Chapter 13: The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
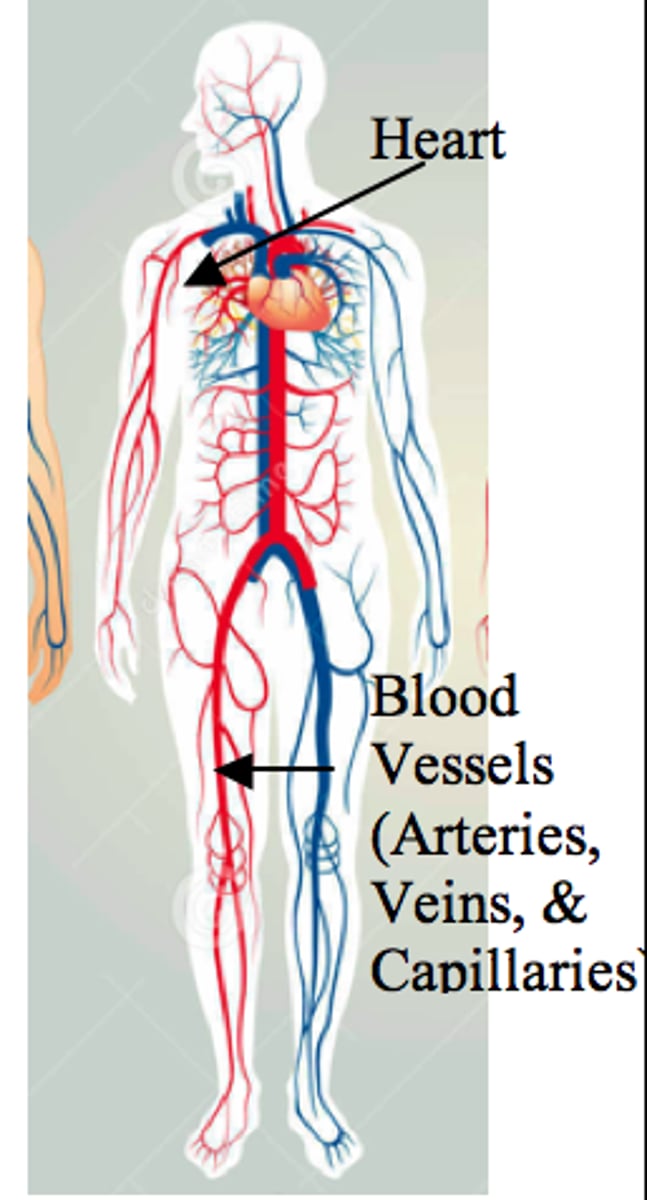
cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
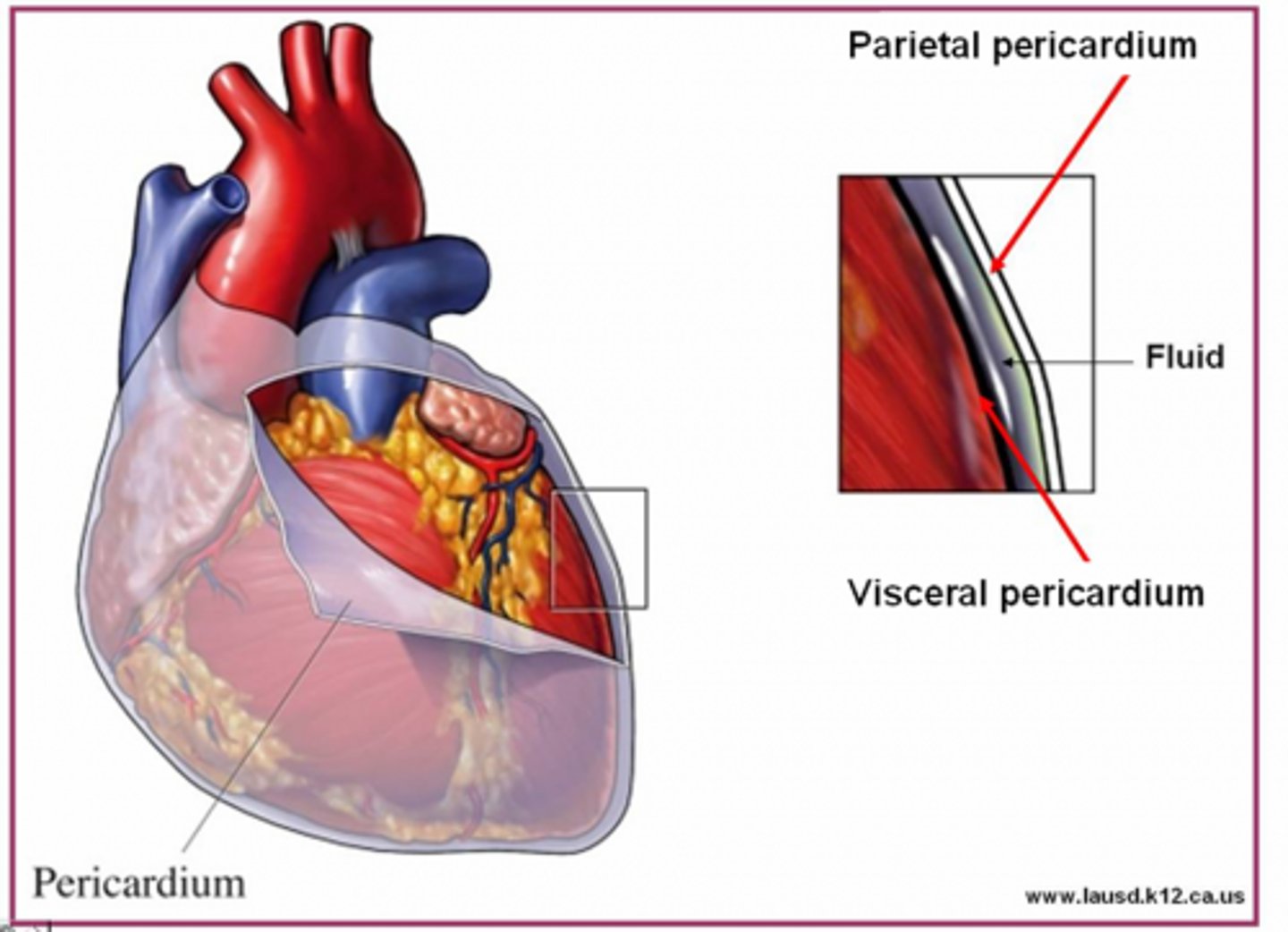
pericardium
Double-layered membrane surrounding the heart.
epicardium
outermost layer of the heart
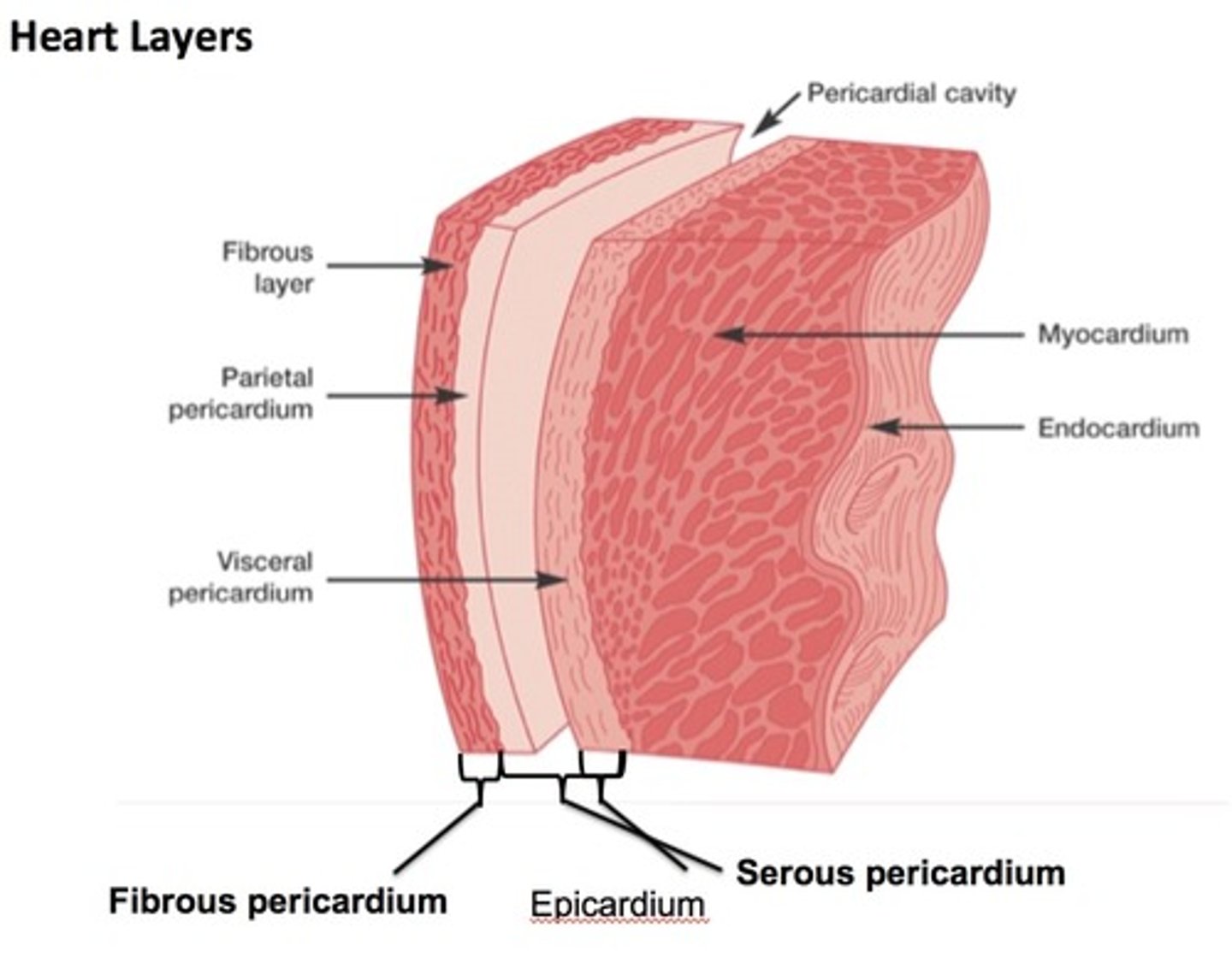
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
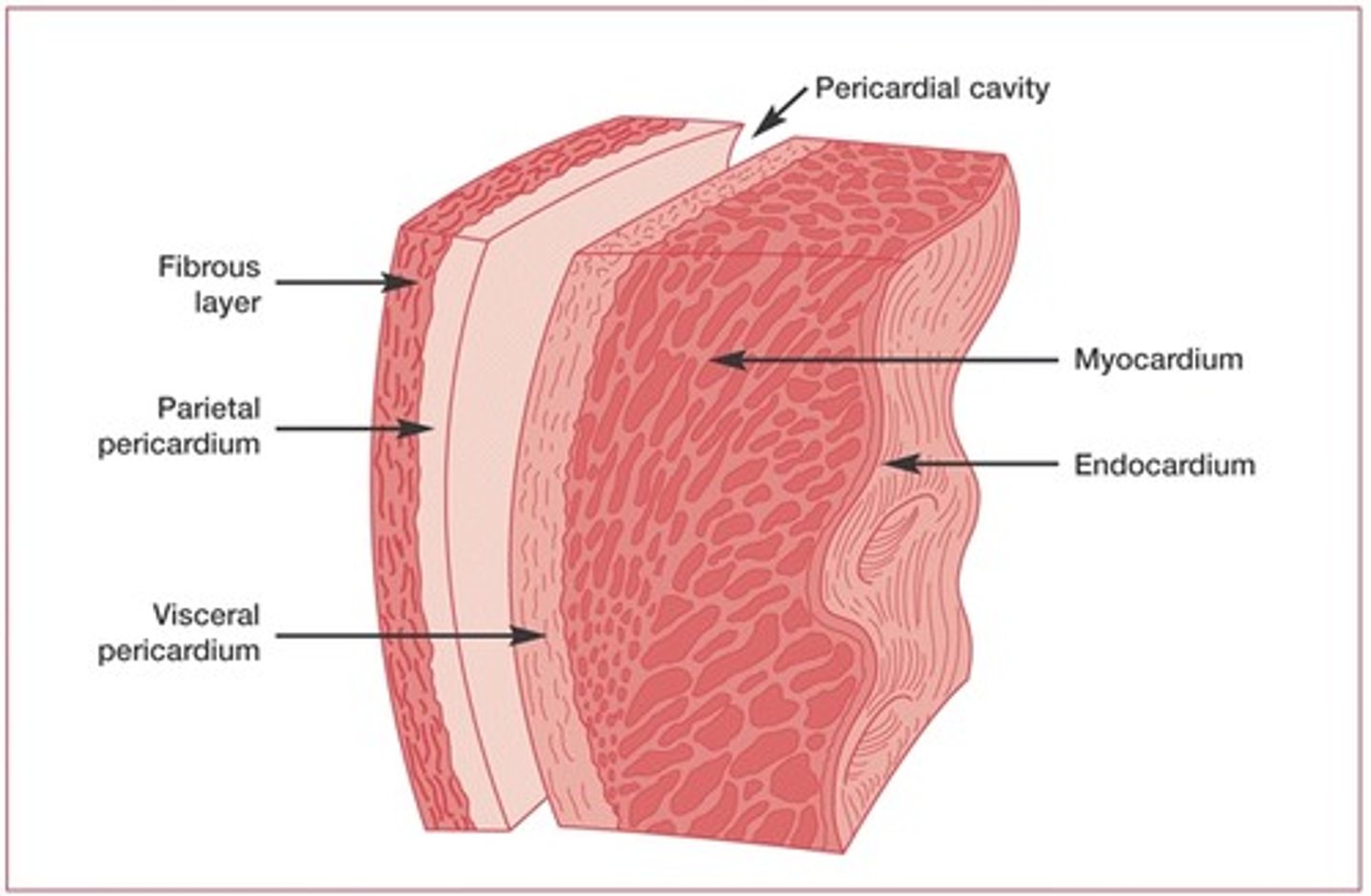
endocardium
inner lining of the heart
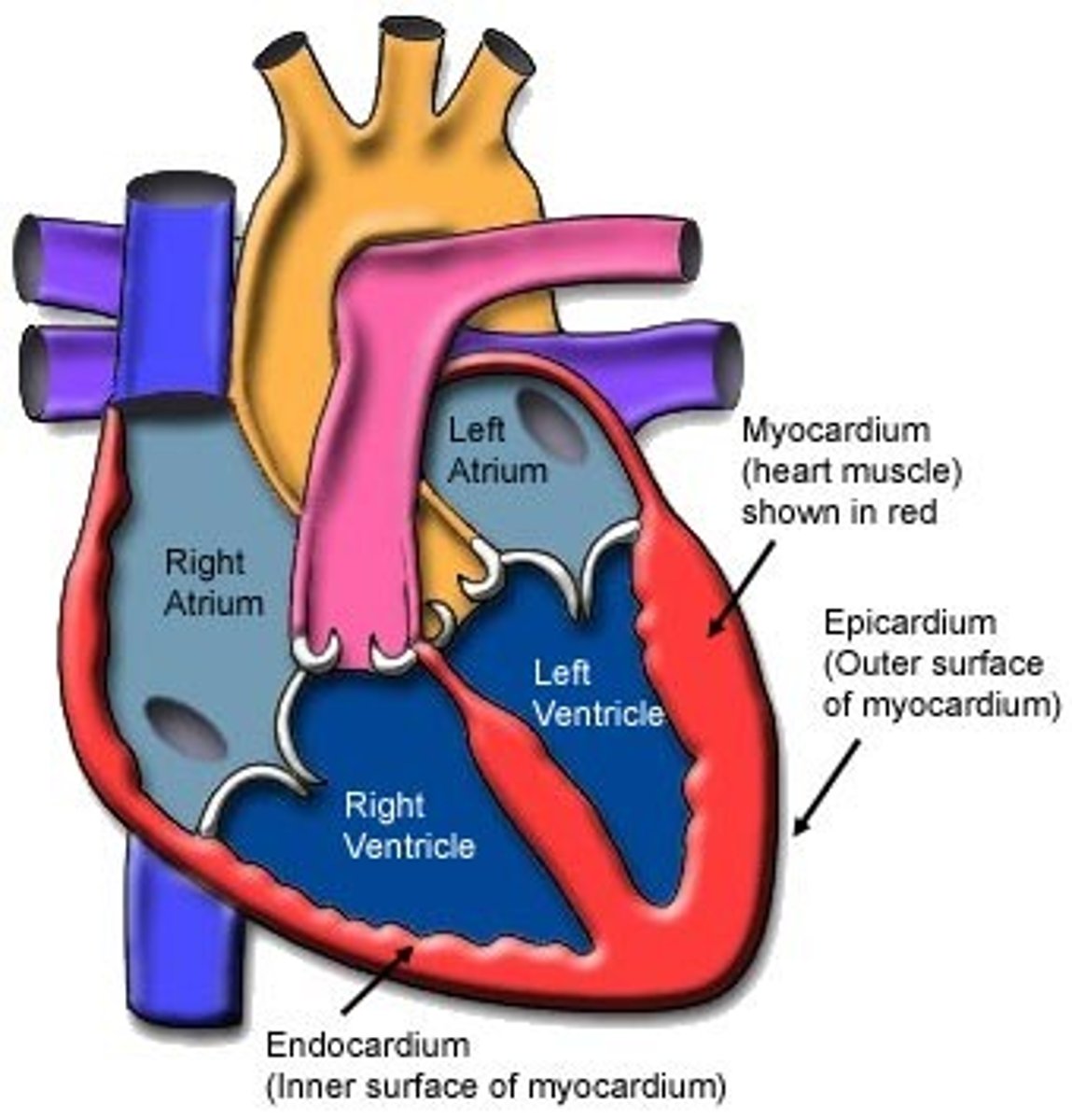
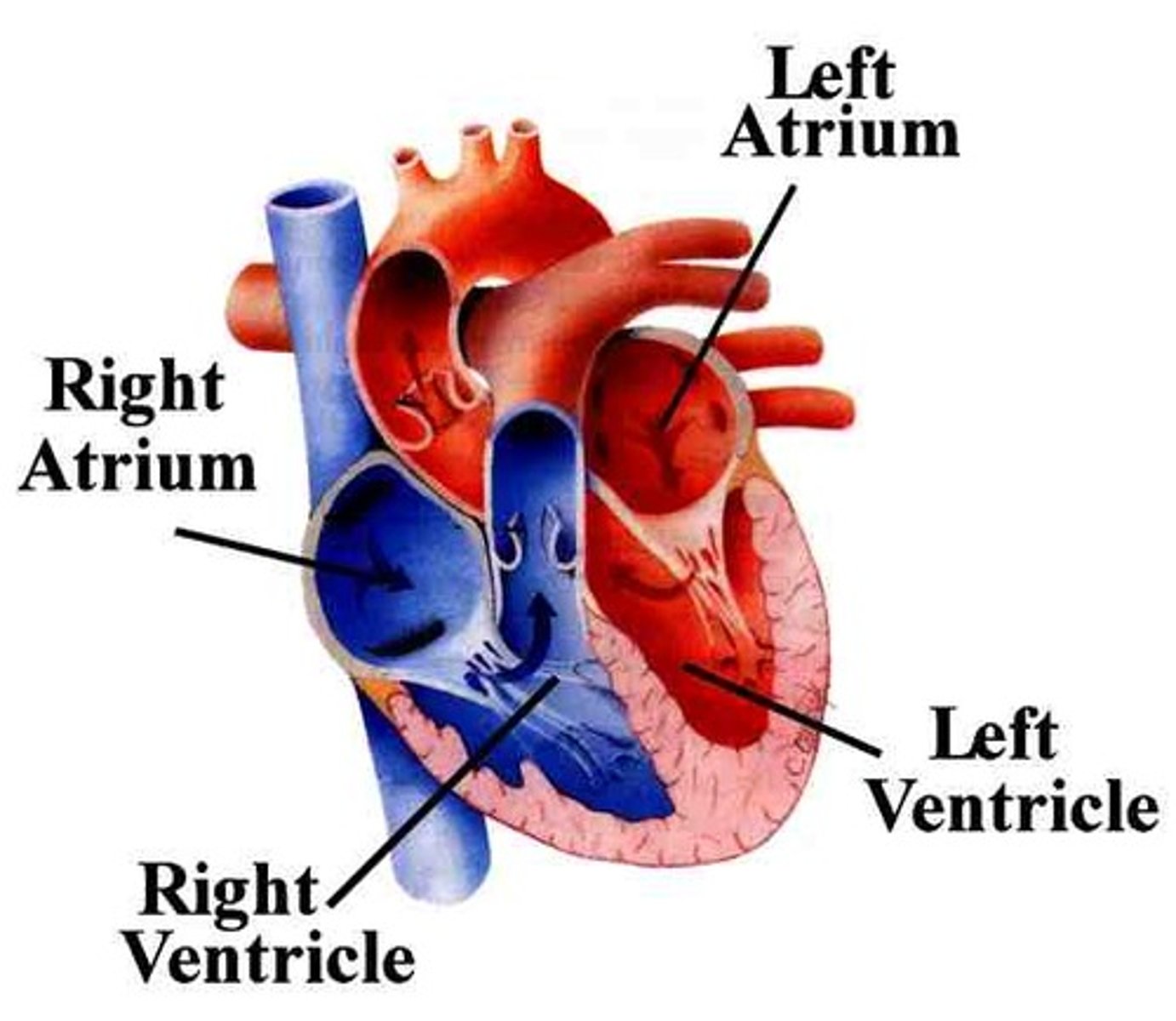
atrium
Each of the two upper chambers of the heart that receives blood that comes into the heart
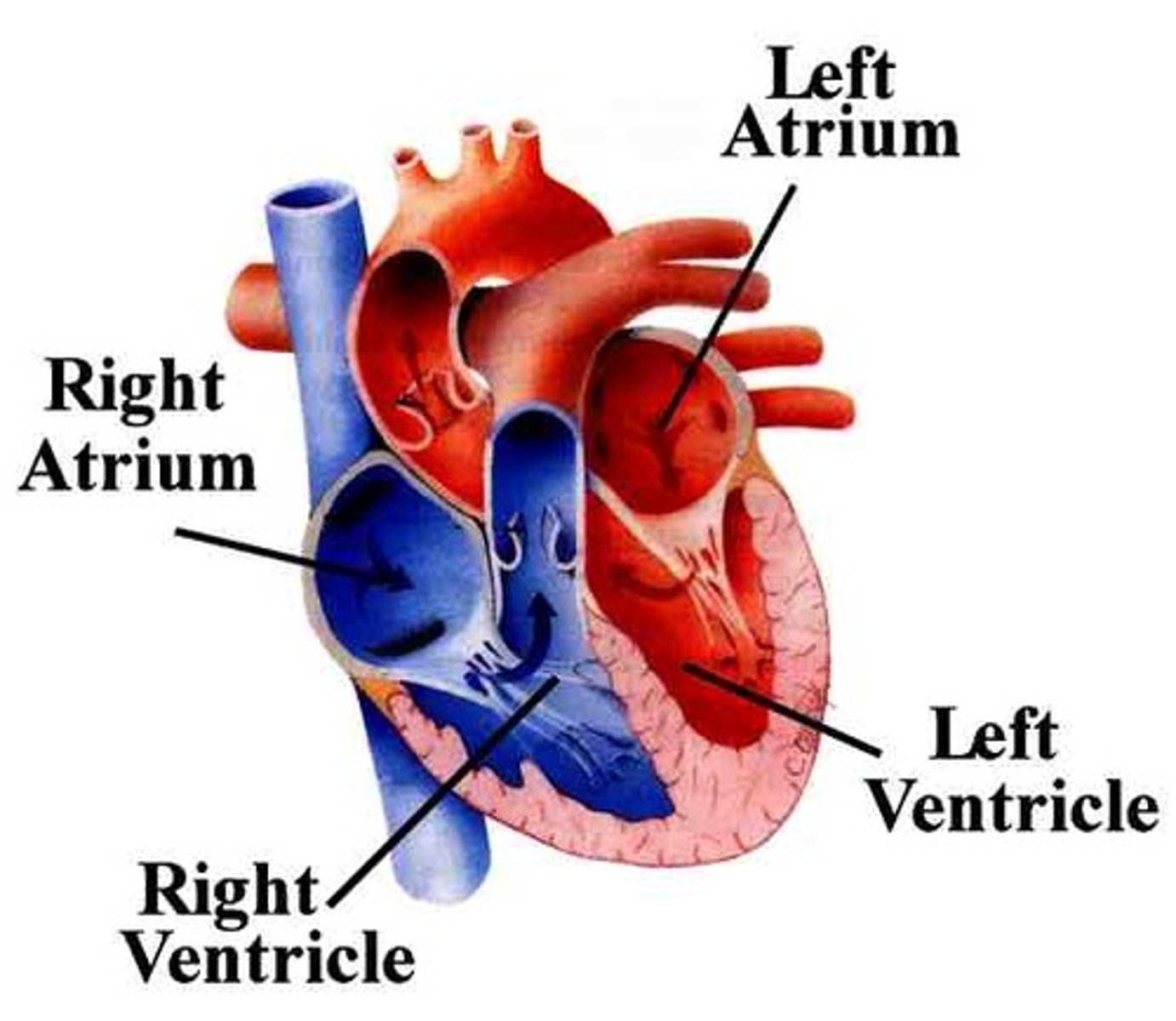
ventricle
one of two lower chambers of the heart
atrioventricular (AV) valves
Valves located between the atrial and ventricular chambers on each side of the heart, prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles are contracting.
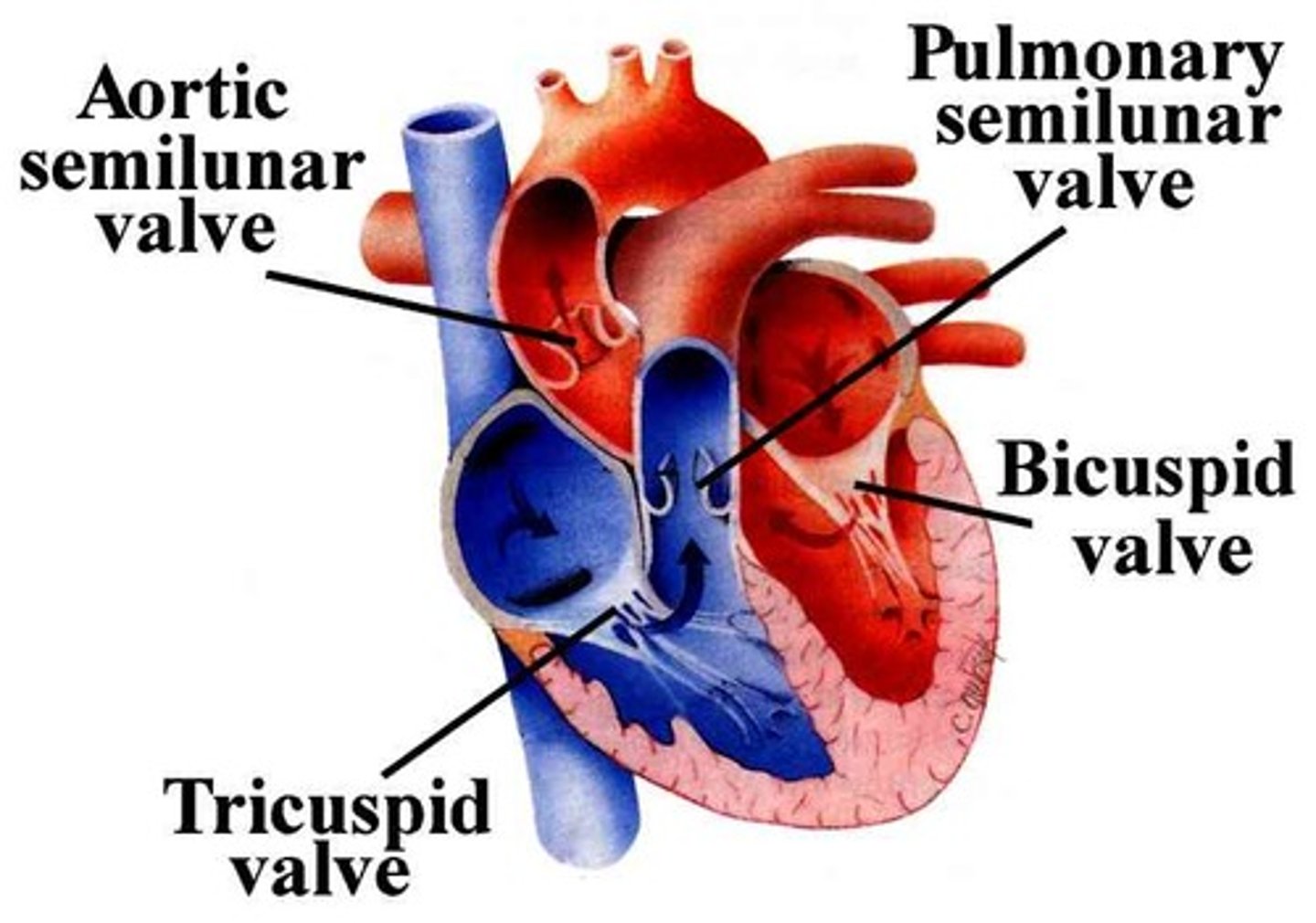
semilunar valves
pulmonary and aortic valves located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and between the left ventricle and the aorta
interventricular septum
partition between the right and left ventricles
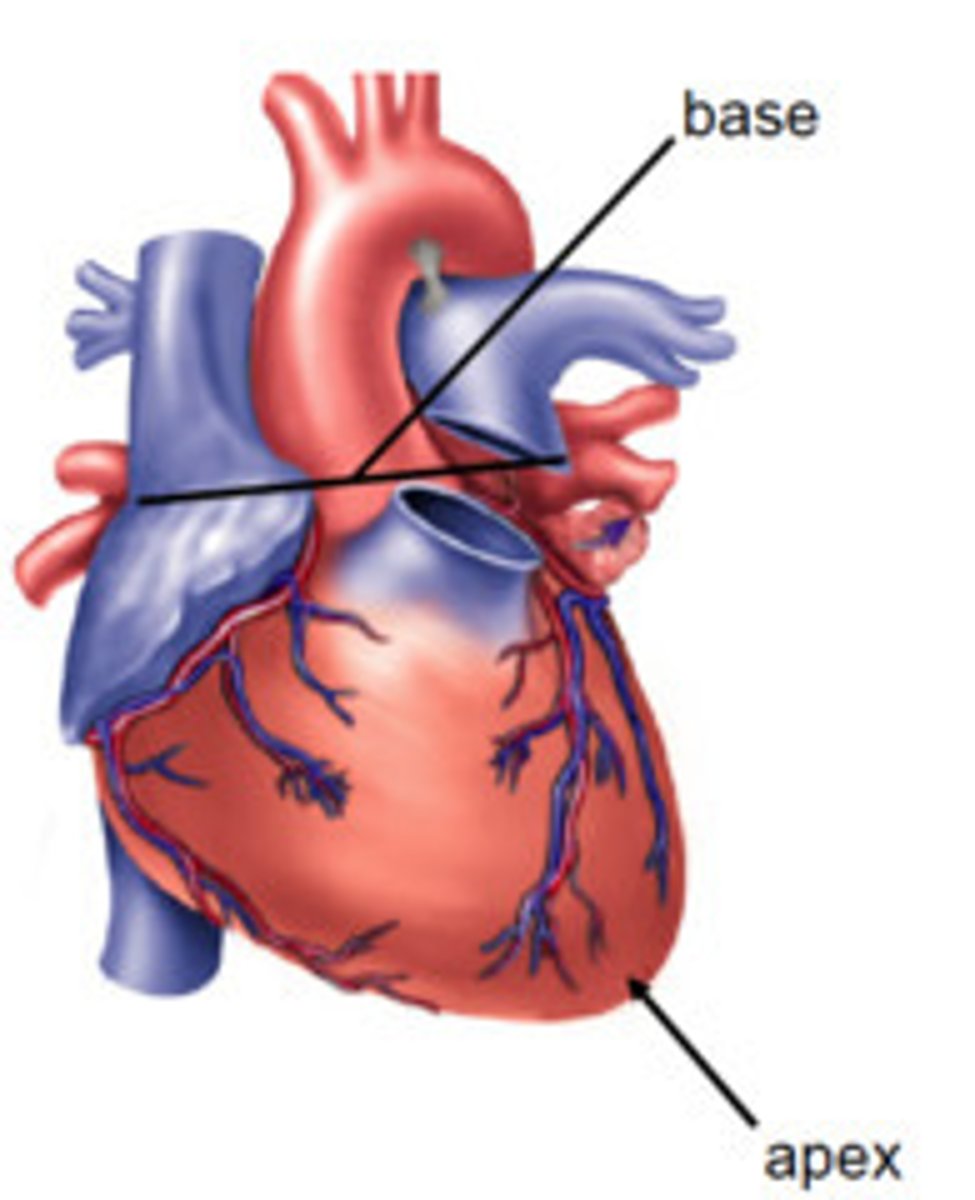
base of heart
the posterior part of the heart formed by both atria, but mainly the left
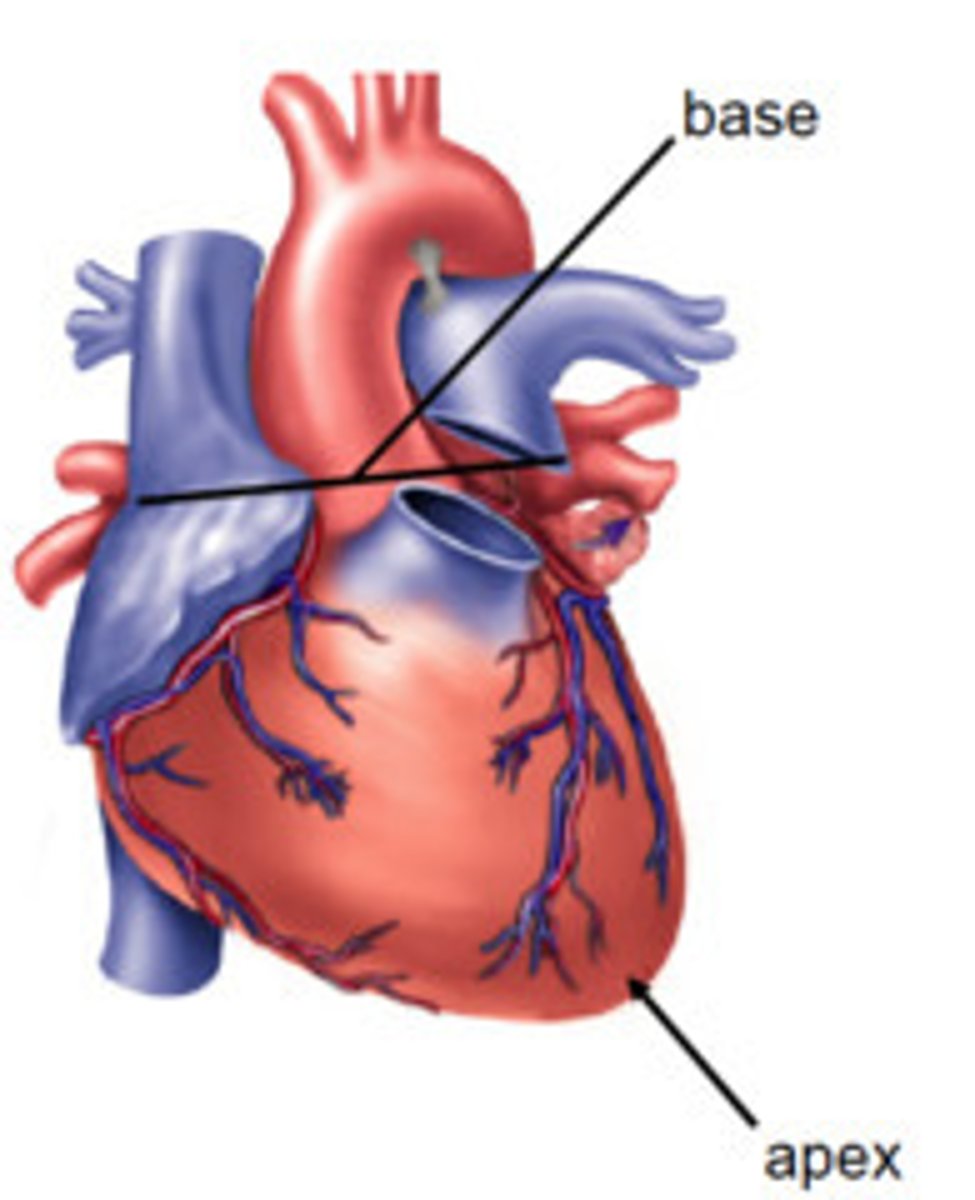
apex of the heart
tip of the heart pointing down toward the 5th left intercostal space
artery
A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
capillary
A tiny blood vessel where substances are exchanged between the blood and the body cells.
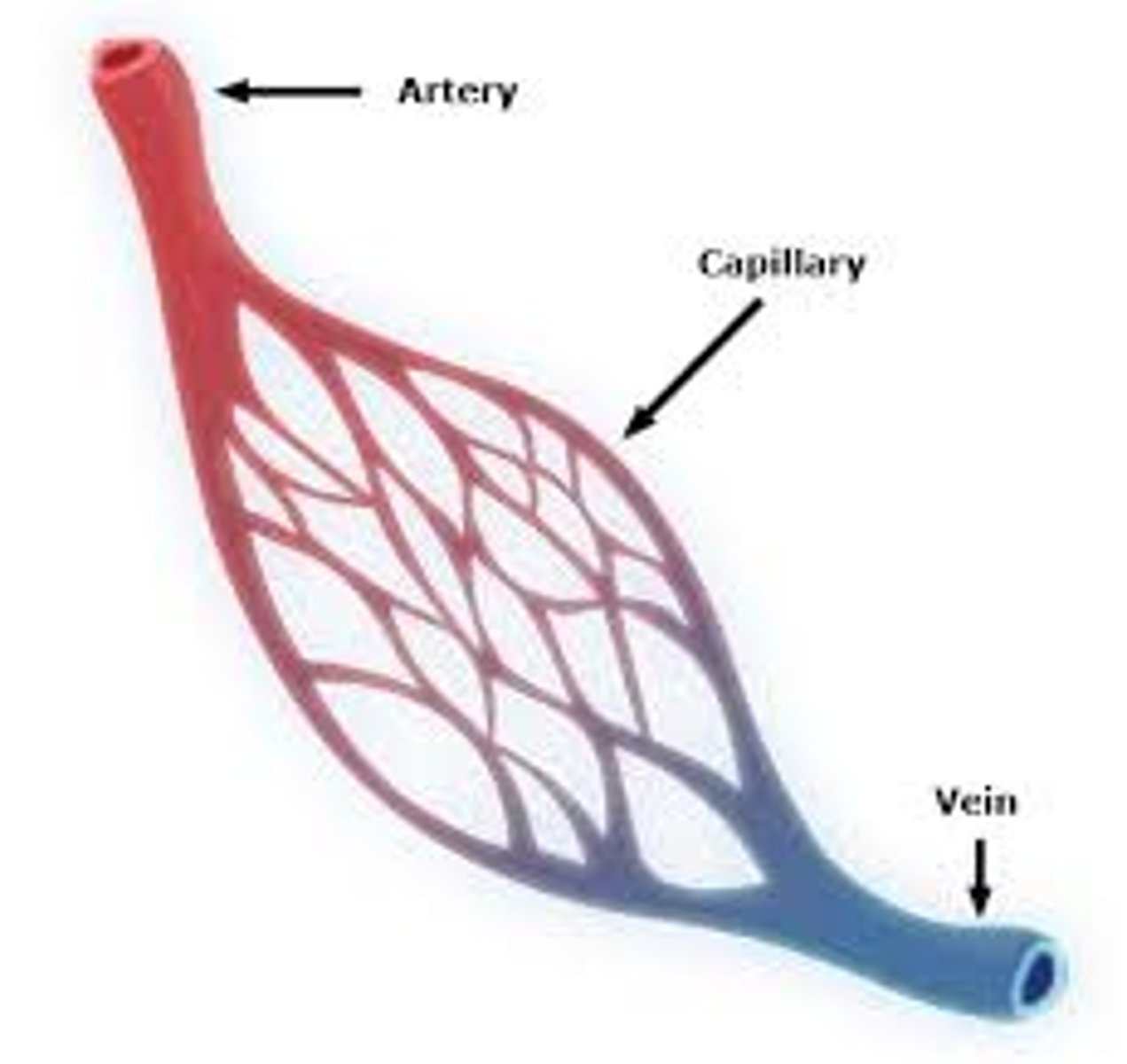
vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart.
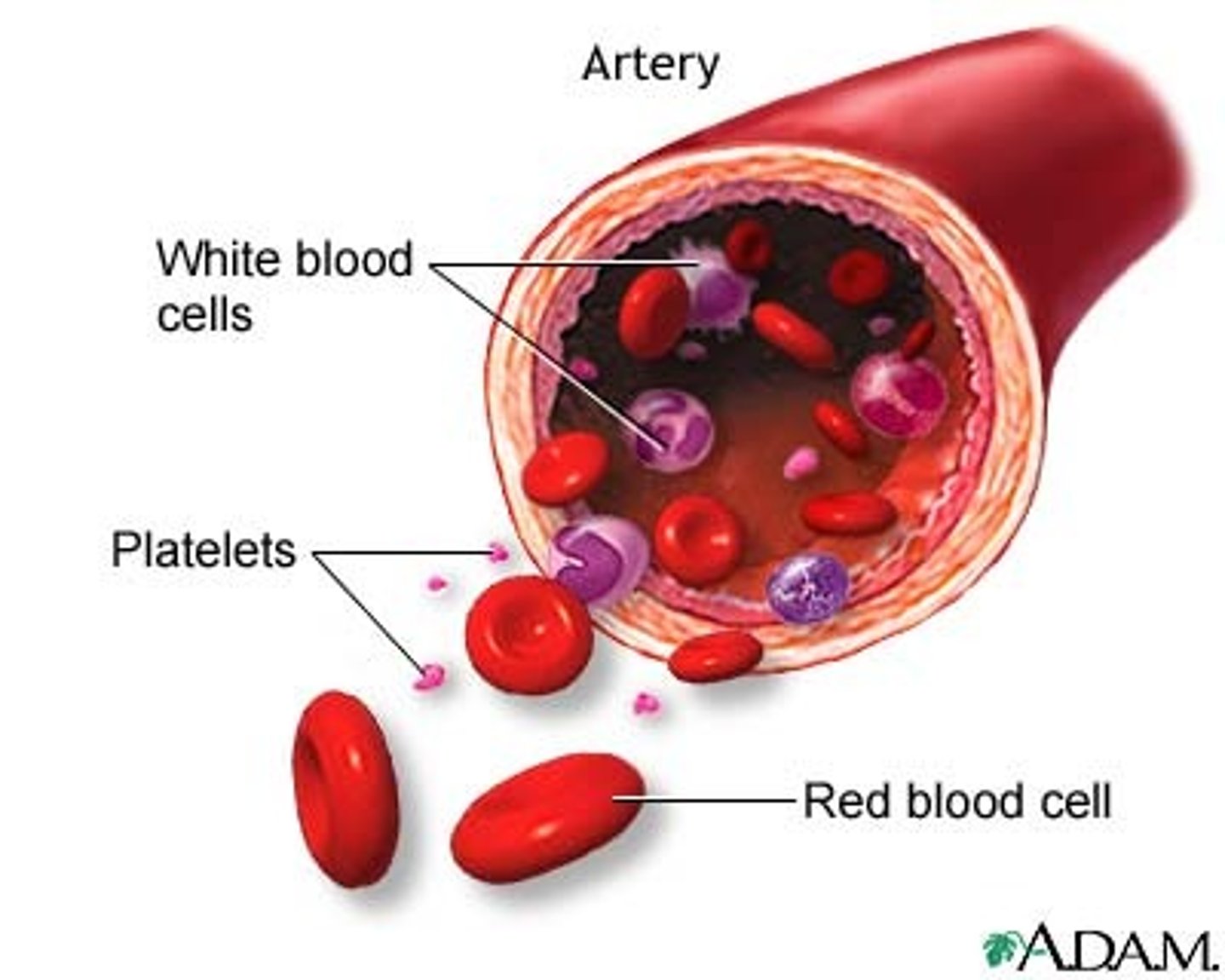
erythrocytes
another name for red blood cells
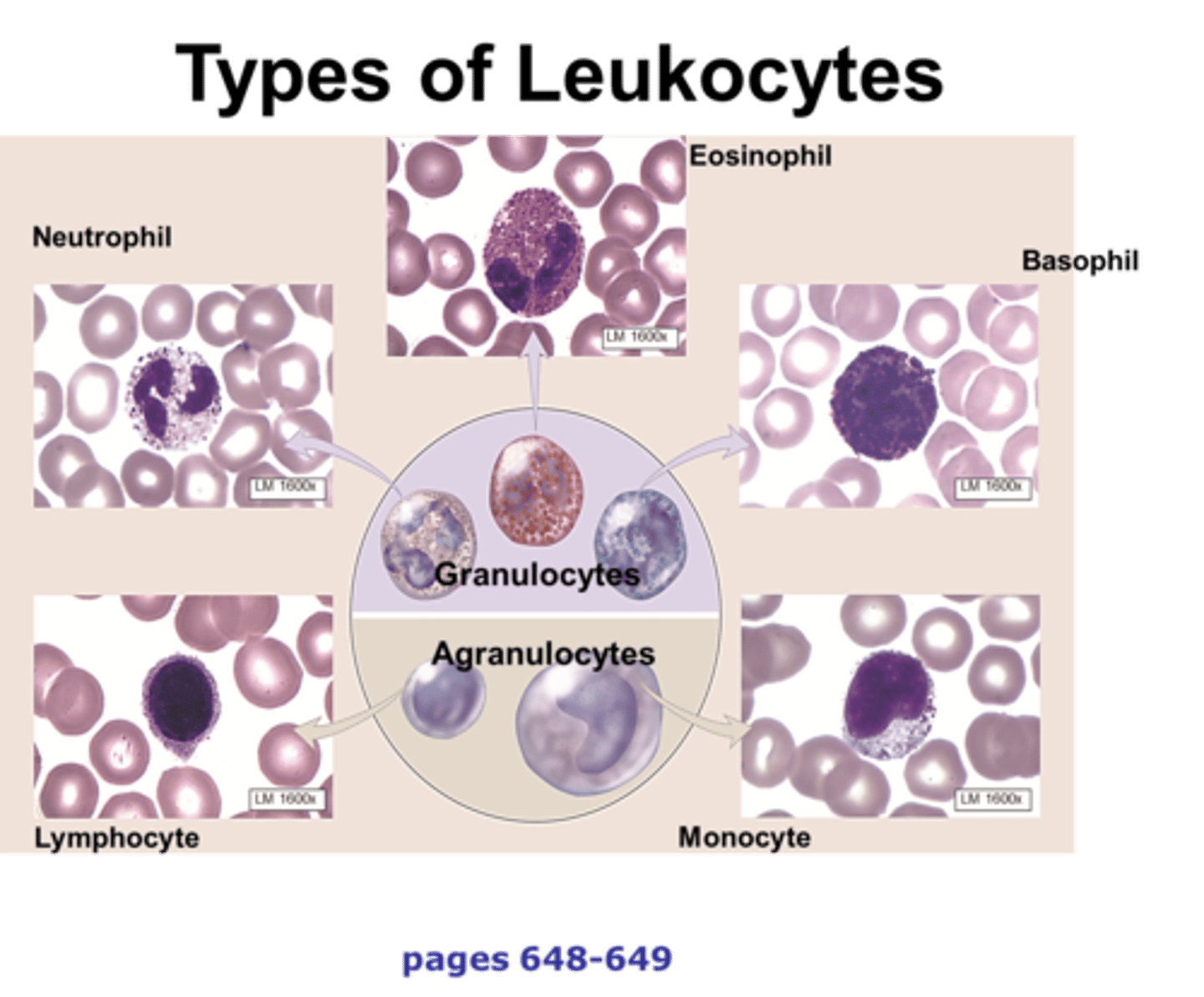
leukocytes
another name for white blood cells
platelets
a small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting
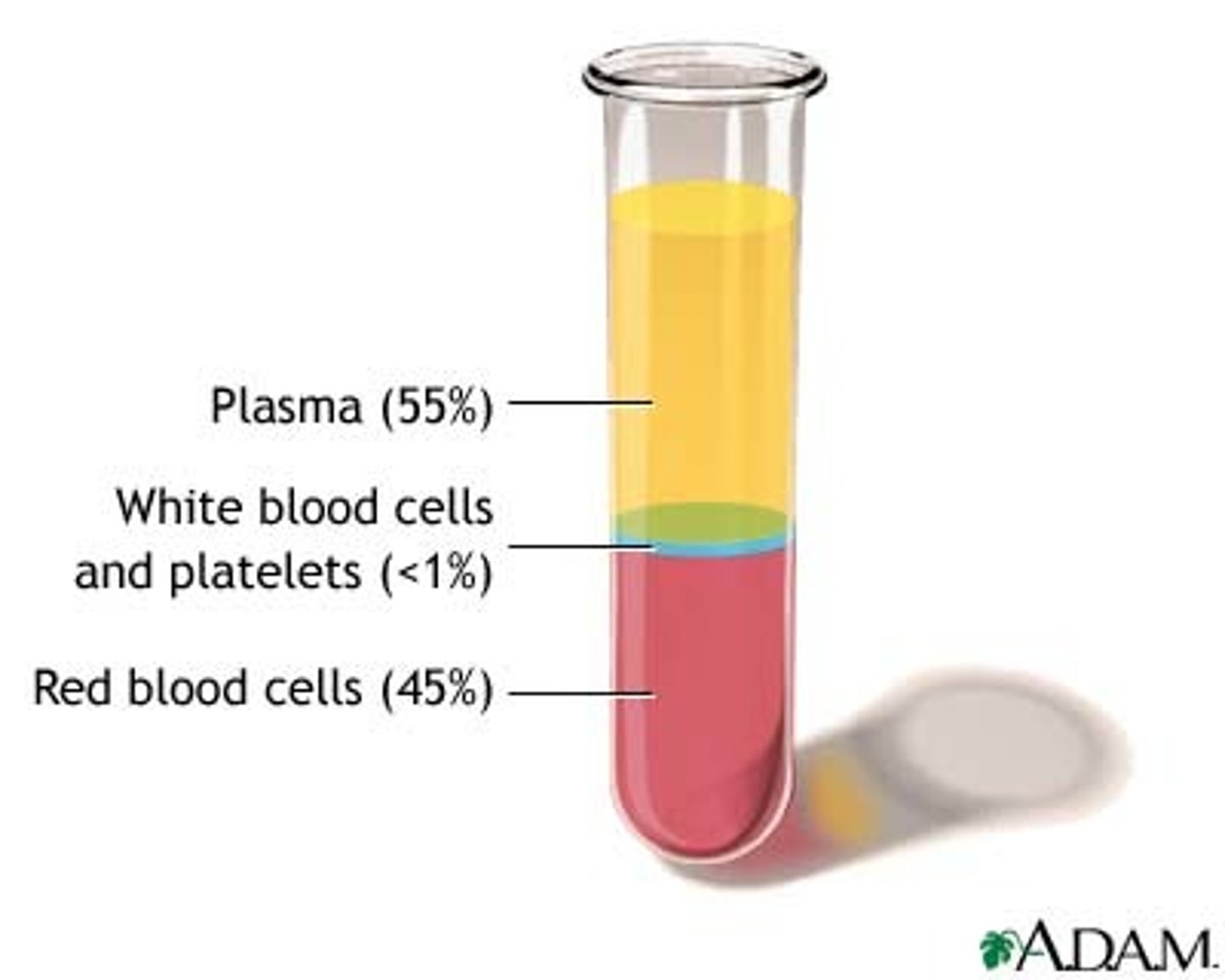
plasma
liquid portion of blood
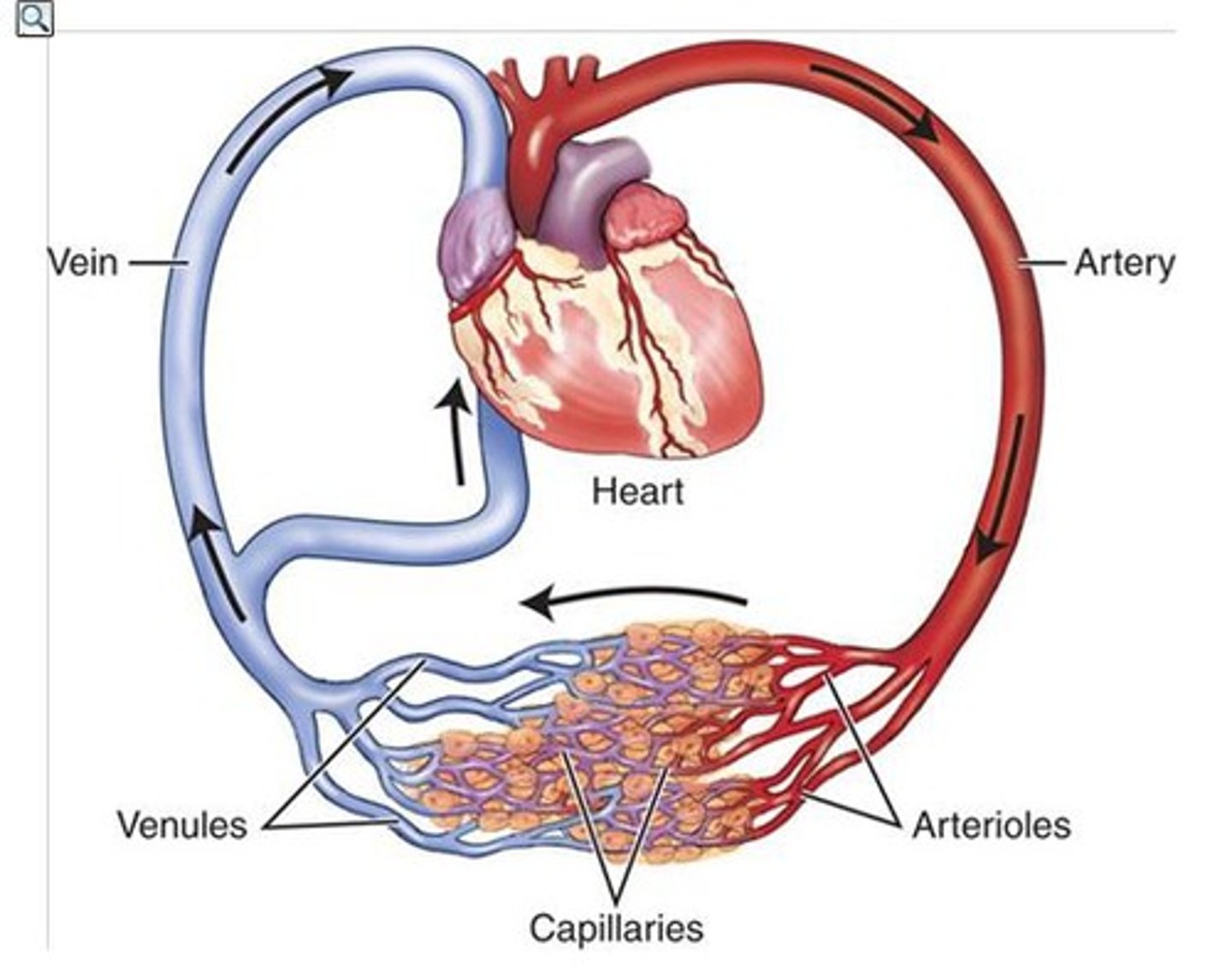
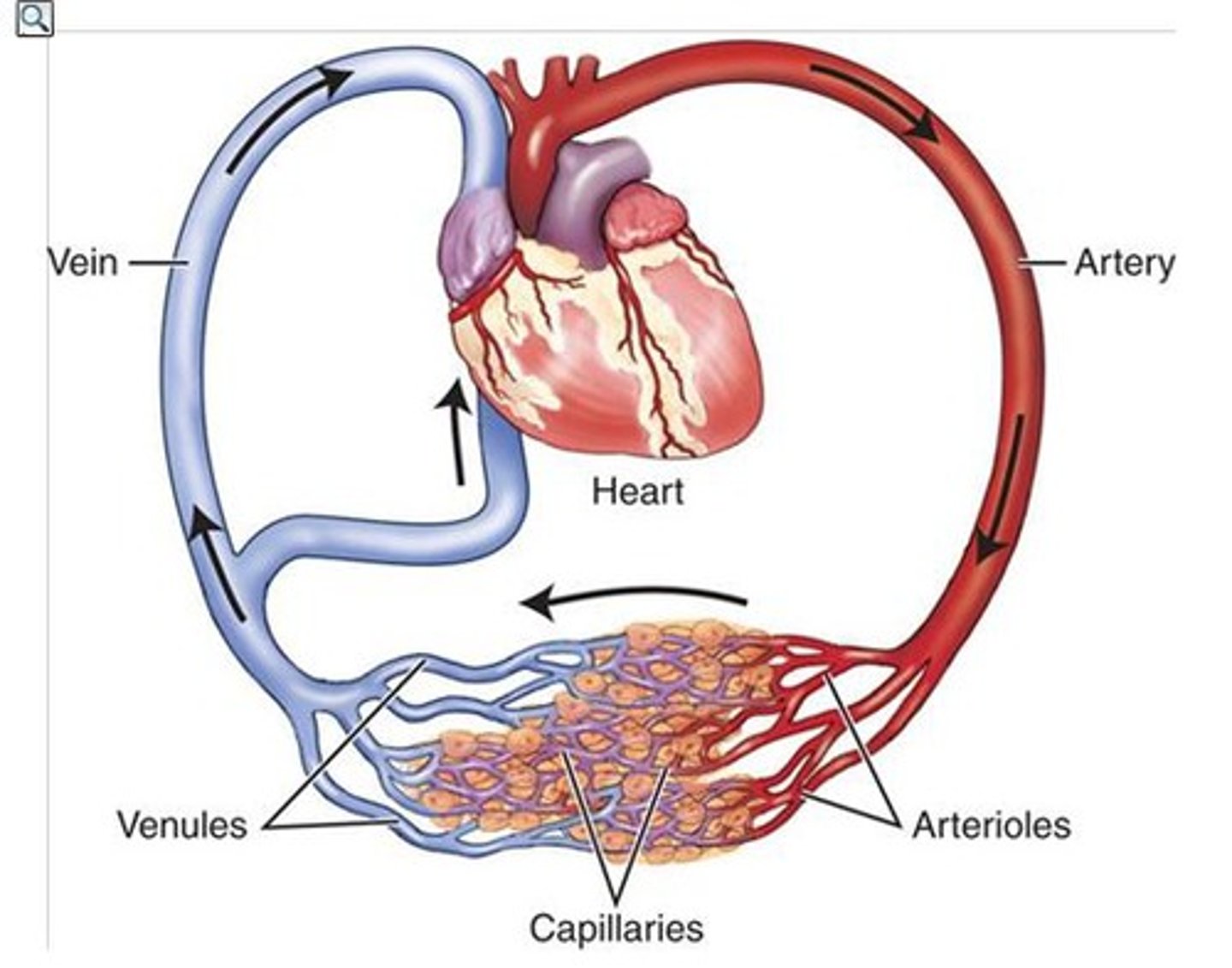
pulmonary circuit
system of blood vessels that carries blood between the heart and the lungs
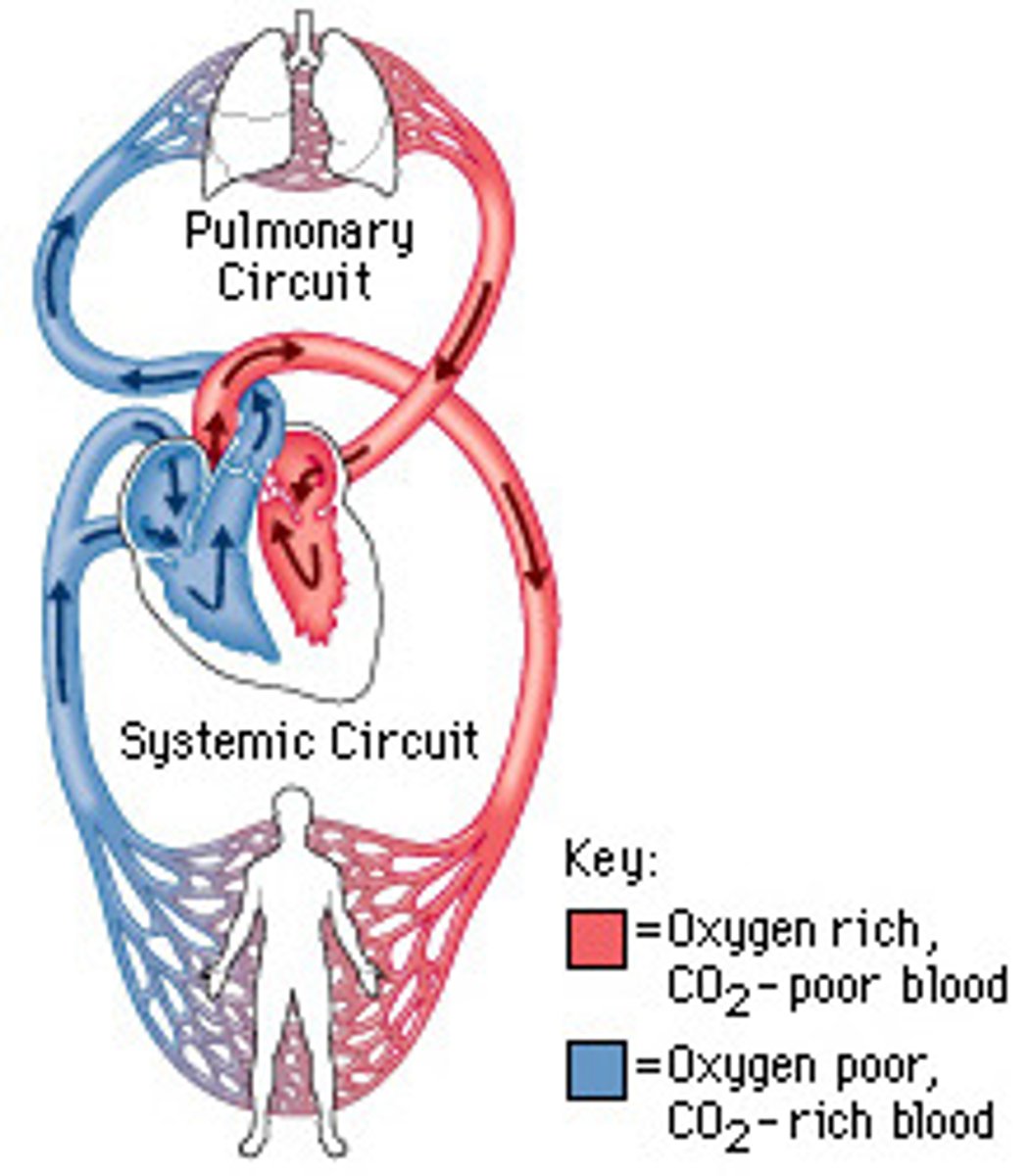
systemic circuit
Circuit of blood that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
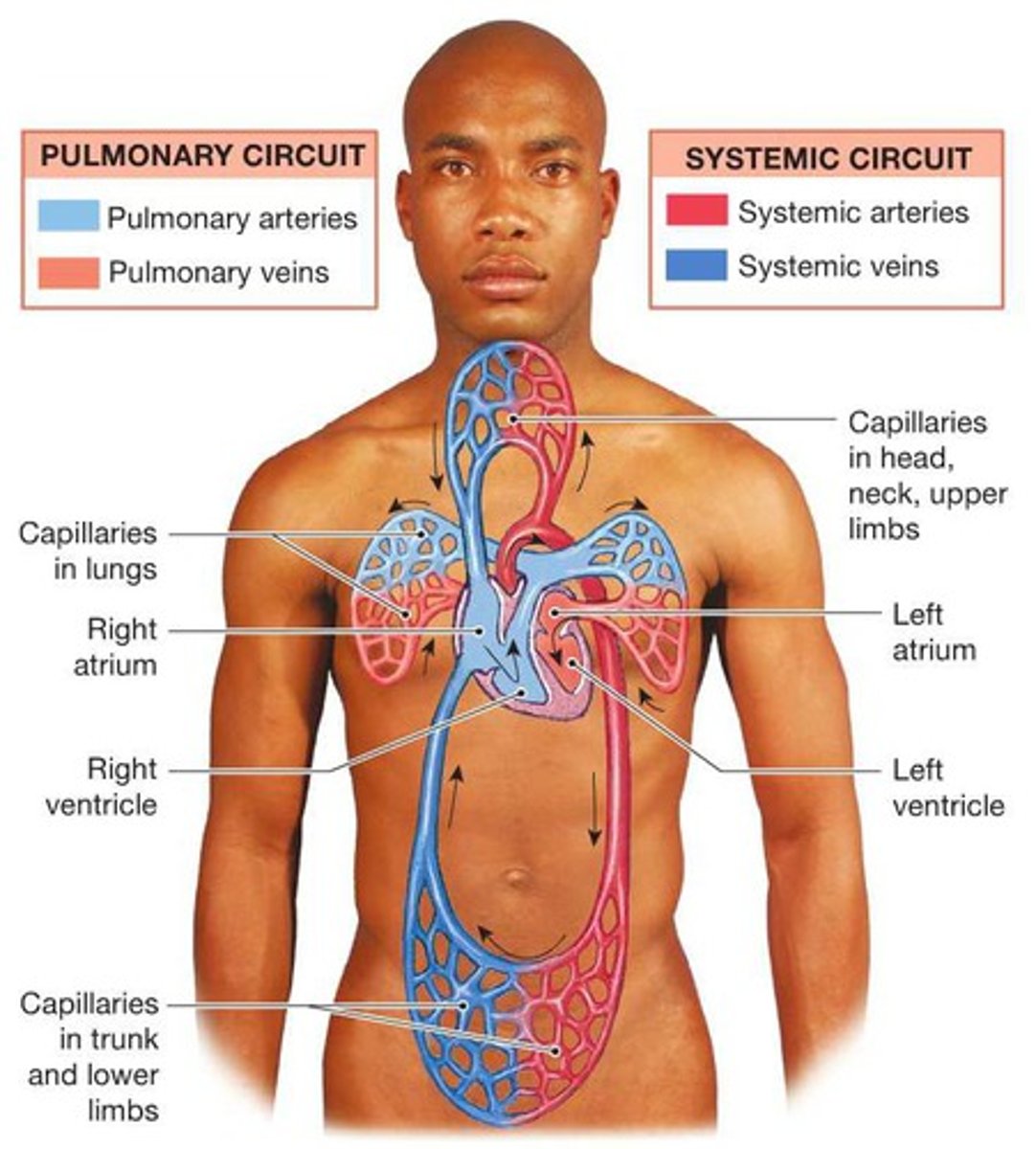
series blood flow
The series of blood flow-related events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to that of the next
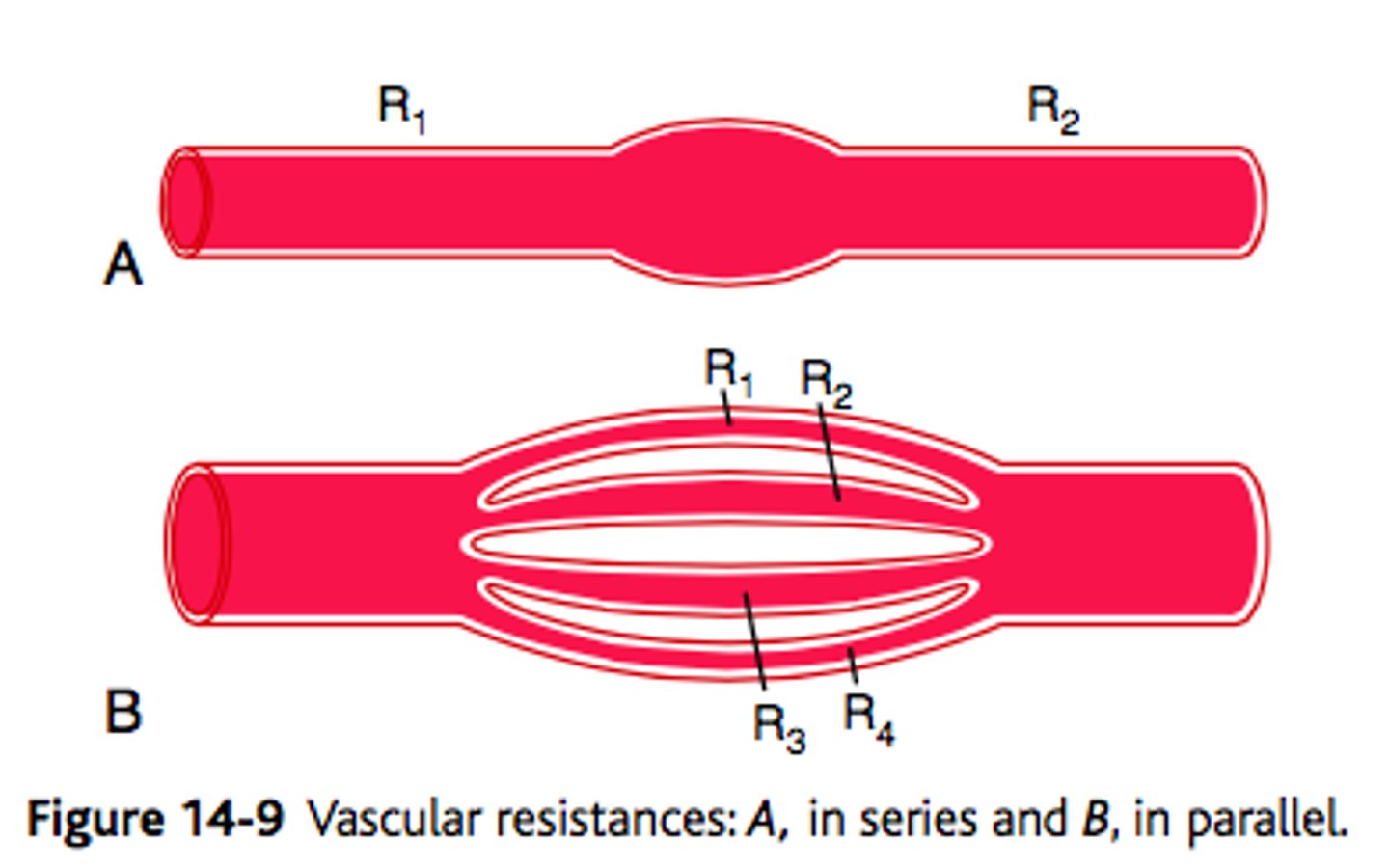
parallel blood flow
1.) Each organ is fed by a separate artery, and each receives fully oxygenated blood
2.) Blood flow to the organs can be independently regulated
-Systemic circulation
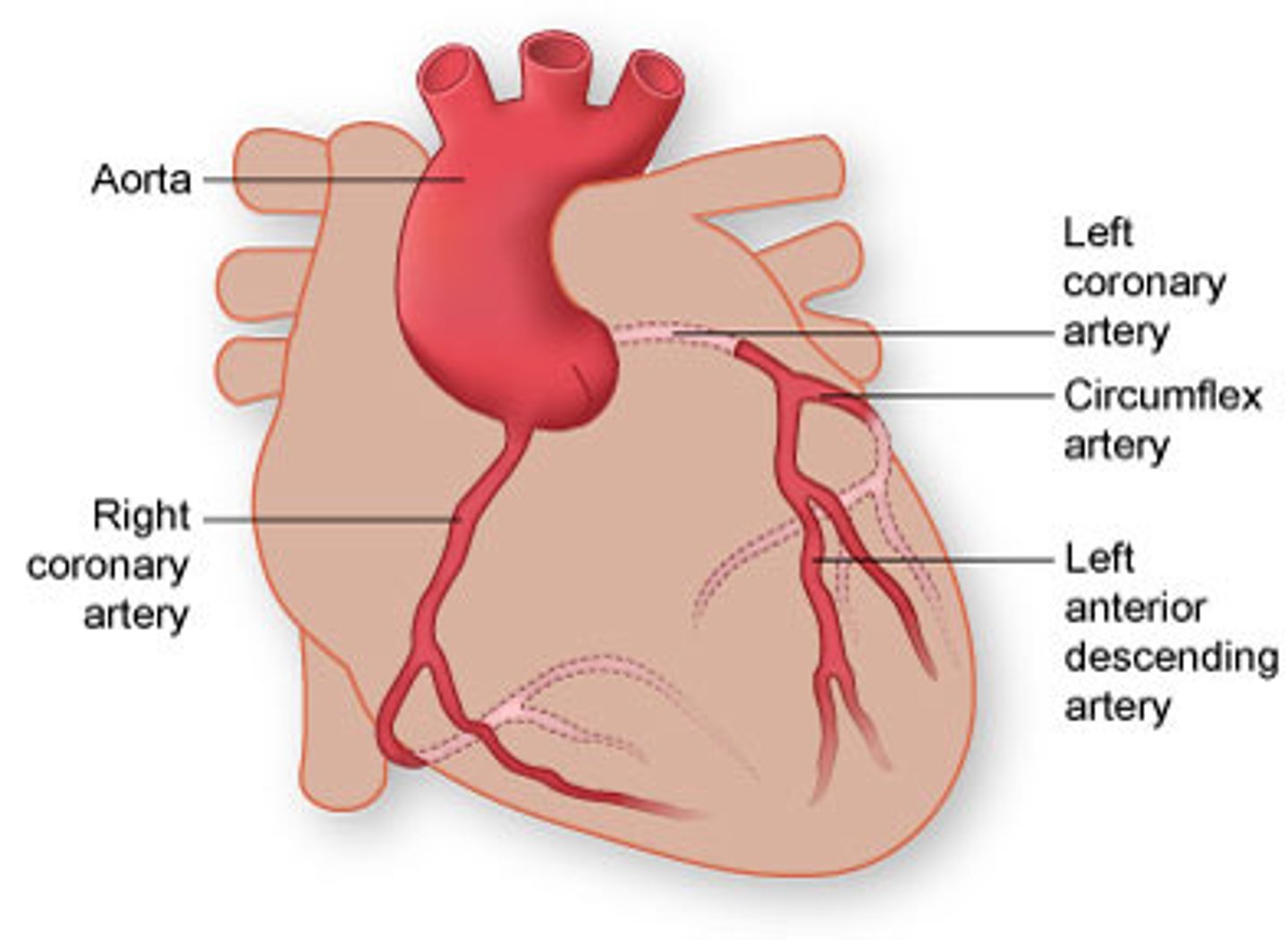
coronary arteries
blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle
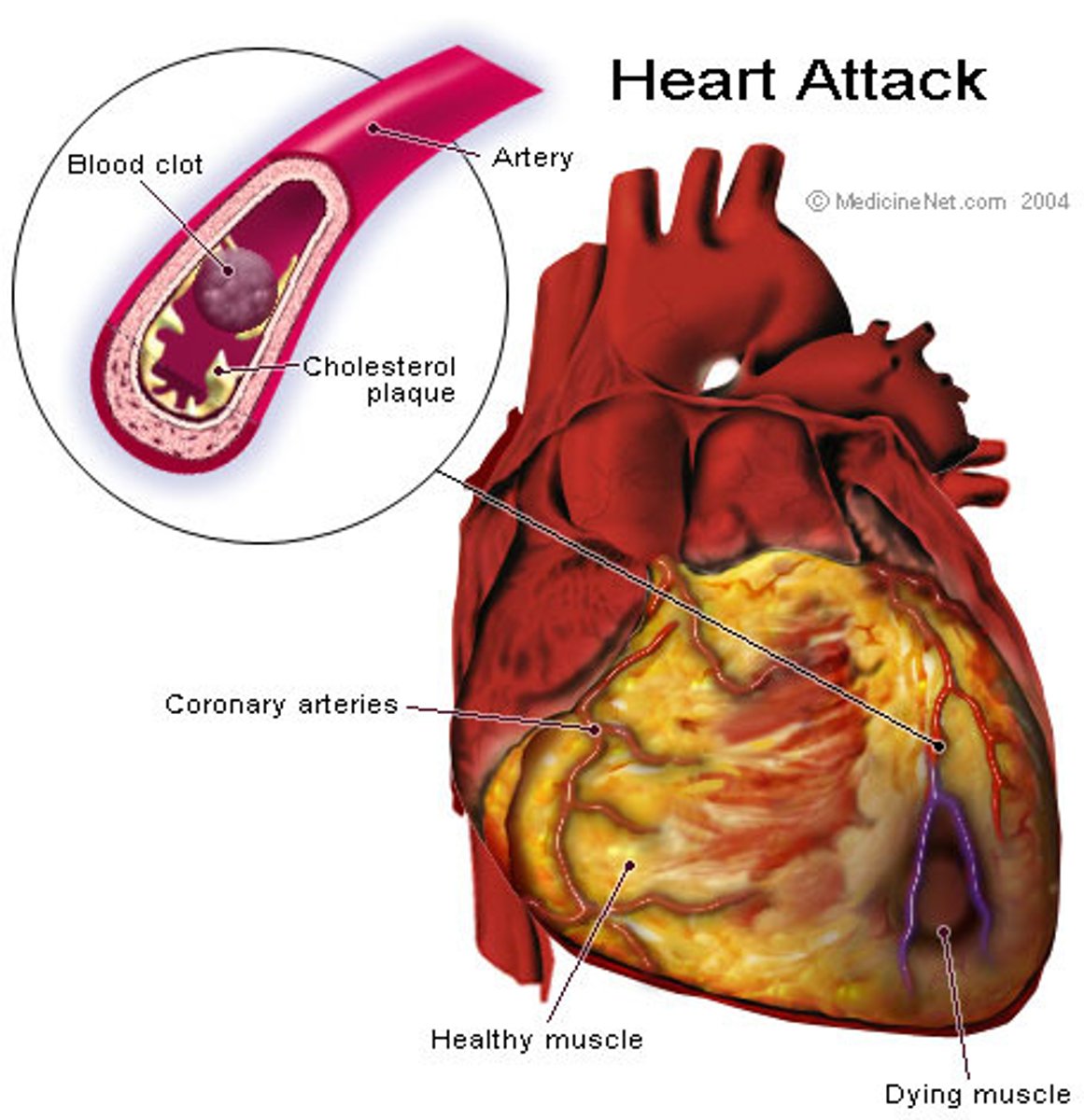
myocardial infarction
the occlusion of one or more coronary arteries caused by plaque buildup (heart attack)
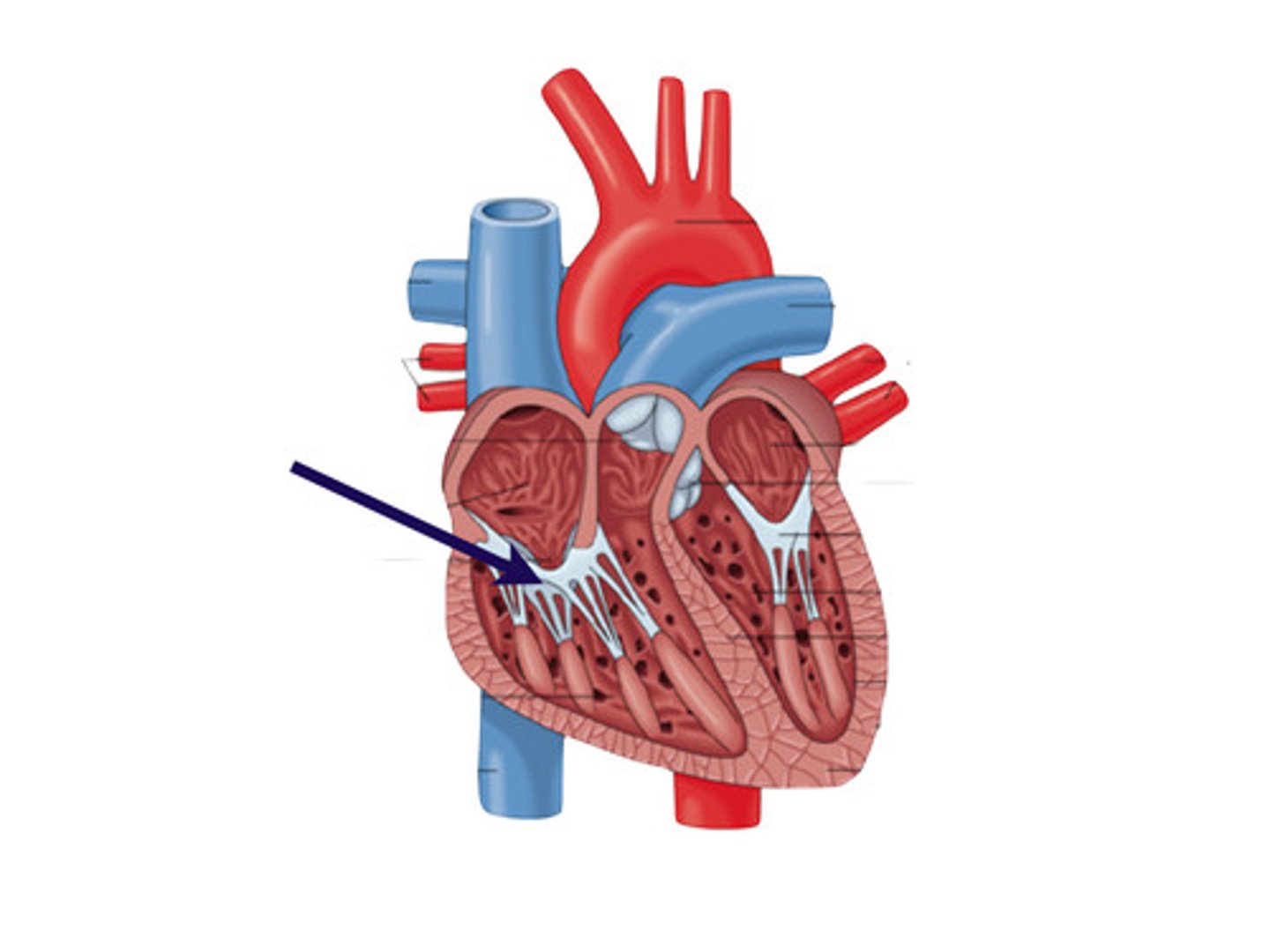
right AV valve
The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle; the tricuspid valve
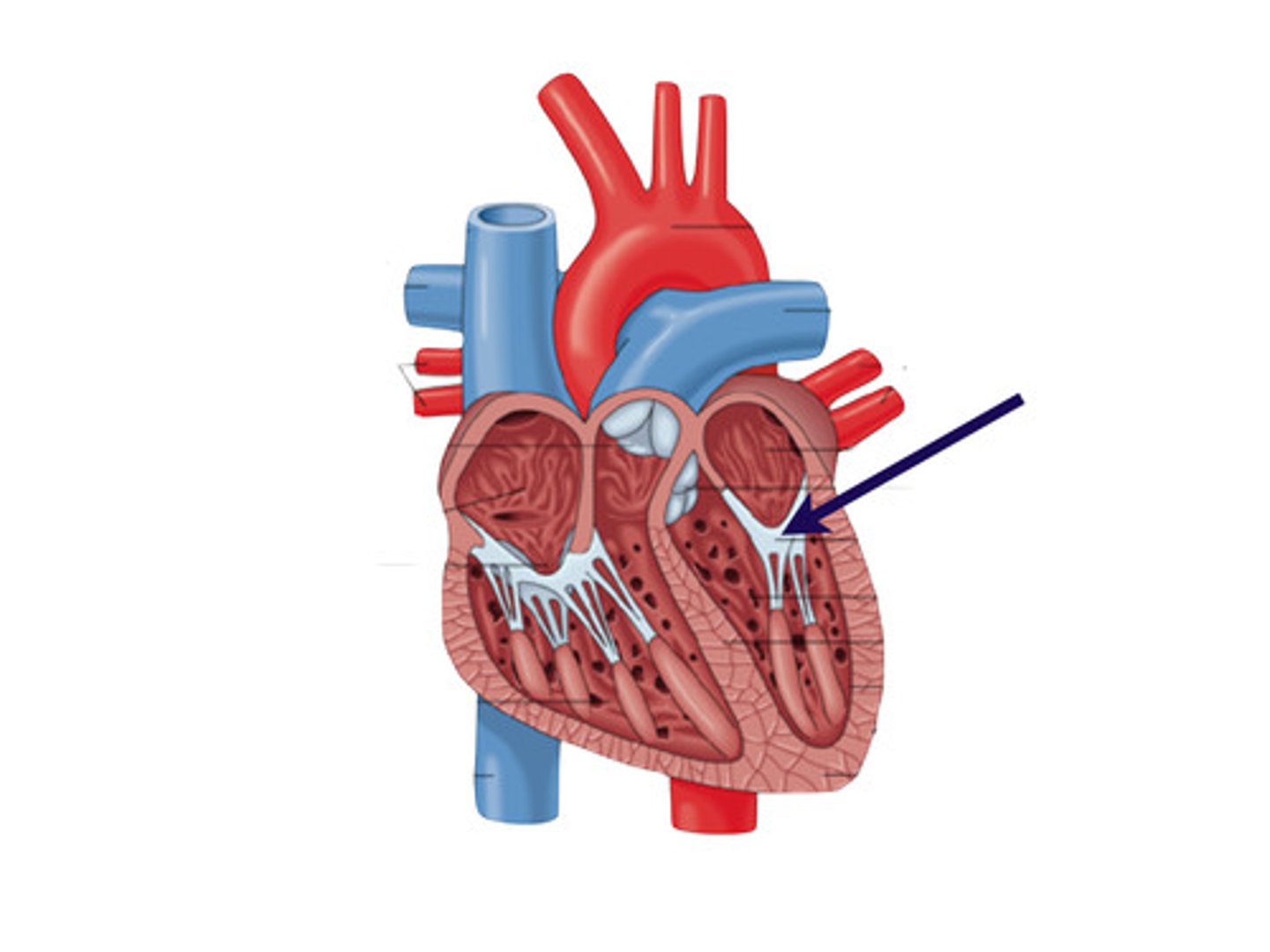
left AV valve
bicuspid valve
aortic valve
The semilunar valve separating the aorta from the left ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle.
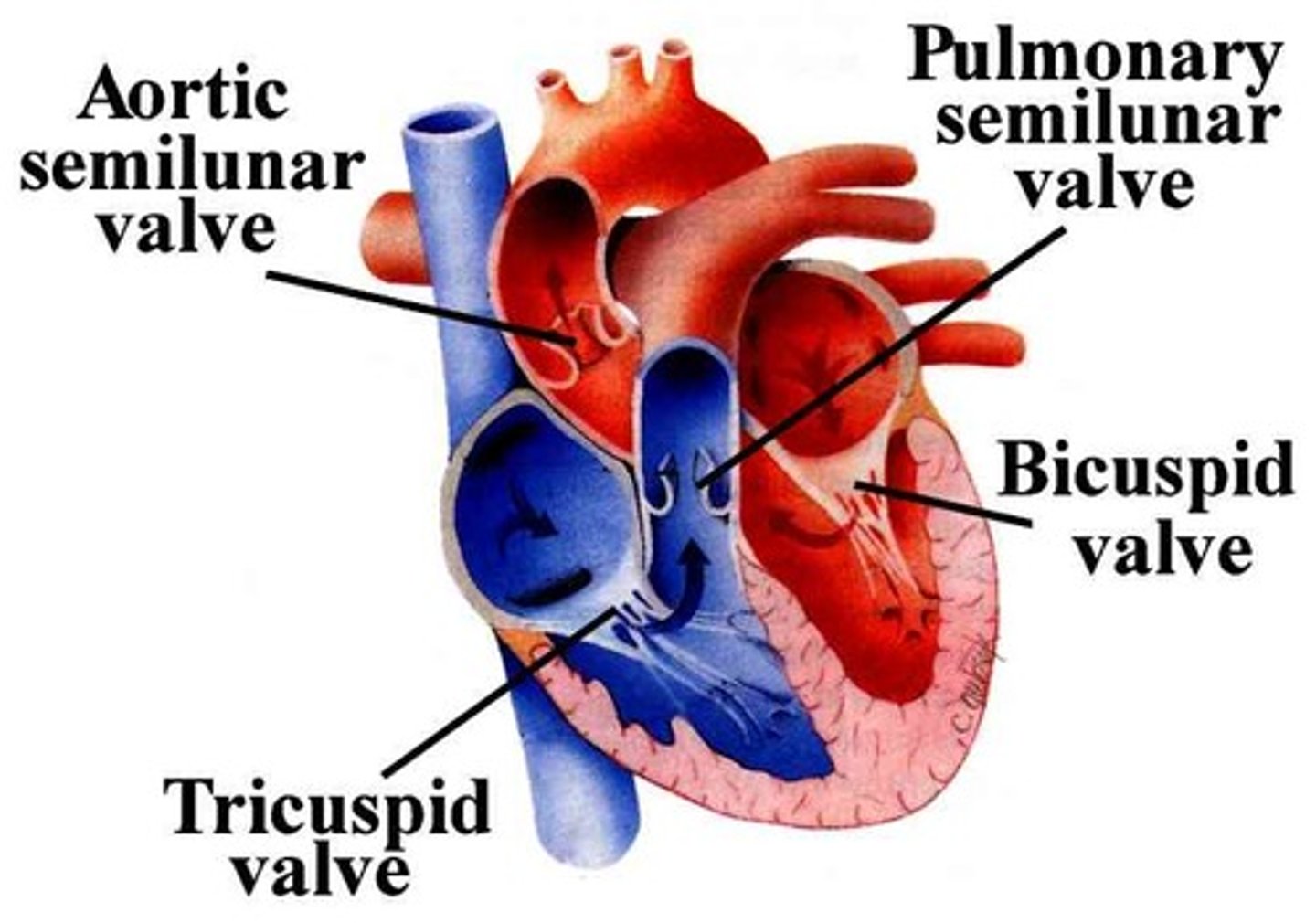
pulmonary valve
valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
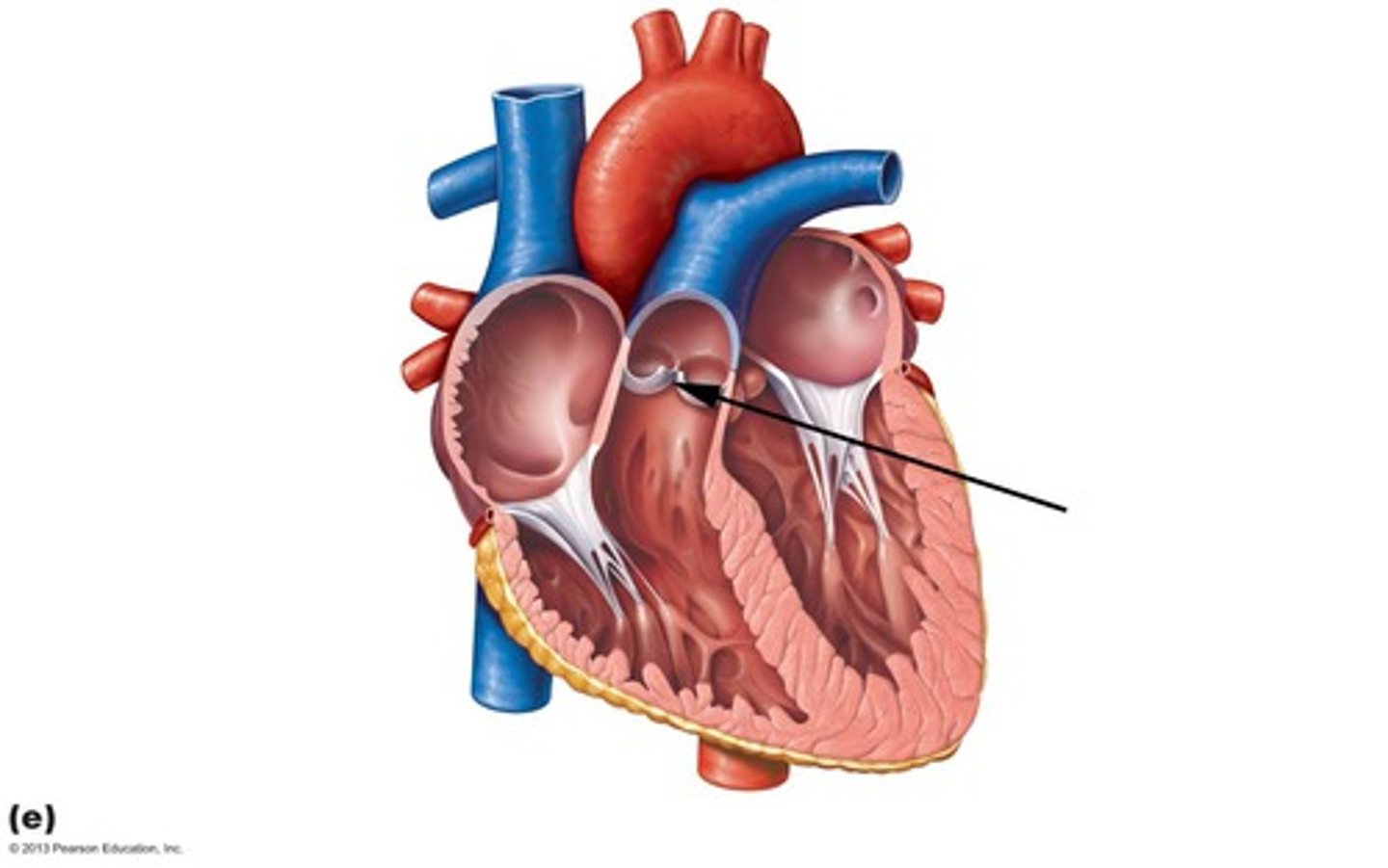
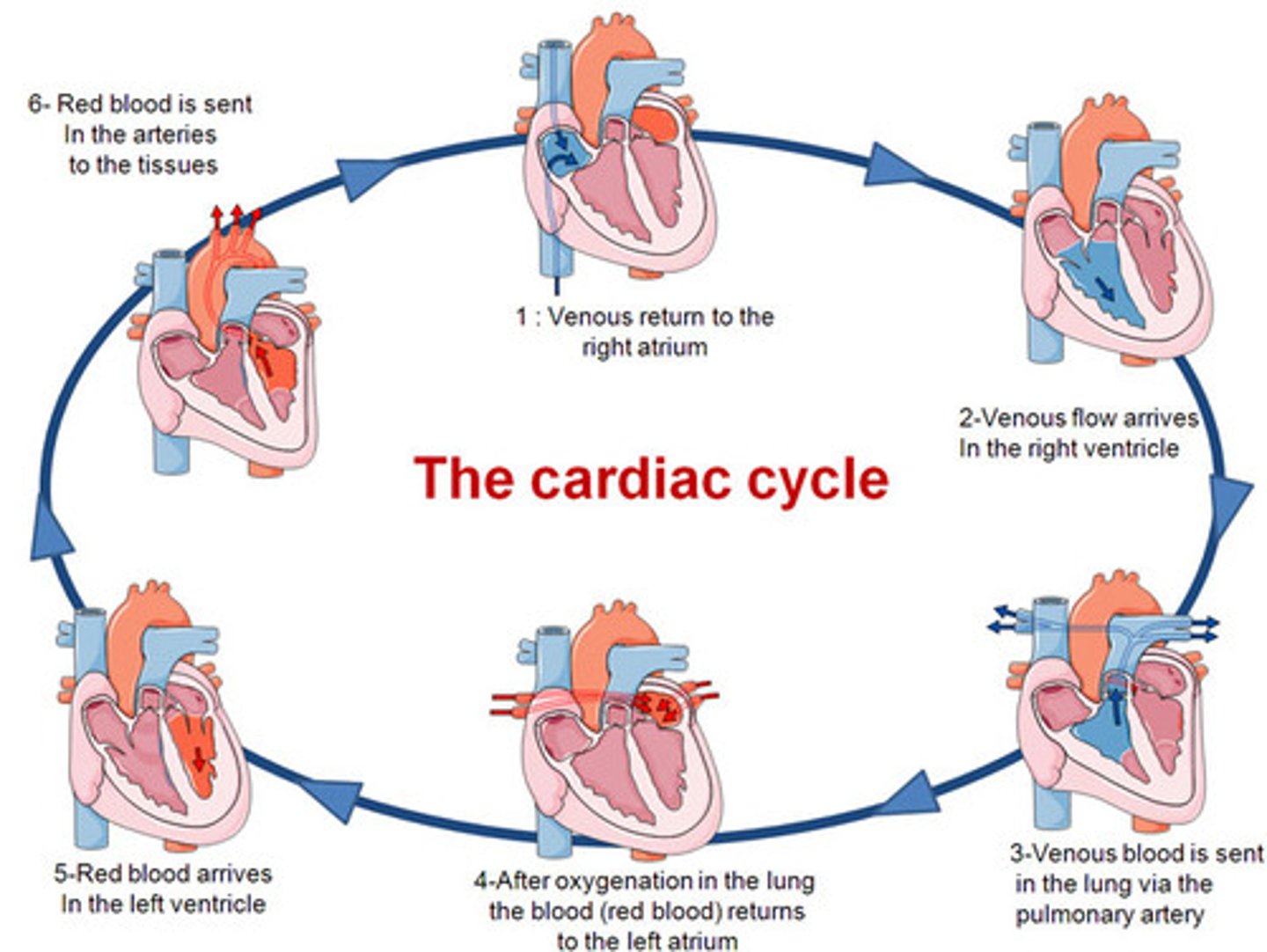
cardiac cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles
pacemaker cells
heart cells that regularly produce spontaneous electrical impulses
conduction fibers
specialized muscle cells that rapidly conduct action potentials through the heart
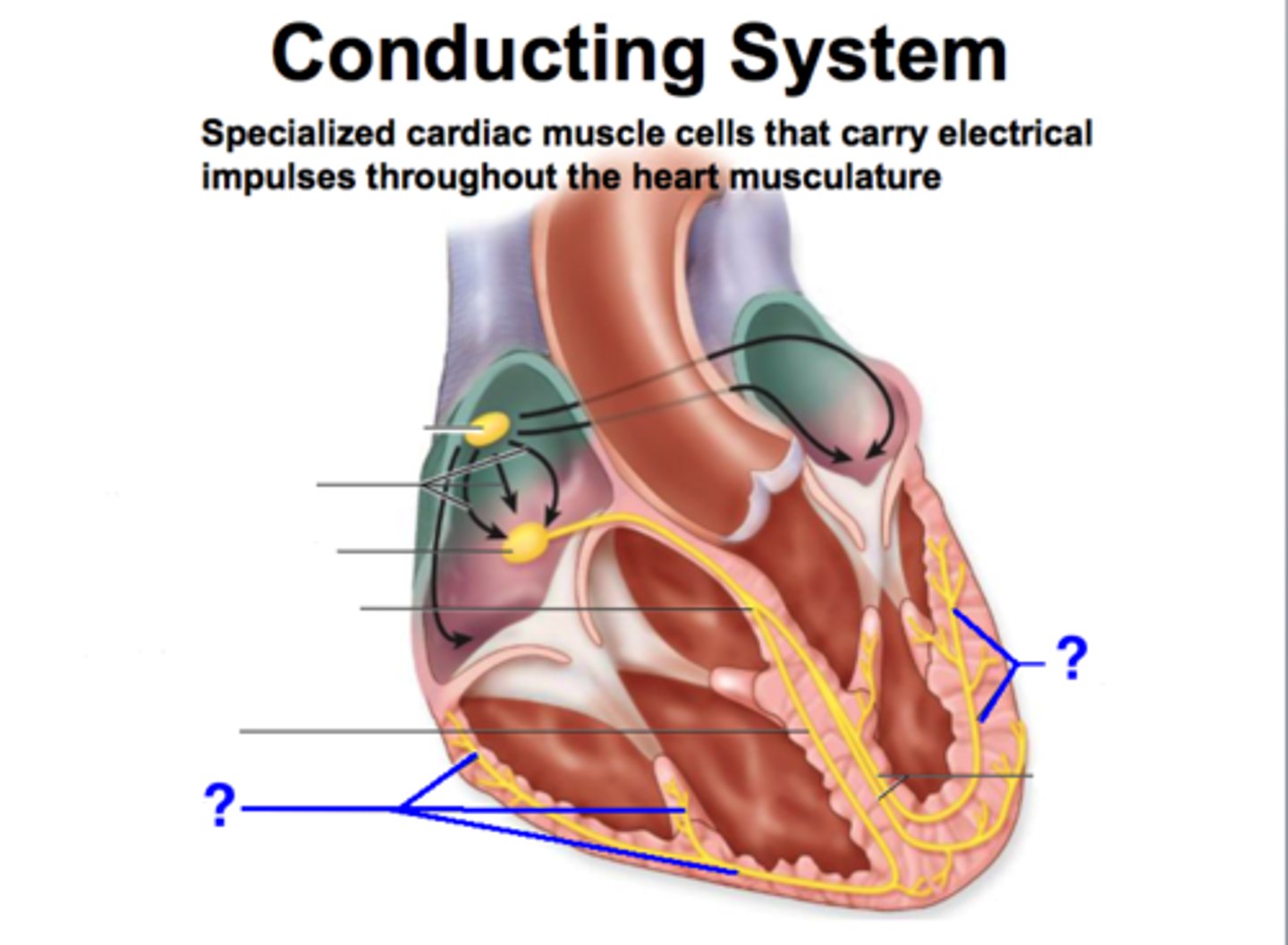
contractile cells
produce contractions that propel blood
autorhythmic cells
Cells fire spontaneously, act as pacemaker and form conduction system for the heart
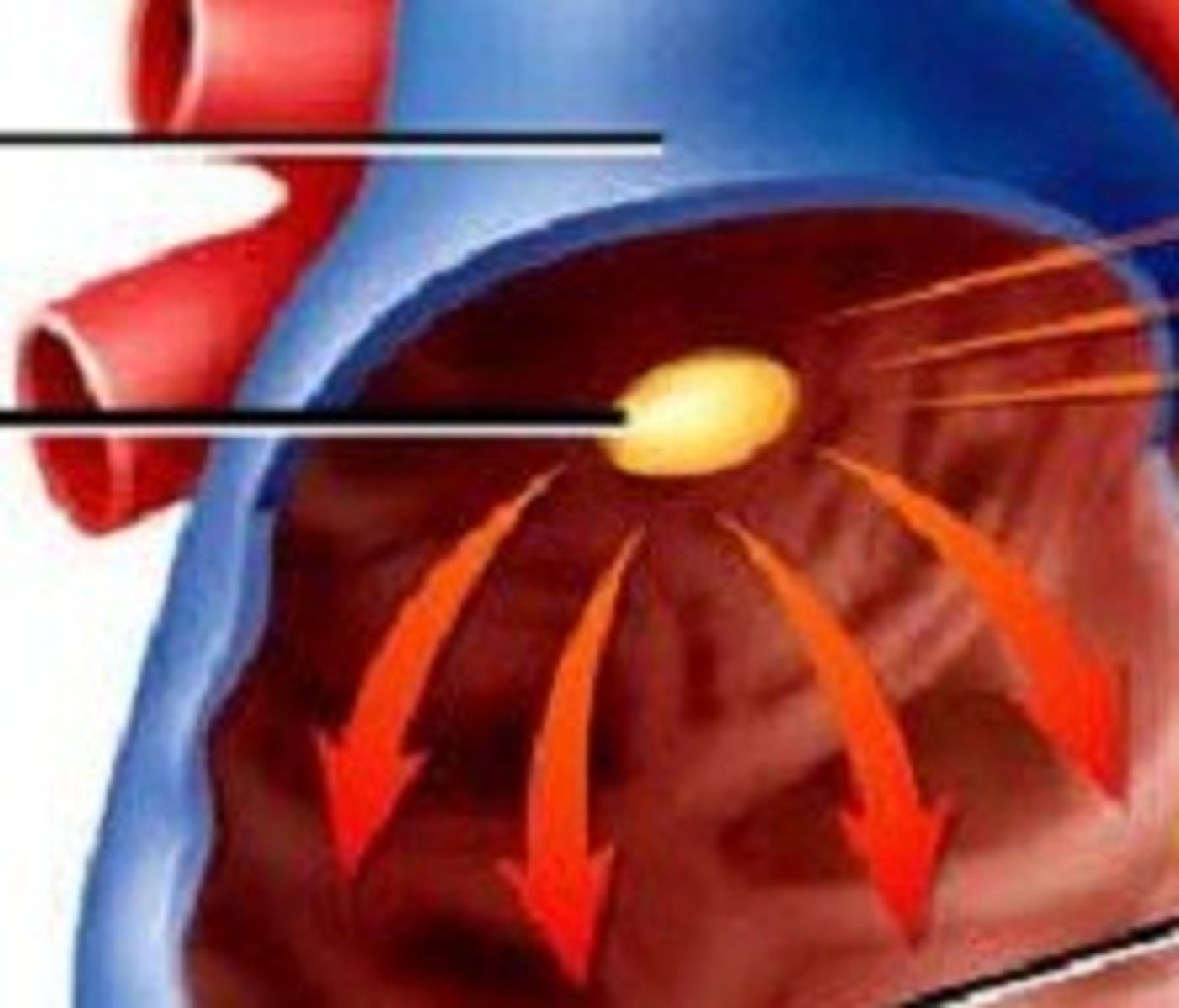
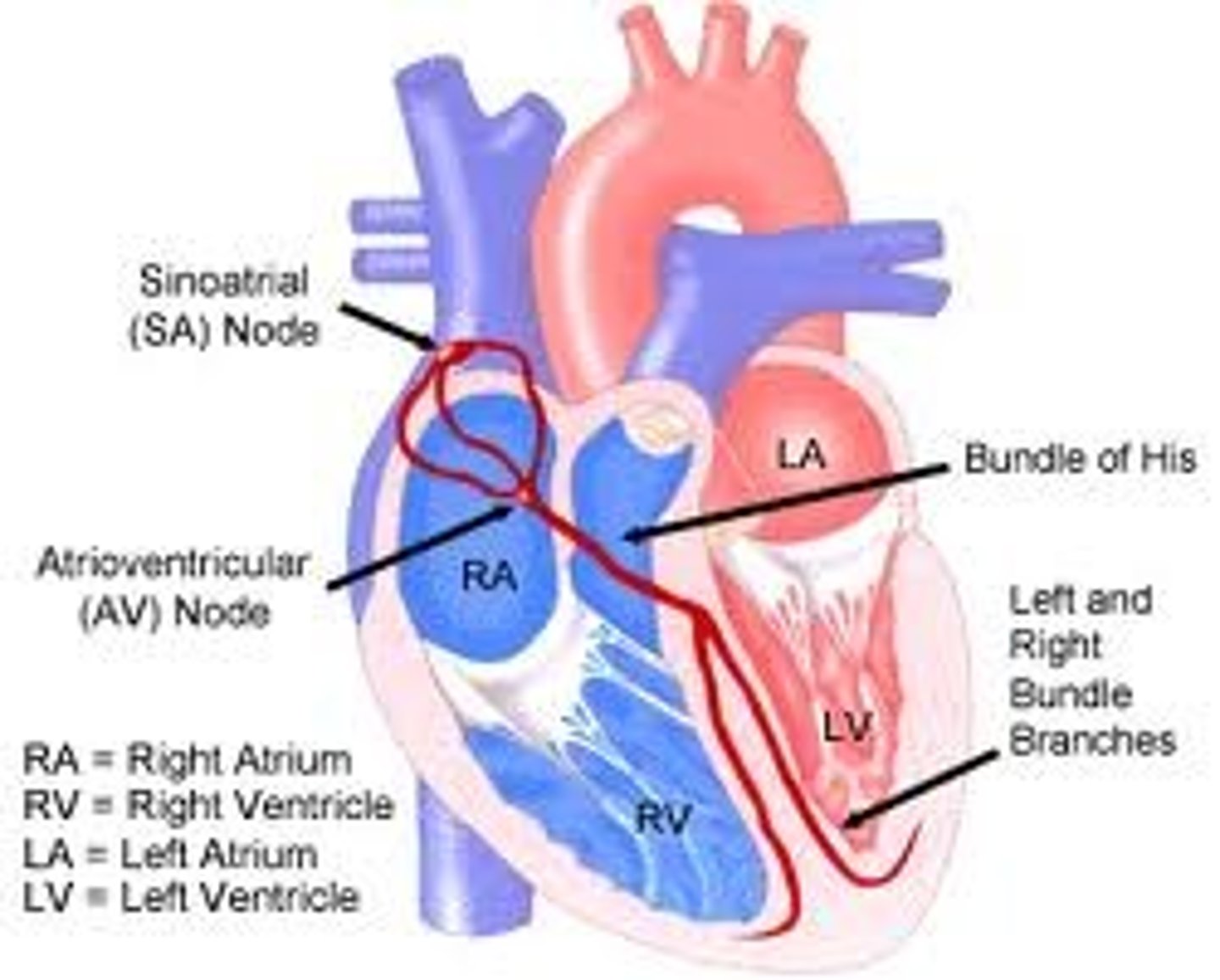
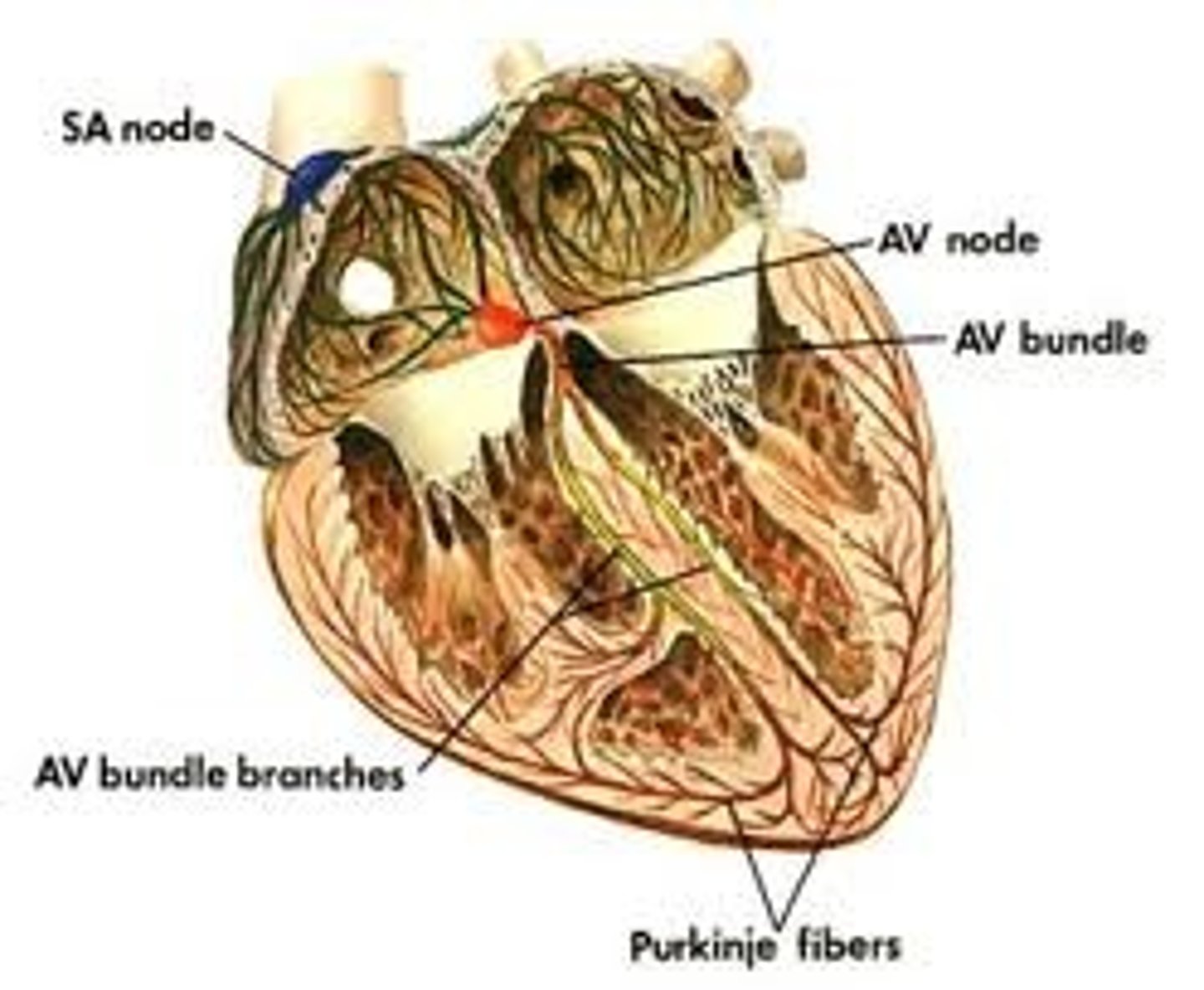
SA (sinoatrial) node
the pacemaker of the heart, located in the wall of the right atrium, that sets the rate and timing at which all cardiac muscle cells contract
AV node
(atrioventricular node) region of the heart between the right atrium and right ventricle from which electrical impulses spread to the ventricles during a heartbeat
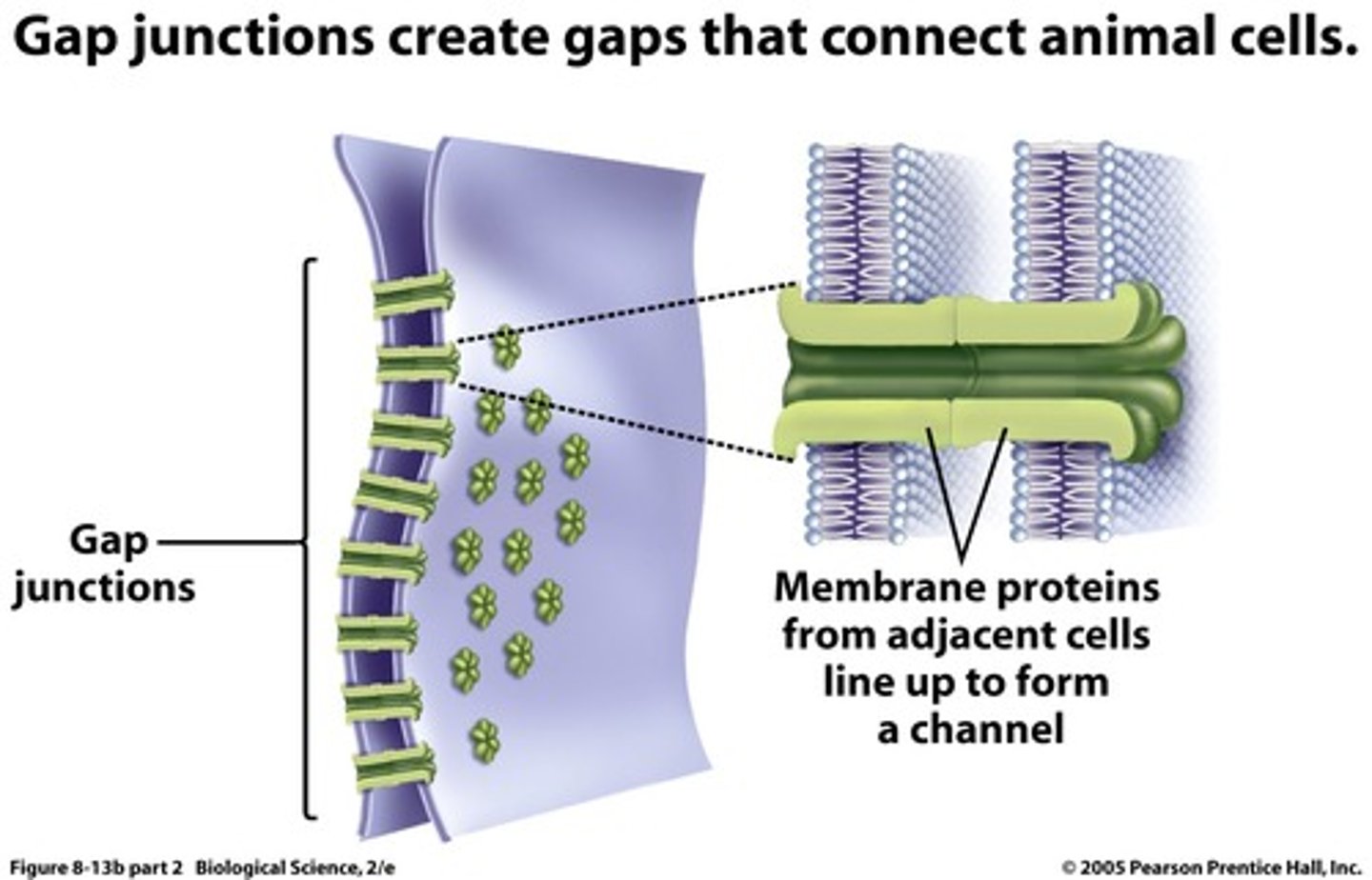
gap junctions
Points that provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another with special membrane proteins. Also called communicating junctions.
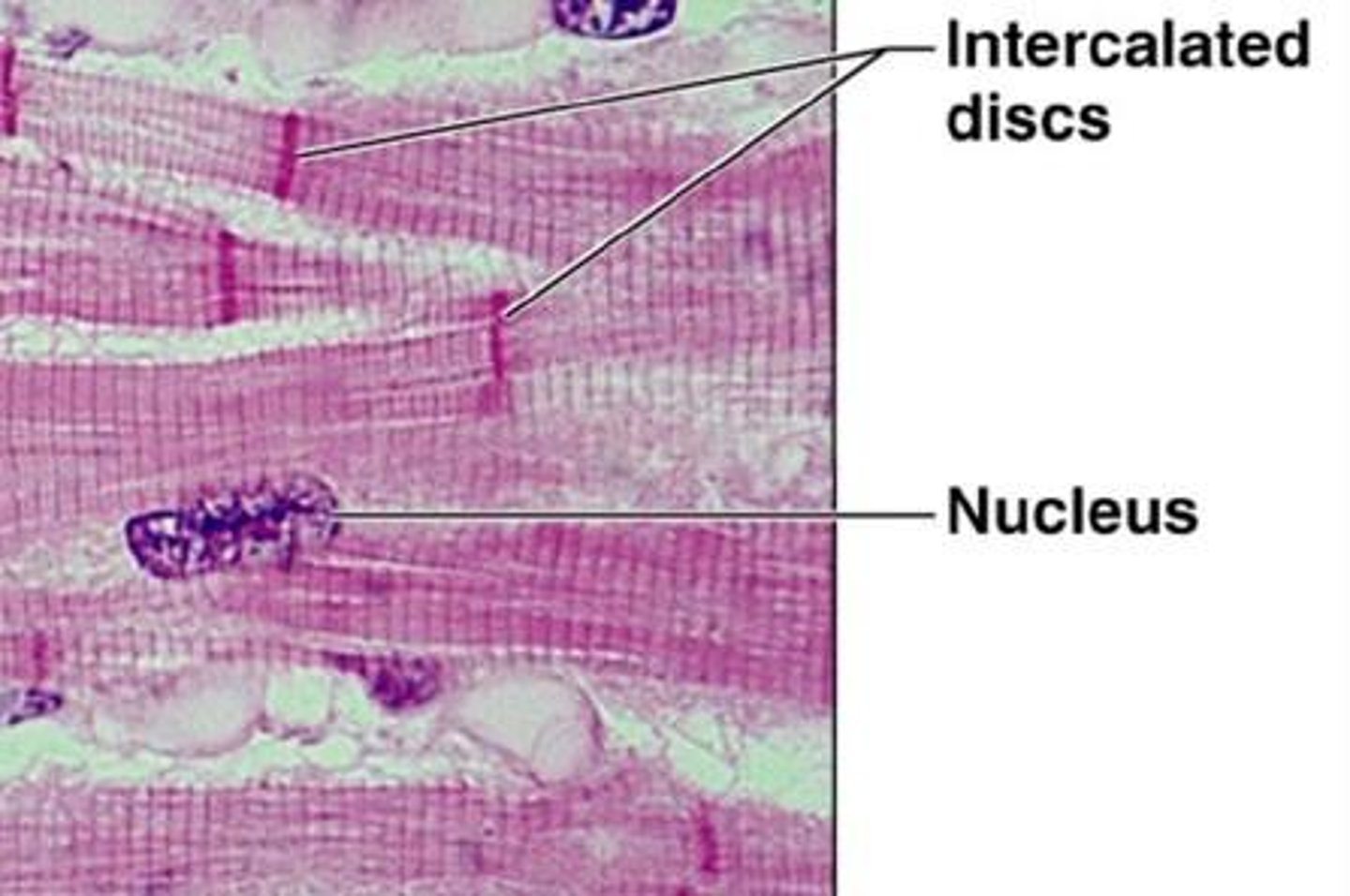
intercalated disks
Specialized cell junctions in the myocardium where one muscle cell connects to the next.
AV node delay
slowing of electrical conduction through the AV node that allows atria to complete contraction before the ventricles begin
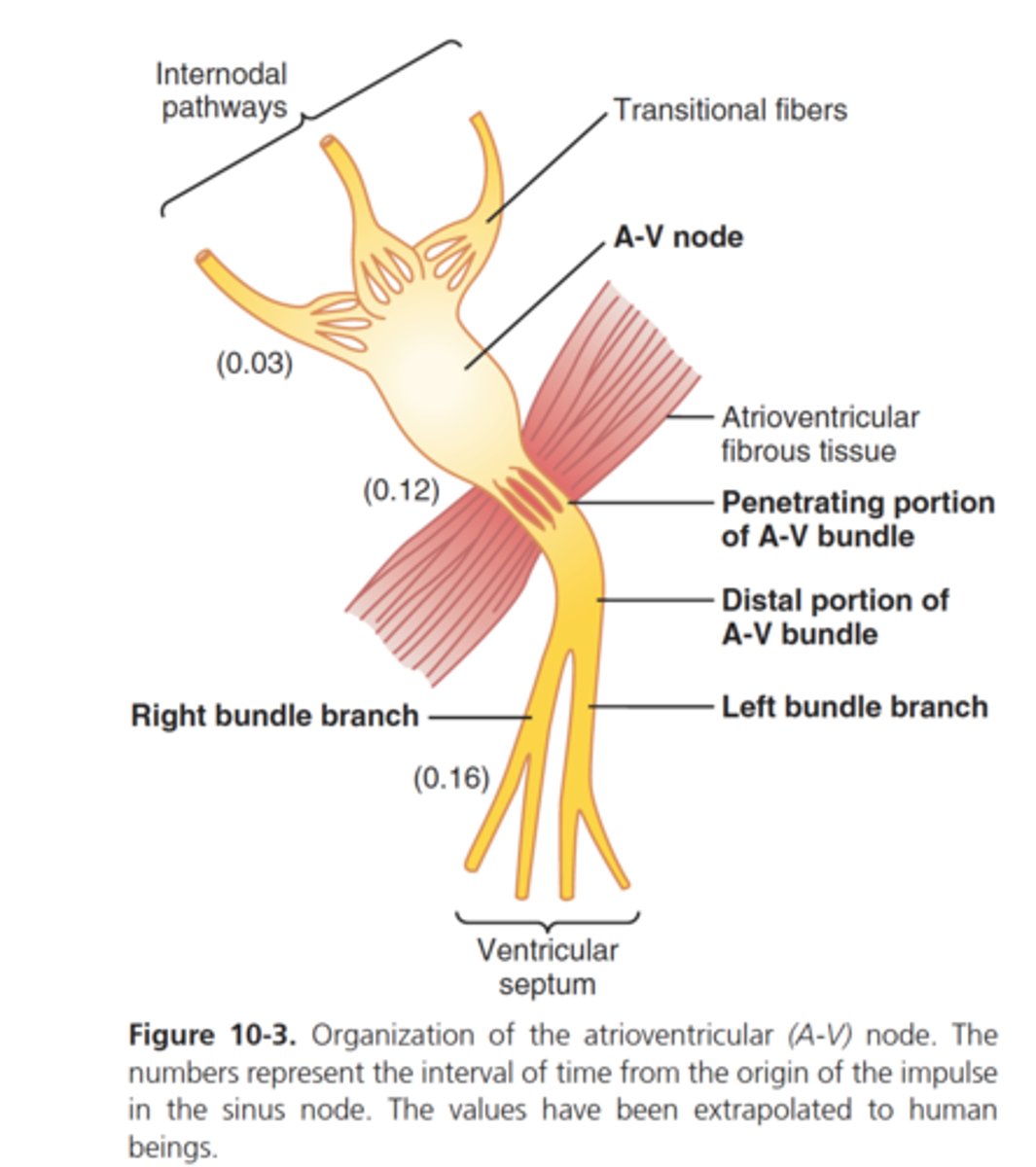
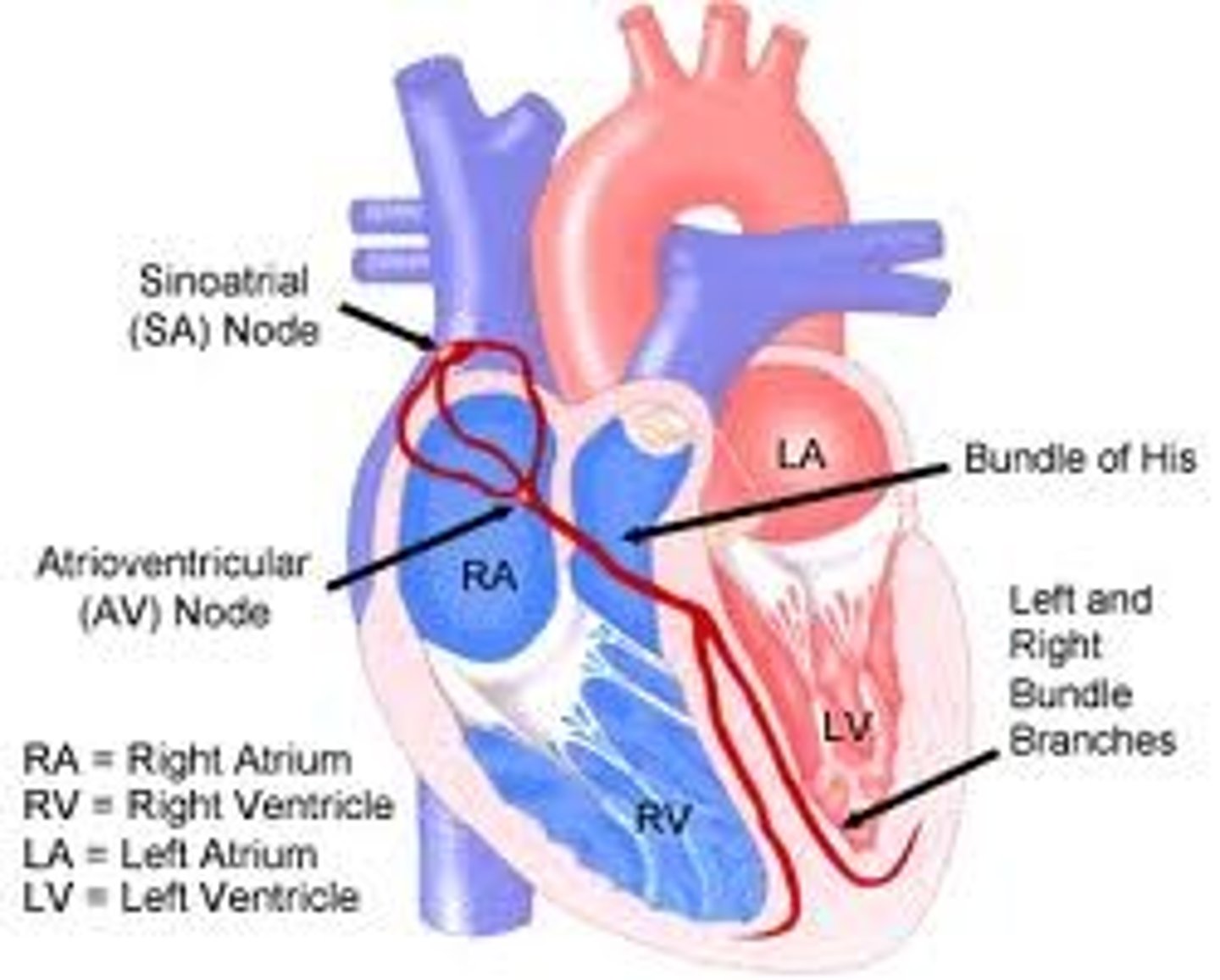
bundle of His
a bundle of modified heart muscle that transmits the cardiac impulse from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles causing them to contract
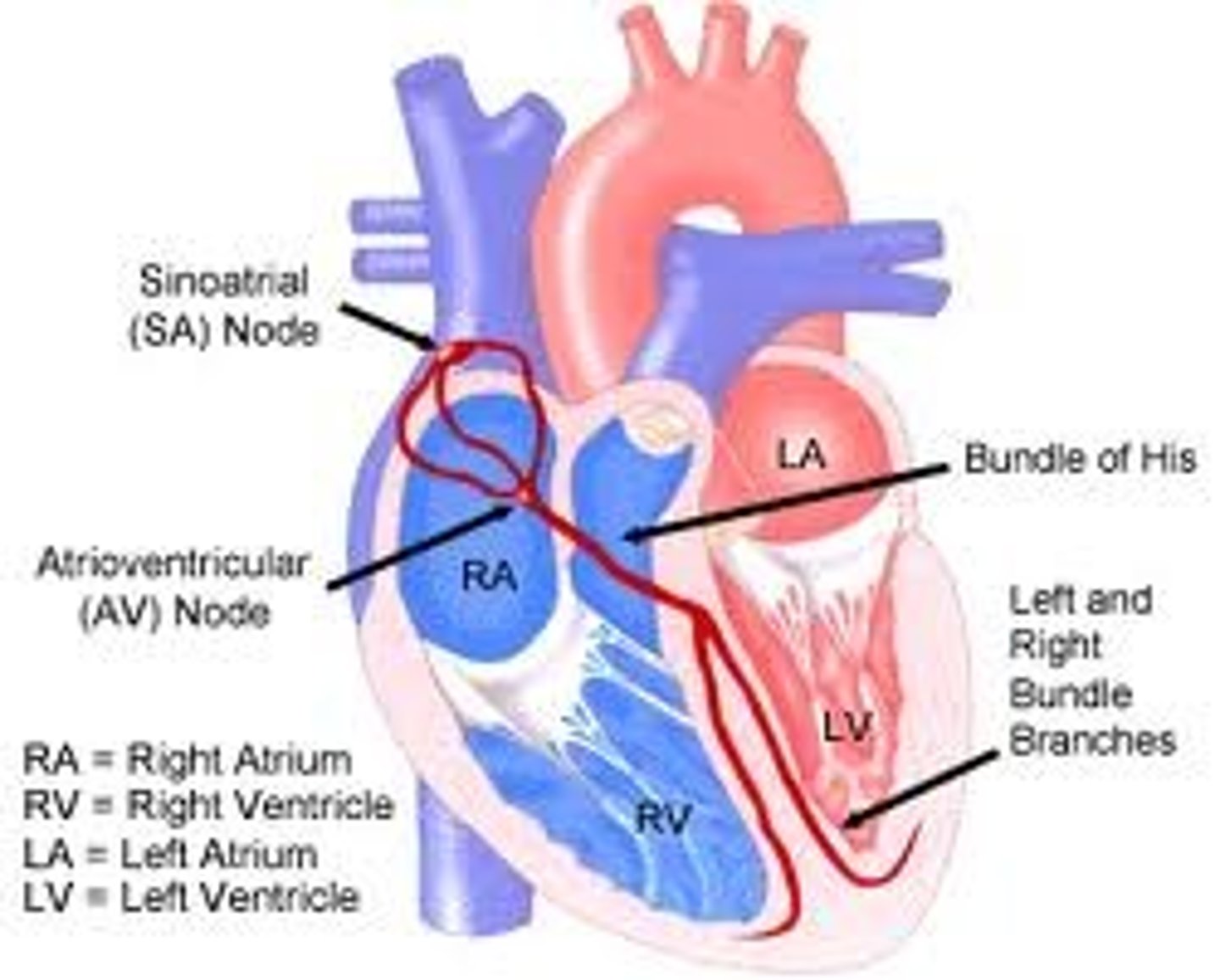
left and right bundle branches
branches from atrioventricular bundle, take signal to apex of heart
Purkinje fibers
specialized conductive fibers located within the walls of the ventricles
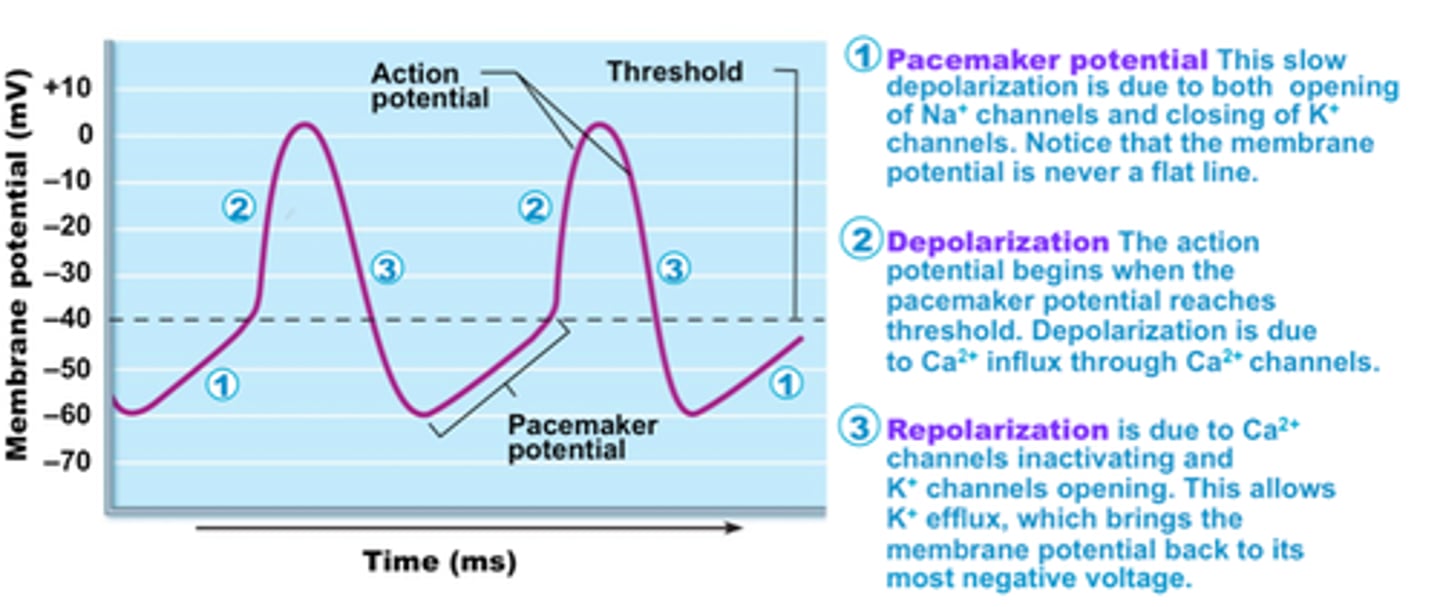
pacemaker potentials (prepotentials)
initiate the action potentials that spread throughout the heart to trigger its rhythmic contractions
funny channels
important part of the electrical conduction system of the heart and form a component of the natural pacemaker
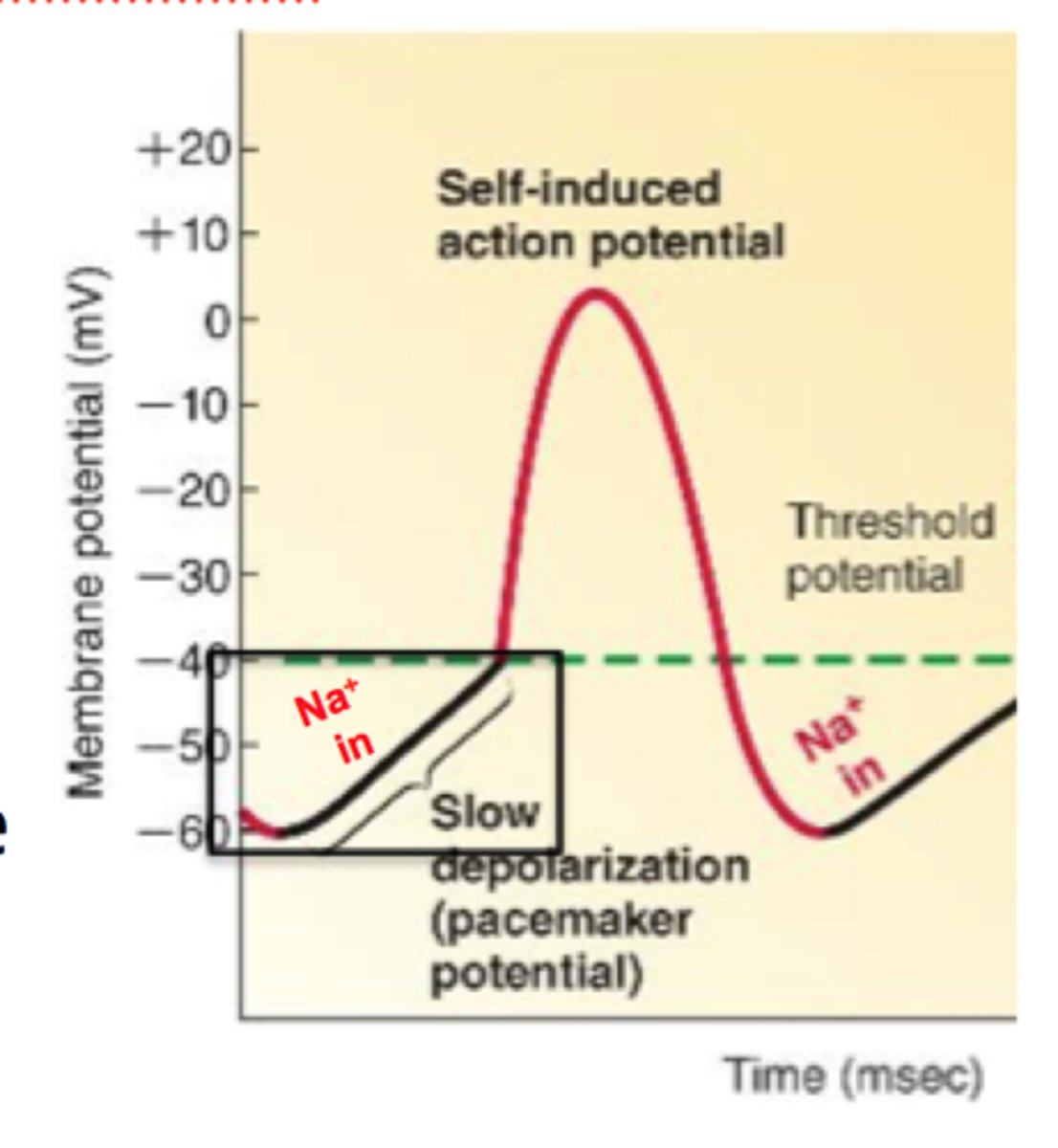
T-type voltage-gated calcium channels
Channels that allow cardiac pacemaker cells to reach threshold.
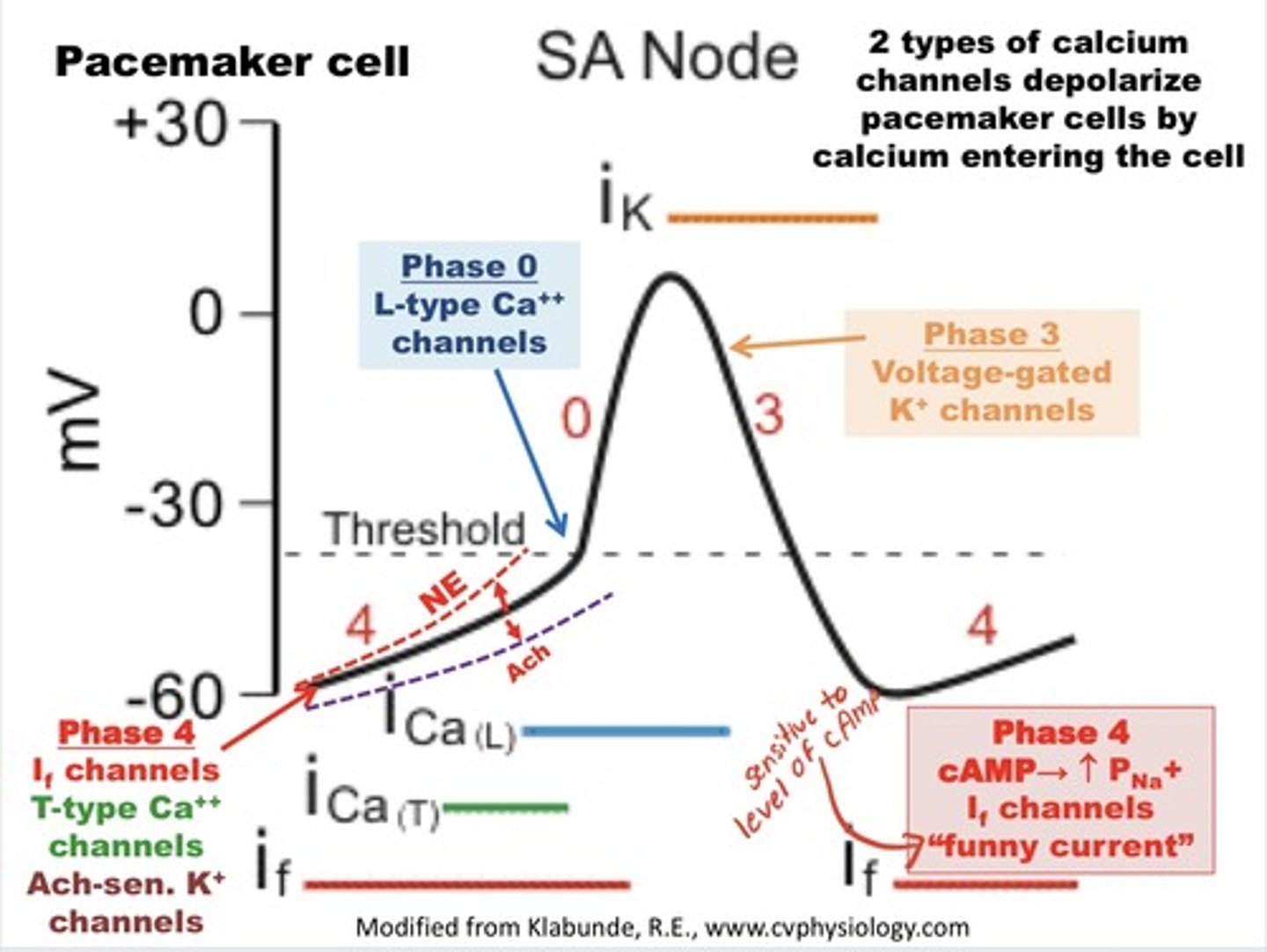
L-type voltage gated Ca channels
transmembrane ion channel proteins that selectively conduct calcium ions through the cell membrane in response to the membrane potential during depolarization
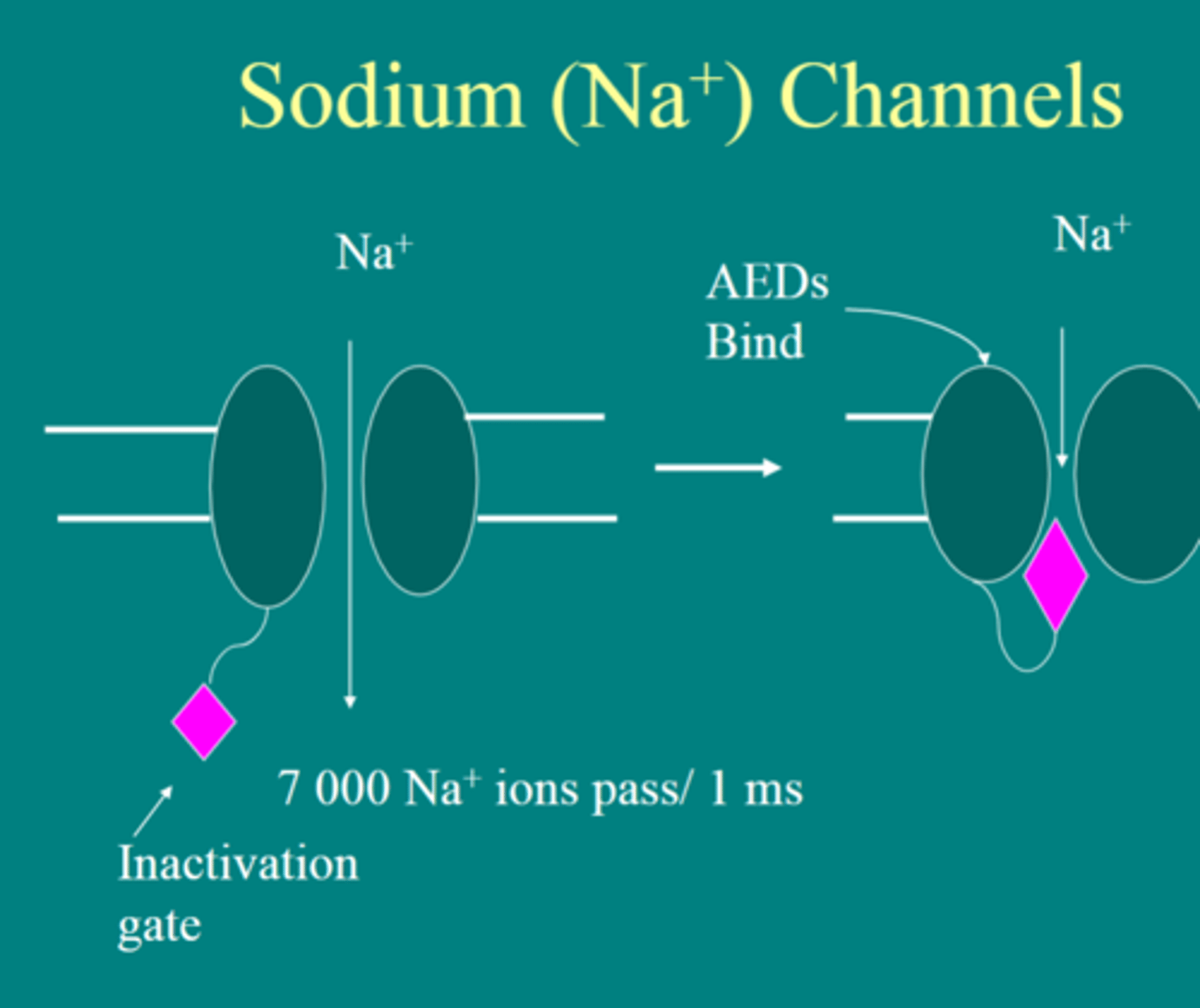
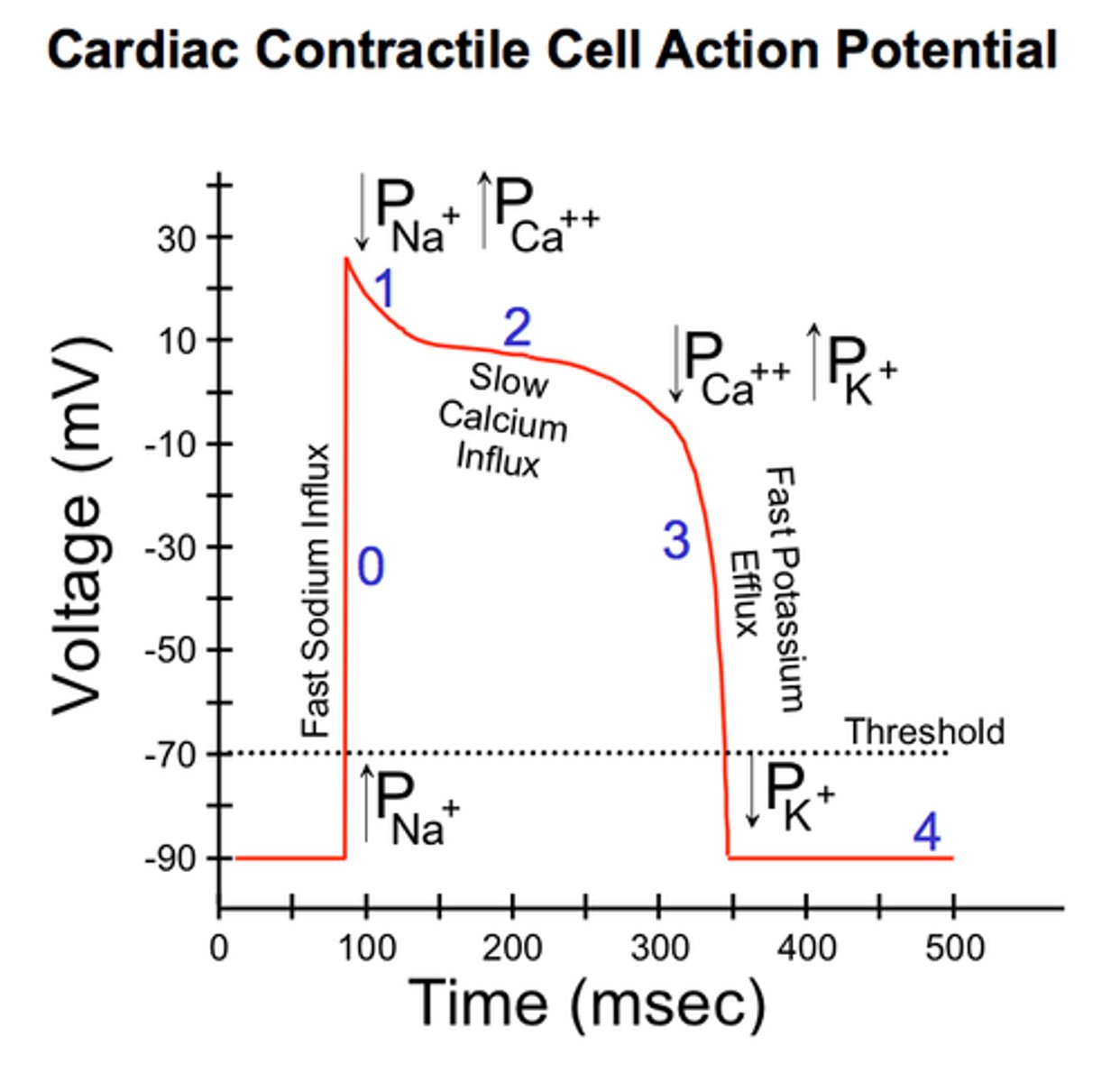
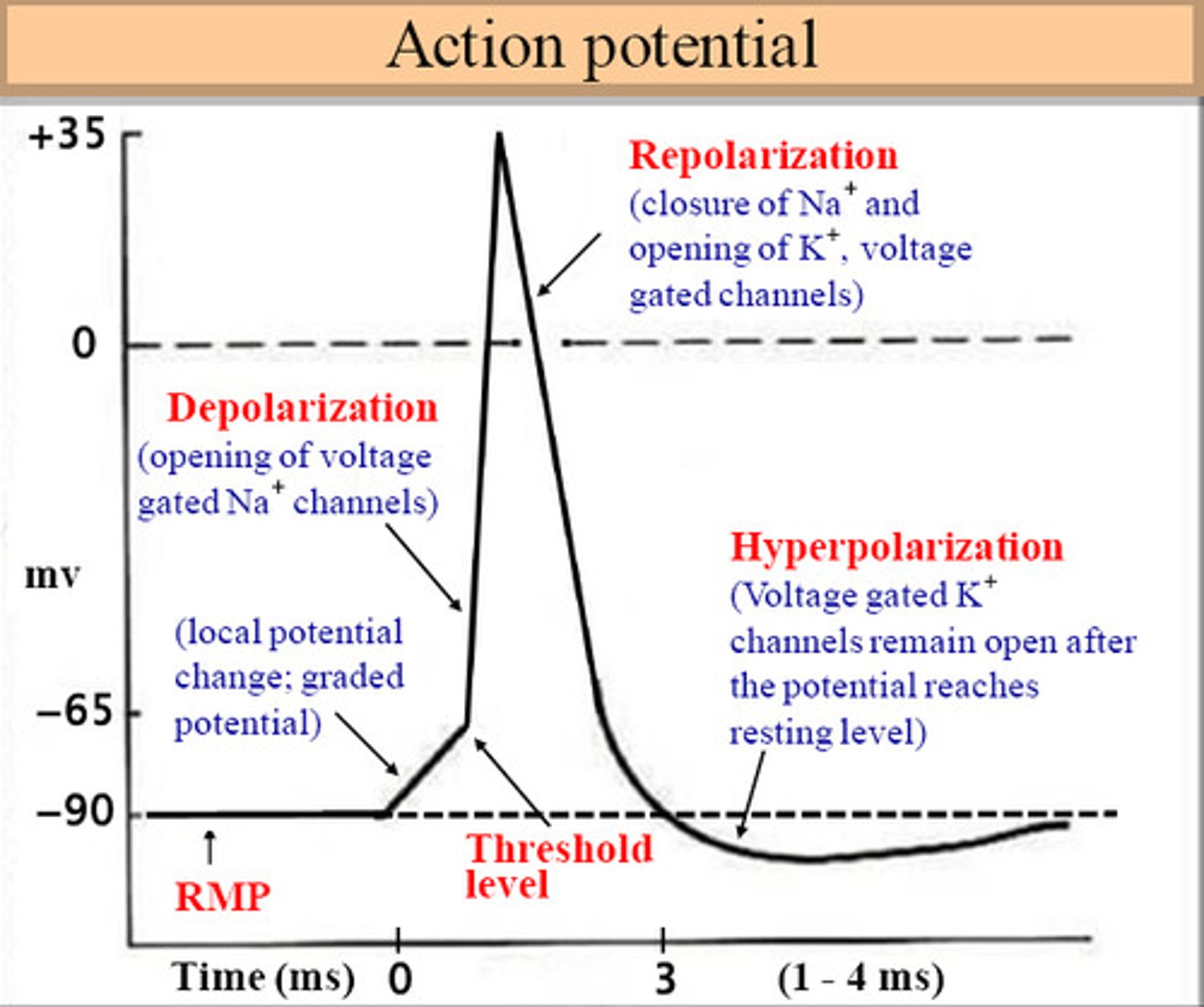
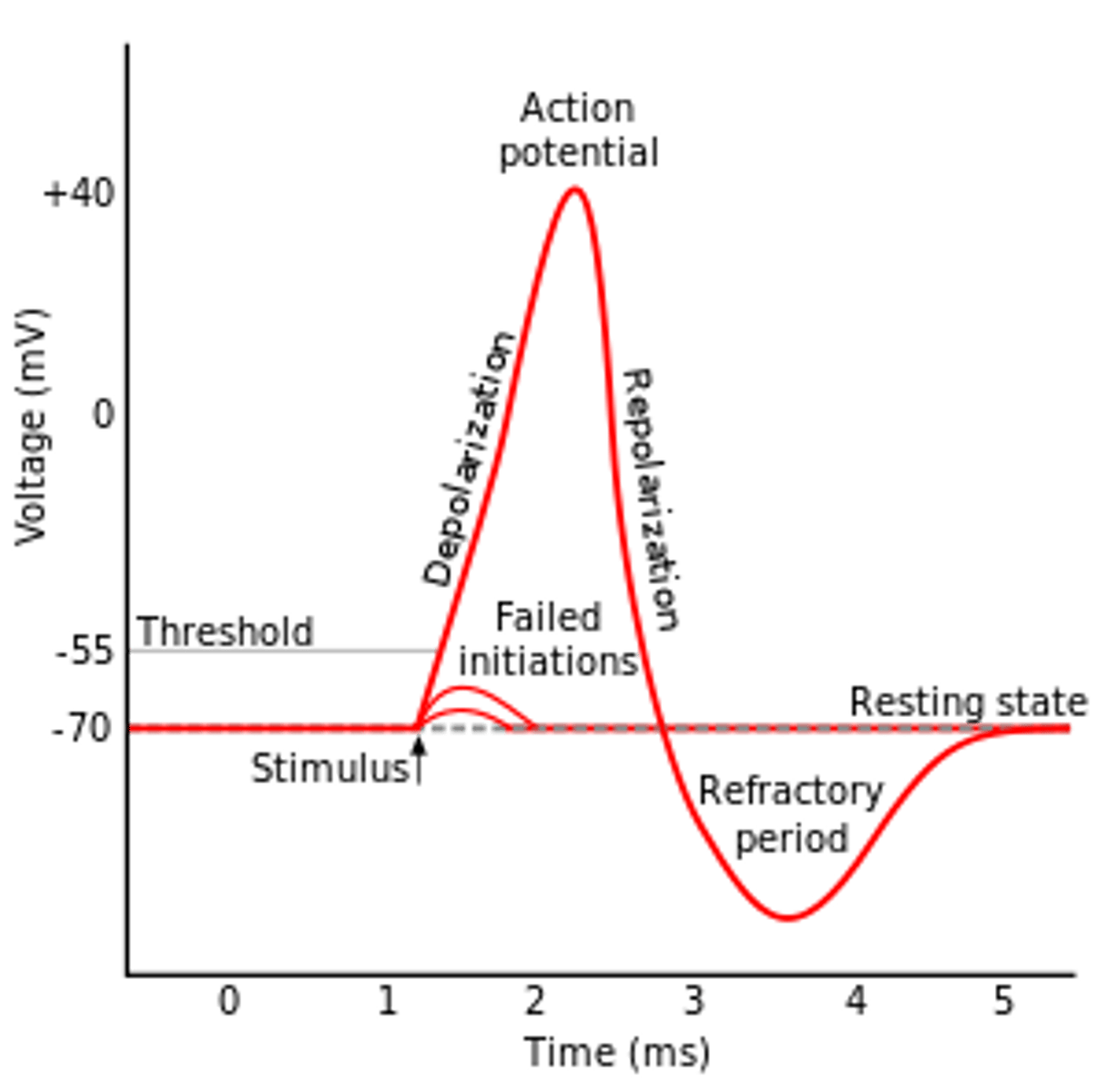
depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
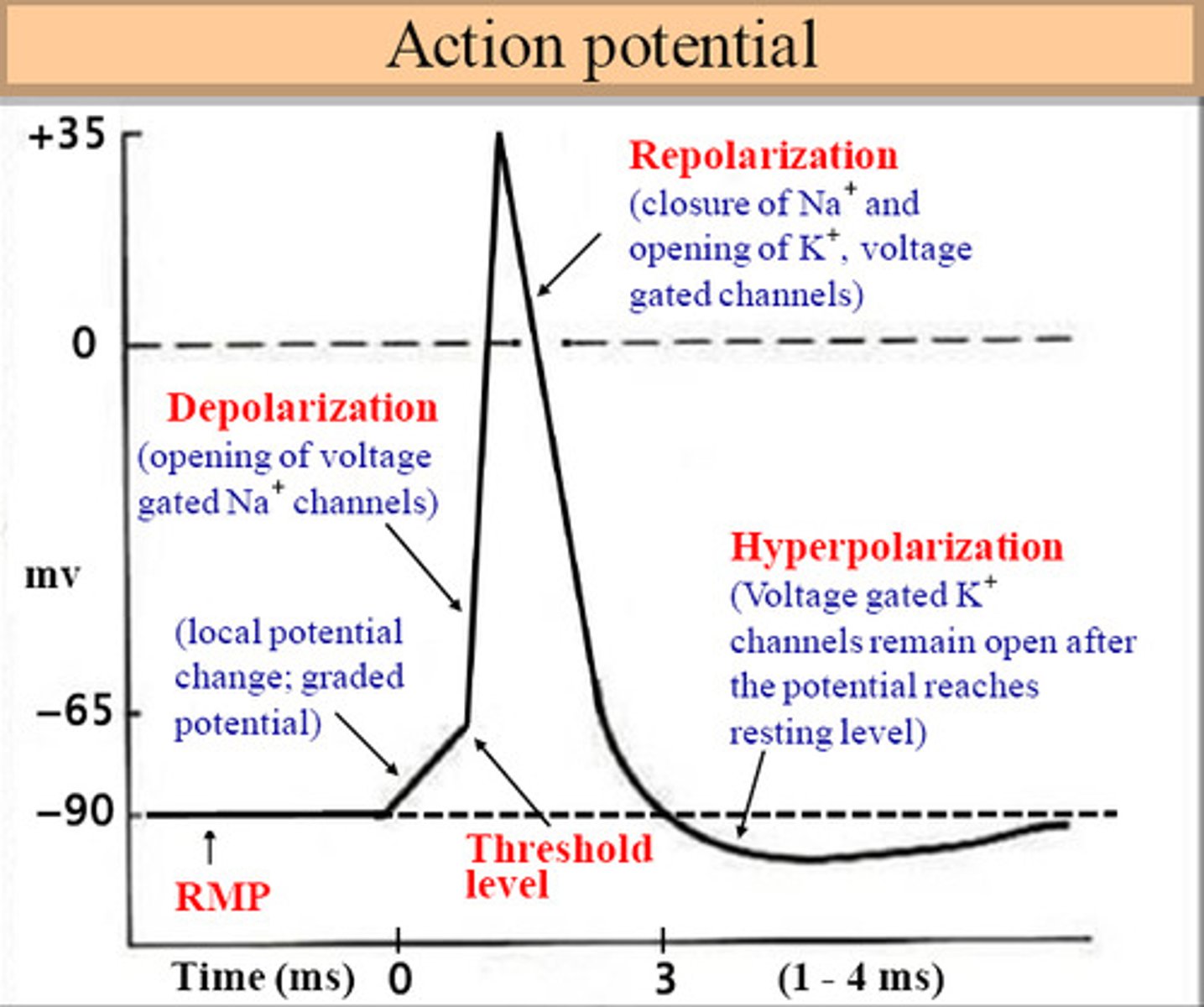
repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.
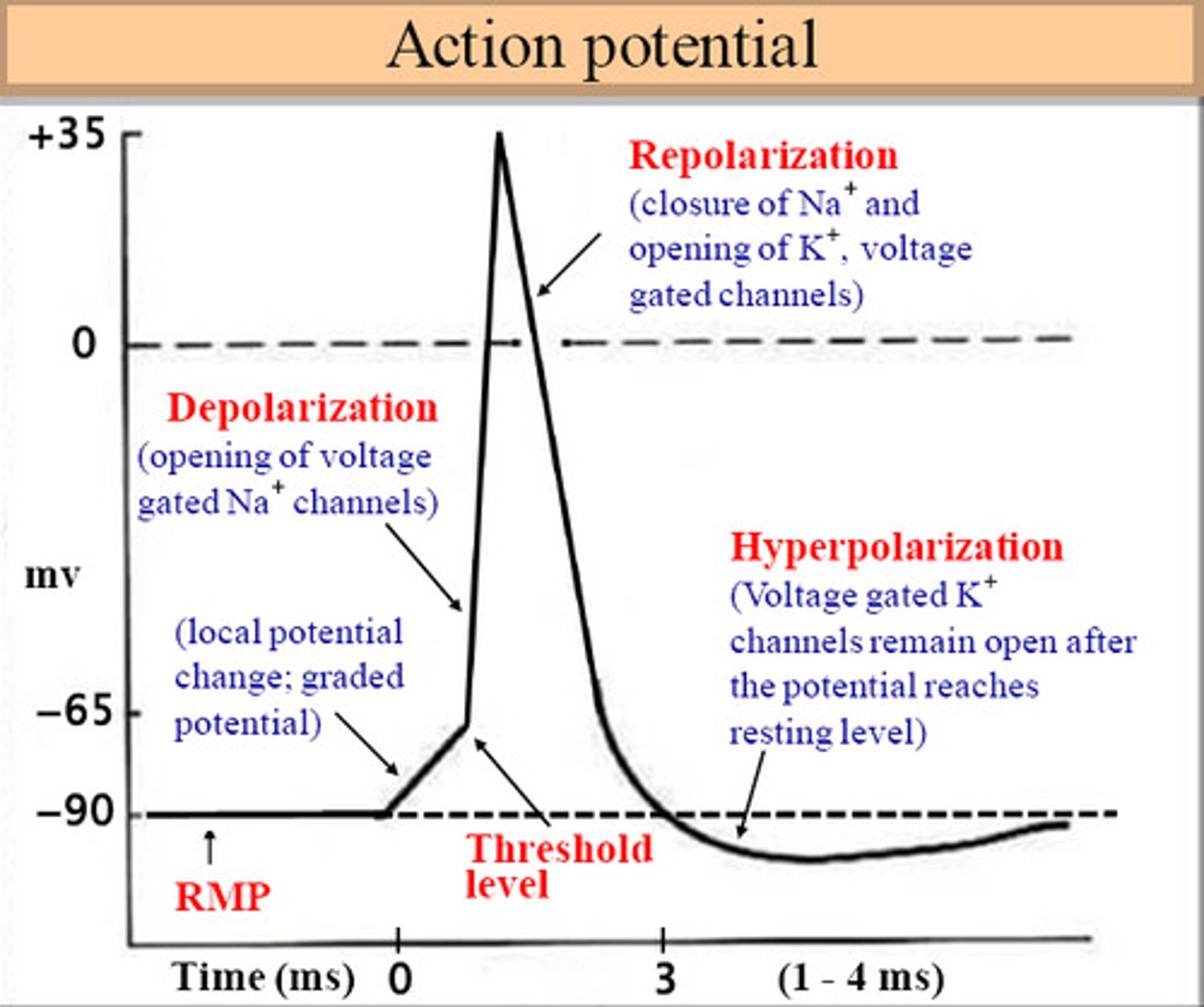
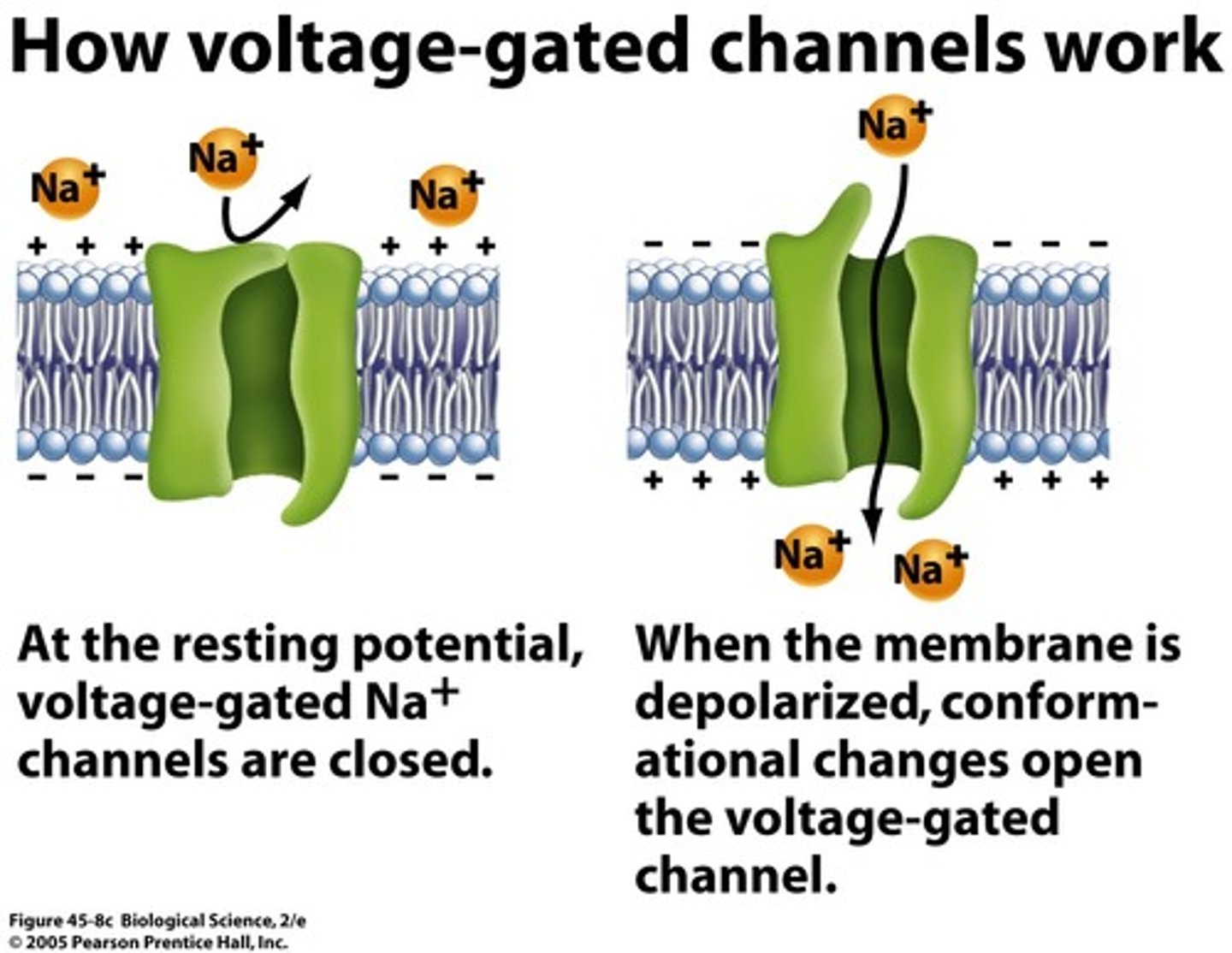
voltage-gated Na+ channels
membrane channels open, bringing about the depolarization phase of the action potential.
voltage-gated K+ channels
open when a particular membrane potential is reached; closed at resting potential
plateau
During the plateau phase of the action potential, calcium ions flow down this steep concentration gradient and enter the myocyte
summation
increased force of contraction by a skeletal muscle fiber when a twitch occurs before the previous twitch relaxes
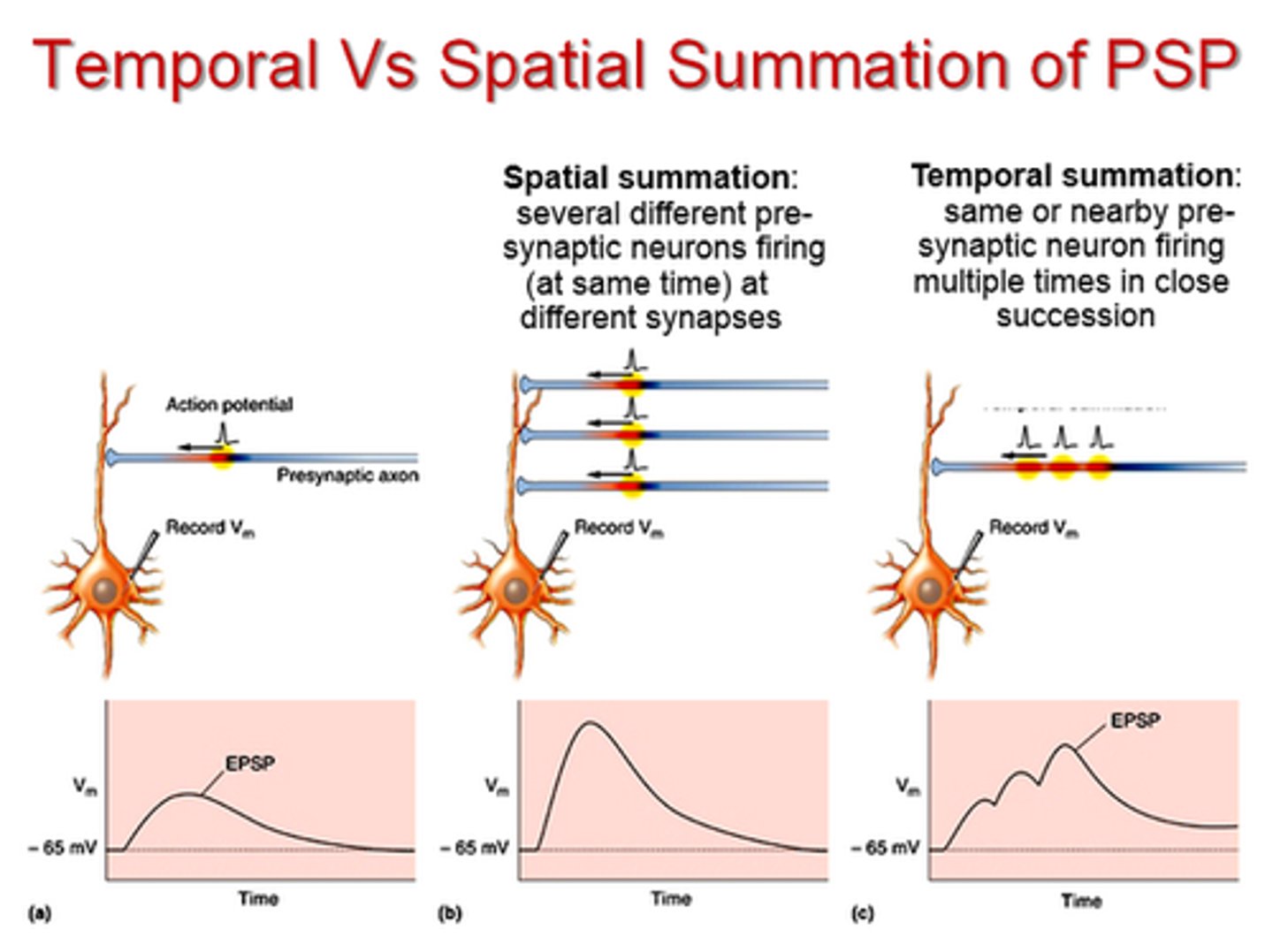
refractory period
the time following an action potential during which a new action potential cannot be initiated
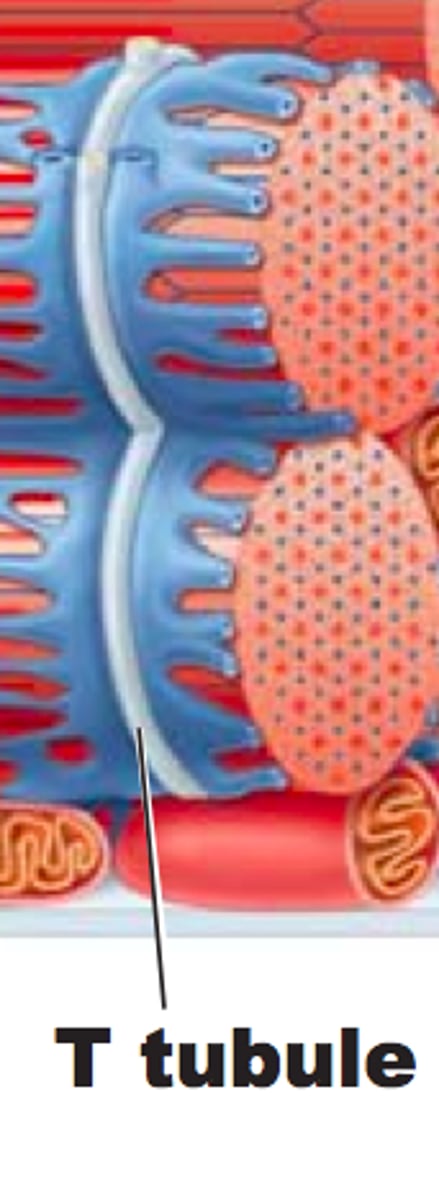
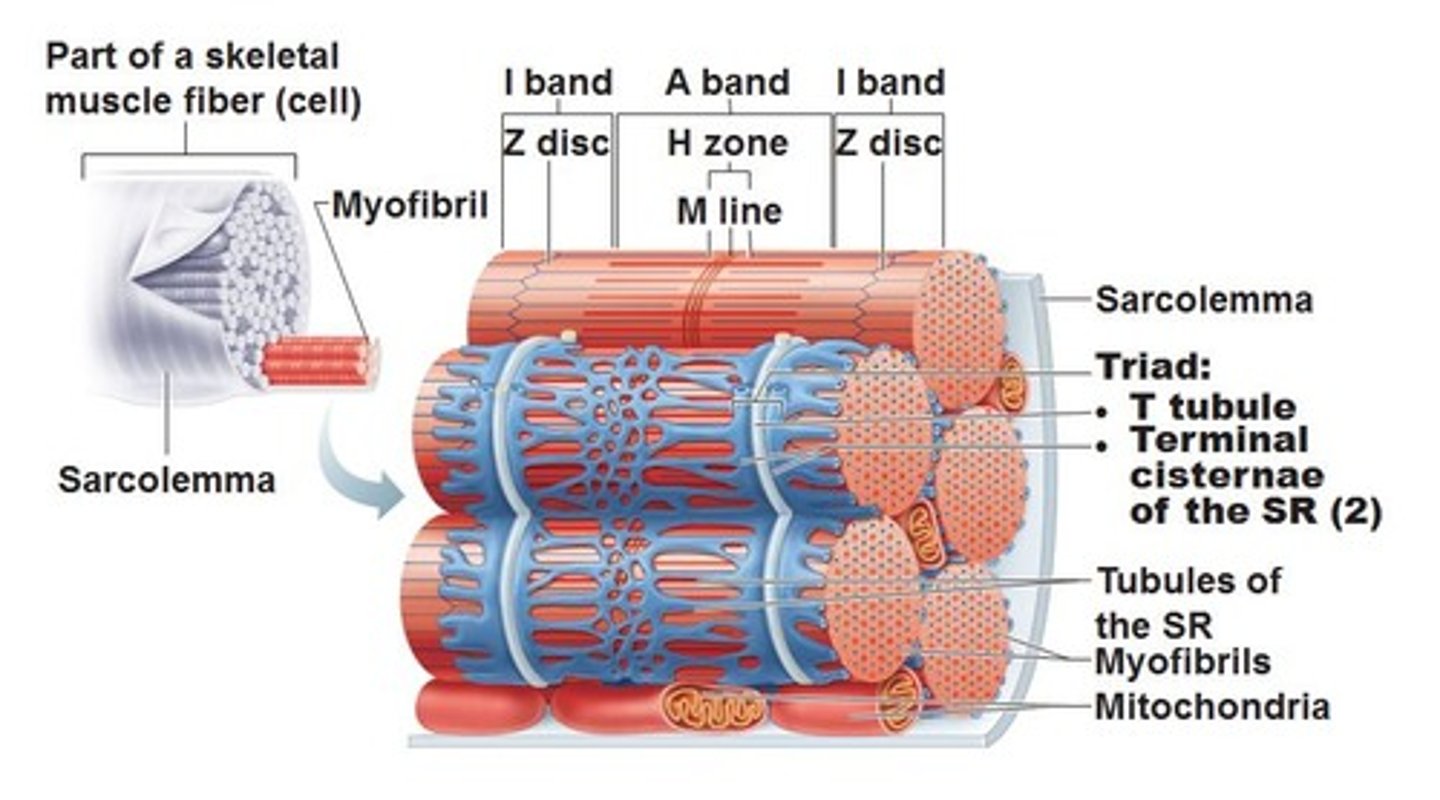
T tubules
Also called transverse tubules, these are deep invaginations of the plasma membrane found in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. These invaginations allow depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate to the interior of the cell.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells
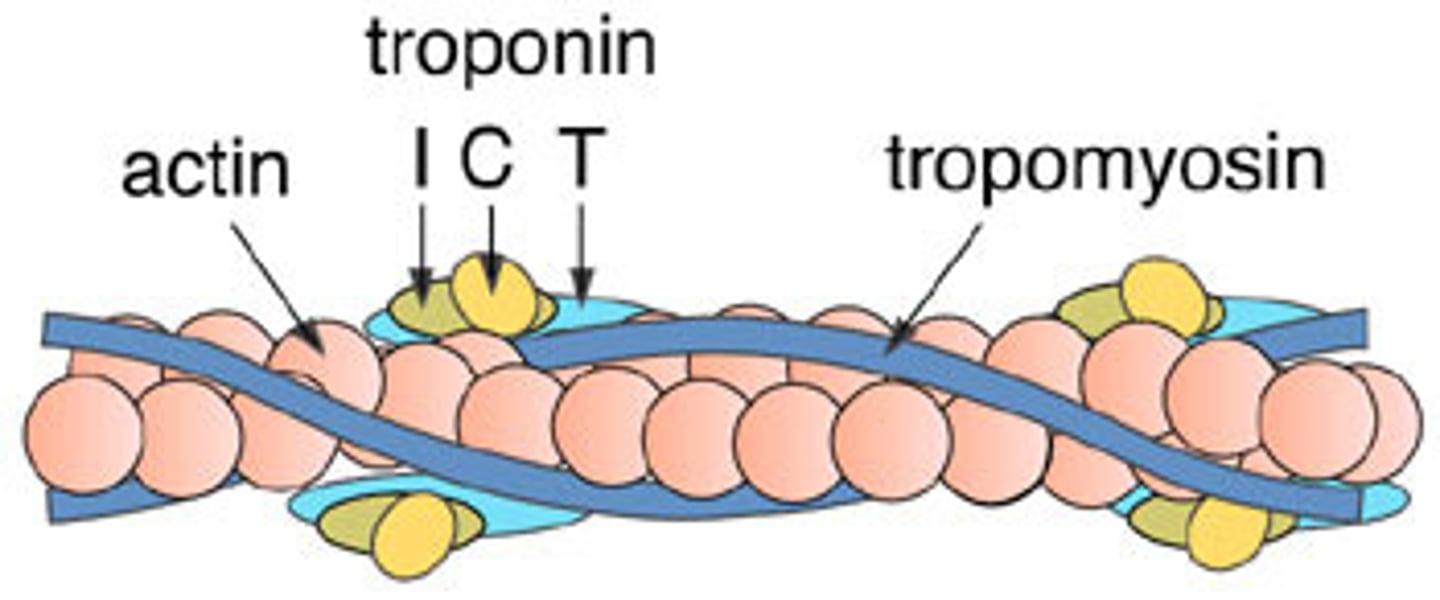
troponin
A protein of muscle that together with tropomyosin forms a regulatory protein complex controlling the interaction of actin and myosin and that when combined with calcium ions permits muscular contraction
crossbridge cycling
1. Crossbridge formation
2. Power stroke
3. Release of myosin head
4. Reset myosin head
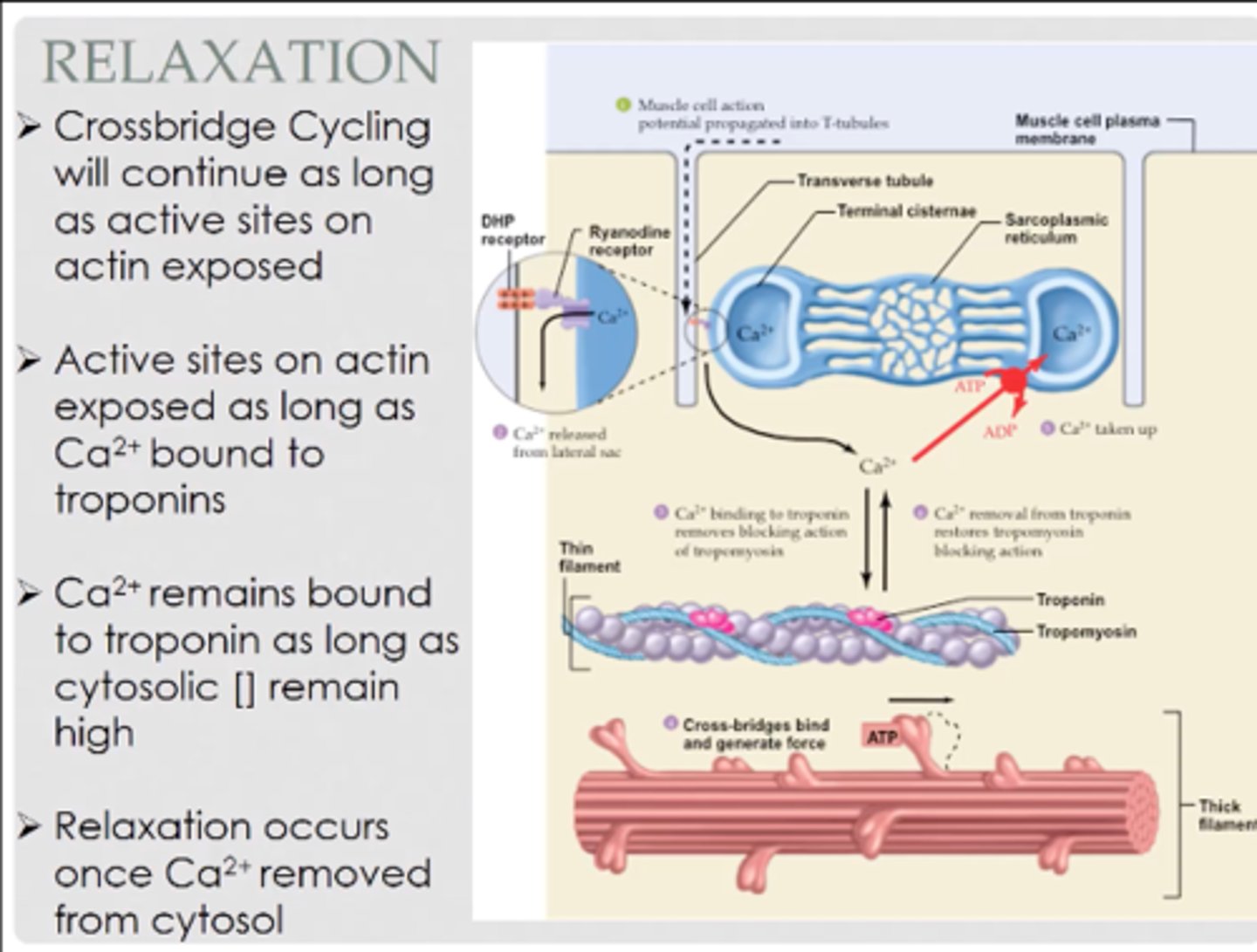
excitation-contraction coupling
sequence of events from motor neuron signaling to a skeletal muscle fiber to contraction of the fiber's sarcomeres
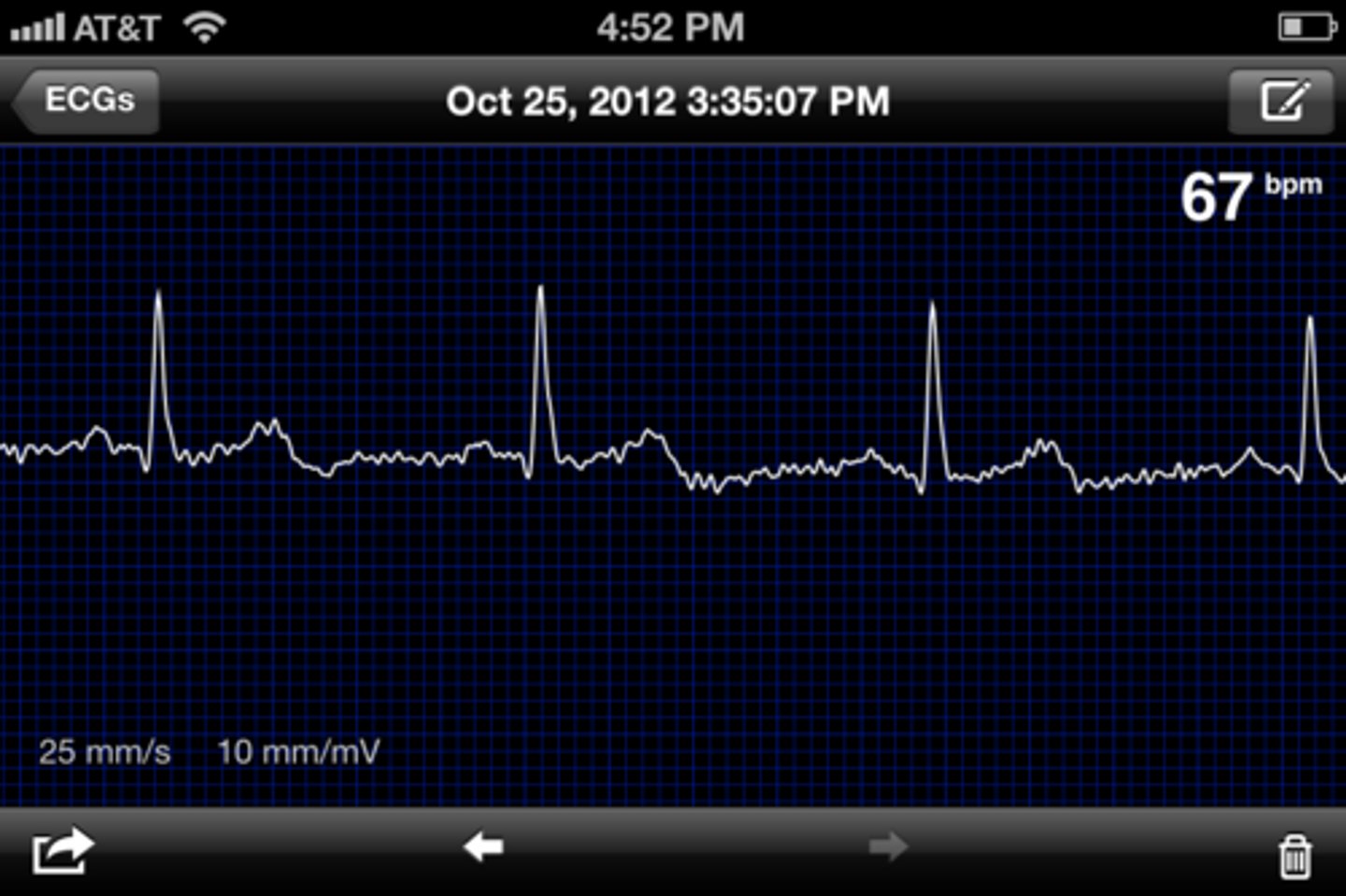
electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
A recording of the electrical activity of the heart
arrhythmia
Abnormal heart rhythm
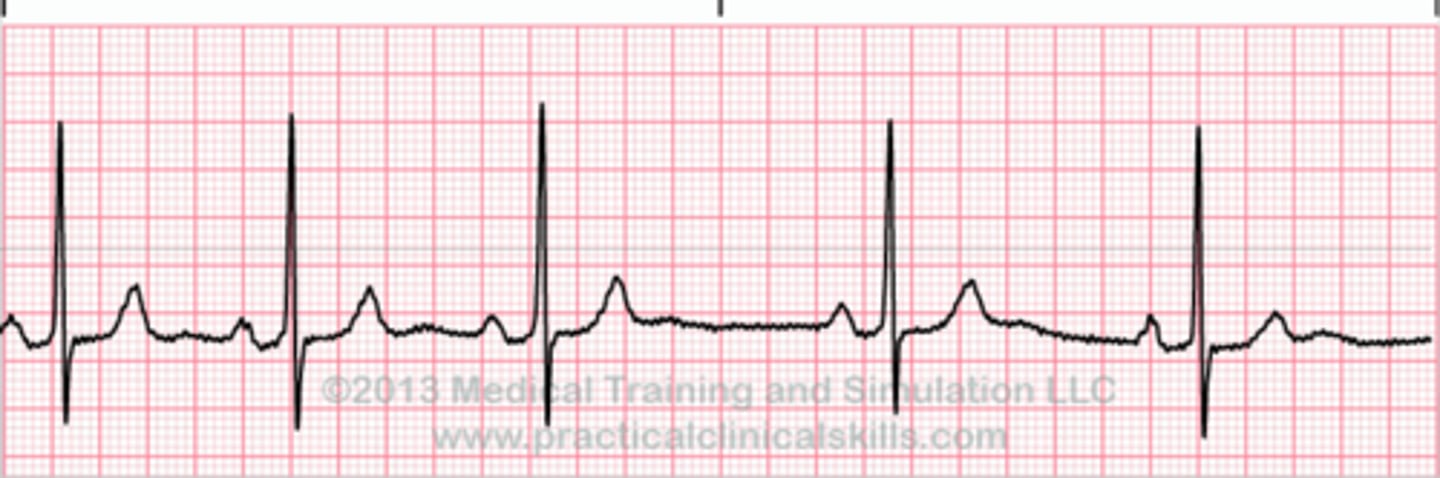
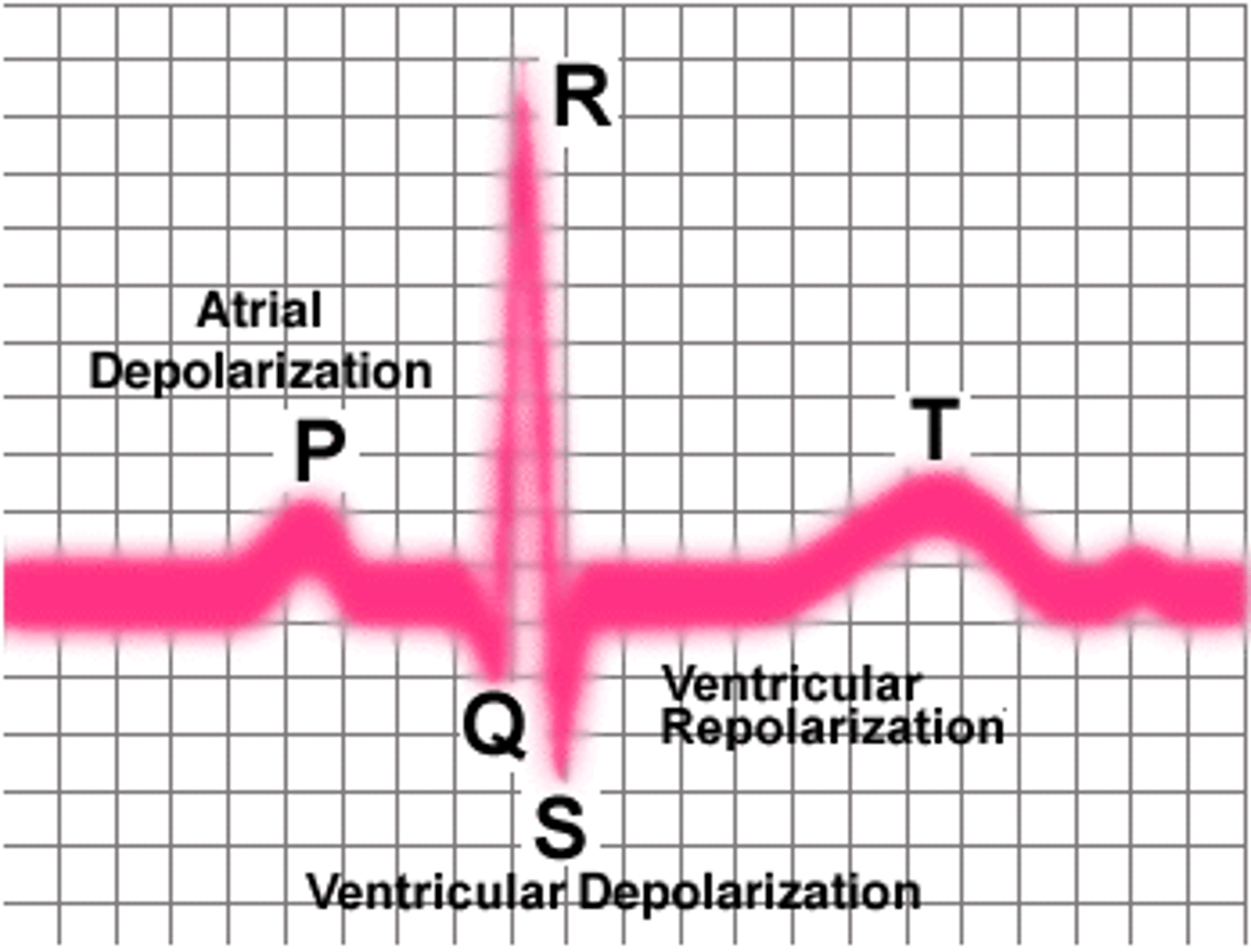
P wave
depolarization of the atria
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
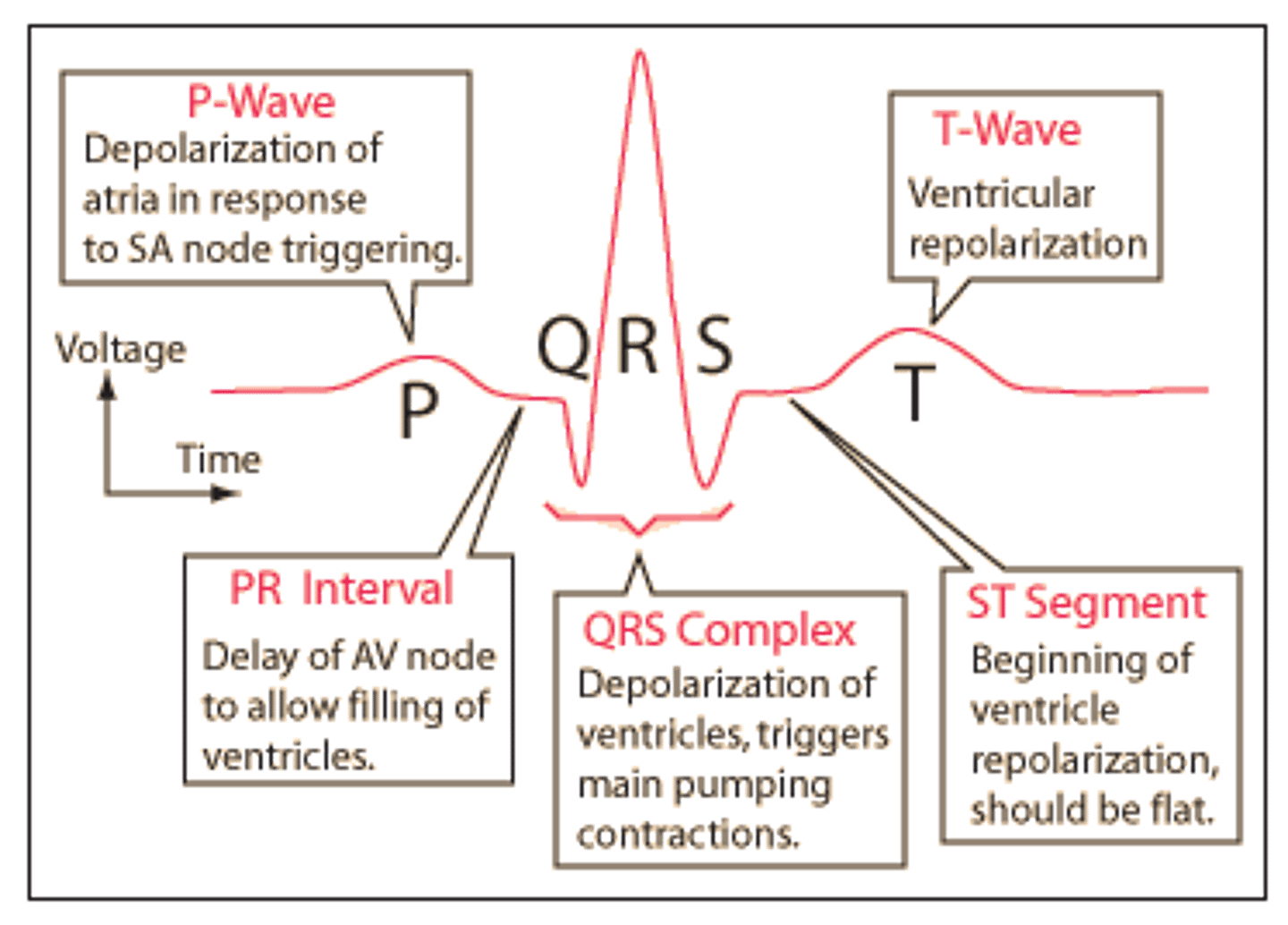
T wave
ventricular repolarization
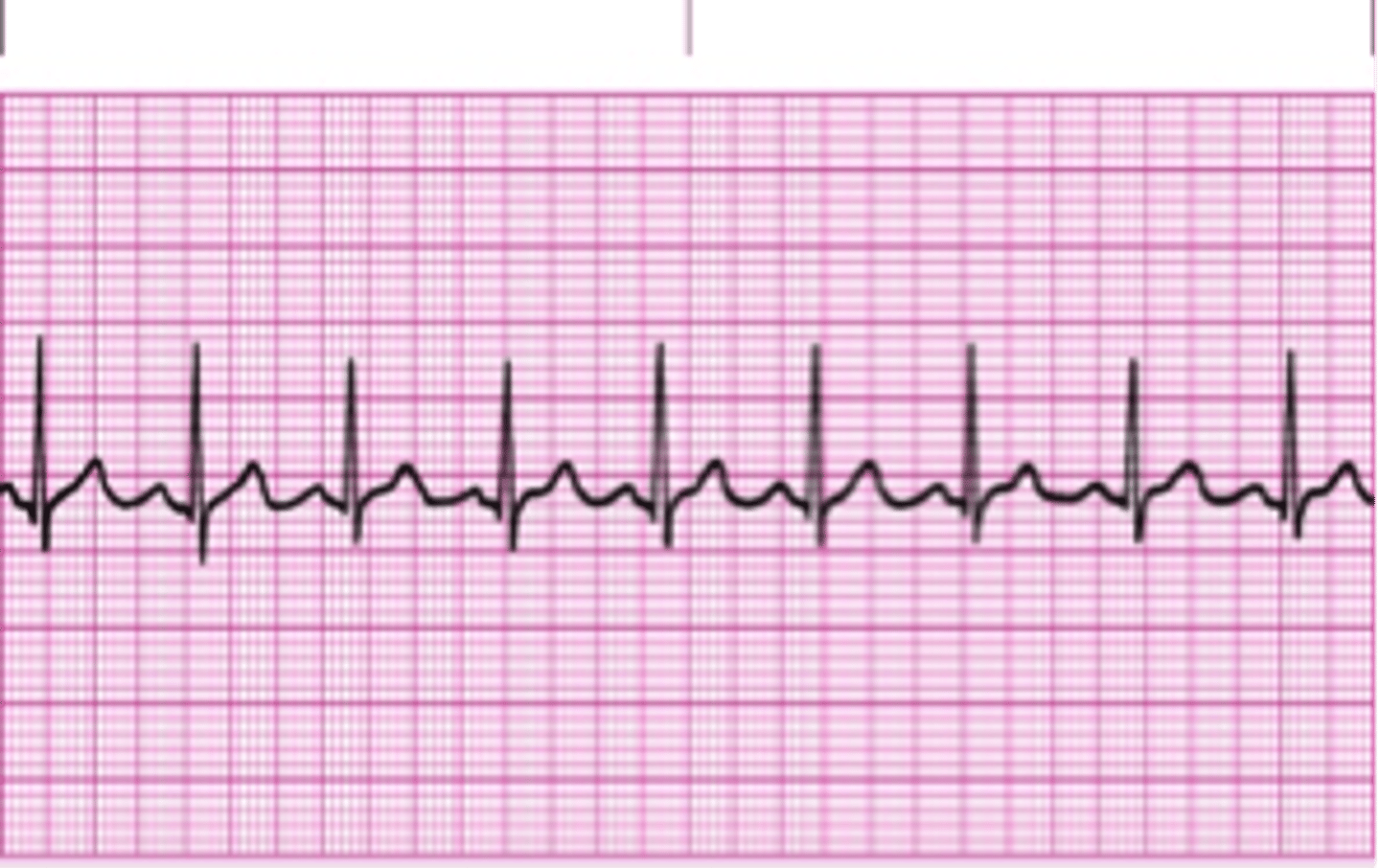
sinus rhythm
the normal (optimal) heart rhythm arising from the sinoatrial node
tachycardia
Abnormally rapid heartbeat
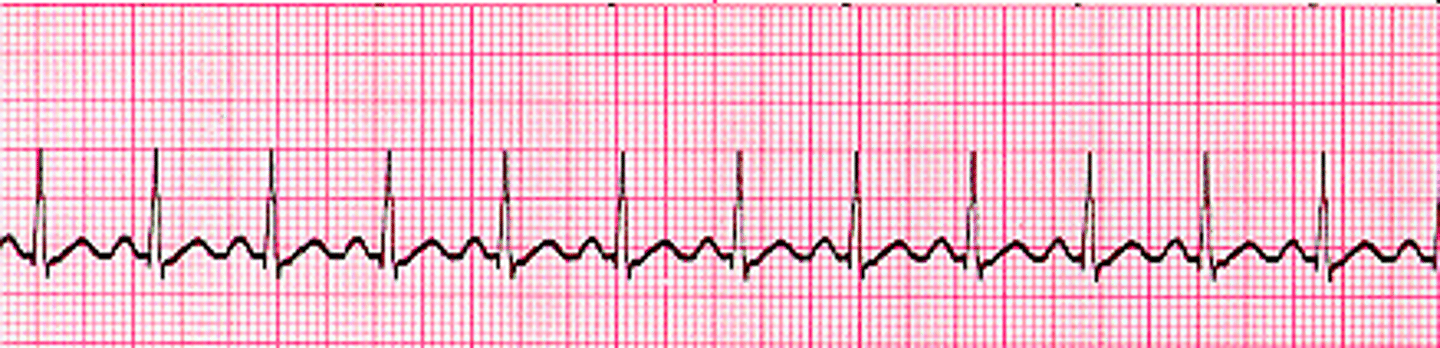
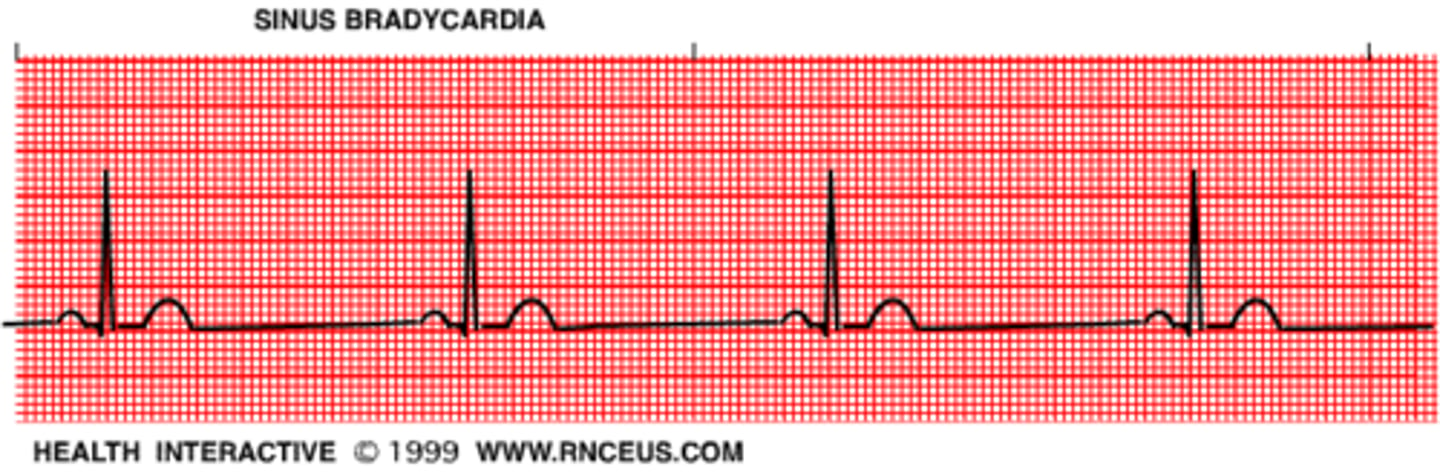
bradycardia
abnormally slow heartbeat
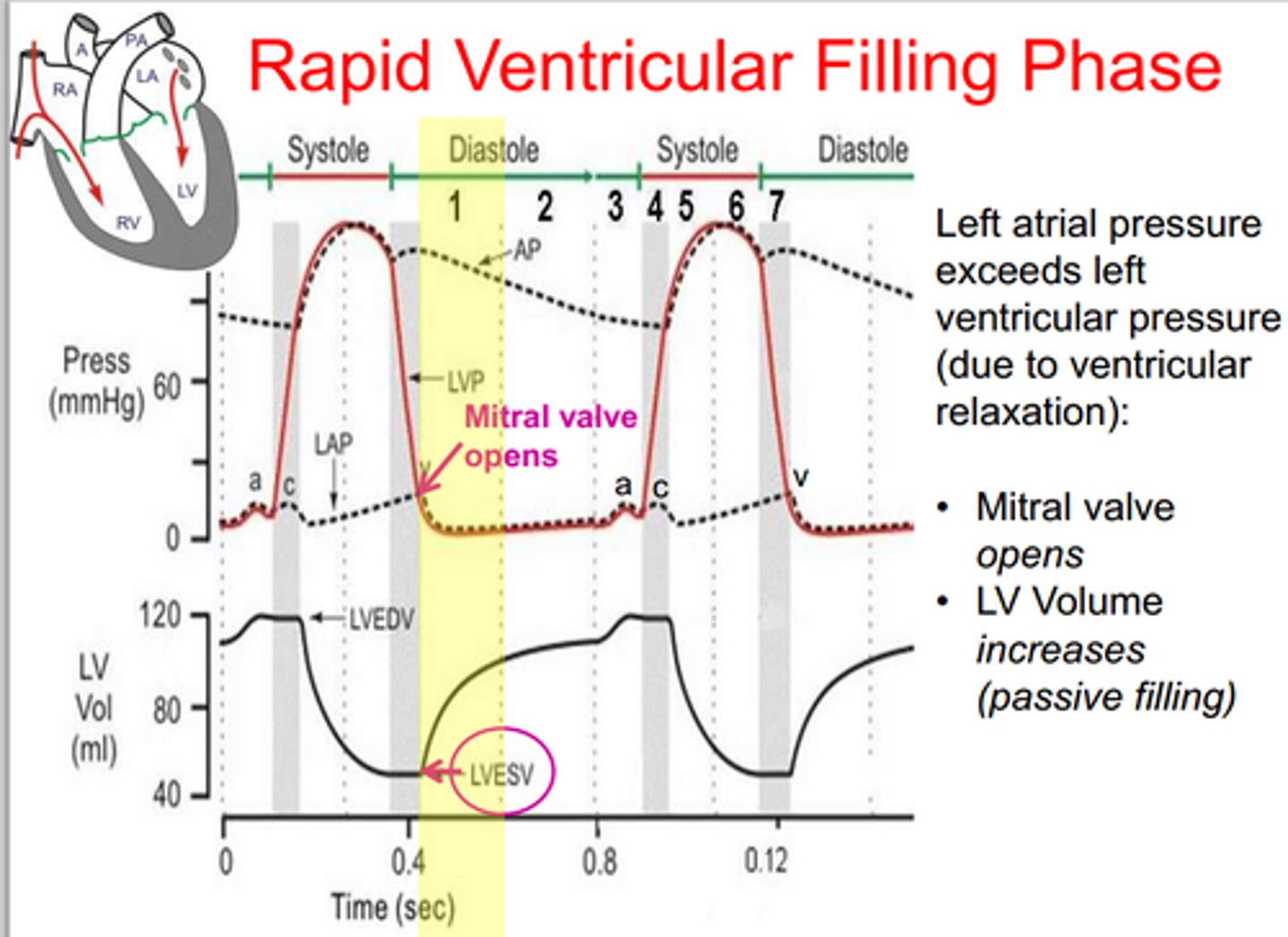
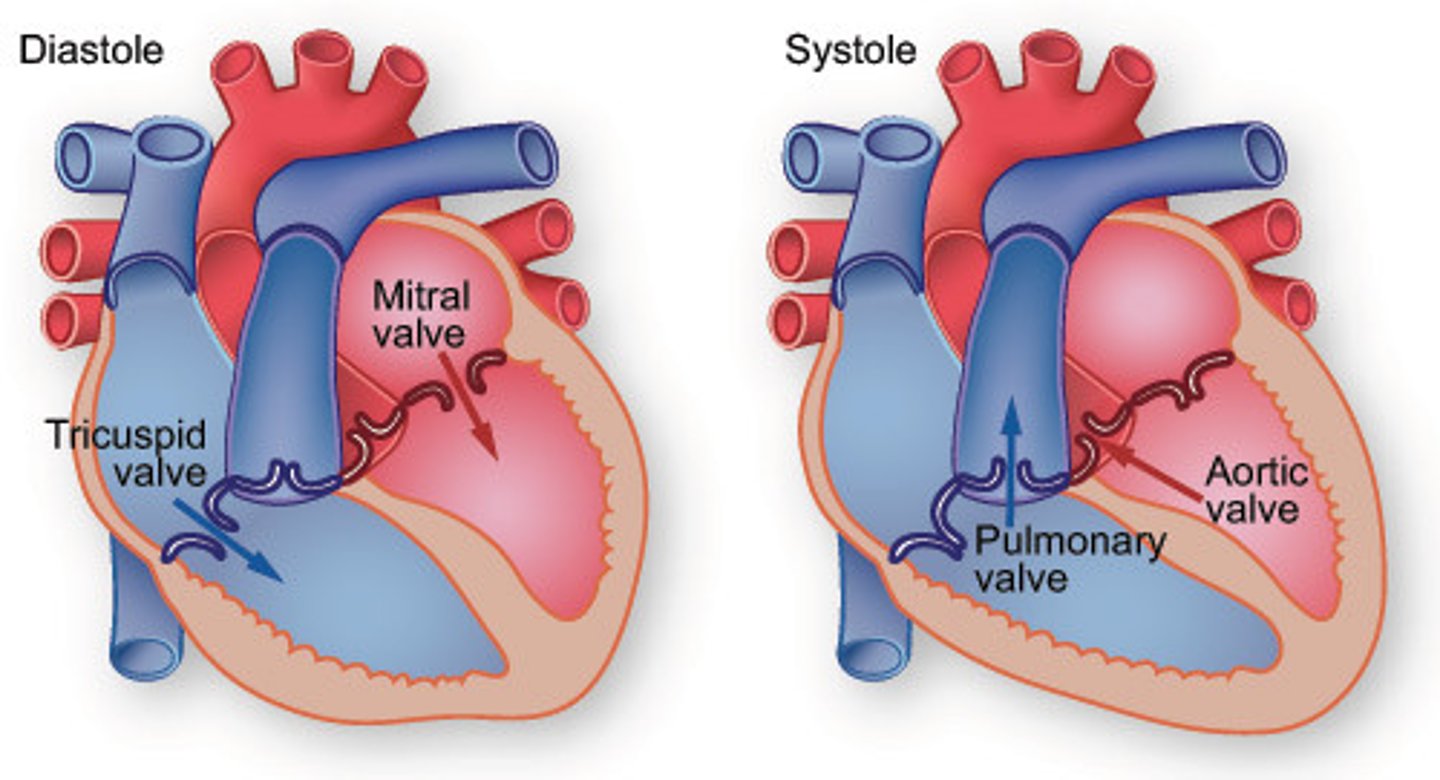
ventricular filling
Phase of the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles expand, their pressure drops, and the AV valves open and blood flows into the ventricles
systole
contraction phase of the heartbeat
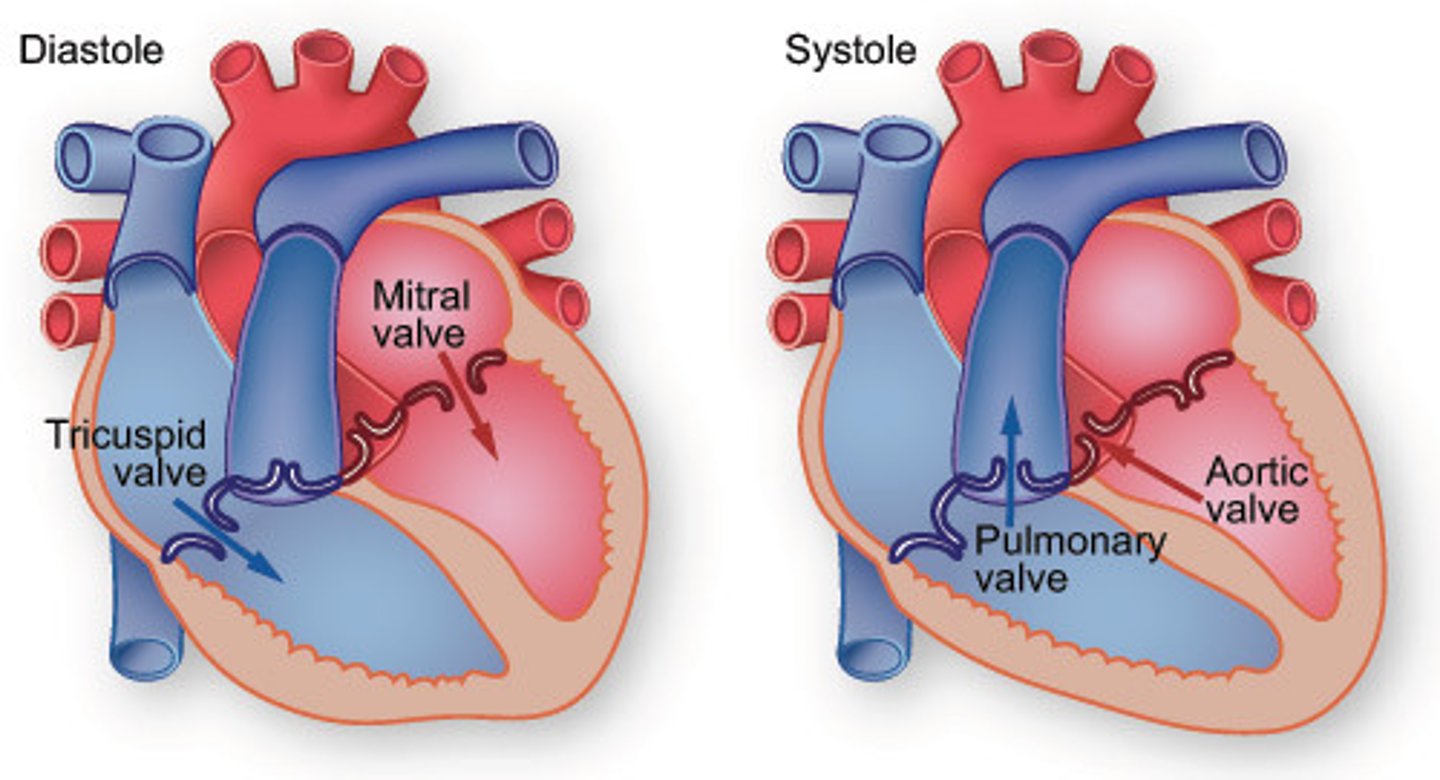
diastole
relaxation phase of the heartbeat
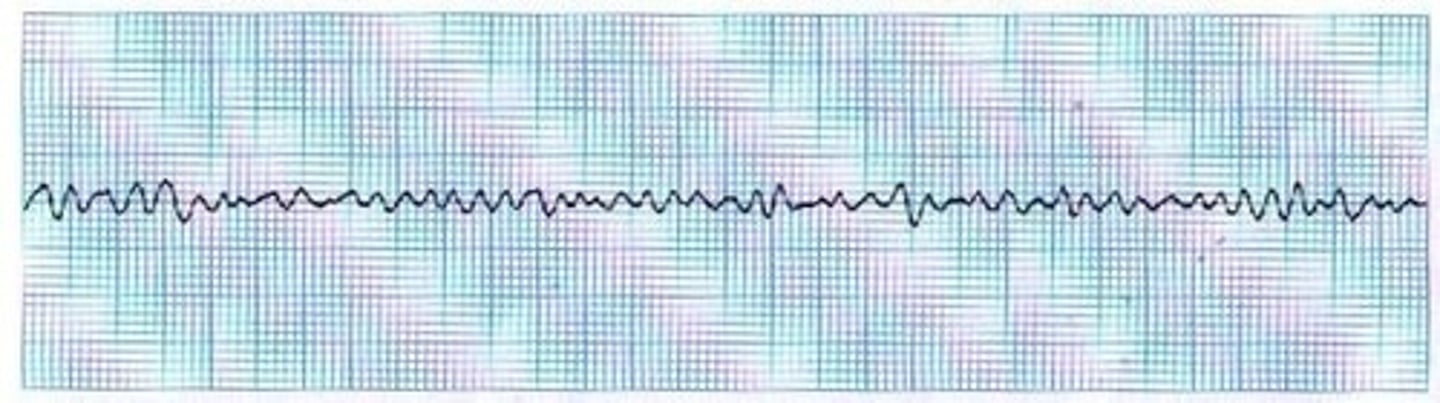
ventricular fibrillation
the rapid, irregular, and useless contractions of the ventricles
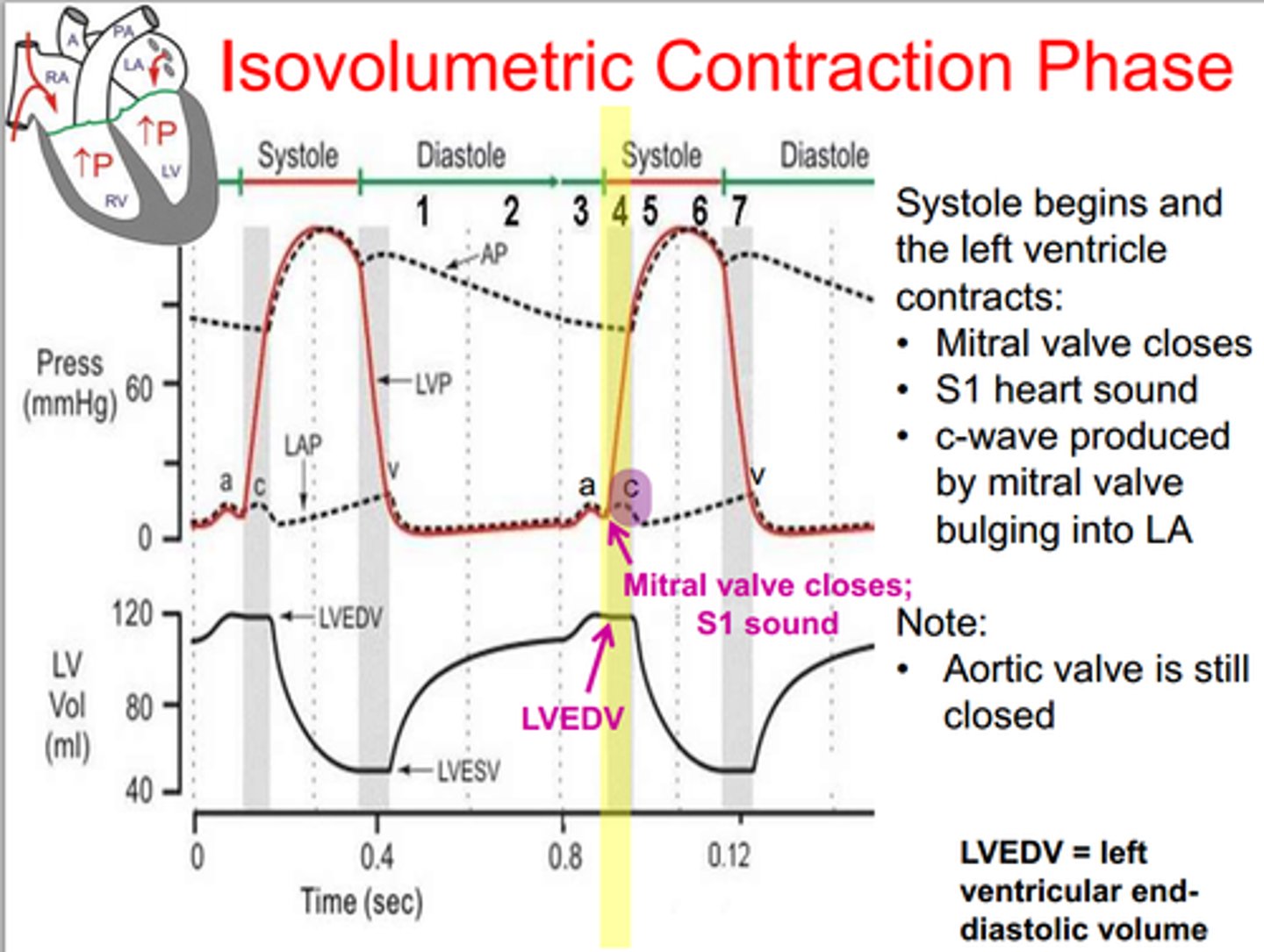
isovolumetric contraction
an event occurring in early systole during which the ventricles contract with no corresponding volume change
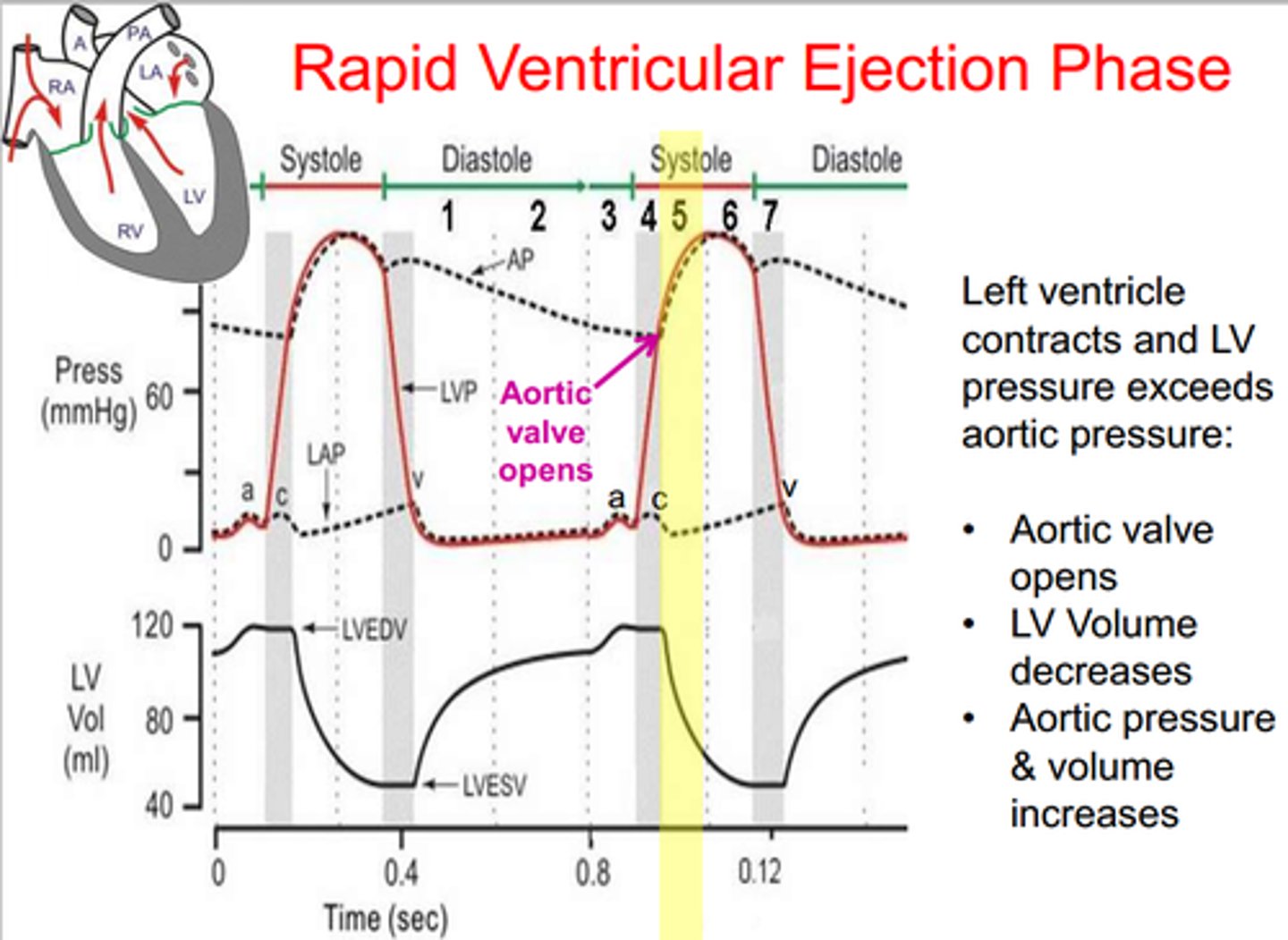
ventricular ejection
the period of time when both semilunar valves are open and blood begins to leave the heart
isovolumetric relaxation
period when all four valves are closed and ventricular blood volume does not change
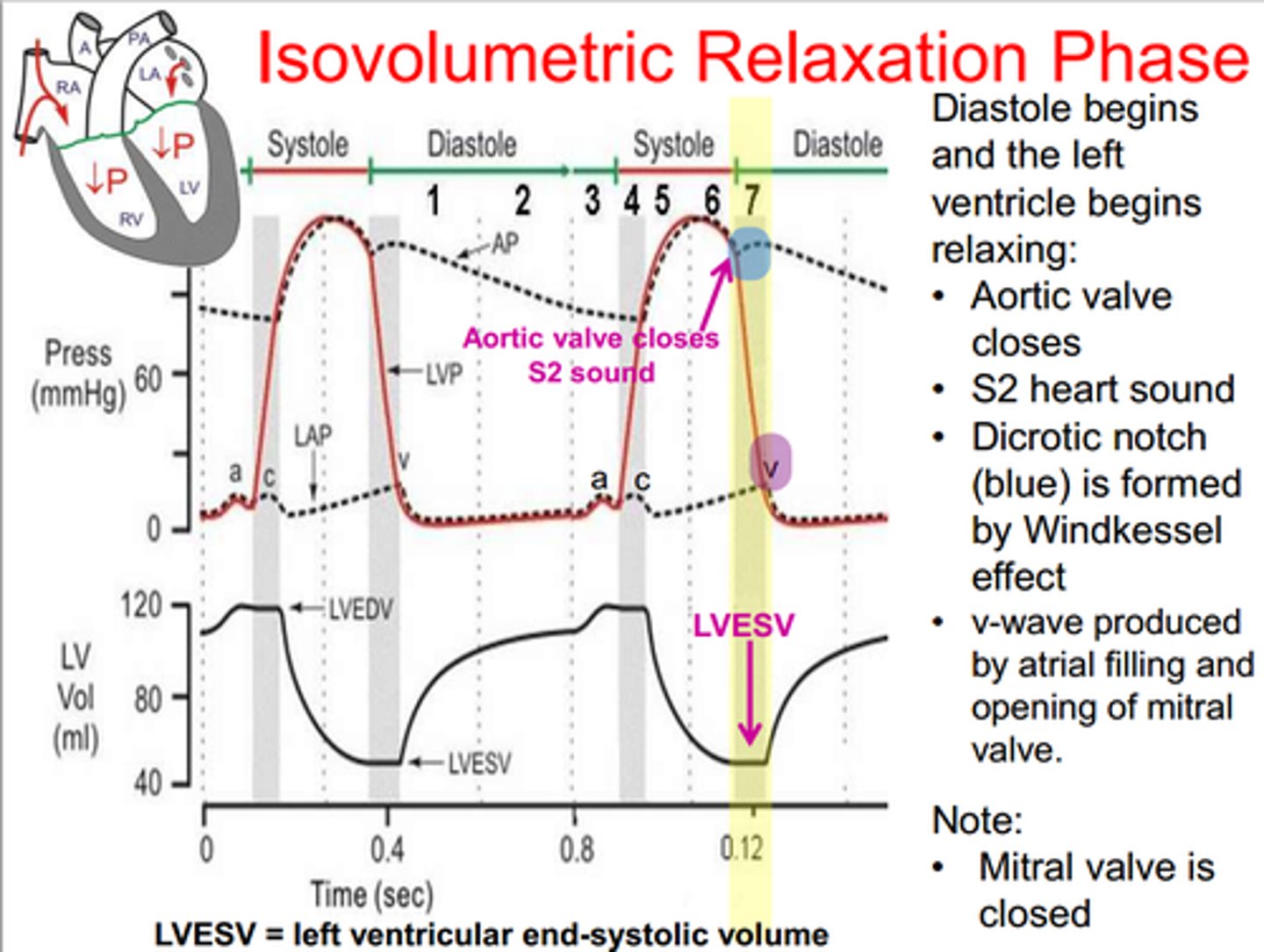
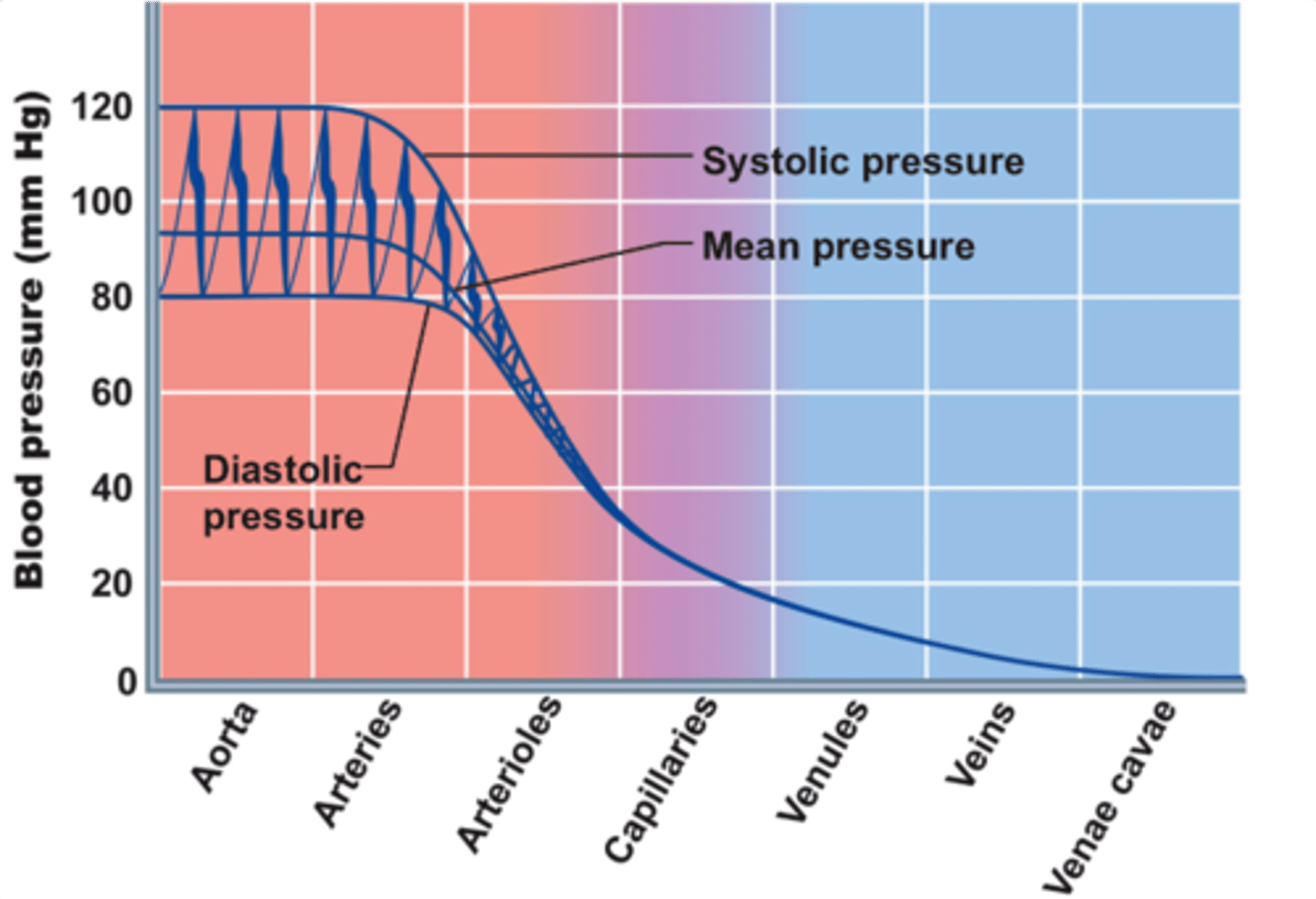
systolic pressure
Blood pressure in the arteries during contraction of the ventricles.
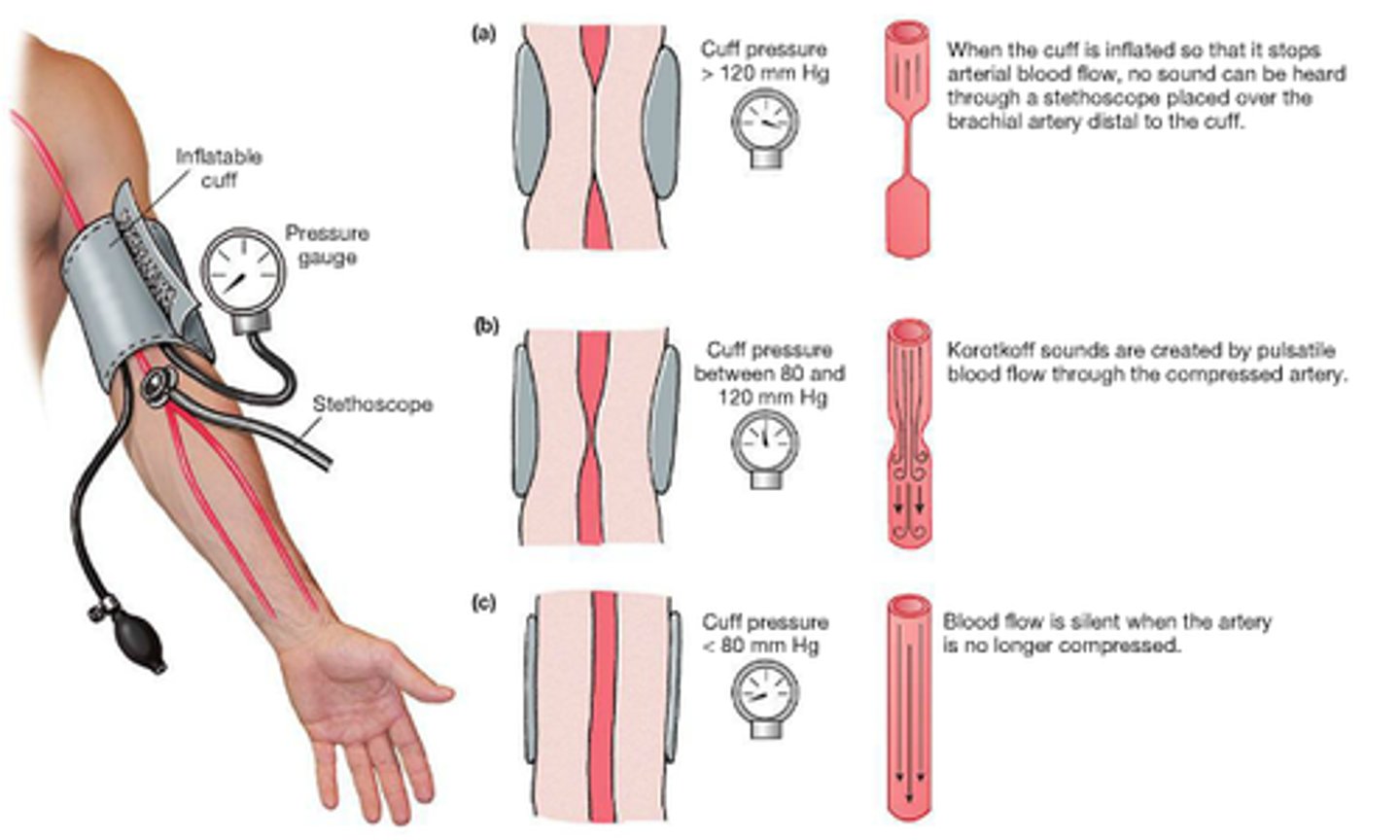
diastolic pressure
occurs when the ventricles are relaxed; the lowest pressure against the walls of an artery
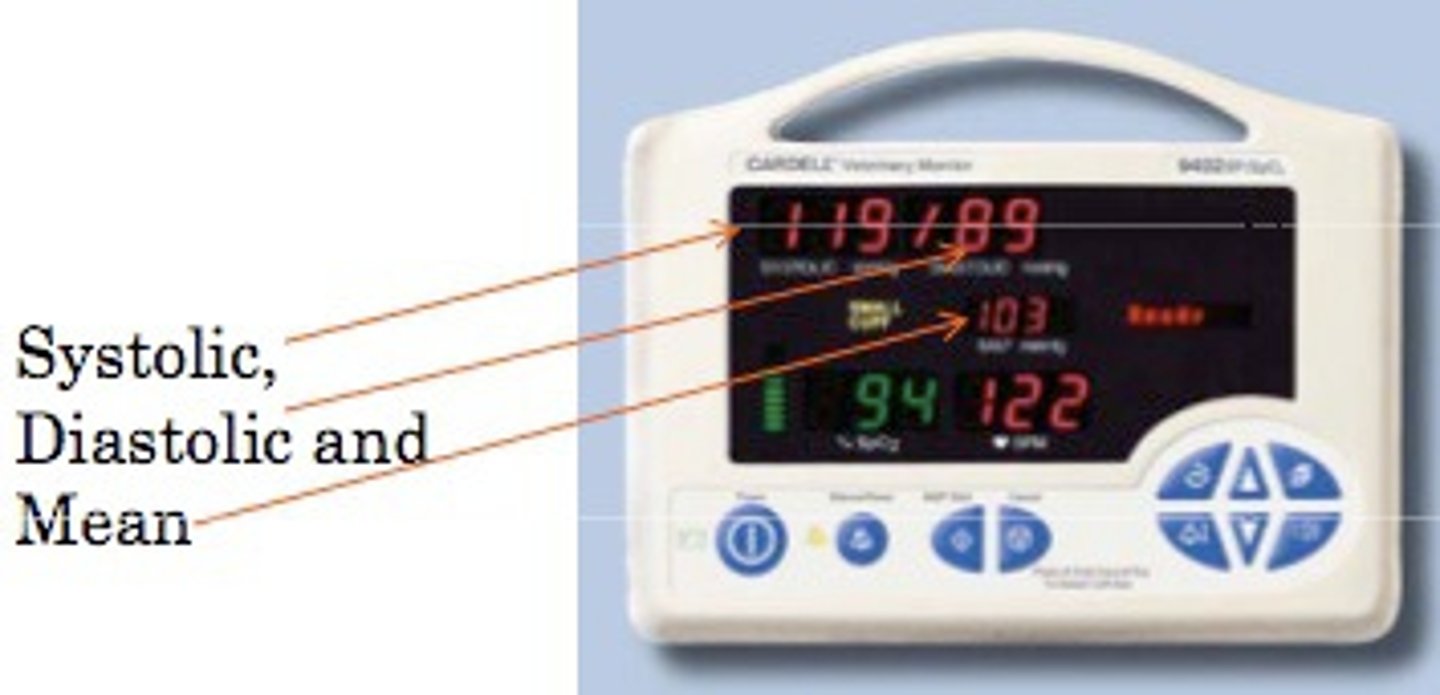

mean arterial pressure
pressure forcing blood into tissues, averaged over cardiac cycle
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
volume of blood in each ventricle at end of ventricular diastole
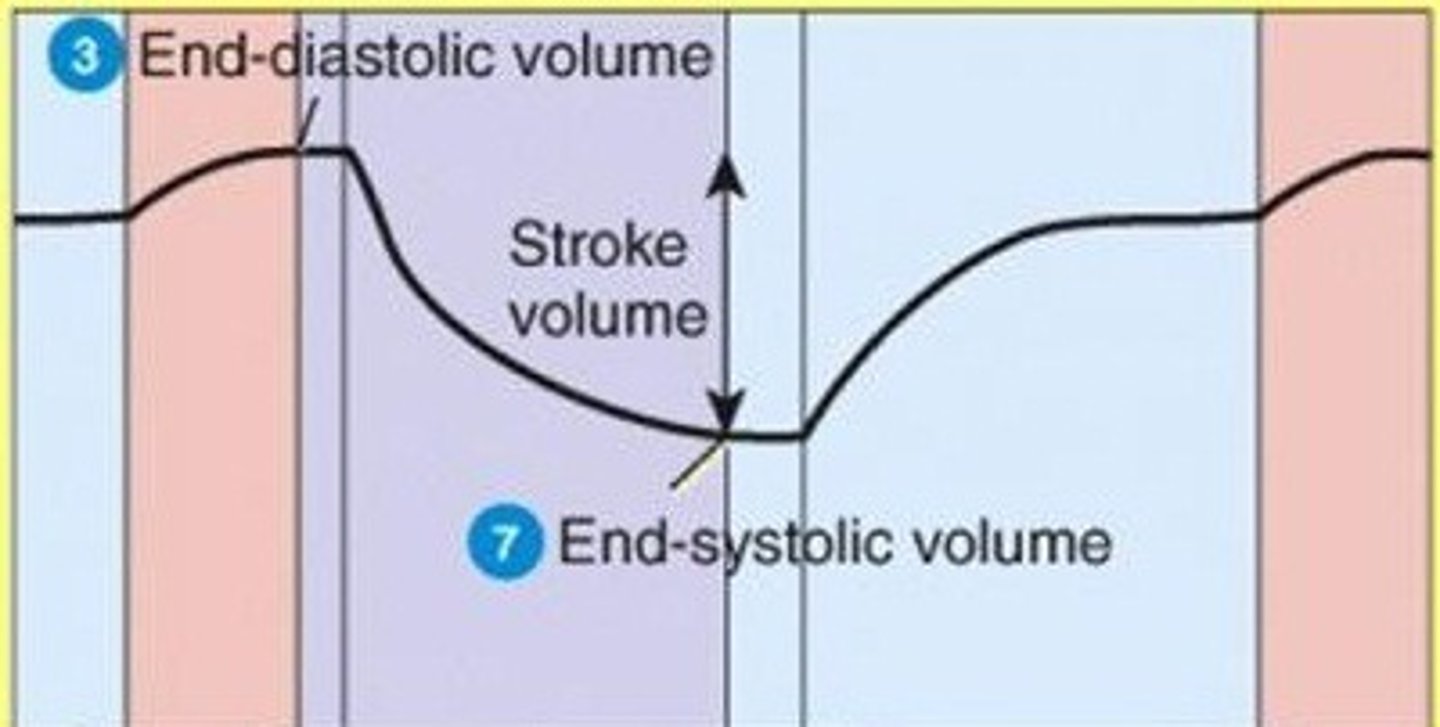
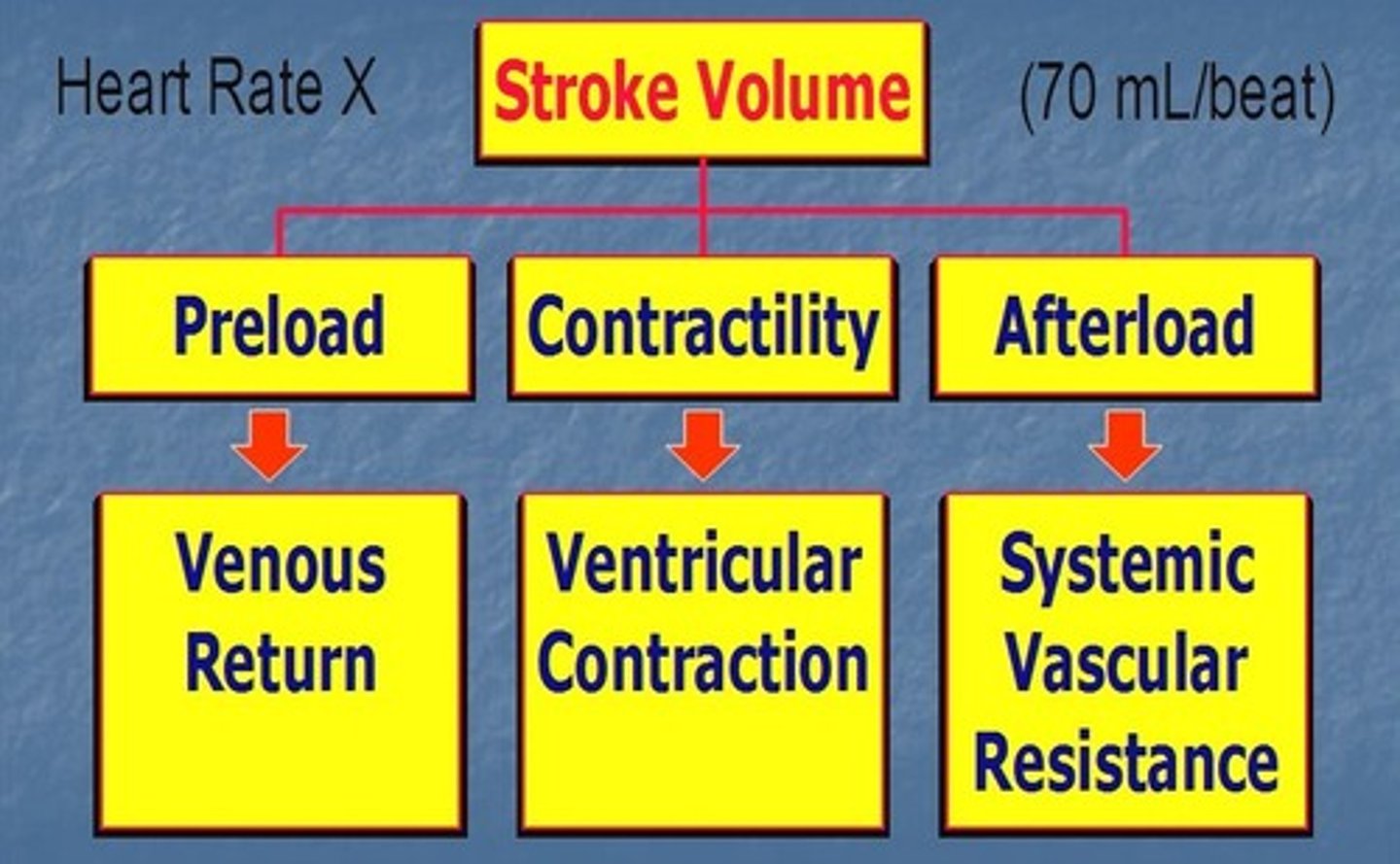
Stroke Volume (SV)
The volume of blood pumped forward with each ventricular contraction.
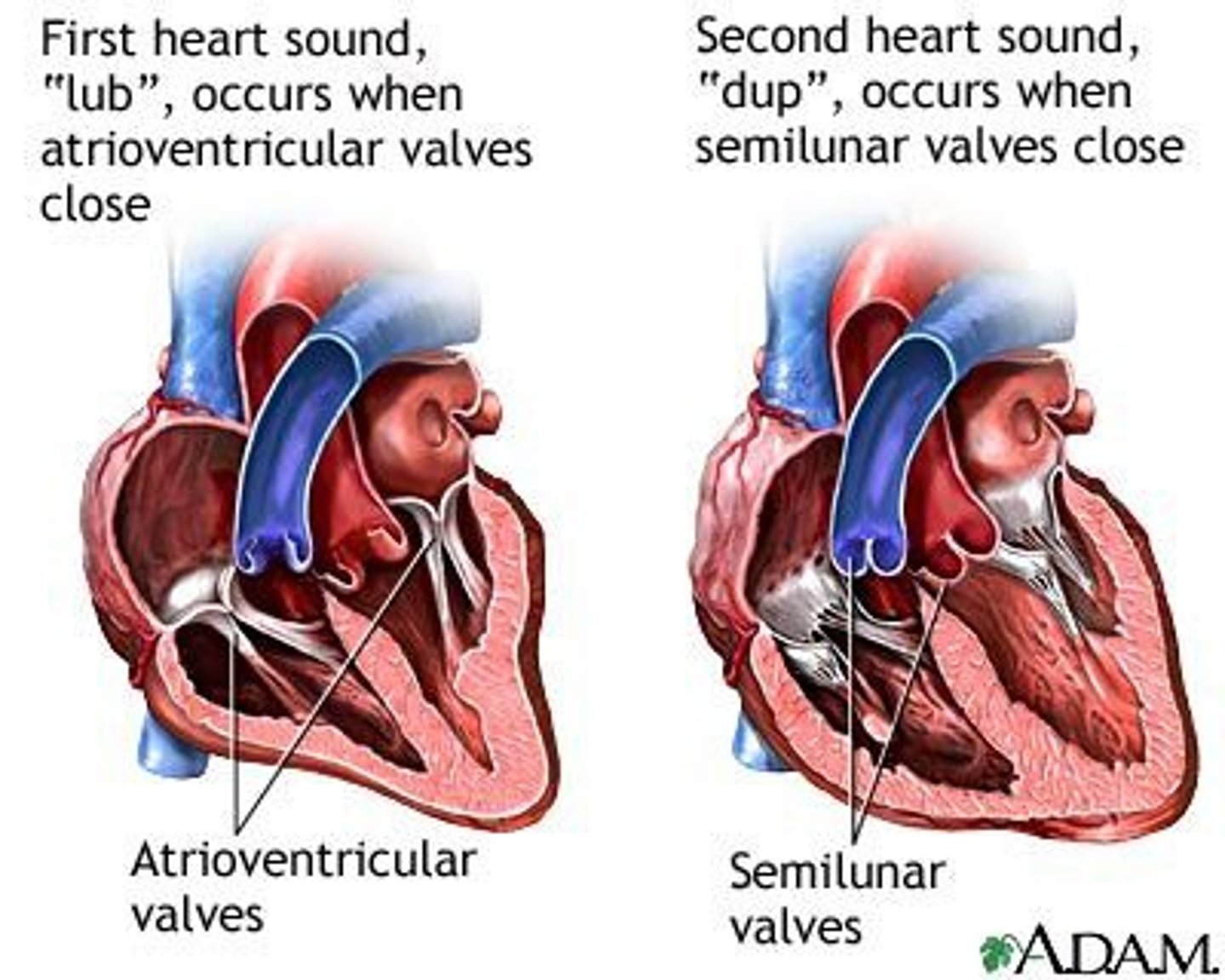
1st heart sound (lub)
closure of AV valves
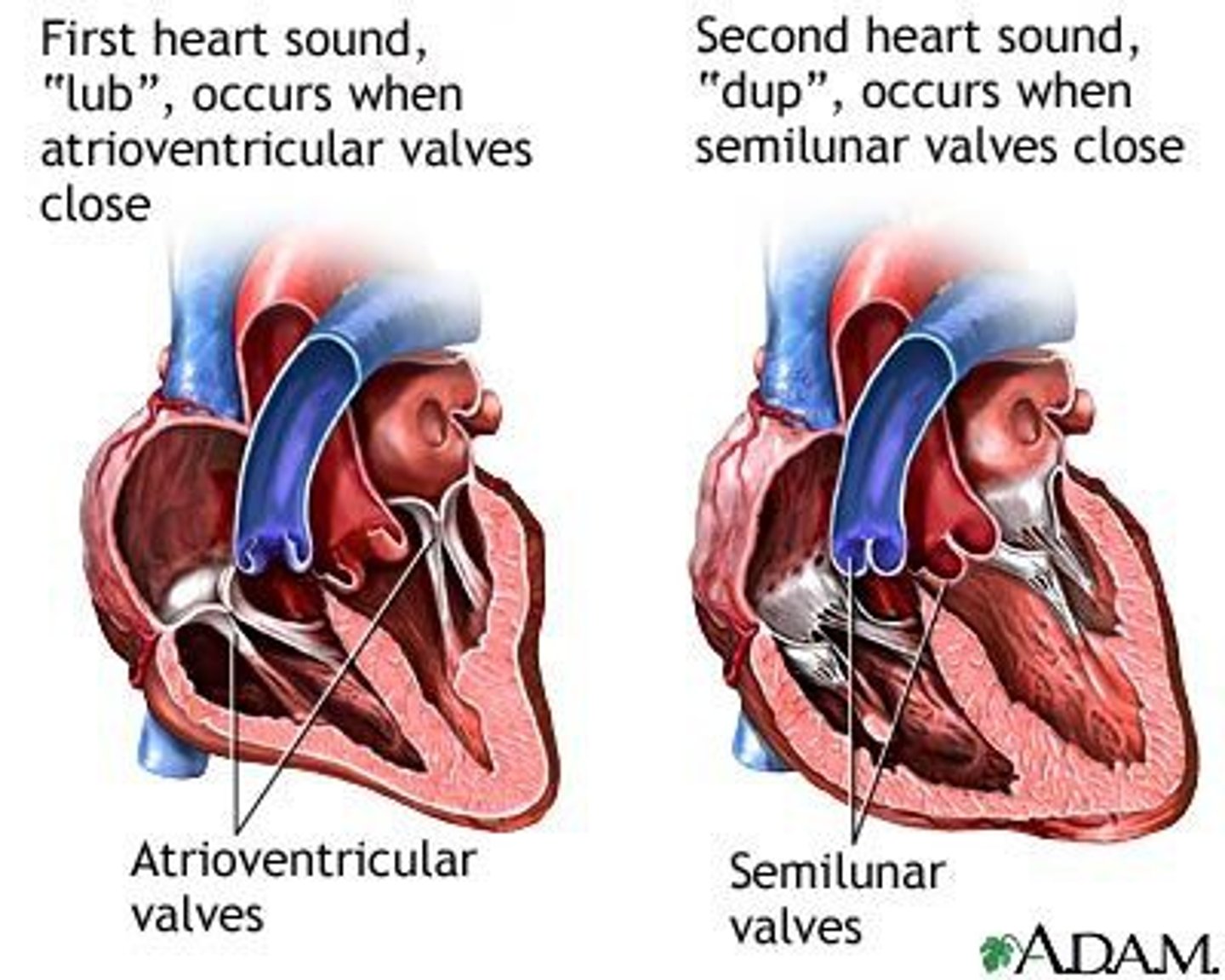
2nd heart sound (dub)
closure of semilunar valves
heart murmur
an abnormal sound from the heart produced by defects in the chambers or valves

echocardiogram
ultrasound of the heart
Cardiac Output (CO)
measurement of the amount of blood ejected per minute from either ventricle of the heart
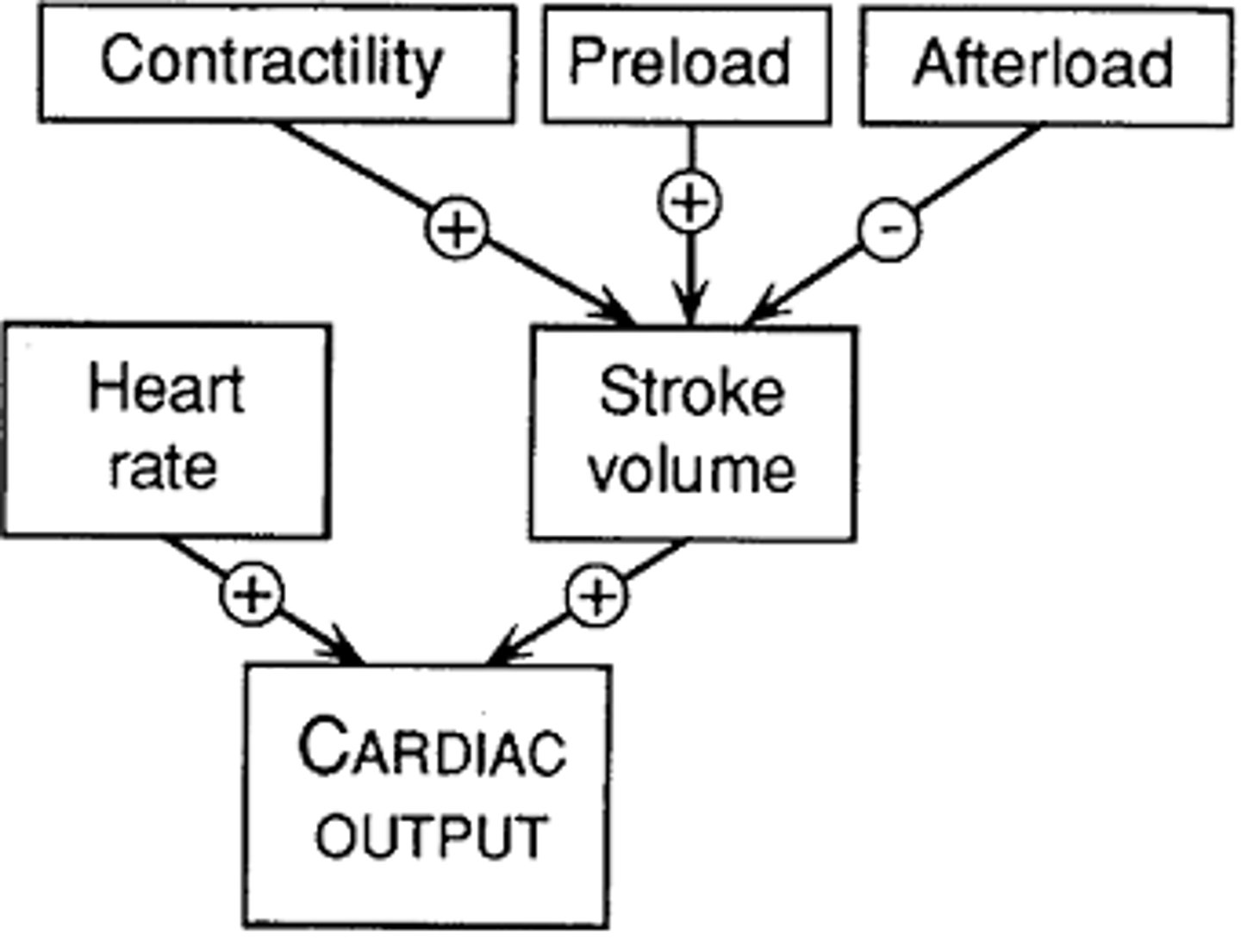
Heart Rate (HR)
number of heart beats per minute

autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
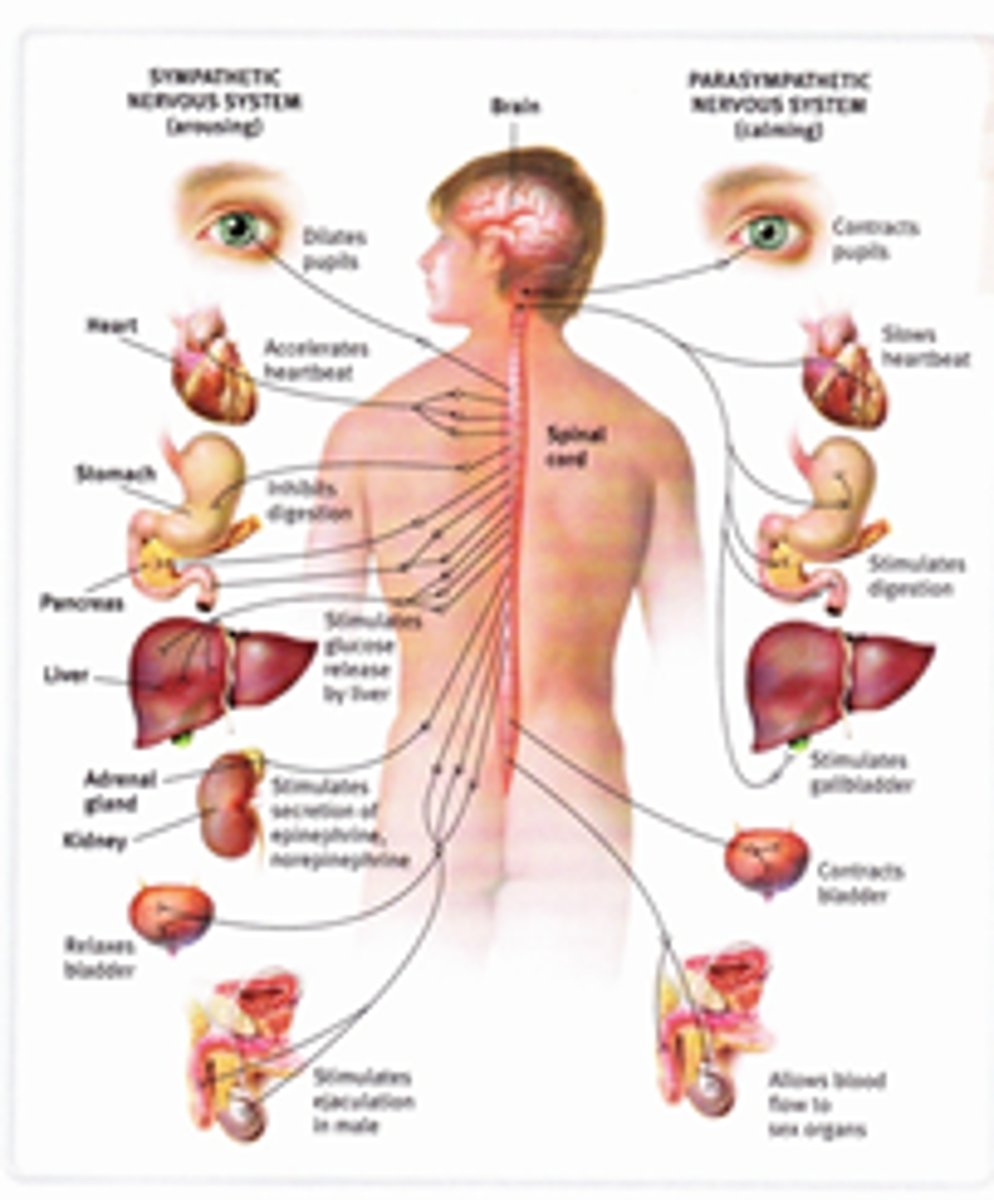
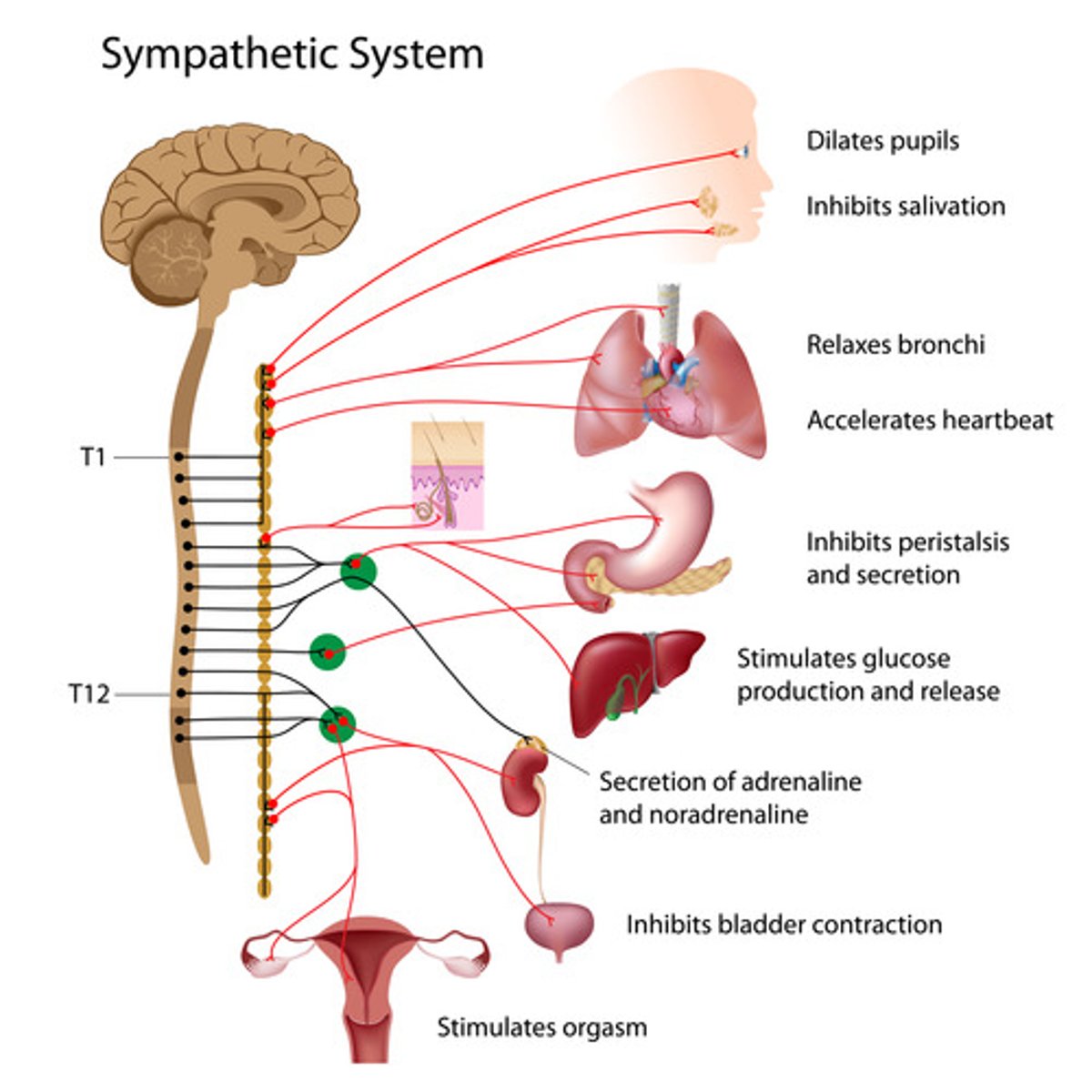
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
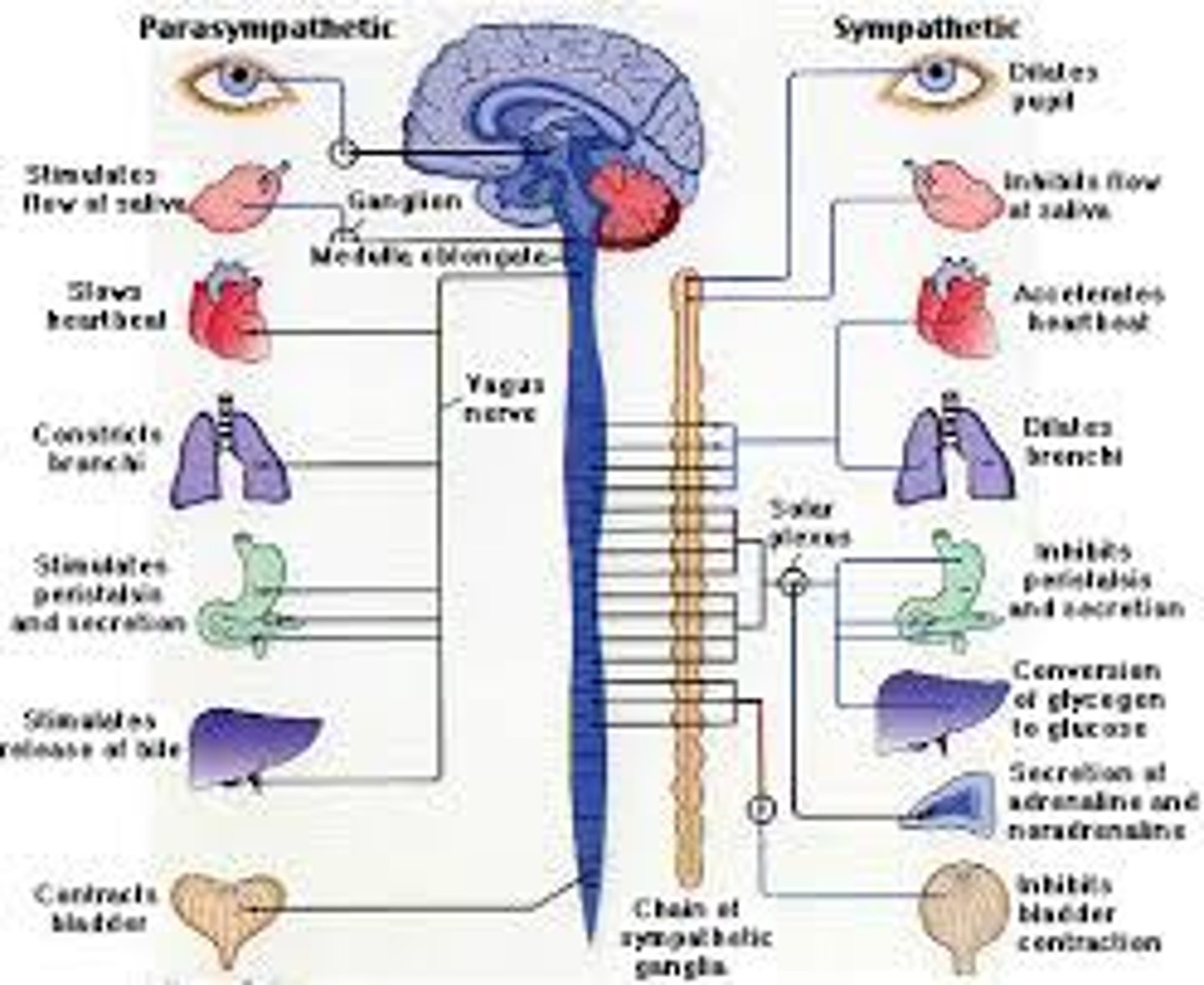
vagus nerve
the tenth cranial nerve that innervates digestive organs, heart and other areas
epinephrine
adrenaline
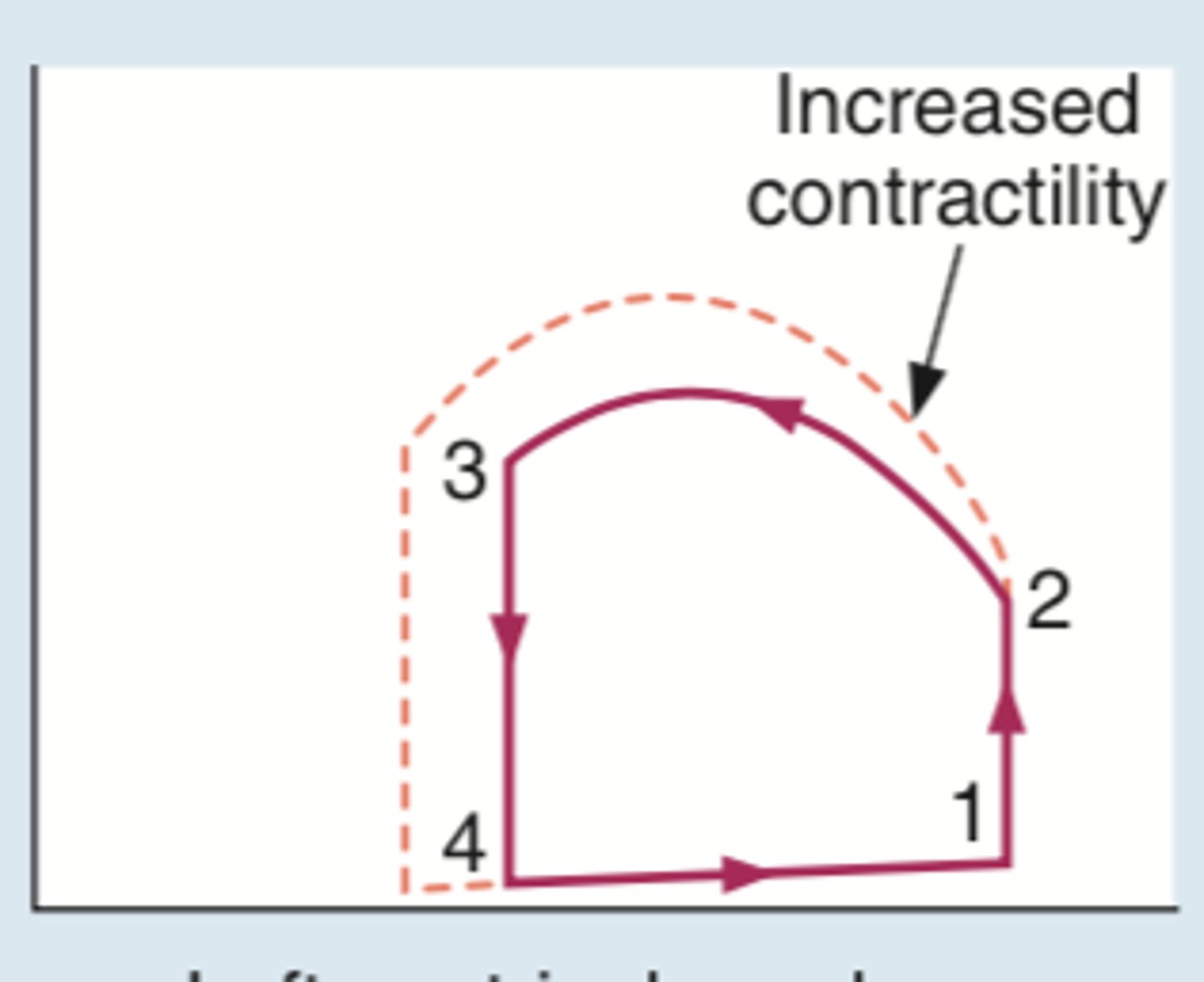
ventricular contractility
Capacity of heart ventricles to contract.
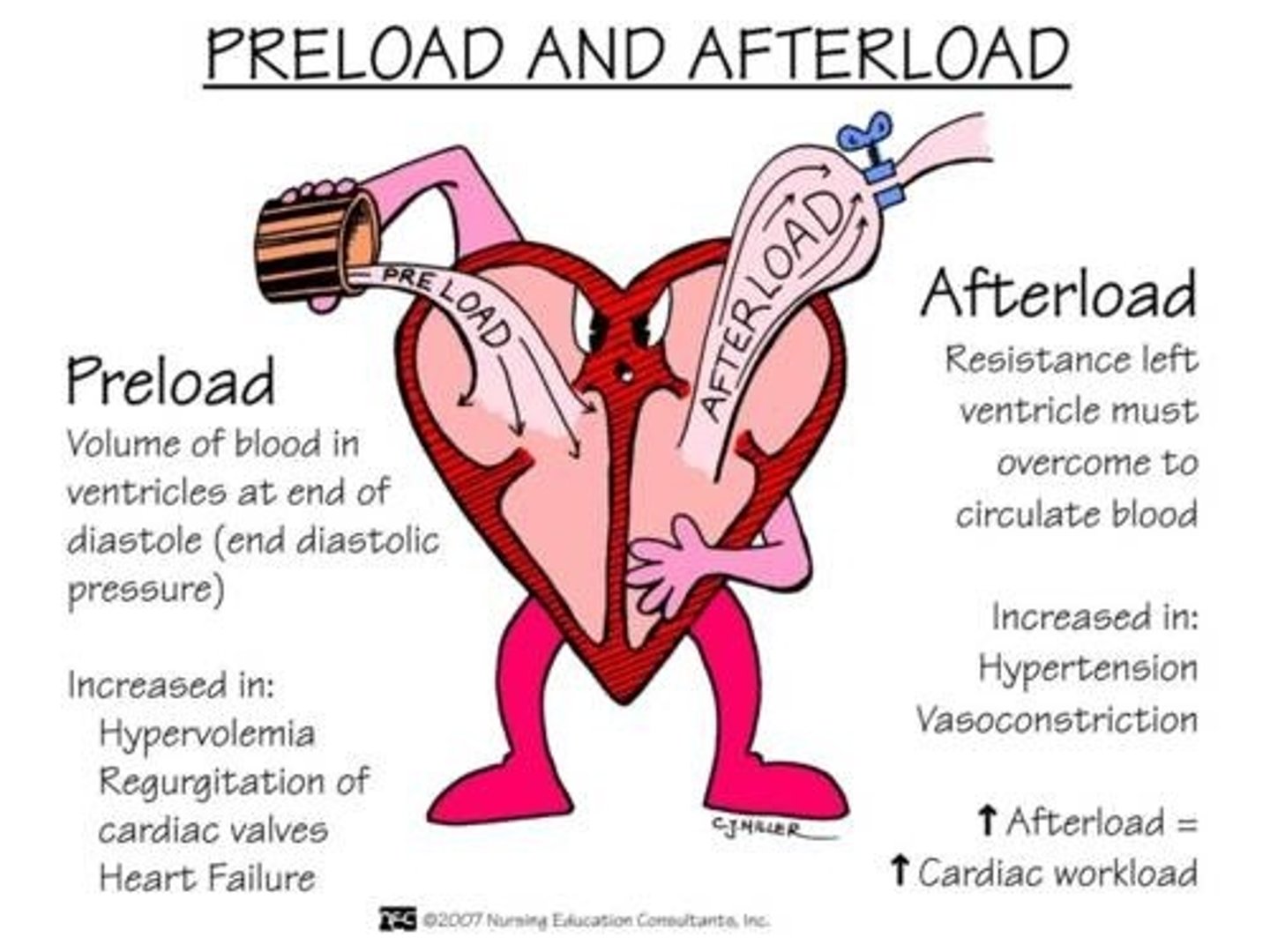
preload
The precontraction pressure in the heart as the volume of blood builds up.
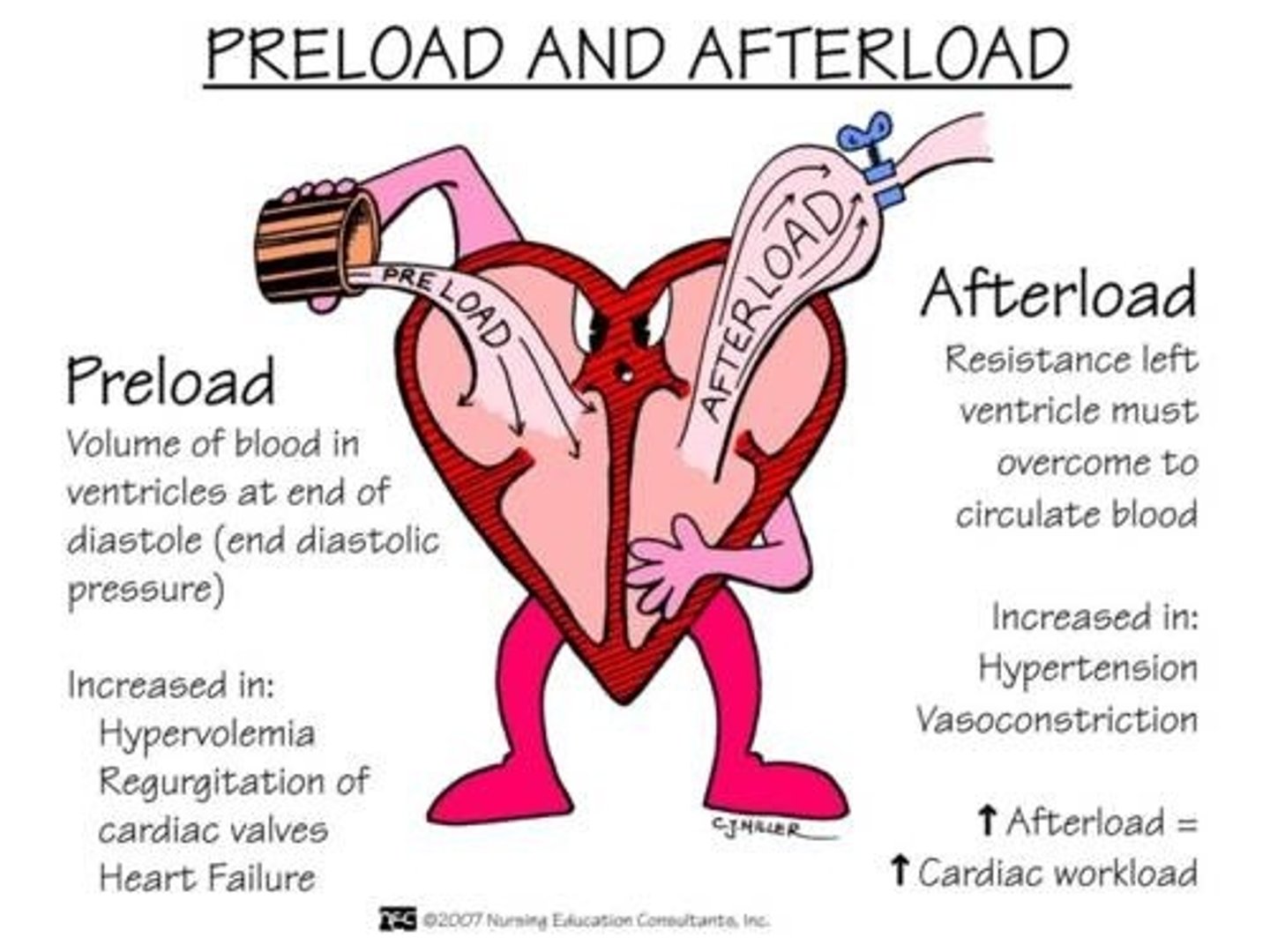
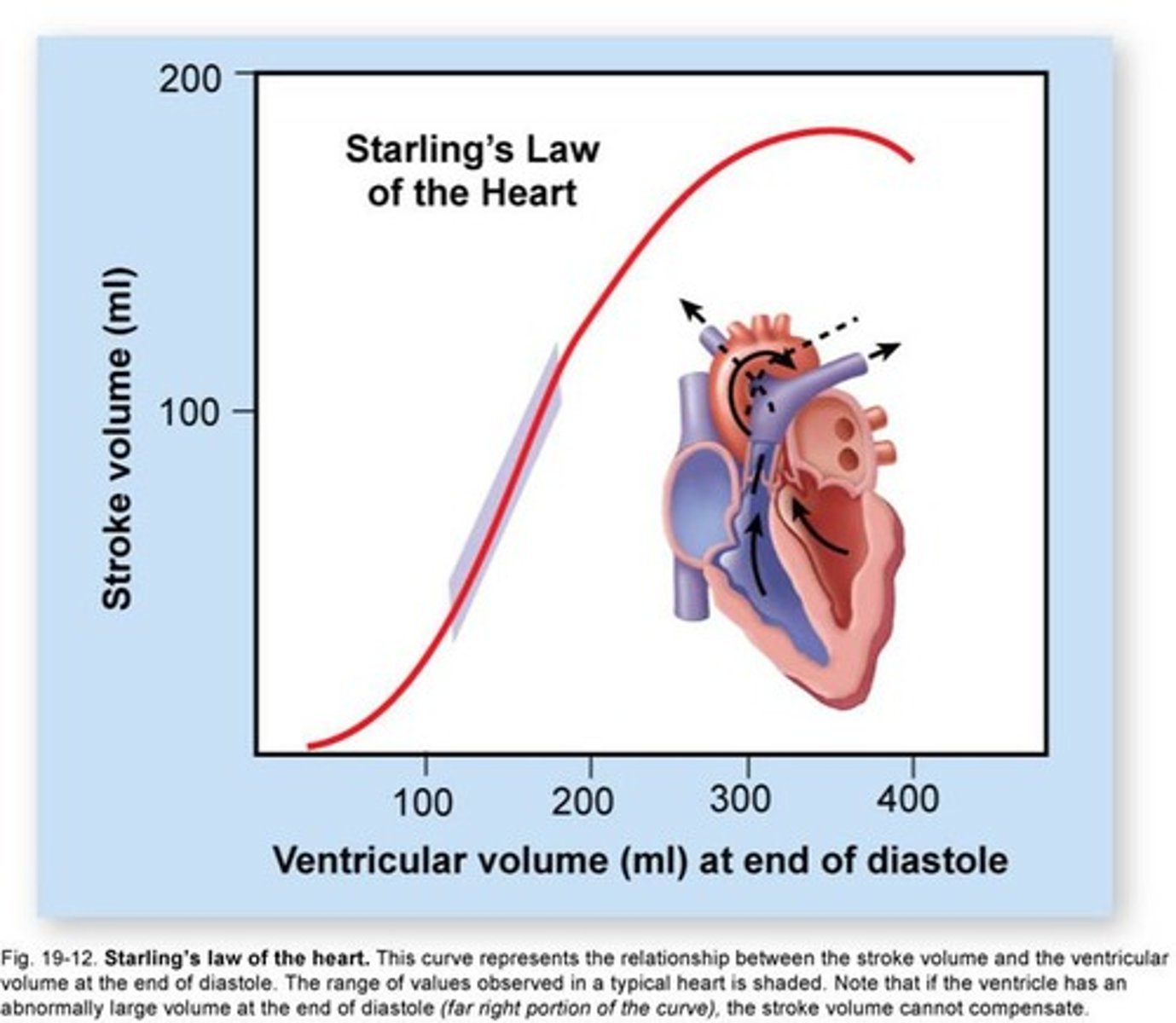
Starling's Law
The more the heart is filled during diastole the more forcefully it contracts
afterload
The force or resistance against which the heart pumps.
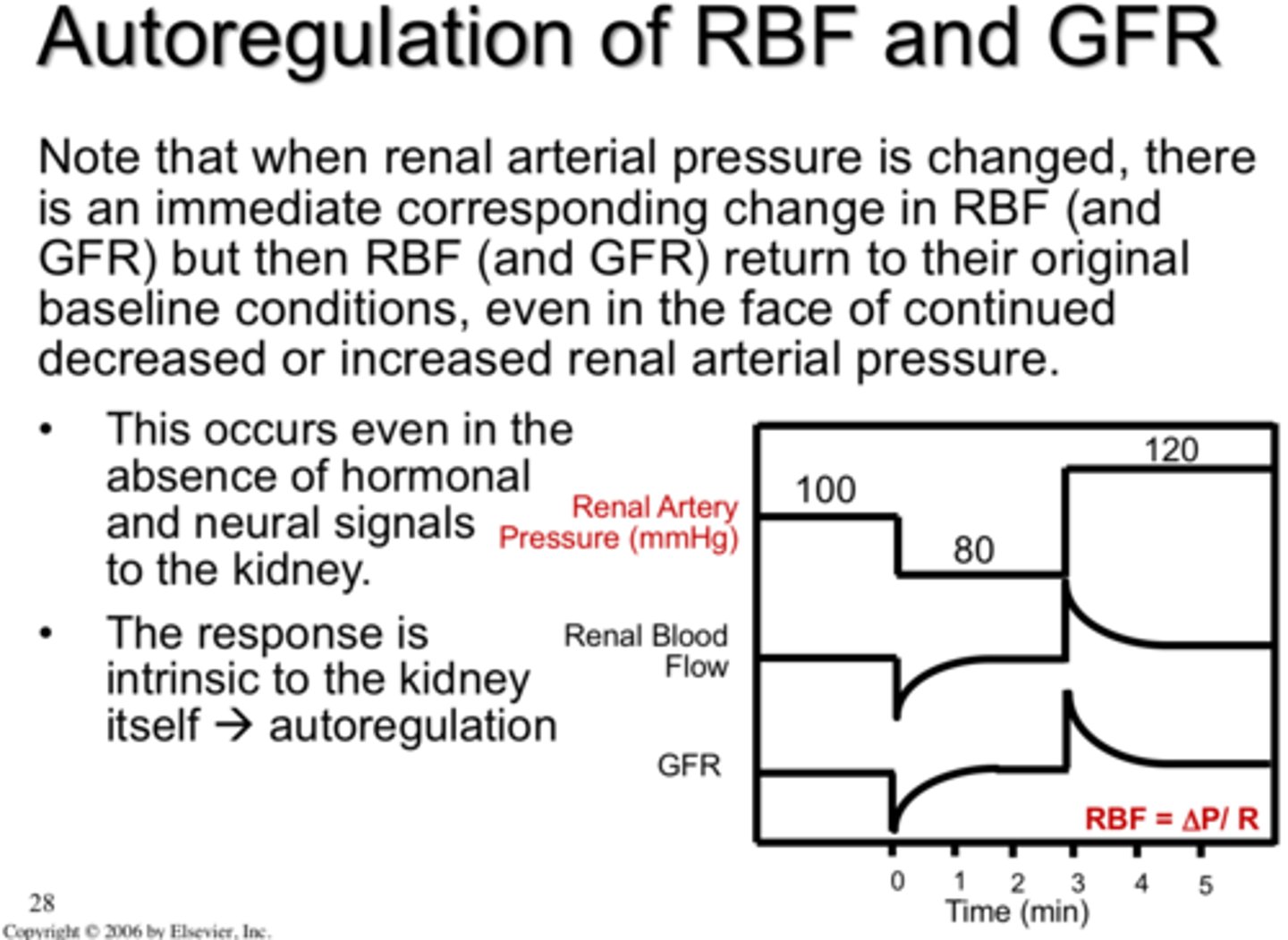
autoregulation
the ability of tissues to regulate their own blood supply
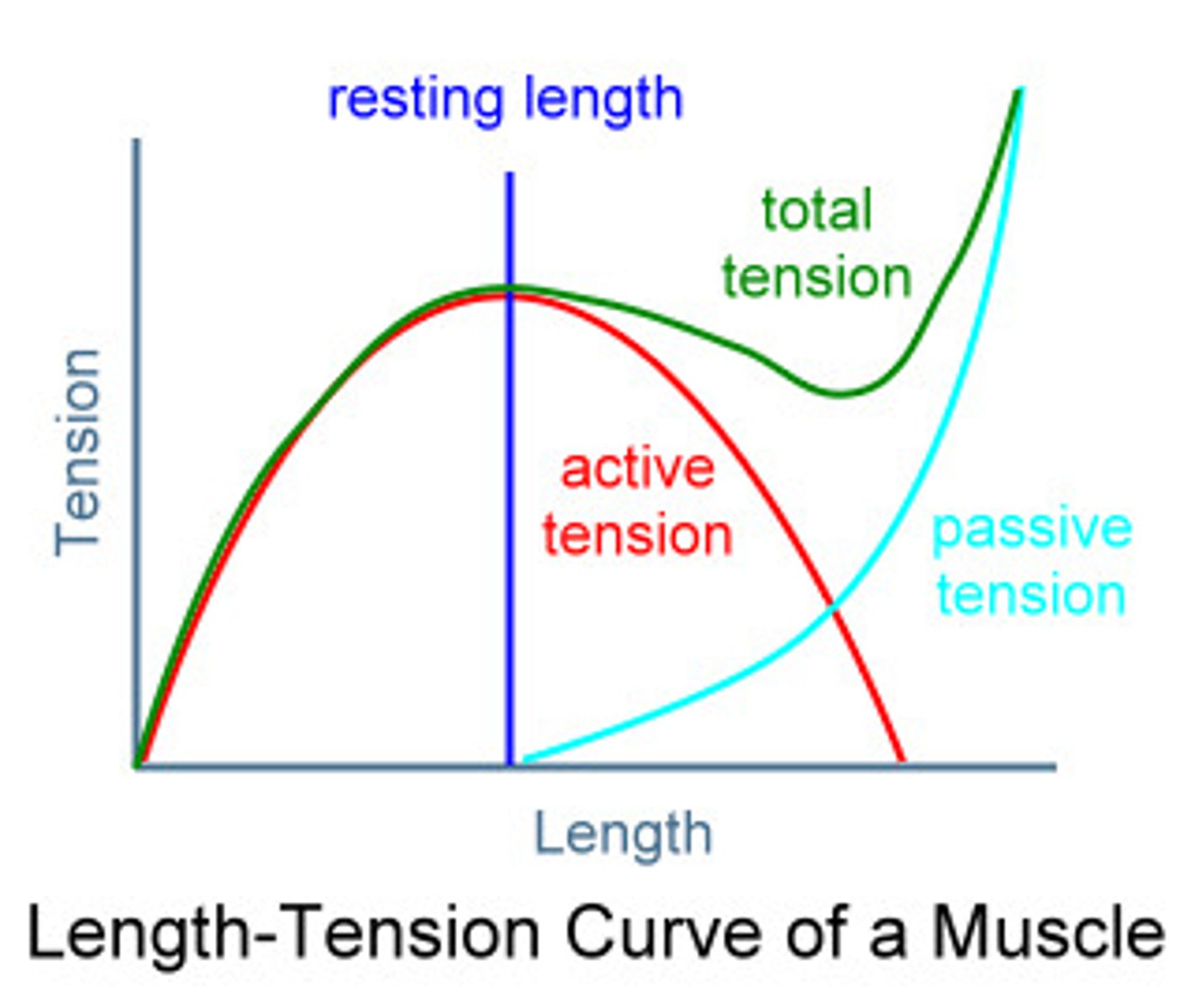
length-tension curve
the curve that accounts for the active and passive elements of muscle tension and dictates that optimal tension is developed at one point known as the resting length, the point in its range where peak torque is developed
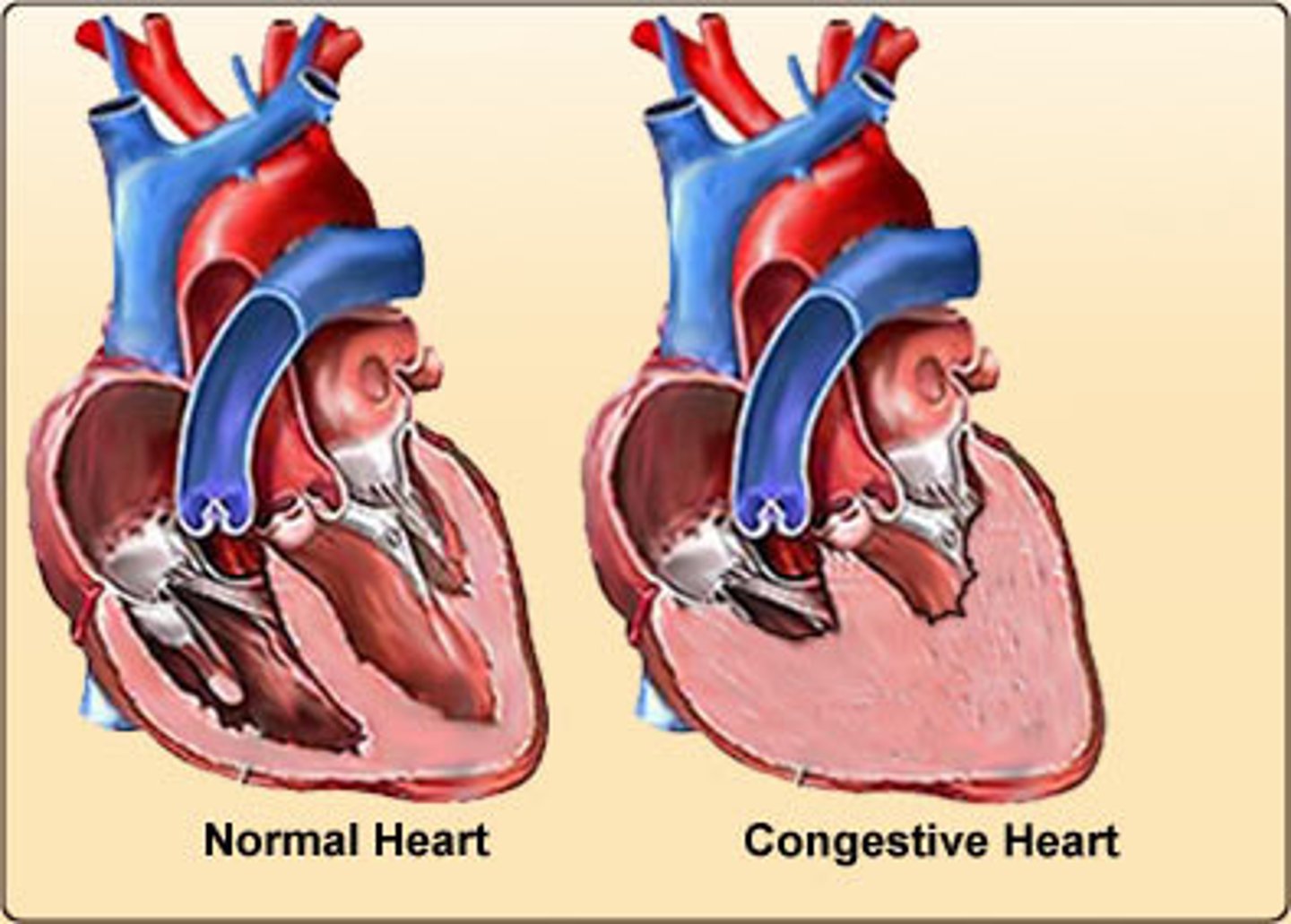
congestive heart failure
A condition resulting from the heart's inability to pump out all the blood that returns to it; blood backs up in the veins leading to the heart, causing an accumulation of fluid in various parts of the body