Unit 2 - Electricity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Electric Charge
Property of matter associated with electric force
Coulumb’s Law
Attractive force between two charged, static particles in a vacuum
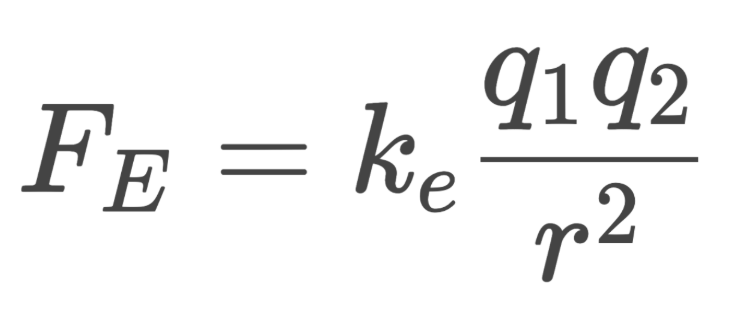
Field Forces
Long range electric force that act through space without physical contact
Field Model
The field is the agent that exerts a force on object
As field decreases
Distance increases
Positively Charged fields
Points outwards
Negatively Charged Fields
Points inwards
If q is positive
Force is with Fe
If q is negative
Force is against Fe
Electric Dipole
System of two equal and opposite charges that are close, separated at distance d (u=qd)
Field Lines
Continuous lines that depict dipole field vectors
Rules for Field Lines
Number of lines proportional to magnitude of electric field
Points in direction of electrical field vector at every point
Arrows go from positive to negative
Field lines are closer together when stronger
Lines DO NOT cross
Electric Field of a Charge Particle is
Independent of position and its magnitude proportional to surface charge density
Conductors only have
1 field from positive to negative
Plates are assumed
To be infinite because the edges aren’t constant
Capacitor
Stores electrical energy by building up charge on each plate, creating a positive and negative plate
Work happens when
Force is in the same direction as motion
Conservative Force
Work of force is independent of the path
Potential Energy is
Relative to something (Wconservative= -U)
If Potential energy is negative
Energy is needed to bring it to the reference point
If potential energy is positive
No energy is needed to get to reference point
As 2 same charged points are brought together,
Energy is needed to keep them there
As 2 opposite charged points are brought together
Energy is needed to keep them apart
What’s the Total Charge on an Electric Dipole?
0C
Work Equation
Fed = qEd
What way does a dipole moment point?
Negative to positive
Electric Potential
Property of space and a function of the position of the charge
Electric Potential at a point represents
Negative work by Fe
Equipotential Surface
All points have the same potential, doesn’t need electric work to move between points and always perpendicular to electric field
Electric Field Points in Direction of
Decreasing Potential
A positive charges slow down when it moves through
a positive V (Ek to PE)
A positive charge speeds up when it moves through
a negative V (PE to Ek)
Change in KE causes
Opposite change in U
Capacitance
Ability of object to store charge, defined by area and distance
Dielectrics
Insulator placed between capacitor to increase capacitance
Capacitor Energy equal to
Amount of work to separate the charge
Magnets
Material that makes magnetic field with north and south poles forming magnetic dipole
Permanent Magnet
Stays magnetized for a long time without ant help
The south pole of the Earth faces
North Pole
The north pole of the Earth faces
South pole
Ampere’s Law
Magnetic field of a straight conductor at a point is proportional to the current and inversely to distance from conductor
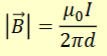
When 2 wires have current in the same direction
They will be attracted to each other
When 2 wires have current in the opposite direction
They will be repulsed by each other
Charges will only feel Fb if
Both charges are moving
North in loops of currents is
Where field emerges
South in loop of currents is
Where field re-enters
Solenoid
Long coiled wires to create helix with strong uniform magnetic field inside it
Cyclotron Motion
UCM from a charge entering a magnetic field with a velocity and Fb that acts as ac
Cyclotron Frequency and Period doesn’t depend on
Charge velocity
Aston’s Mass Spectrometer
Consists of ion source, velocity selector and mass selector
Ion Source
Hot filament ionizes molecules
Velocity Selector
Sorts molecules by velocity so that all particles that reach the mass selector has the same velocity
If molecule is too fast
Fb becomes stronger and goes up
If molecule is too slow
Fe becomes stronger and goes down
Mass Selector
Uses another magnetic field to create cyclotron motion to curve the and separate ions according to m:z ratio