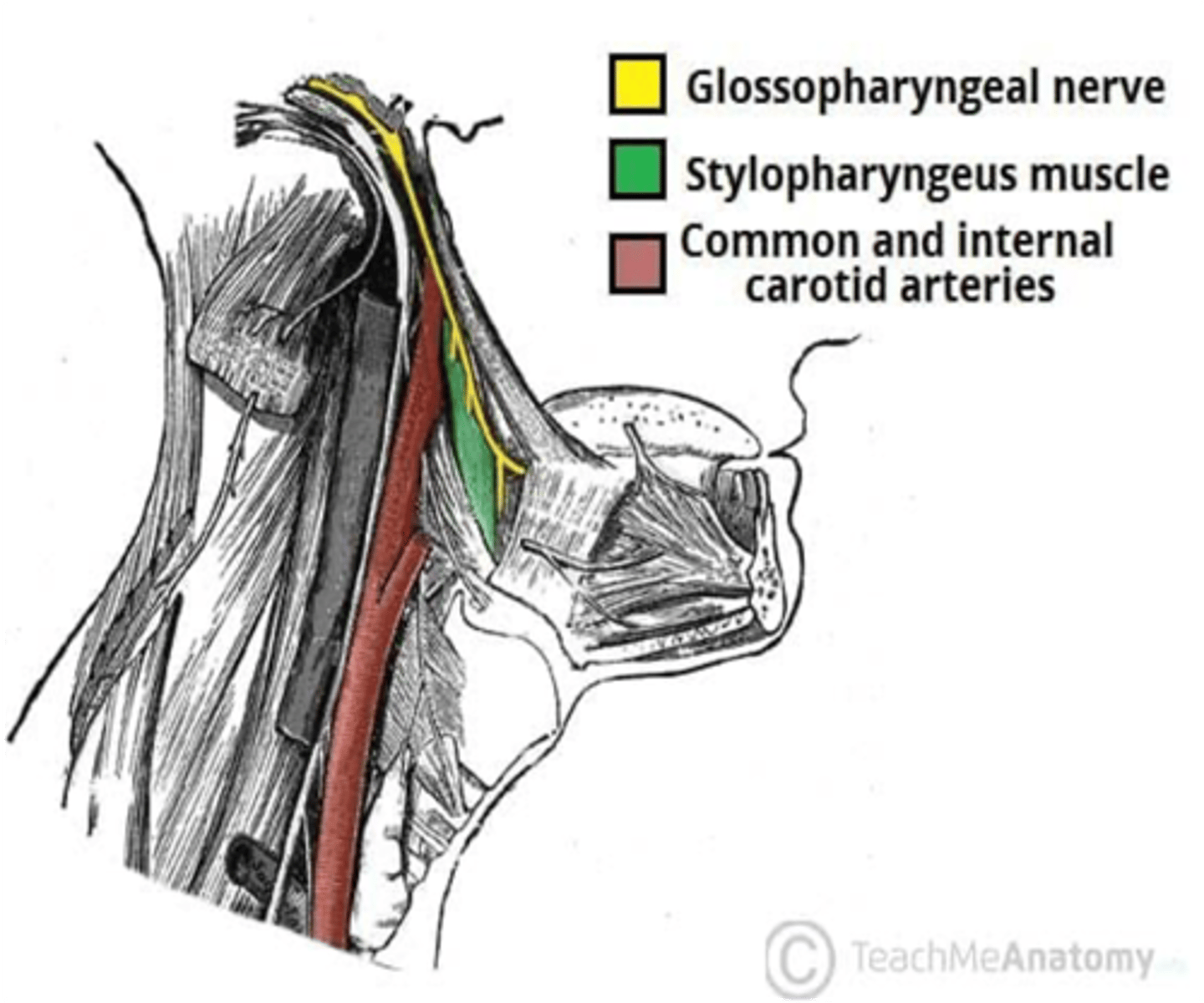
Salivary secretion by the parotid gland is stimulated by the parasympathetic fibers from what cranial nerve?
Glossopharyngeal nerve
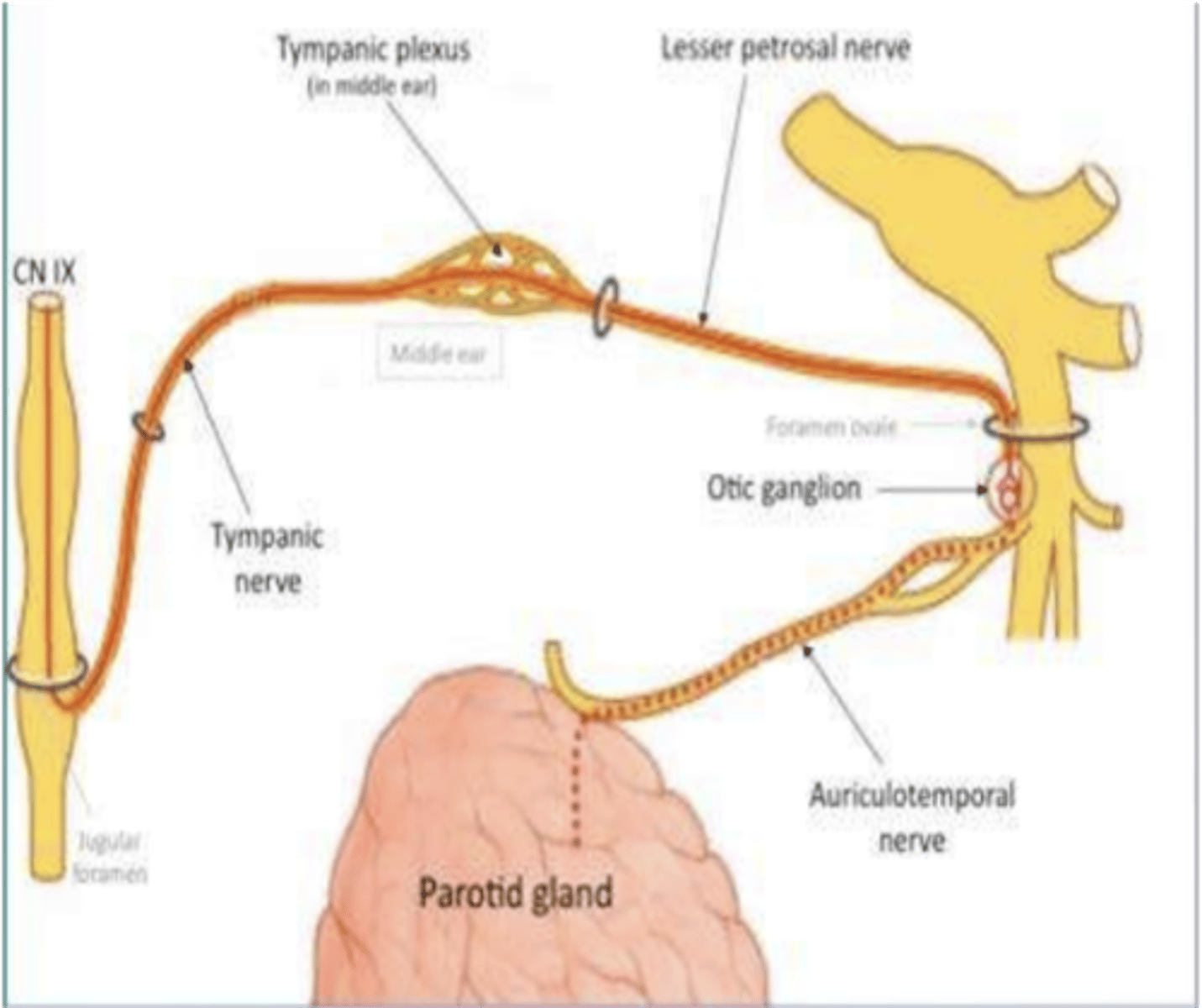
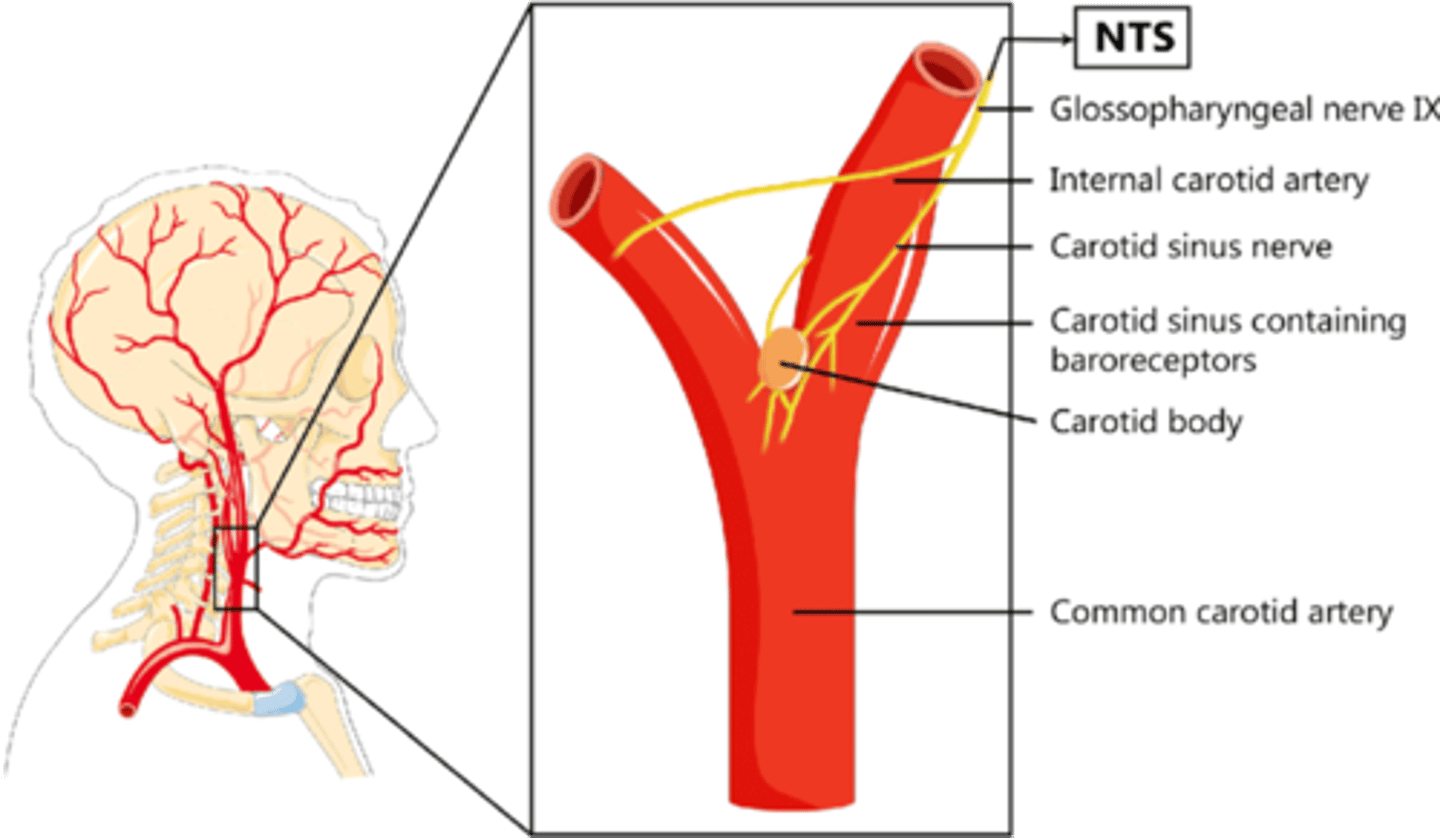
The glossopharyngeal nerve receives visceral sensation from what two structures?
Carotid sinus
Carotid body
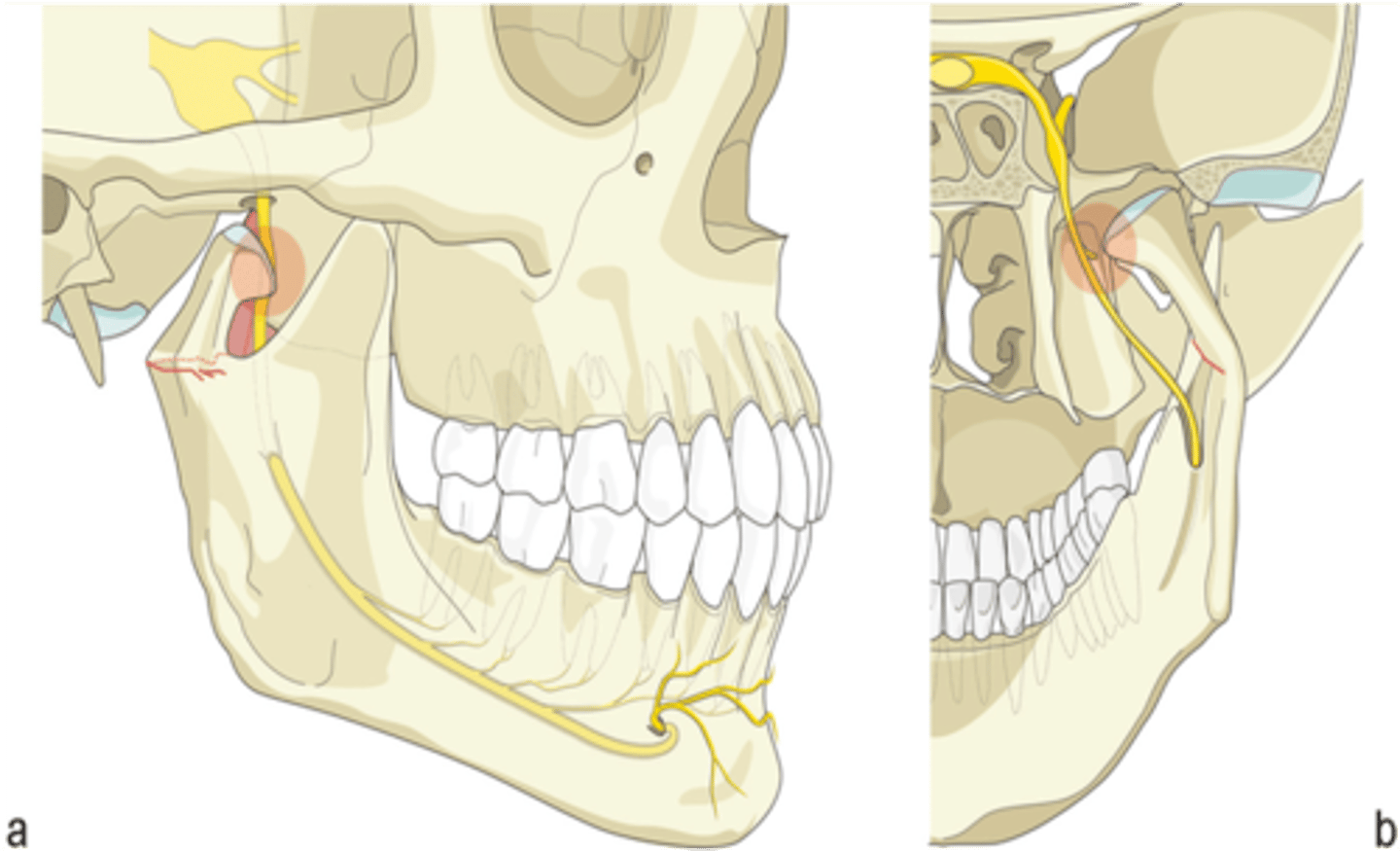
A lesion of what nerve results in lack of sensation to the canine and incisor teeth and skin over the chin?
Inferior alveolar nerve
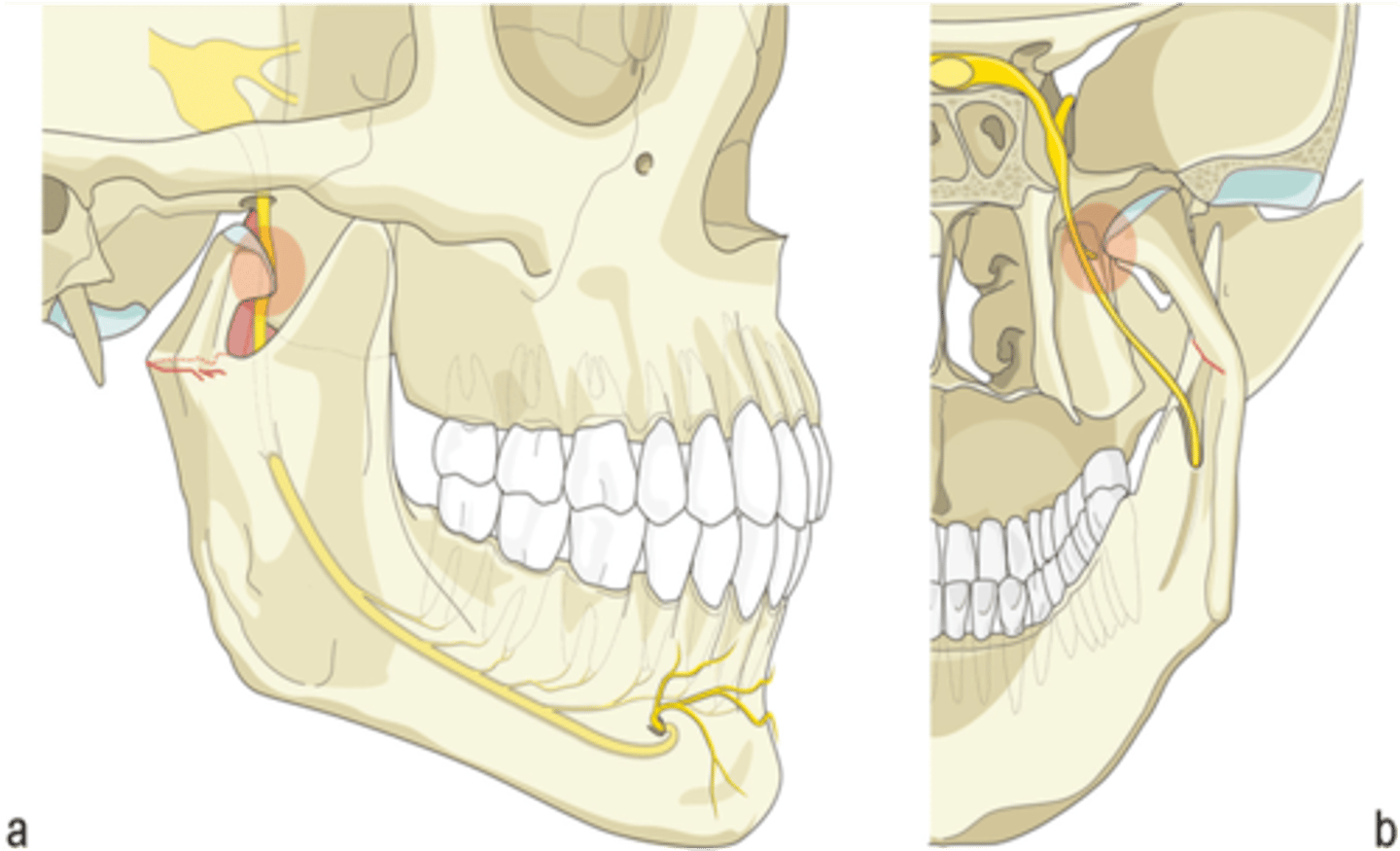
What nerve passes through the mandibular canal?
Inferior alveolar nerve
Lacrimal secretion is stimulated by postganglionic parasympathetic fibers coming from what ganglion?
Pterygopalatine ganglion

Lesion of the abducens nerve leads to what position of the eyeball?
Medial deviation of eyeball (internal strabismus)
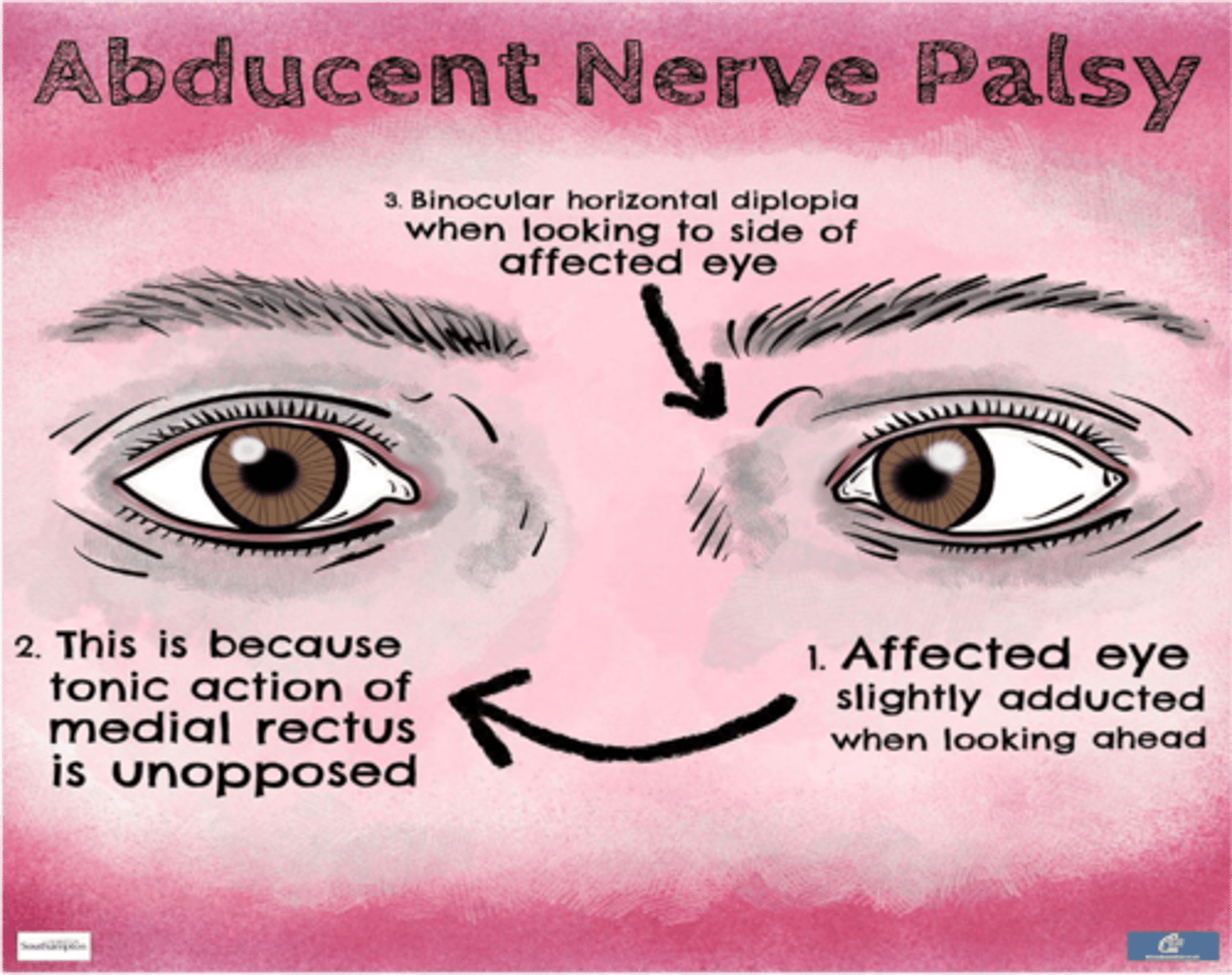
Ptosis of the upper eyelid results from a lesion of what cranial nerve?
Oculomotor nerve
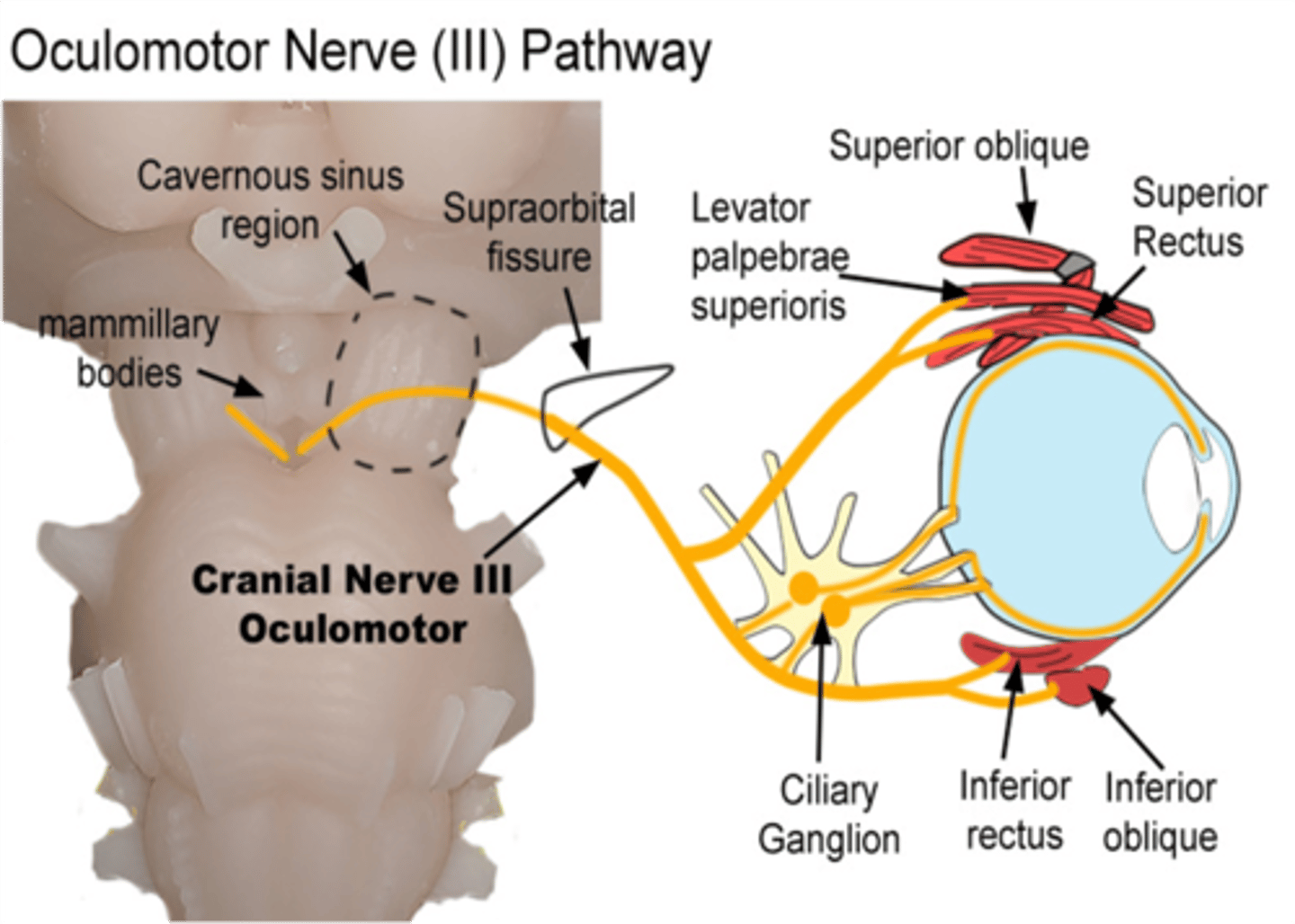
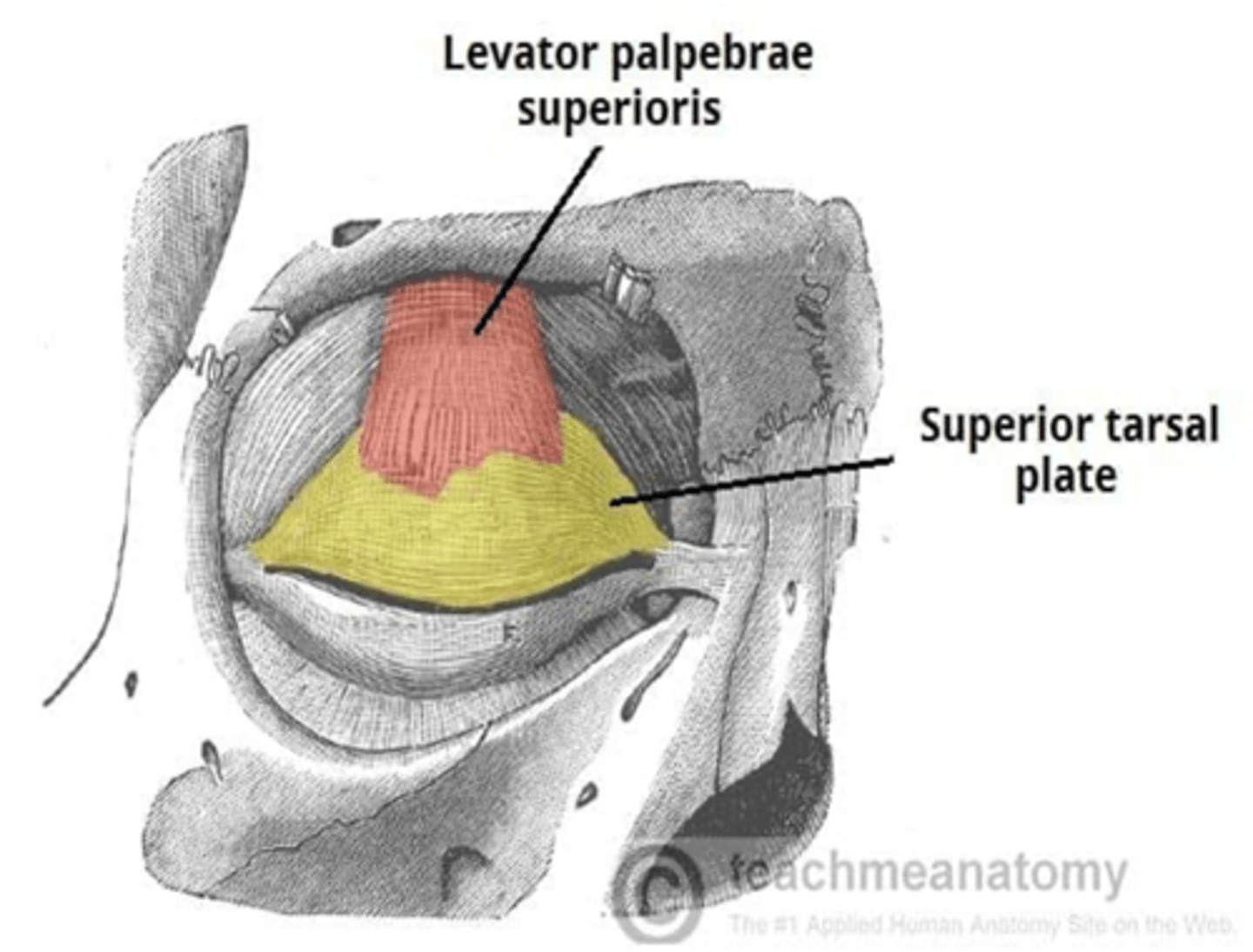
What muscle is involved in the ptosis of the upper eyelid?
Levator palpebrae superioris
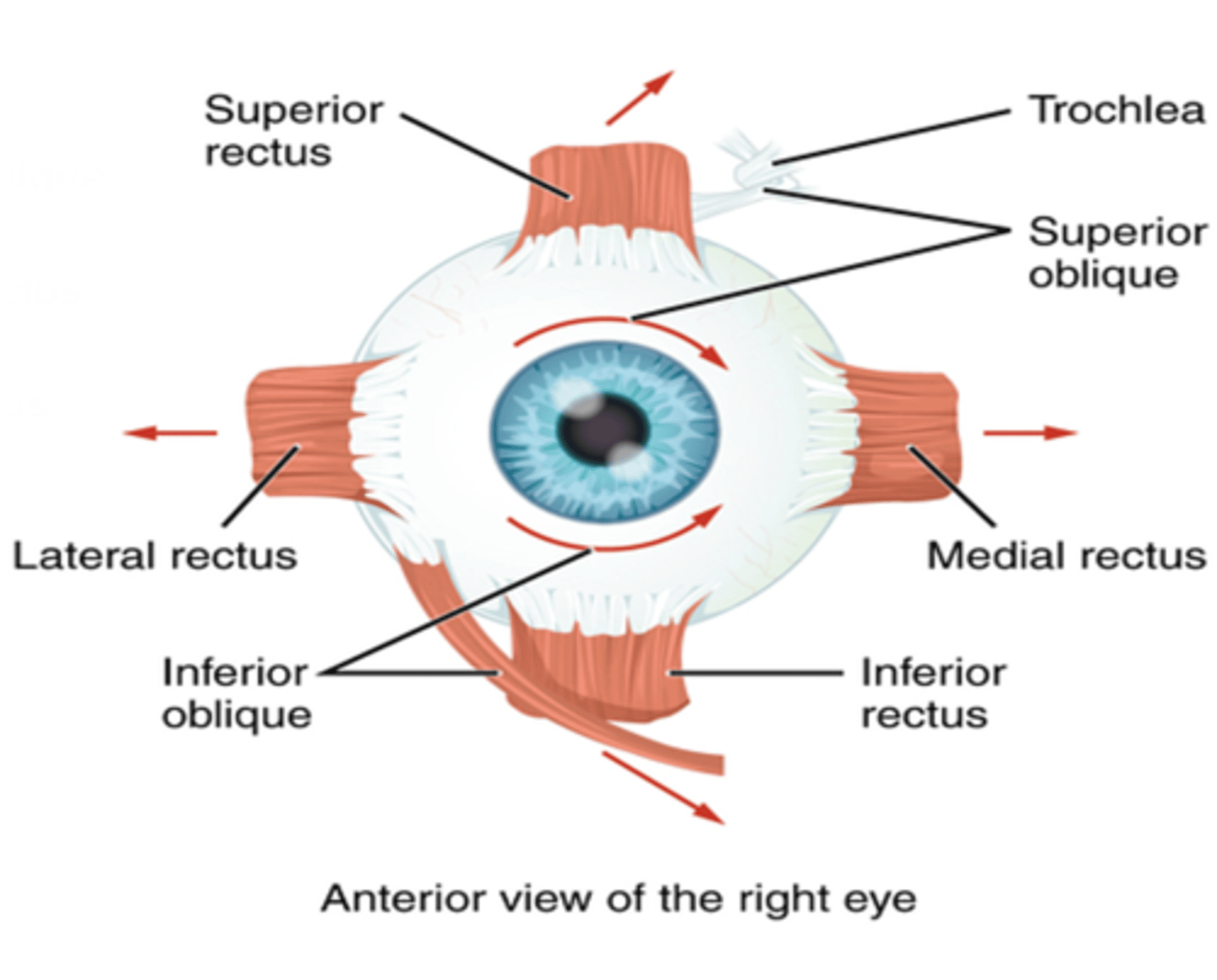
External strabismus (lateral deviation) is caused by paralysis of what extraocular muscle?
Medial rectus muscle
Inability to dilate pupil is caused by lesion of sympathetic nerve to what muscle?
Dilator pupillae
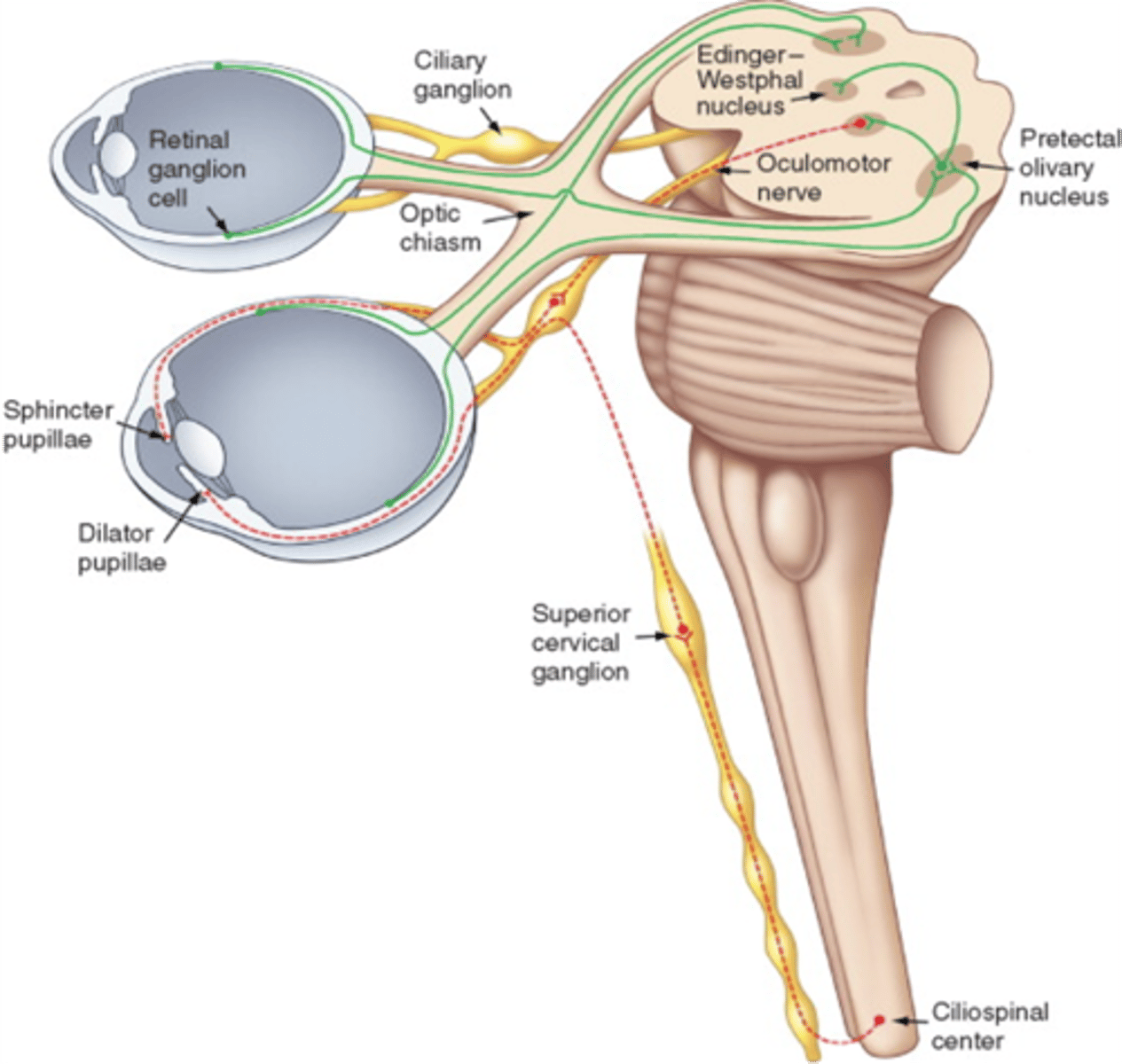
Loss of visual accommodation is due to a lesion of parasympathetic nerve fibers to what muscle?
Ciliary muscle
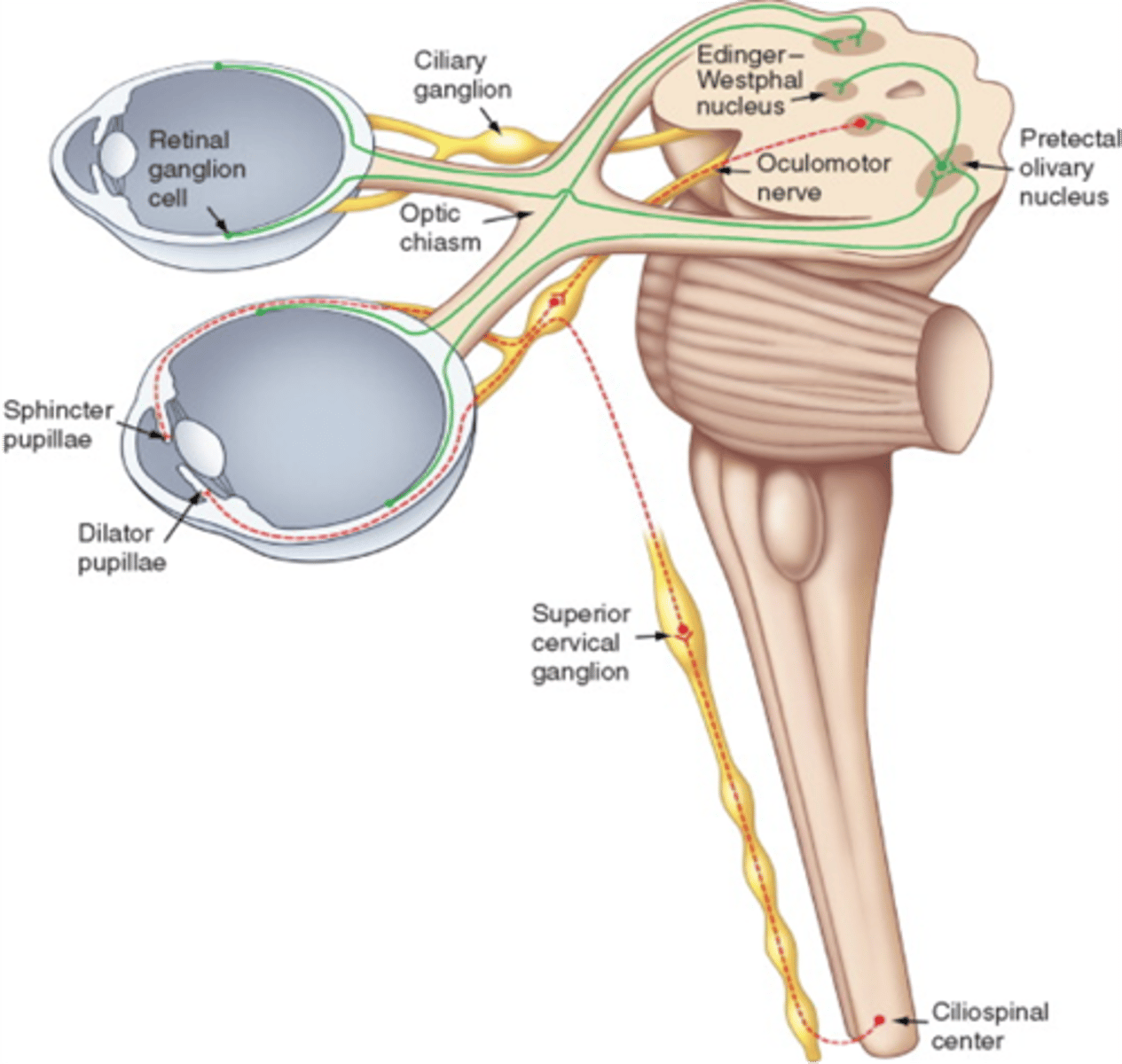
General sensation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is innervated by what branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve?
Lingual branch
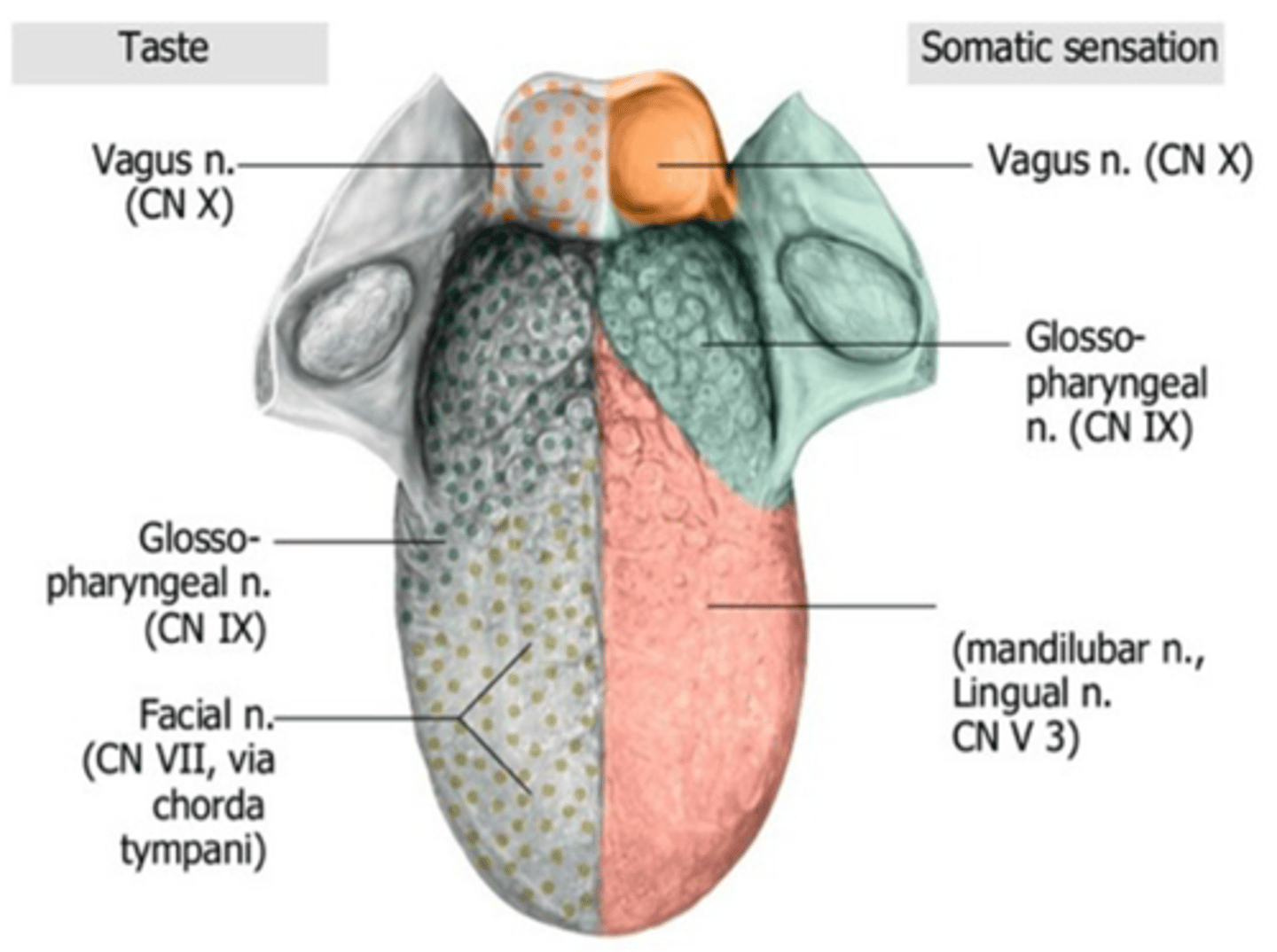
General sensation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is innervated by what division of the trigeminal nerve?
Mandibular Branch (CN V3)

General sensation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is innervated by what cranial nerve?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
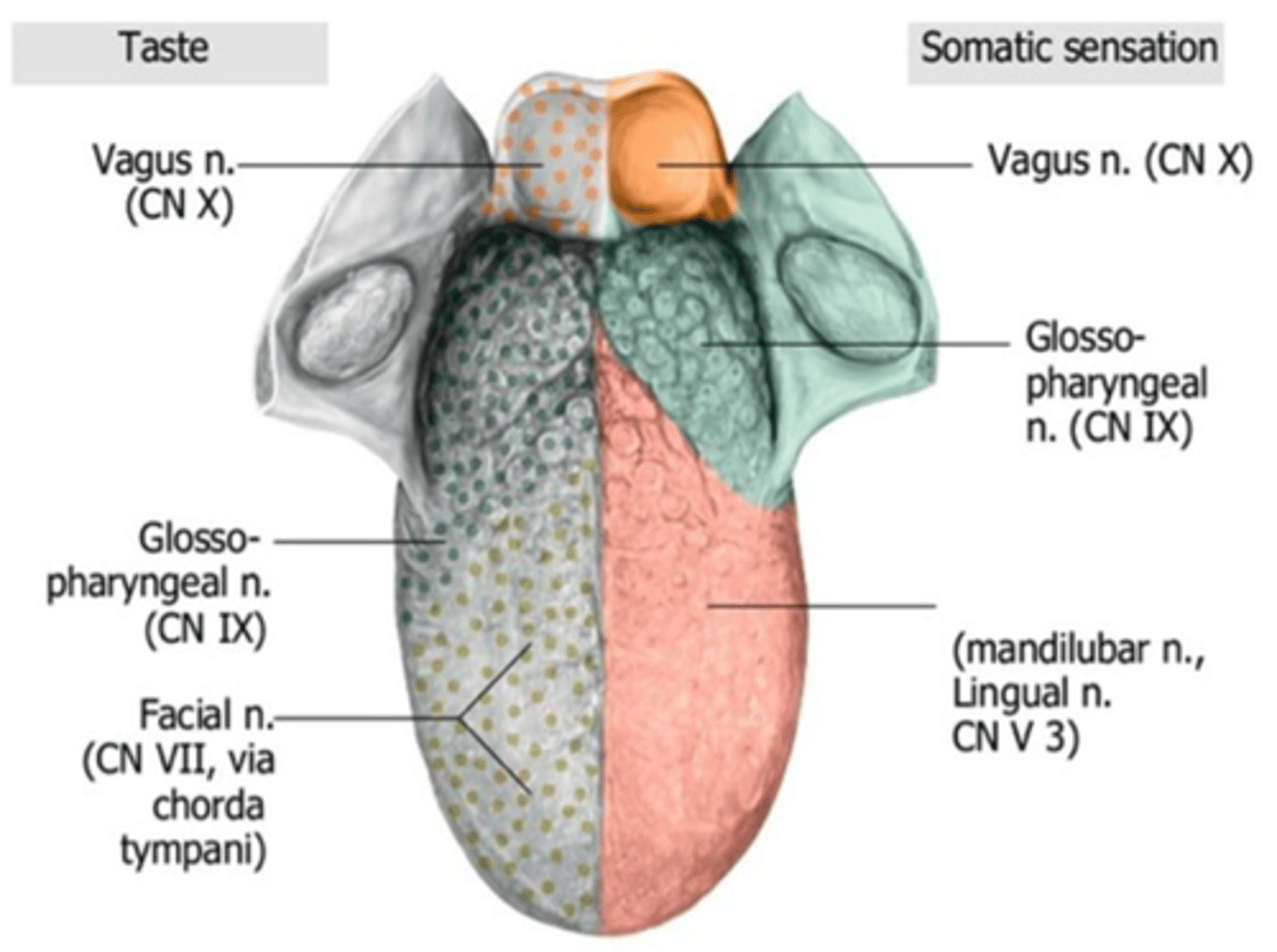
Taste sensation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is innervated by what cranial nerve?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
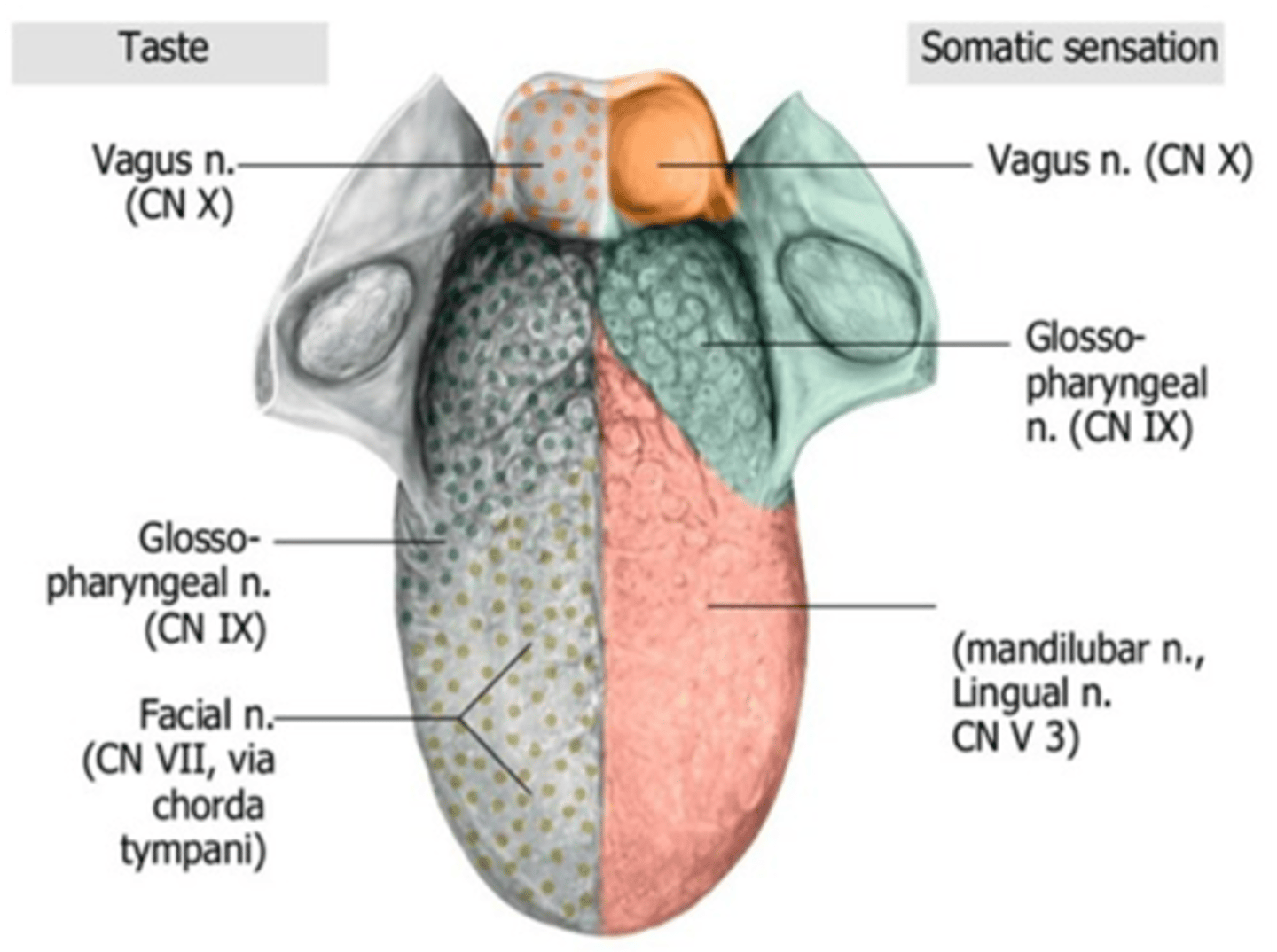
Taste sensation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is innervated by what branch of the facial nerve?
Chorda tympani
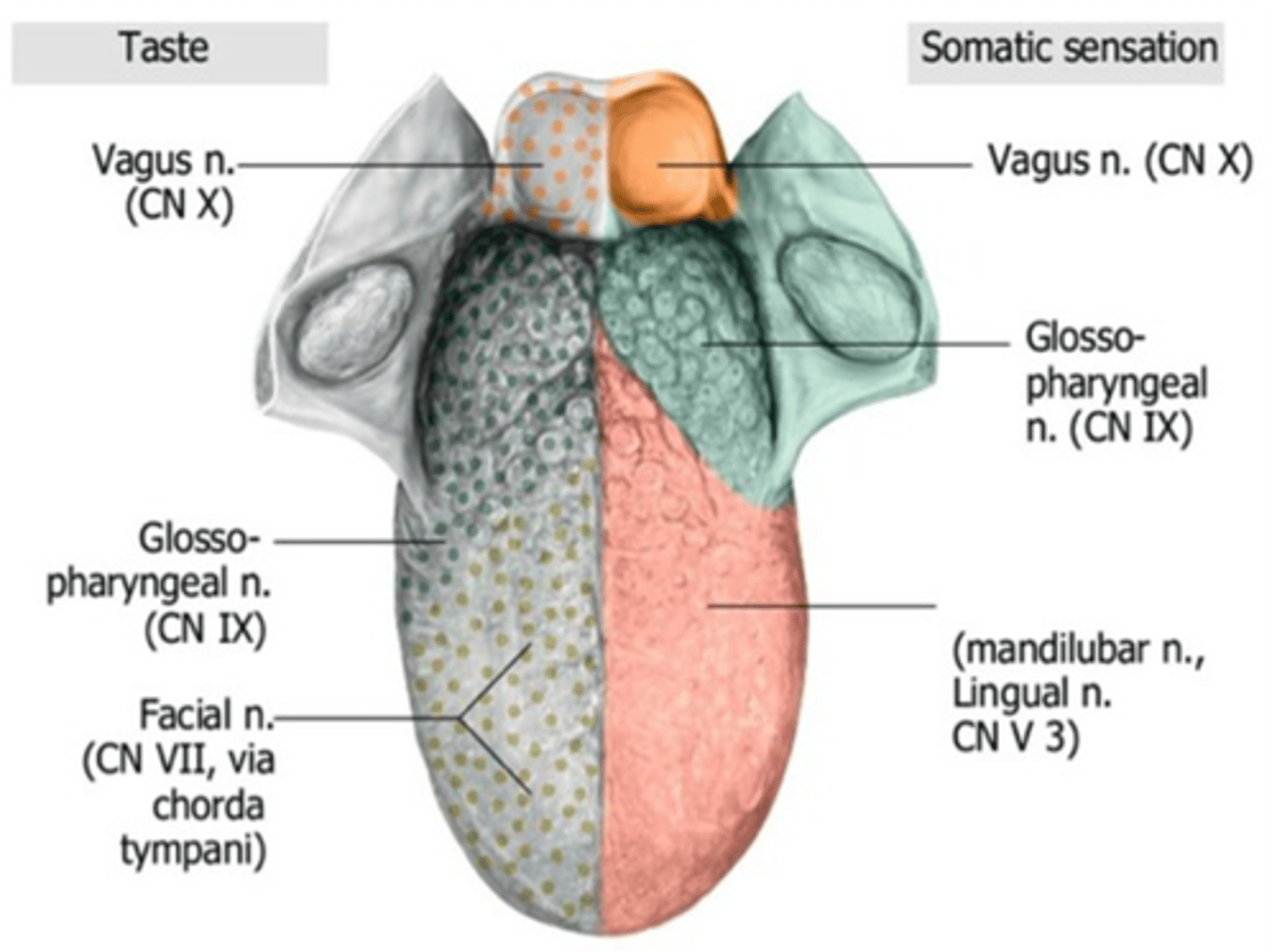
General and taste sensation over the posterior one-third of the tongue is supplied by what cranial nerve?
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
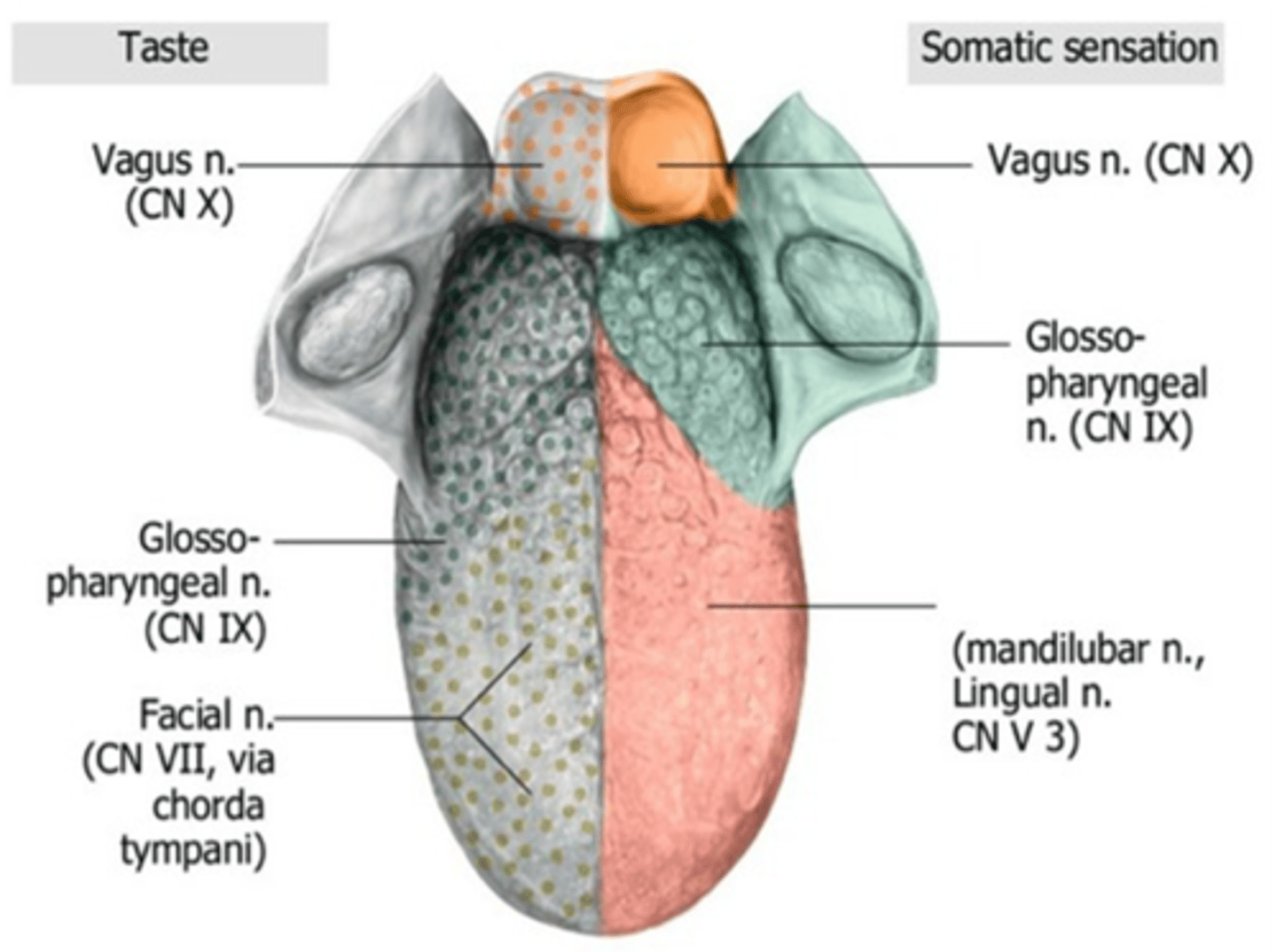
General and taste sensation over the epiglottis is supplied by what cranial nerve?
Vagus nerve

General and taste sensation over the epiglottis is supplied by what branch of the vagus nerve?
Internal laryngeal branch
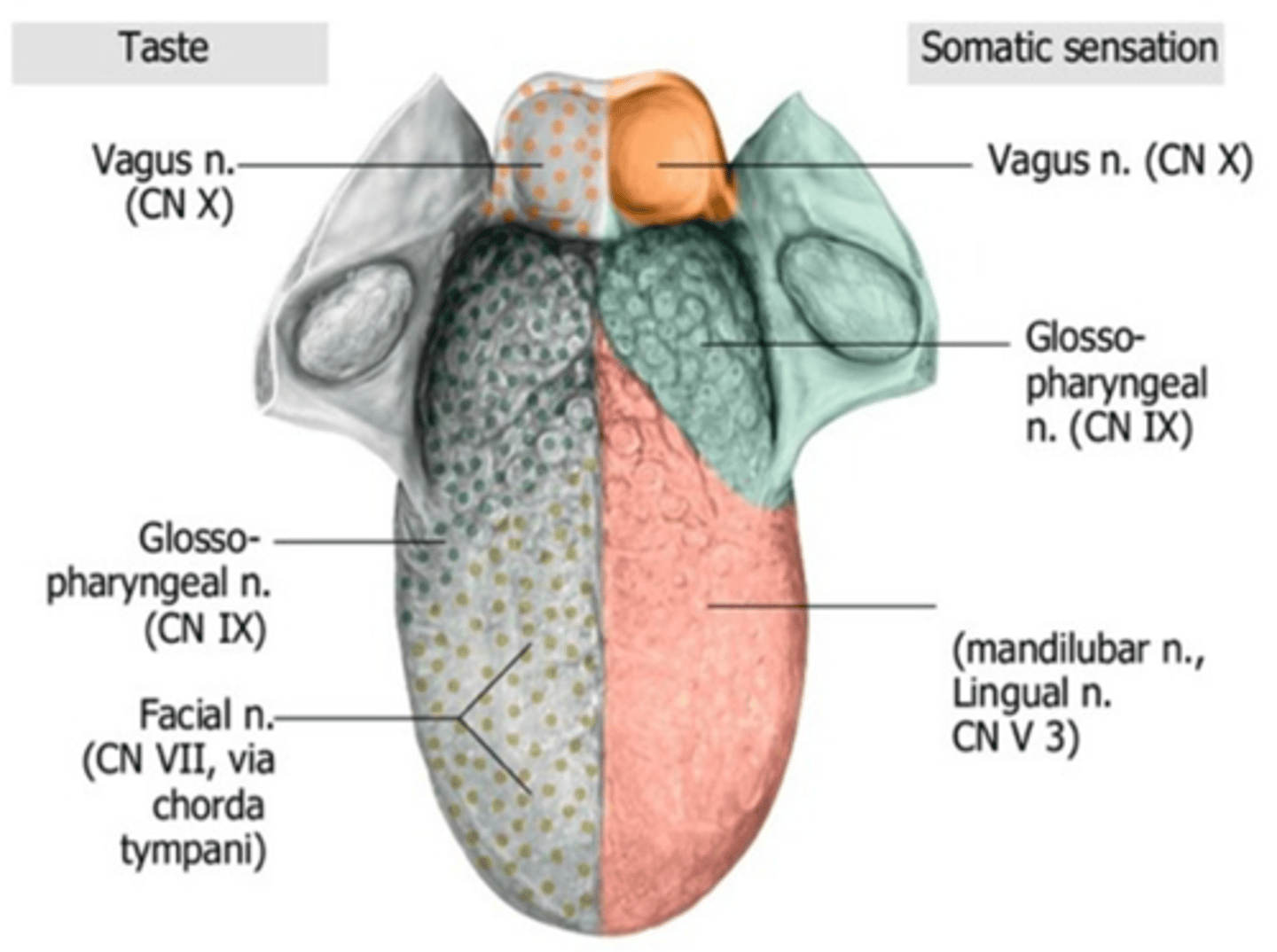
What cranial nerve innervates the tongue muscles?
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XI)
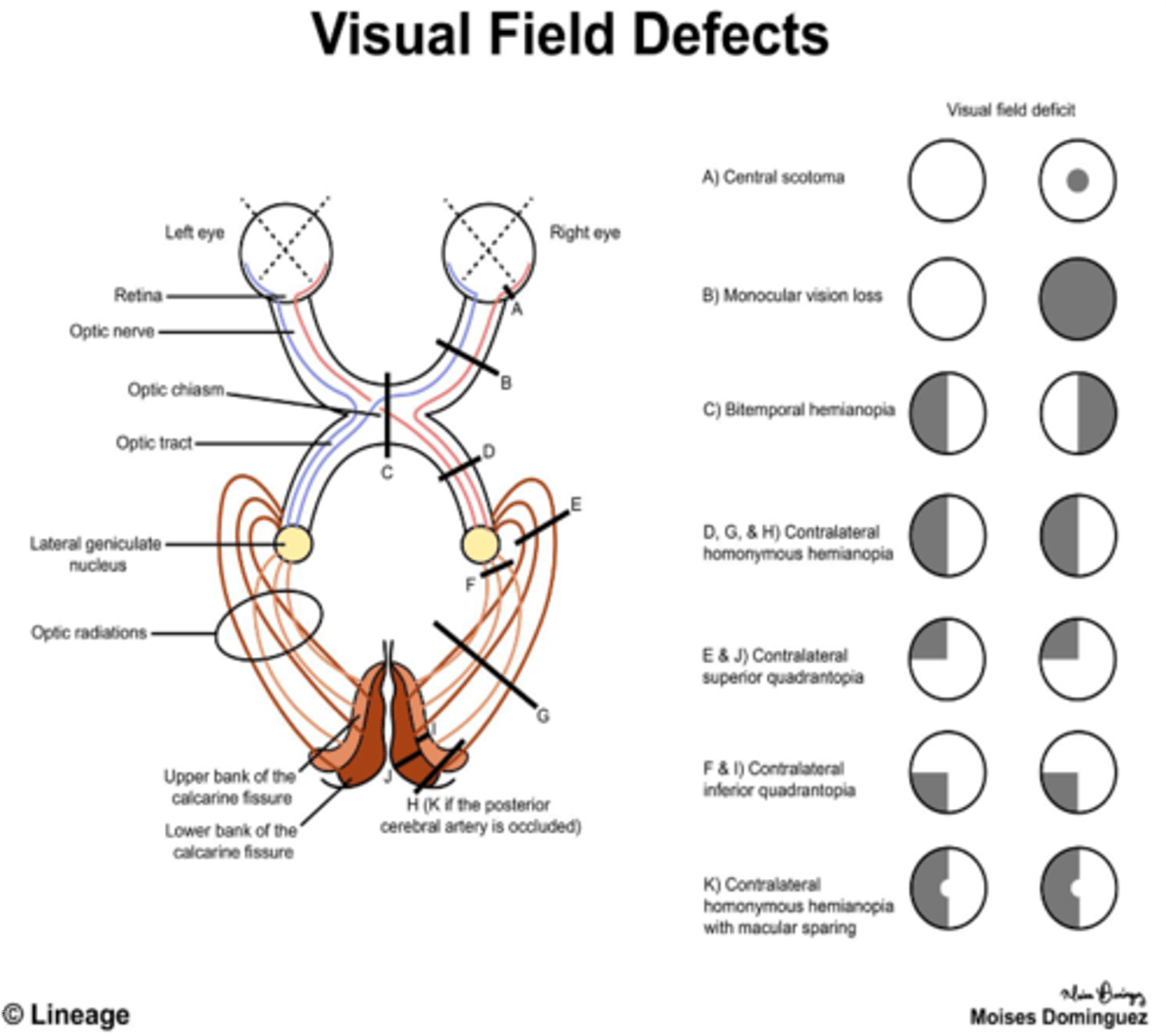
Unilateral blindness is likely due to a lesion on what part of the optic pathway?
Optic nerve
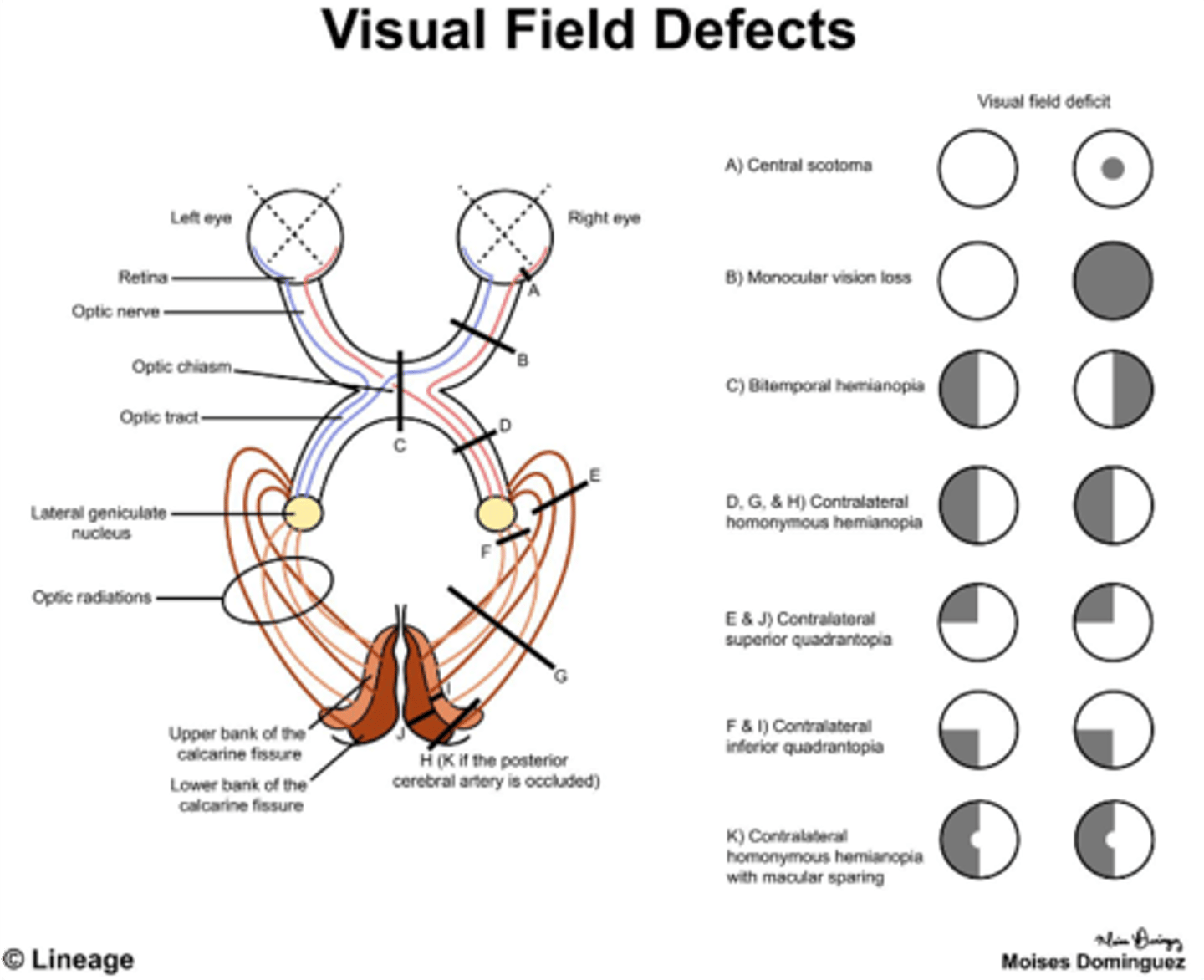
Bitemporal hemianopia is likely due to a lesion on what part of the optic pathway?
Optic chiasm

Homonymous hemianopia is likely due to a lesion on what part of the optic pathway?
Optic tract
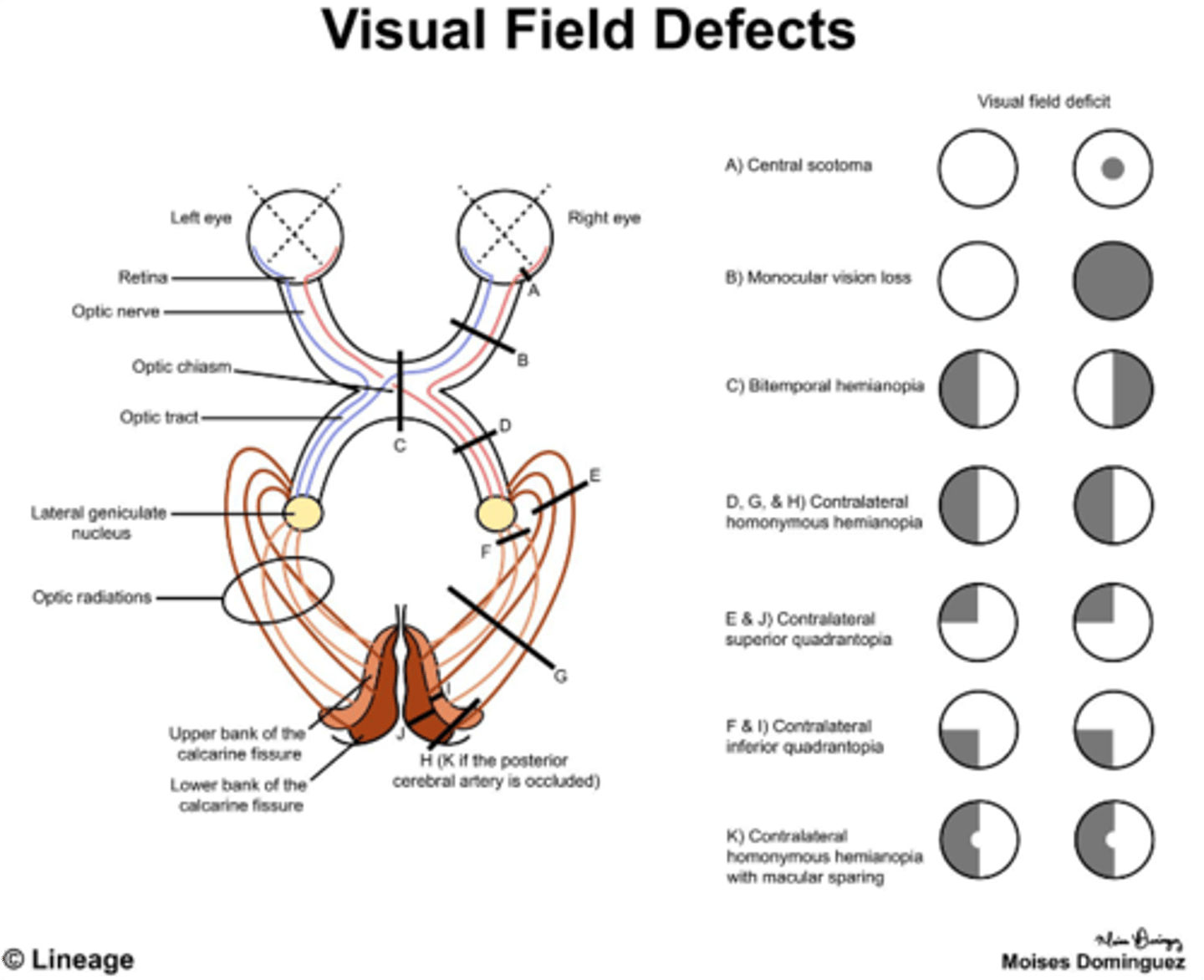
Impaired accommodation results from injury to what nerve?
Short ciliary nerve
Impaired accommodation results from injury to what parasympathetic ganglion?
Ciliary ganglion
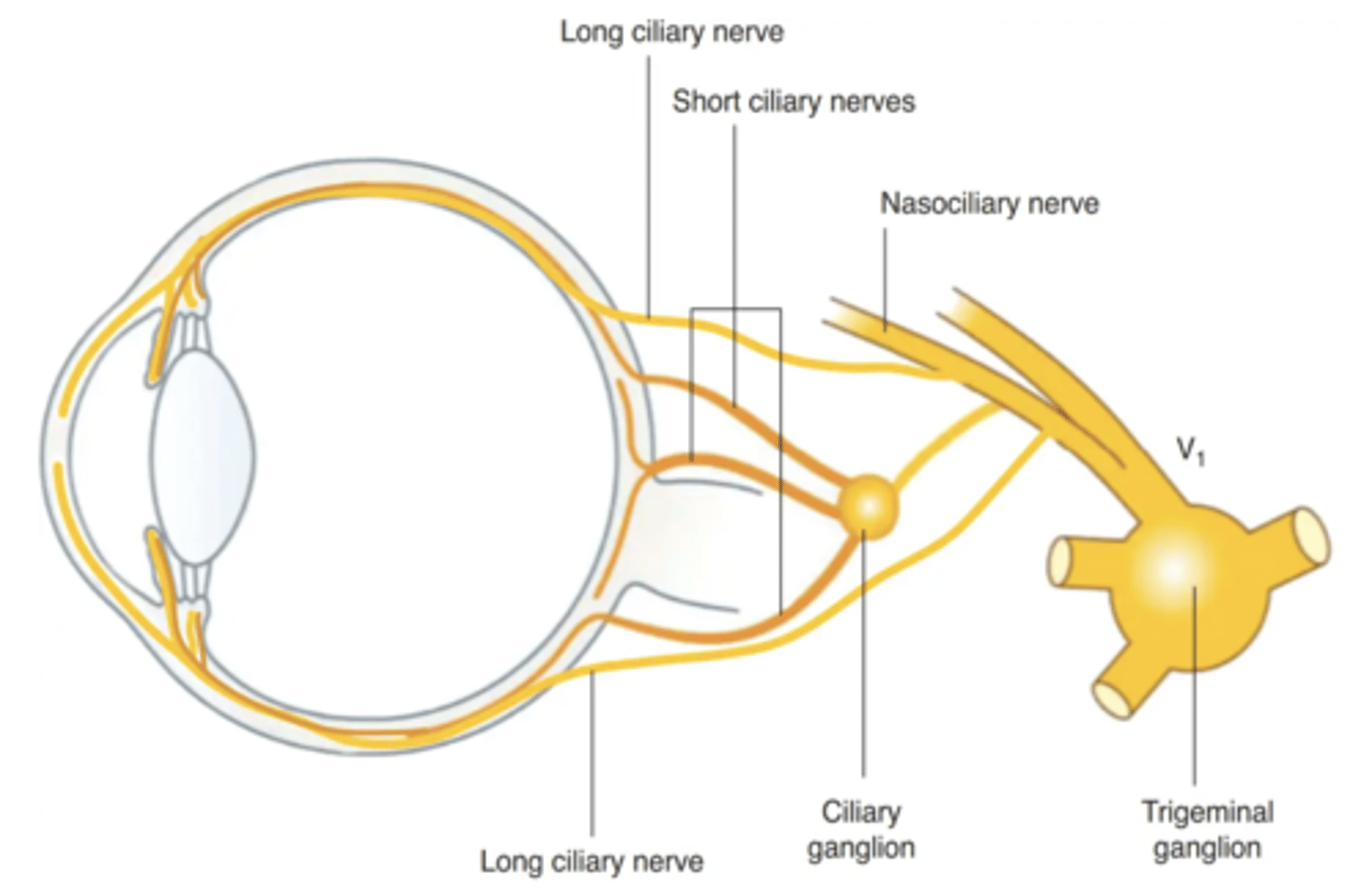
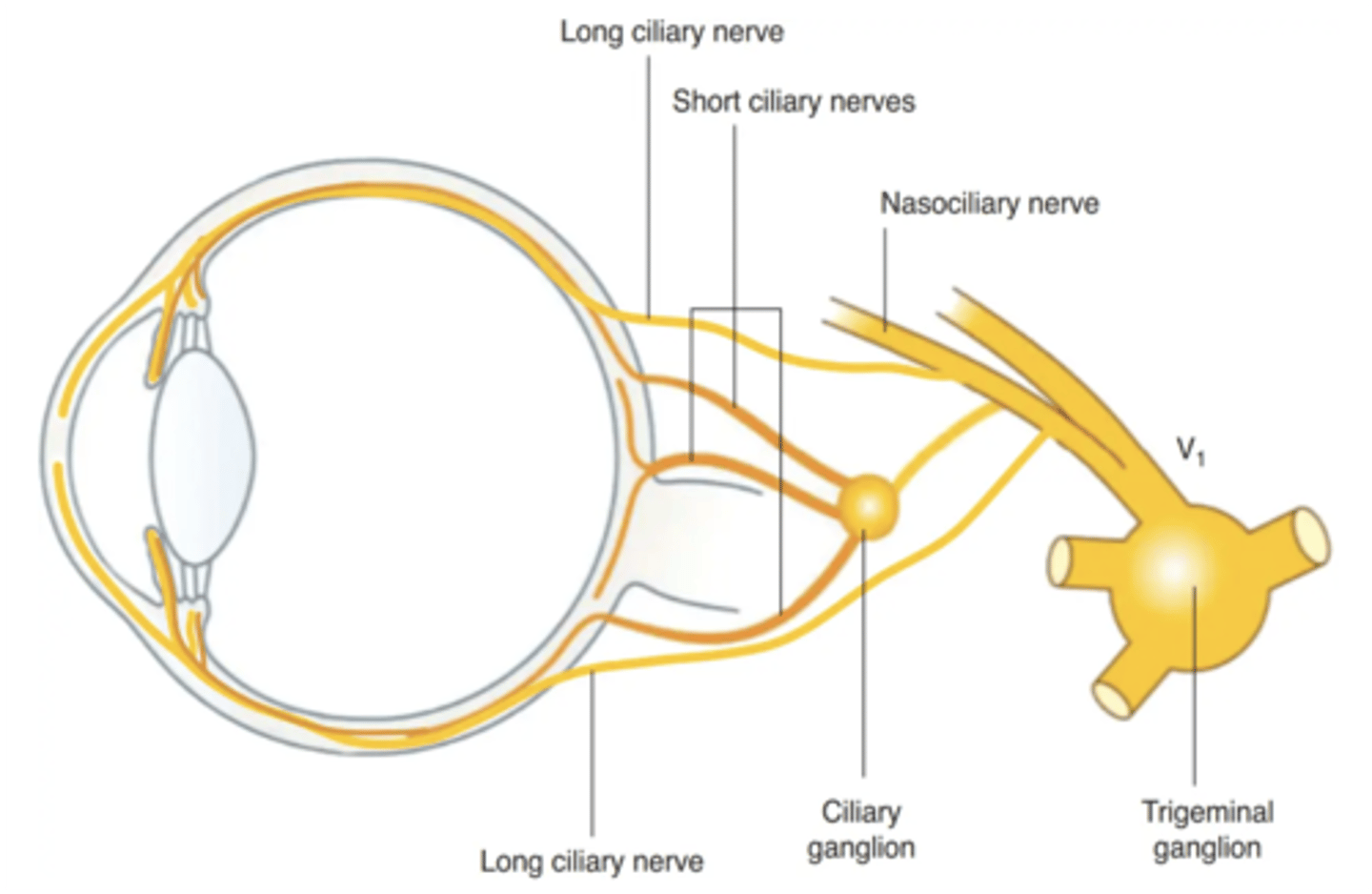
What nerve carries sympathetic fibers to the dilator pupillae?
Long ciliary nerve
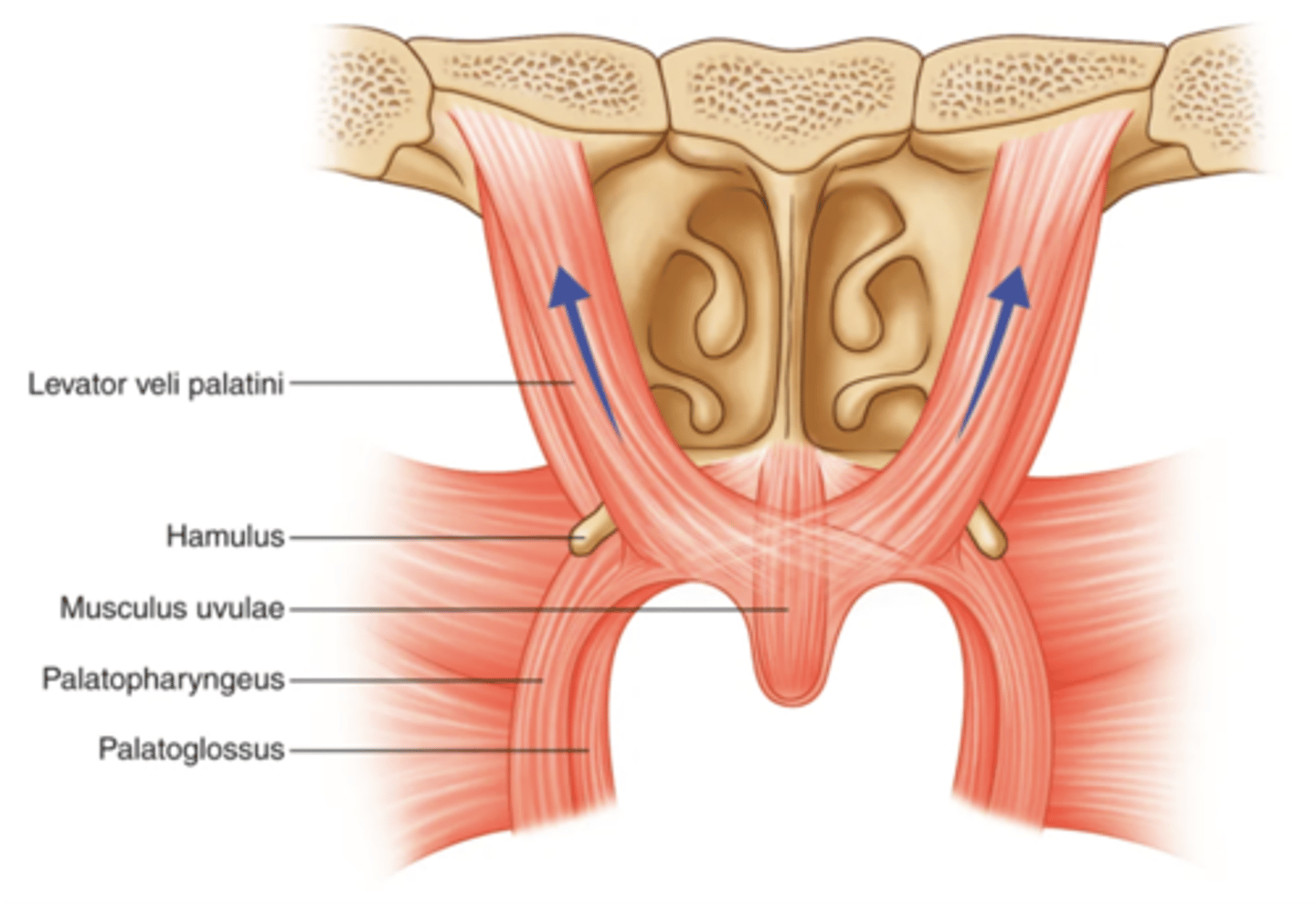
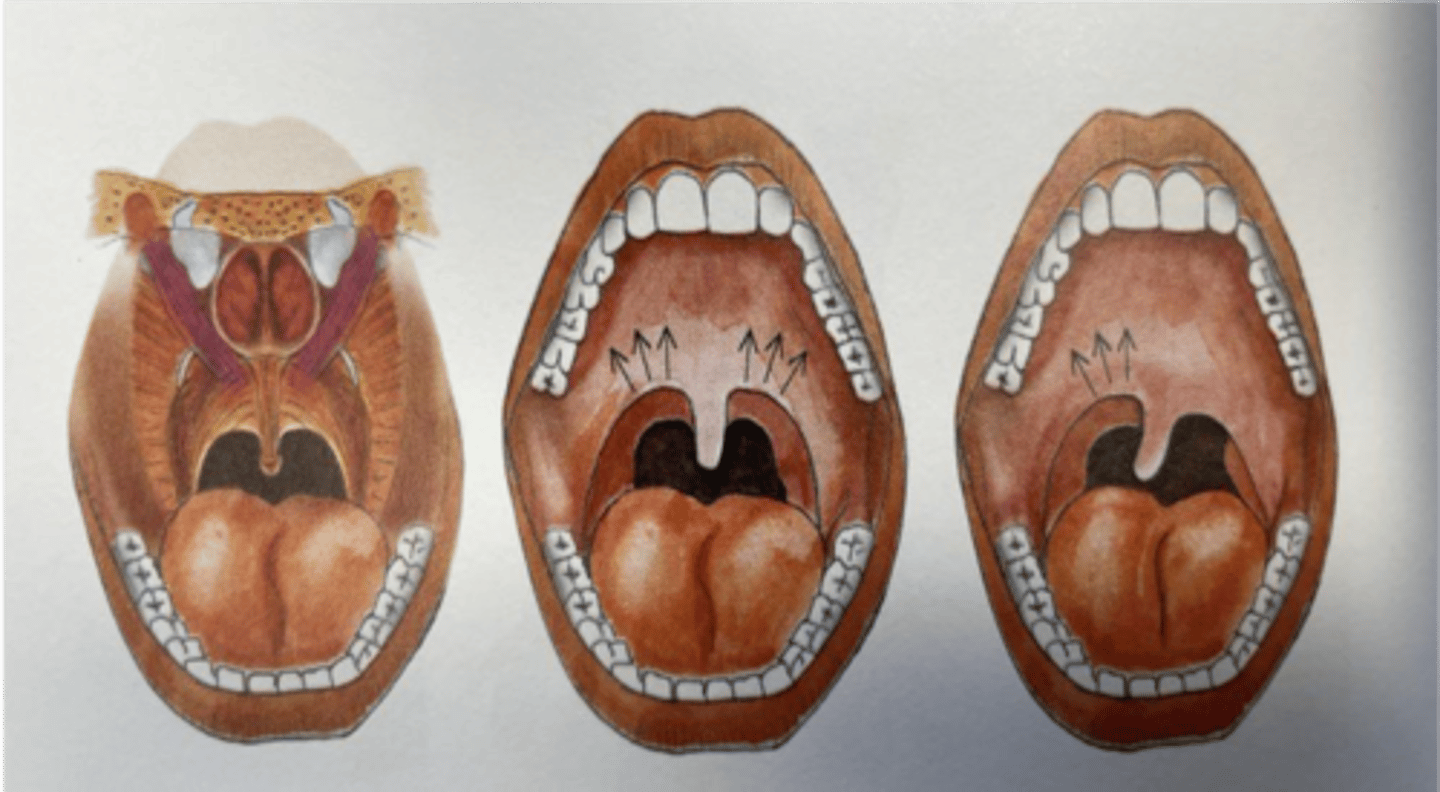
What nerve innervates the musculus uvulae?
Vagus nerve
Lesion of the vagus nerve causes deviation ...(towards/away)... the side of injury?
Away
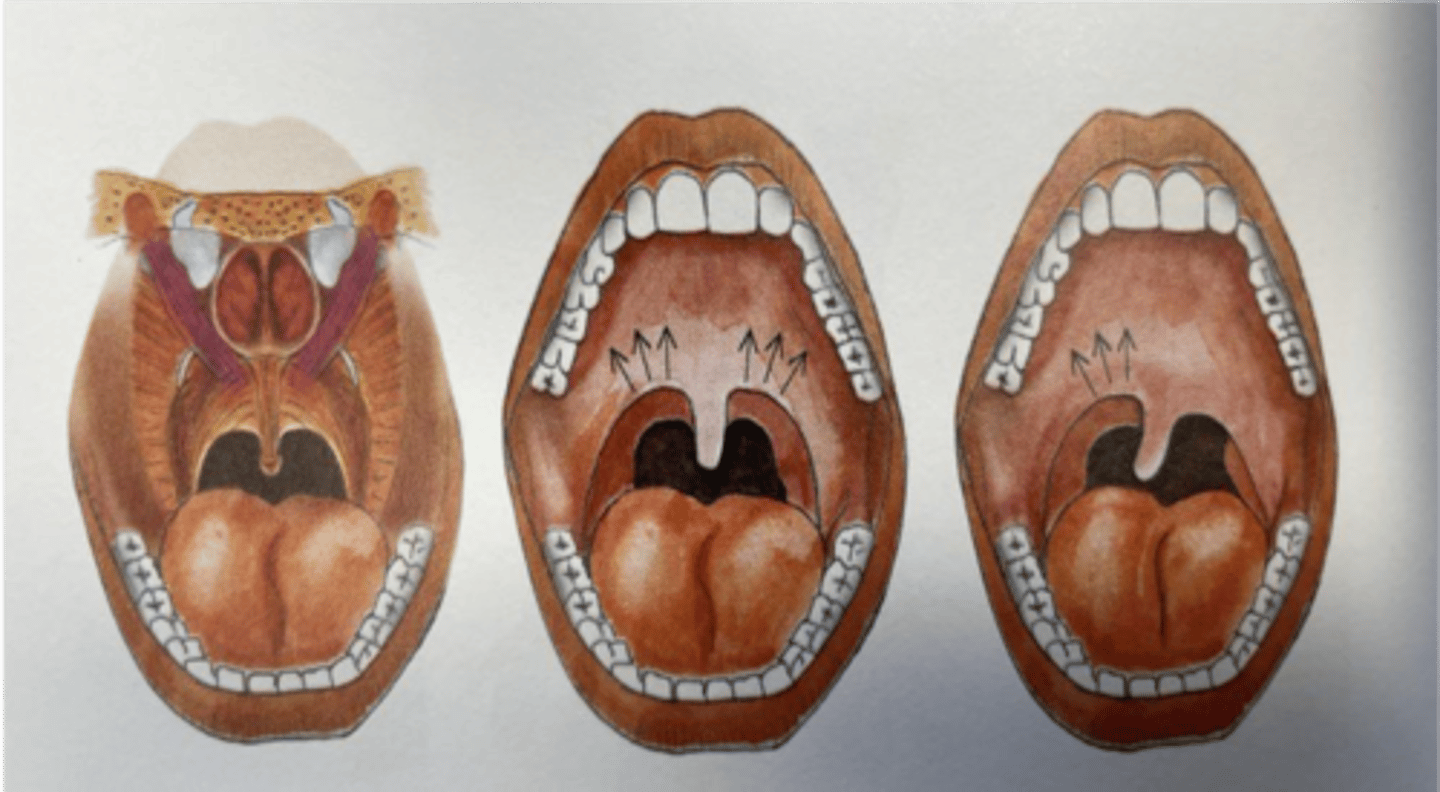
What nerve is damaged if the uvula deviates to the left?
Right vagus nerve
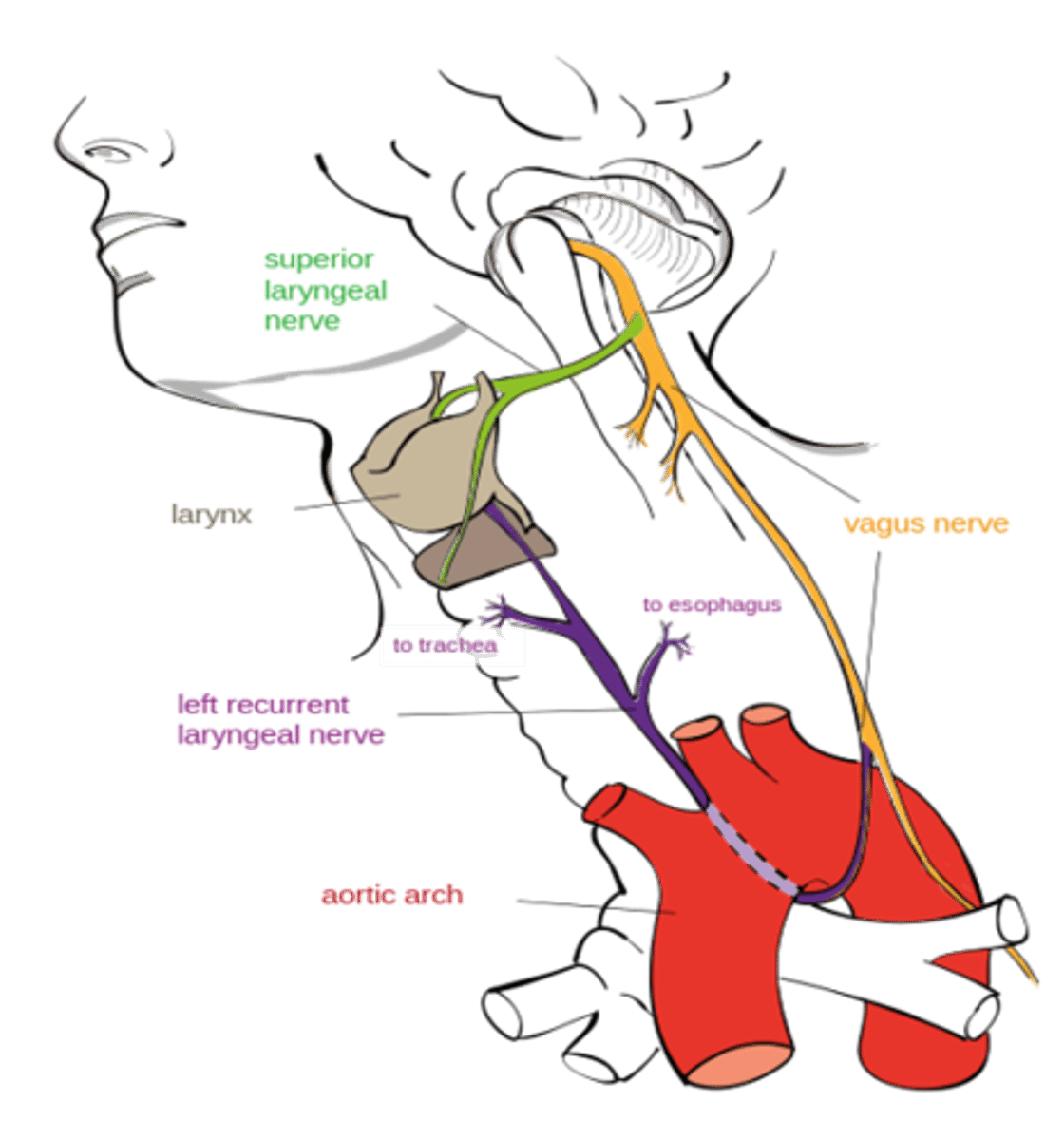
Hoarseness from paralysis of laryngeal muscles result from damage of what branch of the vagus nerve?
Recurrent laryngeal branch
Lesion of the hypoglossal nerve causes deviation of the tongue ...(towards/against)... the injured side on protrusion
Towards
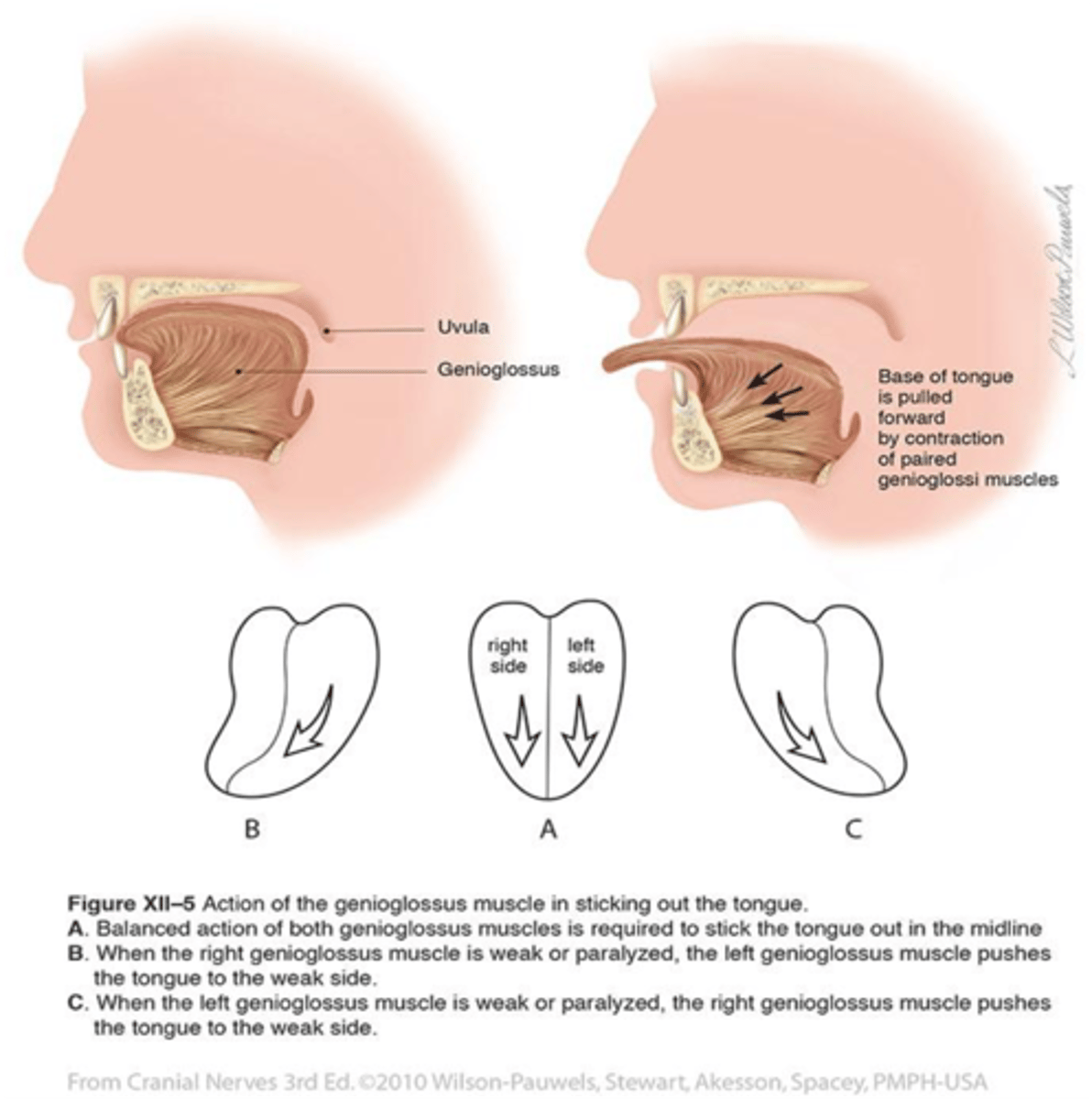
What cranial nerve supplies the intrinsic tongue muscles?
Hypoglossal nerve
Damage to the optic chiasma would lead to what visual field defect?
Bitemporal hemianopsia
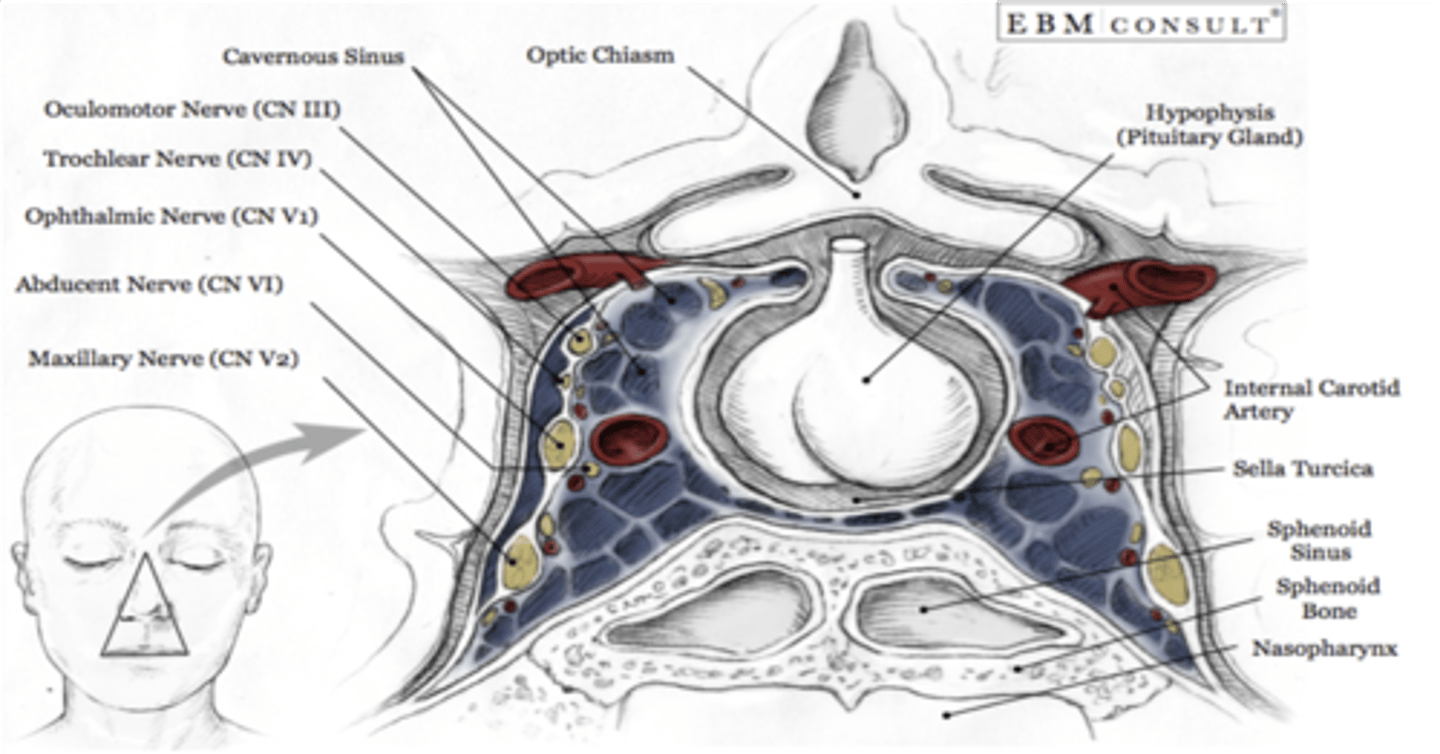
What cranial nerve runs through the middle of the cavernous sinus?
Abducens nerve
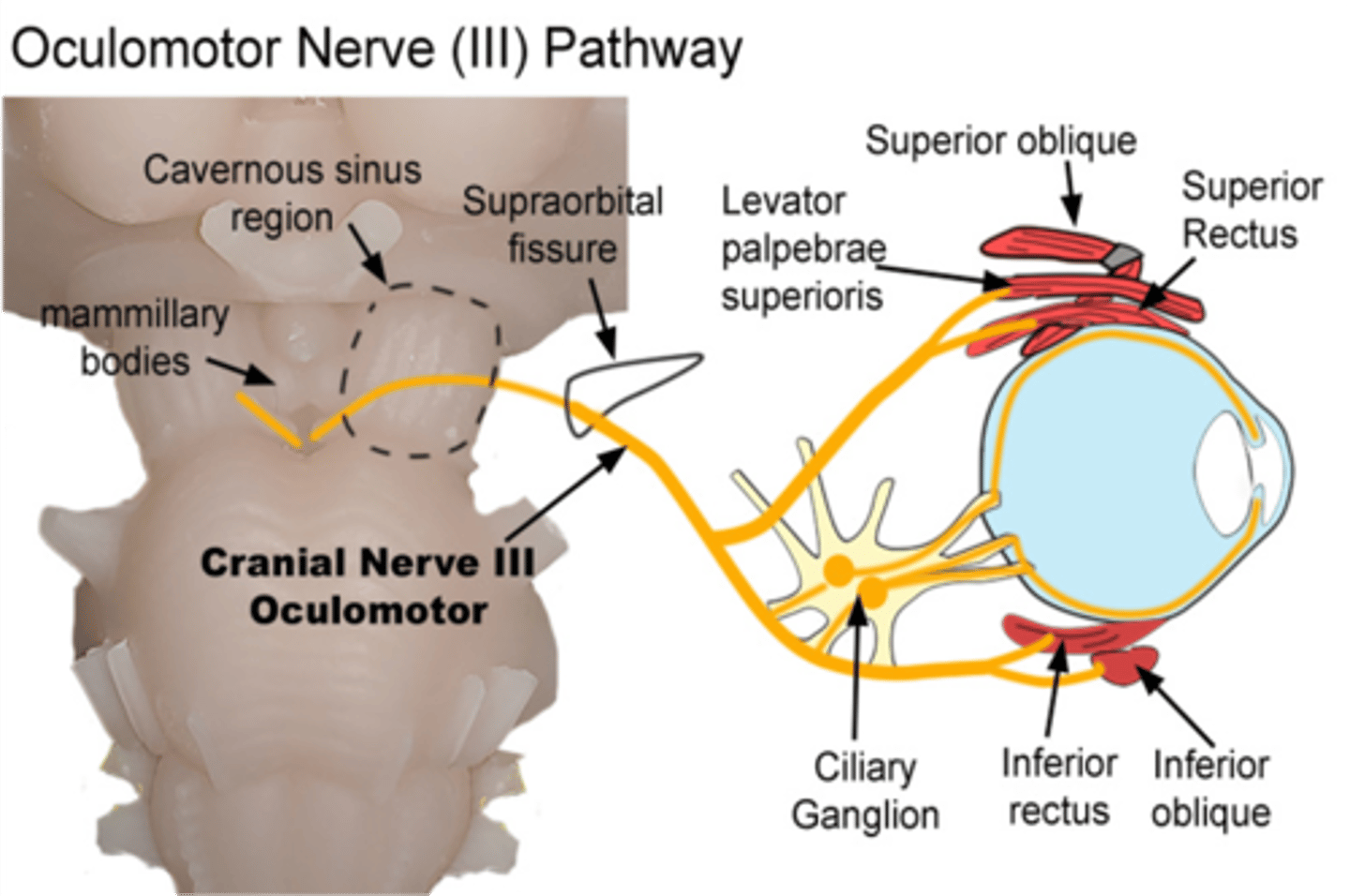
What nerve carries parasympathetic fibers to the ciliary and sphincter pupillae ciliary muscles?
Oculomotor nerve
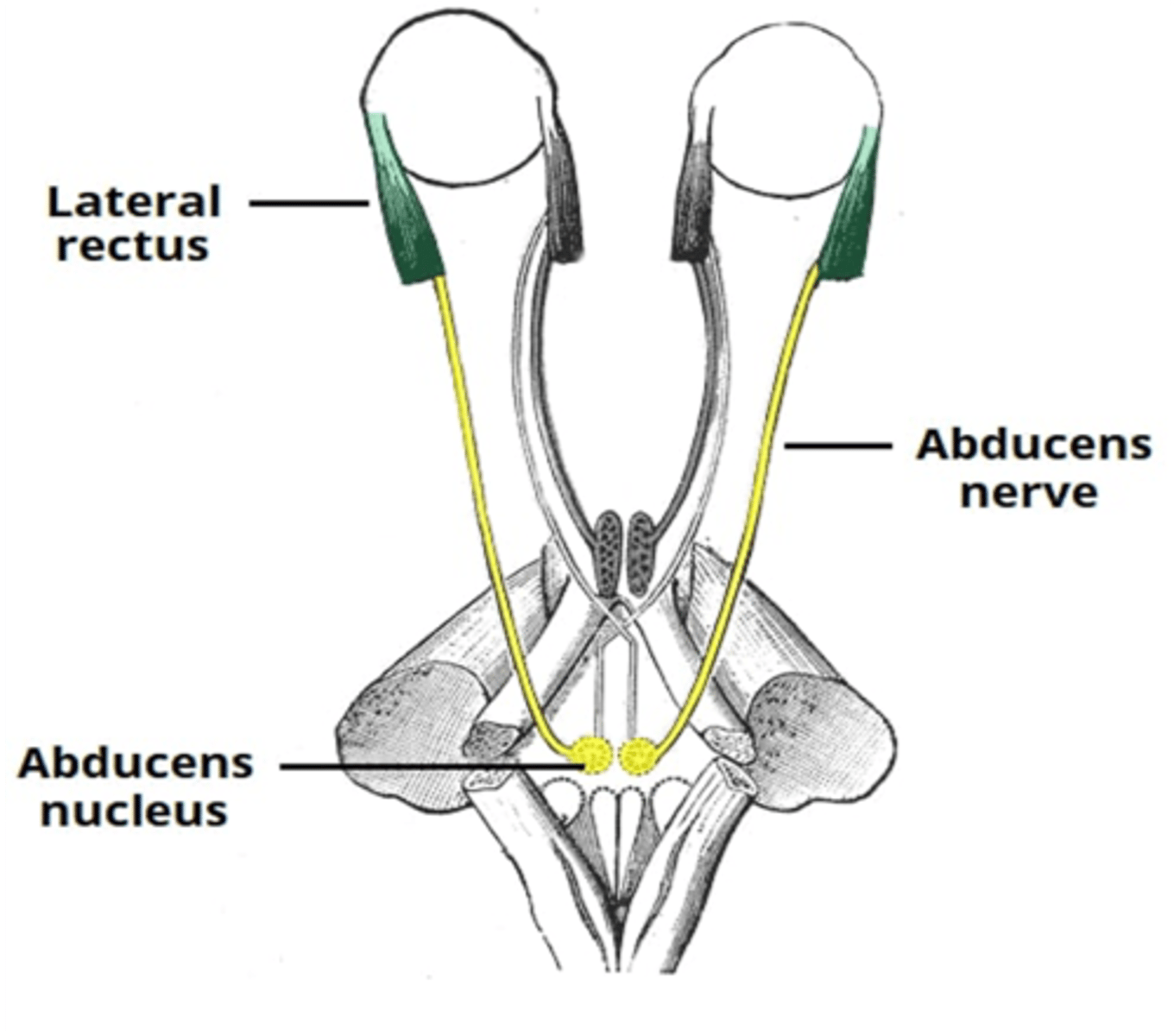
What nerve supplies the lateral rectus muscle of the eye
Abducens nerve
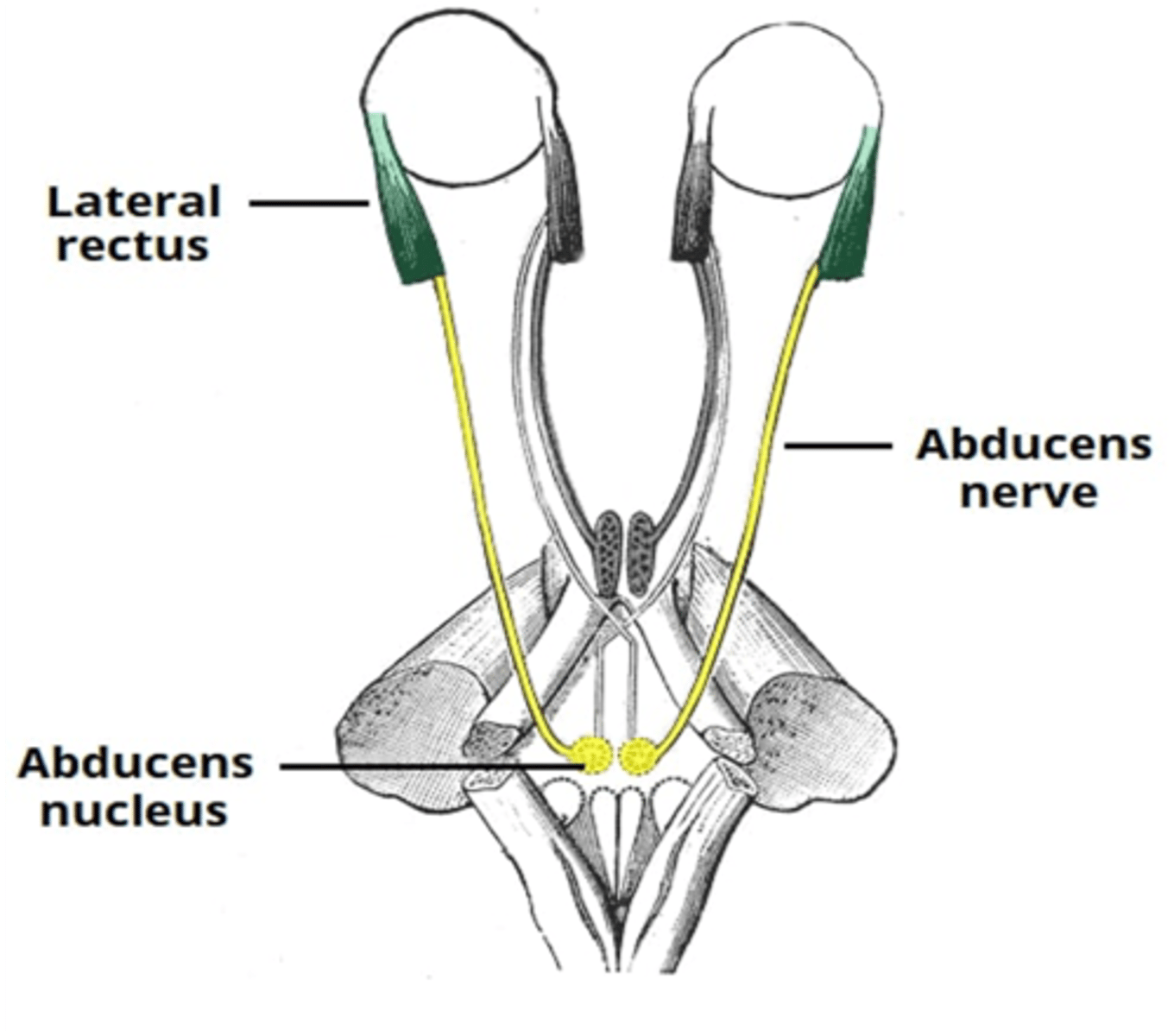
The abducens nerve innervate what extraocular muscle?
Lateral rectus muscle
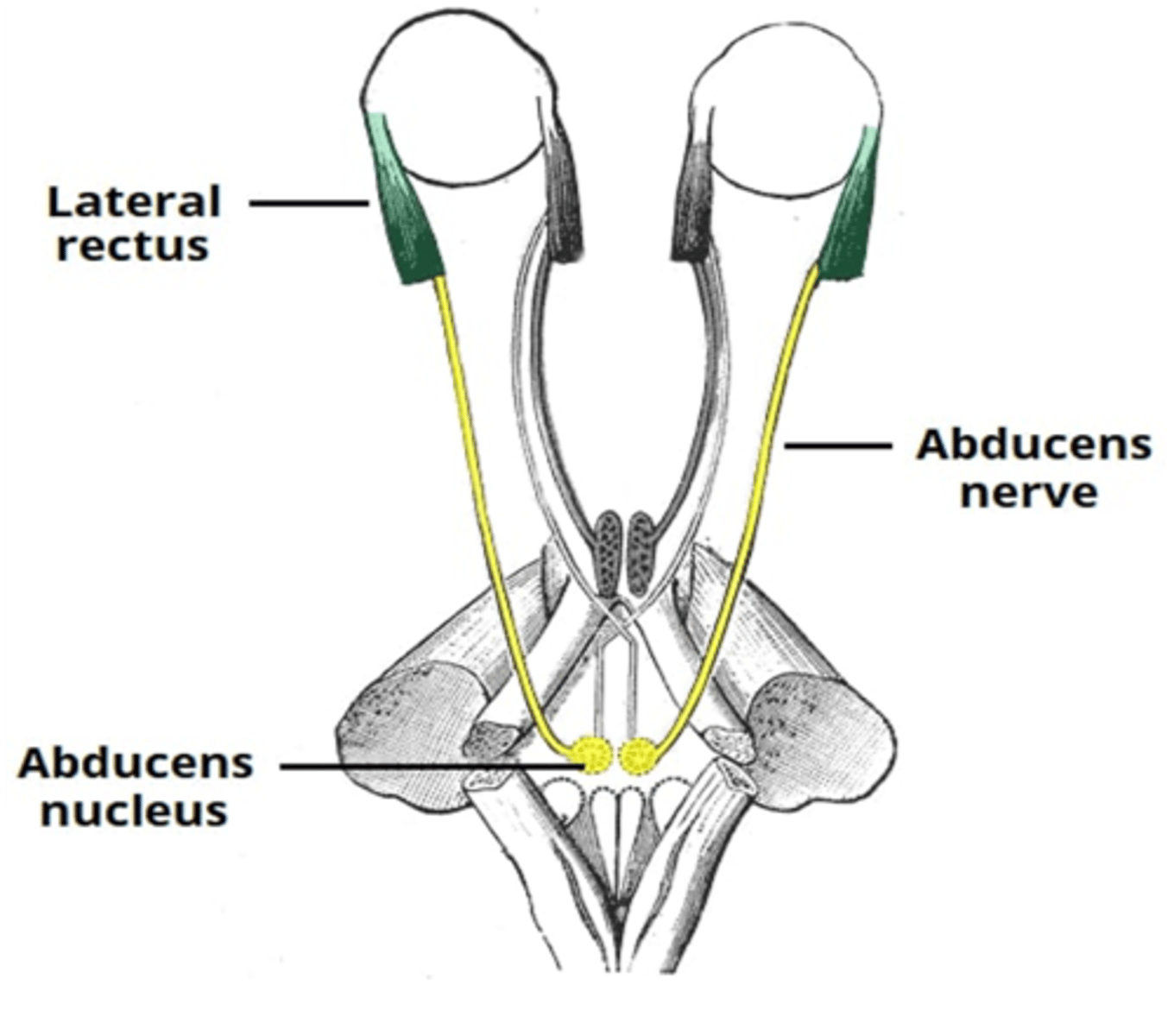
What is the action of the lateral rectus muscle?
Abduction of the eye
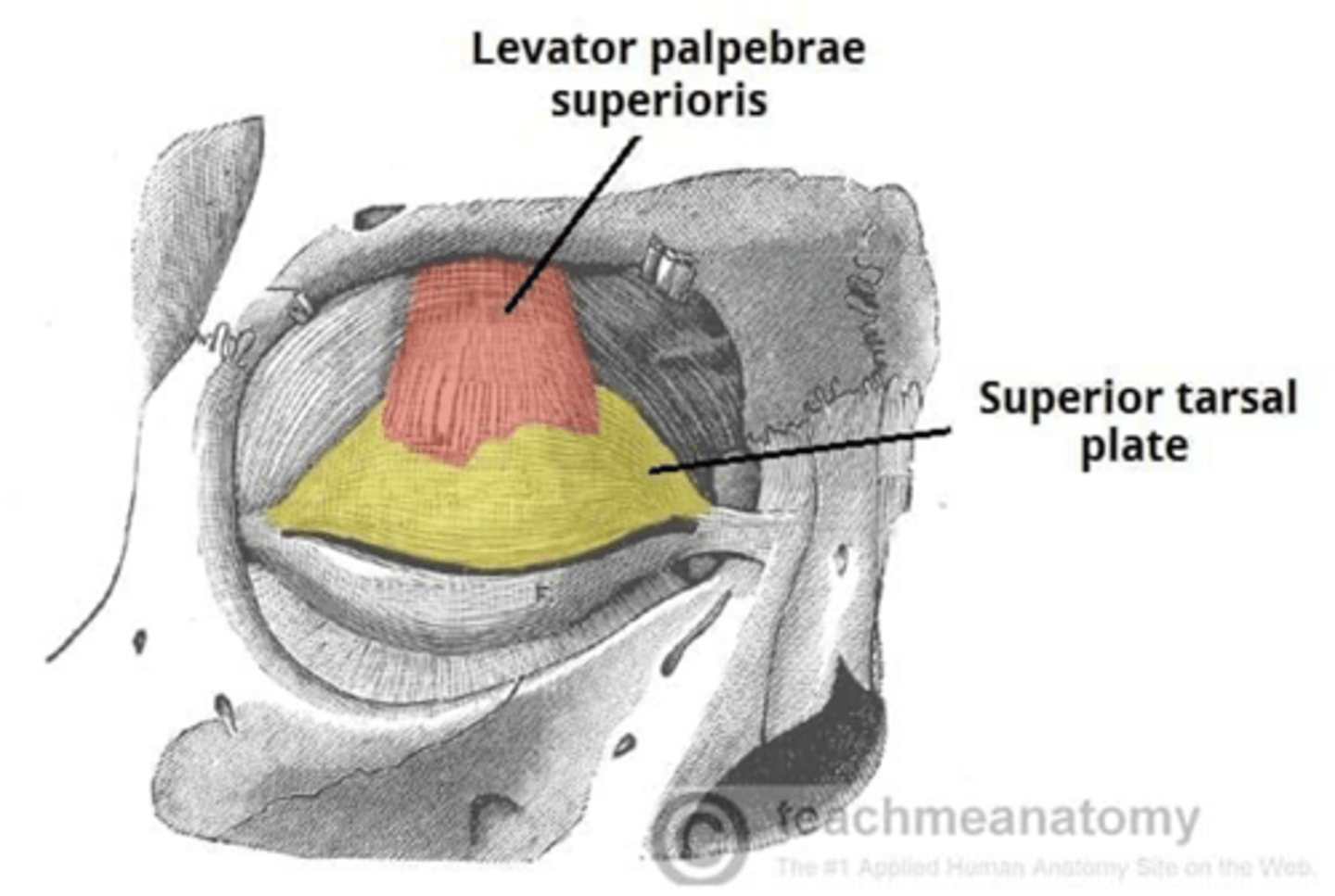
The levator palpebrae superioris inserts onto what part of the upper eyelid?
Tarsal plate
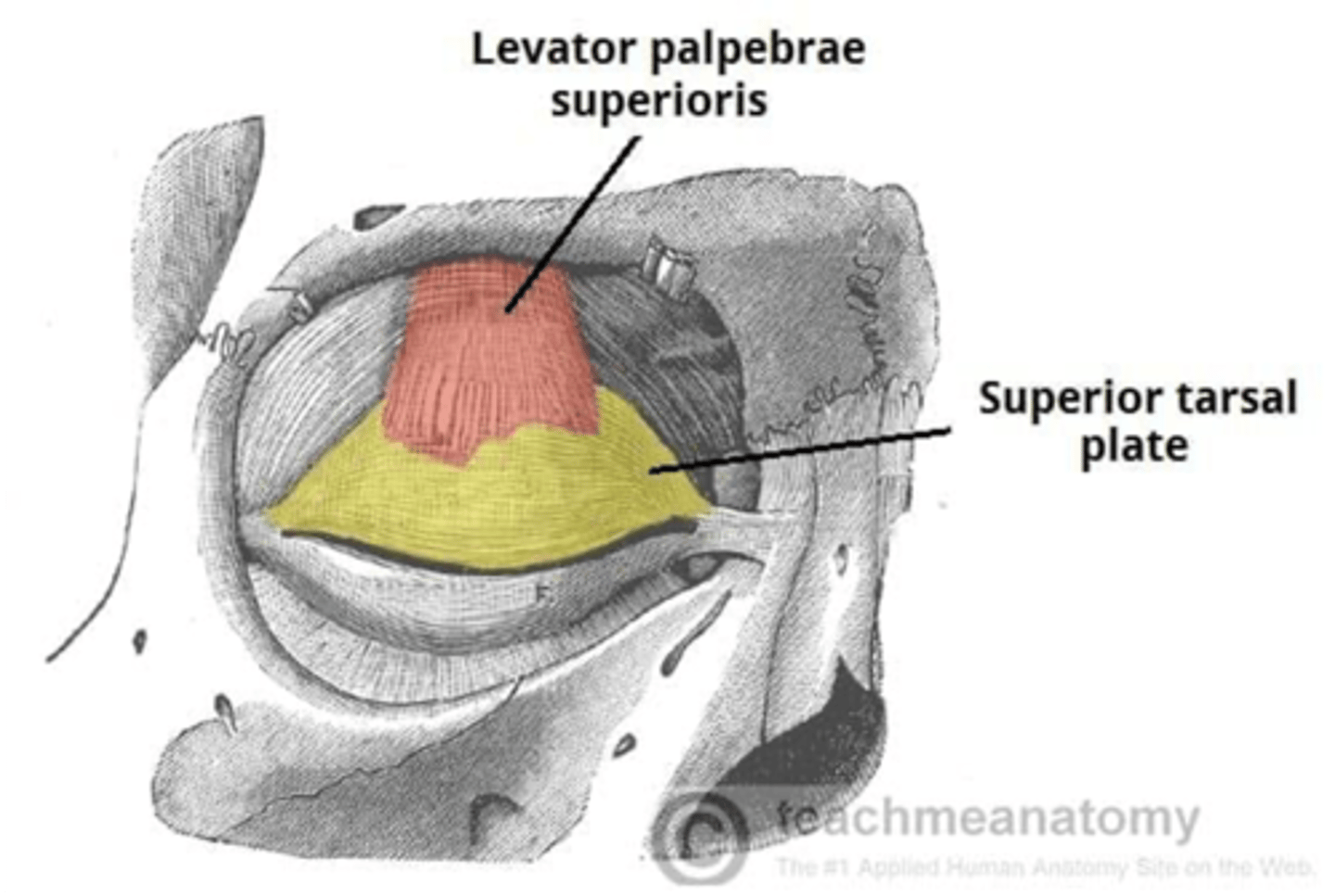
What muscle inserts onto the tarsal plate of the upper eyelid?
Laevator palpebrae superioris
The secretomotor fibers for lacrimal secretion comes through what ganglion?
Pterygopalatine ganglion
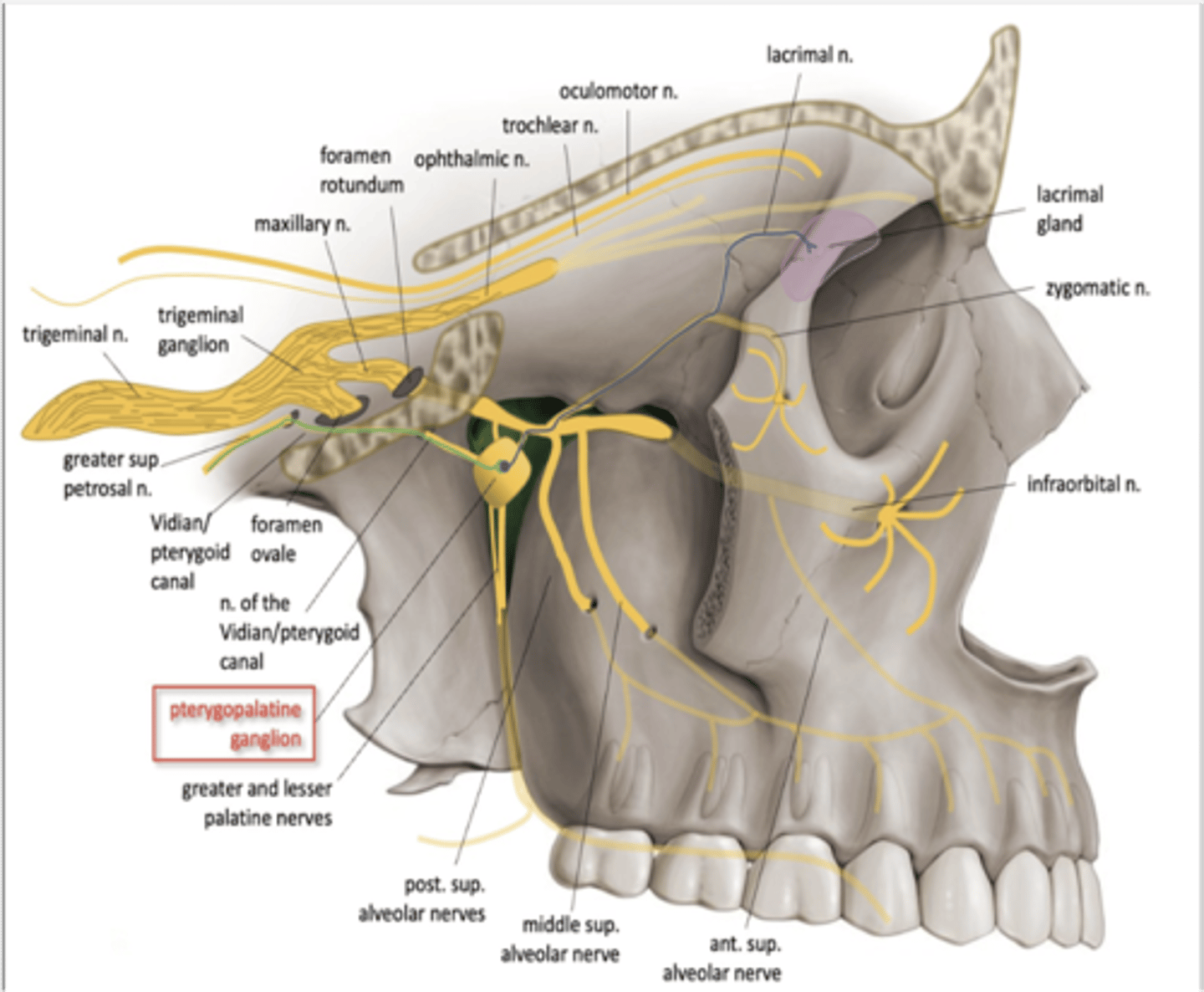
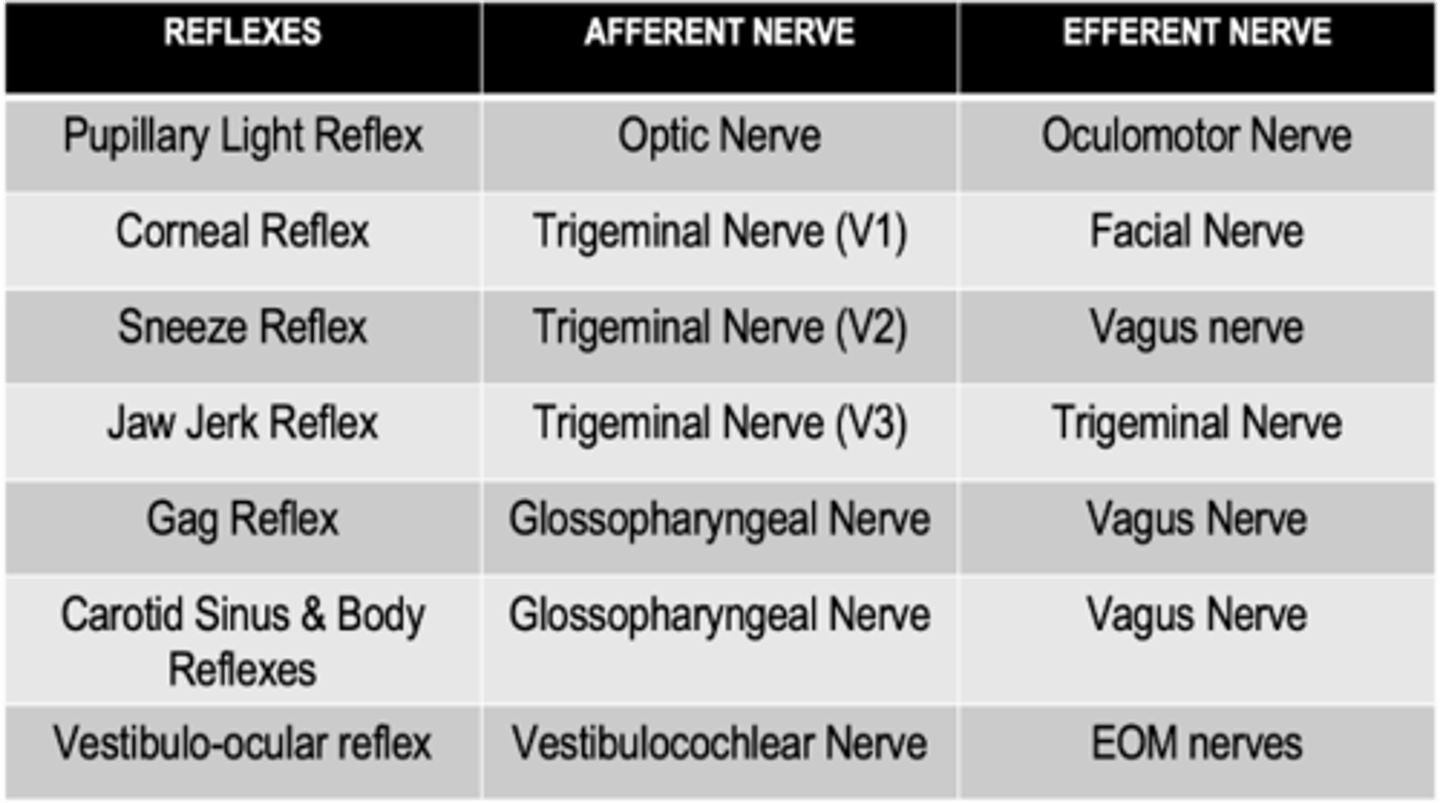
What is the afferent limb of the corneal reflex?
Nasociliary nerve (Trigeminal nerve)
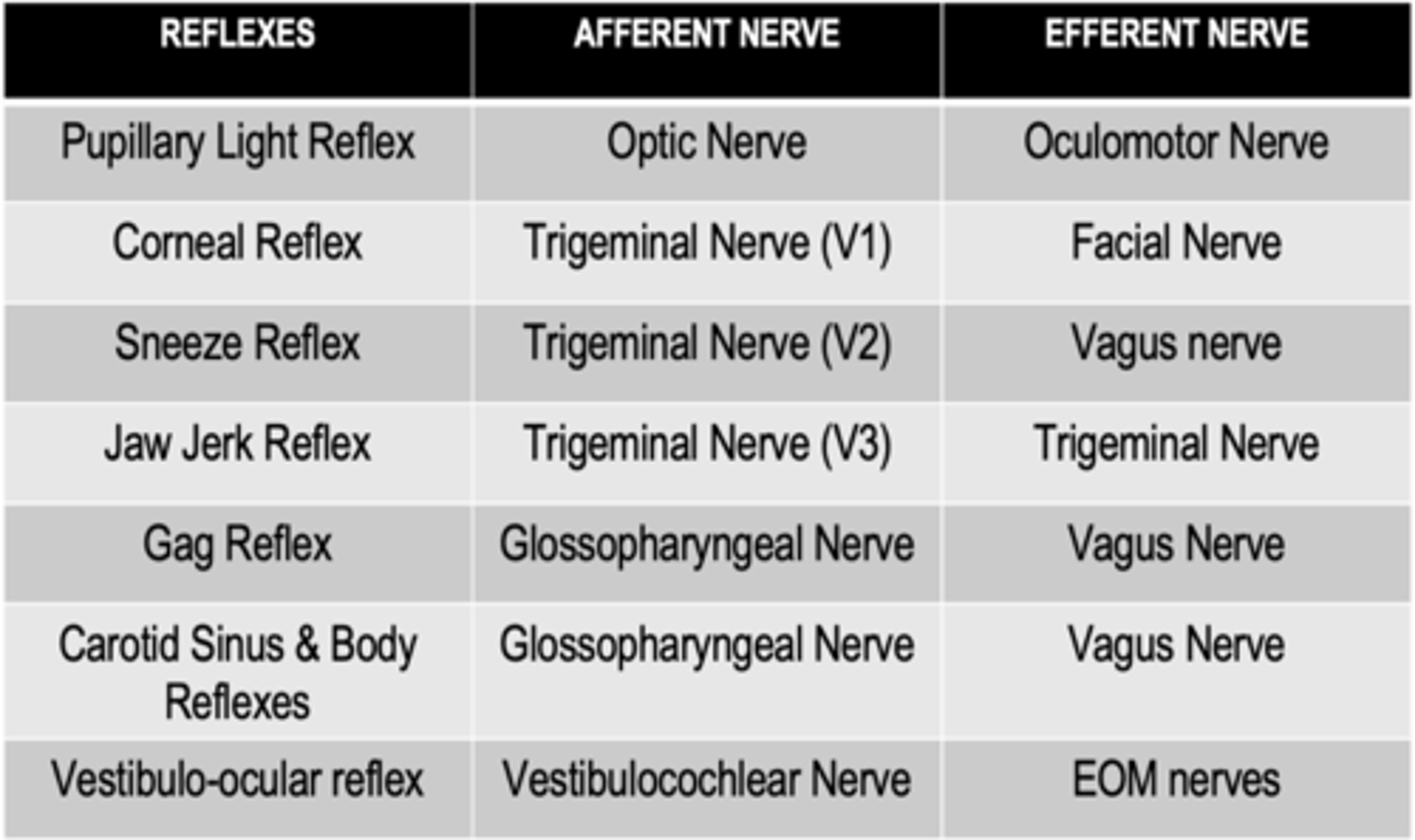
What is the efferent limb of the corneal reflex?
Facial nerve
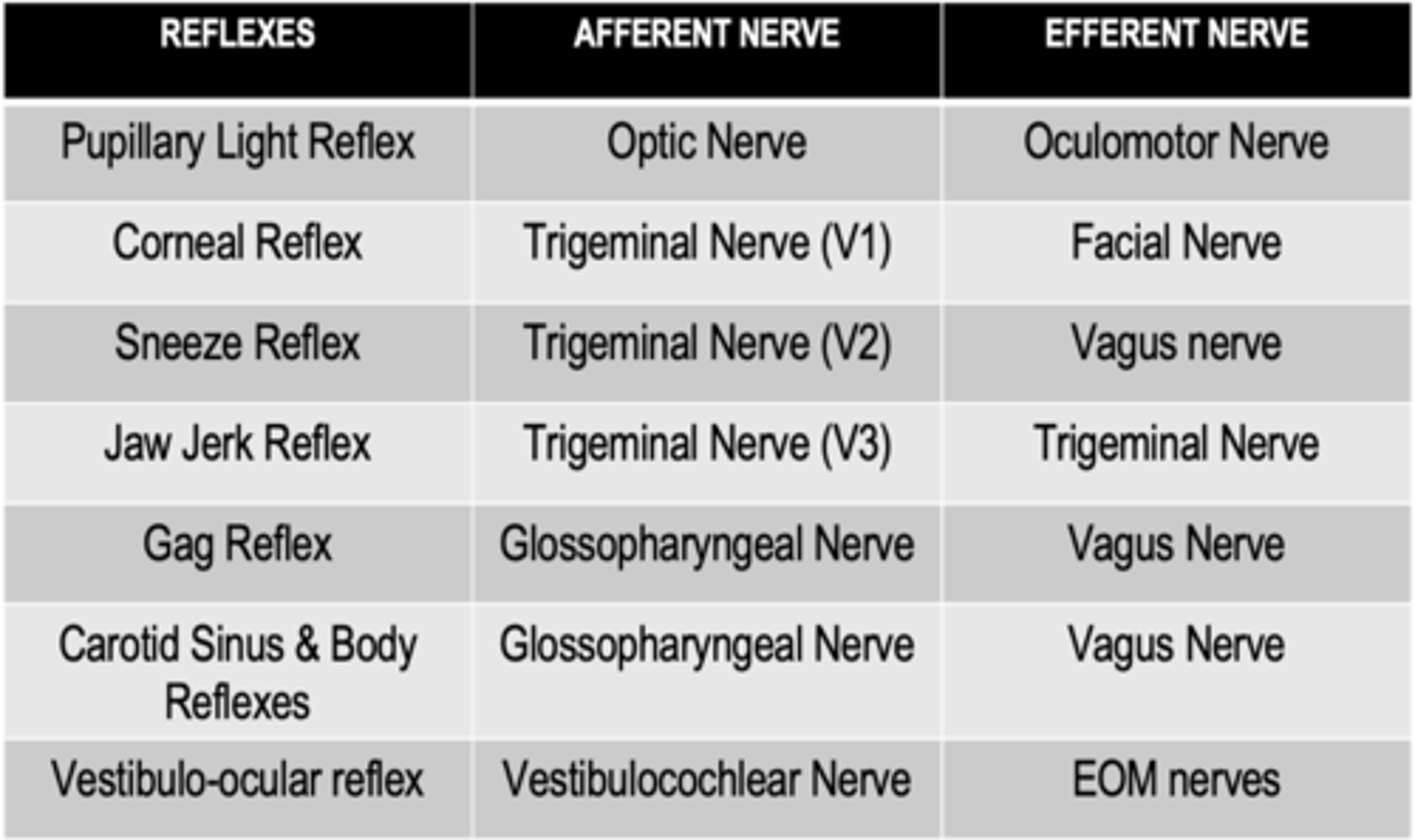
What cranial nerve is involved in the opening of the eye?
Oculomotor nerve
What nerve contains taste fibers (special visceral afferent fibers) from the palate?
Nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve)
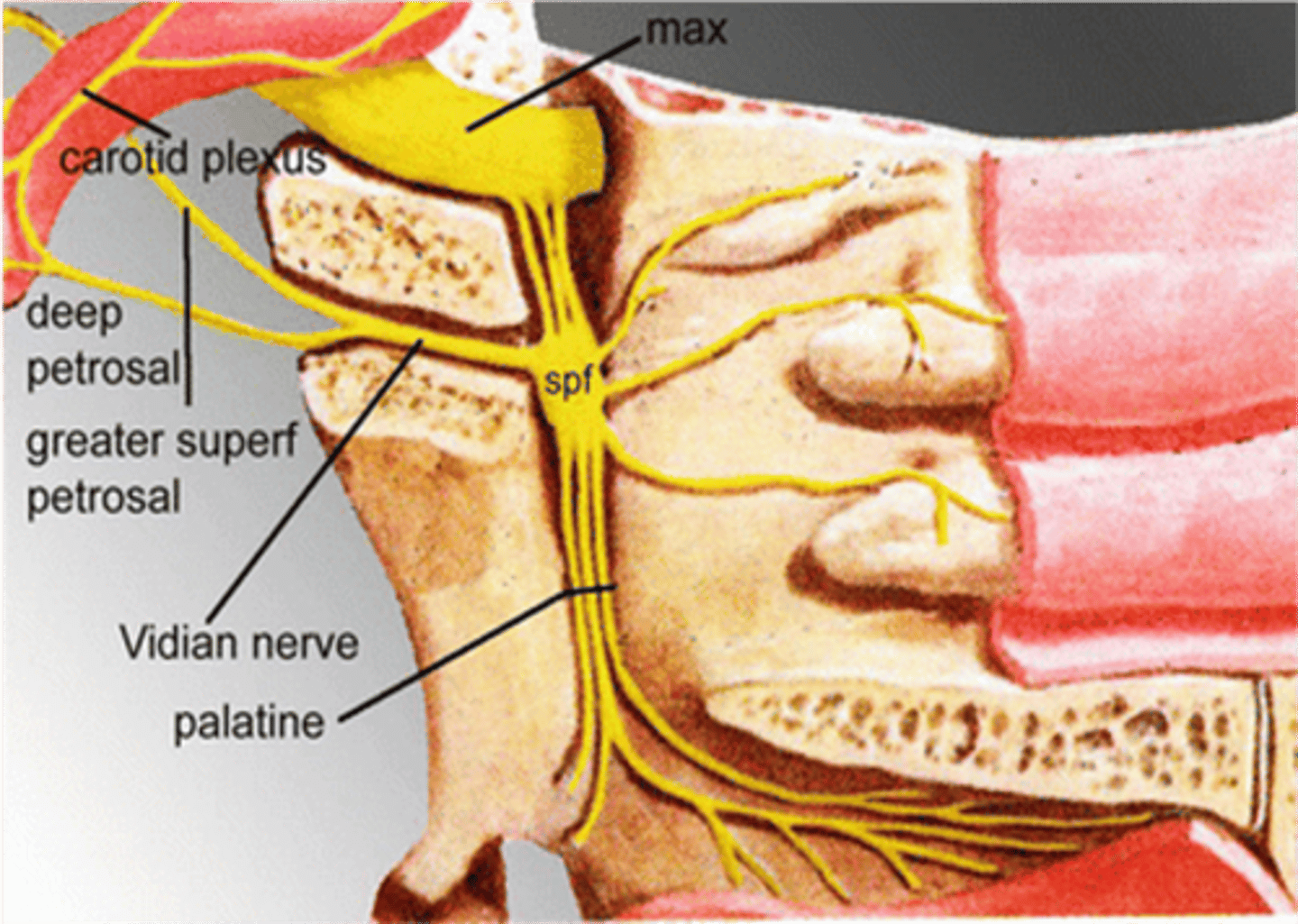
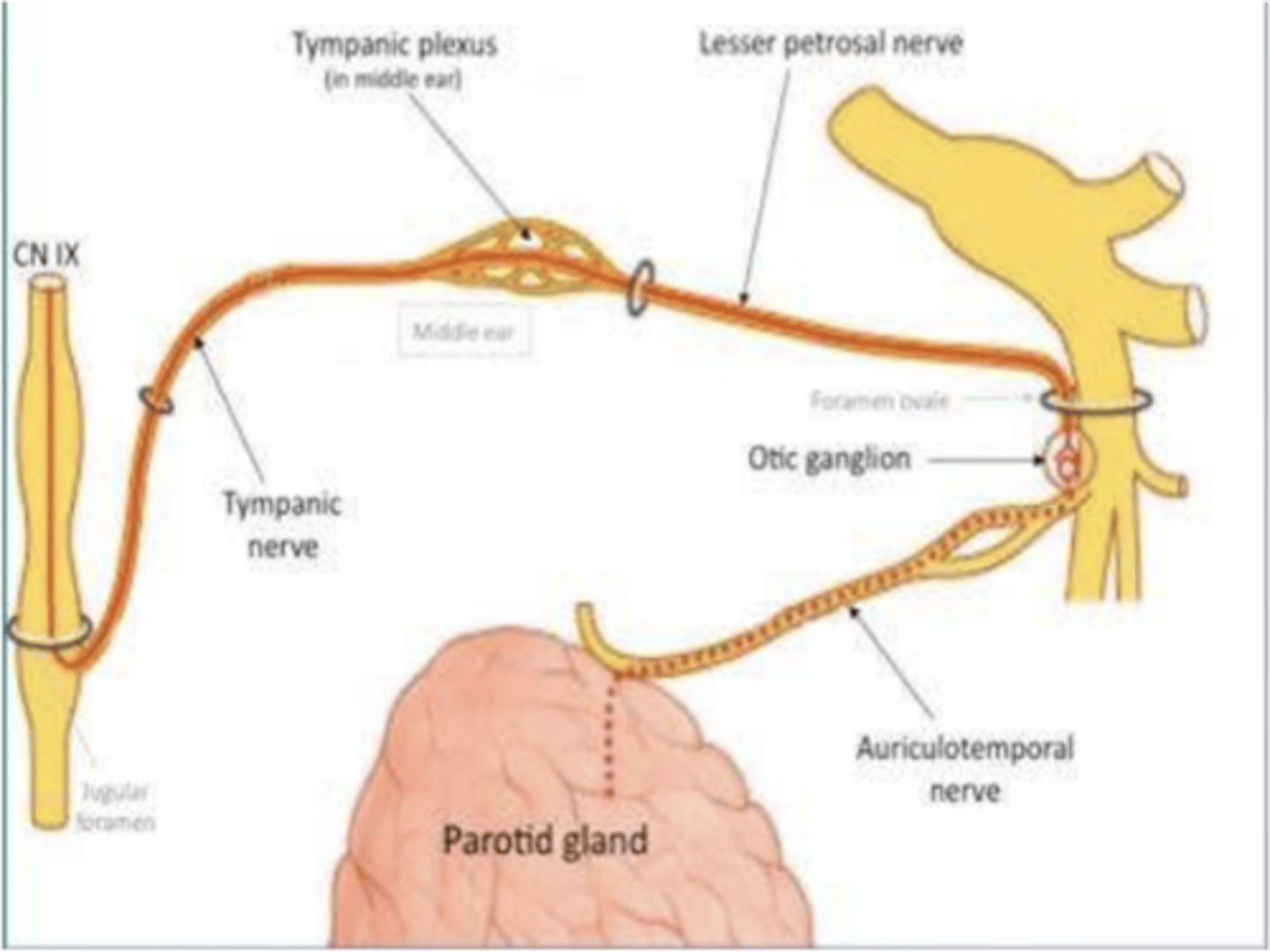
What nerve carries secretomotor (preganglionic parasympathetic) fibers to the parotid gland?
Lesser petrosal nerve
The maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Foramen rotundum
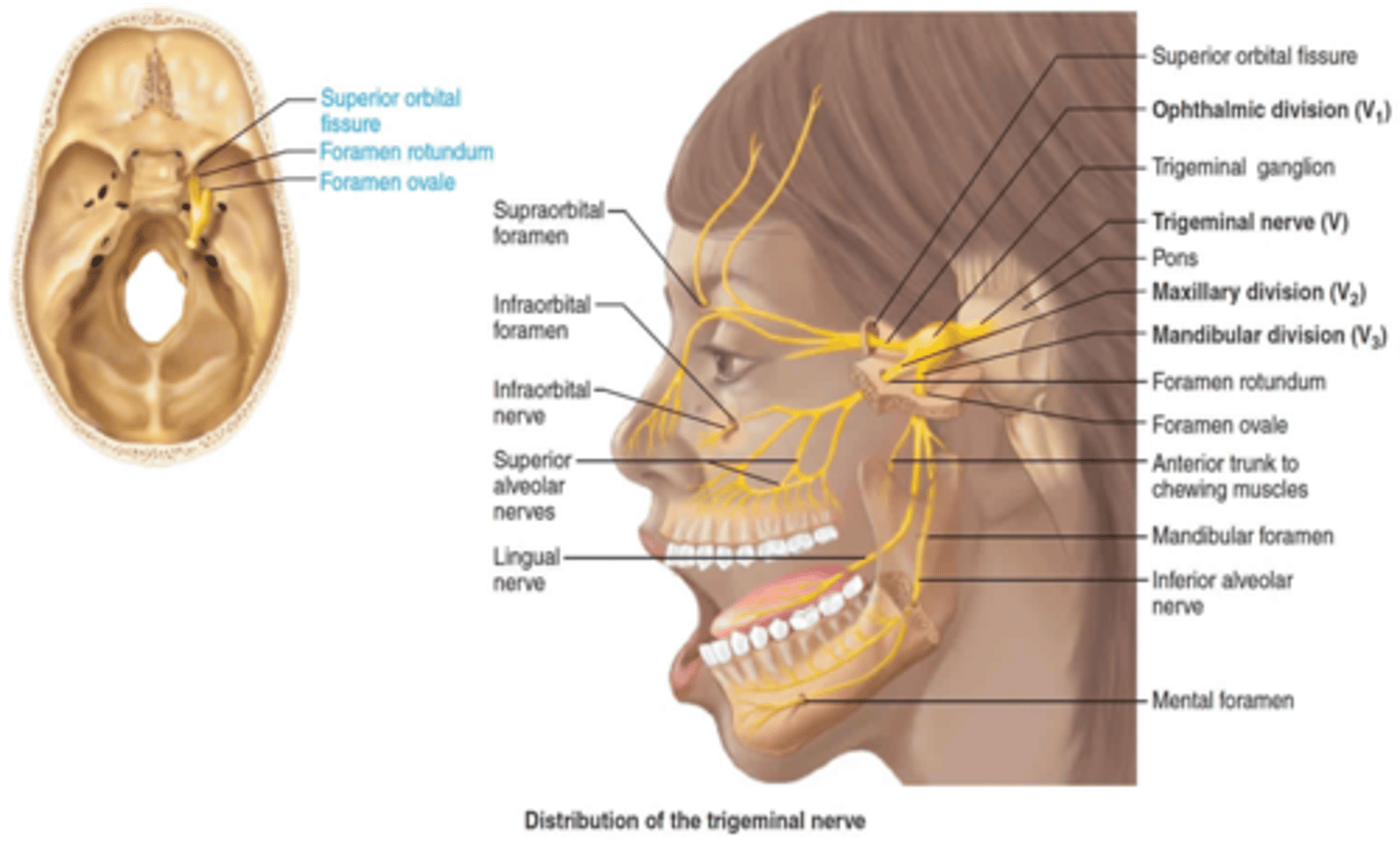
The mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Foramen ovale
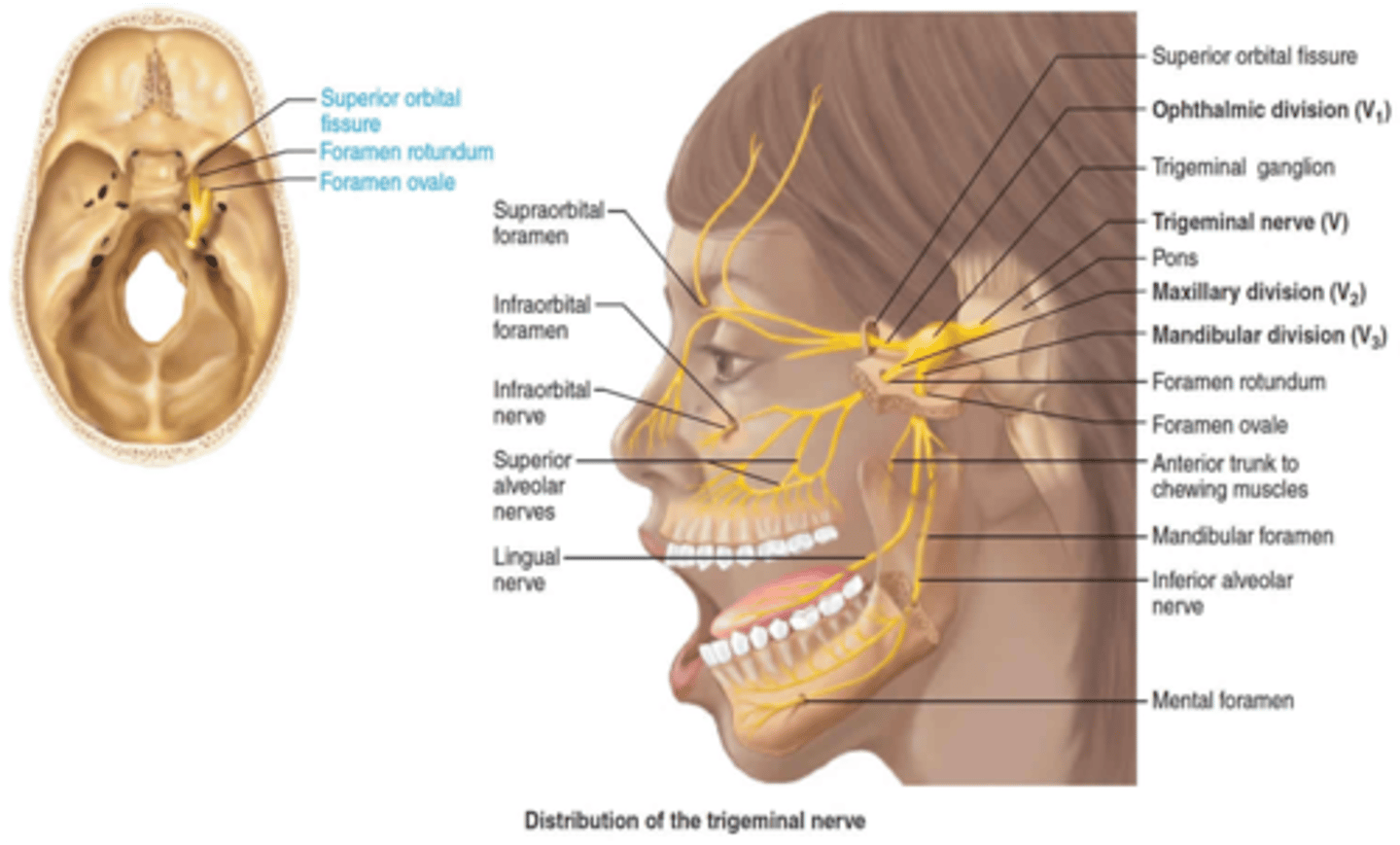
The ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through what foramen?
Superior Orbital Fissure
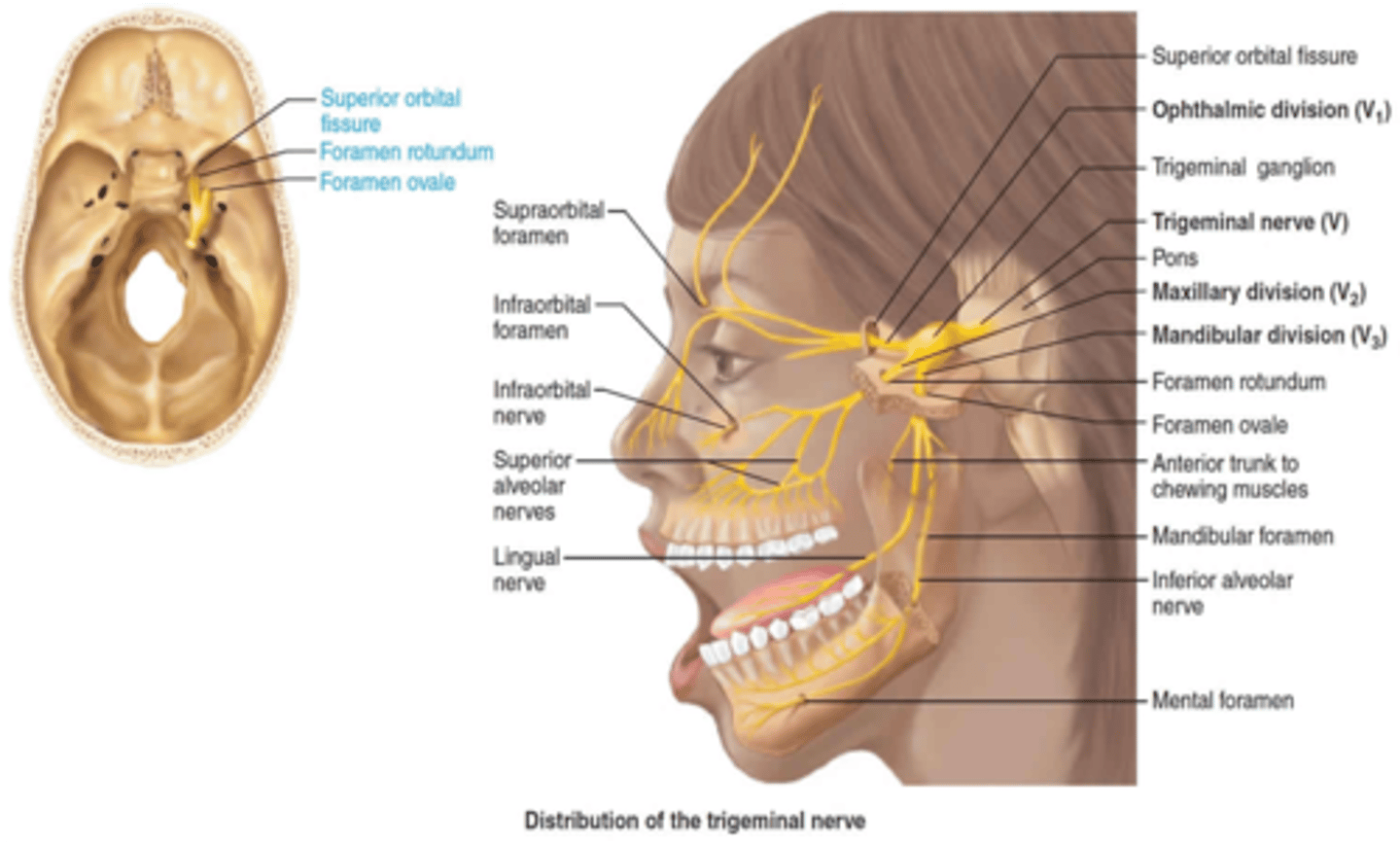
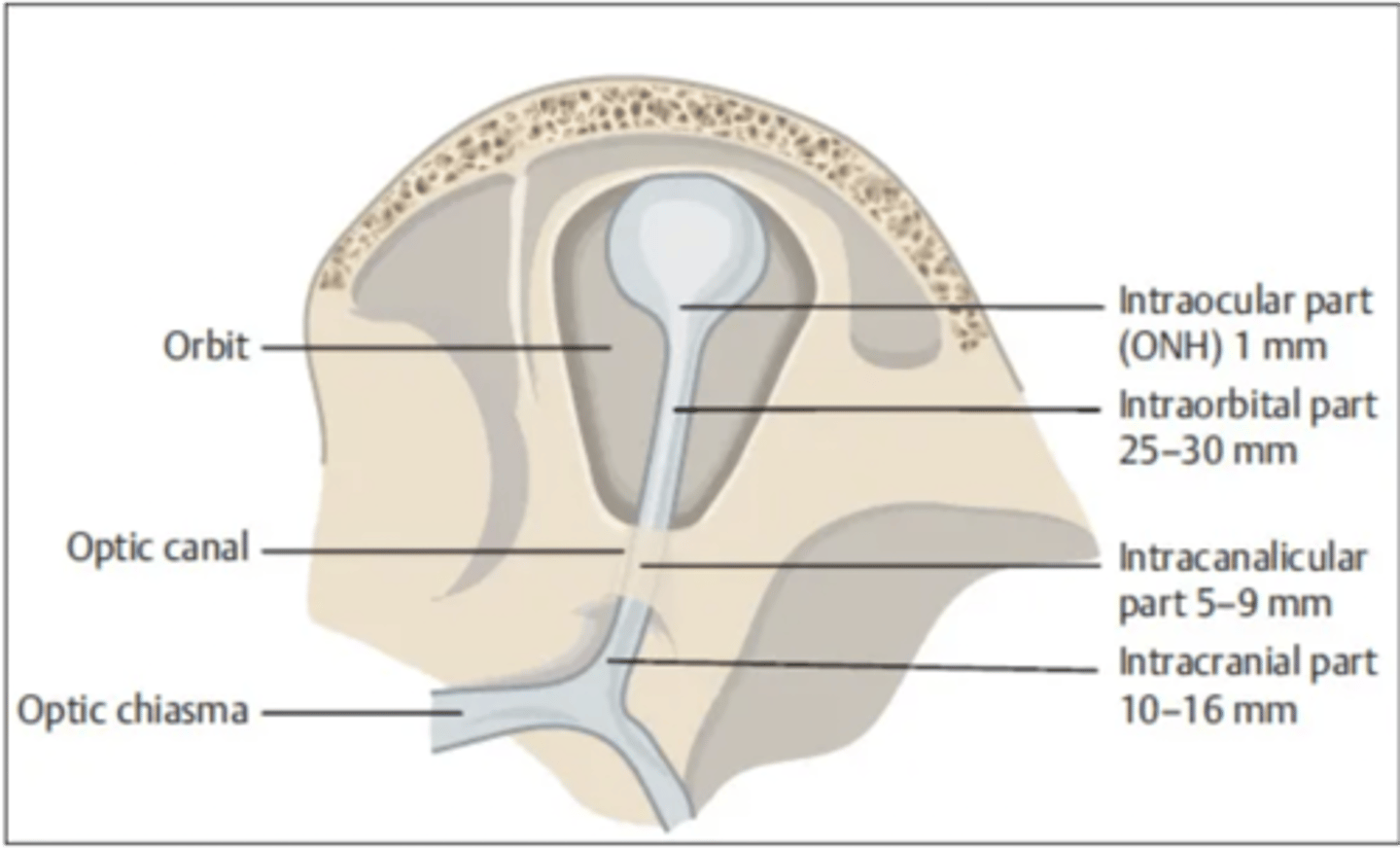
The optic nerve passes through what foramen?
Optic canal
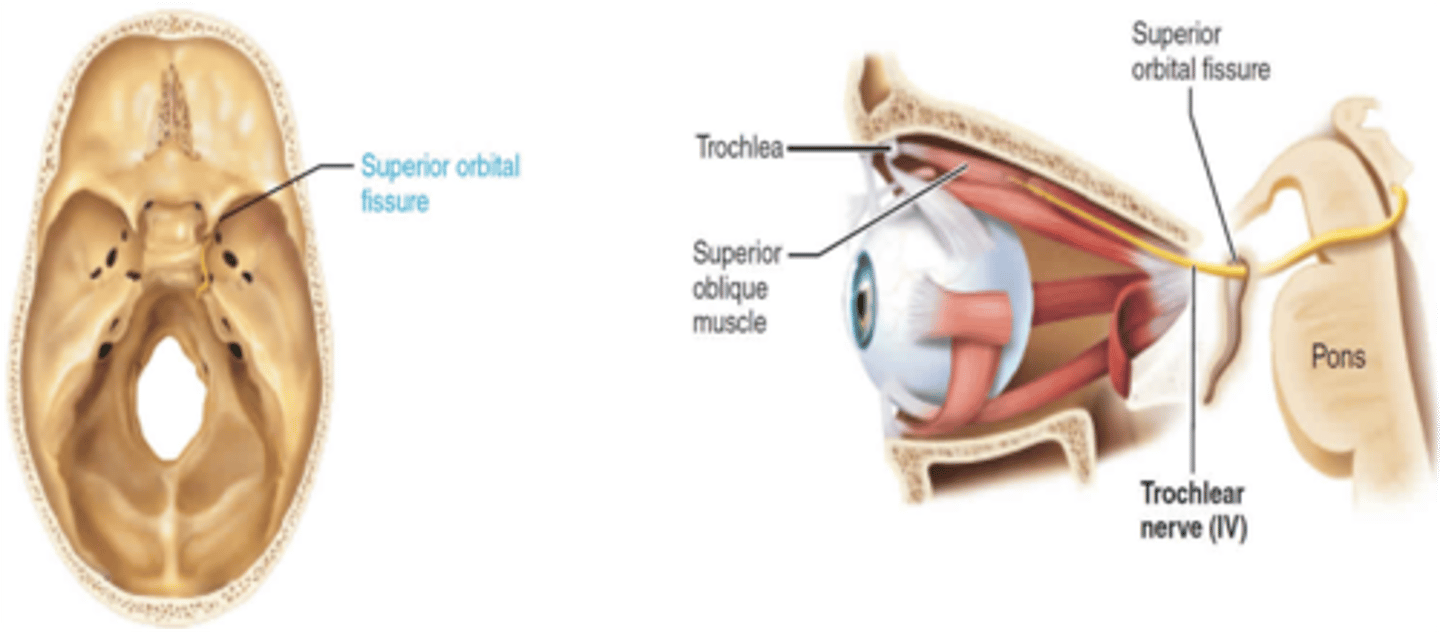
The trochlear nerve passes through what foramen?
Superior Orbital Fissure
Muscles of myotome origin that shrug the shoulder and turn head are innervated by what nerve?
Spinal Accessory Nerve

Bilateral severance of what cranial nerve may result in death?
Cranial Nerve X (Vagus nerve)
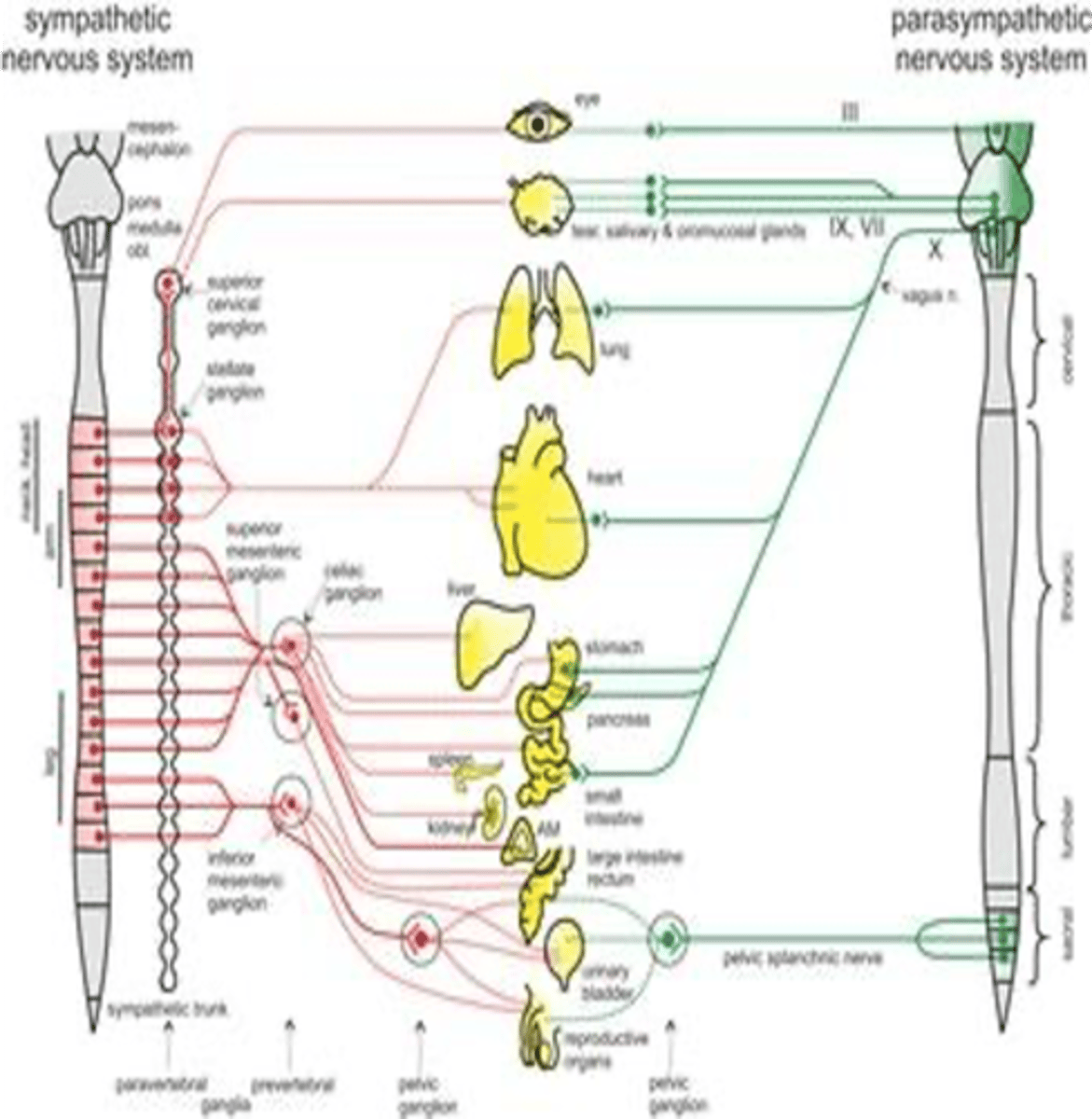
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons are located in what segments of the spinal cord?
Thoracic and lumbar segments
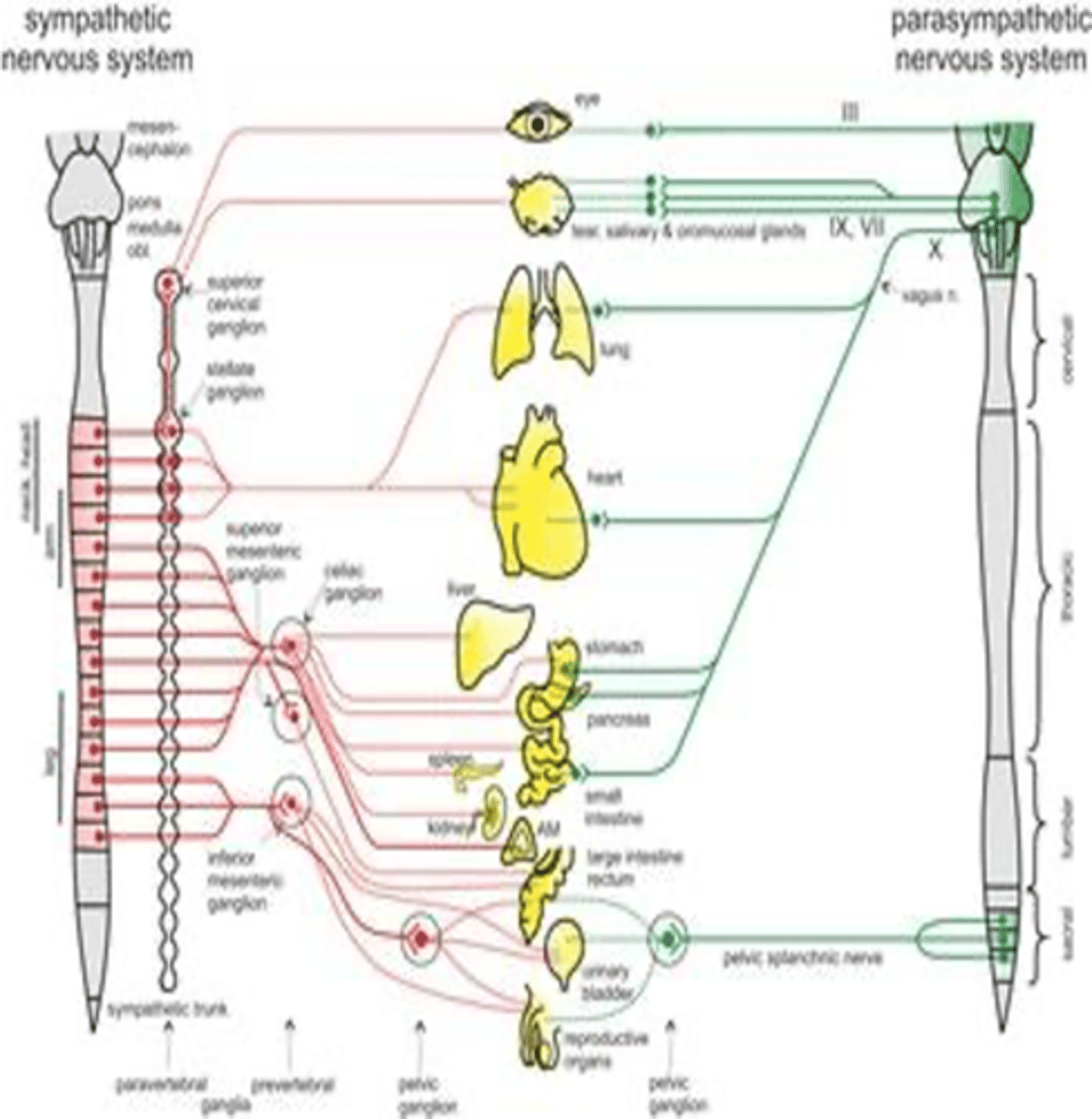
Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are located in what two structures of the central nervous system?
Brainstem
Sacral segment (S2-S4)
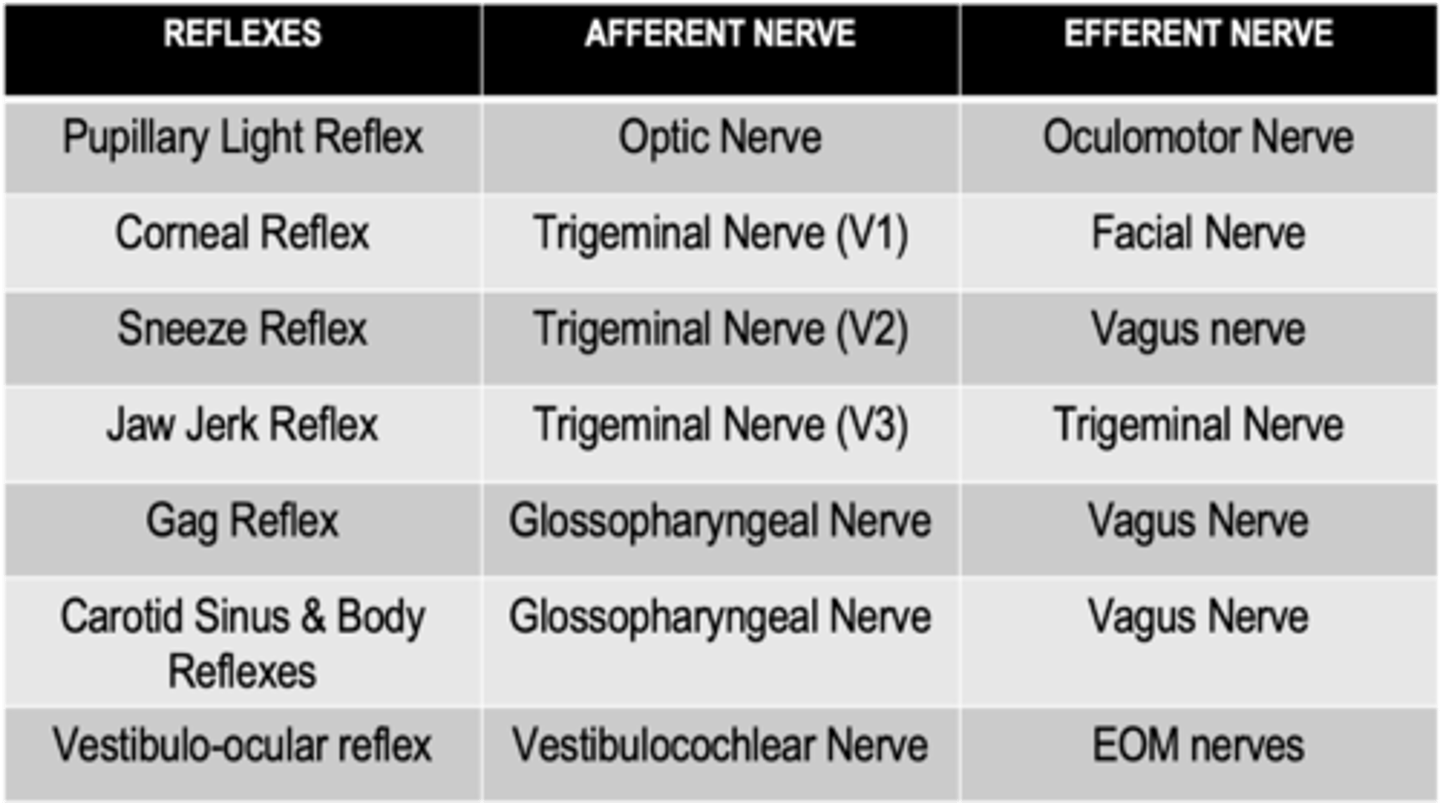
What is the afferent limb of the gag reflex?
Pharyngeal branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve
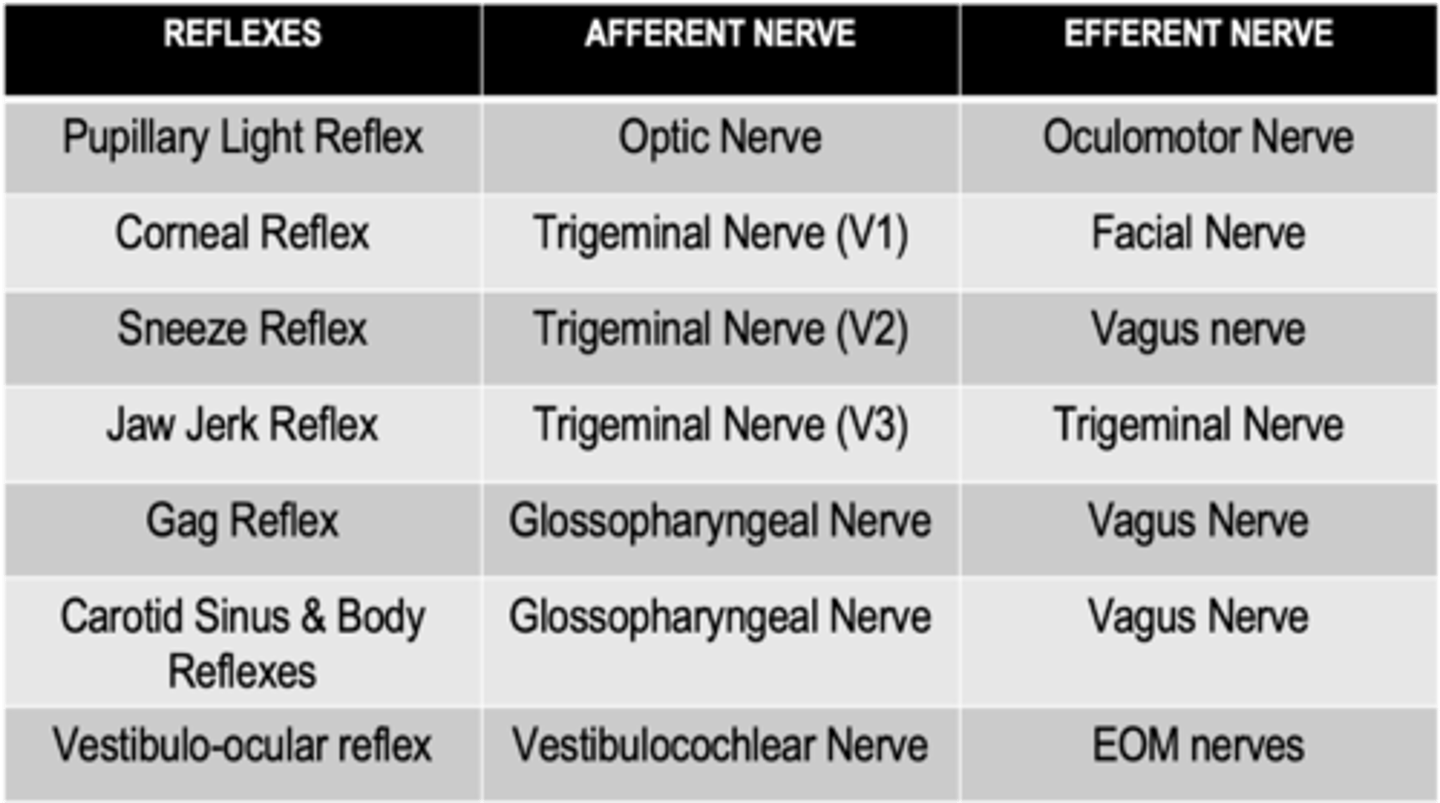
What is the efferent limb of the gag reflex?
Vagus nerve
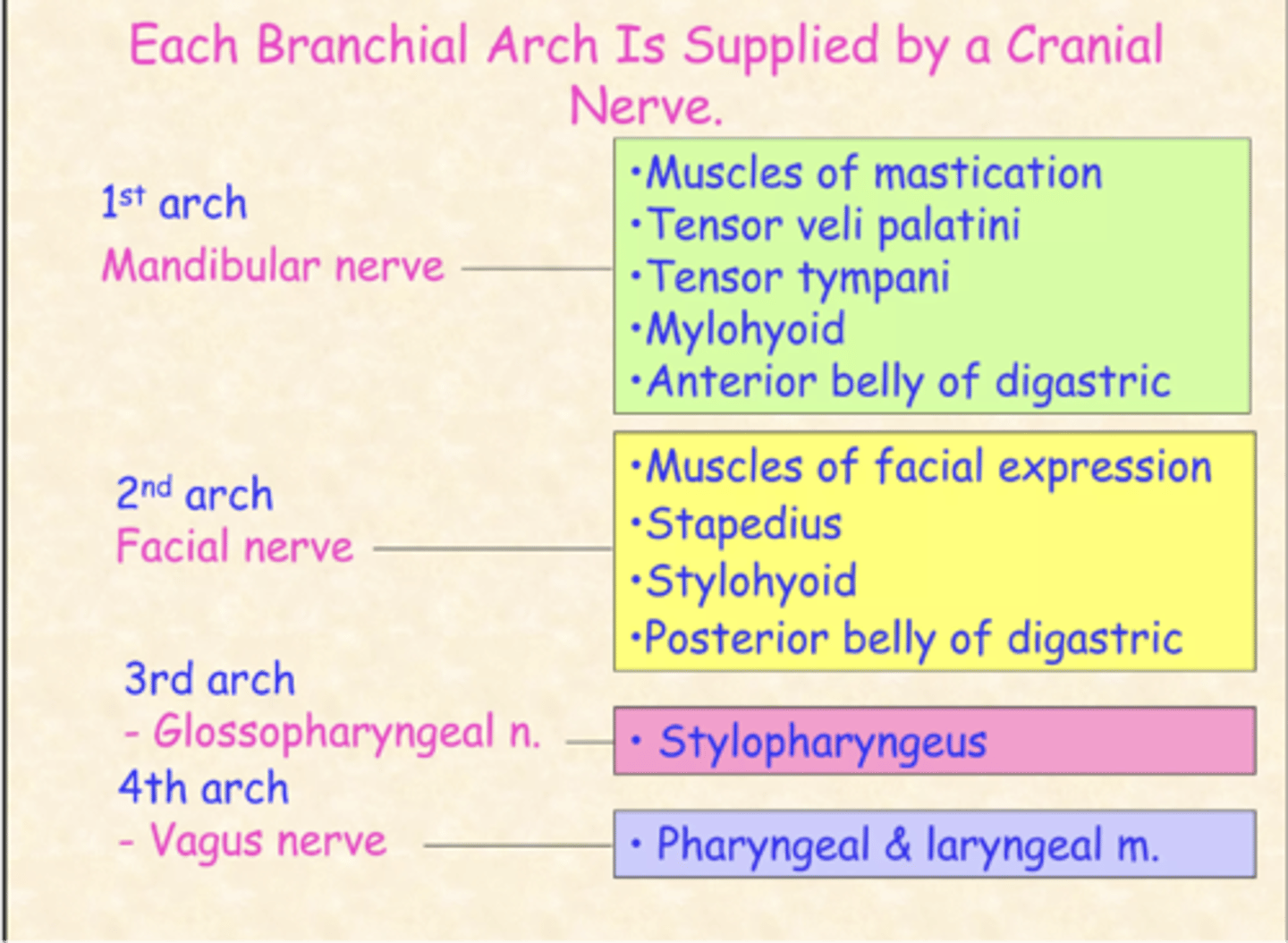
What cranial nerve arises from the first branchial arch?
Trigeminal nerve
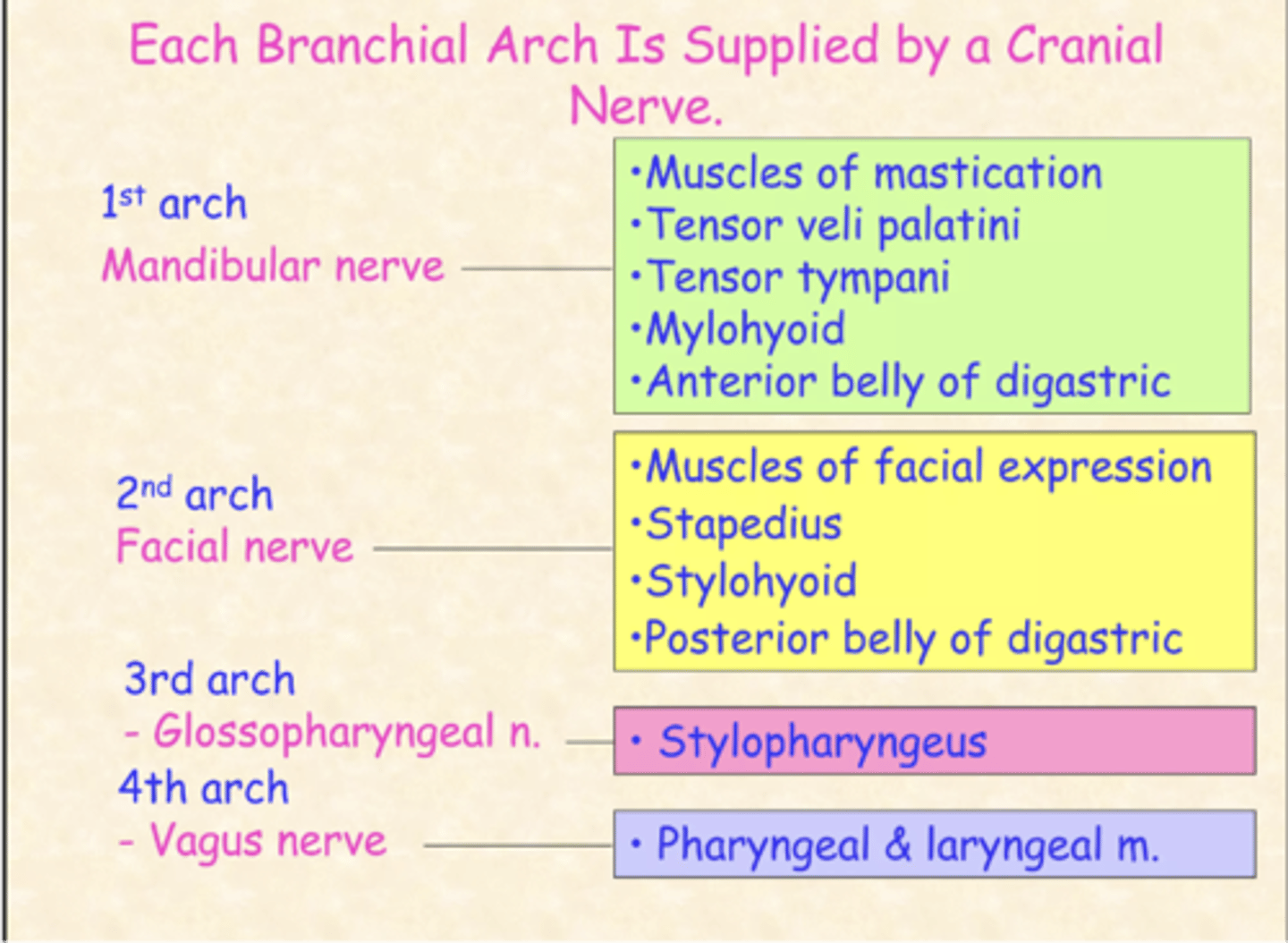
What cranial nerve arises from the second branchial arch?
Facial nerve
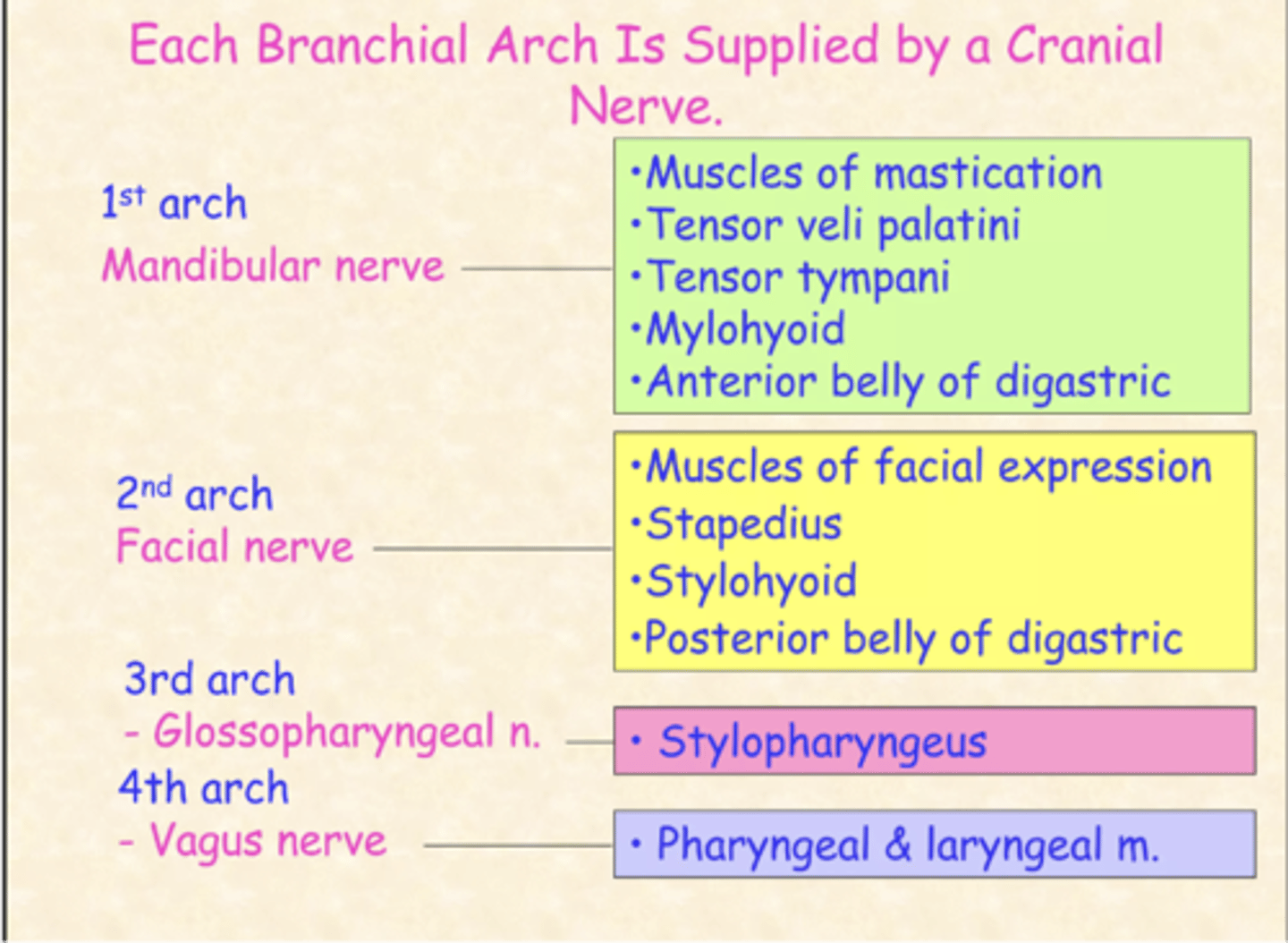
What cranial nerve arises from the third branchial arch?
Glossopharyngeal nerve

What cranial nerve arises from the fourth and sixth branchial arch?
Vagus nerve