Unit 5 Study Guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Last updated 2:07 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
conservation of mass
* matter is neither created nor destroyed.
* during a physical and chemical change, the mass of the product always =’s the mass of the reactants.
* during a physical and chemical change, the mass of the product always =’s the mass of the reactants.
2
New cards
stoichiometry
the calculation of products and reactants in a chemical reaction.
3
New cards
mole ratio
a conversion factor between compounds in a chemical reaction.
4
New cards
Stanisalo Cannizzaro
* italian
* 1826-1910
* Cannizzaro reaction: an organic reaction of an aldehyde without active hydrogen that undergoes a redox reaction under the action of a strong base.
* __1st chemist to see the full significance of avagodro’s law.__
* 1826-1910
* Cannizzaro reaction: an organic reaction of an aldehyde without active hydrogen that undergoes a redox reaction under the action of a strong base.
* __1st chemist to see the full significance of avagodro’s law.__
5
New cards
limiting reactant (reagent)
the reactant that gets consumed first in a chemical reaction and therefore limits how much product can be formed.
6
New cards
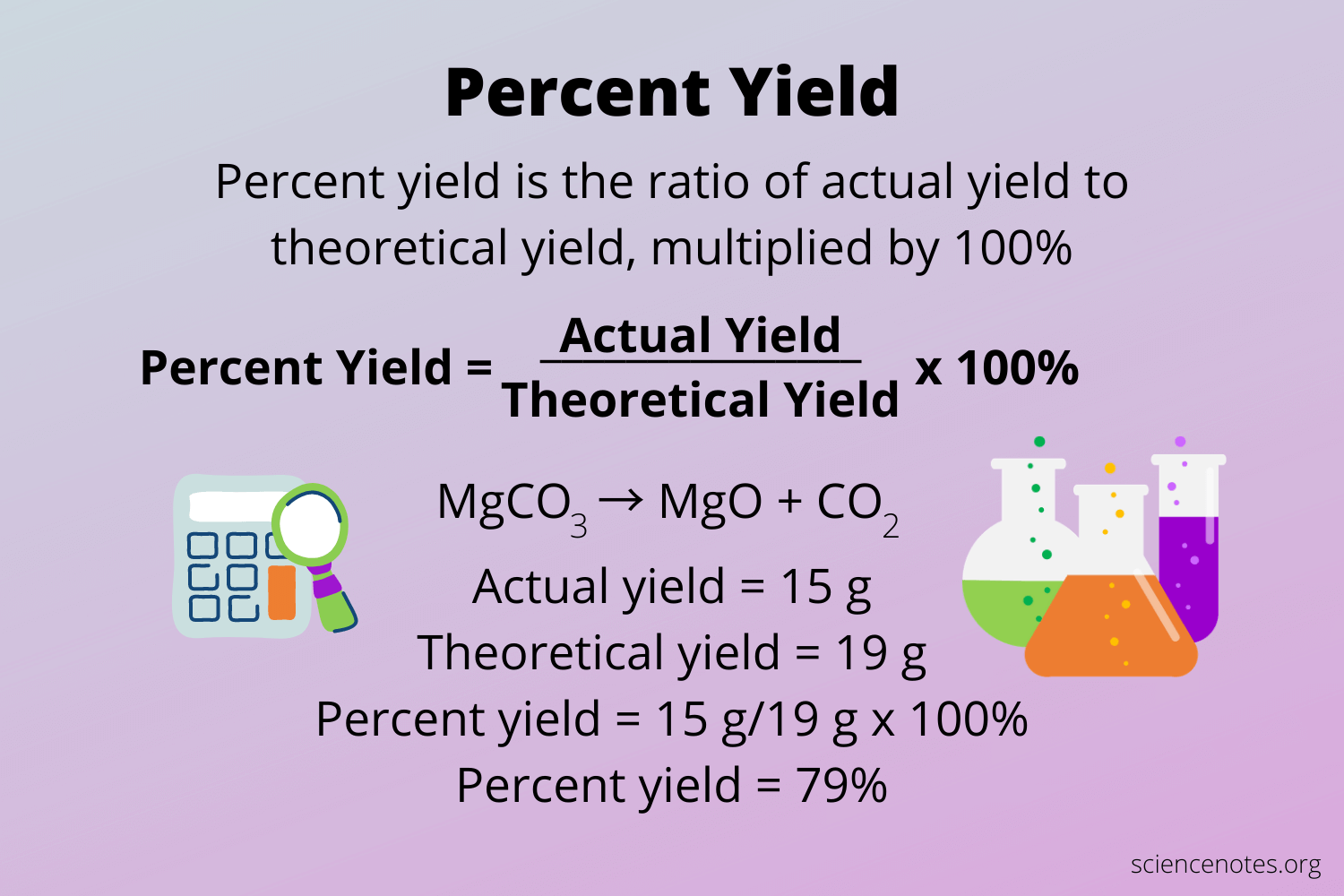
% yield
* measures the effectiveness of a chemical reaction.
* the ratio of the actual yield to the theortical yield multiplied by 100%.
* the ratio of the actual yield to the theortical yield multiplied by 100%.
7
New cards
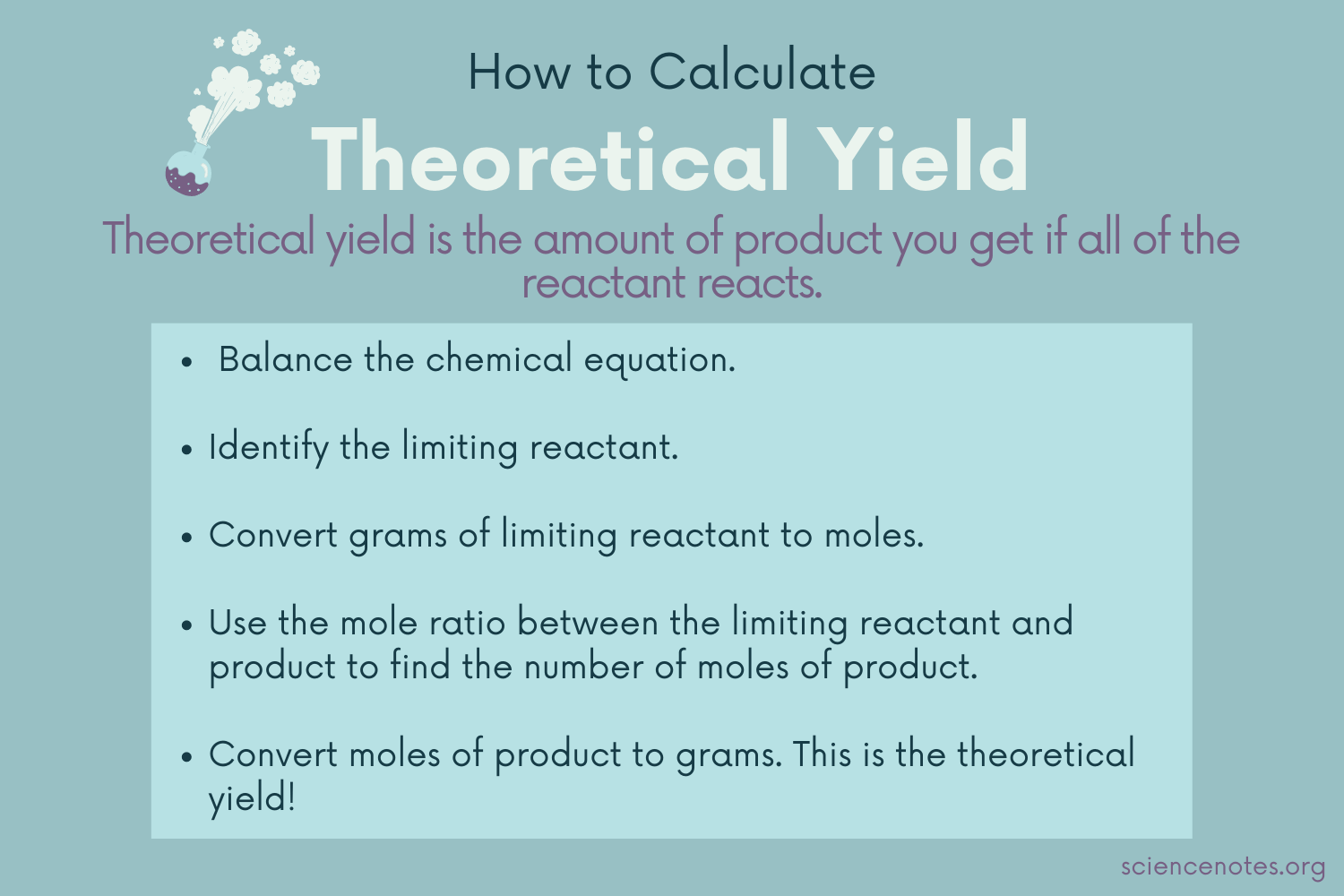
theoretical yield
* obtained using __stoichiometry.__
* the quantity of a product we shld produce from the complete conversion of a given amt of reactant to produce.
* the quantity of a product we shld produce from the complete conversion of a given amt of reactant to produce.
8
New cards
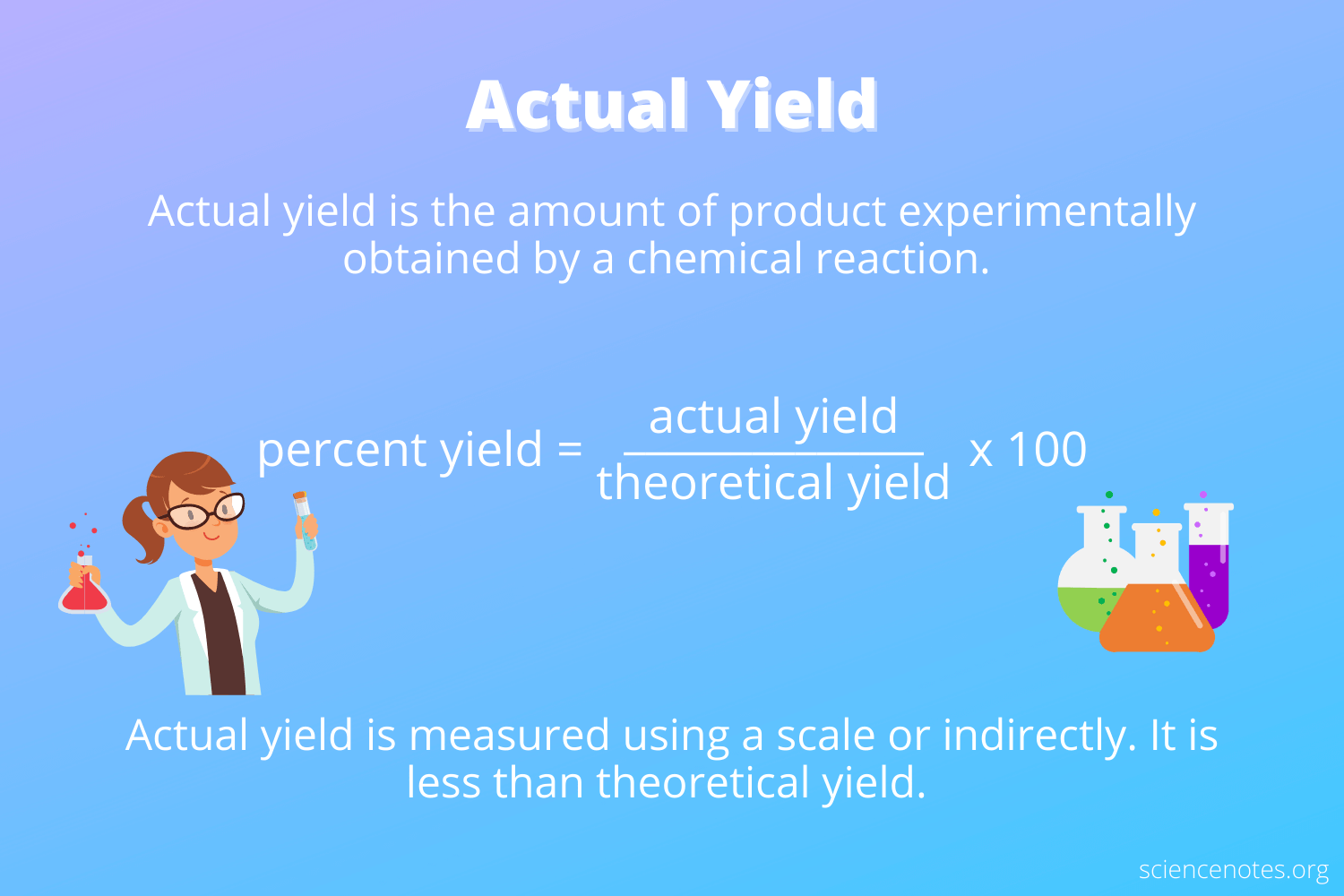
actual yield
the quantity of product actually obtained by __experiment__ from a chemical reaction.
9
New cards
activity series
a list of elements in decreasing order of their reactivity.
10
New cards
Elizabeth Rona
* hungarian chemist
* 1890-1981
* nuclear chemist
* __an expert on isotope seperation and polonium preparation.__
* __confirmed the existance of “uranium-Y.”__
* 1890-1981
* nuclear chemist
* __an expert on isotope seperation and polonium preparation.__
* __confirmed the existance of “uranium-Y.”__
11
New cards
solubility
\n The amount of solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of solvent at a specific temperature
12
New cards
solution
* Homogeneous mixtures
* solute and solvent together
* what occurs when 2 chemicals are mixed.
* solute and solvent together
* what occurs when 2 chemicals are mixed.
13
New cards
saturated solution
* contains max. amt. of solute per volume of solvent.
* shld. not be able to see the solute particles ever.
* additional solute will sink to the bottom and not dissolve
* on line.
* shld. not be able to see the solute particles ever.
* additional solute will sink to the bottom and not dissolve
* on line.
14
New cards
unsaturated solution
* contains less than the max. amt. of solute per given volume of solvent.
* cld contain more solute if you wanted to add it, but will look the same as a saturated solution.
* added solute will dissolve
* below line.
* cld contain more solute if you wanted to add it, but will look the same as a saturated solution.
* added solute will dissolve
* below line.
15
New cards
supersaturated solution
* contains more solute than it shld. for a given set of volume and temp. conditions.
* make it by heating the sample to “cram” in more solute.
* very unstable and can solidify at any moment.
* added solute precipitates out all excess solute and it becomes a solid.
* above line.
* make it by heating the sample to “cram” in more solute.
* very unstable and can solidify at any moment.
* added solute precipitates out all excess solute and it becomes a solid.
* above line.
16
New cards
precipitate
* a solid formed by a change in a solution often due to a chemical reaction or chane in temp. that decreases solubility of a solid.
* holland def: when a substance undergoes a phase change in a solution (gas → liquid or liquid → solid) (rain, snow)
* holland def: when a substance undergoes a phase change in a solution (gas → liquid or liquid → solid) (rain, snow)
17
New cards
diatomics
* H2 (hyrogen)
* O2 (oxygen)
* N2 (nitrogen)
* Halogens
* O2 (oxygen)
* N2 (nitrogen)
* Halogens
18
New cards
\+
separates more than 1 reactant or product.
19
New cards
→
* separates reactants from products.
* indicates direction of reaction.
* indicates direction of reaction.
20
New cards
(s)
identifies as solid state.
21
New cards
(aq)
* aqueous
* identifies that something is dissolved in water.
* identifies that something is dissolved in water.
22
New cards
(L)
identifies liquid state.
23
New cards
(g)
* identifies gaseous state.
* diatomics are (g)
* diatomics are (g)
24
New cards
synthesis
* a + b → ab
* the compound produced is larger and more complex than the reactants.
* the compound produced is larger and more complex than the reactants.
25
New cards
decomposition
* ab → a + b
* the breakdown of a larger compound.
* the breakdown of a larger compound.
26
New cards
single replacement
ax + b → bx + a
27
New cards
double replacement
* ax + by → ay + bx
* inner replaces inner / outer replaces outer
* always involves the formation of a molecular compound like water and either a precipitate or a gas.
* inner replaces inner / outer replaces outer
* always involves the formation of a molecular compound like water and either a precipitate or a gas.
28
New cards
combustion
* Cx + Hy (O2) → CO2 + H2O
* occurs when something is burning.
* 1st reactant is always a compound containing carbon and hydrogen (and sometimes oxygen).
* 2nd reactant = oxygen
* always produces H2O and CO2
* occurs when something is burning.
* 1st reactant is always a compound containing carbon and hydrogen (and sometimes oxygen).
* 2nd reactant = oxygen
* always produces H2O and CO2
29
New cards
molarity
* “m”
* concentration in # of moles of solute, for a liter of solution.
* the scientists’ way of saying the concentration of a solution is or how much of something is dissolved into something else.
* moles/liters
* concentration in # of moles of solute, for a liter of solution.
* the scientists’ way of saying the concentration of a solution is or how much of something is dissolved into something else.
* moles/liters
30
New cards
1000 mL = ? L
1 L
31
New cards
1 L = ? mL
1000 mL
32
New cards
solute
substance that is dissolved
33
New cards
solvent
substance that dissolves solute.fsolub
34
New cards
3 factors that affect the rate something dissolves:
1. increasing temp.
2. stirring (agitation)
3. crushing (smaller particle size)
35
New cards
miscible
used to describe a mizture of soluble liquids.
36
New cards
immiscible
used to describe 2 liquids that don’t dissolve into each other.