Metabolism EOT final qs
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:12 AM on 6/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Co-enzymes of PDH
Lipoic acid
NAD+
FAD
Thiamine pyrophosphate (thiamine = B1)
NAD+
FAD
Thiamine pyrophosphate (thiamine = B1)
2
New cards
Draw pyruvate to lactate
Lactate can be delivered to liver for gluconeogenesis
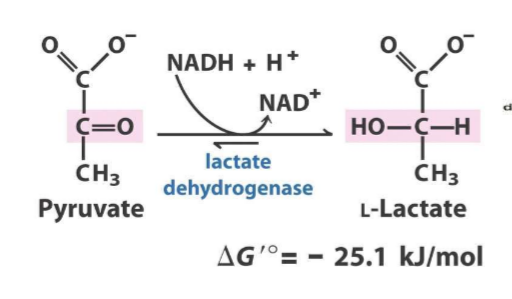
3
New cards
Draw pyruvate to ethanol
Yeast cells
Note the pyruvate decarboxylase also uses TPP
Note the pyruvate decarboxylase also uses TPP
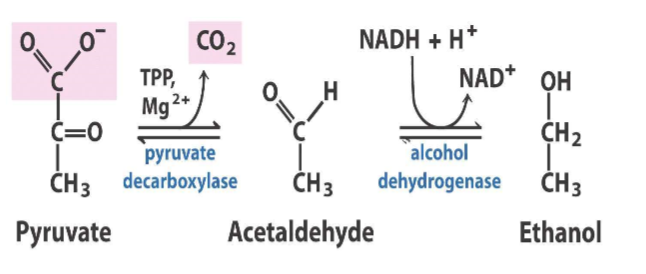
4
New cards
Why is too much fructose bad?
Fructose skips rate limiting step = can either go in at G6P or G3P.
Sugars like fructose and mannose skip energy investment phases and lots of ATP is produced. Thus, the glycolysis pathway is more efficient and not a heap of sugar is needed (body will store away sugar at glycogen/TGs)
Sugars like fructose and mannose skip energy investment phases and lots of ATP is produced. Thus, the glycolysis pathway is more efficient and not a heap of sugar is needed (body will store away sugar at glycogen/TGs)
5
New cards
Draw pathway from pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate
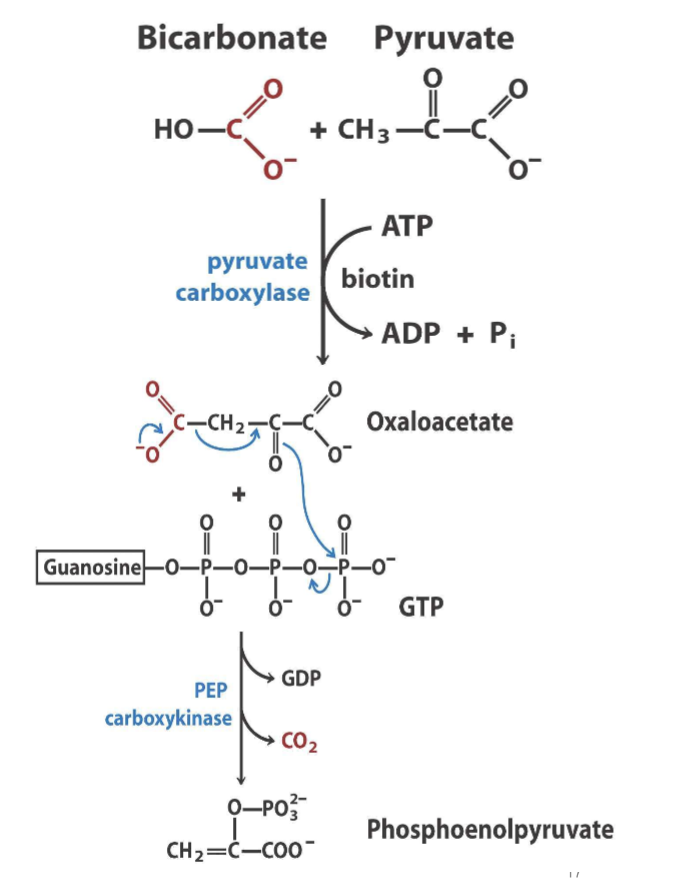
6
New cards
What are the precursors for gluconeogenesis?
Lactate, amino acids, glycerol
(NOT FA’s, only plants can use FAs in glyoxylate cycle)
Therefore, FA’s are not gluconeogenic
(NOT FA’s, only plants can use FAs in glyoxylate cycle)
Therefore, FA’s are not gluconeogenic
7
New cards
How is glycogen formed?
**Start either from glucose** __**or**__ **lactate**
Glycogen synthase - transfers glucose residue of UDP-glucose to a non-reducing end of a branch + forms alpha 1-4 linkages
Each chain is 12-14 residues
Glycogen branching enzyme - takes a terminal fragment (6-7) and adds to a chain of at least 11
Glycogen synthase - transfers glucose residue of UDP-glucose to a non-reducing end of a branch + forms alpha 1-4 linkages
Each chain is 12-14 residues
Glycogen branching enzyme - takes a terminal fragment (6-7) and adds to a chain of at least 11
8
New cards
Give reactants and products of TCA
2C in, 2C out, + acetyl CoA -→ 2x Co2 formed
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 GTP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 GTP
9
New cards
Give the anaplerotic reactions for oxaloacetate
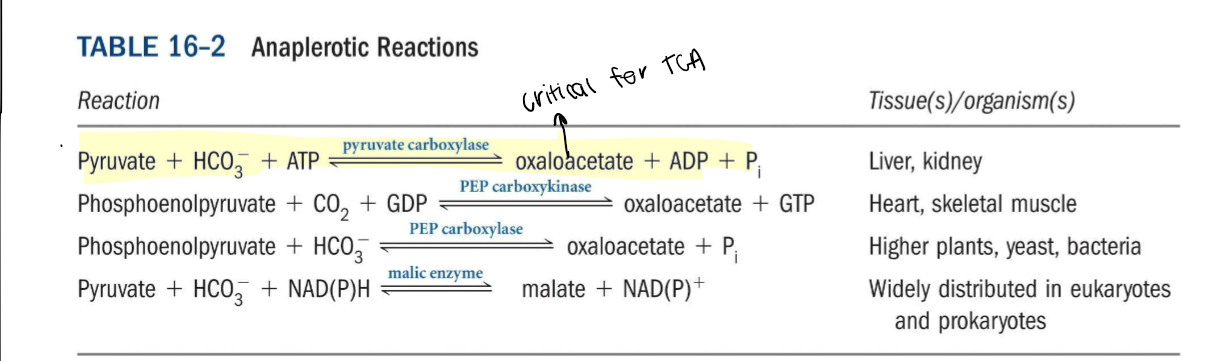
10
New cards
How does oxaloacetate move from mitochondria to cytosol?
As malate via dicarboxylase carrier
11
New cards
gibbs free energy formula
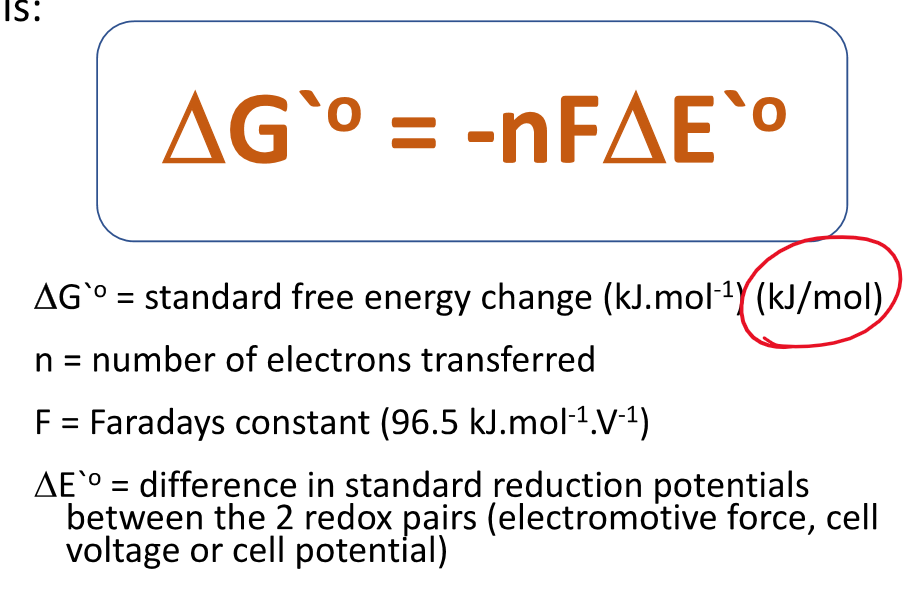
12
New cards
Mitochondrial anatomy:
What processes occur in the outer membrane, inner membrane and matrix?
What processes occur in the outer membrane, inner membrane and matrix?
Outer membrane = FA elongation, phospholipid synthesis
Inner = ETC, oxidative phosphorylation
Matrix= PDH reaction, TCA, FA oxidation and amino oxidation
Inner = ETC, oxidative phosphorylation
Matrix= PDH reaction, TCA, FA oxidation and amino oxidation
13
New cards
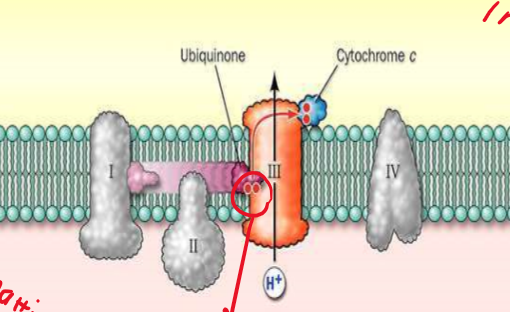
What type of carrier is cyt C?
Mobile carrier + peripheral protein on inner membrane sapce side of cristae membrane
14
New cards
What is the last step of the ETC>
Cyt a3 passing the electron to oxygen to produce water
15
New cards
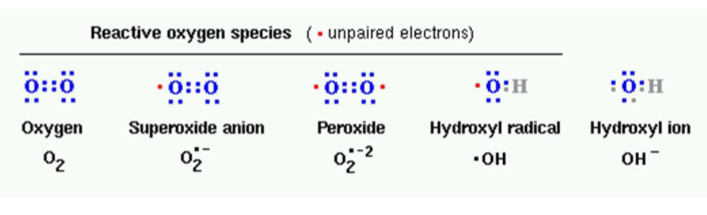
What are oxygen reduction complications associated w mitochondria?
1e- = superoxide anion
2e-= hydrogen peroxide
3e- = hydroxyl and hydroxy radical
4e- = 2 water
2e-= hydrogen peroxide
3e- = hydroxyl and hydroxy radical
4e- = 2 water
16
New cards
What are the two major structural components of ATP synthase?
Complex V/F0F1 ATPase
\
F1 = in matrix
F0 = intermembrane
\
F1 = in matrix
F0 = intermembrane
17
New cards
What does ATPase use to make ATP?
Proton motive force
* amount of ATP is proportional to # of oxygen transferred across membrane (hence, chemiosmotic coupling)
* 3 for NADH as it gets 12 H+
* 2 for FADH2 as it gets 8 H+
* P/O (# ATP epr oxygen)
* amount of ATP is proportional to # of oxygen transferred across membrane (hence, chemiosmotic coupling)
* 3 for NADH as it gets 12 H+
* 2 for FADH2 as it gets 8 H+
* P/O (# ATP epr oxygen)
18
New cards
Favourable conditions for chemiosmotic couple
1. Intact membrane
2. Hydrogen ions cannot flow freely across membrane (keep gradient) and no other ions messing w the gradient
3. Key transporters are asymmetrically located and span the membrane
Absence of compounds that increase proton permeability of inner mitochondrial membrane
19
New cards
Two types of drugs that disrupt chemiosmotic coupling
Inhibitors: cause build up of electrons by preventing a complex’s function
Uncoupling = disrupted inner membrane (oxidative phosphorylation cannot occur)
Uncoupling = disrupted inner membrane (oxidative phosphorylation cannot occur)
20
New cards
Value for oxidation of NADH
\-220kJ/mol (need 220 kJ of free energy to get ATP created, around 31 kJ/mol for each ATP)
21
New cards
Why, if NADH yields 220kJ/mol and ATP needs 31kJ/mol for synthesis, does NADH not have a PO ratio of 7?
Theoretically, to get 3 ATP, only need 93 kJ. Experimentally need -220 kJ - inefficiency in coupling (leakage of protons and electrons and sometime ROS are formed instead)
NADH oxidative phosphorylation si about 42% efficienct
NADH oxidative phosphorylation si about 42% efficienct
22
New cards
Energy yield for one glucose
2 ATP and 2NADH (cytosolic) for glycolysis
2 acetyl Coa and 2 NADH from PDH
2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 from TCA
38 ATP using malate aspartate, 36 realistically (to get NADH into matrix using glycerol phosphate shuttle, convert to FADH2 first)
2 acetyl Coa and 2 NADH from PDH
2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 from TCA
38 ATP using malate aspartate, 36 realistically (to get NADH into matrix using glycerol phosphate shuttle, convert to FADH2 first)
23
New cards
What are the three inner membrane transport systems?
1. Pyruvate transport system (pyruvate in to matrix in exchange for a OH-)
2. Dicarboxylate: succ/malate/fumarate in exchange for succ/malate/fumarate/pi
1. Tricarboxylate: iso/citrate in exchange for iso/citrate (also dicarboxylic acids)
24
New cards
How is ATP transported?
**Adenine nucleotide translocase:** ADP goes into matrix in exchange for ATP (proton gradient helps)
**Phosphate translocase:** H2PO4- in and OH- out
**Phosphate translocase:** H2PO4- in and OH- out
25
New cards
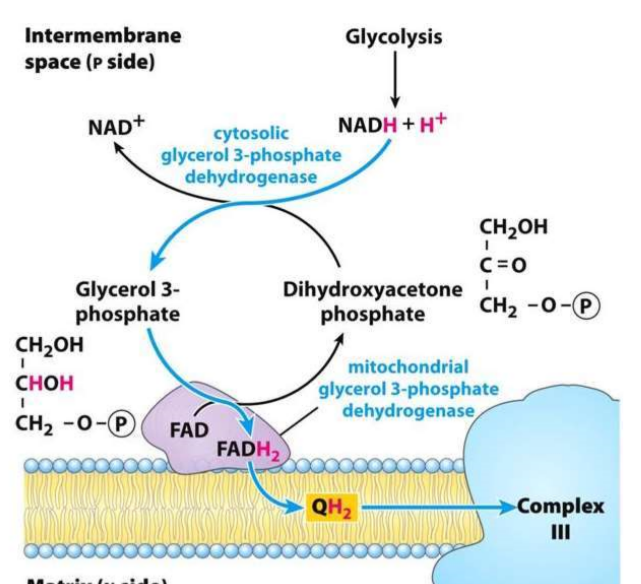
Glycerol phosphate shuttle vs malate aspartate shuttle
Glycerol phosphate = faster (brain and skeletal muscle)
malate aspartate = NADH is used to transport oxaloacetate as malate into matrix from cytosol. Malate goes back to oxaloacetate to produce an NADH in the matrix.
malate aspartate = NADH is used to transport oxaloacetate as malate into matrix from cytosol. Malate goes back to oxaloacetate to produce an NADH in the matrix.
26
New cards
What are the unique enzymes and their action involved in beta oxidation of unsaturated fas
Enoyl Coa Isomerase - converts C3-C4 cis double bond to trans C2-C3
\
2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase = NADPH dependent (converts C2-C3 and C4-C5 cis double bonds to C3-C4 cis bond
\
2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase = NADPH dependent (converts C2-C3 and C4-C5 cis double bonds to C3-C4 cis bond
27
New cards
Odd number of carbons
Last cycle has propionyl CoA -→ sub in at succinyl CoA (6 ATP in last cycle)
28
New cards
How is acetoacetyl CoA synthesised ?
From 2x acetyl CoA by beta-ketothiolase
29
New cards
Draw HMG CoA
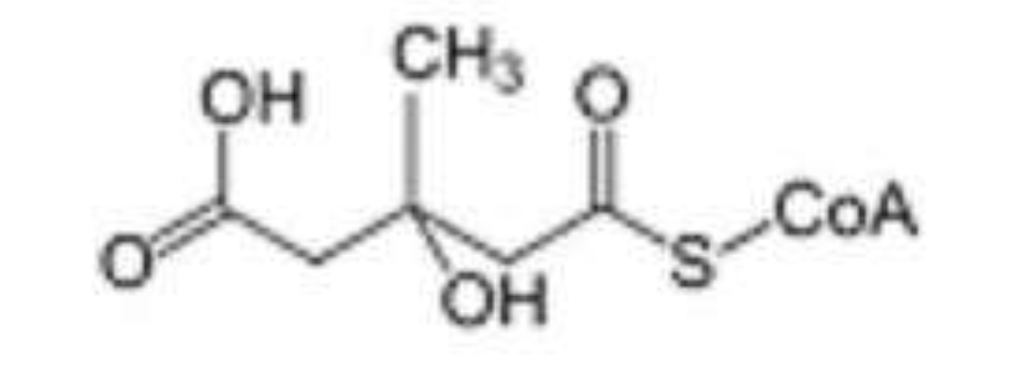
30
New cards
Draw pathway of acetyl CoA being used for ketone synthesis
3x ketones are synthesised
\
\
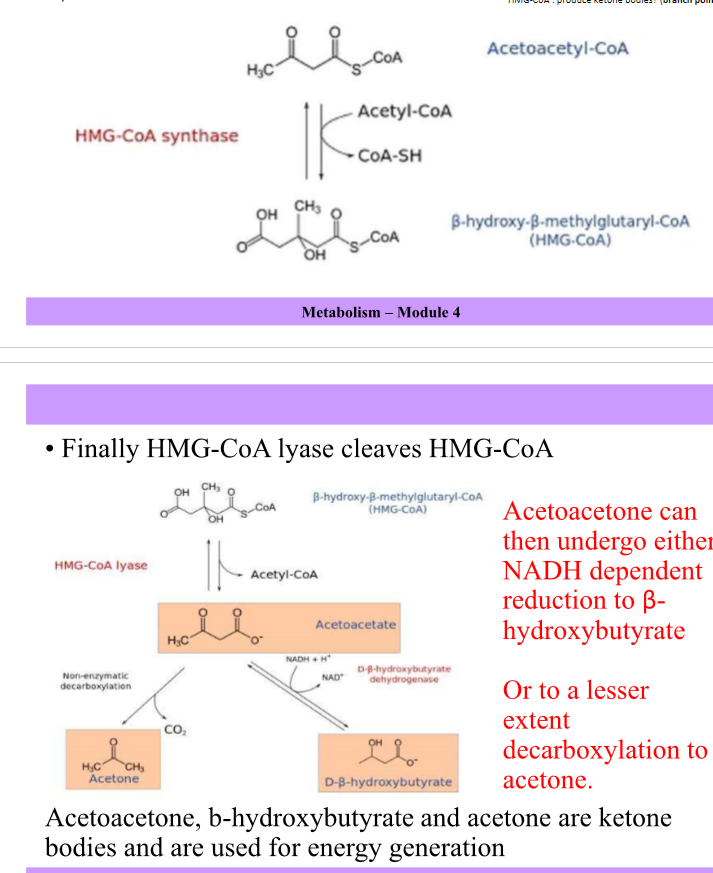
31
New cards
What are the four enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis?
1. Condensation: beta-ketoacyl synthase
2. Ketoreduction: beta-ketoacyl reductase
3. Dehydration: 3-hydroxyacyl dehydrase
4. Saturation: Enoyl CoA reductase
32
New cards
How to synthesis malonyl acp?
With acetyl ACP, biocarbonic and ATP + acetyl CoA-ACP transcylase (or acetyl CoA carboxylase)
33
New cards
How does acetyl CoA leave the matrix?
Via citrate shuttle = combined w oxaloacetate to form citrate and then transported out
FA are elongated in ER after C16
**In ER-→ acyl CoA is now used**
FA are elongated in ER after C16
**In ER-→ acyl CoA is now used**
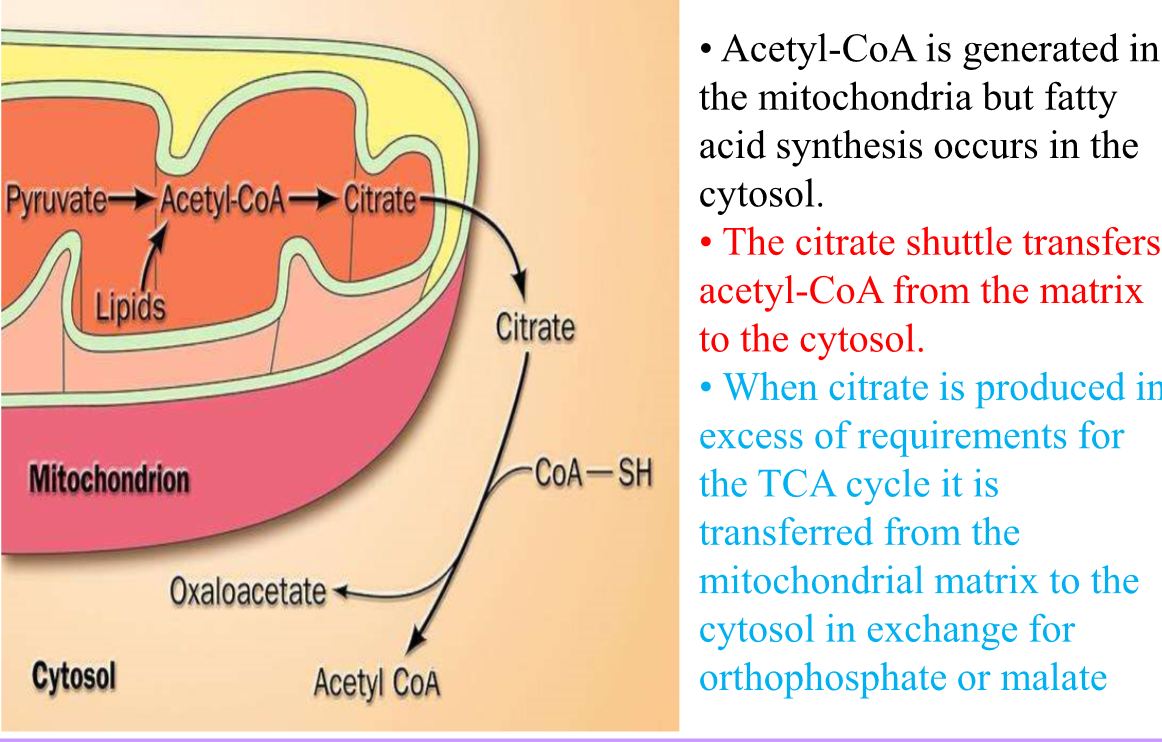
34
New cards
What enzyme puts a double bond?
Fatty acyl CoA desaturase (up to C9)
**NEEDS OXYGEN**
**NEEDS OXYGEN**
35
New cards
How is fatty acid synthesis regulated?
Via acetyl coa carboxylase
* production of palmitoyl coa leads to inhibition
* NADPH
* Insulin (provides more acetyl CoA by activating PDH)
* production of palmitoyl coa leads to inhibition
* NADPH
* Insulin (provides more acetyl CoA by activating PDH)
36
New cards
Nitrogen fixation process
Must be anaerobic (roots)
Oxygen deactivates
Oxygen deactivates
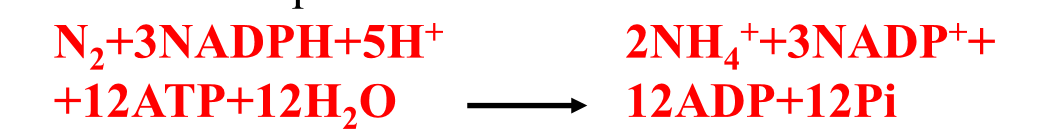
37
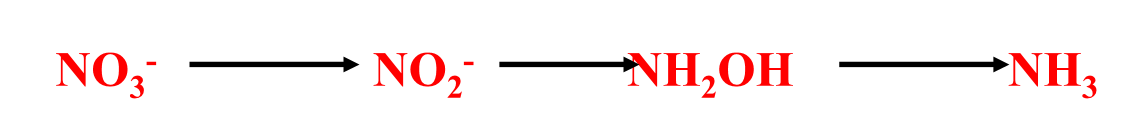
New cards
What can utilise nitrate?
Plants, bacteria and fungi (mostly)
\
\
38
New cards
What are the four signals of protein destruction?
Ubiquitination (mark for destruction)
Oxidation of amino acids (esp pro, lys, arg) (mark for proteases)
PEST signals (recognition sequences for proteases)
N terminal amino acids (FLY WNK)
Oxidation of amino acids (esp pro, lys, arg) (mark for proteases)
PEST signals (recognition sequences for proteases)
N terminal amino acids (FLY WNK)
39
New cards
Type of excretion of birds, fish and humans
Birds: uric acid (very concentration)
Humans: urea
fish: ammonia
Humans: urea
fish: ammonia
40
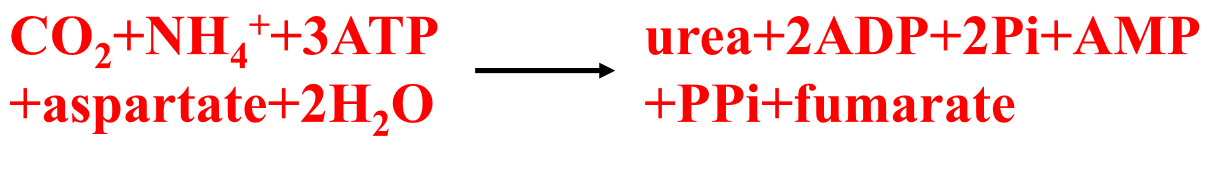
New cards
Net reaction for 1 turn of Krebs-Heinseleit
41
New cards
What are the essential ammino acids
Arginine
Leucine
Valine
Isoleucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Histidine
Threonine
Leucine
Valine
Isoleucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Histidine
Threonine
42
New cards
Two methods of glutamate synthesis + location
Glutamate dehydrogenase (NADPH) - mitochondrial matrix
\
Glutamate synthase (NADPH + glutamine )
\
Glutamate synthase (NADPH + glutamine )
43
New cards
Method of glutamine synthesis
Glutamine synthase : uses ATP + glutamine
* Two feedback mechanisms: partial inhibition by the reaction products and oxidation (adenylation) of the active site when there is high concentration of glutamine
* Two feedback mechanisms: partial inhibition by the reaction products and oxidation (adenylation) of the active site when there is high concentration of glutamine
44
New cards
Two types of CPS
CPSI - in matrix, uses NH4 and HCO3 + 3 ATP= carbamoyl phosphate
CPSII - in cytosol, uses transamination for NH3 source (glutamine) + HCO3- and 2ATP and 2 hydrogen
CPSII - in cytosol, uses transamination for NH3 source (glutamine) + HCO3- and 2ATP and 2 hydrogen
45
New cards
How is creatinine phosphate synthesised?
Arginine in muscle
46
New cards
How is proline synthesised?
Glutamic semi-aldehyde + NADPH + H+ → proline + water + water
47
New cards
How do plants vs animals synthesise cysteine?
Derived from serine and can directly add Sulphur
Humans require to go from methionine first
Humans require to go from methionine first
48
New cards
How does plants derive methionine?
Homoserine + cysteine -→ pyruvate + methionine + NH4
49
New cards
Function of phenylalanine hydroxylase (give chemical equation)
To make tyrosine from phenylalanine by adding an OH
\
Phe + NADPH + H+ + O2 -→ tyrosine + NADP+ + water
\
Phe + NADPH + H+ + O2 -→ tyrosine + NADP+ + water
50
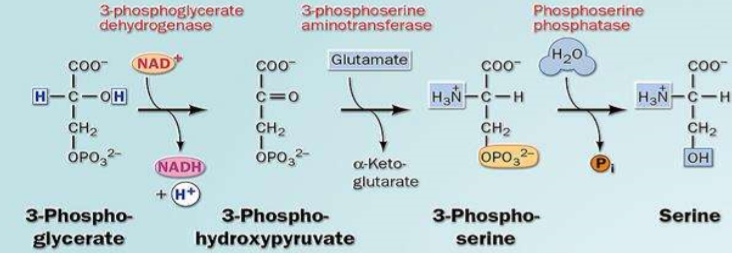
New cards
Describe synthesis of serine
3 phosphoglycerate + NADPH + glutamate
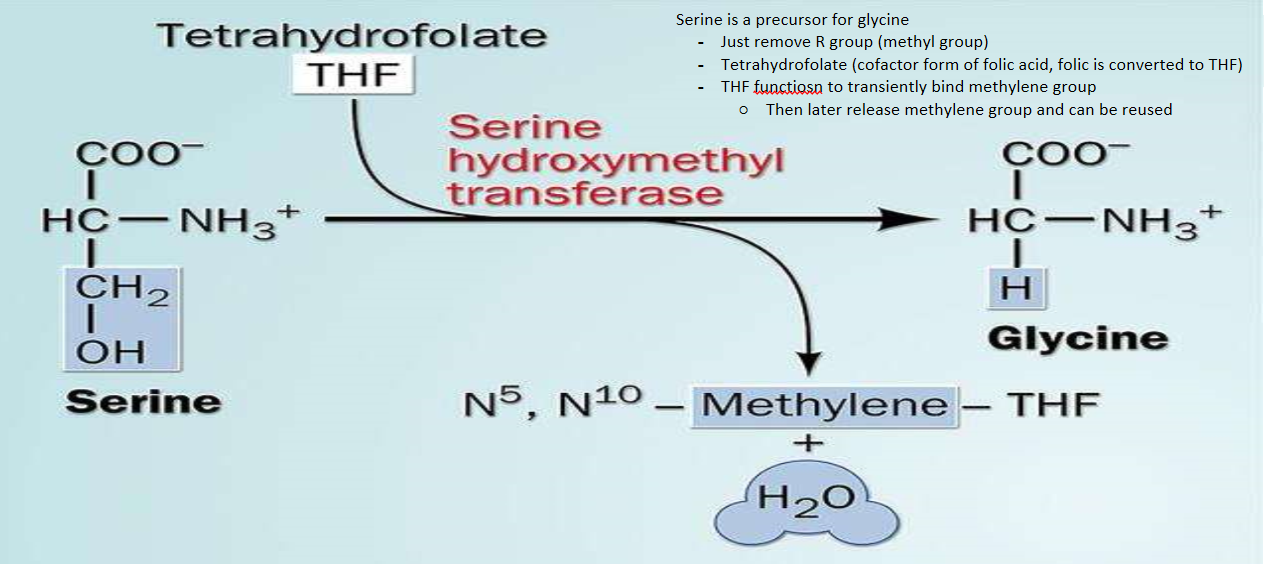
51
New cards
How is glycine created (include enzyme)
Serine + THF -→ glycine
52
New cards
How do plants synthesis threonine?
From homoserine (which is from aspartate) -→ phosphorylation and then uses **pyroxidal phosphate**

53
New cards
NTs as amino acids
Glycine and glutamate are neurotransmitters
Tyrosine and tryptophan are precursors for catecholamines and serotonin
Tyrosine and tryptophan are precursors for catecholamines and serotonin
54
New cards
How is serotonin (the NT) synthesised?
Trp + O2 -→ serotonin + water + carbon dioxide
(peristalsis, BP, neurotransmission, light/dark)
(peristalsis, BP, neurotransmission, light/dark)
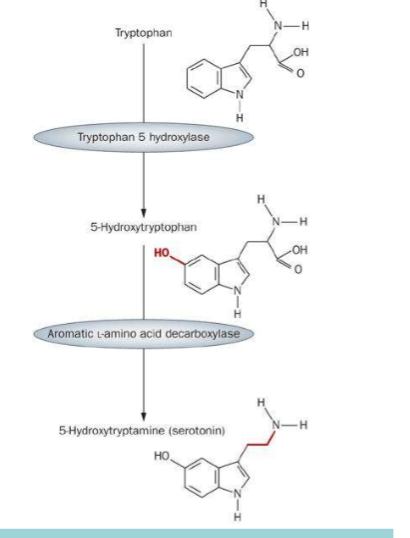
55
New cards
How are the catecholamines synthesised ?
56
New cards
What do phosphoribosyl transferases catalyse?
Transfer of a free base to the ribose of PRPP (5-phosphribosyl pyrophosphate)
\
Base + PRPP -→ NMP + pyrophosphate
\
Base + PRPP -→ NMP + pyrophosphate
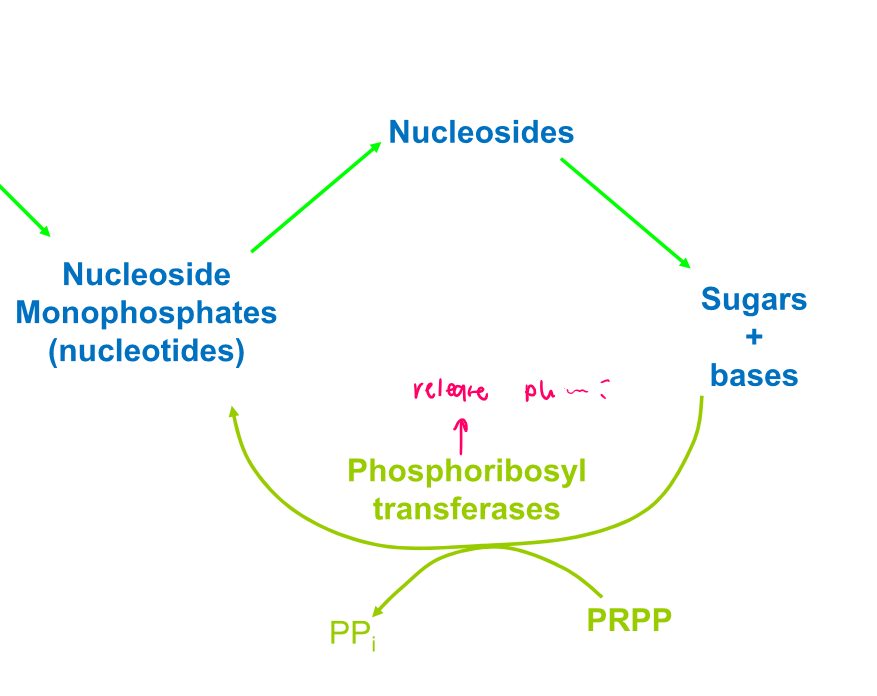
57
New cards
Draw de novo purine synthesis
From here, go to AMP and GMP (via ASp + GTP and Gln and ATP)
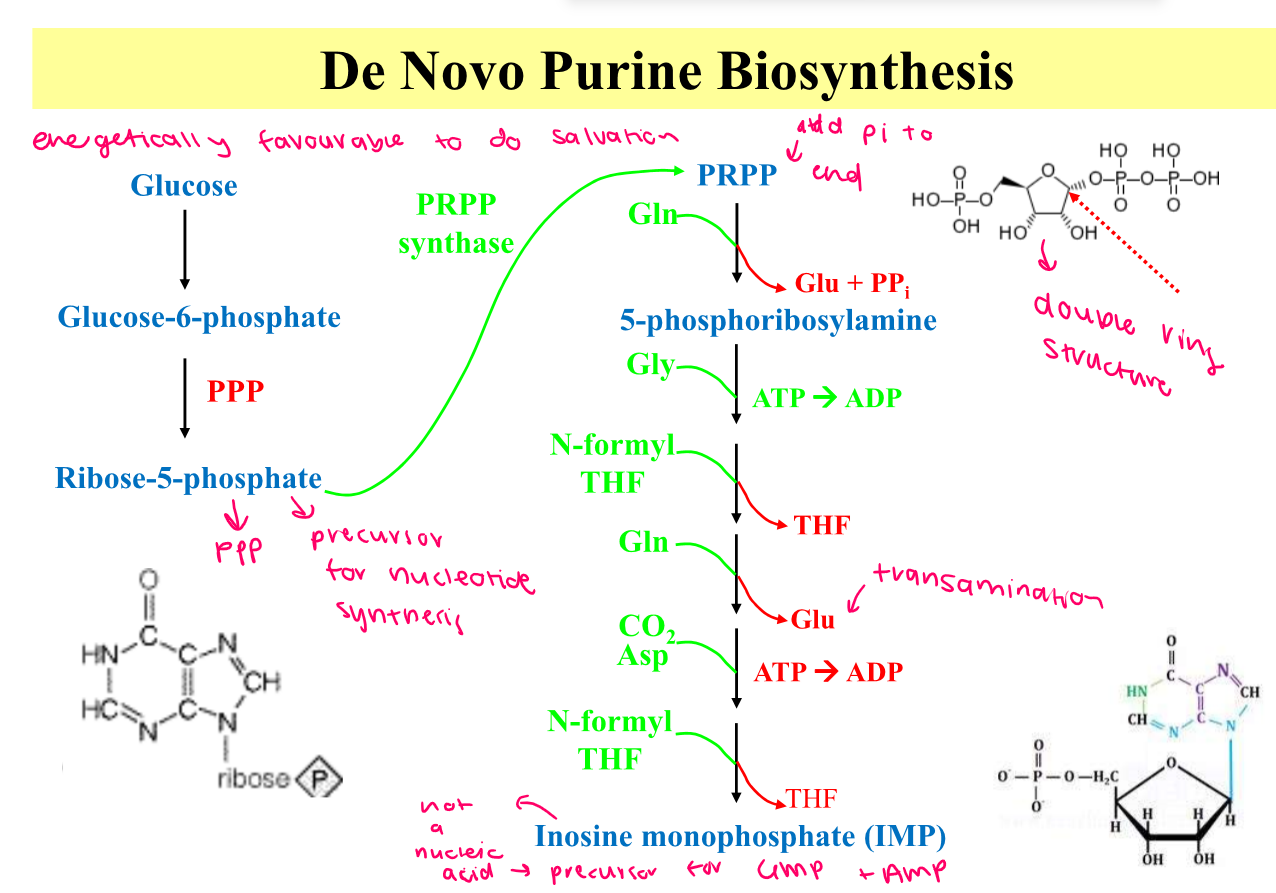
58
New cards
What enzymes phosphorylate NMPs?
Adenylate/guanylate kinases (NMP - NDP)
Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDP - NTP)
Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDP - NTP)
59
New cards
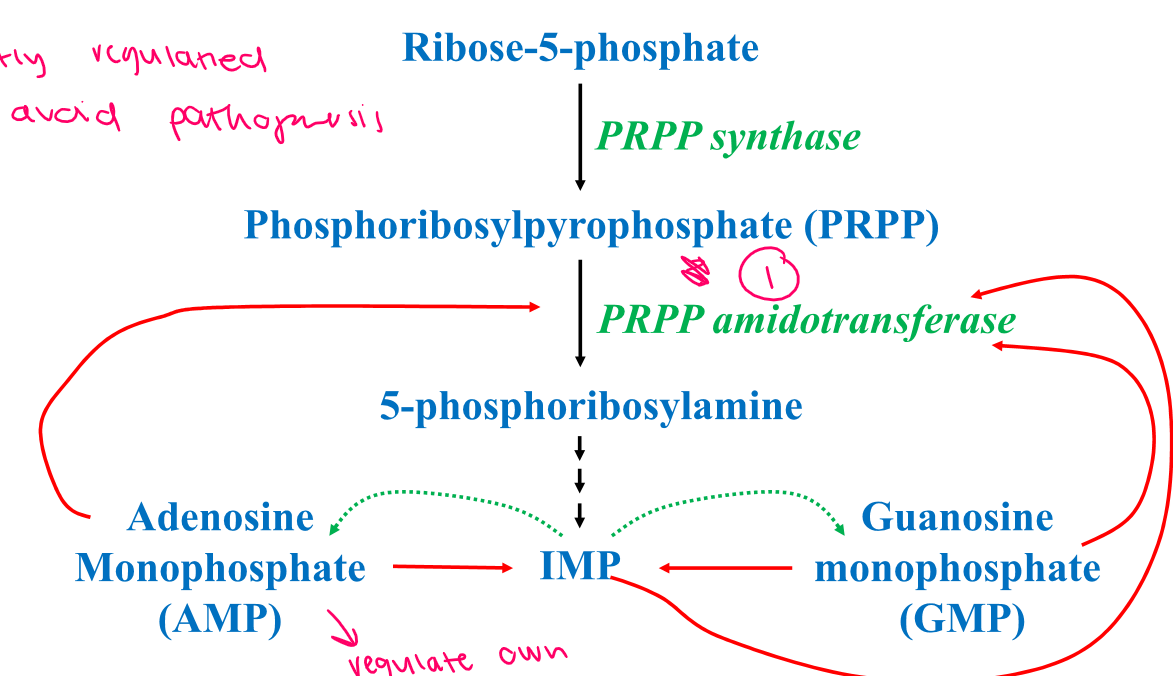
3 mechanisms of regulation of de novo purine synthesis
1. AMP and GMP regulate/inhibit their own synthesis from IMP
2. ADP and GDP inhibit PRPP synthase
1. AMP, GMP and IMP inhibit PRPP aminotransferase
60
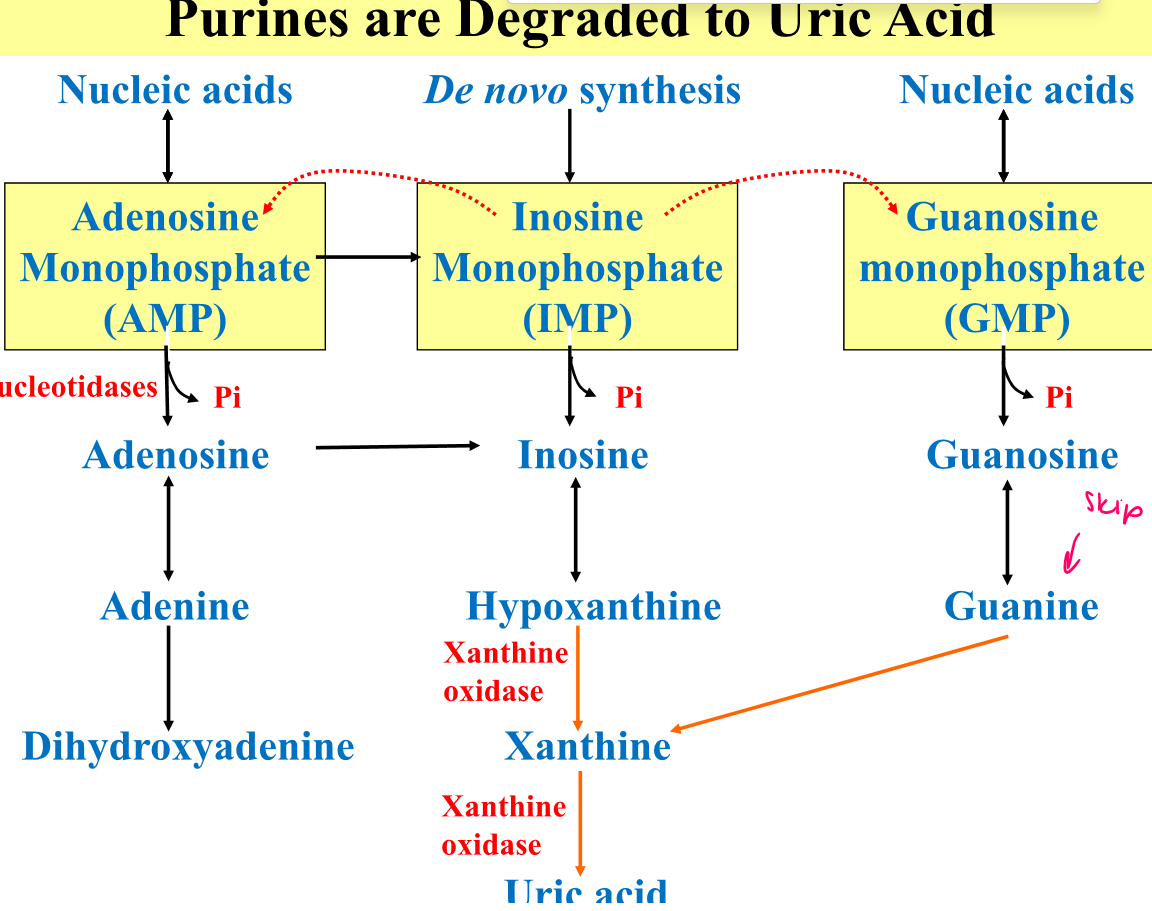
New cards
Draw purine degradation
Recall uric acid can break down further to allantoin and then to urea
61
New cards
What does HGPRT stand for and do?
hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
\
takes hypoxanthine and guanine back to IMP and GMP
\
takes hypoxanthine and guanine back to IMP and GMP
62
New cards
What does uricosuric drug do?
Inhibit tubular reabsorption (more uric acid is excreted)
63
New cards
Why are fasting and alcohol consumption both risk factors for gout?
Fasting = ketoacidosis (inhibit secretion of urate)
Alcohol consumption = lactate formation = competes w urate for excretion
(also water/dehydration is a RF)
Alcohol consumption = lactate formation = competes w urate for excretion
(also water/dehydration is a RF)
64
New cards
What do they treat ATLS with?
Recombinant uric acid oxidase = makes uric acid allantoin which is more soluble
65
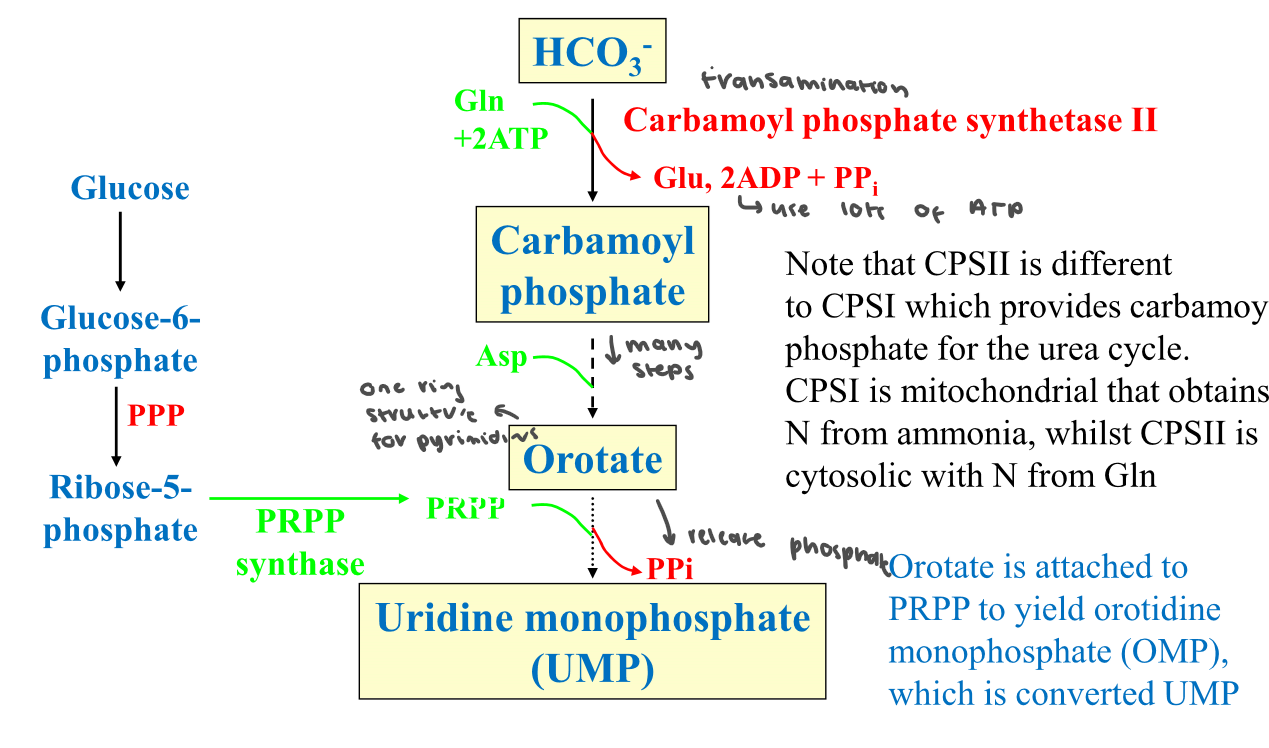
New cards
Draw pyrimidine synthesis
Note that uTP is converted to CTP via CTP synthase w a transamination reaction (Gln) and ATP
66
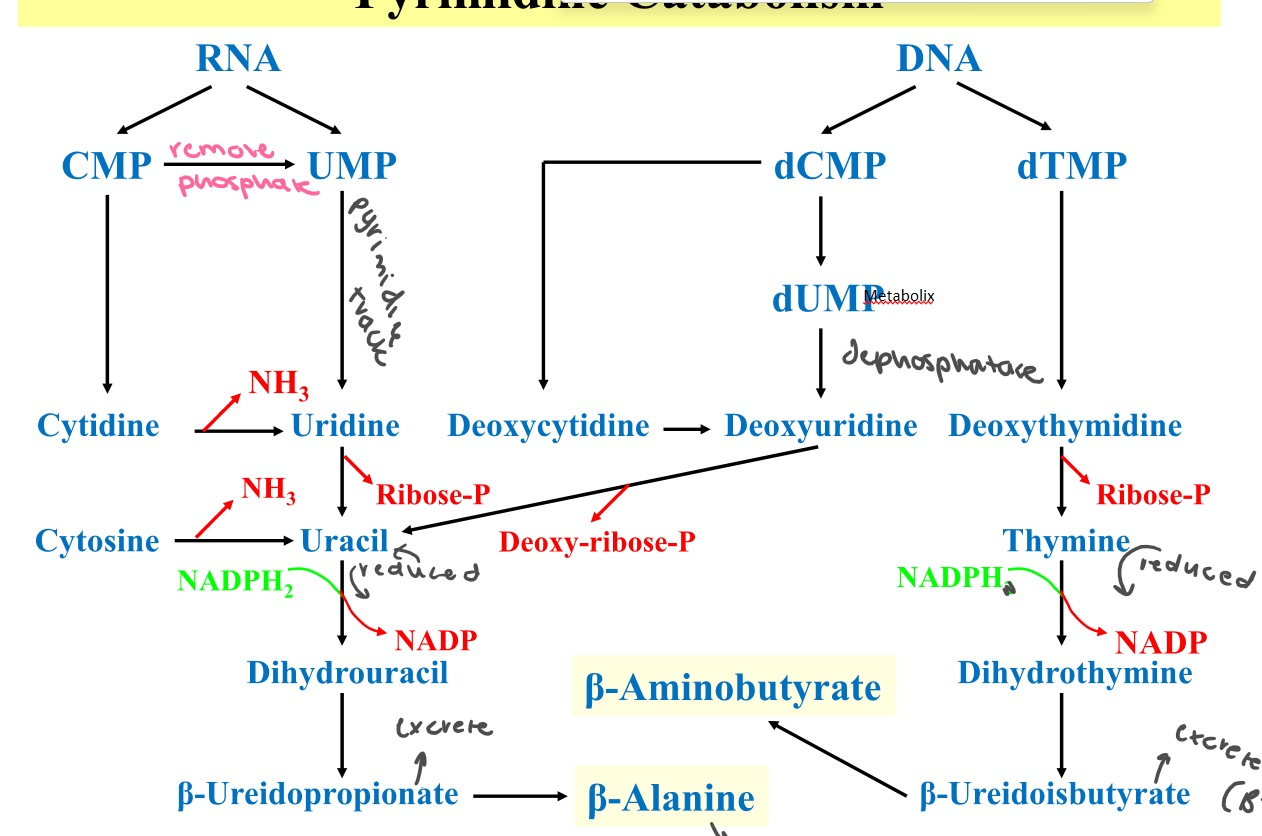
New cards
Draw pyrimidine breakdown
67
New cards
Draw pyrimidine salvage
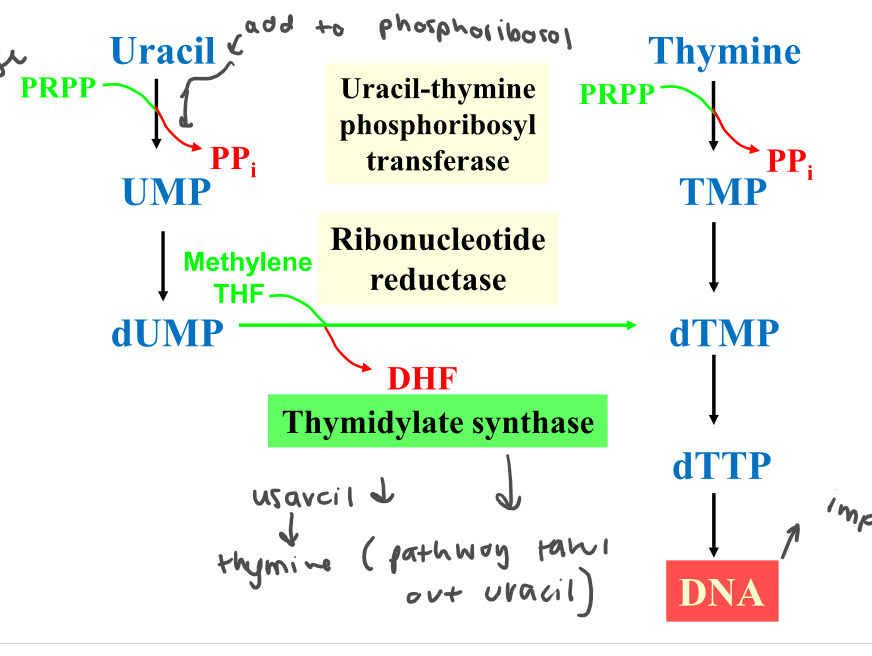
68
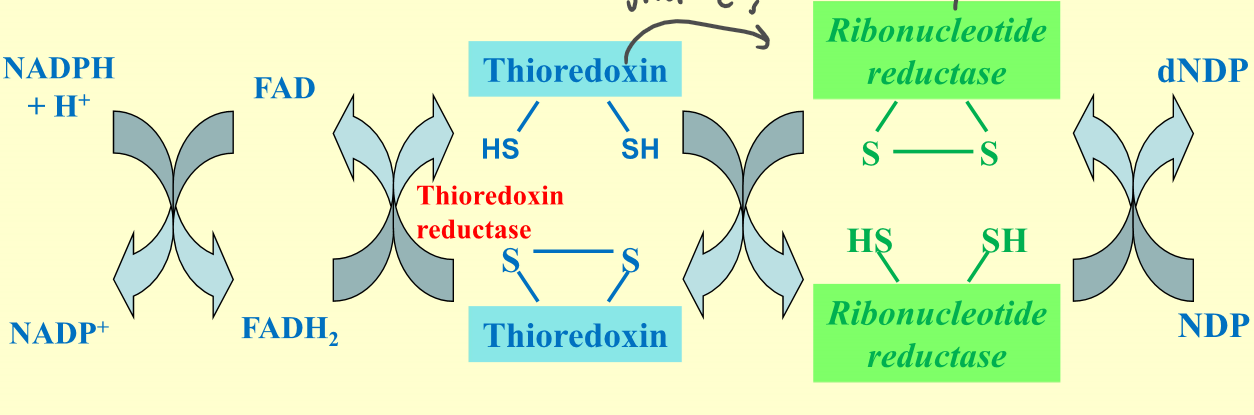
New cards
How are ribonucletides converted to deoxyribonucleotides?
Thioredoxin intermediate + ribonucleotide reductase
\
NADPH → FADH2 → Thioredoxin → Ribonucleotide synthase → NDP=dNDP
\
NADPH → FADH2 → Thioredoxin → Ribonucleotide synthase → NDP=dNDP
69
New cards
How is dTMP synthesised?
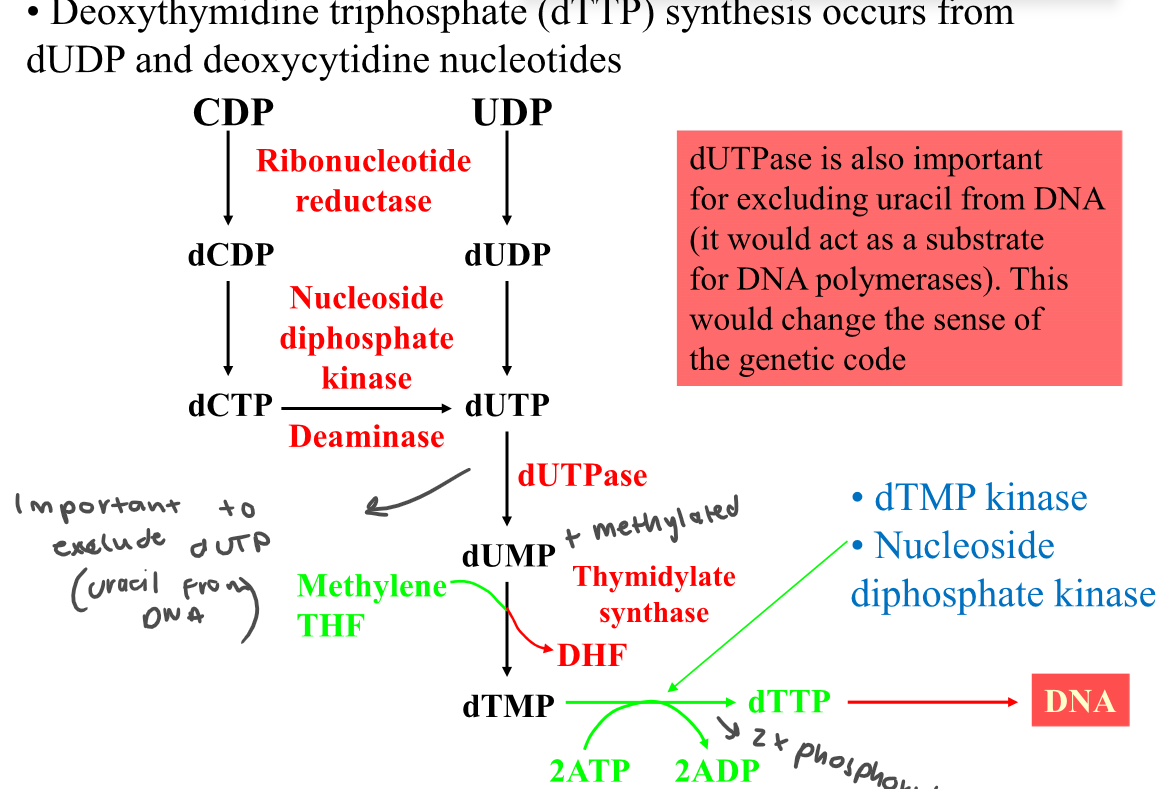
70
New cards
How is deoxyribonucleotide synthesis controlled?
Level of ribonucleotide reductase = has two regulatory sites,
ATP binds = activated, dATP binds = inactivated
ATP binds = activated, dATP binds = inactivated
71
New cards
Mode of mechanism of insulin
* Increases: glucose uptake, glycogen synthase and TG synthesis (acetyl coa carboxylase), protein synthesis
* Decreases: proteolysis, lipolysis, gluconeogenesis + glycogen breakdown
* Decreases: proteolysis, lipolysis, gluconeogenesis + glycogen breakdown
72
New cards
Mechanism of glucagon
* Increases: TG movement, lipolysis (beta oxidation and ketogenesis), gluconeogenesis, glycogen breakdown
* Decreases: glycogen and FA synthesis
* Decreases: glycogen and FA synthesis
73
New cards
Epinephrine
Adrenal medulla: peptide hormone (still water soluble and uses second messengers)
Glycogenolysis = FAs as fuel, glycerol → gluconeogenesis
Glycogenolysis = FAs as fuel, glycerol → gluconeogenesis
74
New cards
Cortisol
Adrenal cortex (long term- steroid hormone)
Increases: Proteolysis and lipolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis
Decrease: tissue glucose utilisation
\
**Acts on muscle, liver and adipose to supply fuel to withstand stress**
Increases: Proteolysis and lipolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis
Decrease: tissue glucose utilisation
\
**Acts on muscle, liver and adipose to supply fuel to withstand stress**
75
New cards
Body’s response to uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
More glucose by gluconeogenesis:
* proteins broken down and amino acids used for gluconeogenesis
* TGs broken down -→ FA oxidation → acetyl coa
* not enough oxaloacetate (from condensation step)
* ketone bodies build up (acetyl coa builds up)
* acidosis
* proteins broken down and amino acids used for gluconeogenesis
* TGs broken down -→ FA oxidation → acetyl coa
* not enough oxaloacetate (from condensation step)
* ketone bodies build up (acetyl coa builds up)
* acidosis
76
New cards
Describe hormones released by anterior and posterior pituitary
Anterior: Thyrotropin, ACTH (adrenal), somatropin, LH/FSH
\
Posterior: ADH, prolactin and oxytocin
\
Posterior: ADH, prolactin and oxytocin
77
New cards
Three types of hormone
peptide (pituitary, glucagon and insulin)
amino acid (epinephrine, thyroid)
^^^^water soluble^^^^
steroid (corticosteroids) (fat soluble)
amino acid (epinephrine, thyroid)
^^^^water soluble^^^^
steroid (corticosteroids) (fat soluble)
78
New cards
What are three ways hormones can function?
Enzyme activation/inhibition via second messengers (E and Gluc)
Stimulation of synthesis of certain proteins
Selective increases in uptake of metabolites (i.e. aldosterone binding to an ion channel)
\
Stimulation of synthesis of certain proteins
Selective increases in uptake of metabolites (i.e. aldosterone binding to an ion channel)
\
79
New cards
What form of insulin is initially synthesised in the beta cells?
Preproinsulin
80
New cards
4 classes of catecholamines
81
New cards
Function of G proteins
When a hormone binds to a receptor, G protein undergoes a conformation change. It can then go activate adenylate cyclase to make cAMP from ATP
Also activate phospholipase C (DAD and InP3)
Also activate phospholipase C (DAD and InP3)
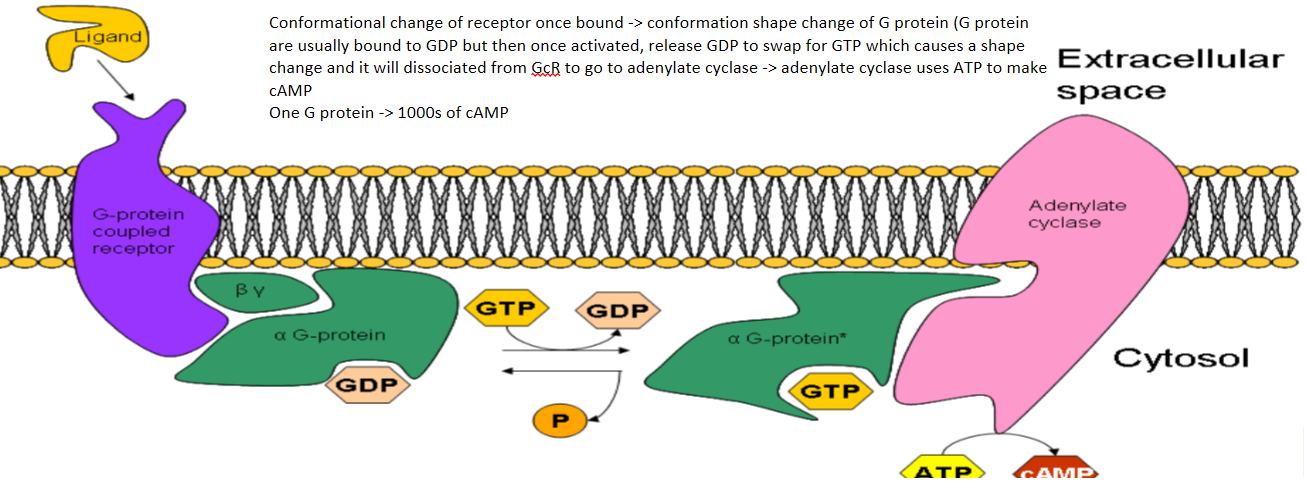
82
New cards
What does cAMP do
Activated by GTP from G protein
A second messenger (as well as calcium)
Bind to PIP to increase intracellular calcium levels
involved in the regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism.
A second messenger (as well as calcium)
Bind to PIP to increase intracellular calcium levels
involved in the regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism.
83
New cards
How does insulin communicate?
Bind to tyrosine kinase which activate GLUT4 (receptor to uptake insulin)
84
New cards
How do steroid hormones work?
Directly diffuse across membrane
Go bind to hormone responsive elements (**HRE**s) in nucleus which manipulates DNA (control transcription of genes)
Is an amplification response but slower and longer lasting
Go bind to hormone responsive elements (**HRE**s) in nucleus which manipulates DNA (control transcription of genes)
Is an amplification response but slower and longer lasting
85
New cards
Describe how alcohol affects metabolism?
1. Ethanol → Acetaldehyde (via alcohol dehydrogenase) produces NADH
* causes oxaloacetate → malate (reducing levels of oxaloacetate inhibits gluconeogenesis: **fasting state**)
2. Acetaldehyde → acetate (via acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) produces NADH
* High level of NADH inhibits Kreb’s and beta oxidation (FAs eaten cannot be metabolised so build up = steatosis)
High level of NADH causes pyruvate to be converted to lactate (via lactate dehydrogenase)
86
New cards
How to treat a hangover?
Hydration
Replenish vitamins loss
Increase intake of FAs + proteins to refuel
Replenish vitamins loss
Increase intake of FAs + proteins to refuel
87
New cards
3 purposes of PPP
1. **NADPH for biosynthesis** (oxidative + non oxidative)
2. **Ribonucleotides for RNA** (just oxidative and non oxidative synthesis of R5P)
3. **Pentose dietary sugars for metabolism** (produce F6P and G3P for glycolysis to pyruvate)
88
New cards
describe the oxidative and non oxidative phase of the ppp
Oxidative:
G6P → 6-phosphogluconate → ribulose 5 phosphate (**2 NADPH produced total)**
Non-oxidative:
3 different pathways to get from 6 5C sugars to 5 6C sugars
1. Ru5P → Septoheludose 7P → F6P → G6P
2. Xylulose 5P → G3P → Erythrose 4P → F6P → G6P
3. Xylulose 5P → G3P (via transketolase) -→ F6P (via gluconeogenesis)
\
Enzymes are transketolase and transaldolase
(Ru5P to Xylulose 5P is via epimerase)
G6P → 6-phosphogluconate → ribulose 5 phosphate (**2 NADPH produced total)**
Non-oxidative:
3 different pathways to get from 6 5C sugars to 5 6C sugars
1. Ru5P → Septoheludose 7P → F6P → G6P
2. Xylulose 5P → G3P → Erythrose 4P → F6P → G6P
3. Xylulose 5P → G3P (via transketolase) -→ F6P (via gluconeogenesis)
\
Enzymes are transketolase and transaldolase
(Ru5P to Xylulose 5P is via epimerase)
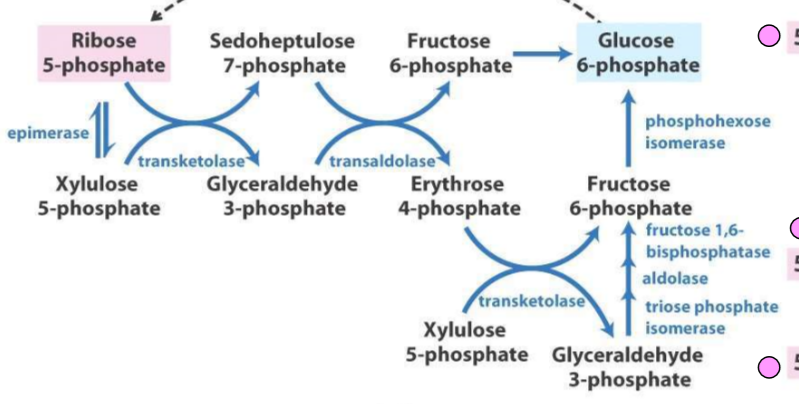
89
New cards
What prevents oxidative damage in RBCs
High oxygen concentrations → prevented by glutathione peroxidase which is needed to reduce glutathione (an antioxidant which scavenges oxidative radicals)
90
New cards
Draw process of cholesterol synthesis
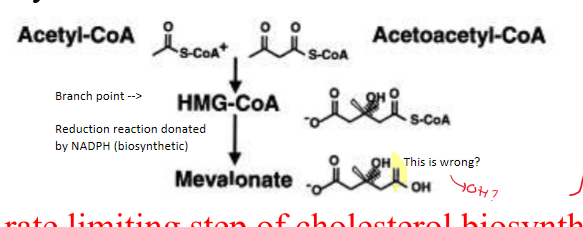
91
New cards
What is the rate limiting step? What controls it?
Insulin increases
Glucagon decreases
Receptor mediated endocytosis of LDL (cholesterol) decreases
Glucagon decreases
Receptor mediated endocytosis of LDL (cholesterol) decreases
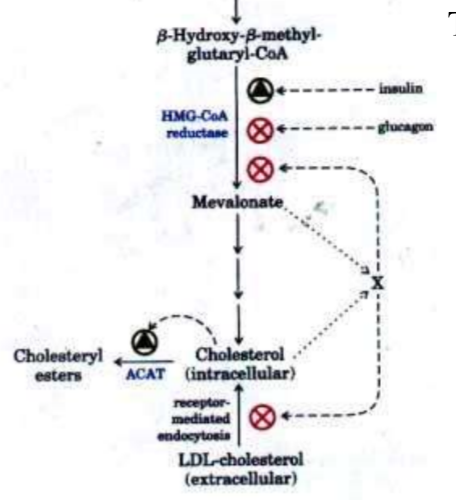
92
New cards
What is the full name for HMG CoA?
Beta hydroxy-beta methyl- glutaryl- CoA
93
New cards
What is the effect of uptaking cholsterol?
1. Inhibiting HMG CoA synthesis of new cholesterol
2. Activating acyl coa acyl transferase (ACAT)
3. Decreasing expression of LDL receptor
94
New cards
What are derivatives of cholesterol?
Bile, steroid hormones (glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, oestrogens, progestins)
95
New cards
Describe how dTTp can be derive from uracil and thymine
1. Uracil-thymine phosphoribosyl transferase (uracil → UMP)
2. Ribonucleotide reductase (UMP → dUMP)
3. Thymidylate synthase (dUMP to dTMP using methylene THF)
4. dTMP to dTTP using nucleotide diphosphate kinase
96
New cards
How is dTMP synthesisised from CDP and UDP?
1. Ribonucleotide reductase (CDP → dCDP)
2. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (dCDP → dCTP)
3. Deaminase (dCTp → dUTP)
4. dUTPase (dUTP → dUMP)
5. Thymidylate synthase (dUTP → dTMP)
6. dTMP kinase + nucleoside diphosphate kinase
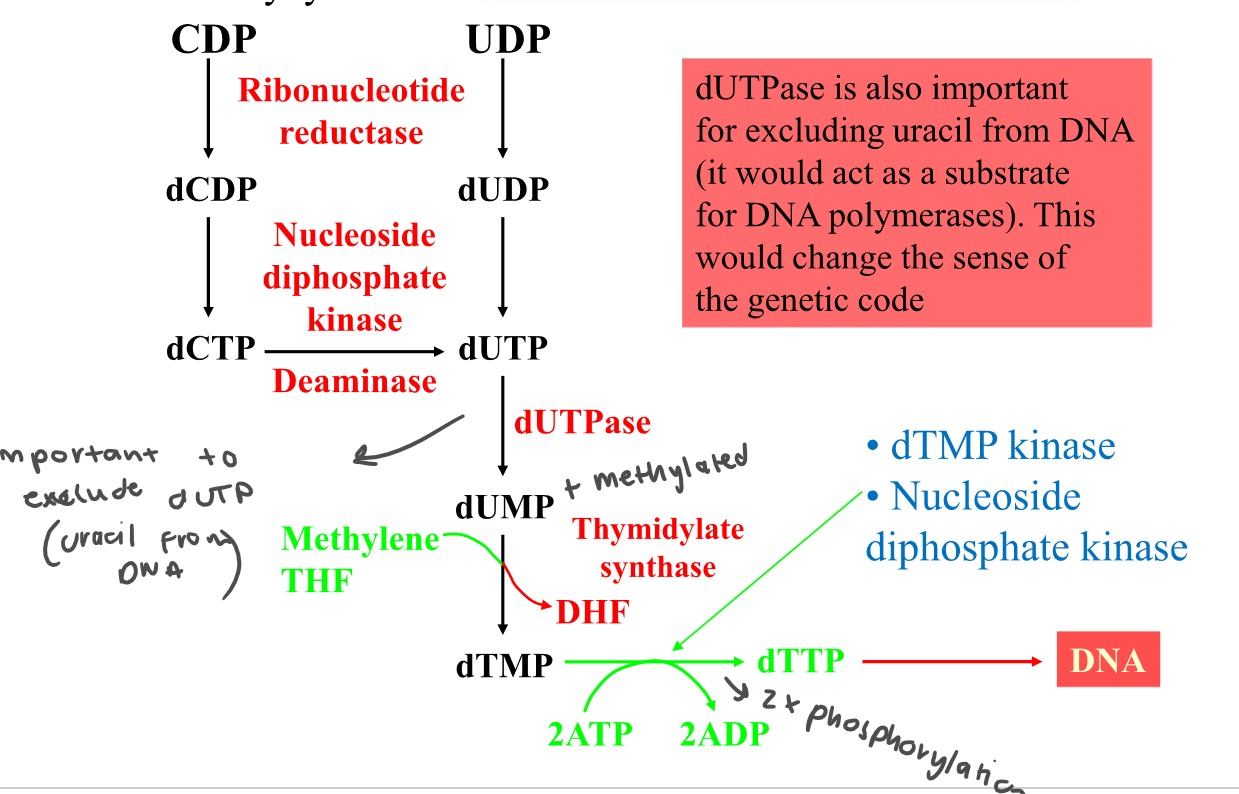
97
New cards
Why is dUTPase important?
Excluding uracil from DNA before it acts as a substrate for DNA polymerase
98
New cards
What are the precursors of TG synthesis?
Fatty acyl Coa and glycer**ol** 3 phosphate
* G3P can come from DHAP from glycolysis or from phosphorylation of glycerol (by glycerol kinase using ATP)
* G3P is → phosphatidic acid (using acyl transferase)
Phosphatidic acid is used in both phospholipid and TG synthesis
\
* G3P can come from DHAP from glycolysis or from phosphorylation of glycerol (by glycerol kinase using ATP)
* G3P is → phosphatidic acid (using acyl transferase)
Phosphatidic acid is used in both phospholipid and TG synthesis
\
99
New cards
How are TG made?
Phosphatidic acid → 1,2 diacylglycerol → triacycl glycerol (using phosphatidic acid phosphatase and acyl transferase)
100
New cards
What is the precursor for most human phospholipids?
Phosphatidic acid + CTP → CDP diacylglycerol (precursor for PS, PE, PG, PI and CL synthesis)