quarter quiz 3 bio 107
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
All membranes contain
Phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates
Amphipathic
Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
Temperature and phophplipid membrane
Temp increases=increase fluidity(more permeable)
Temp decreases=decrease fluidity(more viscous)
Unsaturated fatty acids
More fluid, bends from double bonds increase freedom of movement
Sterols
Regulates fluidity (cholesterol in animal membranes)
Integral proteins
Pass through lipid bilayer, amphipathic
Peripheral proteins
Attached to the surface of the membrane, bind to phopholipid or integral proteins, H bonds or Ionic
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate attached to integral membrane protein,carbohydarte, used for cell to cell recognition(identify other cells)
Glycolipid
Carbohydrate attached to phospholipid, carbohydarte, used for cell to cell recognition(identify other cells)
Diffusion
Tendency of molecules to move down a concentration gradient
Concentration gradient
Move from high to low Concentration, releases energy
Simple diffusion
Small, or non polar molecules pass through bilayer
Facilitated diffusion
Aided by membrane proteins, no energy required, m9 event occurs with conc gradient
Channel proteins
Form hydrophilic channels that allow specific molecules to pass, aquaporins(water molecules) and ions
Carrier proteins
Change shape when specific molecules bind to carry them across memb, glucose
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, water can, solutes cant
Hypertonic
Contains higher solutions concentration
Hypotonic
Contains lower solute concentration
Isotonic
Equal solution concentrations
Concentration gradient for water
Always hypotonic to hypertonic
Cell in hypotonic
Bursts, swells, water moves in, except in organisms with a cell wall(turgid)
Cells in hypertonic
Water moves out, shrivels, except in organisms with cell wall(plasmolysis)
Active transport
Against concentration gradient, moving from low to high concentration, impermiability of membrane allows gradient to for, requires membrane proteins, and energy
Membrane potential
A separation of charges, creates voltage, due to concentration gradient of ions, negative on inside, positive on outside
Primary active transport
Requires transport protien, energy by ATP hydrolysis(causes a change in shape), creates membrane potentials(electrochemical gradient) , proton(H) pump, sodium-potassium pump
Secondary active transport
Uses an ion gradient for energy, transport of solutes is coupled to diffusion of ions, ion gradient created by primary transport that uses ATP as energy source.
Symport
Type of secondary active transport, the transport solution moves in the same direction of the gradient of the driving ion
Antiport
Type of second a ry active transport, the transported solution moves in the opposite direction from the gradient of the driving ion
Membrane vehicle
Small compartments in the cytoplasm
Exocytosis
Cell secretes proteins and other molecules by the fusion of the vehicle with the plasma membrane
Endocytosis
Cells take in materials by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane, has three different types
Phagocytosis, cell engulfs particles using pseuodopidia
Pinocytosys, cells engulf non specific extracelluoar fluid
Receptor mediated endocytosis, used for uptake of high concentration of specific molecule
Prokaryote
No nucleus, no rganelles, no internal memebrane
Eukaryote
Nucleus, organelles(membrane bound)
Bacterial cell structure
Contains cytoplasm which contains cytoplasm, contains ribosome, nucleoid contains DNA, one chromosome per cell
Bacterial chromosome
circular DNA molecule, protien condensed into histones, contains essential genes
Bacterial plasmid
Small circular peices of DNA found in the cytoplasm, not essential, provides cell with an advantage like antibiotic resistance
Eukaryotic cytoplasm
All cellular contents, between nucleus and cell membrane
Eukaryotic cytosol
The semi fluid portion of the cytoplasm, contains dissolved ions and molecules
Eukaryotic nucleous
Contains genetic material, site of DNA replication and transcription, directs all cell activity
Eukaryotic nuclear envelope
Doubles membrane enclosing the nucleous, covered in pores
Eukaryotic nuclear pores
Control movement of the molecules in And out of nucleous, protein complexes that pass through nuclear envelope
Eukaryotic nuclear lamina
Network of protein filaments, lines inside of nuclear envelope, supports shape of nucleous
Eukaryotic chromosomes
Contain Genetic info, DNA condensed by wrapping around histone proteins
Eukaryotic ribosomes
Synthesize proteins from amino acid monomers(ribosomal RNA, robsomal proteins)
Free ribosome, loose in cytoplasm
Bound ribosome, attached to outside of ER and nuclear envelope
Eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membrane tubules and sacs called cisternae, inside space called lumen, ER is continouse with nuclear envelope
Rough ER, civered in bound ribosomes, site of protien synthesis and protein modification
Smooth ER, no bound ribosome, no protiensynthesis, containsenzymes for lipid synthesis, and carbohydrate synthesis
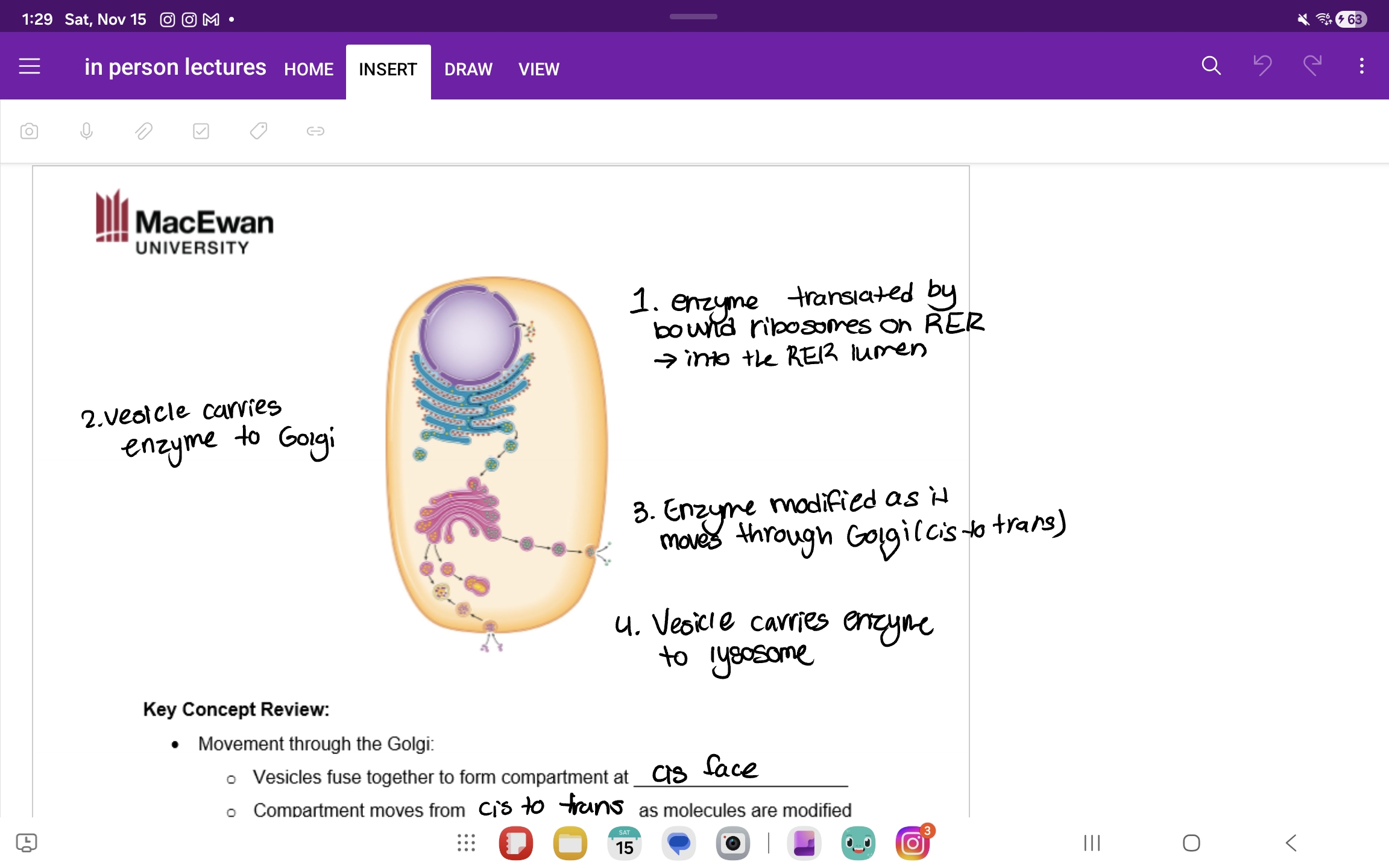
Eukaryotic Golgi complex
Receives material in the ER, modifies proteins and lipids, targets proteins to final destination, flattened sac of cisternae in stacks, two faces cis(recieves vesucles from ER) and trans(vesicles bud off and sent to other sites)
Eukaryotic lysosomes
Membrane bound sac containing hydrolytic enzymes(enzyems function best at acidic pH), catalysts hydrolysis reactions, phagocytosis,autophagy
Eukaryotic Vacoule
Food vacoule
Contractile vacoule(fresh water protistst to pump out water)
Central vacoules(plants, storage)
The endomembrane system
Eukaryotic mitochondria
Not participate of the endomembrane system, site of cellular respiration(makes ATP), double membrane
Eukaryotic chloroplasts
Not part of the endomembrane system, site of photosynthesis, three membranes(inner outer thylakoid), stomach contaisn enzymes ribosomes and DNA
Origins of endomembrane system
Infolding of cell membrane formed nuclear envelopes, ER, and other organlles
Endosymbiotic hypothesis
Small porkayotes(bacterium) was engulfed and began living within larger cell(archean)
Mutually beneficial relationship developed, and two cells began evolving together
Two organisms became dependent on eachother
Serial endosymbiosis
All eukaryotes have mitochondria but only plants have chloroplasts, endosymbiosis happened twice
Two stages
Aerobic respir8ng bacterium engulfed =mitochondria
Photosynthesis bacterium engulfed only by plant cells=chlorplasts
Evidence of this theory(replicate by binary fission,double membrane, own DNA and ribsosomes)
Eukaryotic cytoskeleton: microtubules
Hollow tubes, large(25 nm), made of turbulence protein, dynamic
Support cell shape
Anchor organlles
Provide pathways for oragnelle and vesicles movement
Separate chromosomes during mitosis
Form cilia and flagella in eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cytoskeleton: microfilaments
Two strands twisted around each other, small(7 nm), made of the protein actin, dynamic
Maintains cell shape-cortex, inside plasma membrane
Cell division-cytokinsis, last stage of cell division(cleavage furrow)
Reshaped the cell for phagocytosis and cell crawling
Cytoplasmic streaming
Anchors organlles and nucleous
Supports cell shape
Forms nuclear lamina
Forms desmosomes
Eukaryotic cytoskeleton: intermediate filaments
Thick coiled protein fibers, medium(8-12 nm), made of different protein depending on type(ex, keratin), not dynamic
Motor proteins
Drive movement of objects along cytoskeleton filaments, both micrtubules and microfilaments a t as tracks for the movement, hydrolyze ATP causes motor proteins to change shape = walk along filament
Eukaryotic Centrosome
Microtubule organizing center of the animal cell, made of two centrioles at right angles, centriol = 9 MT triplets in a ring
Eukaryotic cilia and flagella
Movement structure made of microtubules, 9+2 structure(9 doublets(connected by dynein) in a ring, 2 single MTs in center), filaments is anchored by cytoskeleton by the basal body(9 triplets of MTs in a ring) all inside the plasma memebrane
Cilia: shorter many per cells, moves like oars
Flagella:longer, one or few per cells, undulating like a snake
Cell walls
Found in bacteria and archea and many eukaryotes(just not animal), made of peptidoglycan
Protection against mechanical, chemical, and osmotic damage,
gives cell characteristic shape
Provide mechanical support for organism
Barrier ro the entry of large molecules
Protects from pathogens
Cell cell intercation
Peptidoglycan
Polysaccaride chains, NAG, NAM, makes up cell wall
Gram positive
Type of bacterial cell wall

Gram negative
Type of bacterial cell wall

Plasmodesmata
Channels through the plasma membrane and cell wall of adjacent plant cells, physically connect cytoplasm, allow passages ions water etc.
extracellular matrix
Found in animals, network of carbohydrates and proteins outside the cell membrane
Physical support
Adhesion
Communication
Made of collagen(protein), proteoglycan(sugar polymer), fibrinectin(protein), integrins(membrane proteins)
Bacterial capsule
Found in some bacteria, st8cky layer of polysaccaride outside cell wall,
Protects against dehydration
Virulence
Adhesion
Important in forming biofilm
Bacterial flagella
Used for cell movement, external to the cell in prokaryotes, different arrangements, madeof protien flagellin, powered by proton gradient.