alkaloids pt. 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Alkaloids
is commonly used to designate basic heterocyclic nitrogenous compounds of plant origin that are physiologically active
Alkaloids
alkali- like
Alkaloids
Rare in lower plants
Alkaloids
Dicots are more rich in__than Monocots
Apocynaceae
Rubiaceae
Solanaceae
Papaveraceae
FAMILIES RICH IN ALKALOIDS
Dogbane Family
Apocynaceae common name
Coffee Family, Bedstraw Family
Rubiaceae common name
Nightshades
Solanaceae common name
Poppy Family
Papaveraceae common name
Rosaceae
Labiatae
FAMILIES FREE IN ALKALOID
Rose Family
Rosaceae common name
Mint Family
Labiatae common name
Primary amines
R NH- 2
Secondary amines
R2 -NH
Tertiary amines
R3 -N
Norephedrine
Primary amines example
Ephedrine
Secondary amines example
Atropine
Tertiary amines
d-Tubocurarine
Quaternary ammonium salts example
basic
Saturated hexacyclic amines is more __ than aromatic amines
genus of the plant
plant species
common name
name of the discoverer
physiological action
prominent physical character
NOMENCLATURE
alcohol.
Both alkaloidal bases and their salts are soluble in
organic solvents , water
the bases are soluble in __and insoluble in __
soluble, sparingly soluble
Salts are usually__ in water and, ___ in organic solvents.
quinine monosulphate
Salts insoluble in water:
lobeline and apoatropine hydrochlorides soluble in chloroform
Salts soluble in organic solvents:
crystalline solids, few are amorphous.
Most of the alkaloids are (what characteristics)
coniine, nicotine, and sparteine
these few amorphous are which lack oxygen in their molecules, are liquids.
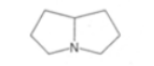
pyrrolidine, tropane, pyrrolizidine
alkaloid class of ornithine
ornithine
biosynthetic precursor of pyrrolidine and tropane, pyrrolizidine
pyrrolidine
tropane

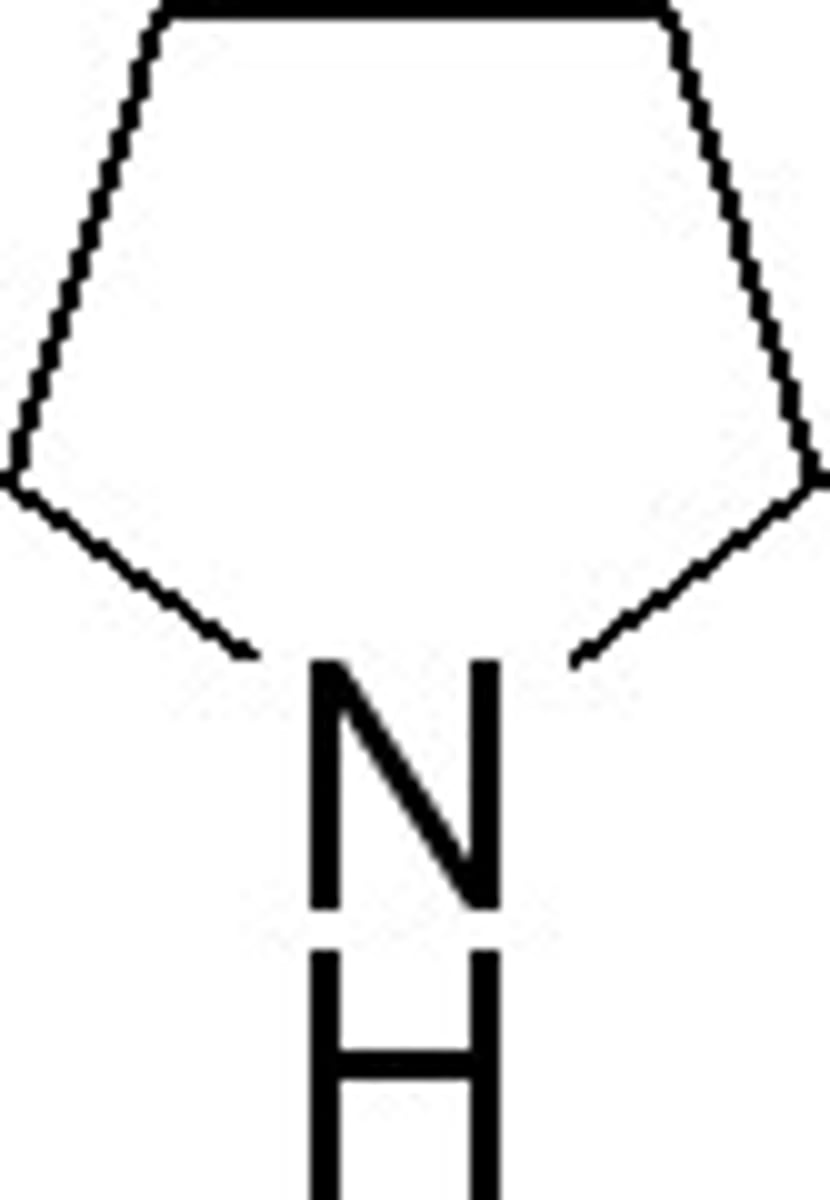
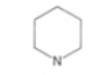
piperidine and quinolizidine
alkaloid class of lysine
lysine
biosynthetic precursor of piperidine and quinolizidine
acetate
other term for lysine
piperidine
pyrrolizidine
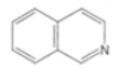
isoquinoline
alkaloid class of tyrosine
tyrosine
biosynthetic precursor of isoquinoline
isoquinoline
indole
alkaloid class of tryptophan
indole
biosynthetic precursor of tryptophan
indole
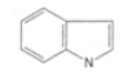
Pyridine and piperidine
Tropane
Quinoline
Isoquinoline
Indole
Imidazole
Purine
Steroidal
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON THE RING STRUCTURE OR NUCLEUS OF THE CHIEF ALKALOID GROUP IN THE PLANT DRUG
Phenylalanine,
Tyrosine,
Tryptophan,
Histidine,
Anthranilic Acid,
Lysine,
Ornithine
The amino acids that most often serve as alkaloidal precursors include
Pyridine
A tertiary base
Pyridine
Upon reduction it is converted into the secondary base, piperidine
piperidine
Pyridine: Upon reduction it is converted into the secondary base
lobeline
areca
nicotine
3 subgroups: Pyridine
lobeline from lobelia
derivatives of piperidine, including
arecoline hydrobromide from areca
derivatives of nicotinic acid, including
nicotine from tobacco
derivatives of both pyridine and pyrrolidine
Swiss chemist Trier
he proposed that nicotine was biosynthesized from nicotinic acid and proline.
Nicotine
is primarily a product of root metabolism, but the formation of small amounts
Nicotine
is bound to an ion exchange resin in a chewing gum base as a temporary aid to the cigarette smoker seeking to give up smoking
Nicorette
of nicotine replacement therapy that mimics the effects of smoking.
Areca, areca nut, or betel nut
other name of areca
Areca
is the dried, ripe seed of Areca catechu Linne
India
is a major producer of areca, but its production is mostly consumed domestically
Areca
is mixed with lime, the leaves of Piper betle Linne’
Areca
The mixture is used as a stimulant masticatory in India and the East Indies.
"punsupari.”
is a traditional Indian preparation that includes areca nut and betel leaf, commonly used as a form of chewing stimulant.
Taenicide
A type of drug used to treat infections caused by tapeworms.
Stimulant Masticatory
Nganga is consumed, why?
Arecoline
the most abundant and physiologically most active alkaloid, is a liquid.
arecaidine methyl ester
a derivative of arecoline, known for its stimulant properties and potential therapeutic effects.
Arecaidine
N-methyl guvacine
Guvacine
tetrahydronicotinic acid
Guvacoline
guvacine methyl ester
N-methyl guvacine
Arecaidine
tetrahydronicotinic acid
Guvacine
guvacine methyl ester
Guvacoline
0.45%.
The total alkaloid content of areca can reach
Areca
is classified as an anthelmintic in veterinary practice and is employed as a vermicide and taenifuge.
2 to 4 g, 4 to 8 g
he usual dose in dogs is ; in sheep, , based on the weight of the animal
Lobelia or Indian Tobacco
Consists of the dried leaves and tops of Lobelia inflata Linne’
1785, 1807
Lobelia or Indian Tobacco: Its emetic properties were first observed in , and the drug was introduced into medicine in _
Emetic Property
The ability of a substance to induce vomiting; often used in medicine to clear the stomach.
Emetic Property
pharmacologic activity of lobeline
nicotine
destroys acetylcholine that the body produces
lobeline
replaces nicotine at the neural receptor sites
acetylcholine
its supply is replenished, without withdrawals