Medical Imaging: Cardio
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Mild vs moderate vs severe CHF x-ray findings
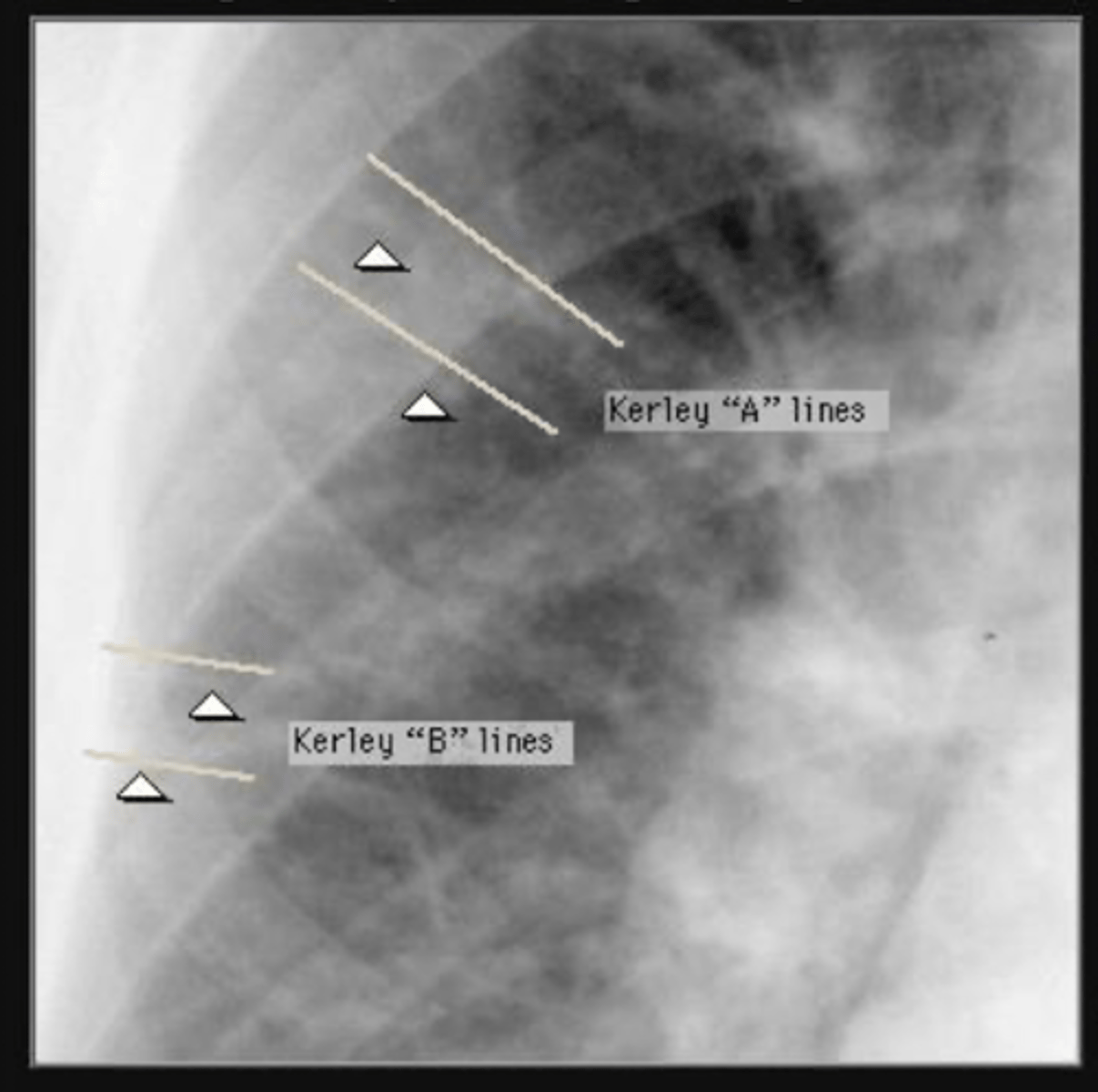
CXR changes are progressive - initially normal then redistribution of pulmonary vascular pattern and cardiomegaly.
Mild - equal pulmonary vasculature in upper and lower lobes (cephalization)
Moderate - Kerley B lines in lateral basilar regions
Severe - pulmonary edema - bilateral perihilar and basilar alveolar infiltrates
What finding indicates pulm edema in CHF?
kerley a and B lines
What should you order in order to evaluate cardiac fx?
you can order either an
echocardiogram or MUGA scan
Normal EF for older pt. WHen is angiogram indicated?
above 50%. angiogram may be indicated if EF , 35%
Pros and cons of Echo vs MUGA
ECHO
1. Very close in accuracy to MUGA in evaluating heart function
2. Can evaluate valves, heart size, clots in heart, wall size etc.
3. No radioactivity
4. cheaper
CONS:
-Poor in pts with lung Dz
MUGA
-most accurate in evaluating heart fx
-good for pt w lung dz
CONS
-radioactive
-needles
-$
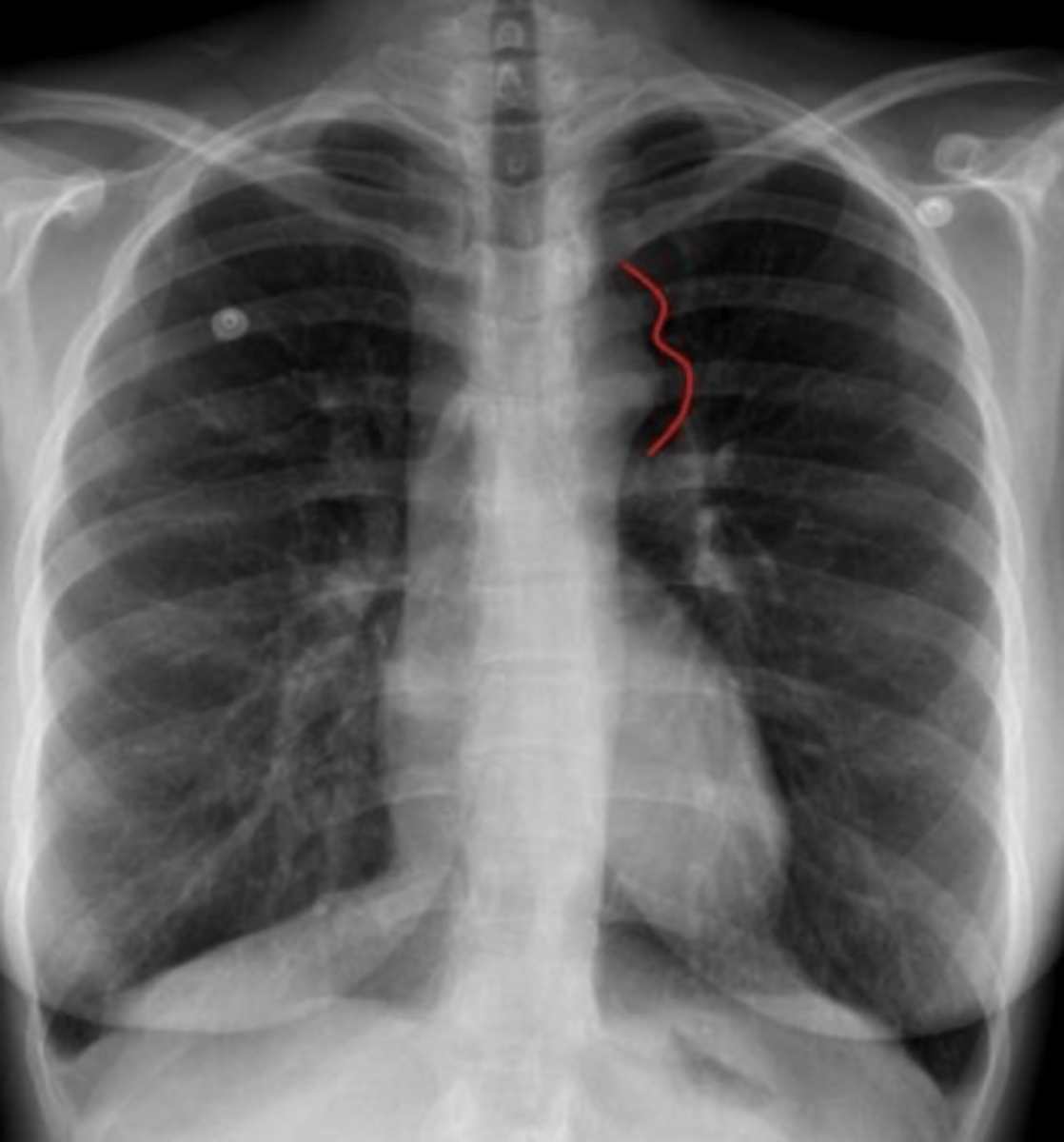
What is the finding on the back of the card?
coarctation of aorta
Common causes of chamber enlargement
Left ventricular enlargement can be due to chronic HTN (most common), coronary artery disease, aortic stenosis or regurgitation, or ventricular aneurysm.
Best imaging to eval LV hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy (wall thickening) is best evaluated by echocardiogram.
What is endocarditis? Epidemiology
Endocarditis = infection of the heart valves
Usually occurs in patients with prior valvular disease or drug addiction.
Imaging used to eval endocarditis
Echocardiogram (usually transesophageal)
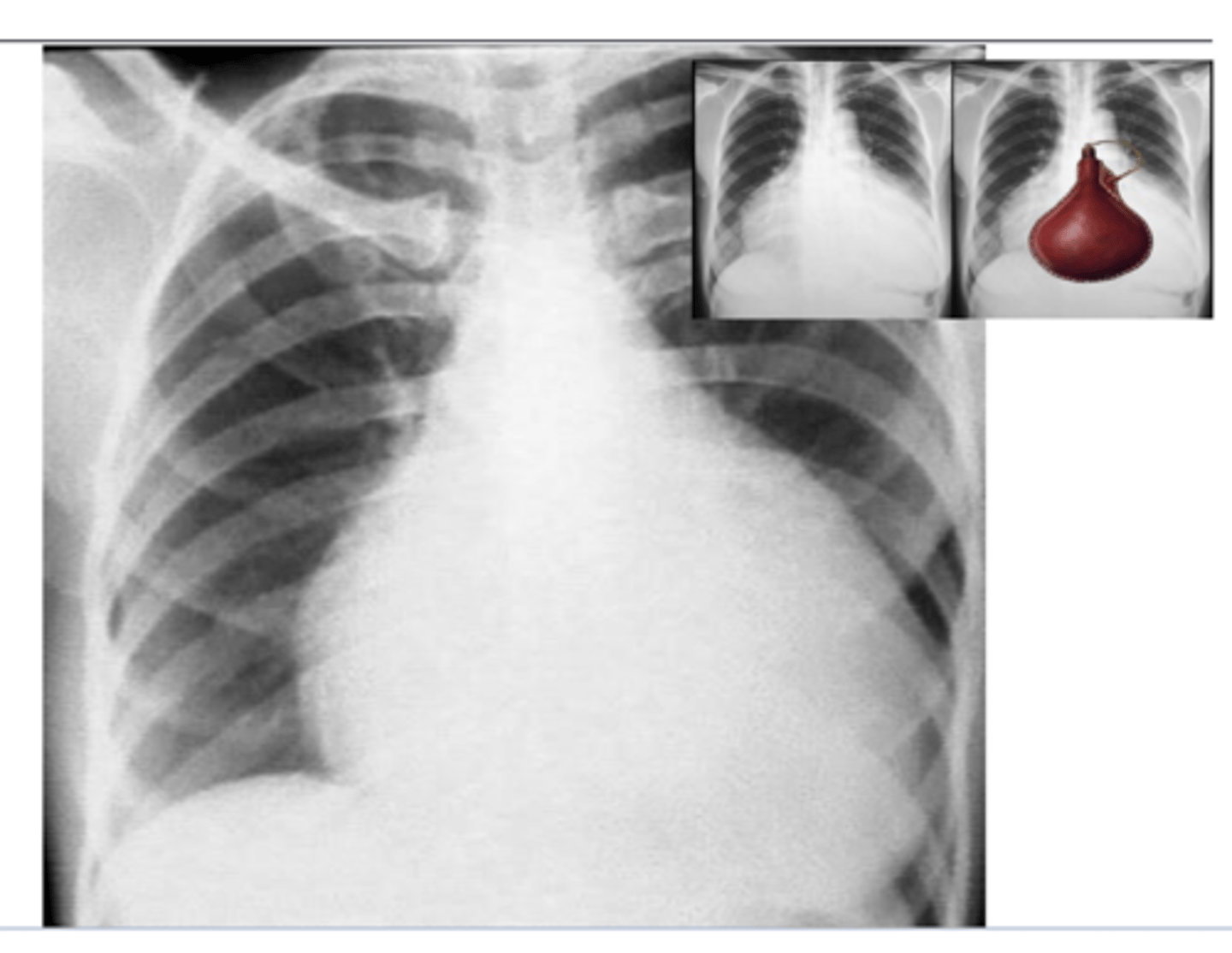
What is the typical appearance of pericardial effusion? Imaging of choice
Pericardial effusion causes an acute marked
enlargement with the heart appearing pendulous and very wide at the base – “water bag appearance.”
echocardiogram is imaging of choice (image here is x-ray)
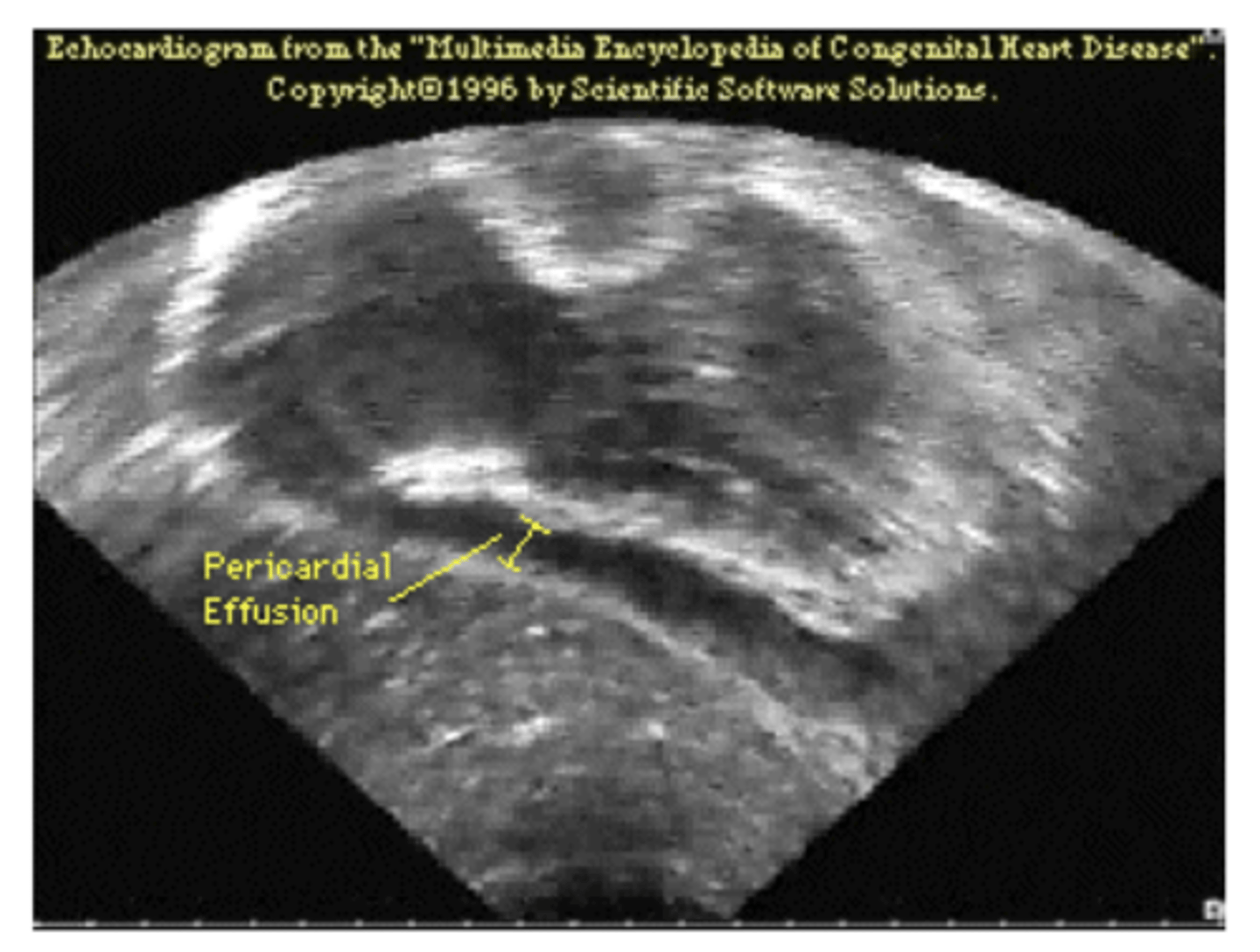
What does epicardial effusion look like on ECG?
area of darkness around heart
What is the most common congenital cardiac deformity in adults?
Atrial septal defect
-blood is going through an additional opening out of the atrium
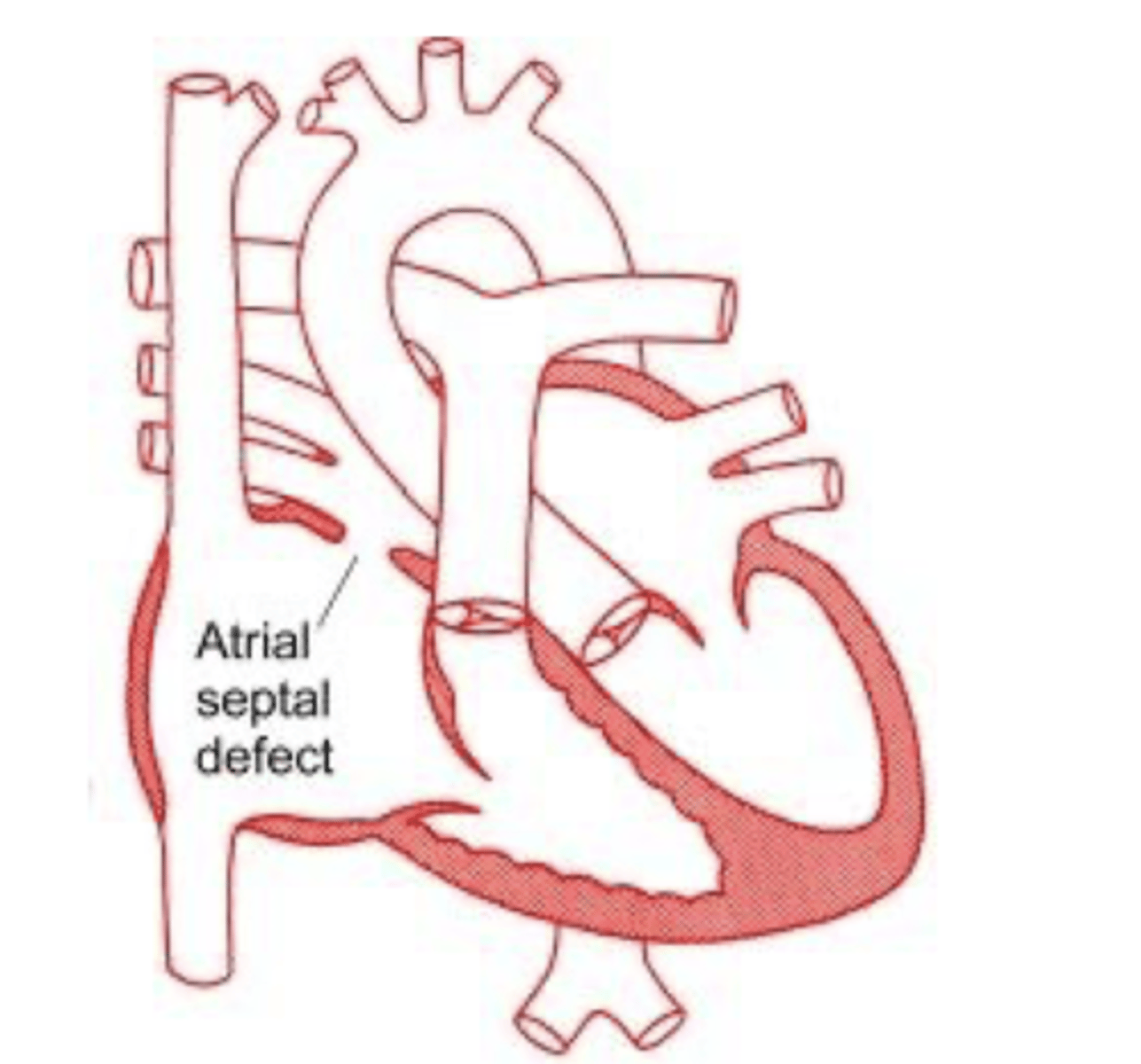
X-ray findings with atrial septal defect
-pulmonary artery
enlargement, right atrial and right ventricular enlargement.
-Film shows filling-in of retrosternal space and
increased size of the pulmonary artery.
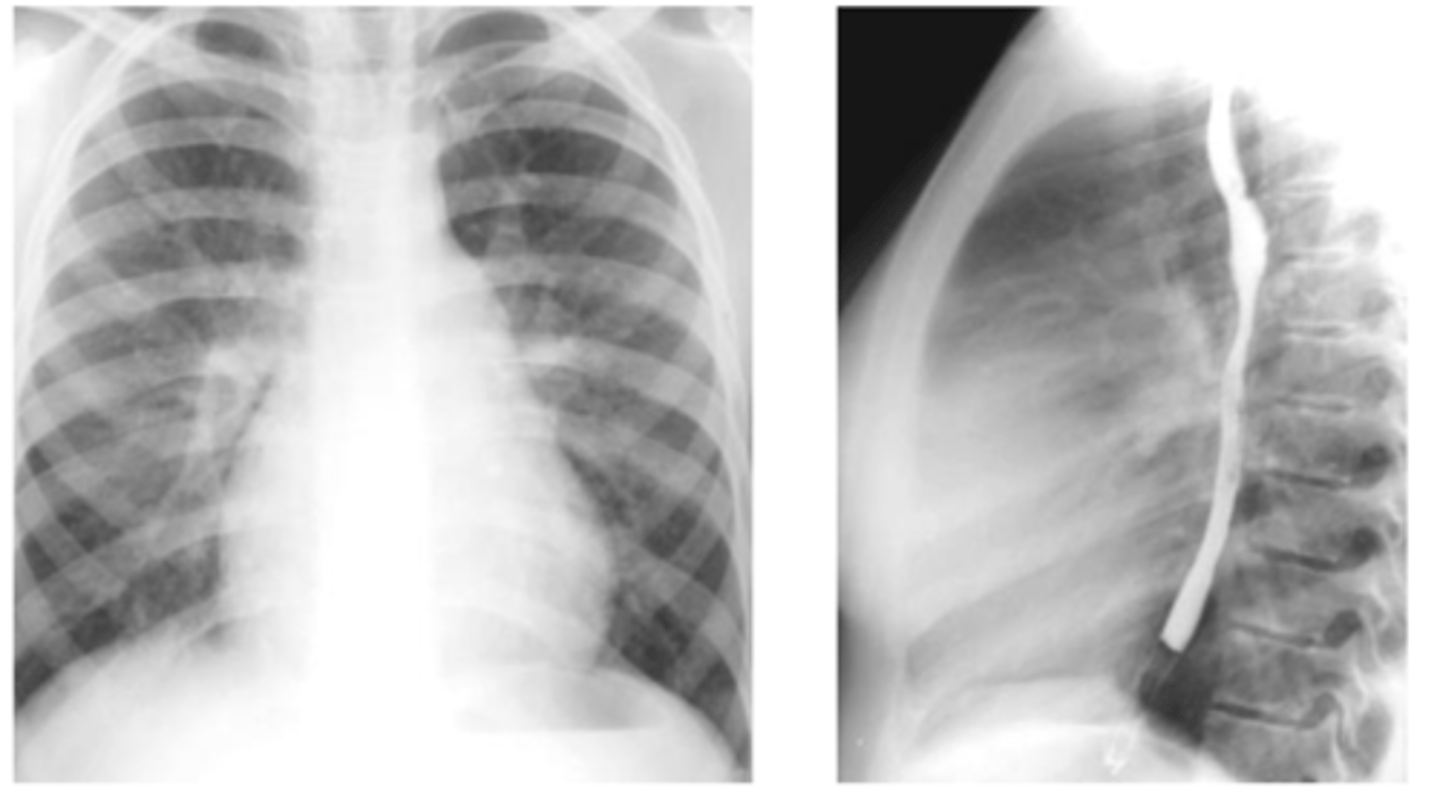
What is hampton's hump?
Wedge shaped pleural based opacity --> indicative of pulmonary embolism
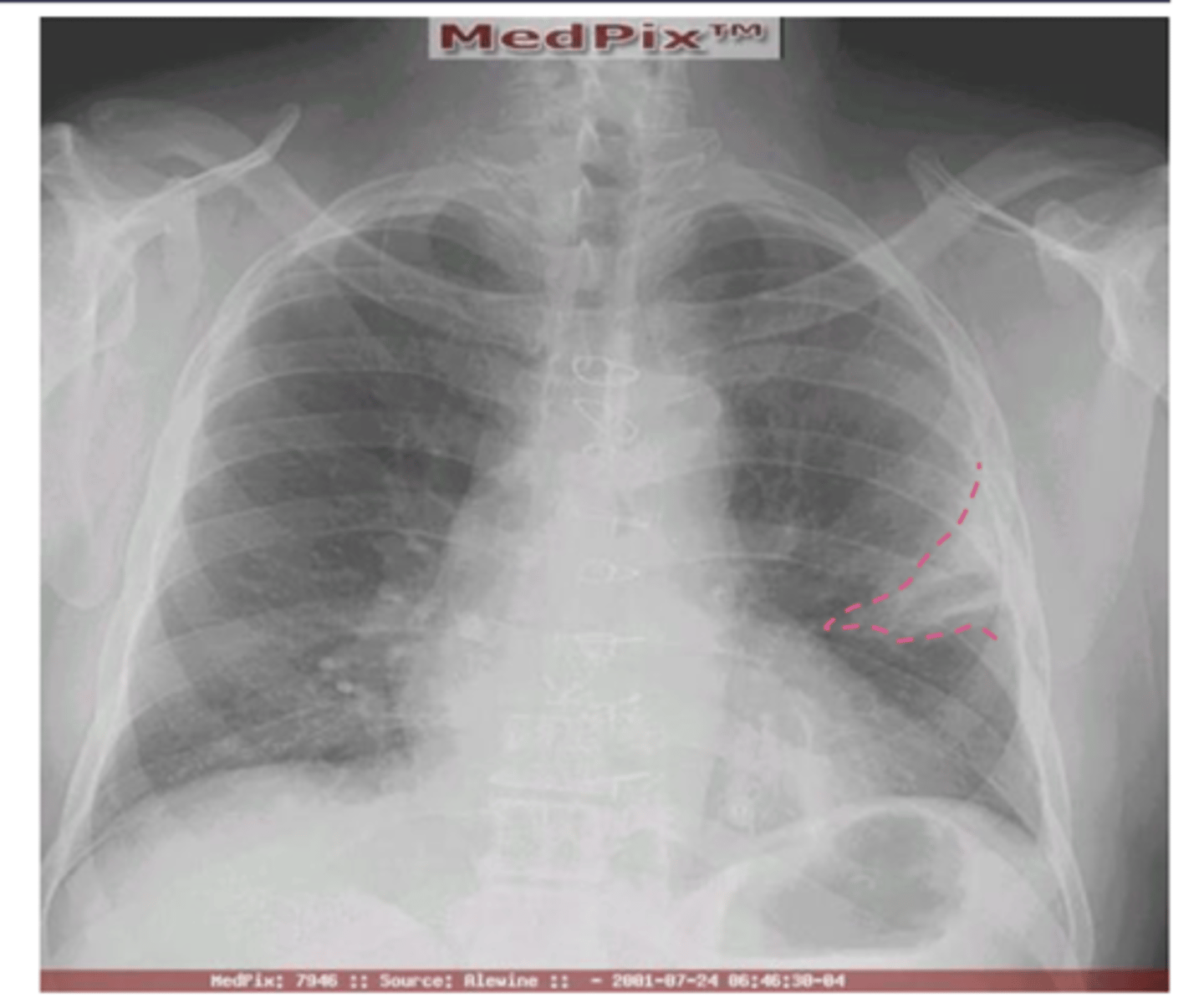
What is westermark's sign? What is it indicative of?
Westermark's sign - the
decreased distal vasculature creating the
appearance of a sharp cut off
*pulmonary embolism
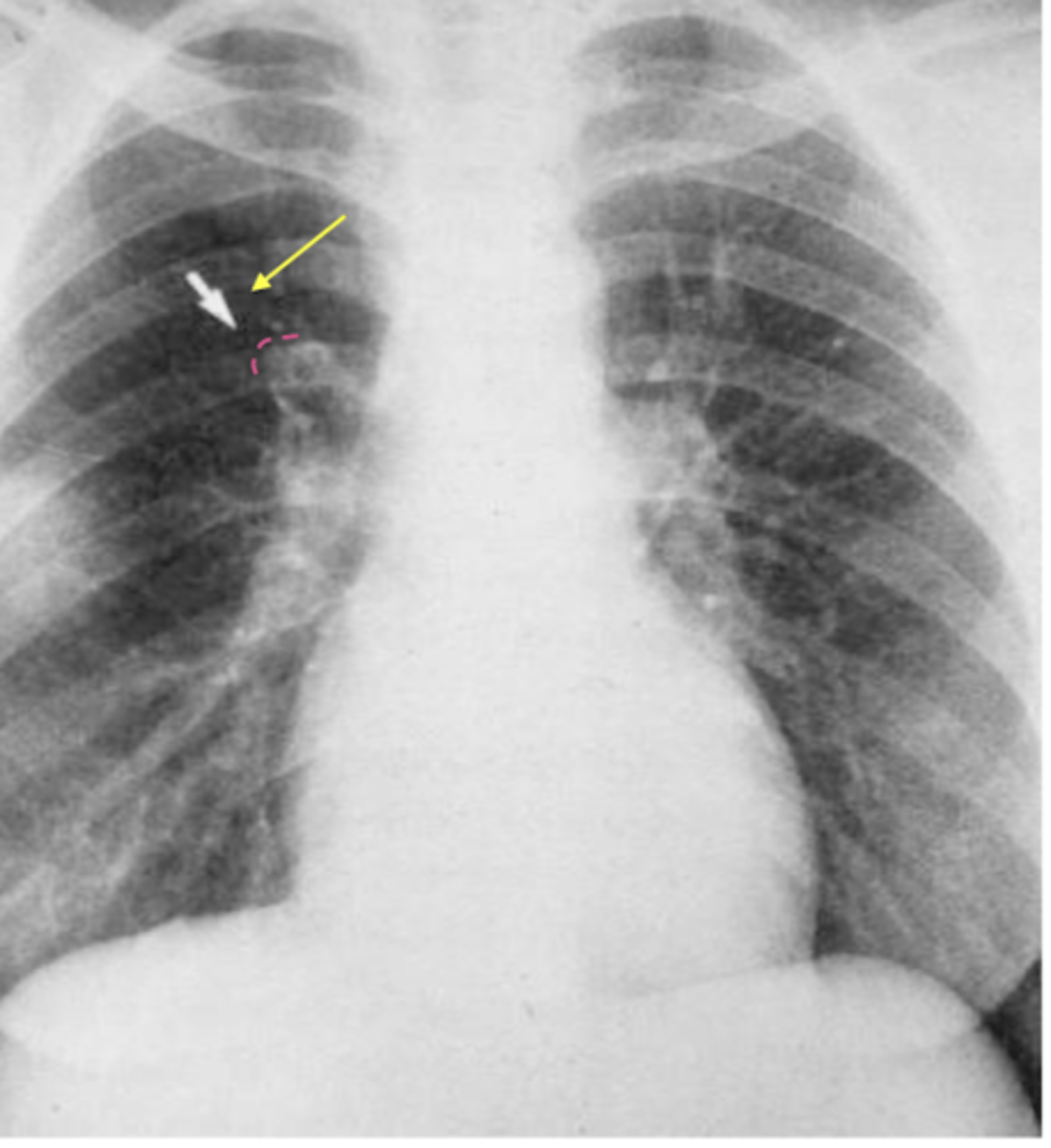
what is the best initial study for suspected pulmonary embolism?
spiral CT with
contrast (CT
Angiography -
CTA)
What imaging/tests can be used to eval coronary artery dz? What does each test look for?
◼ A thallium stress test evaluates the musculature of the
left ventricle during rest and under stress.
◼ The echocardiogram looks for regional wall motion abnormalities – can also be done with stress
◼ Coronary angiography (cardiac cath) is the best study to visualize the coronary arteries but is expensive, invasive and involves a high dose of radiation.
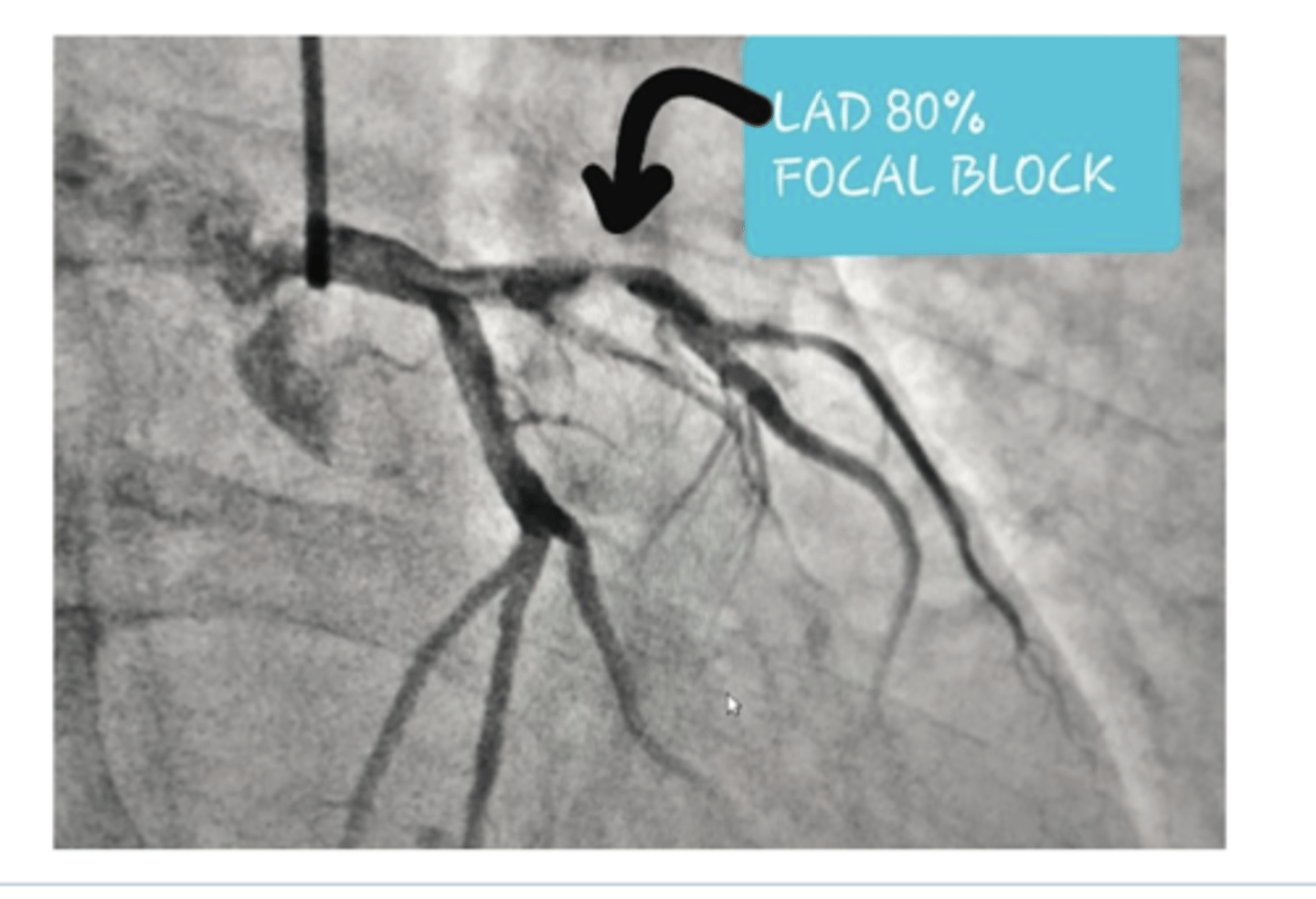
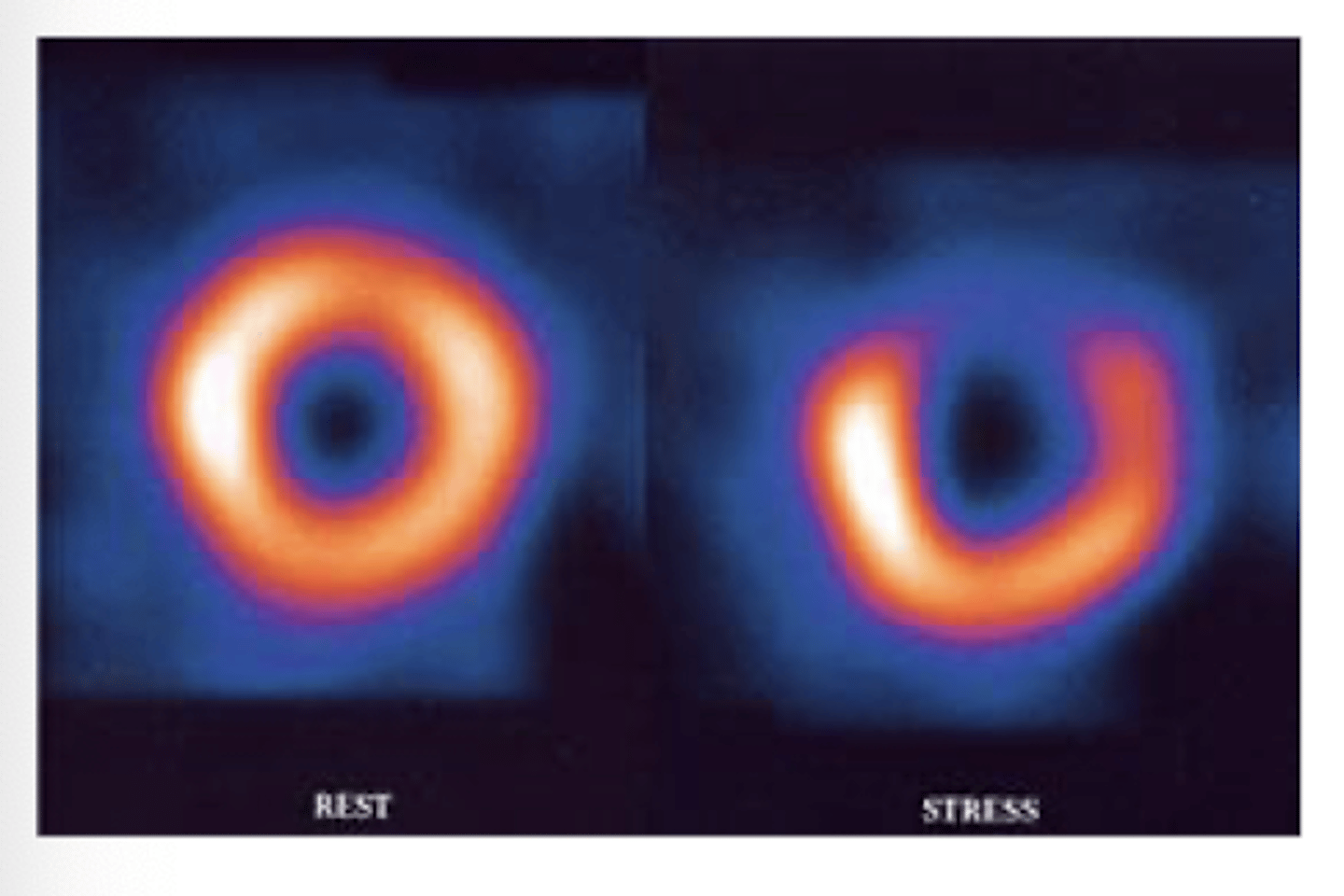
What would an abnormal thallium scan look like?
#1 test for evaluating stress -->.R image indicates void of uptake and dec blood supply
What cause sup to 40% of deaths in MVA's?
aortic tears or ruptures
What is the test of choice for initrial eval of aortic tear or rupture?
CT scan
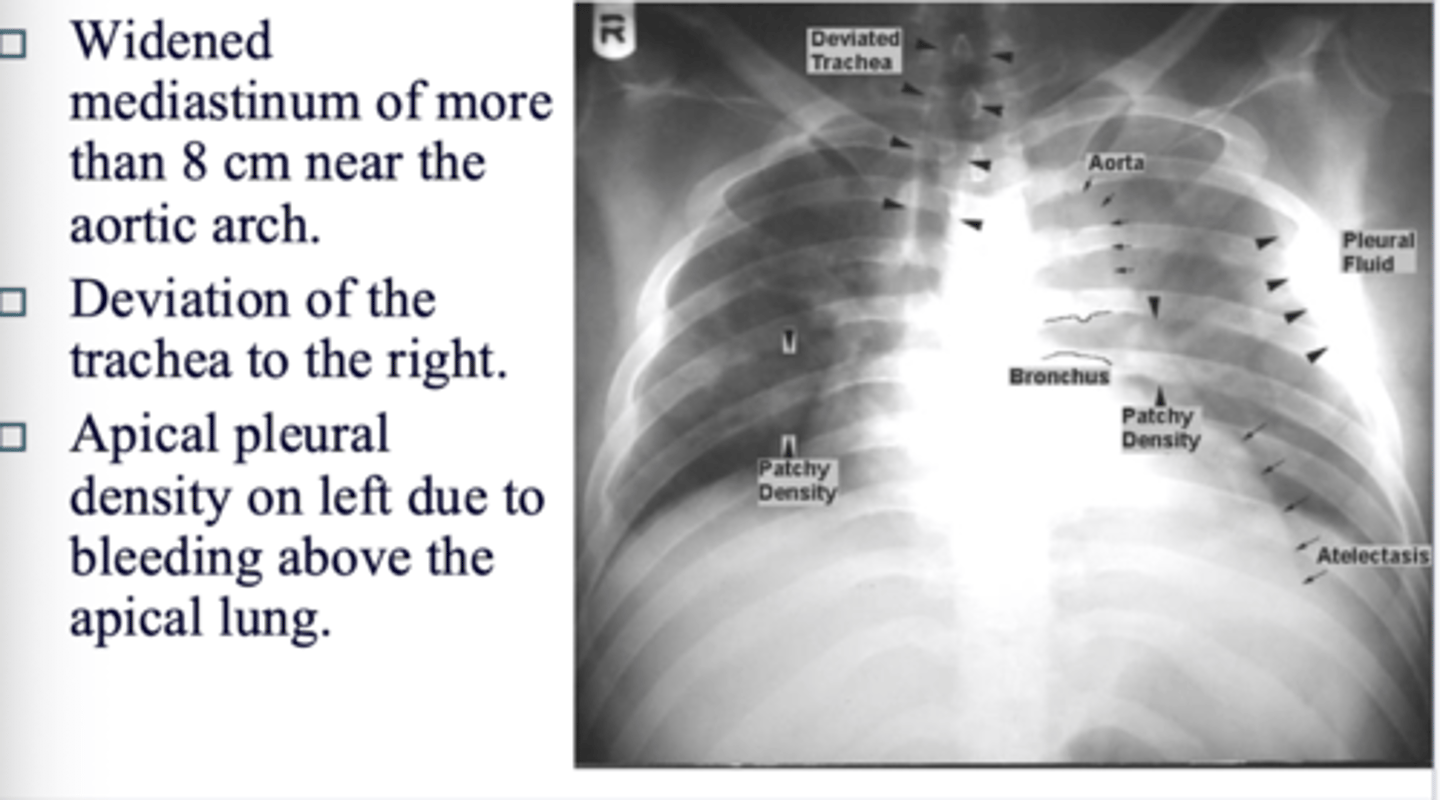
What are the signs of a tear on CT?
◼ Widened mediastinum of more than 8 cm near the aortic arch.
◼ Deviation of the trachea to the right.
◼ Apical pleural density on left due to bleeding above the apical lung.
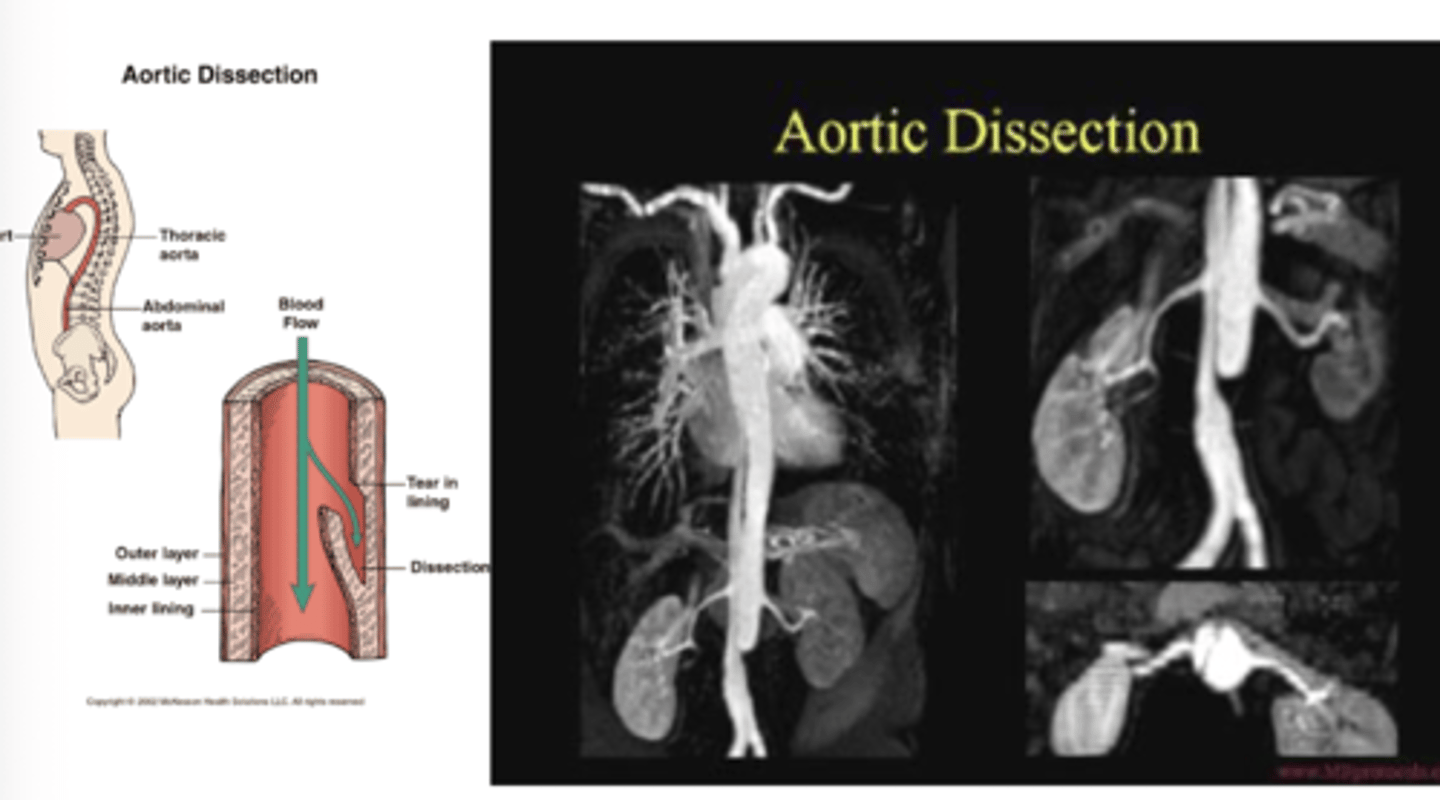
What is aortic dissection?
separation of the layers of the aortic walls allowing blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall. Often associated with aortic
aneurysm.
What is test of choice with aortic dissection?
CT scan with contrast is test of choice
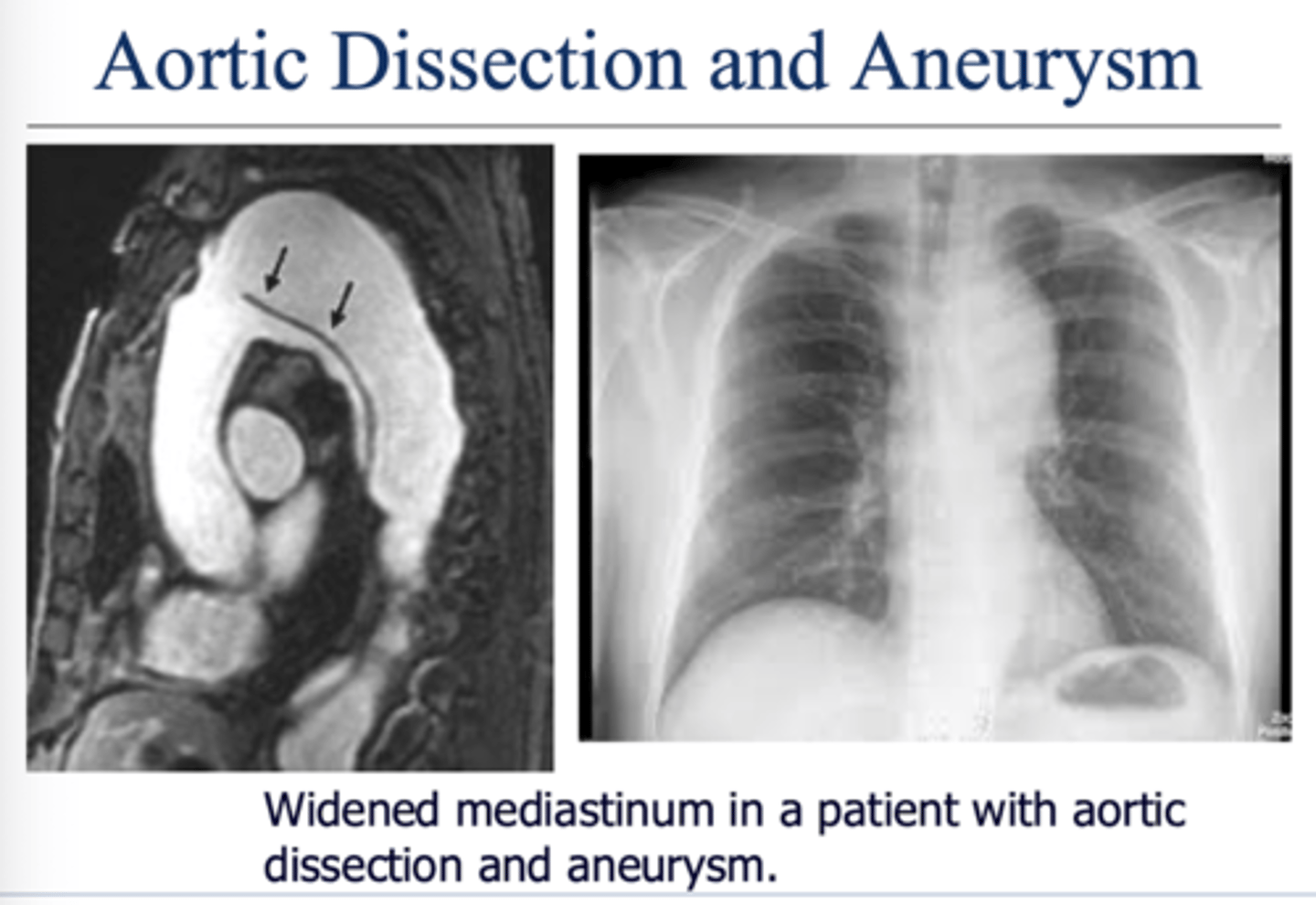
What is an aortic aneurysm? What is test of choice? At what point is there risk for rupture?
Dilation of the aorta with or without dissection of the aortic wall.
Widening of aorta greater than 5 cm is at risk for rupture
CT scan with contrast
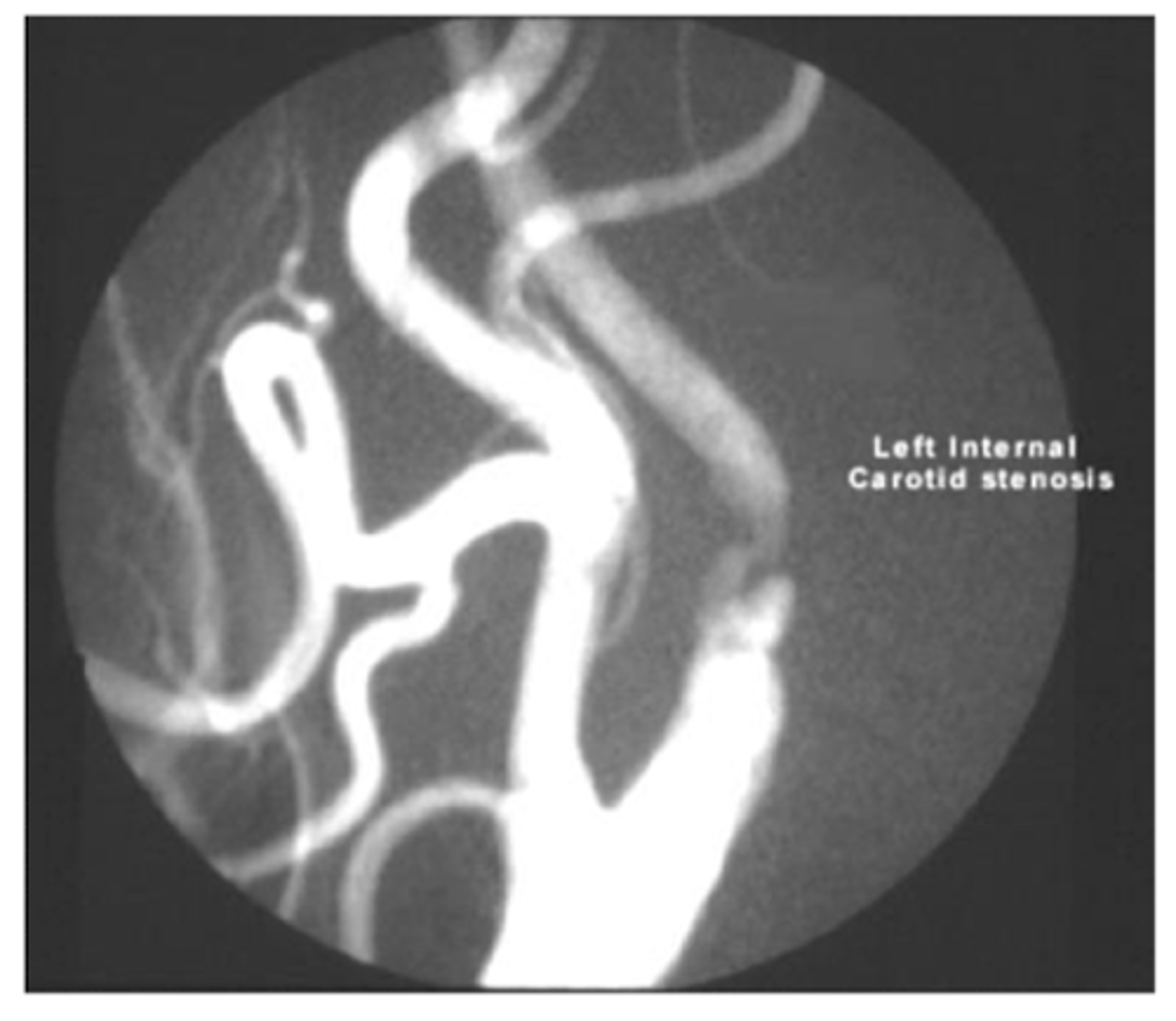
What is the gold standard for evaluating vessels? what is the down side of this testing, and what is used as first line study instead?
contrast angiography - invasive and carries risk of harm to pt
duplex u/s is first line study for vascular dz. can eval anatomy plus direction and magnitude of flow
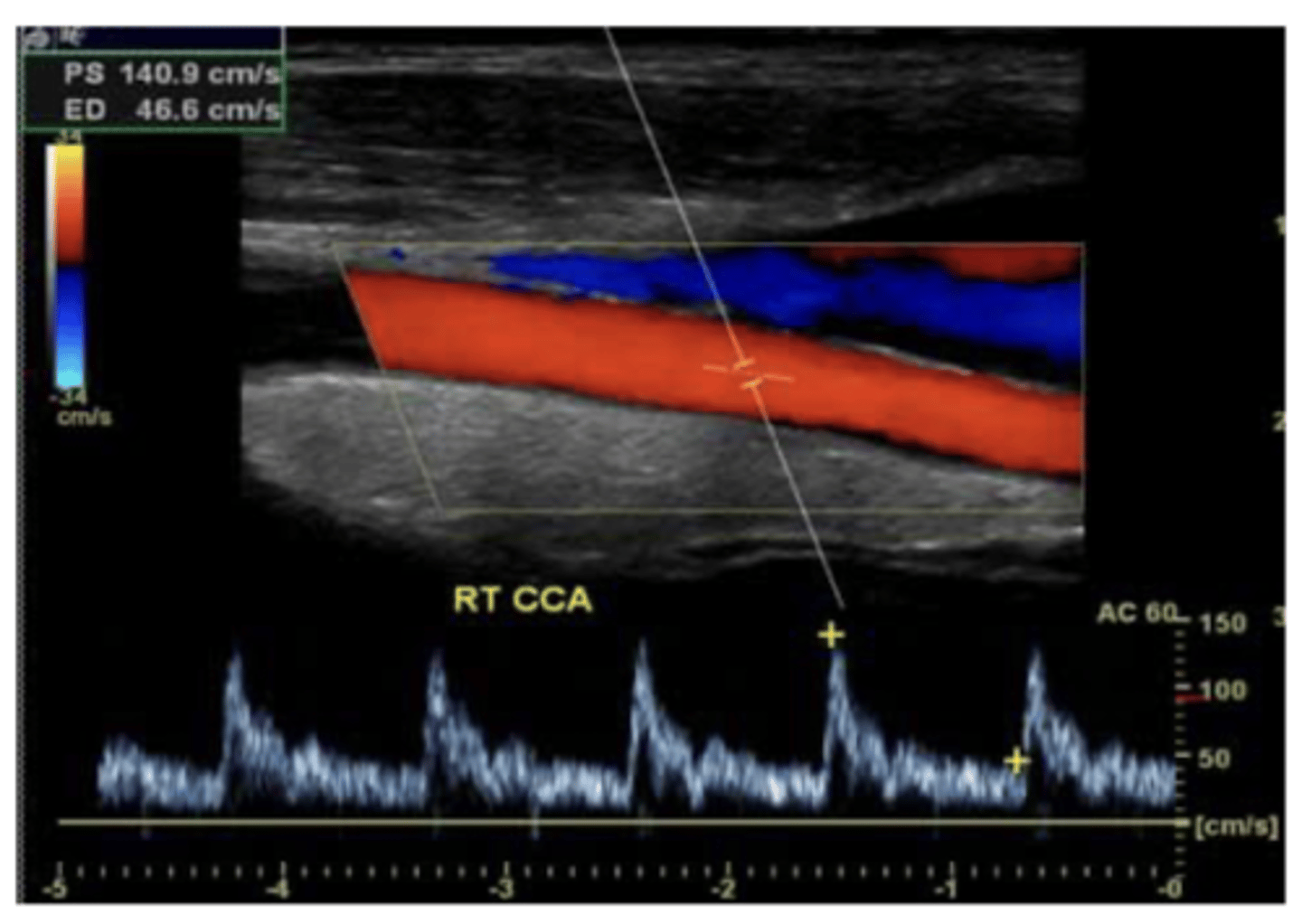
second line study for peripheral vessels
angiography
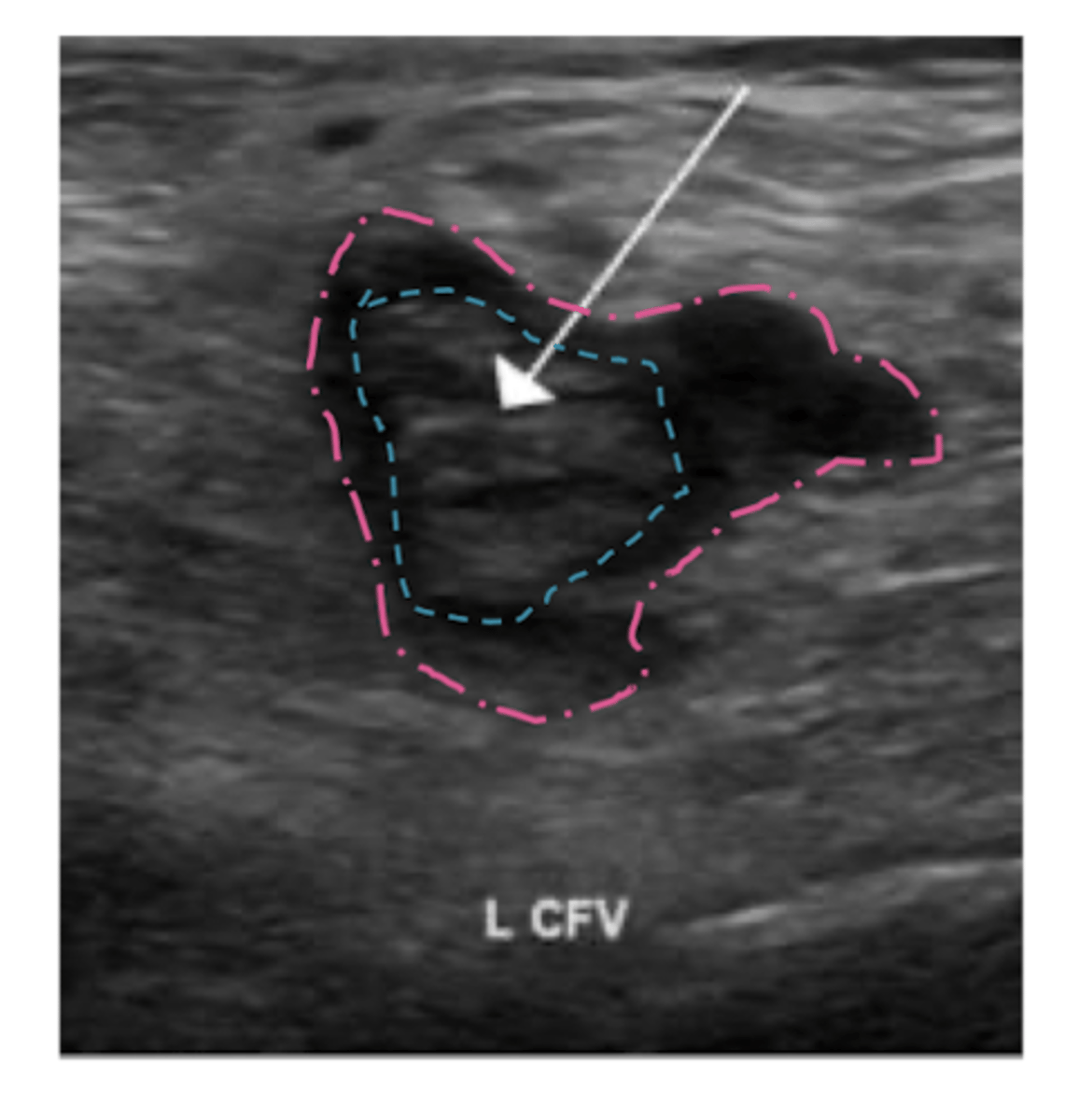
What is initial study of choice for DVT? second line?
duplex u/s of inguinal region, thigh, and popliteal area
second line: contrast venogram