Principles of Human Anatomy: Unit 1 - Cytology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Cells
the most basic structural and functional unit of the human body
What biomolecules make up a cell?
nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
Plasma membrane
divides the intracellular matrix from the extracellular matrix and controls what goes in and out of cell
made up of a lipid bilayer (phospholipids) and proteins
bilayer
hydrophilic, polar heads and hydrophobic non polar tails
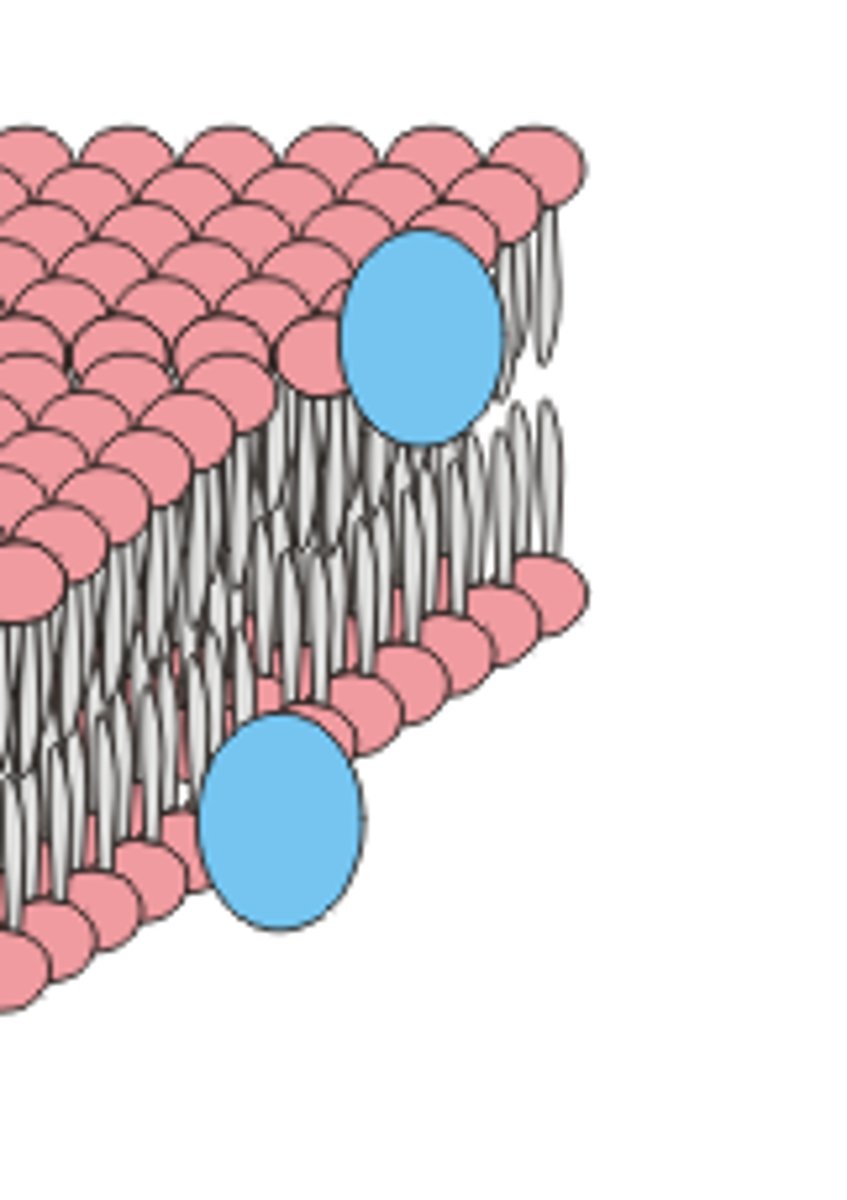
peripheral protein
A protein embedded on surface of a membrane -> either on intracellular matrix side or extracellular matrix side (not both)
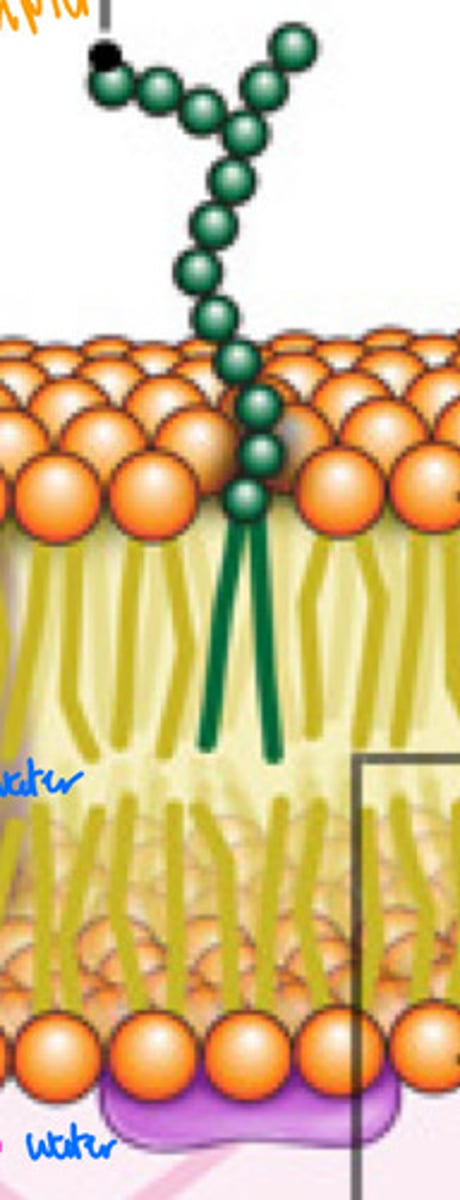
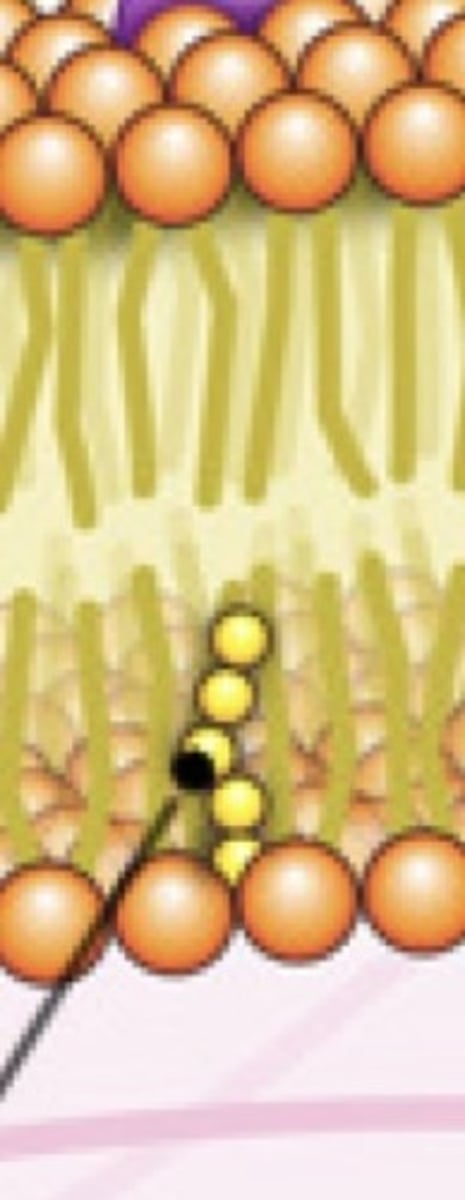
Glycolipid
Carb/sugar attached to a lipid (part of phospholipid)
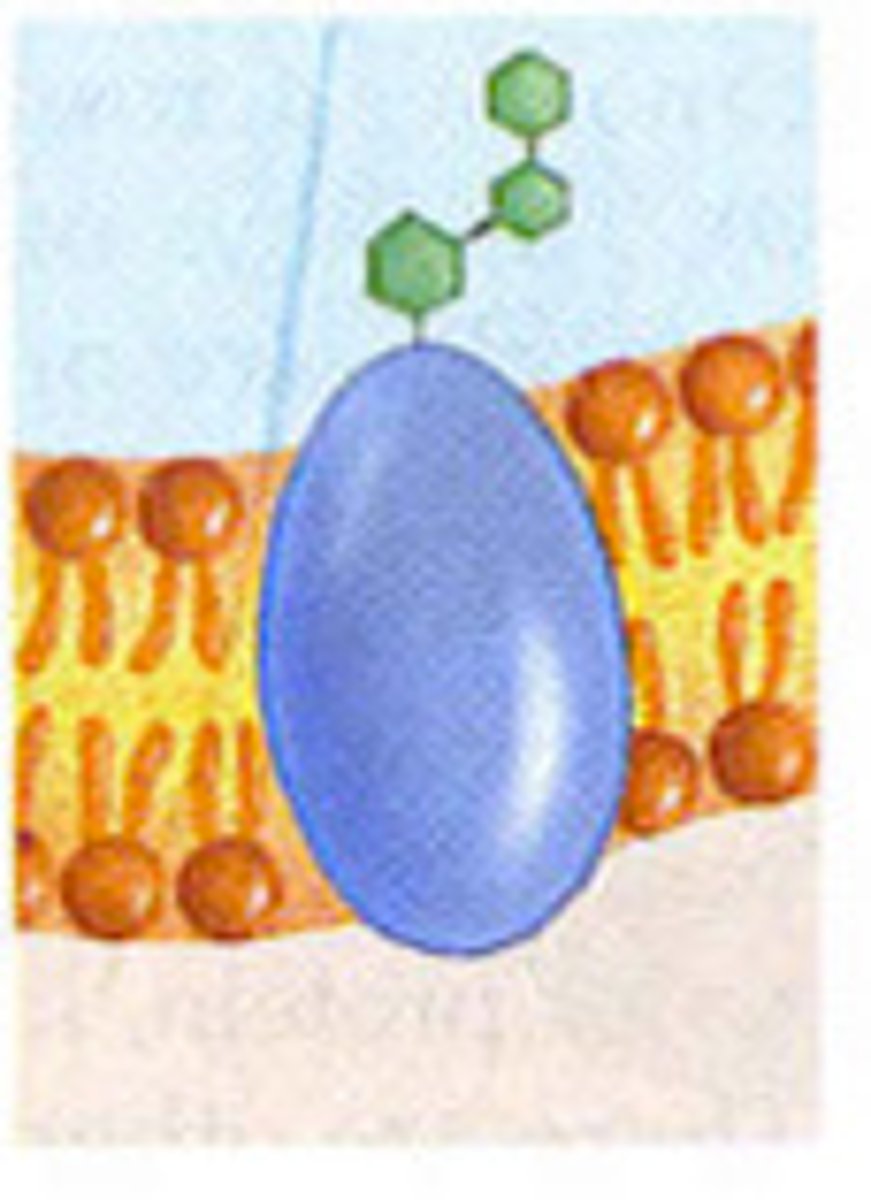
glycoprotein
carb attached to a protein
transmembrane protein
spans the entire membrane, touching the ECM and ICM
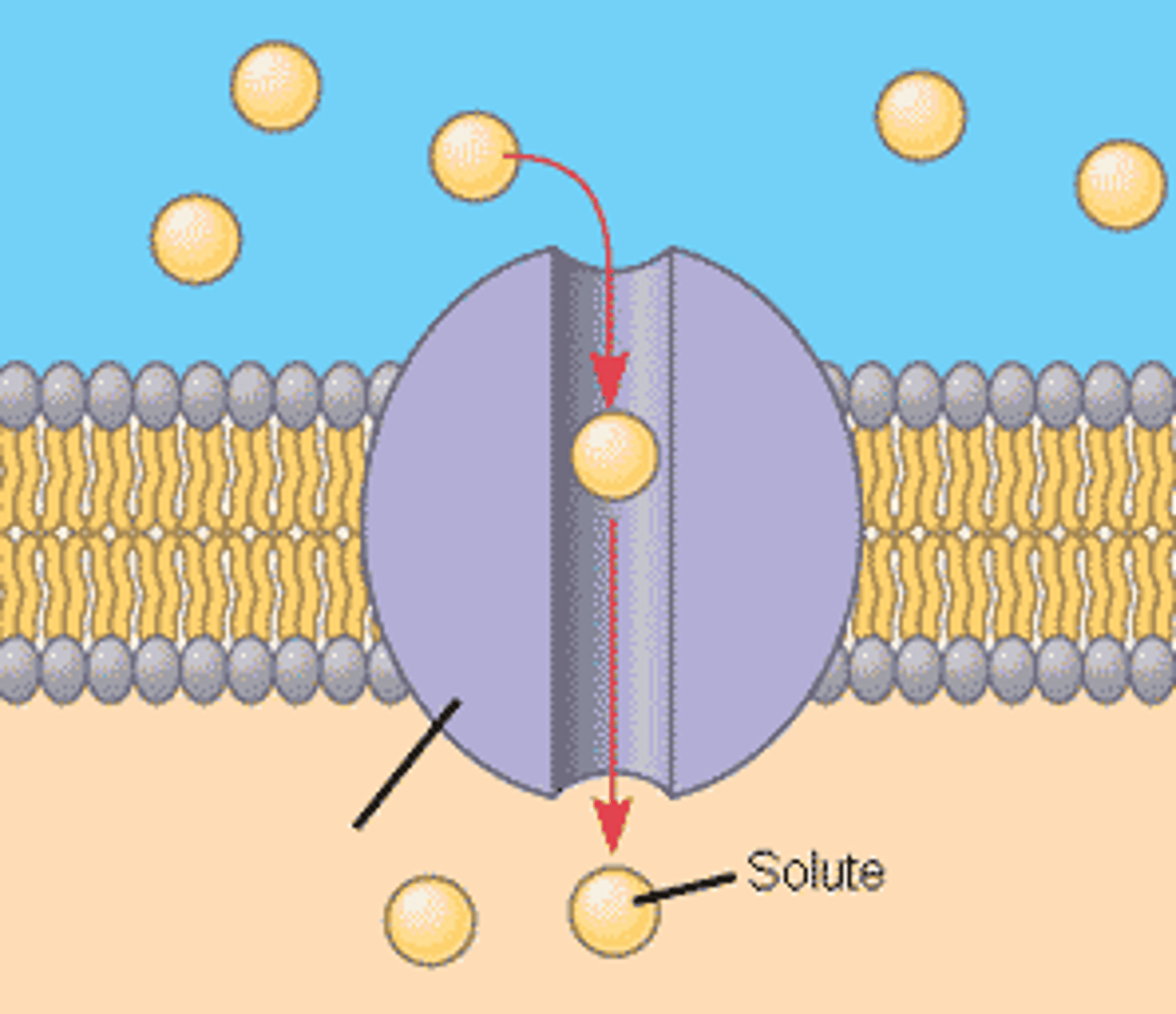
channel protein
a protein that is always open and allows any solute molecule to pass into and out of the cell
cholesterol
regulates membrane fluidity

Glycoprotein
sugar attached to protein (on protein)
Glycocalyx
The external, sugary surface of a plasma membrane that is important for cell-to-cell communication, allowing cells to recognize other cells and decide if other cells are friends or pho
made of glycolipids and glycoproteins
receptor protein function
binds to chemical messengers such as hormones sent by other cells
enzyme protein function
breaks down a chemical messenger and terminates its effect on the target cell
gated channel protein function
channel that opens and closes to allow solutes through only at certain times
cell-identity marker protein function
a glycoprotein acting as a cell-identity marker distinguishing the body's own cells from foreign cells
cell-adhesion molecule
a CAM protein in membrane that binds one cell to another
intracellular matrix (ICM) consists of
cytoplasm (organelles and cytosol)
extracellular matrix
space between cells consisting of fibrous and non-fibrous proteins, organic molecules, and fluid
nucleus
control center of the cell, contains instructions for cell tasks, houses DNA
Golgi apparatus
sorts and packages proteins into vesicles to be delivered in and out of the cell (post office)
centriole
organelle that aids in cell division
ribosomes
produce proteins, some float in the cytoplasm, others attach to rough ER
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes proteins, folds them, and checks their quality. Also functions in transport of proteins within the cytoplasm
Smooth ER
makes lipids and chemically detoxifies
lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes that eat old organelles and cell waste
cytoskeleton
network of fibers that make up the framework of the cell, it helps regulate cell shape
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
Hemidesmosome
attaches cell to basement membrane
desmosome
attaches cell to cell and provides elasticity
tight junction
attaches cell to cell and prevents paracellular diffusion (nothing gets through)
gap junction
attaches cell to cell and establishes a pathway for rapid communication
cell differentation
the development of a more specialized form and function of cell (no cells are the same shape/size or have the same function) NOT COMPOSITE
cell differentation determined by
gene expression (found in nucleus)... different genes are "turned on"
histone
protein that DNA strands wrap around to fit in nucleus
nucleosome (DNA wrapped around a histone)
gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that provides instructions for making a specific protein... controls characteristics and function of cells
protein production
transcription (occurs in nucleus), translation (occurs on ribosomes), and exocytosis (out of cell)
transcription
the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA and leaves nucleus via nuclear pores (occurs in nucleus)
translation
the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein (occurs in a ribosome in the cytoplasm)
exocytosis
process of secretion from the cell through a vesicle
fates of proteins
packaged into lysosome as an enzyme
incorporated into plasma membrane as a membrane protein
exported out of cell by exocytosis to run through blood stream and fine receptor to elicit response in body
cellular permeability
how easy it is for substance to move across cell membrane
filtration
relies on pressure (particles move from high to low)
simple diffusion
move from high to low solute concentration
facilitated diffusion
substance/particle binds on one end of protein causing a change in configuration to channel
active transport
particles move against concentration gradient using ATP and protein pumps
metabolism
what a cell does
catabolic- break down particles
anabolic- build up products
Interphase
Where a cell spends most of its life
G1- growth, normal processes
G1 checkpoint- checks cell size and determines if it’s healthy for division
S Phase- DNA replication
G2- more growth, cells function
G2 checkpoint- ensures DNA was properly replicated
G0- cell leaves cell cycle to differentiate
Prophase
chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks down, spindle fibers grow from centrioles, centrioles migrate to opposite poles
Metaphase
chromosomes align in middle of cell
m checkpoint
checking to make sure cell is properly aligned in center of cell and ready to divide
Anaphase
spindle fibers pull apart sister chromatids

Telophase
chromosomes settle in opposite poles and decondense, nuclear envelope reappears
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm and organelles
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
uncontrolled cell division
start and stop signals fail resulting in improper cell division and a neoplasm
benign= mass of cells that stays in one place (non cancerous)
malignant= moves and spreads (metastatic) (cancerous)