Mechanical Waves: Types and Properties
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Waves
A vibration or oscillation that transfers energy.
Mechanical Waves
Wave motion that requires a medium (ie, water, sound, slinkie).
Transverse Waves
The vibration of the individual particles of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation; the Medium is displaced perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
Longitudinal Waves
The vibration of the individual particles is parallel to the direction of wave propagation; the medium is displaced parallel to the direction of the wave.
Surface Waves
The medium is displaced perpendicular and parallel to the direction of the wave.
Electromagnetic Waves
No medium is needed (light, radio waves, X-rays).
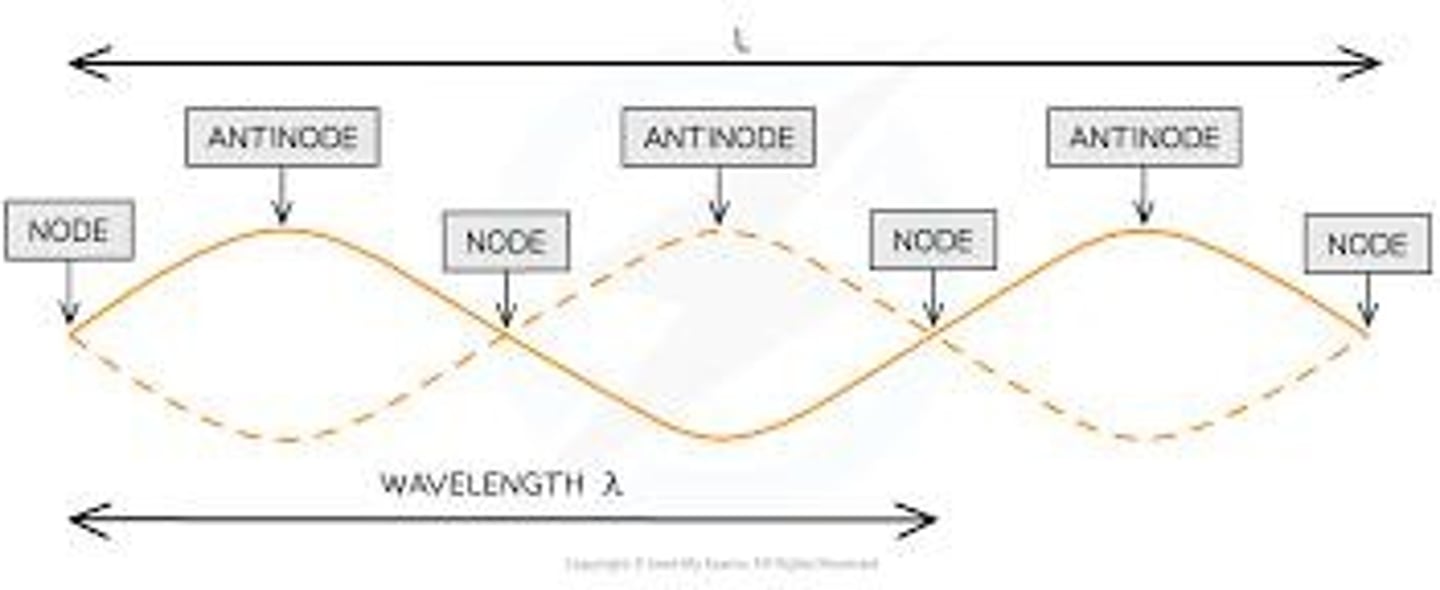
Standing Wave
when two identical waves (same frequency, wavelength, and amplitude) travel in opposite directions and interfere with each other in the same medium.
Pulse
A pulse in the wave is like a single burst of energy - a one-time disturbance that travels through a medium.
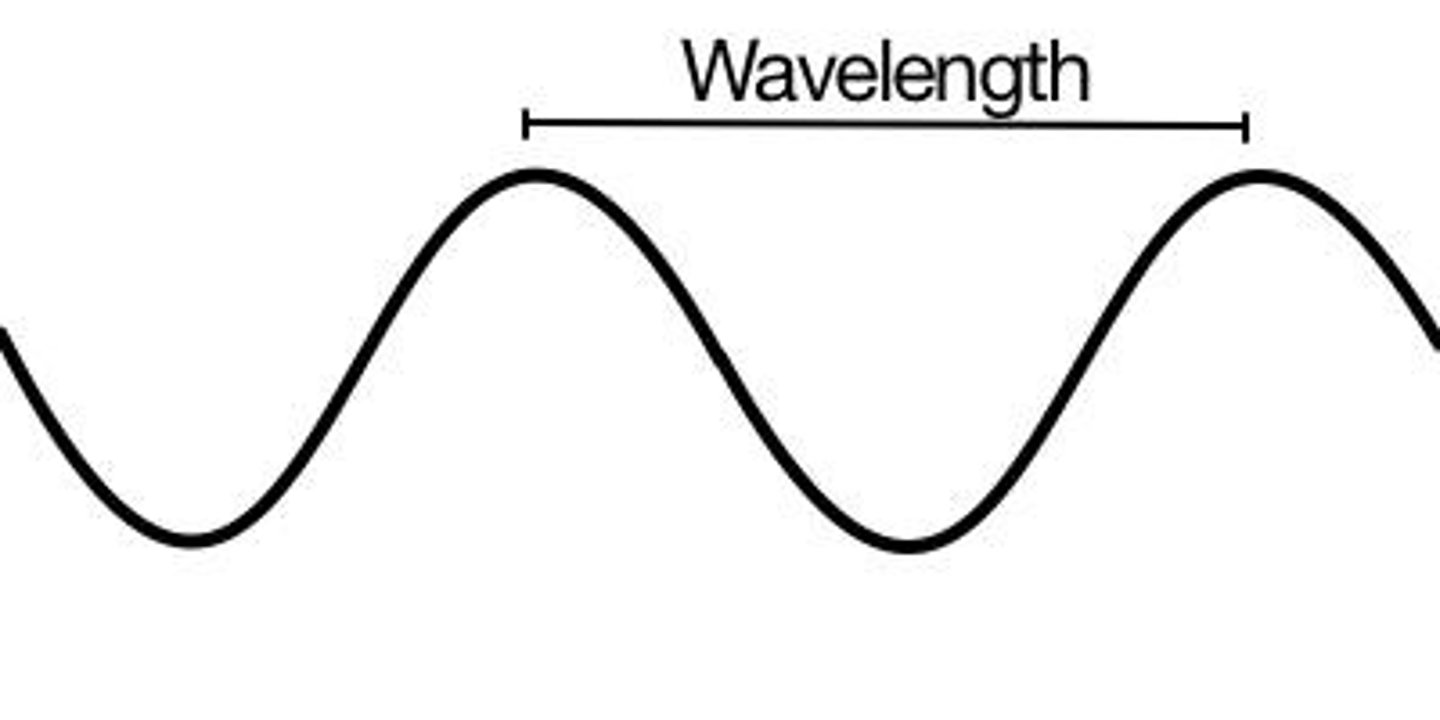
Wavelength
The shortest distance between points of a wave - where the wave patterns repeat themselves.
Node
A point of no displacement resulting from the meeting of a crest with a trough; this form of interference is known as destructive interference.
Antinode
Positions along the medium that undergo maximum displacement from a high upward displacement to a high downward displacement.
Law/Principle of Superposition
When two or more waves exist in the same medium, each wave moves as though the other were absent.
Interference
The result of superposition.
Diffraction
The bending of waves around a barrier; the effects of diffraction get less obvious as the gap gets larger.
Refraction
The bending of light (or any wave) as it passes from one medium into another, causing it to change direction.
Normal
An imaginary line that is perpendicular to the surface at the point where a wave (like light) hits that surface/boundary.
Speed of a Wave
Determined by properties of the medium and the type of wave (mechanical wave or electromagnetic wave).
Frequency
Does not change from one medium to another.
Energy
Does not change from one medium to another.
Wavelength (Change)
Changes when passing from one medium to another.
Amplitude
In incomplete interference, amplitudes change meaning they don't fully increase or decrease.
Crest
The highest point of a wave.
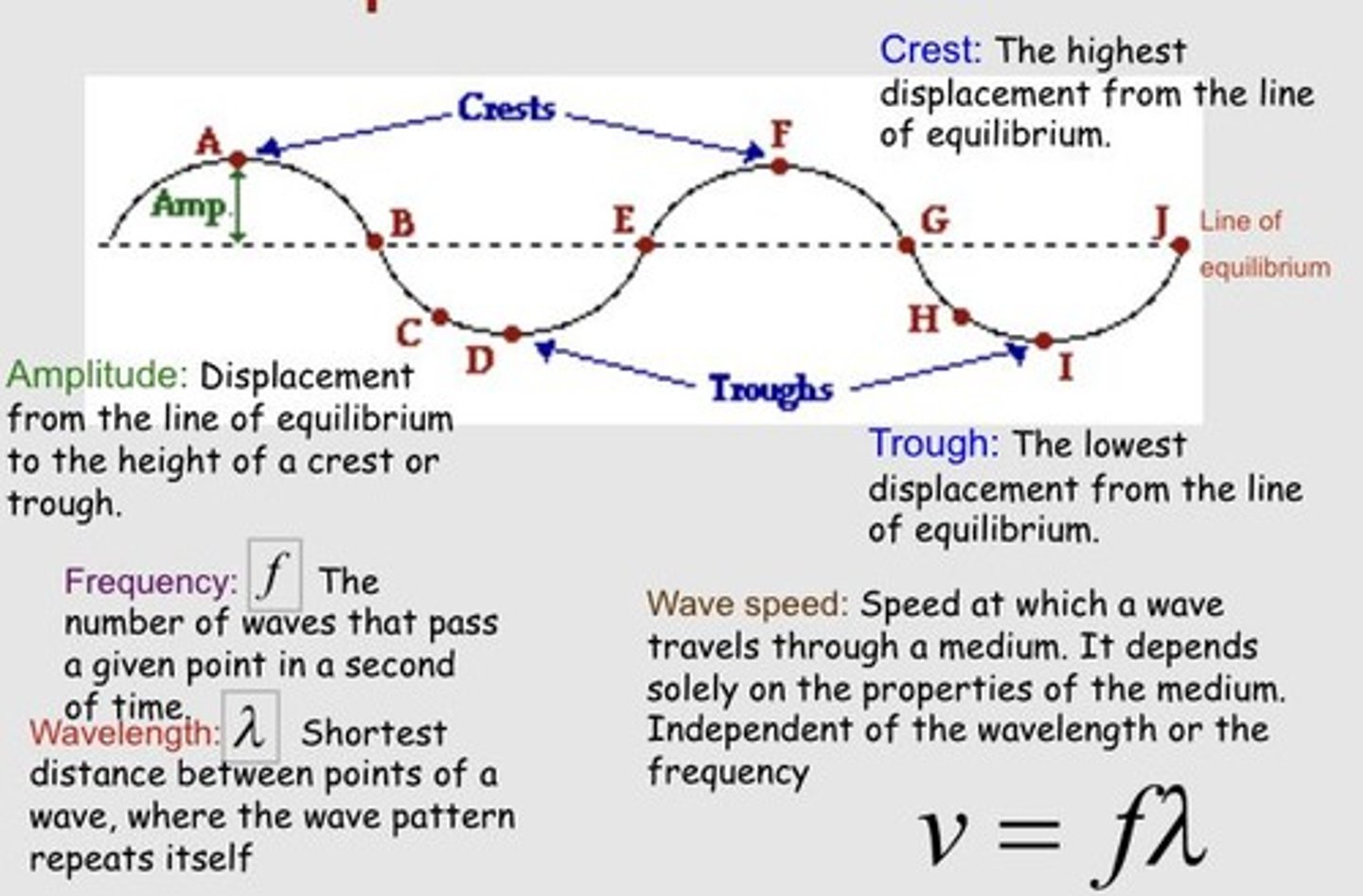
Trough
The lowest point of a wave.
Supercrest
A result of a crest meeting a crest.
Supertrough
A result of a trough meeting a trough.
mechanical
_____ waves require a material medium for energy transfer
transversal
A(n) _____ wave causes the particles of the medium to vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travelling
electromagnetic
______ waves need no medium for travel
pulse
A(n) _____ is a single disturbance traveling through a medium
frequency
The _______ of a wave is the number of waves that pass a given point per second
period
The ______ of a wave is the reciprocal of its frequency, as well as The time needed for an object to complete one full cycle of simple harmonic motion
wavelength
The _______ of a wave is the linear distance between any two corresponding points on consecutive waves
amplitude
The energy content of a mechanical wave is characterized by _____
interference
_____ occurs when more than one wave moves through the same medium at the same time
speed
The ________ of a mechanical wave depends on the medium
frequency
When waves pass from one medium into another, their _____ remains unchanged
standing
A(n) _____ wave is produced when a wave train moving direction meets an identical wave train moving in the opposite direction
node
Two pulses with identical shapes but opposite displacements move toward each other in a medium. The point in the medium that is not displaced is a(n) _____
refraction
_______ is the direction change of waves at the boundary between different medie
diffraction
______ is the bending of a wave around an obstacle
normal
The _______ is a line perpendicular to a barrier at the point where an incident ray strikes the barrier
incidence
When a wave is reflected from a barrier, the angle of _____ equals the angle of reflection
energy
Waves provide a means of transferring ______
small
If the amplitude of the reflected pulse is ______ when a wave passes from one medium to another, most of the energy has been transmitted
frequency
When waves refract, the waves do not change ____
medium
A mechanical wave is different from other types of waves because it requires a(n) ____
longitudinal
Sound waves are ____ waves
both transverse and longitudinal waves
A surface wave is a wave that has characteristics of ____