Econ 202 Exam 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Private Enterprise
The ownership of businesses, resources, production technologies, profit,etc. by private individuals.
Production
The process of combining inputs to produce outputs.
Economic Cost
The total cost of production and distribution, including opportunity costs of resources.
Explicit Costs
Out-of-Pocket costs, financial expenditures.
Implicit Costs
The opportunity cost of using resources that the firm already owns, even when no direct payment is made (i.e. wages/rent).
Total Revenue
Price times quantity (PxQ), earnings or income for the firm.
Firm
An organization that combines inputs of labor, capitol, land, and raw or finished component materials to produce final goods and services.
Accounting Profit
The difference between dollars brought in and dollars paid out.
Accounting Profit
Accounting Profit= Total Revenue - explicit costs
Economic Profit
Includes both explicit and implicit costs.
Economic Profit
Economic Profit = Total Revenue - explicit costs - implicit costs
Technology
The method of how inputs are converted to the final product.
Production Funciton
The relationship between the type of land quantity inputs to the level of production for a good or service.
Short Run
Period of time during which at least some factors of production are fixed.
Long Run
Period of time during which all factors are variable.
Fixed Inputs
Factors of production that cannot be easily increased or decreased in a given period of time.
Variable Inputs
Factors of production that a firm can easily increase or decrease in a given period of time.
Marginal Product of Labor (MPL)
The additional output of one more worker.
MPL
change in Q/change in L (Q2-Q1/L2-L1)
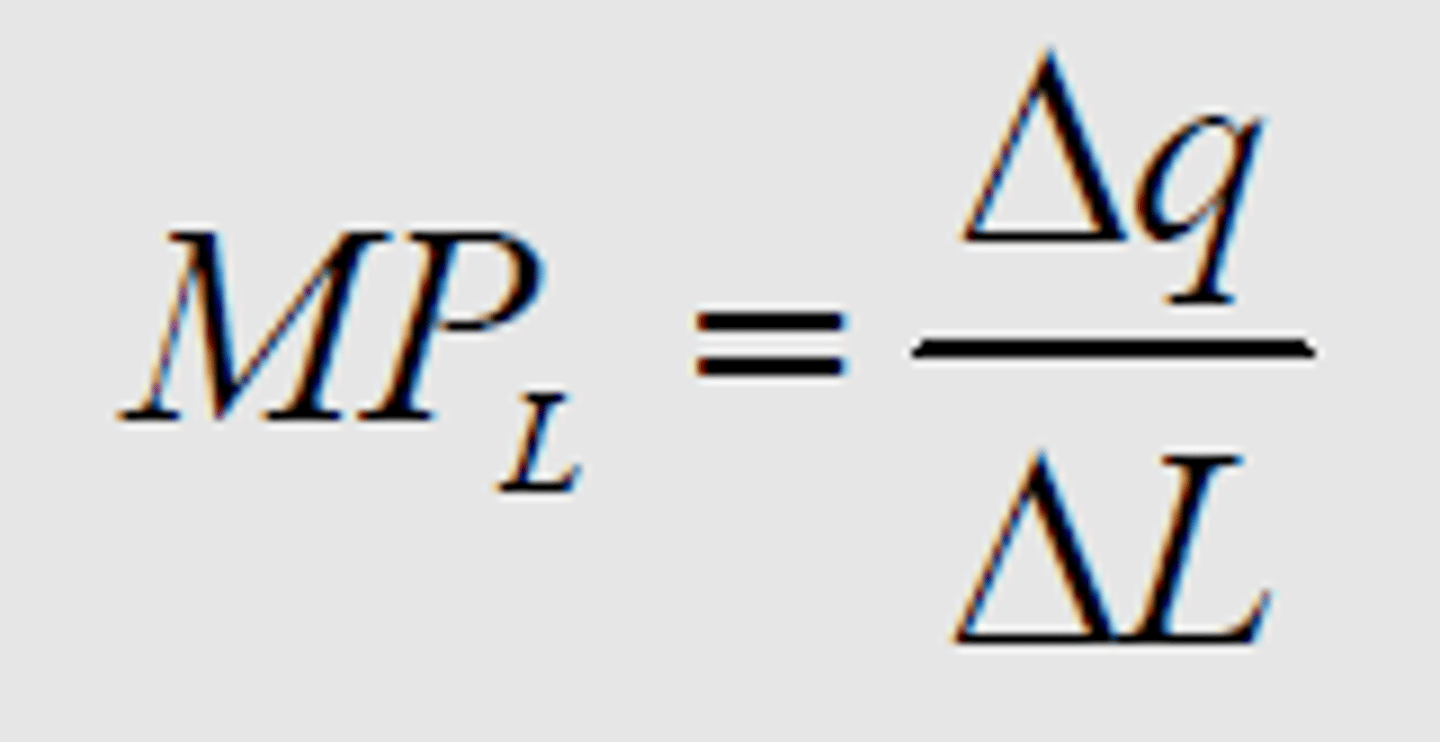
Law of Diminishing Productivity
General rule that as a firm employs more labor, eventually the amount of additional output produced declines. As more/less labor is hired, labor becomes more/less productive
Fixed Reesources
Cannot be adjusted in a given time period. It will still be employed with no production.
Variable Resources
Can be adjusted, either increased or decreased. It will cause the level of output to change.
Total Cost
The economic value of all resources used to produce output level q.
Fixed Cost
Costs of fixed inputs of fixed resources. Costs of production don't change when output is altered.
Variable Costs
Cost of variable inputs or variable resources. Costs of production that change when output is altered.
Marginal Costs
The additional cost of producing one more unit of output.
Marginal Cost
change in TC/change in Q (TC2-TC1/Q2-Q1)
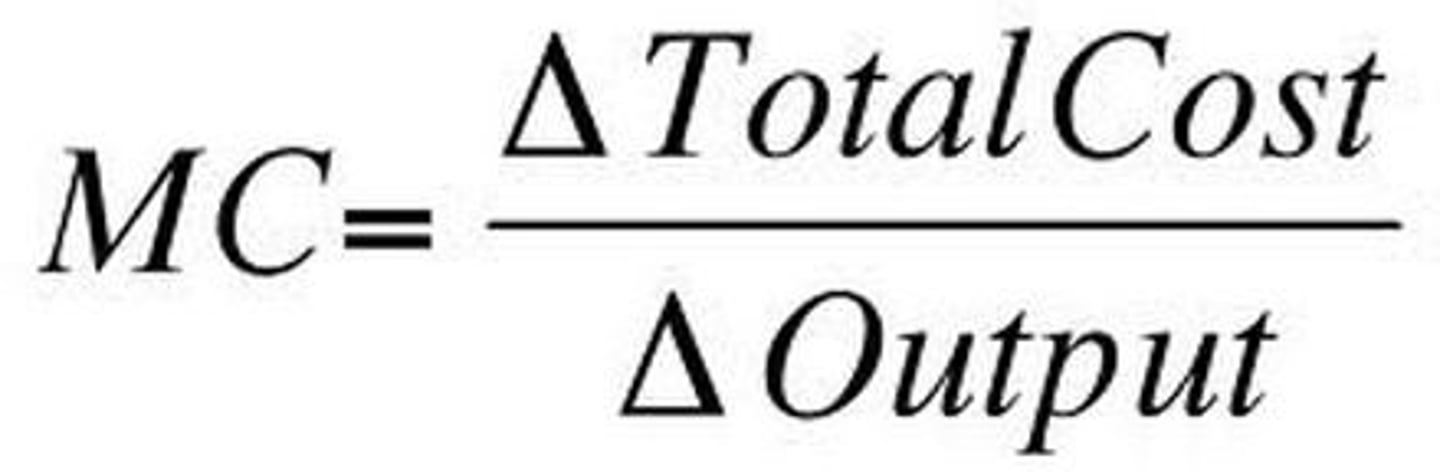
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Total cost divided by the total output in a given time period.
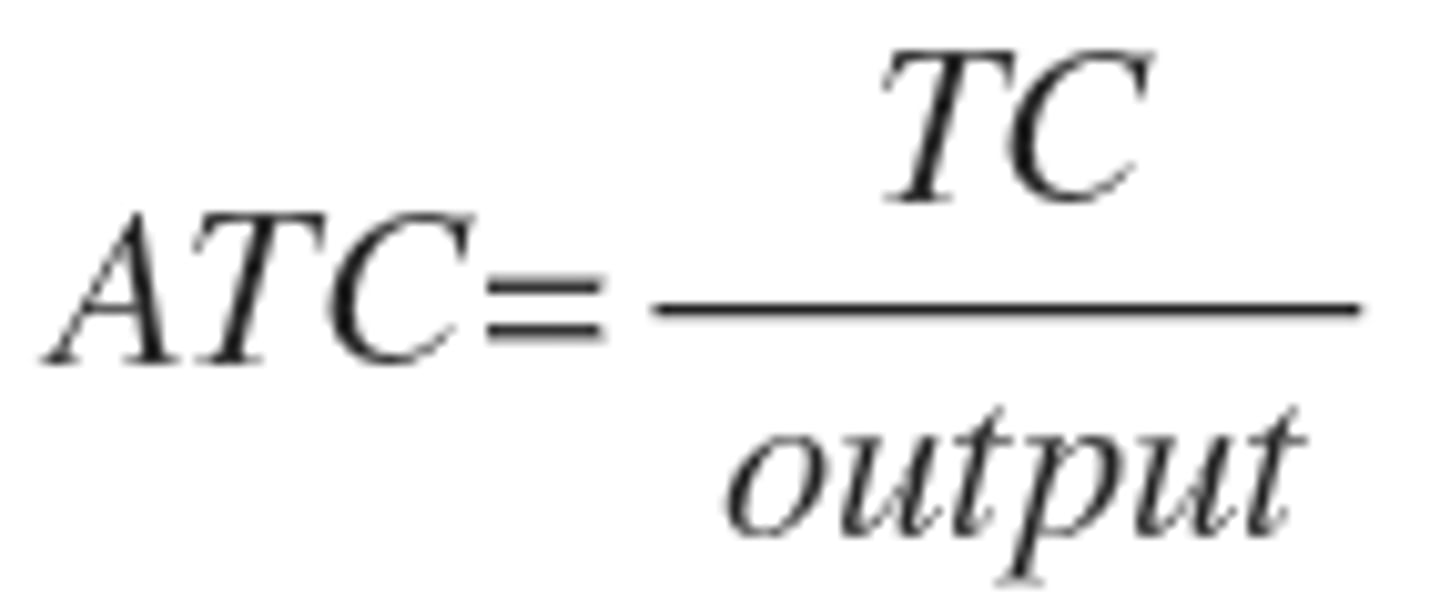
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
Total fixed cost divided by the total output in a given time period.
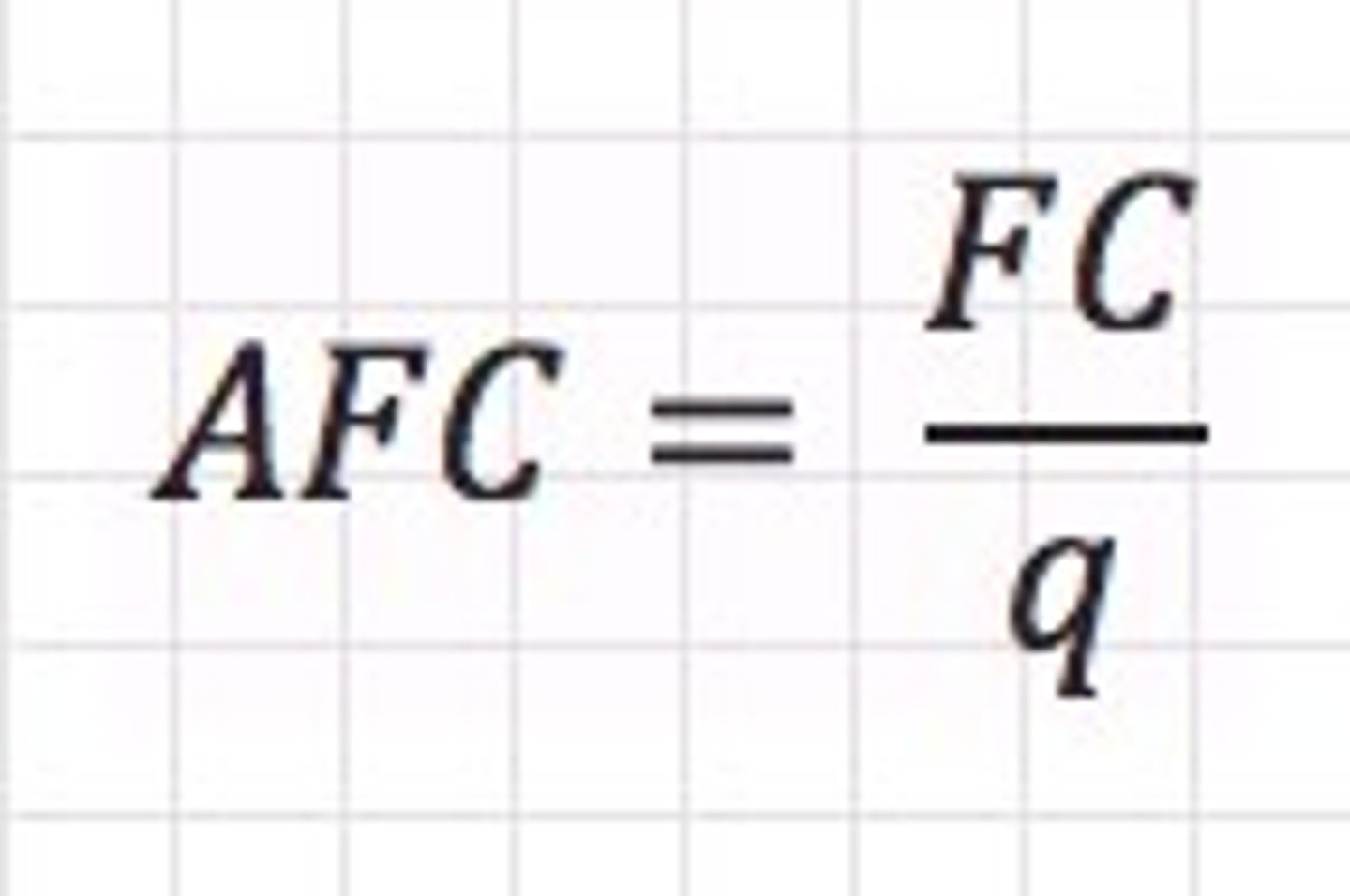
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Total variable cost divided by the total output in a given time period.
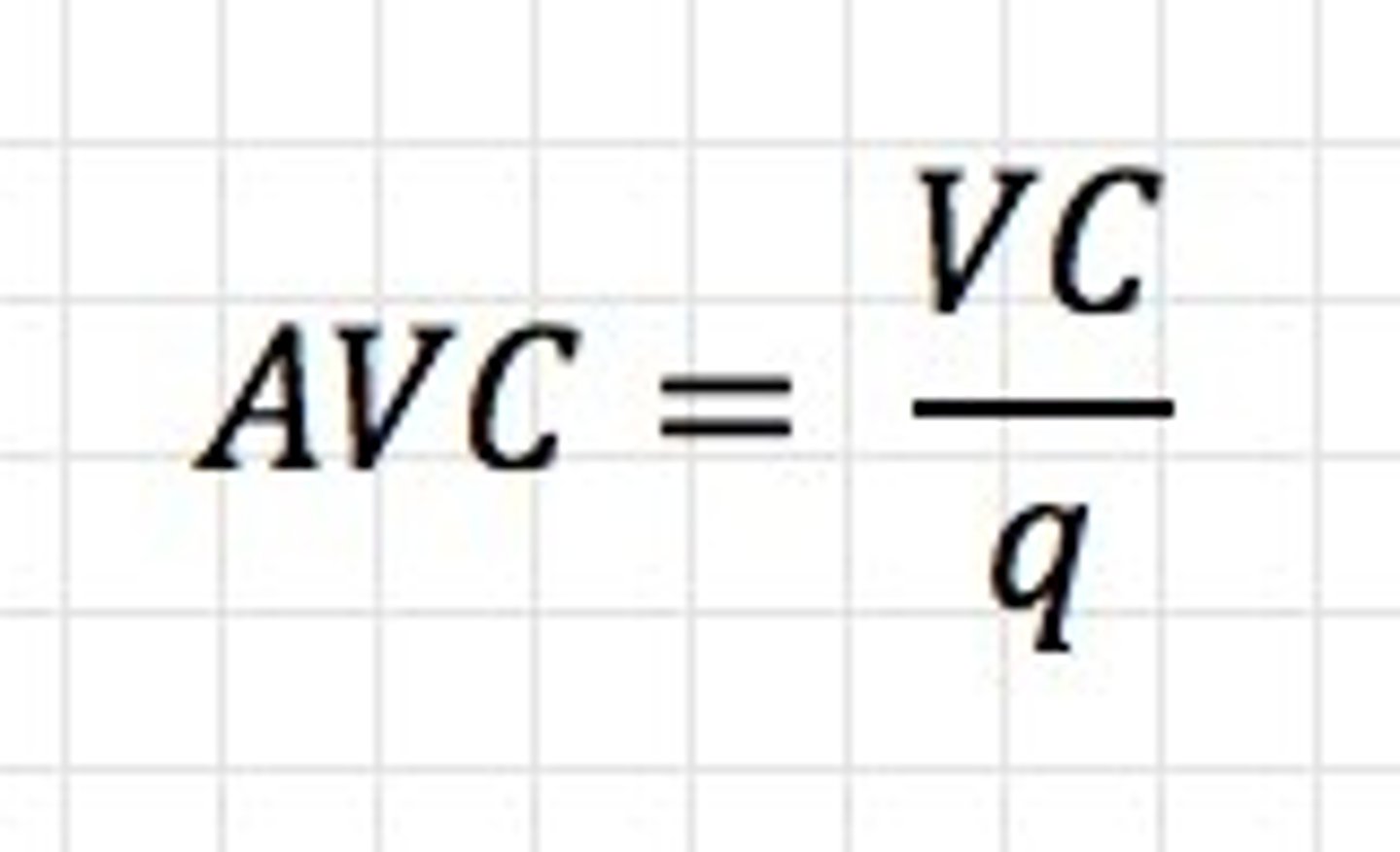
Returns to Scale
If you double your input, your output will more than double.
Constant Return to Scale
The company has maxed out their gains from getting bigger, so their costs are remaining constant.
Perfectly competitive market
A market that meets the conditions of (1) many buyers and sellers, (2) all firms selling identical products, and (3) no barriers to new firms entering the market.
Profit Maxmizing Output (Perfect Competition)
MC=MR
Profit Maximizing Output (Monoploy)
P=MR
MC=MR
Profit is not increasing nor decreasing, this is where profit is mazimizing.
MR>MC
Profit is increasing so profit is not yet maximizied.
MR
Profit is decreasing so profit is no longer maximizing.
Shut-Down Rule
A firm should shut down if the price falls below the ninimum AVC.
Total Cost
FC/Q + VC/Q
Zero Profits
Means at the market price, the firm is covering all of its costs including enough to pay labor and capital their orinary oppourtunity cost.
Entry and Exit Costs
e.g., Entry means drilling an oil well
Costs of drilling an oil well are sunk costs
Sunk Costs
A cost that once incurred can never be recovered
Entering Markets
P>AC, incentive to enter
Exiting Markets
P
Pure Monopoly
A market controlled by one seller with a good or service that has no close substitutes.
Oligopoly
When a few firms have a large majority of market share. (i.e. car industry)
Barriers to Entry
Obstacles that make it harder to join the industry.
Natural Monopoly
When it is more cost effective to have one large producer rather than several smaller competing firms.
Market Power
The power to raise price above marginal cost without fear that other firms will enter the market. Comes from selling a unique good with barriers to enter.
Differentiated Products
Goods that are not identical, and firms are able to capture a piece of the market by making unique goods.
Game Theory
Even if the people or companies rationally follow their own self-intrest, the best outcome is hard to reach when they can't or don't cooperate.
Cartel
Split consumers 50/50 and improve prices illegally.
Price Leadership
When the company changes its prices, and its competitors have to decide if their going to follow suit.