NRSE 470: Exam #1
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Health includes…
Physical
mental
and social well being
Wellness
A lifestyle of holistic health
Social determinants of health (SDOH)
impact health and wellness
Health inequity based on environments where people are born, live and play
responsible for over 30% to 55%% of health outcomes.
Examples…
housing
neighborhoods
education
job opportunities
racial disparities
pollution
language
health literacy
Wellness Continuum
holistic approach
Differs from medical model
Degrees of wellness
Dimensions of Wellness
Physical
Emotional
Environmental
Financial
Spiritual
Social
Occupational
Intellectual
Disease Prevention
Focus: Preventing chronic illness and comorbidities
Nurse’s role
Provide education
Clear communication
Domains of SDOH as outlined by Healthy People 2030…
Economic stability
Education access and quality
Health care access and quality
Neighborhood and built environment
Social and community context
lack of support
Promoting Disease-Prevention Strategies
Clear communication
Needs assessment
Knowledgeable clinicians
Defined health education
Nurse’s role
NIH tool kit
Health policy
CDC recommendations
Health education
Common Chronic Diseases…
Heart Disease
Cerebrovascular Disease
Diabetes
Cancer
Alzheimer’s disease
Chronic lung
Chronic kidney
Osteoporosis
Health Care Support & Health Literacy
Support and assistance across the continuum
Health promotion
Disease prevention
End-of-life care
Wellness for Health Care Professionals
Health care workers
Cause and barriers to wellness
Need for self-care
Resiliency
Approach to stress
Health and wellness promotion
Mental health services
Health Literacy
Clients who have low health literacy
More likely to use the emergency department
Spend more days in the hospital
Less likely to follow health recommendations
Higher mortality
Health insurance
Factors leading to lack of coverage
Affordable Care Act, Medicare, and Medicaid
Gender Dysphoria: Role of Nurse
Affirming gender identity
Review preferred pronouns
Discuss gender affirming therapies
Refer for psychotherapy
Discuss legal affirmation
LGBTQIA: Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Annual STI screening
Cancer
Social Determinants of Health
Healthy People 2030
LGBTQIA: Gender affirming care
Gender- affirming surgeries
Fully reversable
Use of gonadotropin releasing hormone
Partially reversable
Hormone therapy
Irreversible
Surgery
Cancer: Pathophysiology
Changes / damage to cells
Caused by…
Inherited traits
Errors in cell division
Environmental factors
Tobacco
Ultraviolet light exposure
Effect of aging
Progression:
Hyperplasia → Dysplasia → Carcinoma in situ → Malignant
Characteristics of Benign Cancer Cells
Growth rate
Slow, progressive
Cell differentiation
Well differentiated (cells resemble tissue of origin)
Cell size & shape
Uniform
Regular nuclei
Invasion
Encapsulated
Does not invade surrounding tissue
Metastasis
Absent
Recurrence after removal
Rare
Effect on Host
Usually minimal, unless location interferes with vital functions
Characteristics of Malignant Cancer Cells
Growth rate
Rapid
Uncontrolled
Cell differentiation
Poorly differentiated
Undifferentiated (Anaplastic)
Cell size & shape
Pleomorphic
Varying sizes / shapes of cells and nuclei
Invasion
Invades and destroys surrounding tissue
Metastasis
Frequently present via blood, lymph and direct seeding
Recurrence after removal
Common
Effect on Host
Severe can cause…
Cachexia
Organ failure
Death
Cancer: Risk Factors
Smoking
Alcohol consumption
Excess body weight
Sedentary lifestyle
Dietary habits
Viruses & bacteria
Hep B or Hep C can lead to liver cancer
Infection with Epstein- barr: increased risk of lymphoma
HPV increased risk of cervical cancer
HIV increased risk of lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma
Helicobacter pylori can increase risk of stomach cancer and lymphoma
Environmental factors
Protect skin and eyes from UVA & UVB
Stages of Cancer
TNM (tumor, node, metastasis)
T = size and extent of the primary tumor
N = number of nearby lymph nodes that show cancer
M = whether the cancer has metastasized
Stages 0 to 4
Stage 0
Abnormal cells are present but have not spread.
Stage I
Less serious and have a better prognosis.
Stage 2-4
Cancer is larger and has had greater spread beyond the primary site
Cancer: Clinical Manifestations
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Palpable masses
Swelling
Pain
Skin changes / nonhealing lesions
Unexplained / persistent cough
Unexplained bleeding or discharge
Breast Cancer: Screening Recommendation
Age: 45 - 54
Mammogram yearly
Colorectal Cancer: Screening Recommendation
Age: 45 - 75
Stool screening/ visual exam
Ages 75-85
varies per patient, depending on risk factors and overall health
Over 85
screening is no longer required
Stool
Visual
Colonoscopy EVERY 10 years
Prostate Cancer: Screening Recommendation
Screening depends on risk factor
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Retesting every 2 years if PSA is less than 2.5 ng/mL
Cervical Cancer: Screening Recommendation
Age: 25 to 65
Pap test with HPV every 5 years
Without HPV every 3 years
Lung Cancer: Screening Recommendation
Age 50 to 80 years old
Smoking history
Helical CT
Spinal
Cancer: Impact of Overall Health - Physiological
Pain
Infections
neutropenia can develop due to chemo which is a lower wbc
minor infection:lead to sepsis
Gastrointestinal
Lymphedema
Peripheral neuropathy
Many cancer treatments can cause nerve damage
Clinical manifestations
numbness
tingling
decreased ability to sense hot, cold, or pain
Fertility
Fertility preserving
Egg freezing
Embryo freezing
Radiation shielding
Cancer: Impact of Overall Health - Cognitive
Sleep disturbances
Many medications, such as corticosteroids, contribute
Delirium
Concentration problems
Decreased organizational abilities
Impaired memory
Fatigue
Cancer: Impact of Overall Health - Psychosocial stressors
Distress in cancer
Depression
Financial stressors
Cancer: Impact of Overall Health - Health promotion & disease prevention
STOP smoking
Routine screening
Lymphedema
Frequent cancer complication
Can result from any cancer or treatment that impacts lymph node drainage
Clinical manifestations
Heaviness
Swelling
Sensation of tightness
Decreased ROM
Itching
Burning
Sleep disturbance
Administration of chemotherapy
PPE
Chemotherapy gown
Double chemotherapy gloves
Face and eye protection if there is any risk of splashing or emesis
Respiratory protection if there is any risk of inhalation
Extravasation
Potentially severe tissue damage
Many intravenous chemotherapy medications are potentially hazardous to tissues outside of the vein.
Cancer: Education
Oral and topical chemotherapy
Avoid unprotected sex.
experiences nausea and vomiting
Medication Administration
Gloves and Safe disposal are required
Venous access devices: central venous catheter (CVC)
keeping all CVC dressings dry and intact
Monitoring for manifestations of infection at the insertion site
Keeping the catheter from getting pulled
Abides by the routine flushing schedule
Cell counts
Anemia
may stop treatment
blood transfusion
thrombocytopenia
low platelet count
Symptom management
Preventing infections
Radiation
Clinical manifestation:
Fatigue
Alopecia
Skin changes: Erythema, irritation, swelling, blisters or changes in pigmentation
Biotherapy/ Immunotherapy
Cancer treatment using the client’s own immune system by stimulating the immune system in order to attack cancer cells and help restore function of the immune system
Nursing role
Patient and family education
Medication admin same as chemotherapy
Cancer Treatment: Procedures
Tumor Reduction
Destruction of the main arteries that provide blood flow to the tumor
Tumor Excision
Cancer Treatment: Nursing Considerations
Perioperative care
Prevent general complications postoperatively
Prevent and treat pain
Education
Support for patient and family
Chemotherapy
Use
Help control progression
Use to cure a disease
palliative treatment for terminal disease
Damage a cell’s DNA
Chemotherapy: Oral
just as toxic to patient and nurse administering/ handling
Chemotherapy: Parenteral
Closely monitor IV infusions
Parenteral Chemotherapy: Extravasation
Prevention of and monitoring…
Ensuring intravenous access is functioning properly
Nursing interventions
Stop the infusion
Notify provider
under some circumstances, aspirating any remaining drug from the line.
Additional Treatments
Applying hot and cold therapy
Admin of antidote medications to minimize tissue damage.
In serious cases
Surgical management
Extravasation: Clinical Manifestations
Pain
Swelling
Redness
Problems with intravenous access.
Chemotherapy: Other Routes
Intraventricular (ventricles of the brain)
Intracavity (intraperitoneal cavity)
Some discomfort may be present during administration
Intravesicular (bladder)
Intrapleural (pleural cavity)
intrathecal (spinal cavity)
Chemotherapy: Complications
Immunosuppression/ neutropenia
Nausea/ Vomiting/ Anorexia
Alopecia
Hypersensitivity
Oral effects
Anemia/ Thrombocytopenia
Chemo-induced peripheral neuropathy
Cognitive impairment.
Chemotherapy: Patient Education
Precautions
Avoid crowds
Hand Hygiene
Avoid foods that may contain bacteria
Eat small meals
Encourage high protein, high calorie nutrient dense foods
Protect scalp/ skin from sun exposure (after hair loss)
Managing active bleeding / prevent injury
Strategies to improve memory and concentration
Radiation Therapy
High Energy radiation to targeted tissue and destroy cells
Delivered internally or externally
Given as a series of small doses over time
May be used Preoperatively to decrease the size of the tumor
Radiation Therapy: Side effects
Skin changes
Hair loss
Stomatitis
Fatigue
Anorexia
Bone marrow suppression
Other Cancer Therapies
Hormone therapy
Effective against tumors that are supported or suppressed by hormones
Breast and Prostate cancer
Immunotherapy
Nursing role
Wear the proper PPE and use safe practices
Oral and topical therapy
Precaution: others are not exposed to the client’s blood or bodily fluids
Targeted Therapy
Oncologic Emergencies: SIADH
Excess levels of antidiuretic hormones are produced.
Causes the body to retain water. This causes dilution of electrolytes (sodium in the blood).
Often associated with lung and brain cancers.
Clinical Manifestations
Nausea & Vomiting (early)
Lethargy
Hostility
Seizures
Coma (late)
Nursing interventions
Monitor sodium
Administer Lasix
0.9 NACL fluids IV, or hypertonic fluids.
Monitor Vital signs.
Oncologic Emergencies: Hypercalcemia
Common complication: Breast, Lung head and neck cancers- leukemia and lymphoma multiple myeloma and bony metastases of any cancer.
Clinical Manifestations:
Anorexia
Nausea & Vomiting
Short QT interval
Kidney stones
Changes in mental status
Nursing interventions
Administer 0.9 NACL
Administer Lasix, and phosphates as prescribed
Oncologic Emergencies: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Obstruction of venous return and engorgement of the vessels from the head and upper body
Clinical Manifestations
Periorbital and facial edema
Erythema of the upper body (skin redness)
Dyspnea
Epistaxis.
Nursing management
High fowlers position: lung expansion
High dose radiation for emergency temporary relief
Oncologic Emergencies: Hematologic disorders
Caused by the cancer itself or by the chemotherapy
Nursing interventions
Monitor for bleeding
Admin clotting factors
Medication: Heparin
Used to slow the events that makes the body overuse its blood clotting factors
Oncologic Emergencies: Sepsis
Patients that are neutropenic are at increased risk
Nursing interventions
Administer medications as ordered
Antibiotics
Fluids
Vasopressors
Blood cultures & blood lactate may also be ordered to diagnosis
Oncologic Emergencies: Spinal Cord Compression
Occurs when the spinal cord degrade secondary to cancer or tumors invading the spinal column. Permanent neurologic damage can occur without intervention
Nursing interventions
High dose corticosteroids: reduce inflammation
Monitor neurological status
Prepare client for surgery or radiation therapy to relieve spinal cord compression
Oncologic Emergencies: Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Tumors are rapidly destroyed releasing content into the bloodstream faster than the body can process them.
This rapid release can cause hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia.
Clinical Manifestations:
GI distress
Flank pain
Muscle cramps
Seizures
Weakness
Mental status changes
Nursing interventions
Encourage fluids
Administer medication
Hemodialysis and intensive care may be required.
Cancer: Pain Management
NSAIDS
Opioids
Antidepressants
Anticonvulsants
Corticosteroids
Topical
Palliative Care
Holistic care for those who are experiencing severe medical illness and clients approaching end of life
Implemented earlier in the course of life-threatening health events
Helps with…
Improve quality of life
Reduce time in the hospital
Improve client satisfaction
Hospice Care
For terminal illness
Focus on Comfort, Dignity, Personal growth in the face of death
Holistic treating the patient and their family
Breast Cancer: Risk Factors
Gene mutations
Advanced age
Family history
Obesity
Alcohol use
Radiation exposure
Breast disease
Dense breast tissue
Estrogen exposure
Breast Cancer: Clinical Manifestations
Mass or lump
Swelling
Discharge
Nipple retraction
Skin changes
Swollen lymph nodes
Breast Cancer: Lab and diagnostic studies
Mammograms
Screening
Diagnostic
Clinical breast exam
MRI
Biopsy
Hormone-sensitivity testing
Growth factor testing
Breast Cancer: Treatments and Therapies
Surgery
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Hormone therapy
Targeted therapy
Lung Cancer: Risk Factors
Smoking
Radon gas
Secondhand smoke
Exposure to
Asbestos
Radiation
Air pollution
Diesel exhaust
Metals
Chemicals
Lung Cancer: Clinical Manifestations
Cough
Hemoptysis
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Weight loss
Chest pain
Respiratory infections
New wheezing
Hoarse voice
Lung Cancer: Diagnostic tools
Chest imaging
Biopsy
Sputum cytology
Lung Cancer: Treatment and Therapies
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Targeted therapy
Prostate Cancer: Risk Factors
Age (50 and older)
Family history
Smoking
Increased body weight
Survival rates
Racial disparities
Black individuals in the United States
Prostate Cancer: Clinical Manifestation
Urinary frequency
Problems with urine flow
Erectile dysfunction
Blood in urine or semen
Prostate Cancer: Diagnostic tools
Digital rectal examination
PSA
blood test
Higher PSA levels correlate with an increased risk of prostate cancer
Ultrasound
MRI
Biopsy
Prostate Cancer: Treatment and Therapies
Surgery
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Hormone therapy
Targeted therapy
Colorectal Cancer: Risk Factors
Excess body weight
Low activity level
Smoking
Diet
Alcohol intake
Medical conditions
Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Manifestations & Diagnostic tools
Changes in bowel habits
Blood in stool
Rectal bleeding
Anemia
Abdominal discomfort
Weight loss
Fatigue
Diagnostic tools
Fecal occult testing
CEA levels
Colonoscopy
Biopsy
Colorectal Cancer: Treatments and Therapies
Surgery
Surgical resection
A colostomy is often required
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Targeted therapy
Immunotherapy
Radiofrequency ablation
A probe is inserted, and small electrodes kill the cancer cells
Pancreatic Cancer: Risk Factors
Smoking
Medical conditions
Family history
Genetic conditions
Increased body weight
Alcohol consumption
Pancreatic Cancer: Clinical Manifestations
Jaundice
Skin itching
Dark urine
Light colored bowel movements
Pain
Anorexia
Weight loss
Nausea and vomiting
Pancreatic Cancer: Labs and diagnostic testing
Liver function testing
Tumor markers
Biopsy
CT scans
Ultrasound
Cholangiopancreatography
Uses MRI to visualize the pancreatic and bile ducts.
Pancreatic Cancer: Treatments and Therapies
Surgery
the entire pancreas (total pancreatectomy) or the distal pancreas (distal pancreatectomy)
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Targeted therapy
Skin Cancer: Risk Factors
Advanced age: Major risk factor
Ultraviolet radiation
Family history
Advanced age
Moles
Immunosuppression
Skin Cancer: Clinical Manifestations & Lab testing
Skin changes
Lab testing
Biopsy
Skin Cancer: Treatments and Therapies
Chemical peels
Option for Actinic Keratoses
Photodynamic therapy
Surgery
First line of treatment
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy
Brain and CNS Tumors: Risk Factors
Environmental exposure
Infection
Older adults
Brain and CNS Tumors: Clinical Manifestations
Headaches
Seizures
Nausea and vomiting
Visual changes
Balance issues
Behavioral changes
Brain and CNS Tumors: Lab testing
CT
MRI
PET
Biopsy
Brain and CNS Tumors: Treatments and Therapies
Active Surveillance
Surgery
Partially or fully remove a tumor
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy wafer
Delivers medication directly to the tumor site.
Intrathecal chemotherapy
Instilled directly into the brain or spinal co
Radiation
Targeted therapy
Liver, Pancreas & Gall bladder
Liver
Vital role with coagulation factors
Pancreas
Regulate blood sugar
Gallbladder
Stores bile
Stores bile necessary for fat digestion
Releases bile after food ingestion
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder
Can be acute or chronic
Acute cause
Due to being NPO on TPN
Caused by the blocking of the common bile duct
Cholecystitis: Risk Factors
High fat diet
Females
Hormonal therapy
Pregnancy
Obesity
Family history
Patients older than 65 years old
Cholecystitis: Clinical Manifestations
Right upper quad pain
Nausea
Vomiting
Fever
Jaundice (rare)
Cholecystitis: Testing and imaging
Testing
CBC
CRP
CMP
amylase & lipase.
Imaging:
Ultrasound
HIDA scan
CT
MRCP
Cholecystitis: Impact on overall health
First line of defense: Take out gallbladder
Older patients
May not be able to have surgical intervention
Medical management instead
Cholecystitis: Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances
Patient will experience
Decrease appetite
Nausea
Vomiting leading to dehydration
Patient will be NPO they require…
IV fluids for rehydration
Monitor electrolytes
IV electrolytes correction
Cholecystitis: Nursing role
Frequent oral care for NPO patients
Allow pt to be in comfortable position
Pain control
NSAIDS or Opioids management
Cholecystitis: Patient Education
Dietary changes
Reduce fried and fatty foods
Encourage regular exercise and weight management
Cholecystitis: Treatments and Therapies
NPO status to rest gallbladder
IV fluids and antibiotics
Cholecystectomy
standard treatment
Usually Laparoscopy
Removal of gallbladder
Delayed treatment
Can cause peritonitis
Rigid abdomen
Pancreatitis: Cause and Risk Factors
Most frequent causes
Alcohol abuse
Gall stones
Risk Factors
Drinking
Smoking
Increase age
Family history
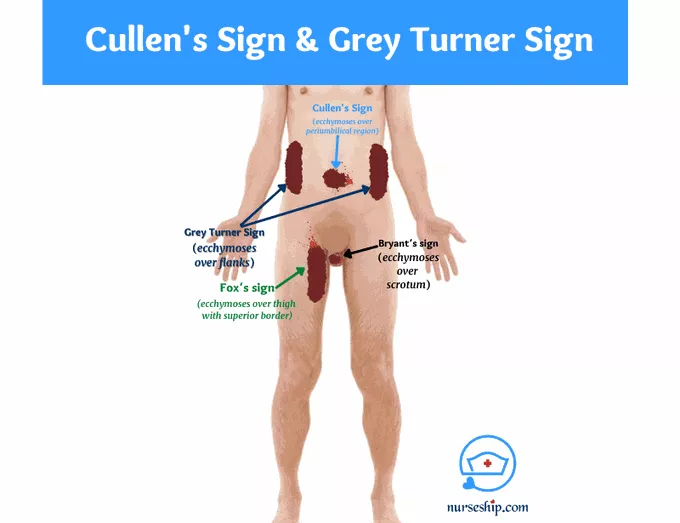
Pancreatitis: Clinical Manifestations
Nauseas
Vomiting
Severe abdominal pain
Grey Turner’s (flanks), Cullen’s (belly button) and Fox’s sign (thigh / /hip area)
Pancreatitis: Labs & Diagnostics
Labs:
Blood amylase
WBC count
Platelets
Blood Ca & Mg
Liver enzymes & bilirubin
Serum glucose
ESR
Diagnostic
CT scan (With contrast)
Pancreatitis: Nursing Intervention
Keep patient NPO
Give patients fluids
Pain management
NSAIDS
Mild moderate pain
Morphine or hydromorphone
Acute pain
Antibiotics
Proton Pump Inhibitors
reduce the production of stomach acid
Pancreatic Enzymes
Pancreatitis: Patient Education
Pain management
Metabolic needs
Nutritional and fluid status
Support groups for patient and family
Pancreatitis:Hypocalcemia
Present in patients with severe Pancreatitis
Clinical manifestations
Muscle cramps and weakness
Tingling
Seizures
Provide patient with Tele
Seizure precaution