Principles of Biomedical Science Study Guide
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Current History
Chief complaint and any other current health issues.
Previous History
Past medical procedure and health issues.
Social History
Aspects of a patient's life that could have a direct impact on health such as drug and alcohol use, living situation, and safe sex practices.
Family History
Medical information about your family members and close relatives that can help physicians determine if you are at a higher risk of certain diseases.
Patient Interviews
Important to take a patient history and how physicians need to demonstrate a positive demeanor, empathy, and tact.
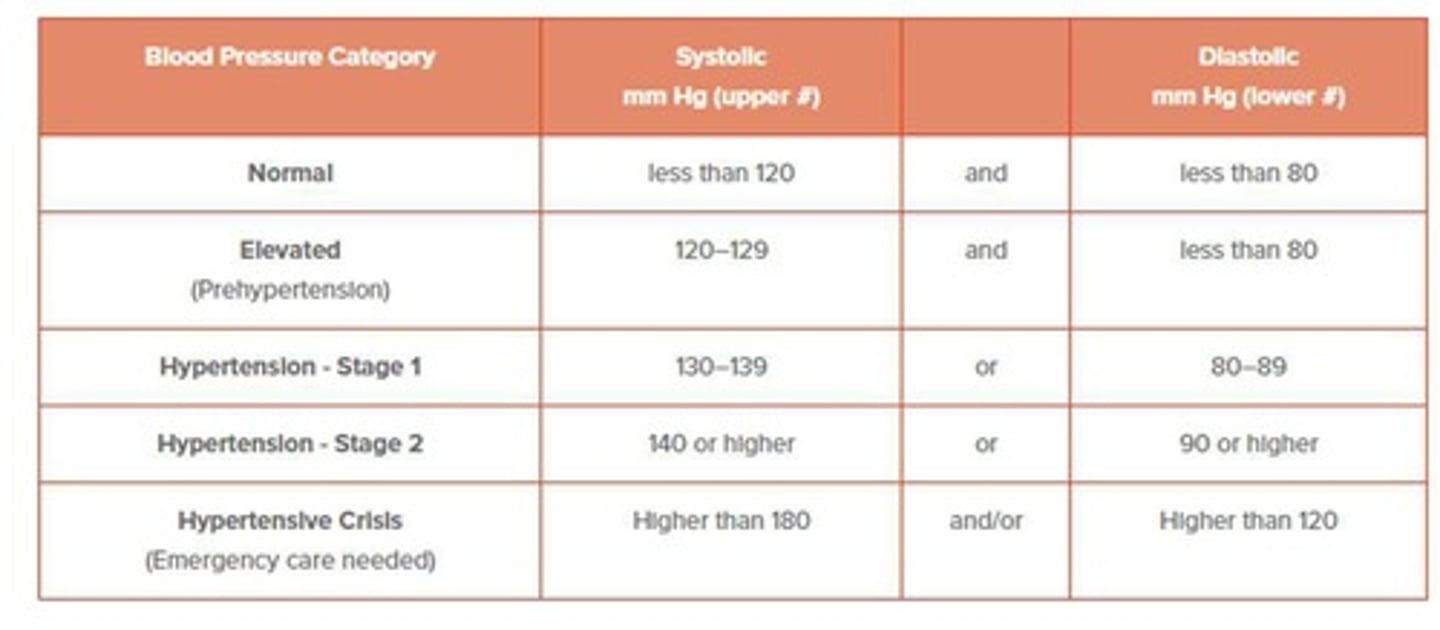
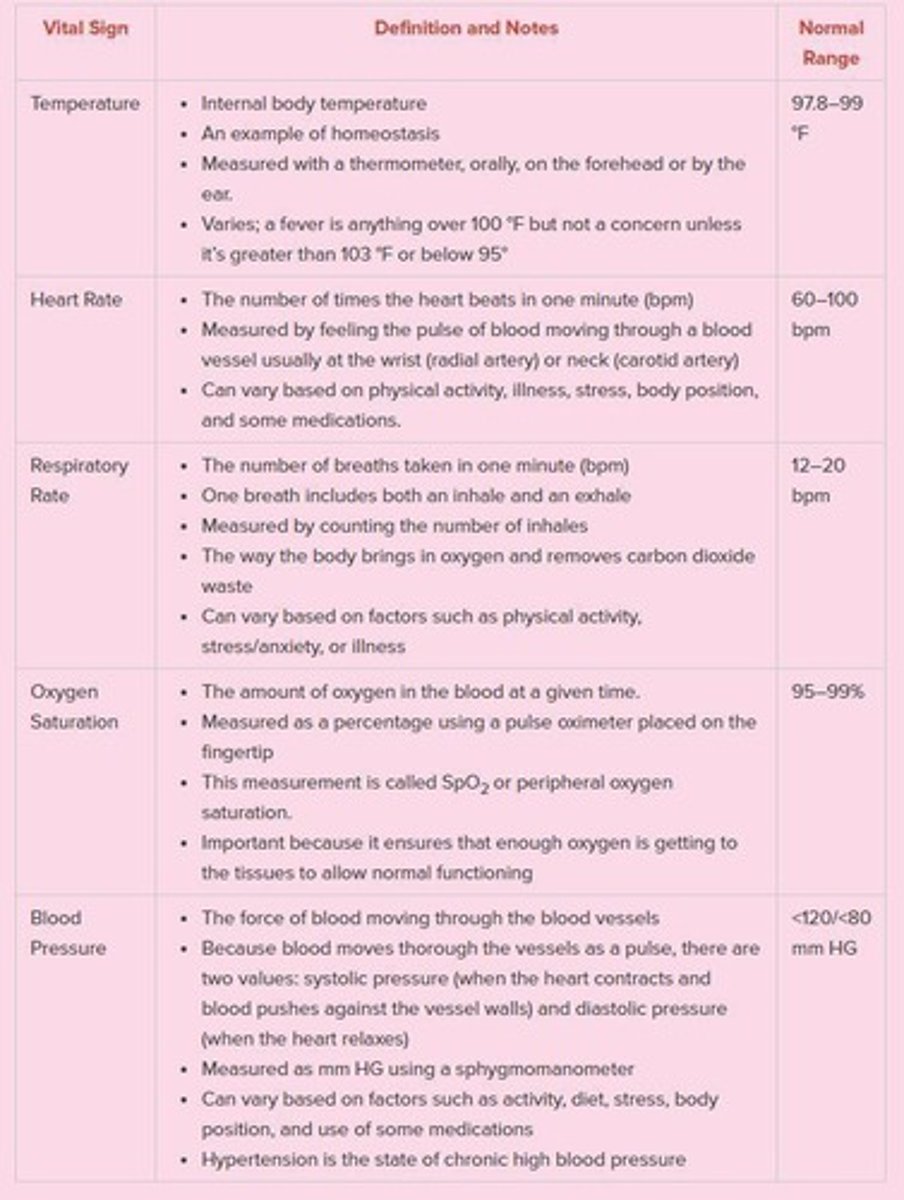
Vital Signs
Measurements that indicate the state of a patient's essential bodily functions.
Sphygmomanometer
Instrument used to measure blood pressure.
Stethoscope
Instrument used to listen to internal body sounds.
Calculator
Tool used for calculations in medical assessments.
Tape Measure
Instrument used to measure length or distance.
Thermometer
Device used to measure body temperature.
Pulse Oximeter
Device used to measure oxygen saturation in the blood.
Scale
Instrument used to measure body weight.
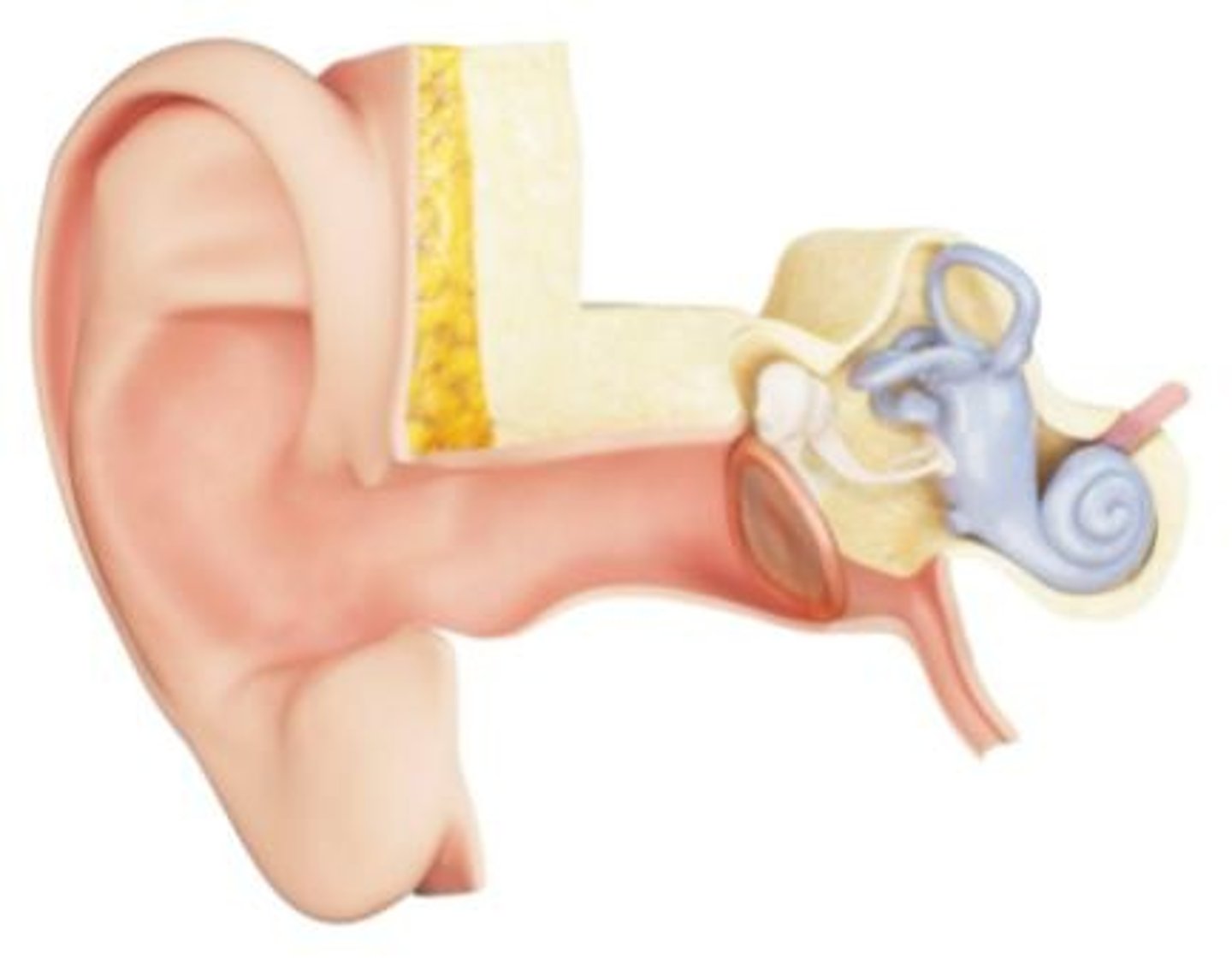
Otoscope
Instrument used to examine the ear.
Ophthalmoscope
Instrument used to examine the interior of the eye.

Snellen Eye Exam
Test that measures visual acuity, where the top number refers to the distance in feet from the chart and the bottom number indicates the distance at which a person with normal eyesight can read the same line.
20/20 Vision
Ability to see what an average person can see on an eye chart when standing 20 feet away.
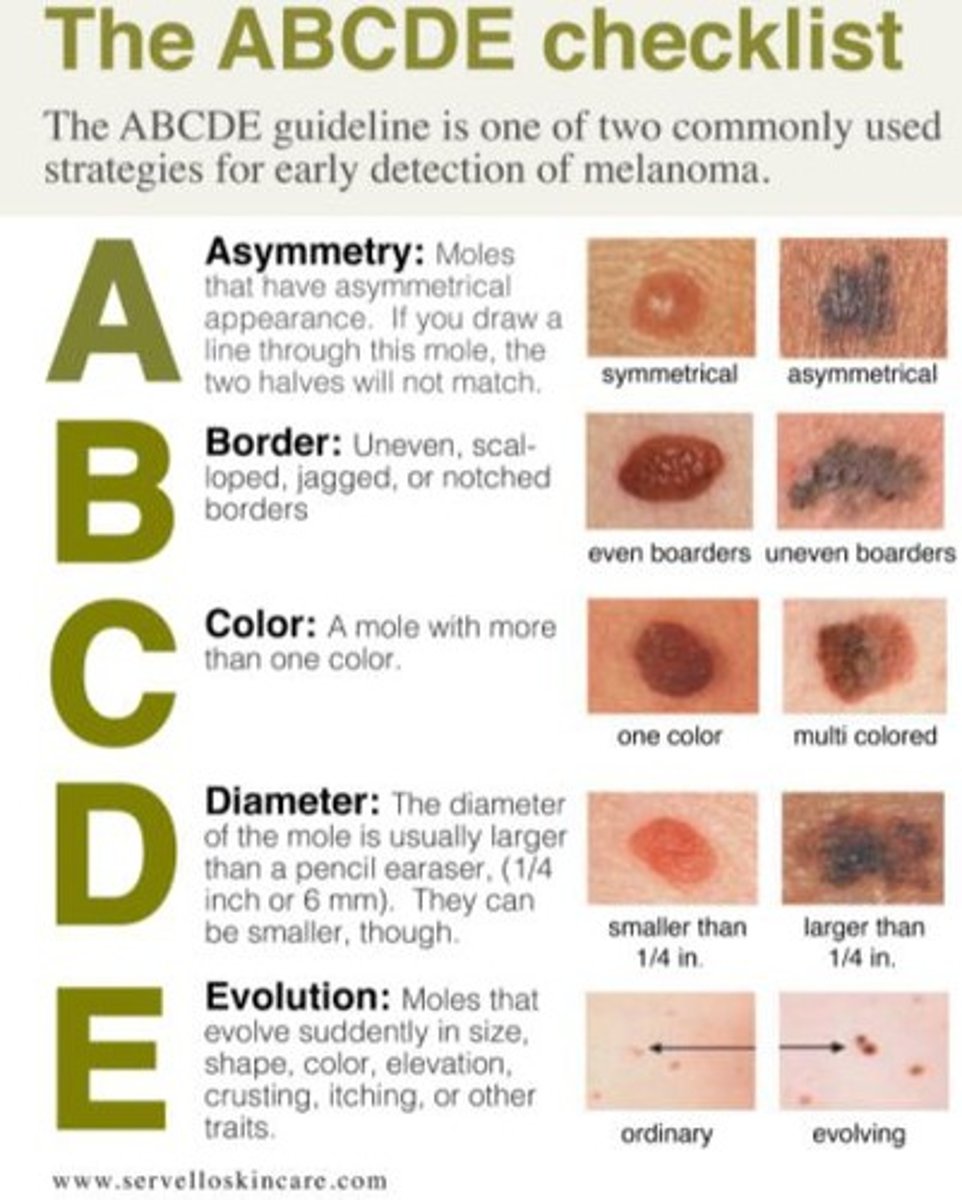
ABCDE Checklist
Method for identifying melanoma by assessing Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolving characteristics of moles.
Complete Blood Cell (CBC) count
A blood test that evaluates overall health and detects a variety of disorders, including anemia and infection.

Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
A blood test that measures glucose, calcium, and electrolytes to assess metabolic functions.

HDL
High-density lipoproteins, known as 'good' cholesterol that helps remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream.
LDL
Low-density lipoproteins, known as 'bad' cholesterol that can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
Hematocrit
Percent Red Blood Cell Volume calculated as (Red Blood Cell Level / Total Blood Level) x 100.
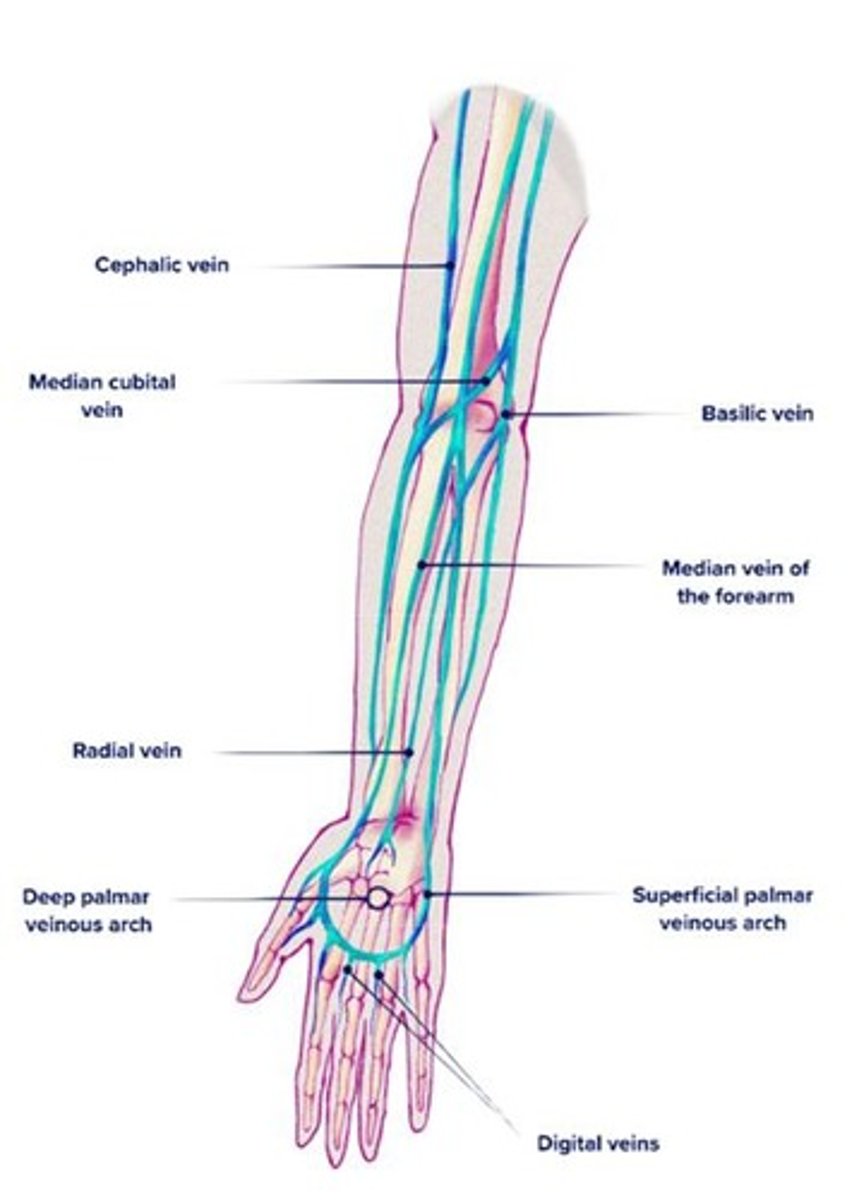
Phlebotomy
The technique of drawing blood from the median cubital vein.
Needle Bevel Placement
The bevel of a needle should be placed facing up during blood draw.
Blood Draw Angle
The angle for drawing blood should be between 15-30 degrees.
Tourniquet Removal
The tourniquet should be removed BEFORE the needle is removed.
Veins for Blood Draw
Veins are used to draw blood because they are closer to the surface, under less pressure than arteries, and easier to access.
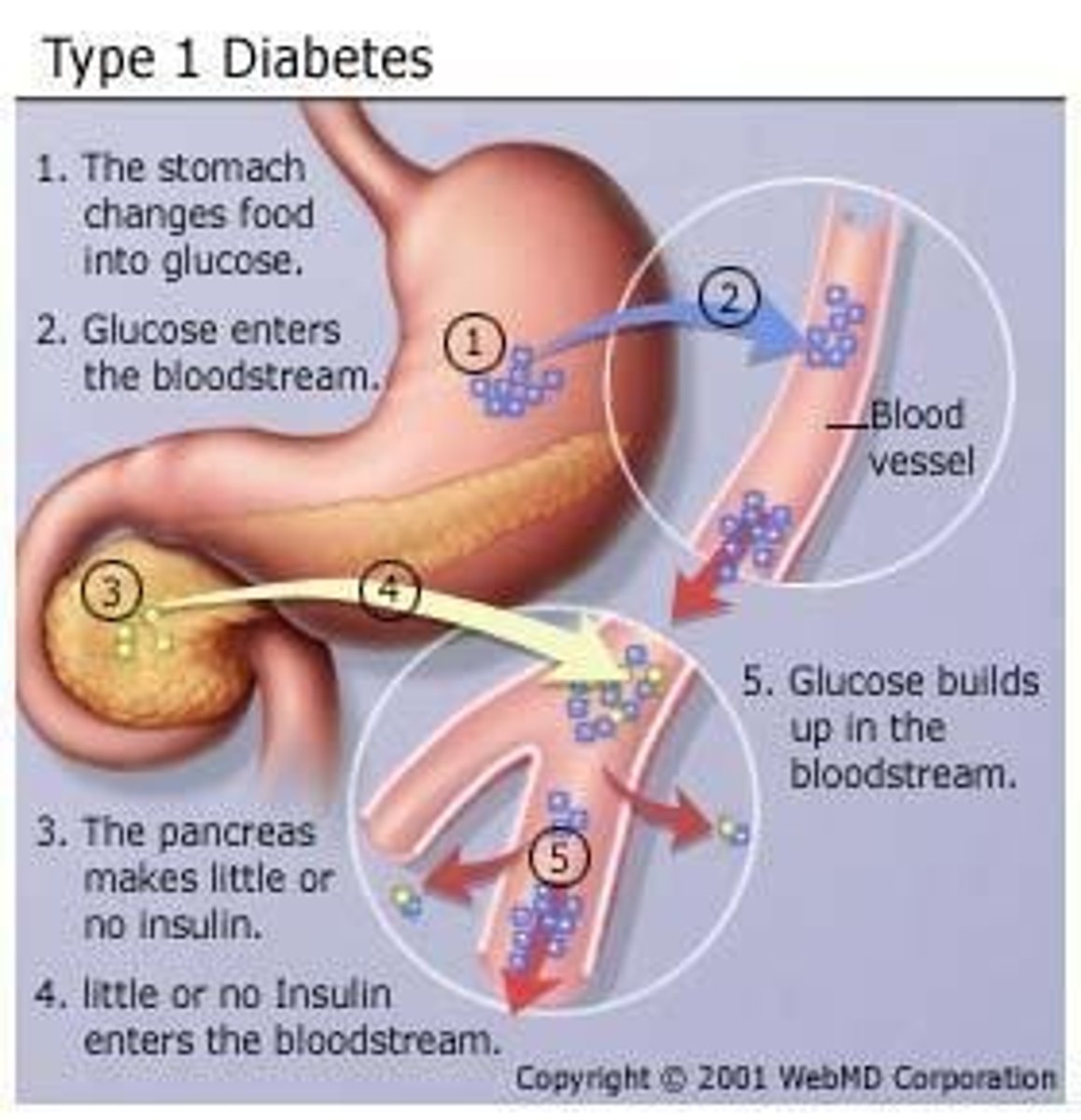
Diabetes
A disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels caused by insufficient insulin or the inability of insulin to function properly.

Type 1 Diabetes
Usually occurs in children, characterized by the inability of sugar to enter cells.
Type 2 Diabetes
Usually occurs in adults, especially those who are overweight, resulting in hyperglycemia and dehydration of cells.
Hyperglycemia
A condition of having high blood sugar levels.
Effects of Sugar on Blood
Excess sugar thickens the blood, causing less flow, which stresses the cardiovascular system and can lead to high blood pressure and blood clots.
Effects of Sugar on Cells
Too much sugar in blood means not enough is reaching cells, leading to fatigue as cells lack energy (ATP).
Isotonic Solutions
Solutions that have the same concentration in blood and cells.
Hypertonic Blood
Blood with a greater concentration of solute compared to cells.
Hypotonic Cells
Cells with a lesser concentration of solute compared to blood.
Osmosis in Diabetes
Osmosis draws water out of cells into the bloodstream, dehydrating cells.
Constant Hunger and Thirst in Diabetes
A symptom of diabetes where hunger and thirst are not properly satiated.
Insulin Function in Diabetes
The development of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes relates to how the body produces and uses insulin.
Endocrine Disorder
Type 2 Diabetes is an endocrine disorder caused by lifestyle habits that make cells reject insulin.
Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune disorder, in which the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas (beta cells). Creates severe insulin deficiency.
Type 2 Diabetes
Not typically treated with insulin—usually treated with lifestyle changes (exercise, limiting carbohydrates, etc.) & oral medications.
Insulin Resistance
Sugar can't get into cells because they've become 'insulin-resistant' & no longer recognize it as the 'key'.
Cardiovascular Problems
Can lead to cardiovascular problems (high blood pressure, heart attacks).
Blindness
Can lead to blindness.
Amputation
Can cause need for amputation of toes or even limbs, due to poor circulation.
Positive Feedback Mechanism
Moves away from homeostasis (target set point) to accomplish a goal.
Negative Feedback Mechanism
Tries to bring the body back to homeostasis.
Examples of Negative Feedback
Temperature, Blood pressure, Blood sugar levels, Erythropoiesis (creation of new red blood cells).
Examples of Positive Feedback
Labor until child is born, Growth until maturity, Blood clotting until clot forms, Menstrual cycle until menstruation.
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. The main goals of HIPAA are: Protect the privacy and security of a patient's health information, Provide for electronic and physical security of a patient's health information, Increase accountability and prevent health care fraud and abuse, Allow patients to decide who health care providers can share their information with.
Electronic Medical Records
Understand the differences between Electronic Medical Records, Protected Health Information, Privileged Communication, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Charlie Nowak
Migraines & Dehydration.
Cassandra Cassa
Type 1 Diabetes.
Kylan Ali
COPD.
Ocie Ryan
Sickle Cell.
Jenny Sanders
Lupus.
Sid Khan
Alzheimer's and Heart Murmur.
Bobby Goldman
Epilepsy.
Nutritionist/Dietitian
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Hematologist
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Phlebotomist
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Medical Student
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Medical Assistant
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Medical Technician
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Patient Liaison
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Primary Care Physician
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.
Pediatrician
Know the responsibilities and job of each career we covered.