Day 7 - Biosynthesis of Teeth and Caries
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is saliva?
a complex of fluid produced by a number of specialized glands that discharge into the oral cavity

How much saliva is produced daily?
500-1500 mL

What percent saliva does each gland produce?
- submandibular: 65%
- parotid - 20%
- sublingual: 5%
- remaining 10% from labial, buccal, and palatal glands

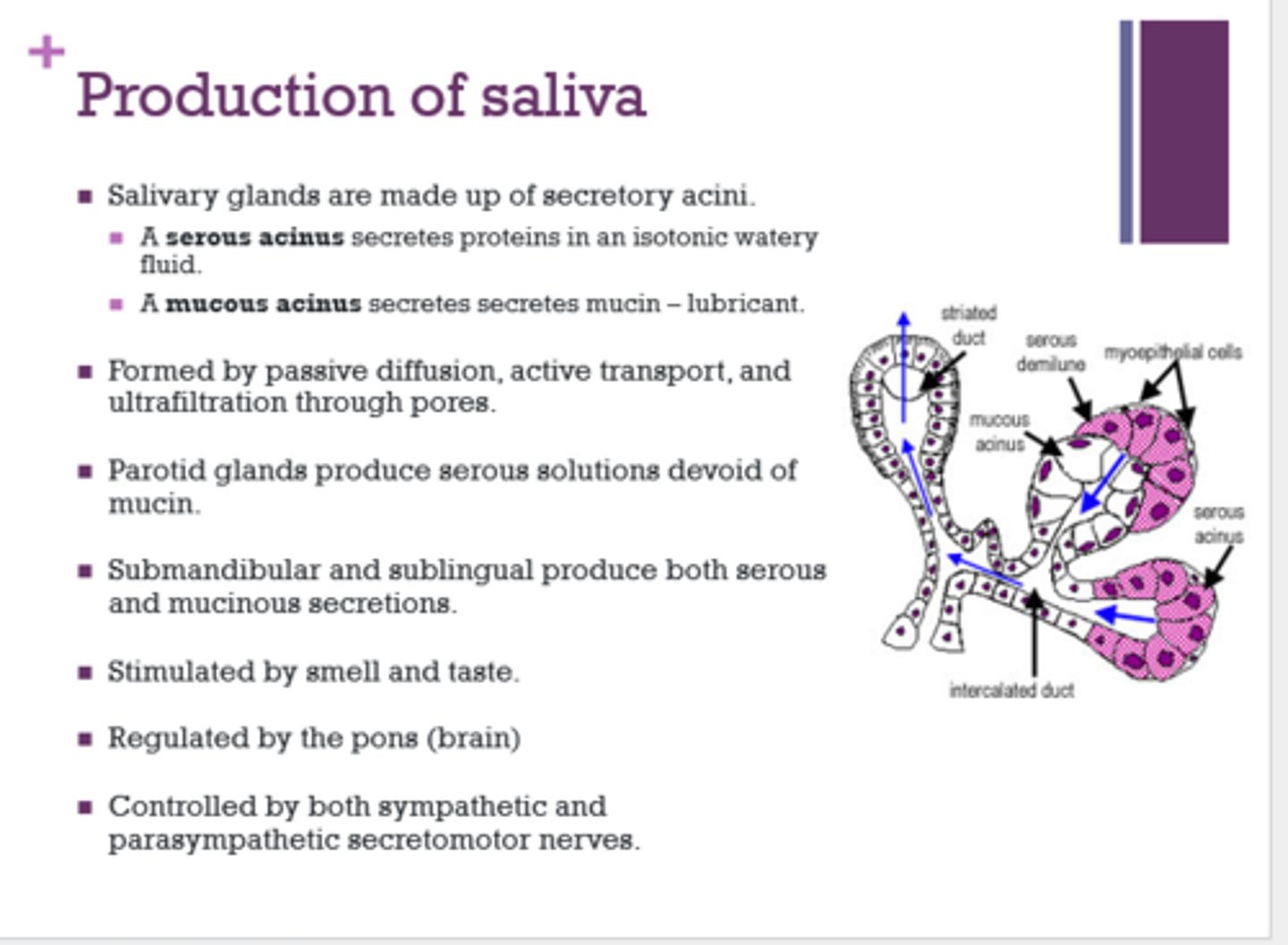
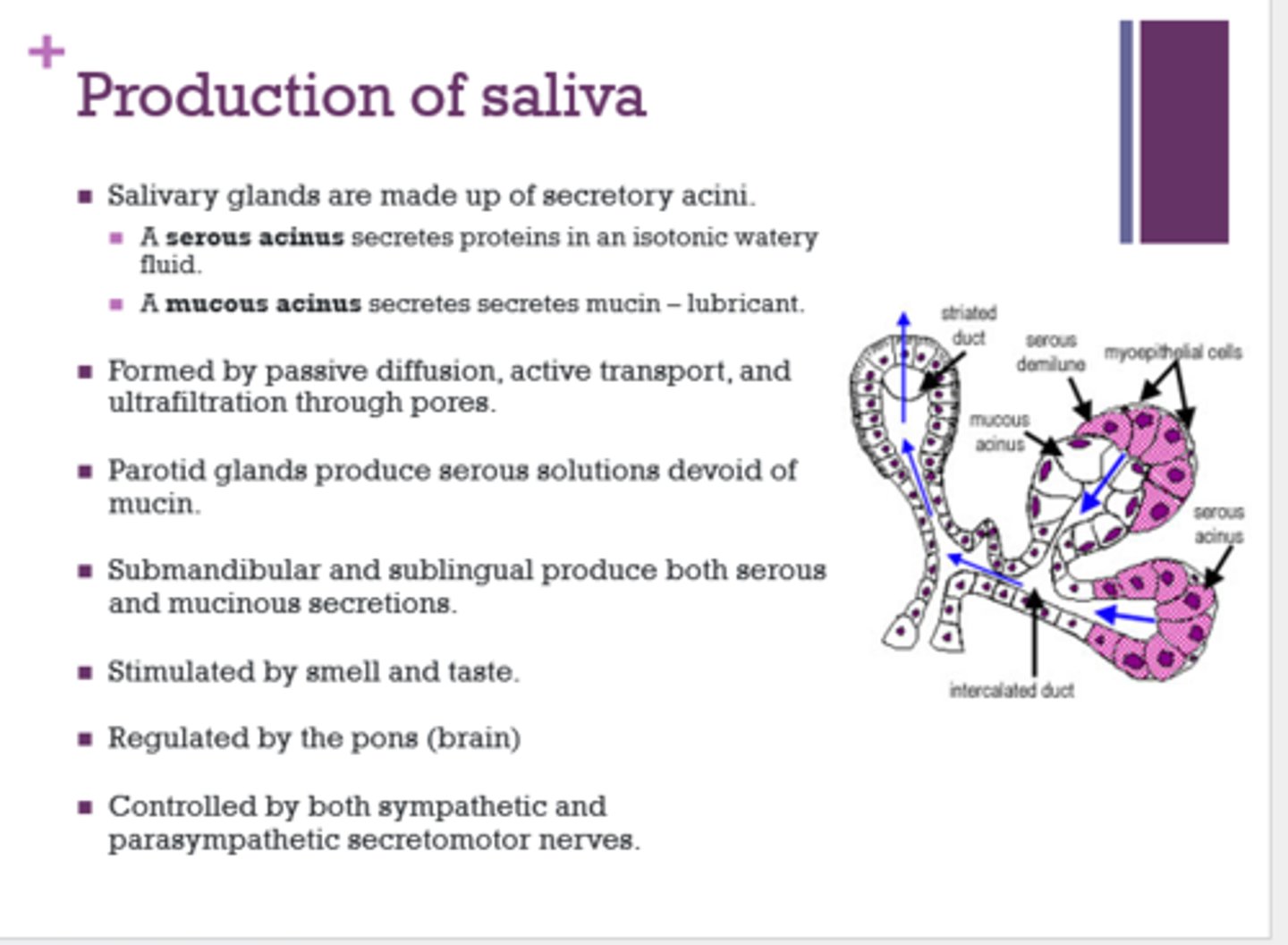
What gland produces serous solutions devoid of mucin?
parotid
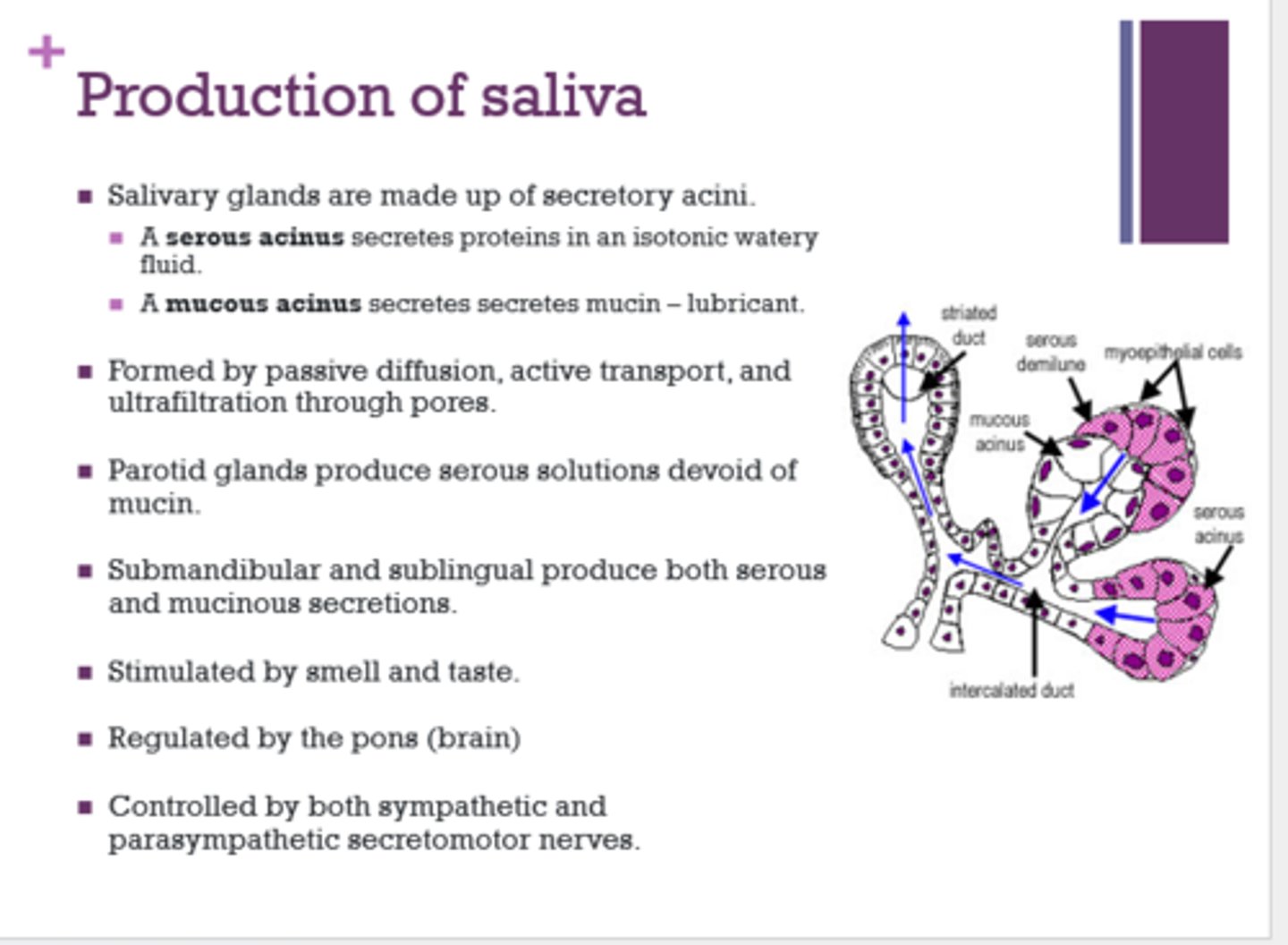
Which glands produce both serous and mucinous solutions?
submandibular and sublingual
What regulates the production of saliva?
pons
What are the functions of saliva?
- antibacterial
- buffering
- digestion
- mineralization
- lubrication

What are the principal inorganic components of saliva?
Na, K, Cl, HCO3

What is the pH of saliva?
6.2-7.6

What proteins are found in saliva?
mucin, statherins, histatins, lysozyme, proline-rich proteins (PRPs), carbonic anhydrase, lingual lipase, amylase, peroxidase, lactoferrin, IgA

What is the major carbohydrate in saliva?
glucose (10-20 mg/dL)

What mucins are found in saliva? What do they do?
- MG1 and MG2
- contain negatively-charged groups like sialic acid and sulfate making them hydrophilic and the contribute to elasticity and viscosity

What has a primary role in formation of the acquired pellicle?
mucins

What is salivary amylase secreted by?
parotid glands

What is the optimum pH of amylase?
6

What does salivary amylase do?
claves a-1,4-glycosidic bonds producing maltose and monosaccharides

What does lingual lipase act on?
triglycerides

What does carbonic anhydrase do?
buffering action of saliva

What do peroxidases do?
bactericidal

What do lysozymes do?
break down peptidoglycan (bacterial cell walls)

IgA
- active against cariogenic bacteria
- low in people with dental caries

Lactoferrin
- chelates Fe and inhibits bacterial growth

Statherins
- maintain supersaturated calcium phosphate in ductal saliva from crystallizing; this reduces the formation of dental calculus

Proline-rich protein (PRP_
- 40% + proline
- secreted by parotid glands
- reduce precipitation of calcium phosphate, slows loss of Ca and P
- aids in formation of enamel pellicle

What does Sialadenitis do to saliva?
increase Na and Cl, decrease P

What does Sjogren's Syndrome do to saliva?
CT disease with dry eyes and dry mouth

What does radiation to the oral cavity do to saliva?
decrease salivary flow, increase NaCl, Ca, MG

at are periodontal disease biomarkers?

What do Cystic fibrosis, Addison's disease, Cushing's syndrome, hyperparathyroidism, and other immunological disorders do so saliva?
affect flow rate and composition

What are periodontal disease biomarkers?
Immunoglobulins, salivary esterase, lysozyme, peroxidase, chitinase, acid phosphatase, arginase, Mucins, lactoferrin, histatin, fibronectin, cortisol, volatile sulfur compounds

What AA are present in collagen?
30% glycine, 30% proline and lysine

What is the main inorganic component of teeth?
apatite

What is the main organic component of teeth?
collagen

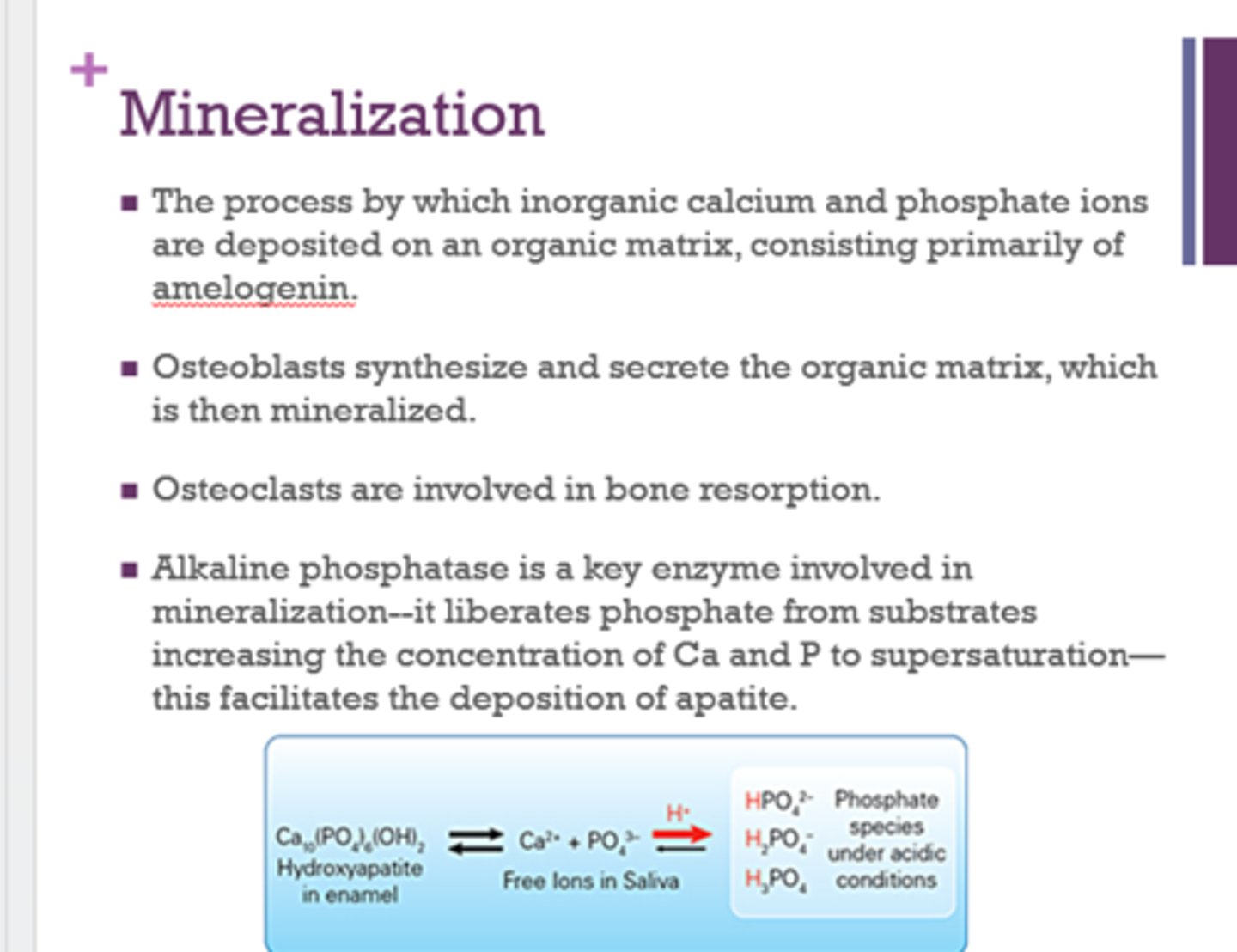
What is mineralization?
the process by which inorganic calcium and phosphate ions are deposited on an organic matrix, consisting primarily of amelogenin
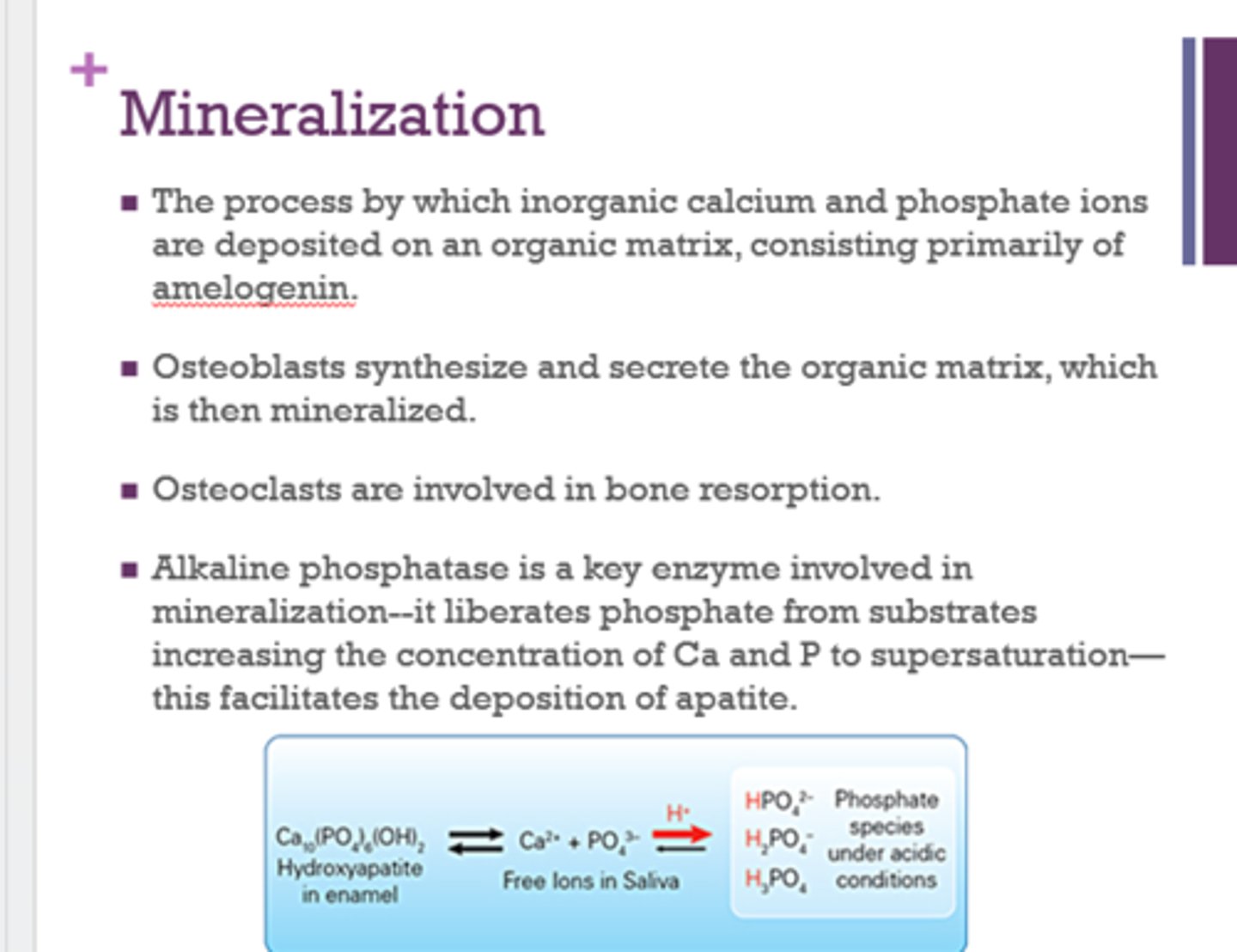
What is a key enzyme involved in mineralization?
alkaline phosphatase
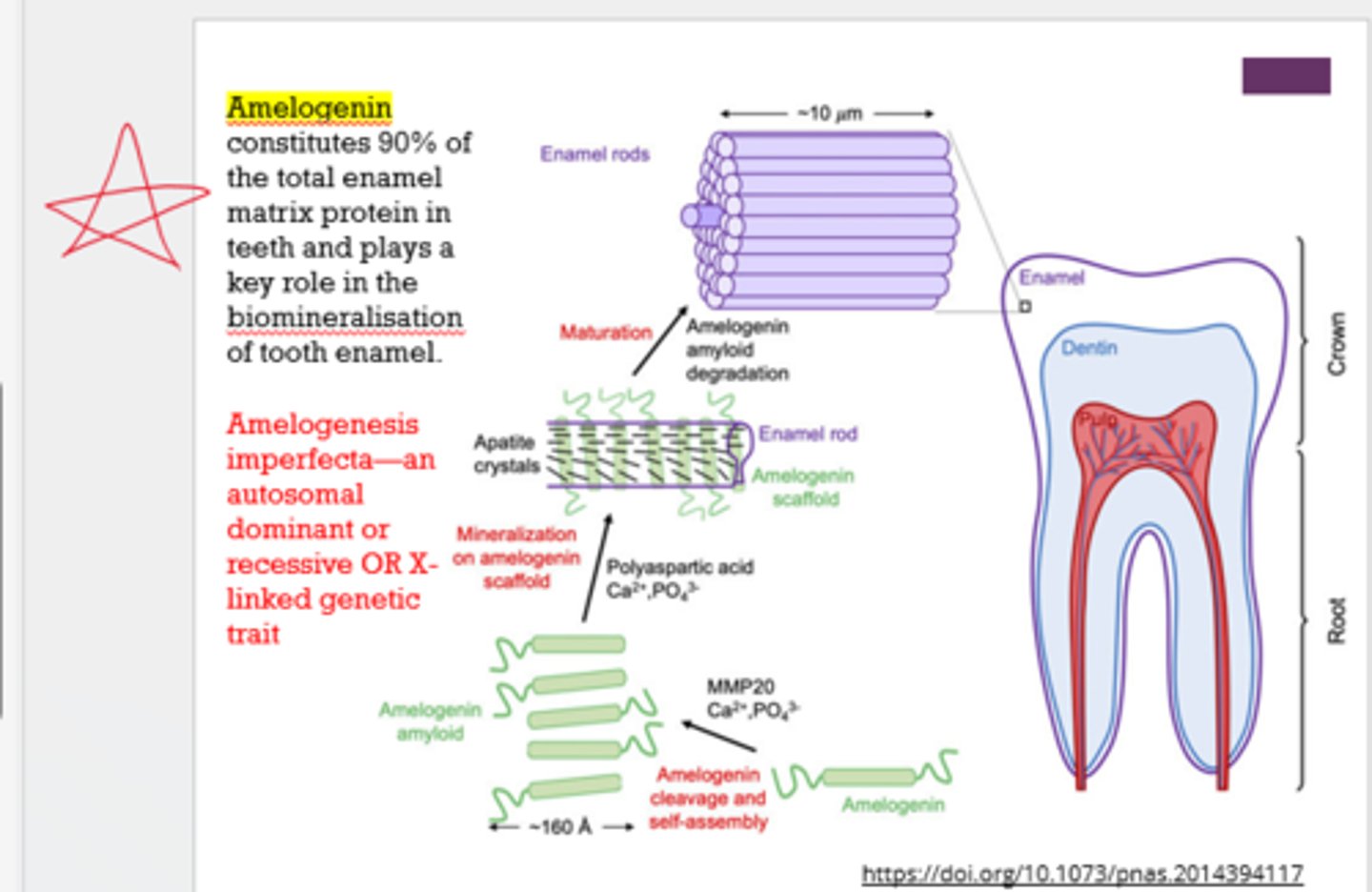
What is amelogenin?
protein that forms the matrix upon which enamel is mineralized
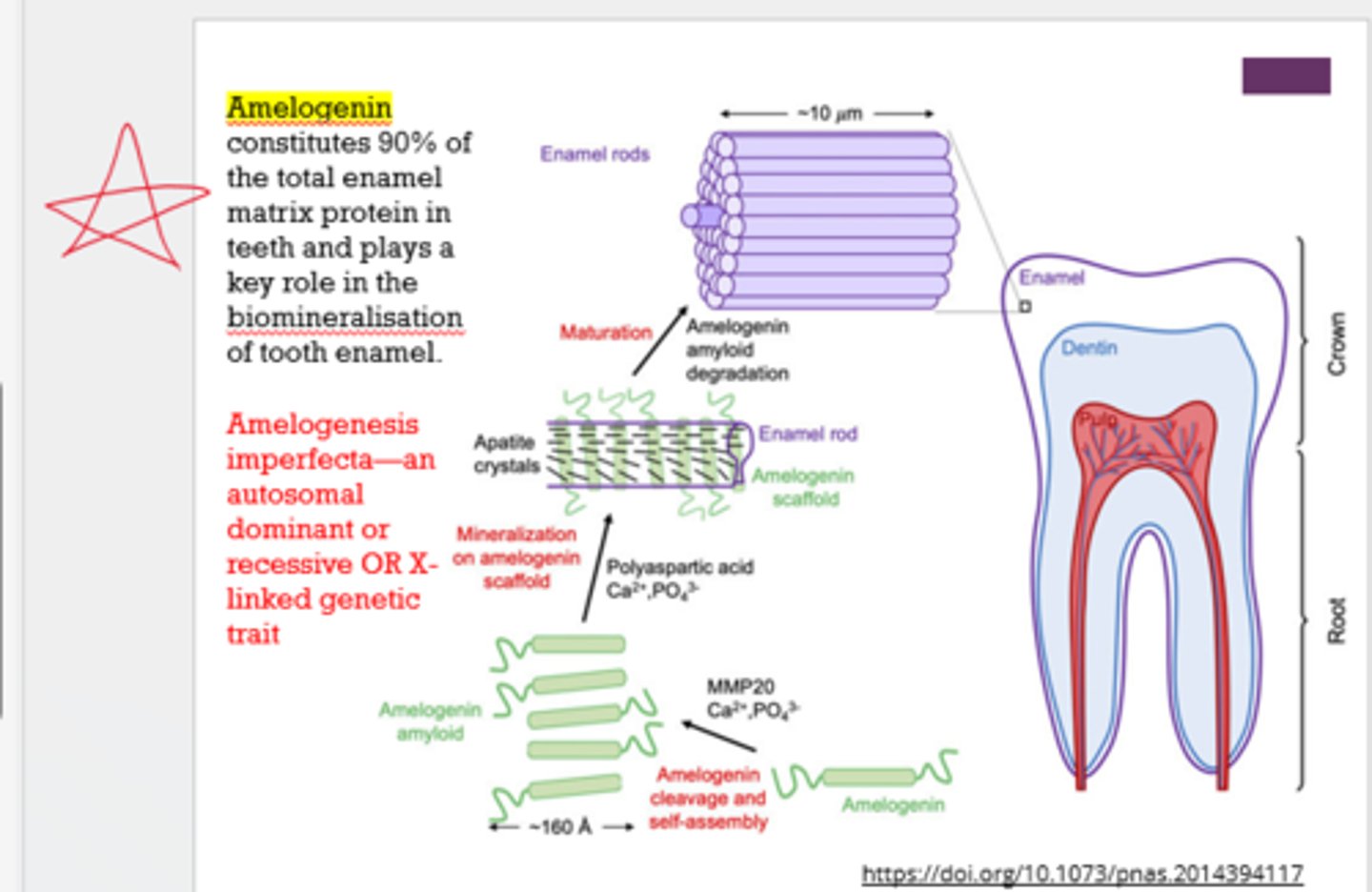
What is amelogenesis imperfecta?
defective enamel formation due to autosomal dominant or recessive OR X-linked genetic trait
How do dental caries arise from the actions of microorganisms?
Bacteria on teeth metabolize foods producing acids that destroy tooth enamel and lead to tooth decay
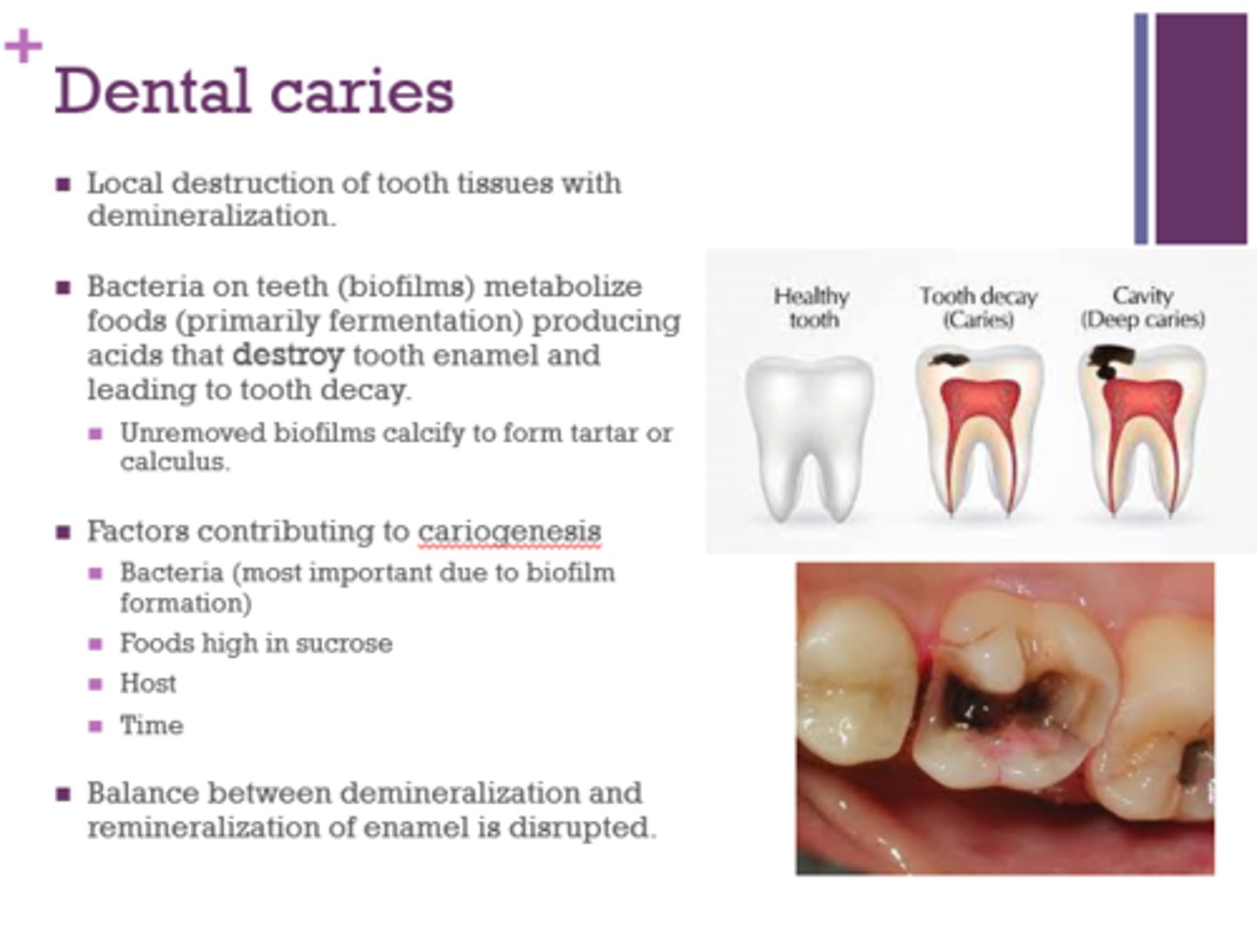
What are the factors that contribute to cariogenesis?
- bacteria
- foods high in sucrose
- host
- time
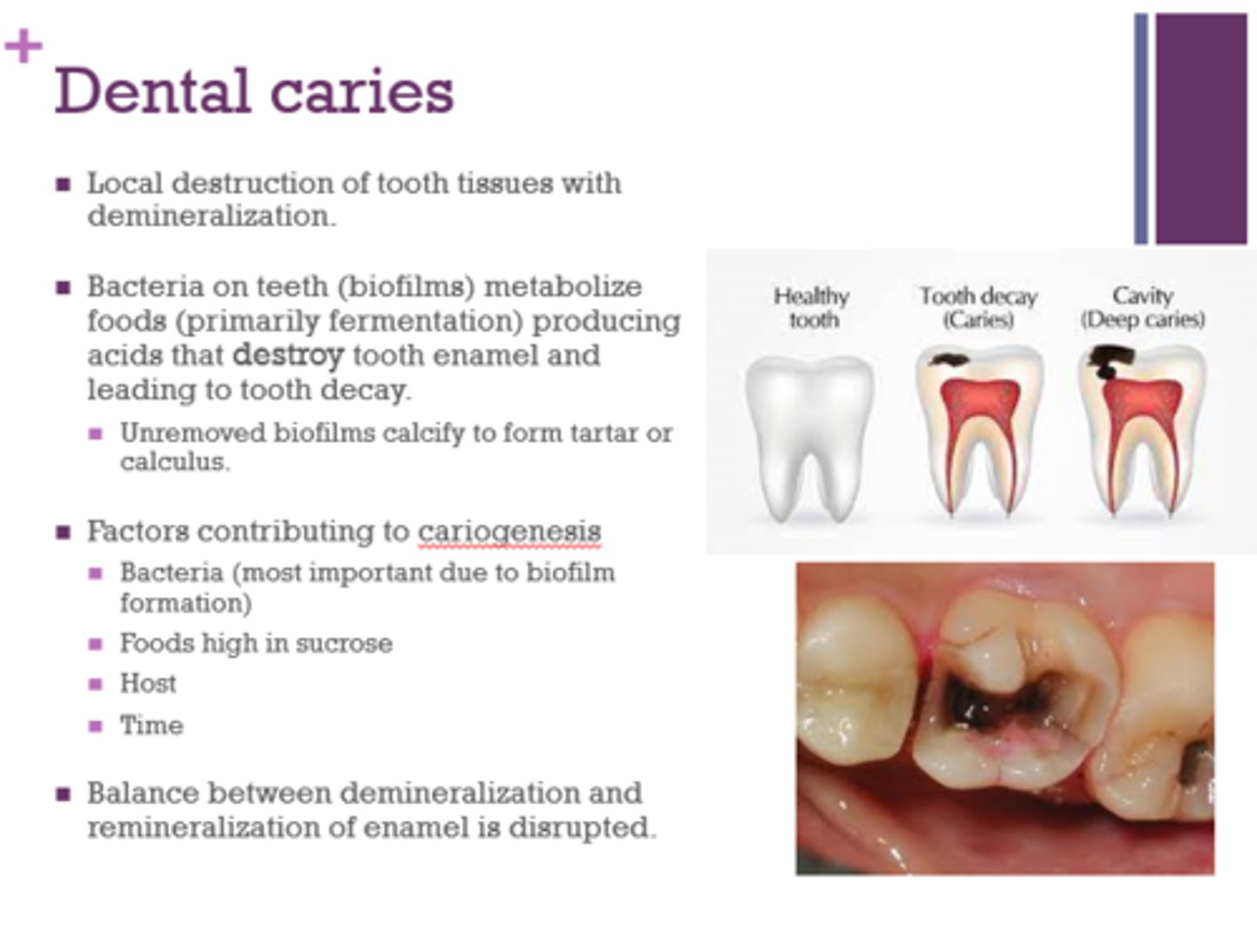
What is the main cariogenic bacteria?
S. mutans

Do Koch's postulates apply to caries?
No - no microorganisms have been found to conform to the postulates that can prove that caries is an infectious disease caused by a single species

How does fluoride help control decay?
- enhancing remineralization
- makes tooth less soluble

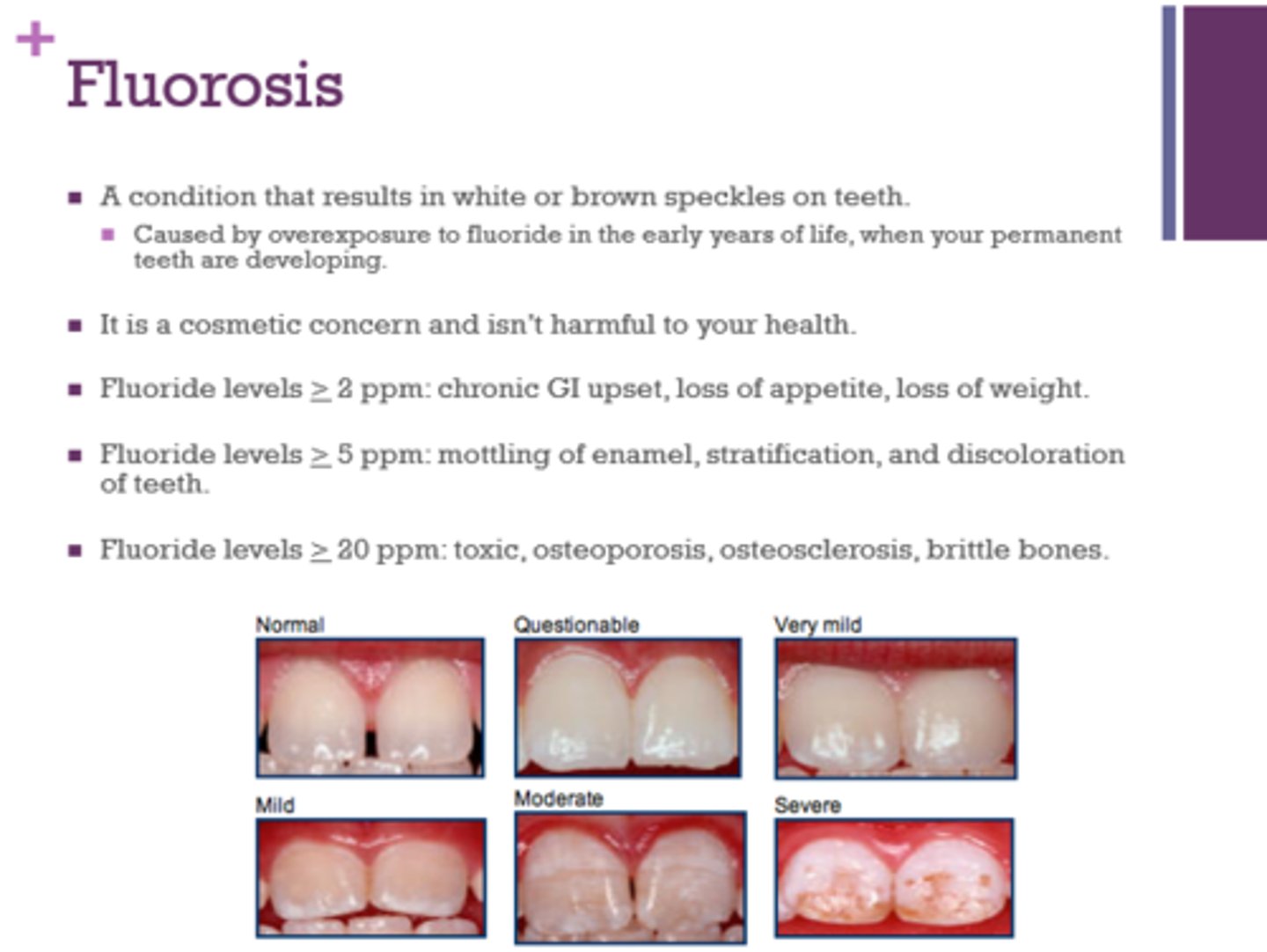
What is associated with fluoride levels greater or equal to 2 ppm?
chronic GI upset, loss of appetite, weight loss
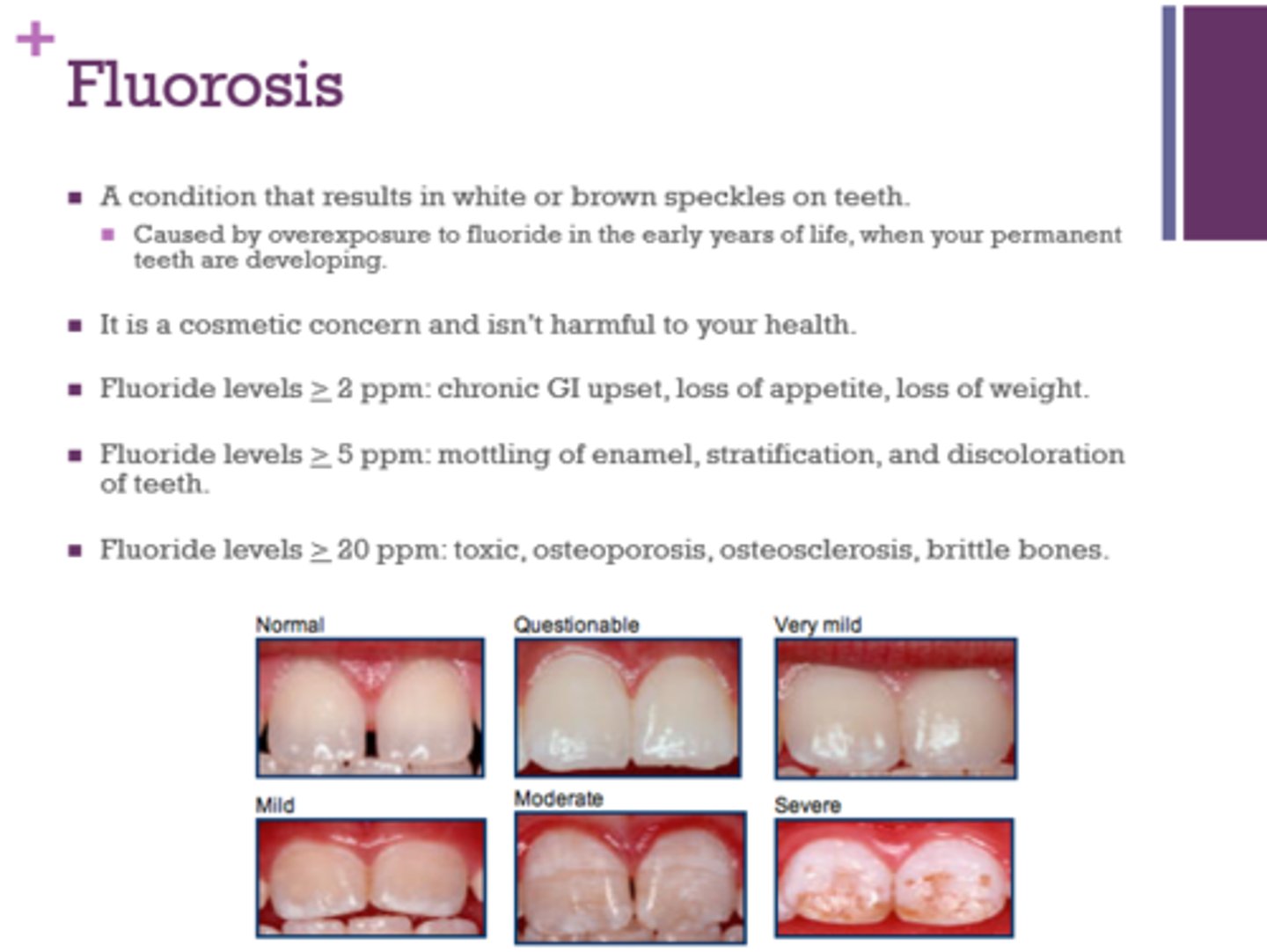
What is associated with fluoride levels greater or equal to 5 ppm?
mottling of enamel, stratification, discoloration of teeth
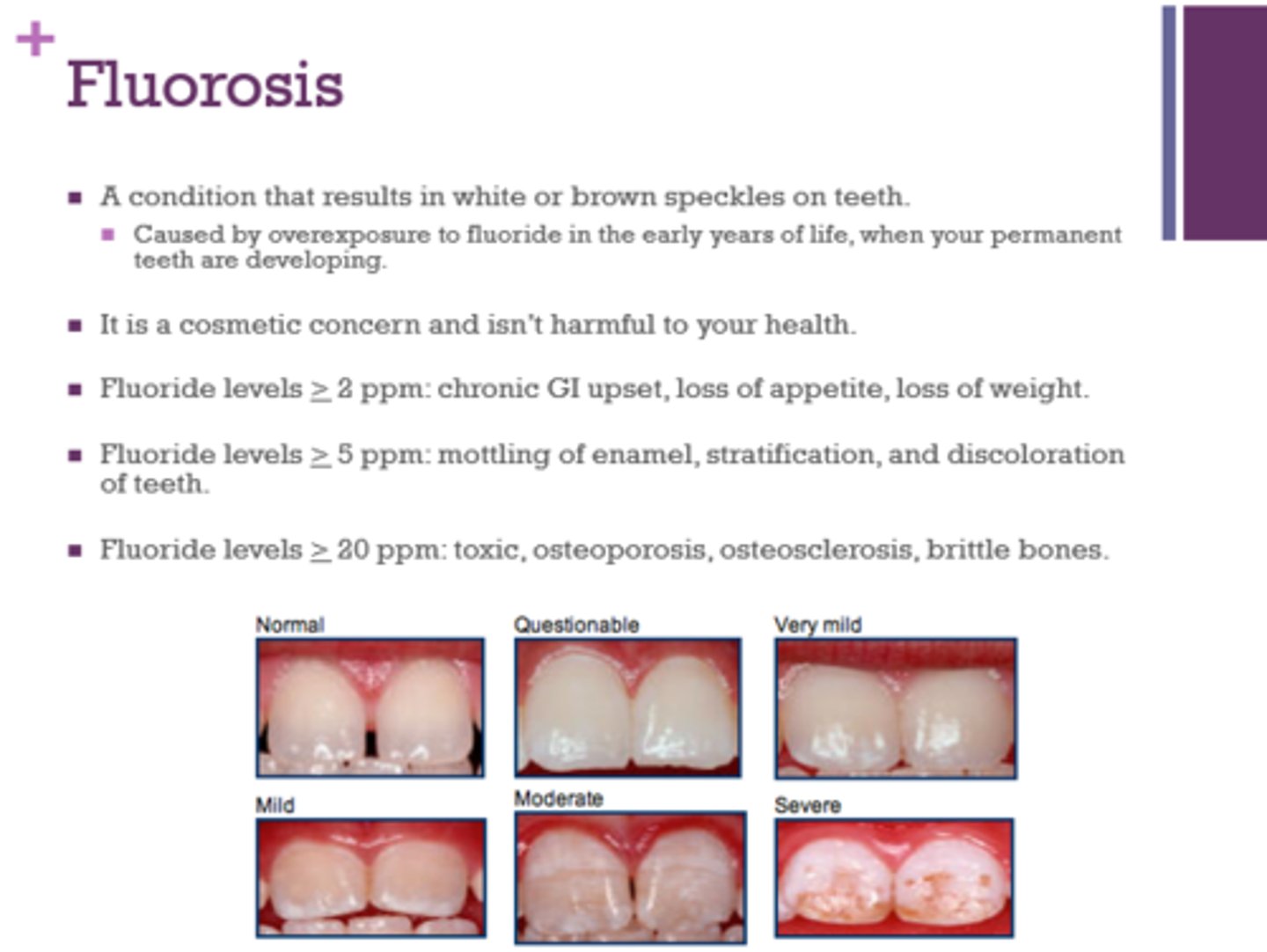
What is associated with fluoride levels greater than or equal to 20 ppm?
toxic, osteoporosis, osteosclerosis, brittle bones