CHEM 1020 final reivew all units
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
How to calculate equilibrium constants using Kf and Kr
Concentration of products / Concentration of reactants
Dont forget about the coefficient
Kf / Kr
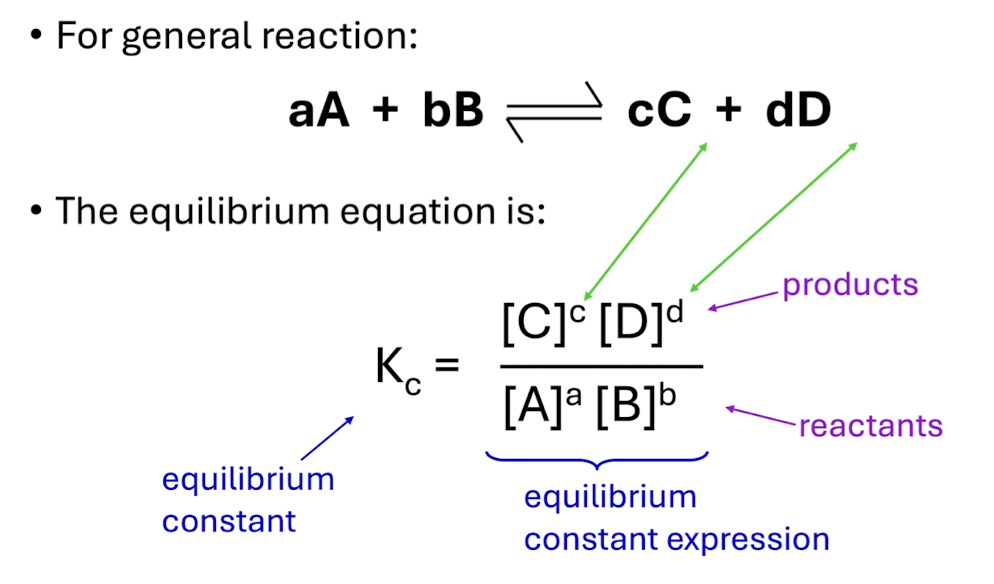
Equilibrium equation (Kc)
Kc
When to use KP and how to calculate it
reactions involving gases and is based on the partial pressures
Same equation as Kc if using partial pressures instead of concentratiosn
Uses diffrent equation if given concentration

What is homogeneous equilibria
Involve reactants and products in the same phase
Heterogeneous equilibria
Involve reactants and products in more than one place
Pure solid and pure liquids in equibrium
Its concentration is not included in the constant expression for the reaction
If Kc > 10³ products predominate over reactants at equilibrium, meaning
the reaction favors the formation of products.
Shifts in the forward direction
If Kc < 10-³ reactants predominate over products at equilibrium, meaning
the reaction favors the formation of reactants. Shifts in the reverse direction.
What does Q indicate
predicts direction of reactant
Equation uses concentrations at non-equilibrium conditions
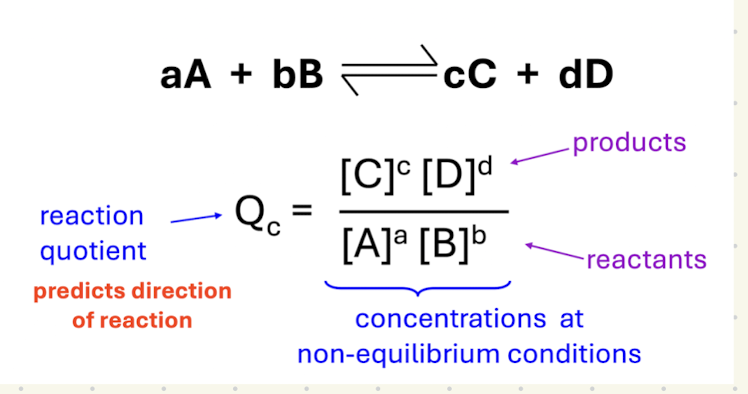
If Q is less than K
Shifts in the foward direction
If Q is greater than K
Shifts in the reverse direction
If Q is equal to K
The system is at equilibrium
3 factors of Le châtelier’s principle
Concentation
Pressure/volume
Temperature
If reactant or product is added than the reaction will shift in
the opposite direction the substance is added in
If reactant is added than it will shift towards the products
If a reactant or product is removed than the reaction will shift in
The direction the substance is removed in
If reactant is removed, it will shift towards the reactants
If volume decreases
If pressure increases
The reaction will favor the side of the reaction with the smaller number of molecules
If volume increases
If pressure decreases
The reaction will favor the side with the large number of molecules
When will volume and pressure have no effect
If the reaction has no change in the number of molecules
In an exothermic reaction heat should be treated as a
product
In a exothermic reaction if the temperature of a system increases
The equation will shift to the left (reverse direction)
In an exothermic reaction if the temperature of a system decreases than the equation will
will shift to the right (forward direction)
What do you treat heat as in an endothermic reaction
as a reactant
What happens if temperature increases in an endothermic reaction
Shifts to the right
What happens if temperature decreases in an endothermic reaction
Shift to the left
What is Go at equilibrium
0
What does a large negative ΔGo mean in relation to K
Large K
mostly products
What does a small negative ΔGo mean in relation to K
Small K,
Mix of products and reactantss at equilibrium
What does a postitive ΔGo mean in relation to K
Small K
The nuclear reaction that takes place in our sun is
fusion
The nuclear reaction which can be used to produce heat for the generation of electricity is
fission
How to find the Kc for the reserve reaction if given the forward Kc
it is the reciprocal of the equilibrium constant for the forward direction
How to calculate ΔGo based of the Gof for reactants and products
Gof PRODUCTS - Gof REACTANTS
Q and ΔG
Largest Q has the largest ΔG
the rate of a reaction with a lower activation energy is ——- than that of a reaction with a higher activation energy because ———
Greater
number of successful effective collisions is higher
What three things is collision theory dependent on
Concentration
Temperature
Orientation
The rate of reaction is primarily related to what
the number of collisions, which is related to concentration
The greater the frequency of collisions the more opportunity for reaction
What is Activation energy
The potential energy barrier that must be surmounted before reactants can be converted to products
2 qualifications for molecules to colldie with eachother
sufficient energy
proper orientation
As actiivation energy decreases what happens to K (rate constant)
Increases (indirect relationship)
As temperature increases what happens to K (rate constant)
Increases (direct realtionship)
How much will the temperature increase by if the reaction rate is doubled
10 degrees Celsius
If the products have a higher final energy than the reactants then the reaction is ,
endothermic
Overall reaction vs elementray steps
Overall: A → D
Elementrey:
A → B
B → C
C → D
What is a reaction intermediate
a substance formed in one elementary step of the mechanism and consumed in another elementary step
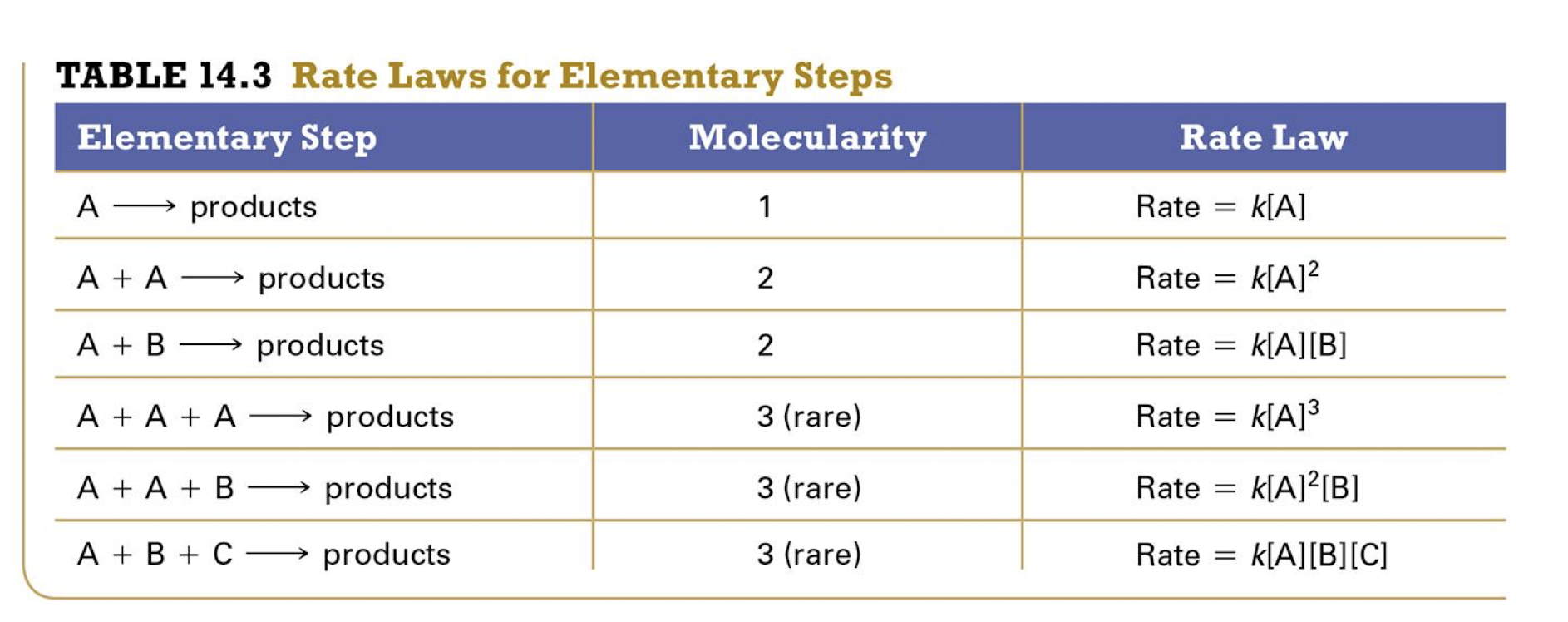
Molecularity
The number of molecules (or atoms) on the reactant side of the chemical equation
Unimolecular elementary reactuion
First order
Has a single reactant molecle
Bimolecular elementary reaction
Second order
Has two reactant molecules
Know how to form an overall reaction from elementary steps
Cross out any intermediate products
Find the final reactants and products
Put them together
Termolecular
Third order
Not as common
three reactant molecules
How to determine rate law for overall reaction
Must be determind expiermentally
How to determine rate law for elementary steps
From its molecularity
The experimentally observeved rate law for an overall reaction is dependent on waht
the reaction mechanism, which is the sequence of elementary steps
What is the RDS
Rate determining step
It is the slowest elementary step in a multistep reaction
The rate of the overall reaction is determined by the rate of this step
IMPORTANT NOTE about writing rate law for the overall reaction
an intermediate cannot be part of the reaction rate
What is a catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy
How to identify a catalyst in a reaction
Not consumed in reaction
Not in final products
Homogeneous catalyst
The catalyst exists in the same phase as the reactants
Heterogenous catalyst
The catalyst and reactants are in diffrent phases
Know how how calculate rate by looking at pictures
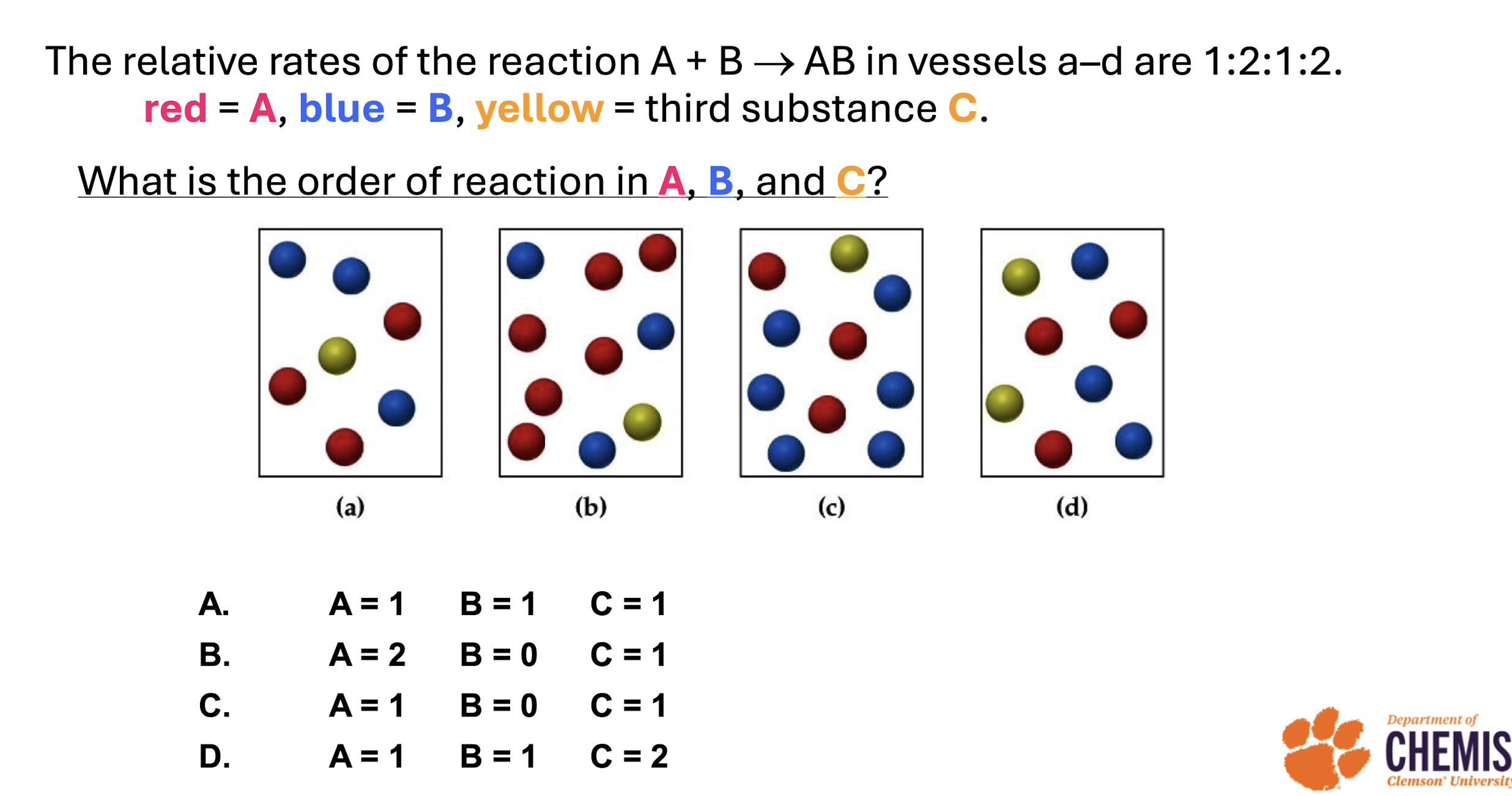
which reaction requires the most energetic collisions to reach the transition state
The one with the highest activation energy
rate constant in comparison to activation energy
lowest AE has the highest rate constant
Highest AE has the lowest rate constant
activation energy and rate limiting
The reaction with the highest activation energy is considered to be rate limiting
What number is at the top of an isotope (A)
The mass number
Protons + neutrons
What number is at the bottom of an isotope
Atomic number
Alpha particles
42H
Beta particles
Released in the products
0-1 e
One proton gets added to the element (changing the element)
Gamma radiation
Accompanies in alpha and beta emission
00Y
Positrons
01e
occurs when a proton is converted into a neutron and a positron
Electron capture
In the reactants
-10e
Ionizing power
the ability of radiation to ionize molecules and atoms
penetrating power
the ability of radiation to penetrate matter
alpha particls ionizing and penetrating power
Highest ionizing power
Lowest pentrating power
Beta partcles ionzing and penetrtating power
Middle of both
gamma rays ionzing and penetrating power
Lowest ionizing power
Highest penetrating power
Important half life equation to remeber
In( Nt / N0) = -kt
What is an important measure for determining the stability fo the nucleus
Neutrons to protons ratio
(N/Z)
What happens if the N/Z ratio is too high
Neutrons are converted to protons via beta decay
What happens if the N/Z ratio is too low
Protons are converted to neutrons via positron emission or electron capture
or via alpha decay though not as efficiently
Possible trick for N/Z ratios
If isotope mass is lower than it is positron emission
If isotope mass is higher than it is beta emission
What is nuclear fission
the fragmentation of heavy nuclei to form lighter, more stable ones
What is nuclear fusion
The formation of heavier nuclei by the joining of lighter ones
What is nuclear transmutation
The change of one element into another
What equation should you use to calculate energy changes during nuclear reactions
E = mc²
How to find m in E = mc²
m = mreactants - mproducts
Bronsted Lowry Acid/Base
Acid: Proton donor
Base: Proton acceptor
Lewis Acid/Base
base: donate pairs of electrons
Acids: accept pairs of electrons
what does HA stand for
HA is undissociated acid
% ionization and Ka relation
Higher Ka value acids lead to higher % ionization
concentrations and percent ionization relation
Lower concentrations have higher % ionizations
Acids and the periodic table groups
Acid strength increases down a specific group
If the pH @ equivalence is higher than 7
weak acid + strong base
Which way do electrons flow
Electrons flow from anode to cathode
If an element is doing the reducing it is being —-
oxidized
How to get rid of log
10^ans
How to get rid of ln
e^ans
Dead battery Ecell and Q
Ecell = 0
Q = K
Voltanic Cell, Ecell, G and K
Ecell > 0
G < 0
K > 0
Standard reduction potentials and oxidizing/reducing agents
More positive = Strong oxidizing agent
More negative = Strong reducing agent
Formula for Pka
Pka = -log(ka)
Strong base + Strong acid @ equivalence point
7