Animal Cells Specialized
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
elate the structure of selected cells to their function;
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
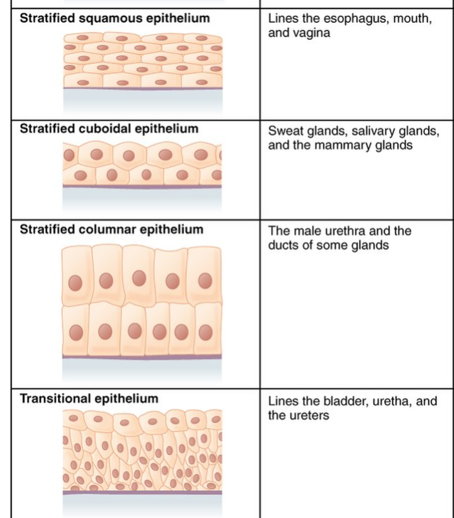
Red Blood Cells
Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body.
contains hemoglobin in their cytoplasm
biconcave disc shape
fairly flexible
has no nucleus
eukaryotic and are produced in bone marrow. They are vital for maintaining proper blood function and overall oxygen delivery to tissues. They facilitate gas exchange due to their unique structure and abundant hemoglobin content.
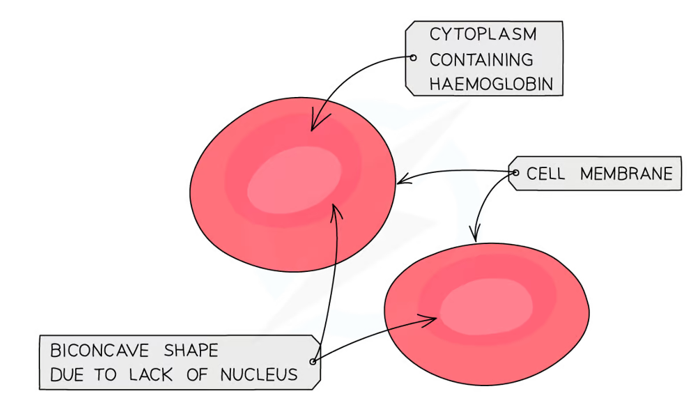
Muscle Cells
shorten or lengthen its length to produce movement
made up of many myofibrils
well supplied with blood vessels and nerves, enabling efficient contraction and energy supply.
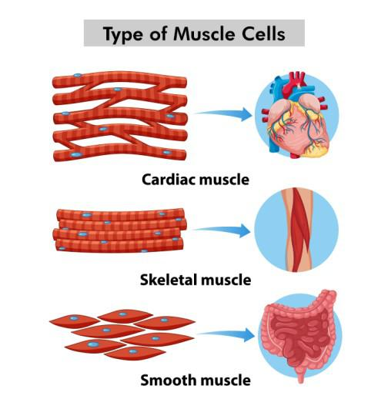
Nerve Cells
transmission or conduction of impulses
structure: elongated so that nerves can run to and from different parts of the body to the CNS
cell has axons and dendrites
axon is covered with a fatty sheath
Sperm Cell
male reproductive cell that fertilizes the ovum, characterized by a flagellum for swimming and a compact head containing genetic material.
head contains genetic material from the father
acrosome in the head contains a digestive enzyme
mid-piece is packed with mitochondria (produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), fueling the sperm’s movement as it swims toward the egg for fertilization.)
tail enables the sperm to swim towards the egg for fertilization

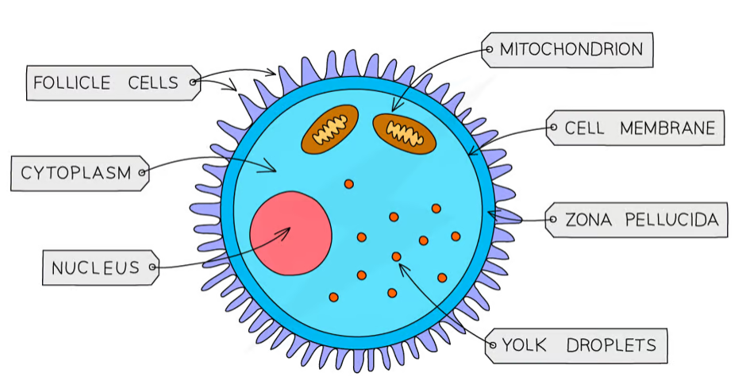
Egg Cell
female reproductive cell that is typically larger than the sperm and contains nutrients for the developing embryo. The cytoplasm is rich in organelles and genetic material, waiting to be fertilized by the sperm.
has a nucleus
contains a lot of cytoplasm
cell membrane changes after fertilization to prevent mutliple sperm from entering
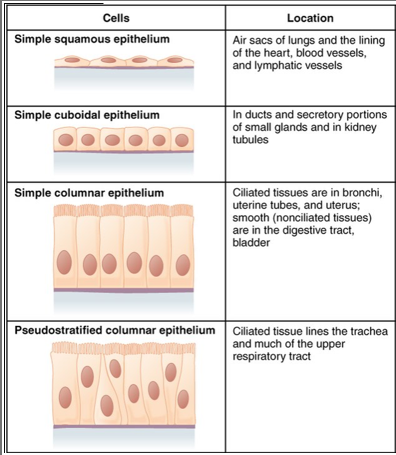
Epithelial cell
sensory receptors as they line major cavities in the body
responsible for making new cells
sheets of tissue bound together → epithelia
tissue formed lacks blood
varying shapes that cover body surfaces and line cavities. They serve protective, absorptive, and secretory functions.