cells - MCAT
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credit to khan academy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Describe the function of cholesterol in animal cell membranes.
Acts as buffer for fluidity
At high temperatures, membrane tends to become more fluid; cholesterol helps maintain rigidity
At low temperatures, membrane tends to become more rigid; cholesterol helps maintain fluidity
Why is the assembly of a cell membrane from free phospholipids spontaneous?
Free phospholipids are surrounded by water in an orderly fashion
When they assemble into a bilayer, it disturbs that orderly arrangement, increasing entropy which increases thermodynamic favorability of the process
What is the function of saturated and unsaturated fatty acid tails in the phospholipid bilayer?
Saturated fatty acids allow for tight packing, increasing membrane rigidity/integrity and conferring heat resistance
Unsaturated fatty acids prevent tight packing, increasing membrane fluidity and conferring freeze resistance
Define and compare: Simple diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, Primary active transport, Secondary active transport
Simple diffusion = movement of small nonpolar molecules along concentration gradients
Facilitated diffusion = movement of polar molecules and ions along concentration gradients using channels
Primary active transport = movement of ions against concentration gradient using ATPase pump
Secondary active transport = movement of molecule with positive ion against concentration gradient (created by primary active transport)
3 types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis for undissolved molecules
Pinocytosis for dissolved solutes
Receptor-mediated endocytosis for engulfing ligand + receptor
Phagocytosis
endocytosis of undissolved / insoluble molecules
1) contact made and surface receptors bind
2) pseudopods reach around and enclose food in membrane → phagosome
3) phagosome + lysosome = phagolysosome → acid digestion
3 main cell-cell connections
Desmosomes = sticky webs → impermeable connections with space between cells
Tight junctions = cell membranes connected into impermeable barrier
Gap junctions = tubes that hold cells together

Plasmodesmata
Gap junctions for plants
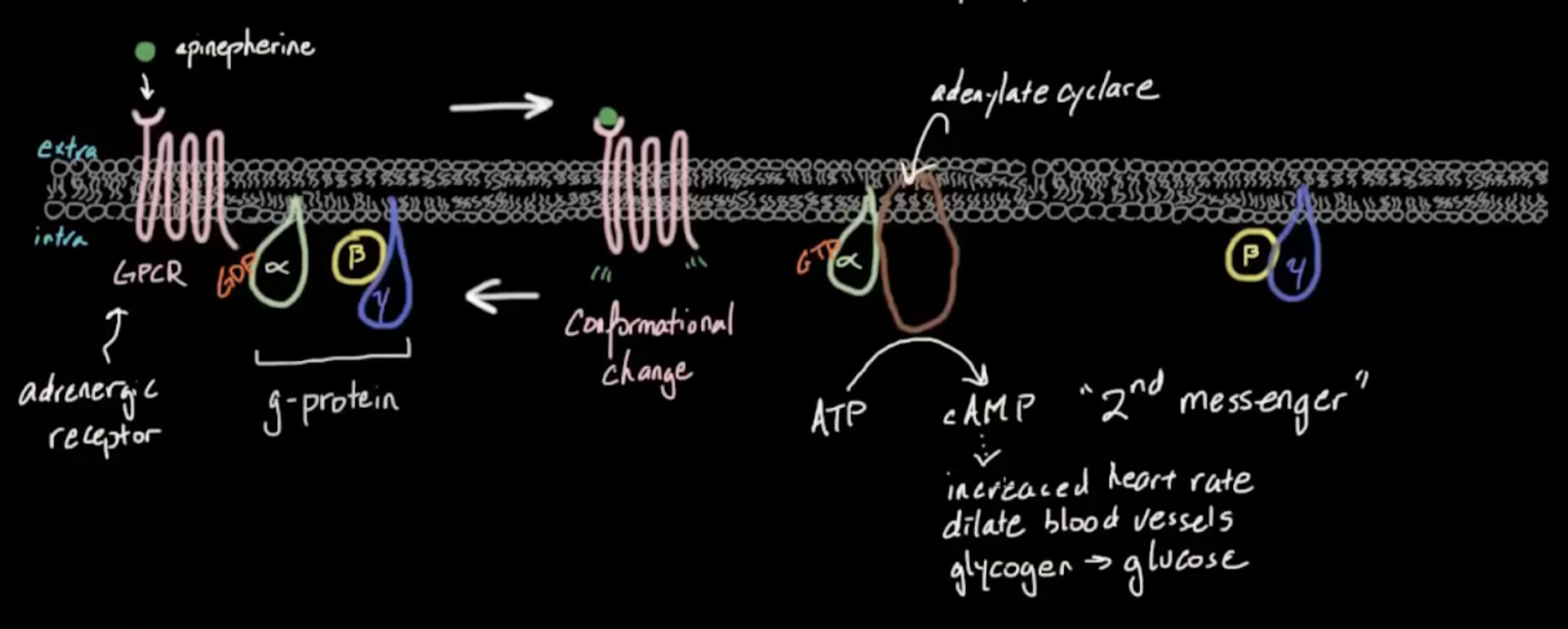
What is a G-protein coupled receptor, and how does it work?
Receptor protein with 7 transmembrane alpha helices
Start with receptor bound to G-protein’s alpha subunit bound to GDP
Ligand binds → conformational change → G-protein alpha subunit swaps GDP for GTP and detaches
G-protein & GTP go phosphorylate adenylate cyclase
activated Adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP, a secondary messenger which relays signal to cellular machinery
When G-protein hydrolyzes GTP back to GDP it reassociates into inactive trimer and interacts with GPCR to release ligand
What is a receptor tyrosine kinase, and how does it work?
Enzyme-linked receptor that binds growth hormones
Ligand binds → 2 RTKs cross-link and dimerize → tyrosine residues get phosphorylated by the other RTK → phosphorylated tyrosines serve as binding sites for signaling proteins (help shi phosphorylate and activate each other i guess)
Give roles of these organelles:
Nucleus, Mitochondria, Rough ER, Smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, Lysosome, Peroxisome
Nucleus contains DNA
Mitochondria does cellular respiration to produce ATP
Rough ER makes proteins, especially for export
Smooth ER produces lipids and does detox
Golgi apparatus modifies & ships proteins
Lysosome breaks down proteins
Peroxisome breaks down lipids & contains oxidative enzymes
What are the 3 main components of the cytoskeleton? What are their component materials and characteristic functions?
Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments, Microtubules
Microfilaments: made of actin, do cytokinesis, phagocytosis and muscle contraction
Intermediate filaments: material depends on cell (eg. keratin, lamin, desmin). Mostly provide structural integrity, but also help w/ cell migration & subcellular organization
Gram-positive vs. Gram-negative bacteria
Thick peptidoglycan cell wall vs. Thin peptidoglycan cell wall and outer membrane w/ lipoproteins & polysaccharides
Binary fission vs. Mitosis
Binary fission does not involve mitotic spindle, binary fission has DNA duplicate during replication instead of before
4 methods of prokaryotic genetic variation
transformation, conjugation, transduction, transposable elements
Describe and name the 2 ‘processes’ that prevent our body’s stem cell supplies from being depleted.
Obligate asymmetric division = stem cells divide to produce 1 differentiated cell and 1 ‘replacement’ stem cell
Stochastic differentiation = when a stem cell divides to produce 2 differentiated cells, a neighboring stem cell takes notice and divides to produce 2 ‘replacement’ stem cells