TEAS part of speech
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
verb
describes an action or experience
run, walk, push, eat
noun
names a person, place, things, or idea
house, teacher, cup, shop
adjective
describes a noun or pronoun
short, beautiful, red, old
adverb
describes a verb, an adjective, or an adverb. Tells us How often, How , Where, or When
slowly, yesterday, always
adverb
Ex:
Lola is ALWAYS late.
LAST NIGHT, I slept really early.
pronoun
replaces the name of a person, place, thing, or an idea in a sentence
I, she, our, They, It
interjection
express strong emotions and is often followed by exclamation mark
Wow!
Oh!
conjuction
connects words, phrases, or clauses, in a sentence
and, but, although, or
My friend is very loud, WHEREAS, i am very quiet
FANBOYS(acronym)
preposition
describes the place, time, or direction. It is used before a noun or pronoun.
under, above, In, during
The cat jumped OVER the box
Get INTO the car quickly before we are late for school
subject
it tells who what the sentence is about
ANGEL played football
The WATERMELON is green
predicate
it tells what someone or something is or does
Mr Smith lost his dog
A bee buzzed around me
modifier
word or phrase that adds information about another word or phrase
I have a GREY truck
subject complement
a noun that renames the subject
Melissa is a TEACHER
He is HANDSOME
object complement
a noun, adjective, or phrase which adds information about the direct object
They call Melissa GENIUS
They find him intelligent
Most consider her admirable.
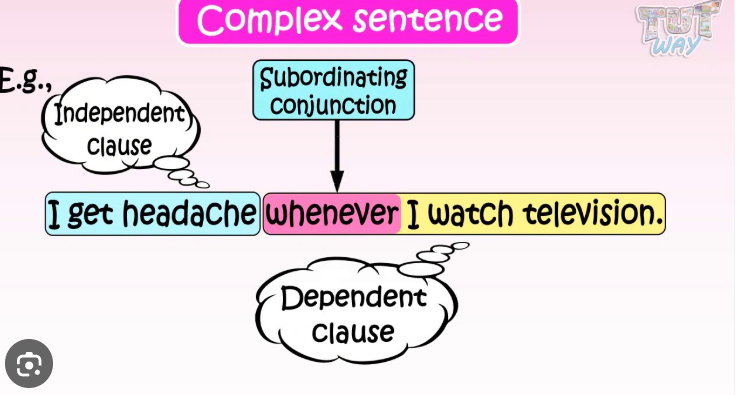
Independent clause
a completed thought
The cat is sleeping.
dependent clause
needs more information and not a complete thought
When the cat is sleeping.
dependent clauses start with a subordinating conjunction….
since
when
if
while
because
who
that
which
as
although
whether
until
unless
in case
even though
simple sentence
one independent clause
one verb
completed thought
Grace opened the door.
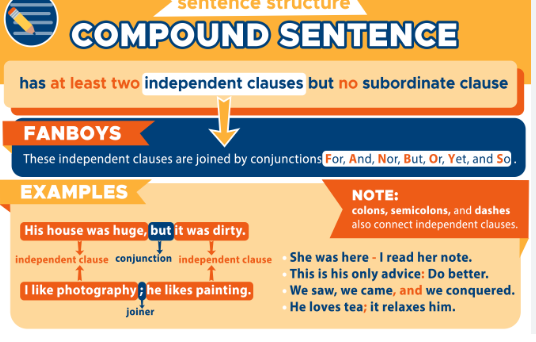
compound sentence

complex sentence


imperative sentence

Transition words

past simple tense
an action that has already happened
I walked to work today.
past perfect tense
an action that was finished before another past action
He had visited China.
past progressive tense
a past action that was ongoing
We were walking home when i got the call.
progressive (memory tip)
was
were
will
verb (-ing)
future simple tense

future perfect tense

future progressive tense

diction

narrative writing



subject pronouns
Perform the action of the verb
Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
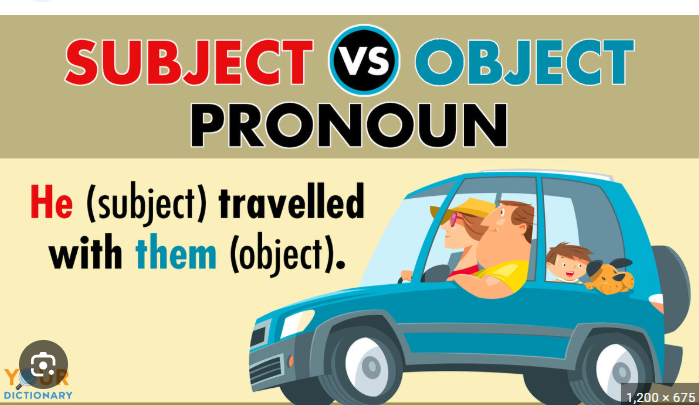
object pronoun
Receive the action of the verb or are the object of a preposition.
Examples: me, you, him, her, it, us, them.
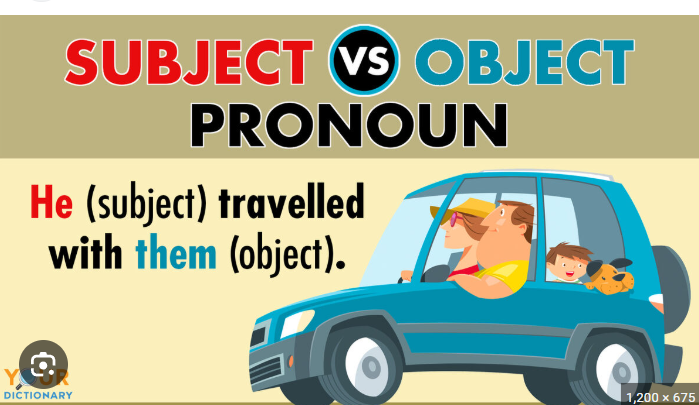
How to Remember: object vs subject!
Find the Verb: First, identify the action in the sentence.
Ask "Who?" or "What?": Ask "Who or what is doing the action?" This will be your subject.
Ask "To Whom?" or "For Whom?": Ask "To whom or for whom is the action being done?" This will be your object.
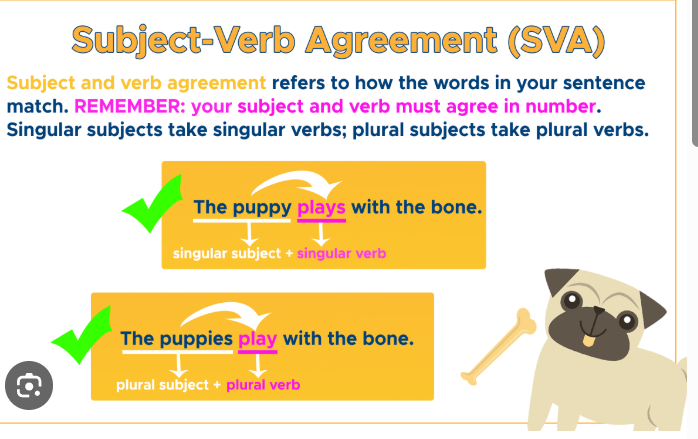
subjective verb agreement
compound sentence
complex sentence