4 Mastering the Art of Image Acquisition
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Radiography provides image of …?
internal anatomy ---- not visible on clinical examination (we need high quality or diagnostic radiographs for this)
what term describes the Reliability of image to represent true state of anatomic region?
image quality (diagnostic radiograph)
what are the 3 parameters of diagnostic radiographs?
detail (image sharpness and resolution)
contrast resolution
magnification and distortion (we want minimal)
what are the 5 principles of projection geometry in radiography?
X-rays should originate from a small Focal Spot
SOD should be as long as possible
ORD should be as short as possible
Long axis of object should be parallel to the receptor
Central ray should be perpendicular to receptor
X-rays should originate from a …?
small Focal Spot (smaller focal spots produce a sharper image)
however, reality is that they originate from an area and not a point source
SOD should be as short/long as possible
long
makes X rays less divergent
sharper images
less magnification
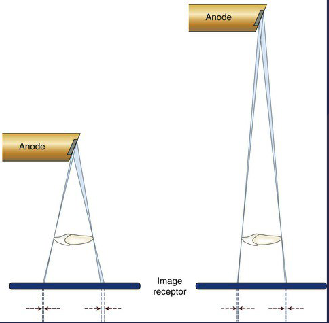
clinically, how is a long SOD achieved?
collinated extensions in intra-oral radiography (8, 12, or 16 inches)
ORD should be as short/long as possible
short
less magnification
sharper image
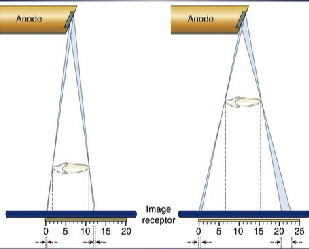
clinically, how is a short ORD achieved?
place anatomy of interest closest to receptor
however, intra-oral imaging can be challenging
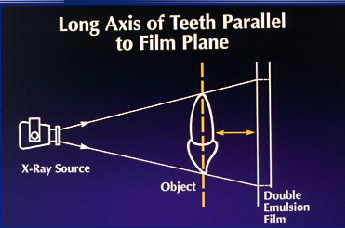
Long axis of object should be ______ to the receptor
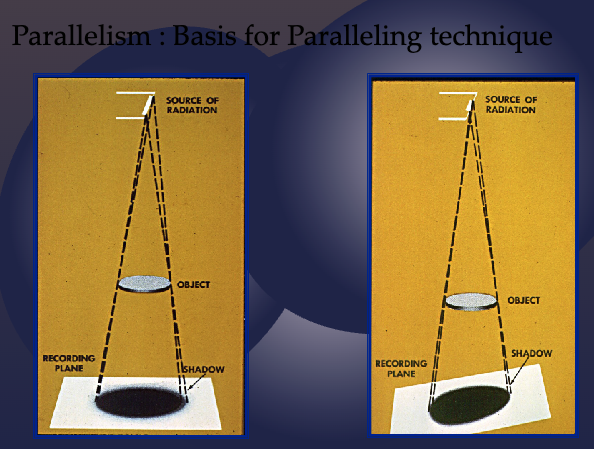
parallel
decreases distortion
improves image sharpness
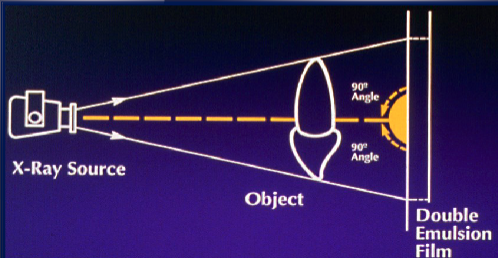
Central ray should be _________ to receptor
perpendicular
reduces geometric distortion
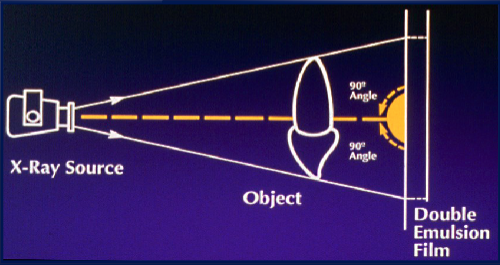
image shape distortion is a result of…?
unequal magnification of different parts of same object
how can image shape distortion be minimized?
position image receptor parallel to long axis of object
orient central ray perpendicular to object and image receptor
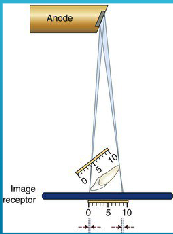
what happens when central ray is perpendicular to the image receptor but the object is not parallel with the image receptor?
foreshortening
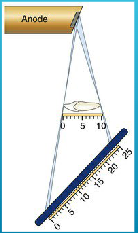
what happens when central ray is perpendicular to the object but not to the image receptor?
elongation
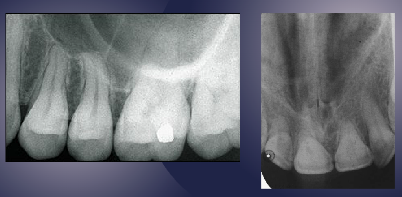
foreshortening (long axis of teeth not parallel to receptor)
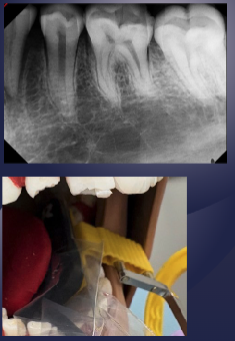
foreshortening (receptor not parallel to object)
image should look like this
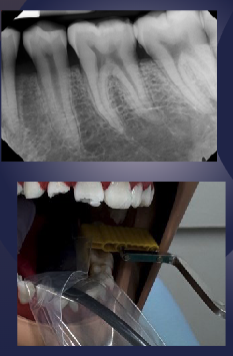
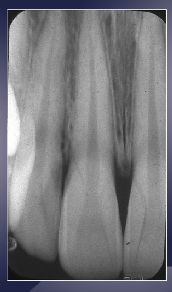
elongation
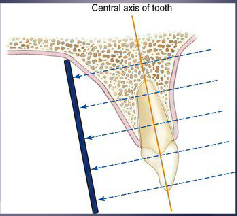
what is the paralleling technique?
The central ray is directed at right angle to the central axes of Object and Receptor (preferred method to minimize distortion)
what is the bisecting angle technique?
The central ray is directed at a right angle to the imaginary plane that bisects the angle formed by the image receptor and the central axis of the object (less frequently used because of more distortion)
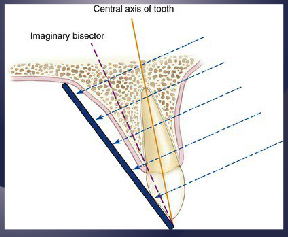
the bisecting angle technique is less frequently used but can be useful in what pt populations?
Useful in patients with severe gag reflex and small mouth opening
what term describes How well a boundary between two areas of differing radiodensity is revealed?
sharpness
what term refers to the ability of an imaging system to differentiate between two nearby objects?
spatial resolution (aka How well a radiograph reveals small objects that are close together)

sharpness and resolution are _____________
interdependent
sharpness + resolution = __________
detail
what 5 factors affect detail (sharpness + resolution)?
focal spot size
SOD
OFD
movement (tube or patient)
contrast resolution
what term describes the overall degree of darkening of a radiograph?
radiographic density (how dark image is)
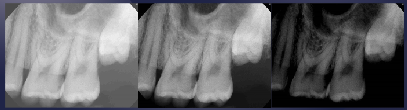
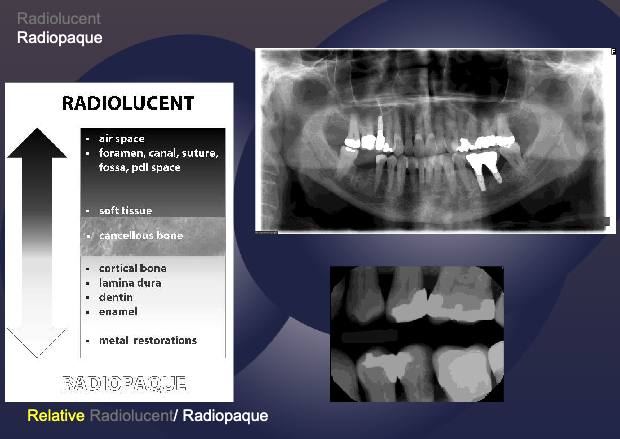
what structures are more radiolucent?
air space
foramen, canal, suture, fossa, pdl space
soft tissue
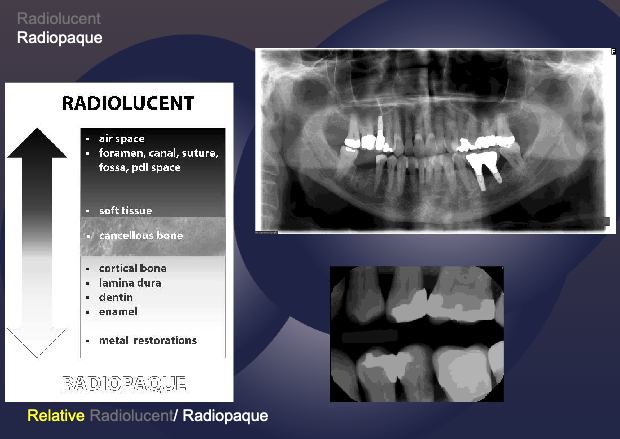
what structures are more radiopaque?
cortical bone
amina dura
dentin enamel
metal restorations
how do artifacts such as lead aprons, film reversal, earrings, and thyroid collars affect density?
lighter areas in film
what term refers to the difference in densities between the light and dark regions in radiograph?
contrast
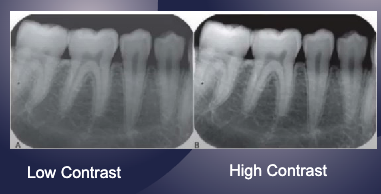
the range of densities observed on a radiograph is a result of…?
attenuation/ absorption of xray photons
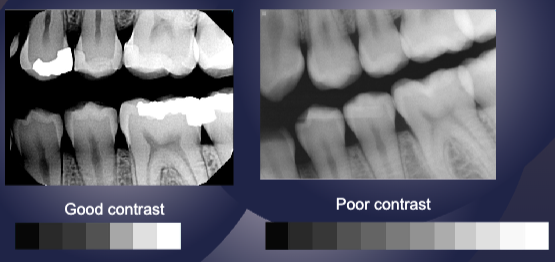
how does scatter radiation affect radiographic contrast?
produces fog (overall darkening reduces contrast)
localization can be used to observe what type of pathoses?
impacted/supernumerary tooth
root canal
foreign bodies
fractures
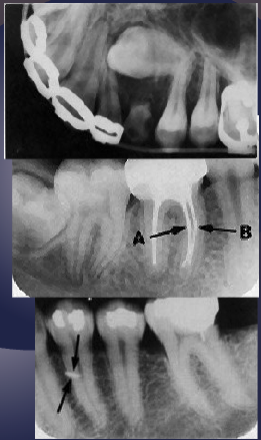
describe the right angle technique.
Obtain 2 radiographs at 90 degrees to each other of the area of interest. For example,
periapical and occlusal radiographs
Lateral cephalometric and postero-anterior view of skull
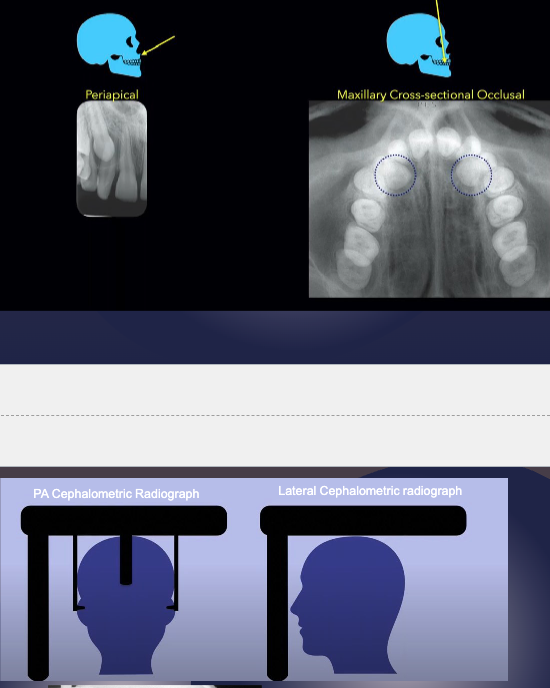
what radiographic techniques can be used in localization?
right angle technique
tube shift technique
special studies
what is the SLOB rule (tube shift technique)?
Same
Lingual
Opposite
Buccal
Images of objects that are superimposed can be separated by changing the angle of projection
Object moves in the same direction as x ray tubehead → Lingual Object
Object moves in the opposite direction as x ray tubehead → Buccal Object
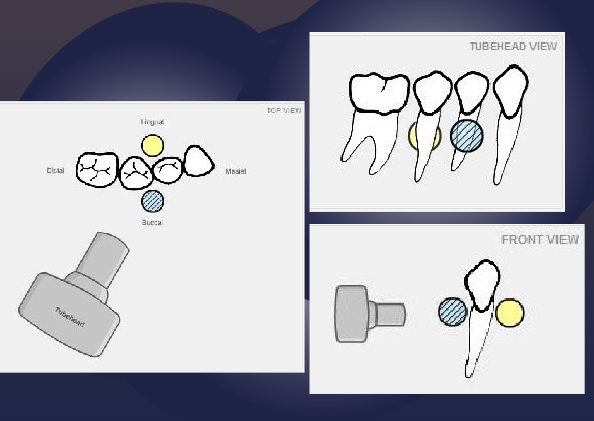
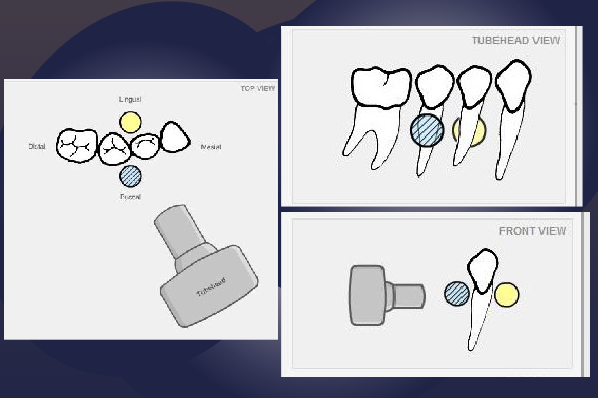
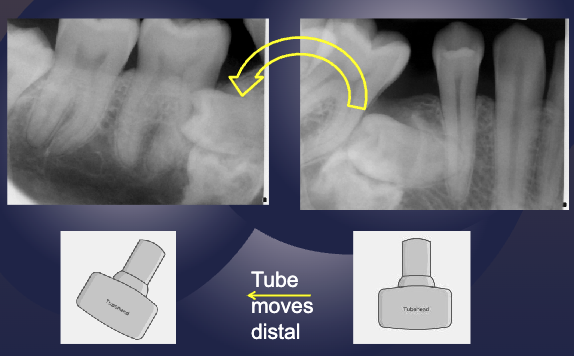
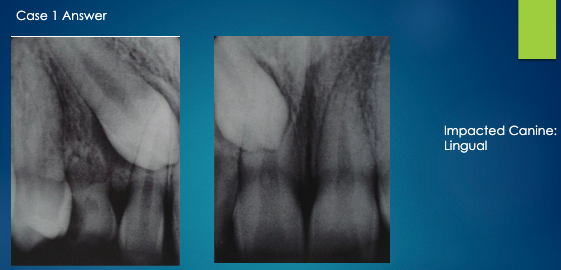
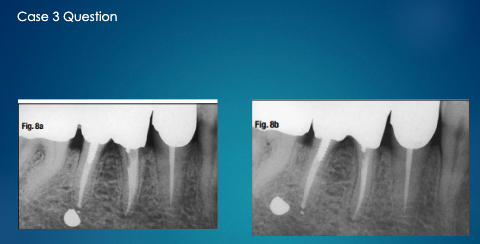
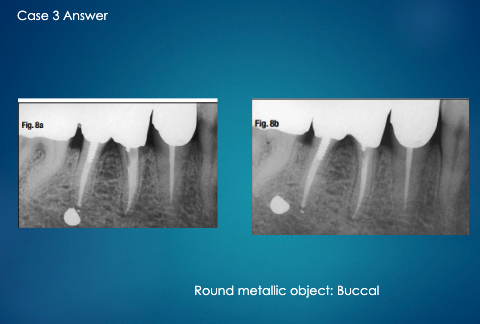
apply the SLOB rule (tube shift technique) to determine if the impacted tooth is lingual or buccal
impacted tooth moves distally as tube move (same direction), therefore it is lingual
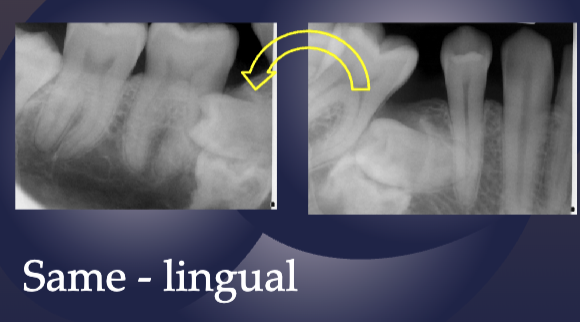
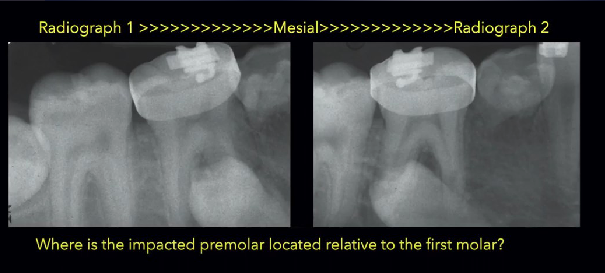
As the tube is moved mesial, the impacted premolar moves distal
Opposite= Buccal to the root of 1st premolar
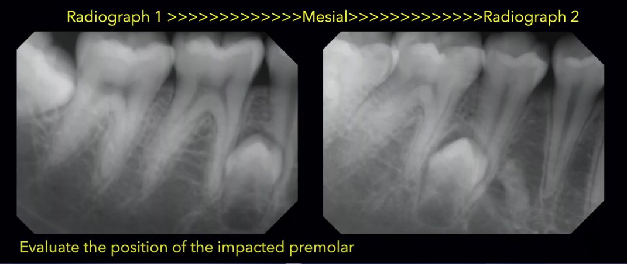
Tube Moves= Mesial, Impacted tooth moves= Mesial
SAME= LINGUAL to the roots of 2nd premolar and 1st molar
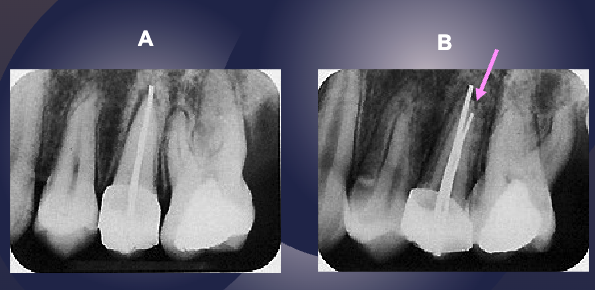
more canine is showing so it has moved mesially
pink arrow is buccal canal
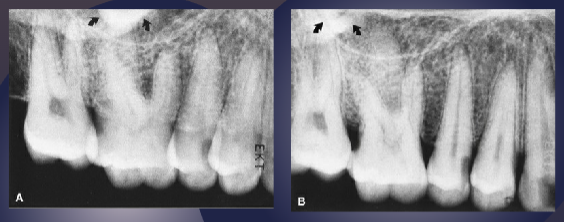
buccal
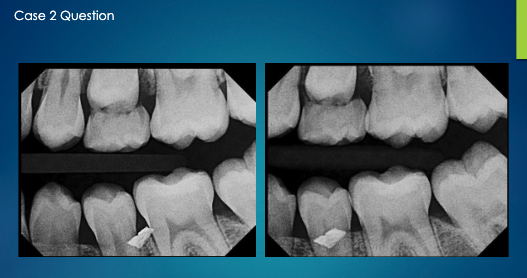
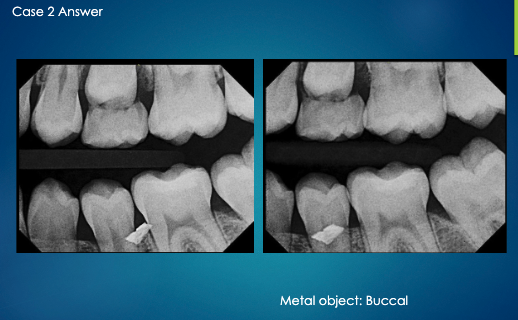
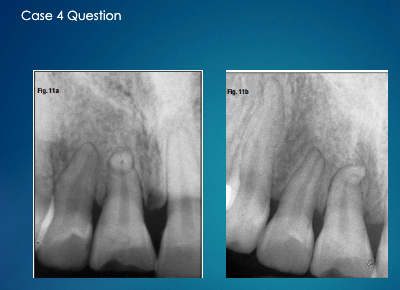
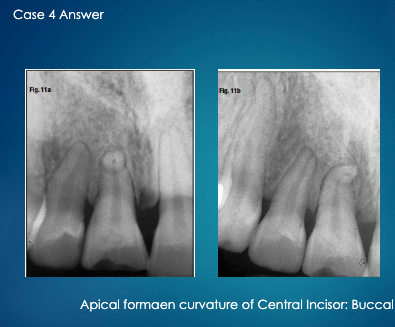
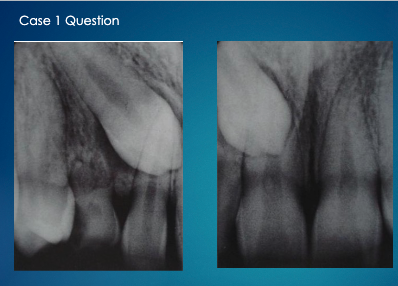
not sure about this one ask professor