A.1.2.1 (3) Thermoregulation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is thermoregulation?
the regulation of body temperature
What does it rely on?
cardiovascular, muscular, nervous, and integumentary systems
What is the core temperature?
temperature deep within the body
What is the shell temperature?
temperature near the body’s surface
What is the metabolic rate?
the amount of energy your body uses to perform basic functions
What is the relationship between metabolic rate and body temperature?
the higher the metabolic rate the more heat your body generates (proportional)
What are some factors that affect metabolic rate?
exercise, hormones, nervous system, body temperature, ingestion of food, age and sex
How is the core body temperature managed?
through the balance of between heat production and loss to the environment
How can heat be transferred away from the body?
conduction, convection, radiation and evaporation
What can an imbalance in body temperature lead to?
hyperthermia
What is hyperthermia?
an elevated body temperature usually above 39°C
Convection
heat transfer through fluid mediums (air/water)
Sporting example of convection
cool breeze moving across your body carrying heat away, cooling you
Conduction
direct transfer of heat between two objects in contact
Sporting example of conduction
a swimmer, when in contact with the cooler water in a pool, heat is transferred from the body to the water regualting body temp during intense sessions
Radiation
transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves (without direct contact)
Sporting example of radiation
the body absorbing radiant heat when the environment temp is higher than body temp
Evaporation
heat loss when sweat (liquid) on the skin surfaces turns into vapor
Sporting example of evaporation
sweating when doing exercise, the evaporation from sweat cools you down as it removes heat
What are some other thermoregulatory mechanisms?
vasodilation
vasoconstriction
shivering thermogenesis
non-shivering thermogenesis
What is vasodilation?
widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow = helps release heat from the body
What is vasoconstriction?
narrowing of blood vessels to reduce blood flow conserving heat
What is shivering thermogenesis?
production of heat via involuntary muscle contractions (shivering)
What is non-shivering thermogenesis?
increasing metabolic processes in brown adipose tissue
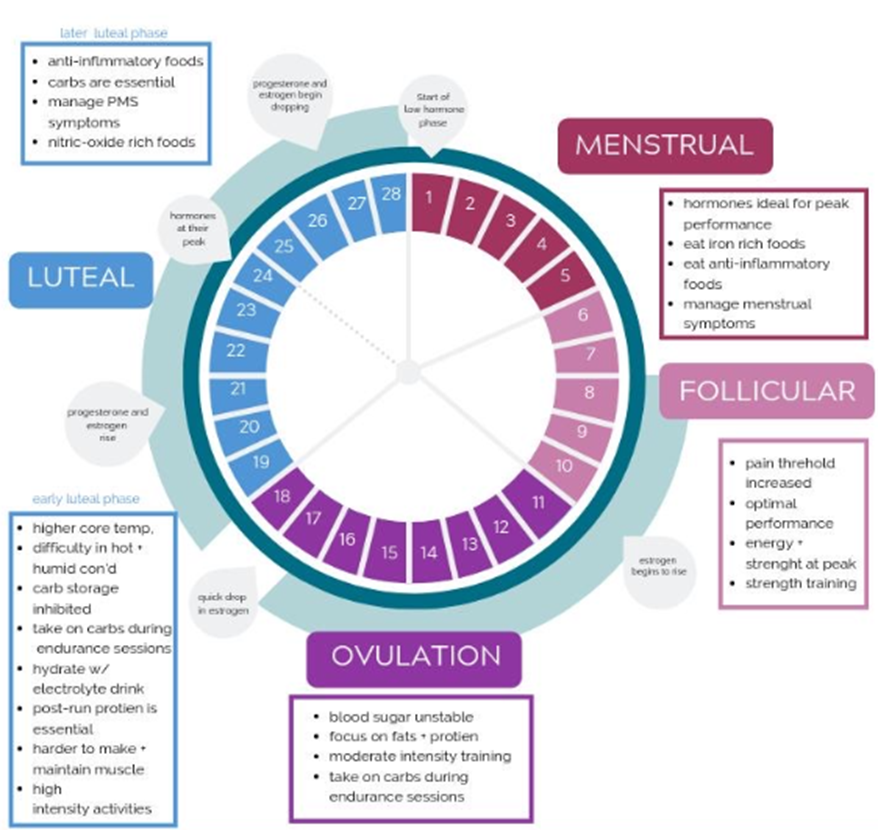
How does a woman's menstrual cycle affect thermoregulation?
hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle
What are the hormones involved in the thermoregulation of the menstrual cycle?
estrogen and progesterone
What happens during the follicular phase?
estrogen is dominant so body temperature is lower as it promotes vasodilation
What happens during the luteal phase?
progesterone is more dominant, raising the core temperature, sweating threshold increases
Diagram for thermoregulation and the menstrual cycle