psychodynamic and humanistic theories of personality
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Psychodynamic Theory
Consists of Conscious, Preconscious, and Unconscious mind
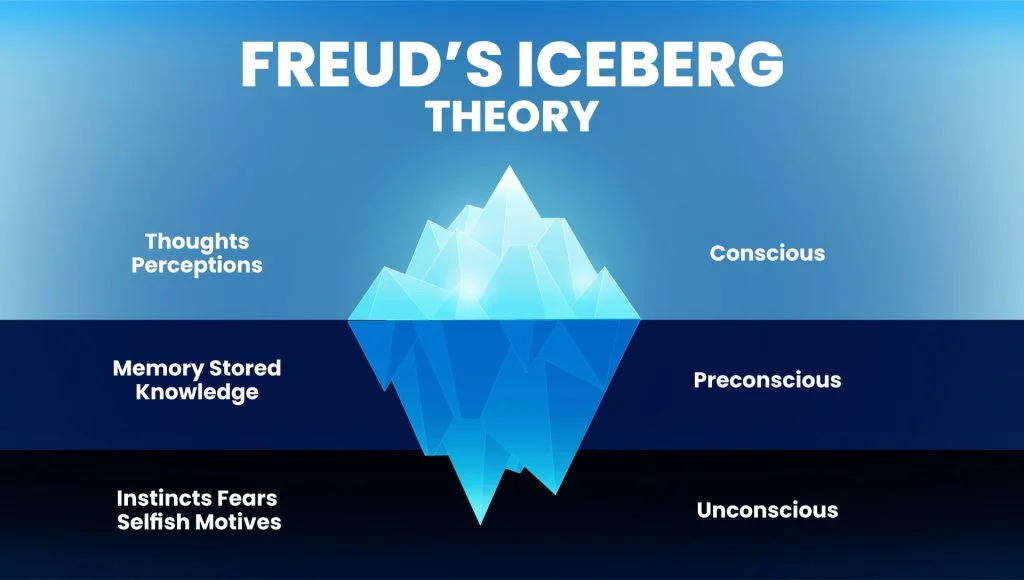
Conscious
This is the part of the mind we are aware of. It's everything we are currently thinking, feeling, or perceiving.
Exp: If you're aware that you're feeling anxious about an upcoming event, that anxiety is part of your conscious experience.
Preconscious
Thoughts and memories that are not currently in our awareness but can easily be brought into consciousness with focus or effort. It's a sort of "waiting room" for thoughts
Exp: If you’re asked to recall your childhood friend's name, you might not be thinking about them right now, but with a little thought, you can bring the name into consciousness.
Unconscious
holds thoughts, feelings, memories, and desires that are not accessible to the conscious mind. These are typically repressed or hidden because they may be too uncomfortable or anxiety-provoking.
Exp: A person might have a phobia of dogs without consciously knowing the source of that fear. The unconscious might hold a traumatic childhood experience involving a dog that was repressed.
The psyche
The entirety of a person’s mind, encompassing both conscious and unconscious aspect.
Includes id, ego, and superego
id
-The most primal part of the psyche, driven by instinctual desires and unconscious impulses.
-It operates on pleasure
ego
The mediator part of the psyche between the id and the external world
The ego helps us make decisions that are practical , realistic, and socially acceptable.
concious
super ego
The moral component of the psyche, representing internalized societal rules, values, and ethics.
Repression
Unconscious mechanism by which the mind prevents certain thoughts, memories, or feelings from entering conscious awareness.
Exp. not remembering child abuse/ traumatic events
Regression
a defense mechanism where an individual reverts to an earlier stage of development in response to stress or anxiety. a person may unconsciously adopt behaviors or attitudes from a younger, more childlike stage of development.
Exp: thumb sucking, bed wetting, tantrums
Projection
is a defense mechanism where an individual attributes their own undesirable feelings, thoughts, or behaviors onto someone else. Instead of recognizing these traits in themselves, they project them onto others as a way to avoid facing their own flaws or emotions.
Exp: a person who has feelings of jealousy may project those feelings by accusing others of being jealous.
Displacement
A defense mechanism where someone transfers their emotions (usually anger or frustration) from the original source of those feelings to a less threatening target
Exp: if someone has a difficult day at work and is angry at their boss, they might go home and take out their frustration by yelling at a family member
Reaction Formation:
defense mechanism in which a person unconsciously behaves in a way that is opposite to their true feelings or impulses, often because those feelings are considered unacceptable or anxiety-provoking.
Exp: Insecure men acting like they are all that
Having hate for someone but acting friendly to their face
Rationalization
a defense mechanism in which a person justifies or explains their behavior, thoughts, or feelings in a way that makes them seem more acceptable, logical, or reasonable, even if the true reasons are less favorable or more uncomfortable. This helps protect the individual from feelings of guilt, shame, or anxiety.
Exp; gaslighting youself
someone who fails an exam might rationalize the failure by saying, the test was unfair, or i didn't really want to pass anyway.
Denial
defense mechanism where an individual refuses to accept or acknowledge a reality or fact, especially when it is uncomfortable or threatening.
exp: Someone dealing with substance abuse might deny they have an addiction
Sublimation
a defense mechanism where an individual transforms socially unacceptable impulses or desires into socially acceptable or constructive activities. Instead of expressing negative or harmful urges directly, the person channels those feelings into productive or creative outlets
Exp: Someone more aggressive might put that aggression into a sport like boxing or sm might stay busy in order to overcome loneliness
Psychodyamic personality psychologist
Psychologist who study how unconscious drives early childhood experiences, and internal conflicts shape a person’s behavior and personality. They focus on influence of past experience.
Projective tests
A personality assessment that asks people to interpret ambiguous images or situations
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Test involving presenting a subject with images of inkblots. The person then describes what they see in these bolts.
Thematic Apperception Test
Test where people are shown pictures and asked to make up stories about them. Used to explore a person’s thoughts, feelings, and motives.
Humanistic Theory
perspective that emphasizes the inherent goodness of people. Focuses on individual experience, personal growth, and fulfillment of potential.
Unconditional positive regard
Showing complete support and acceptance of a person no matterr wht that person says or does.
Self actualizing tendency
Concept regarding the inherent drive or motivation within every individual to realize their full potential and achieve personal growth and fulfillment.
Ideal self
Who I want to be
real self
who I actually am
Social cognitive theory
Theory emphasizing the dynamic interaction between people, their behavior, and their environments
Reciprocal determinism
Theory that a person’s behavior is influenced by and simultaneously influences both their personal factors (thoughts and beliefs) and their environments
Self concept
Perception that we have of ourselves
Self-efficacy
An individual’s beliefs in his or her capacity to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific skills
Self esteem
How we value and perceive ourselves based on opinion and belief
Trait theory
a psychological approach that focuses on identifying and measuring individual personality characteristics, or traits. Traits are stable characteristics or patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion that define how a person typically behaves across different situations and over time. Trait theory suggests that personality can be understood by examining the various traits that make up a person's overall personality.
big five theory of personality
A personality model that describes personalities using 5 broad traits (openness to experience, conscientiousness,extraversion, agreeableness, and emotional stability)
Openness to experience
Personality trait describes how open-minded, creative, and curious a person is
Conscientiousness
an individual’s tendency to be organized, responsible, reliable, and goal-oriented.
Extraversion
an individual's tendency to seek out social interaction, stimulation, and excitement. People high in extraversion are typically outgoing, energetic, and enthusiastic. They are often described as sociable, talkative, and action-oriented.
agreeableness
an individual’s tendency to be compassionate, cooperative, and empathetic towards others. People high in agreeableness are generally kind, friendly, and considerate, often prioritizing harmony in their relationships and avoiding conflict.
Emotional stability
a person’s ability to remain calm, resilient, and balanced, even in stressful or challenging situations. Experience little fluctuation in emotions
Objective tests
standardized assessments used to measure various aspects of a person's personality, intelligence, or mental health. These tests are designed to provide clear, consistent, and quantifiable results, making them useful for diagnosing psychological conditions, assessing traits, or predicting behaviors.
Personality inventories
A self assessment method, standardized questionaire
Factor analysis
a statistical method used to simplify complex data by finding groups of related variables. It helps identify patterns or trends by combining similar items into fewer, more meaningful factors.