ANS 151 practical 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:49 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
still nursing its mother
calf
2
New cards
an animal that is a year old
yearling –
3
New cards
name: Glove and Semen collection vessel
function: collecting semen from boar for breeding (AI)
Species : Swine
function: collecting semen from boar for breeding (AI)
Species : Swine
\

4
New cards
Species: Swine
Function: AI
Hard Spiral AI Catheter
Function: AI
Hard Spiral AI Catheter

5
New cards
Species: Swine
Function: AI
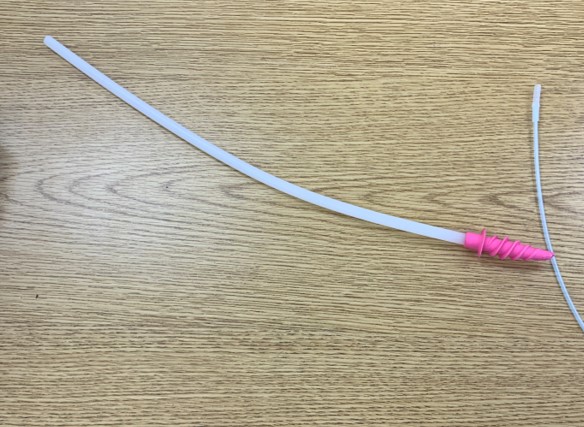
Soft Spiral AI Catheter
Function: AI
Soft Spiral AI Catheter

6
New cards
Species: Swine
Function : AI
Single Piece Post Cervical AI Catheter
Function : AI
Single Piece Post Cervical AI Catheter

7
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Artificial Insemination
Double Piece Post Cervical AI Catheter

8
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Artificial Insemination
Foam Tip AI Catheter (Golden Pig)
\
**Function:** Artificial Insemination
Foam Tip AI Catheter (Golden Pig)
\

9
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Assisting during parturition
Palpation Sleeve

10
New cards
Species: Swine
Function": Storage of semen for AI
Semen Bottle
Function": Storage of semen for AI
Semen Bottle

11
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Storage of semen for Artificial insemination
Semen Tube

12
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Storage of semen for Artificial insemination
Cochette

13
New cards
**Species:** Swine
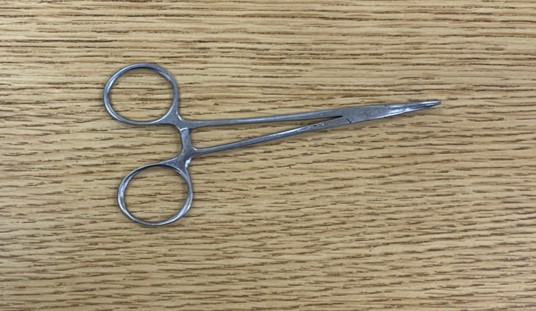
**Function:** Fixing ruptures
Hemostatic forceps
14
New cards

Species: Swine
Function: Permanent Identification
Ear Notcher
Function: Permanent Identification
Ear Notcher

15
New cards
Speckies : Swine
Function: Castration
Side Cutting Pliers
Function: Castration
Side Cutting Pliers

16
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Cutting needle teeth
Needle Teeth Pliers

17
New cards
Speckies: Swine
Function : keep pre-weaned piglets warm
Heat Lamp
Function : keep pre-weaned piglets warm
Heat Lamp

18
New cards
S: Swine
F: treatment of rectal prolapse
Prolapse Retainer
F: treatment of rectal prolapse
Prolapse Retainer

19
New cards
swine
what species is infrared thermometer used on aka no contact
20
New cards
Air flow Meter
Swine
Ventilation monitoring
Swine
Ventilation monitoring
\

21
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Administration of multiple doses and injections of medication
Multiple Injection Multi Dose Syringe

22
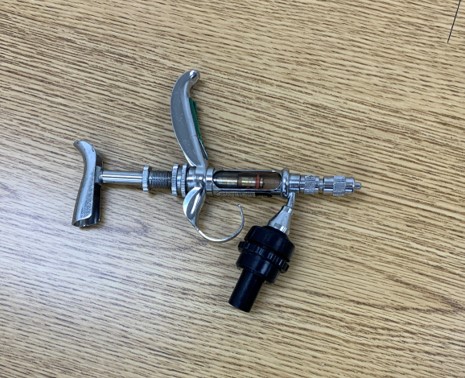
New cards
**Species:** Swine
**Function:** Administration of multiple doses and injections of medication
Single Injection Multi Dose Syringe
23
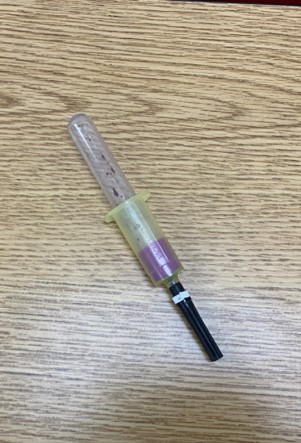
New cards
S: Swine
F: Blood Collection
Blood Sampling
F: Blood Collection
Blood Sampling
24
New cards
Pietran
What swine breed?
pink w black spots
pink w black spots

25
New cards
Hampshire
breed?
all black except 1 pale pink strip on front leg
all black except 1 pale pink strip on front leg

26
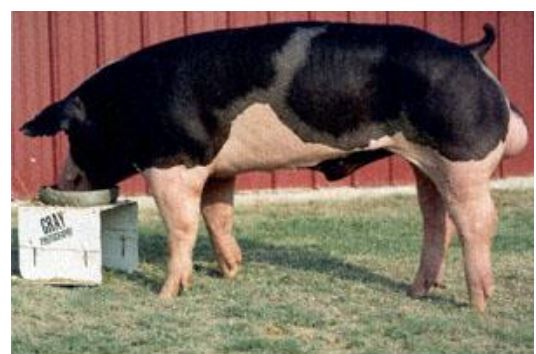
New cards
Spot
breed?
top half black and bottom pale pink
top half black and bottom pale pink
27
New cards
Berkshire
breed?
all black except feet n snout which are white
all black except feet n snout which are white

28
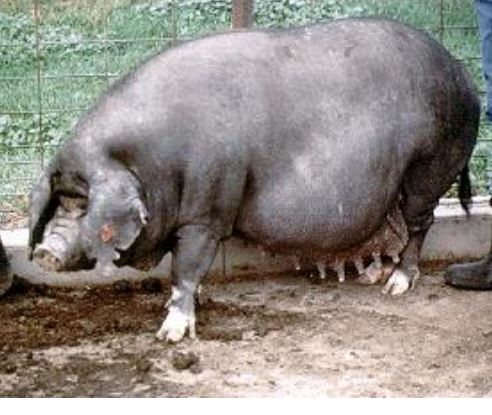
New cards
Meishan
breed?
\-very wrinkly, big, gray
\-very wrinkly, big, gray

29
New cards
Yorkshire
breed?
pinkish white and furry all over
pinkish white and furry all over

30
New cards
landrace (pretty sure its the pigs nc state has)
breed?
all pink look hairless
all pink look hairless

31
New cards
Duroc
breed?
mostly dark brown all over
mostly dark brown all over

32
New cards
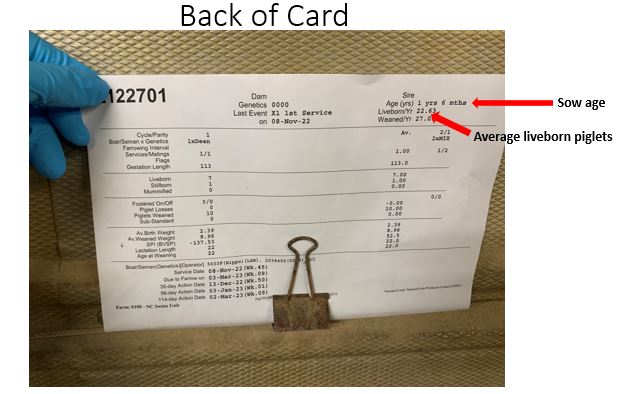

33
New cards
weight / days since born
Grades are below:
* Piglets more than 0.75 lbs per day of age = excellent
* Piglets between 0.50 and 0.74 = good
* piglets less than 0.50 = at risk ( not growing well after weaning)
Grades are below:
* Piglets more than 0.75 lbs per day of age = excellent
* Piglets between 0.50 and 0.74 = good
* piglets less than 0.50 = at risk ( not growing well after weaning)
How to calculate weight per day of age and understand if the pig is good/marginal/bad to be weaned
34
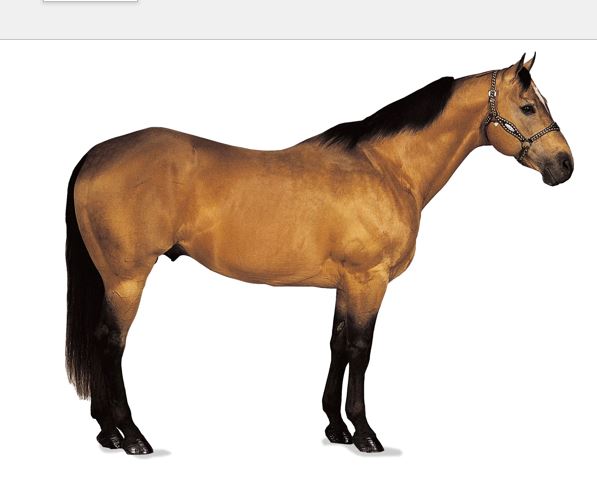
New cards
Quarter Horse
breed?

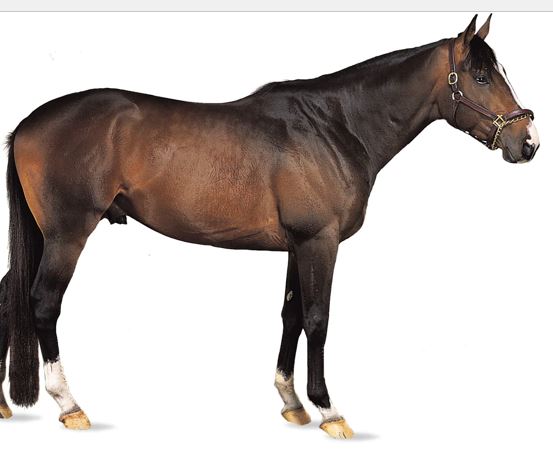
35
New cards
Thoroughbred
breed?

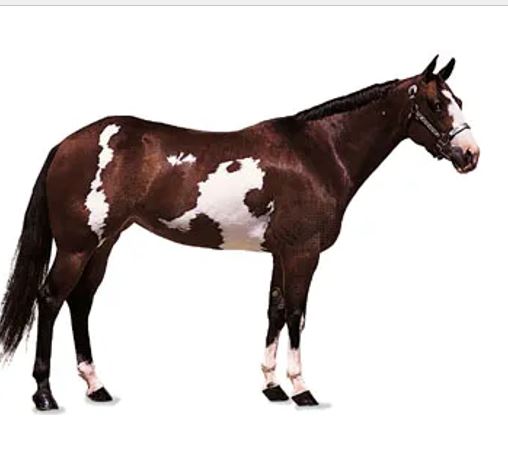
36
New cards
paint horse
breed

37
New cards
draft horse
hairy hoofs/feet
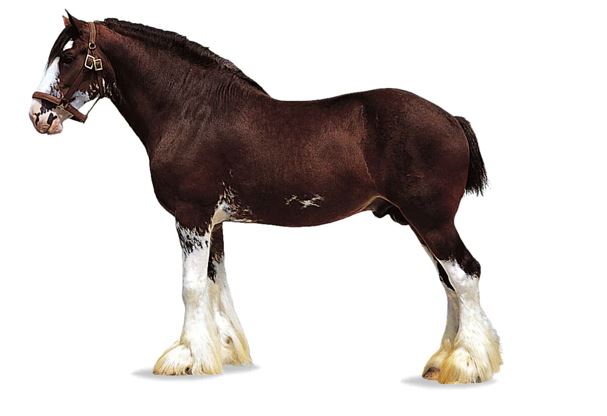

38
New cards
shetland pony
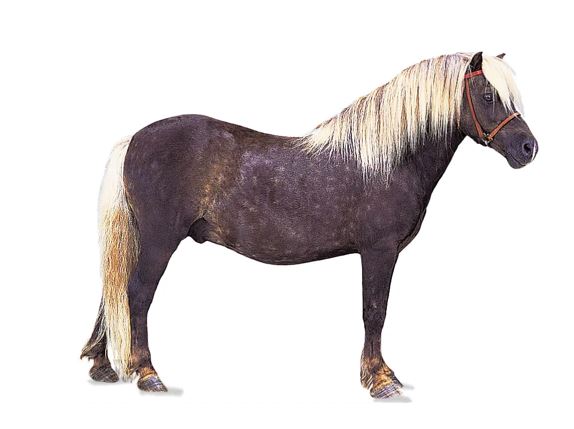

39
New cards
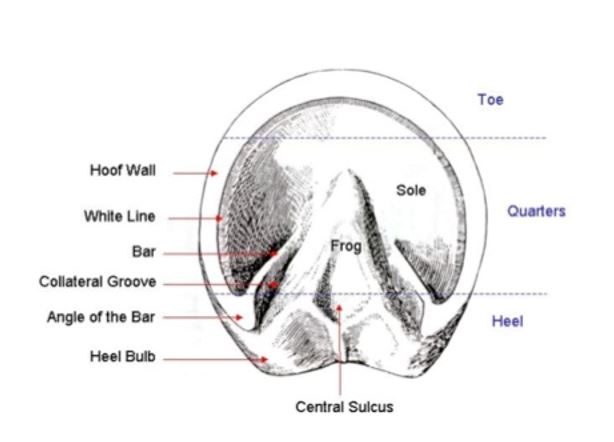
Parts of hoof
40
New cards
Horses prefer to run from danger. However, if flight is not an option, horses will fight to protect themselves from a perceived danger
1. What does the phrase fight or flight mean in relation to equine behavior?
41
New cards
from the left side at the shoulder
how to approach a horse?
42
New cards
Approaching from the front or back puts one at risk of being kicked or harmed. The horse cannot see directly in front or behind.
1. Why do we not approach the horse from directly in front or behind?
43
New cards
Safety is the #1 priority and understanding how and why horses (prey animals) respond to danger is essential as a handler
1. Why would all of the above matter in relation to equine behavior and handler safety?
44
New cards
Not too loose, not too tight. Horses have thin bone that turns to cartilage on their muzzle, so the nosepiece needs to sit comfortably on the muzzle. The chin strap should also be loose enough to provide comfort to the animal
1. Demo putting a halter on. What are some ways we can tell a halter fits properly?
45
New cards
To prevent lameness (usually in the form of abcesses)
Why should you pick a horse’s feet regularly?
46
New cards
Abscess and white line disease
What are two common problems seen in a hoof?
47
New cards
4 to 6 months is ideal
1. How often should an average horse be trimmed by a farrier?
48
New cards
Boer (goat)
breed?
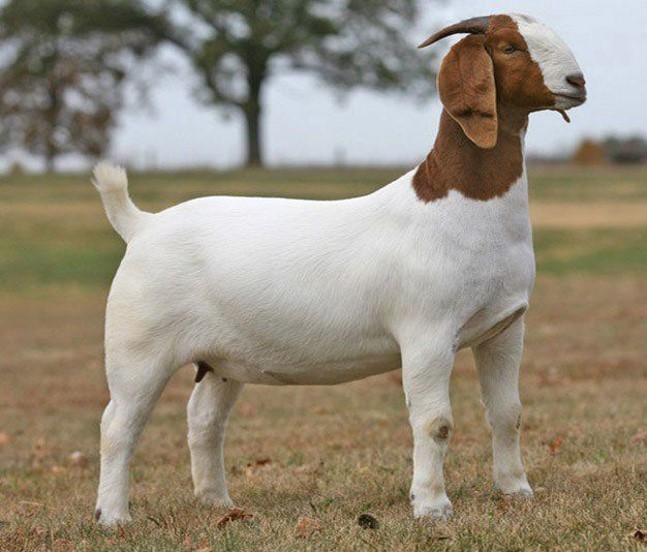

49
New cards
kiko (goat)
breed?
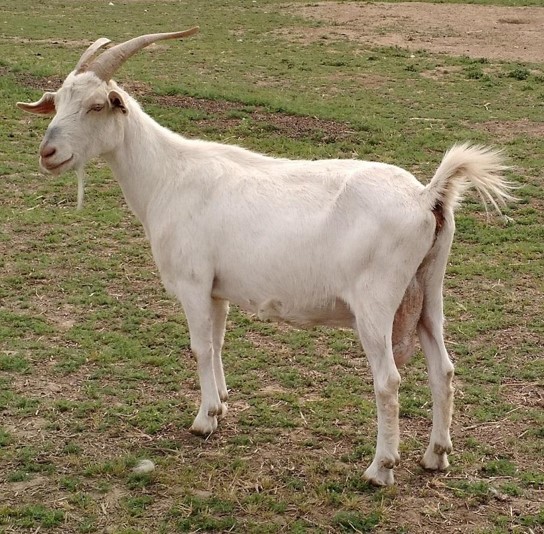

50
New cards
* polled dorset (sheep)
* founded by NCSU
\
* founded by NCSU
\
breed?
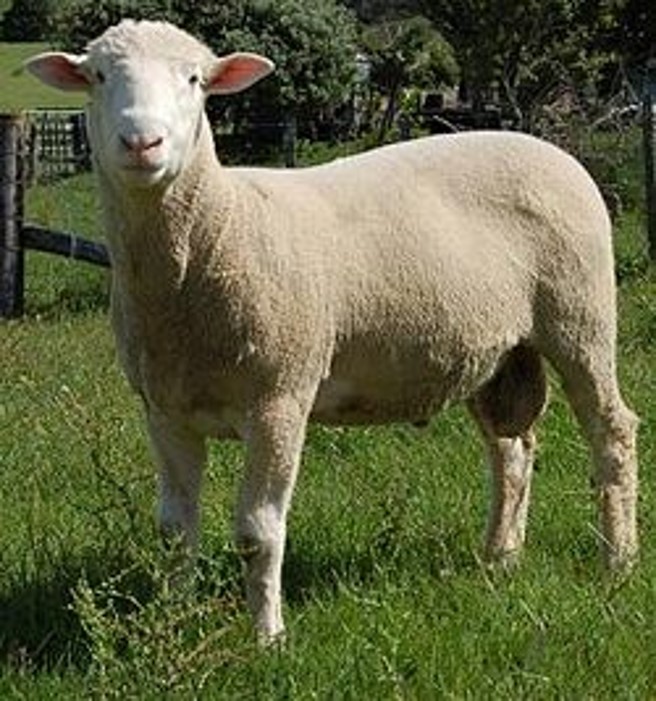

51
New cards
katahadin (sheep)
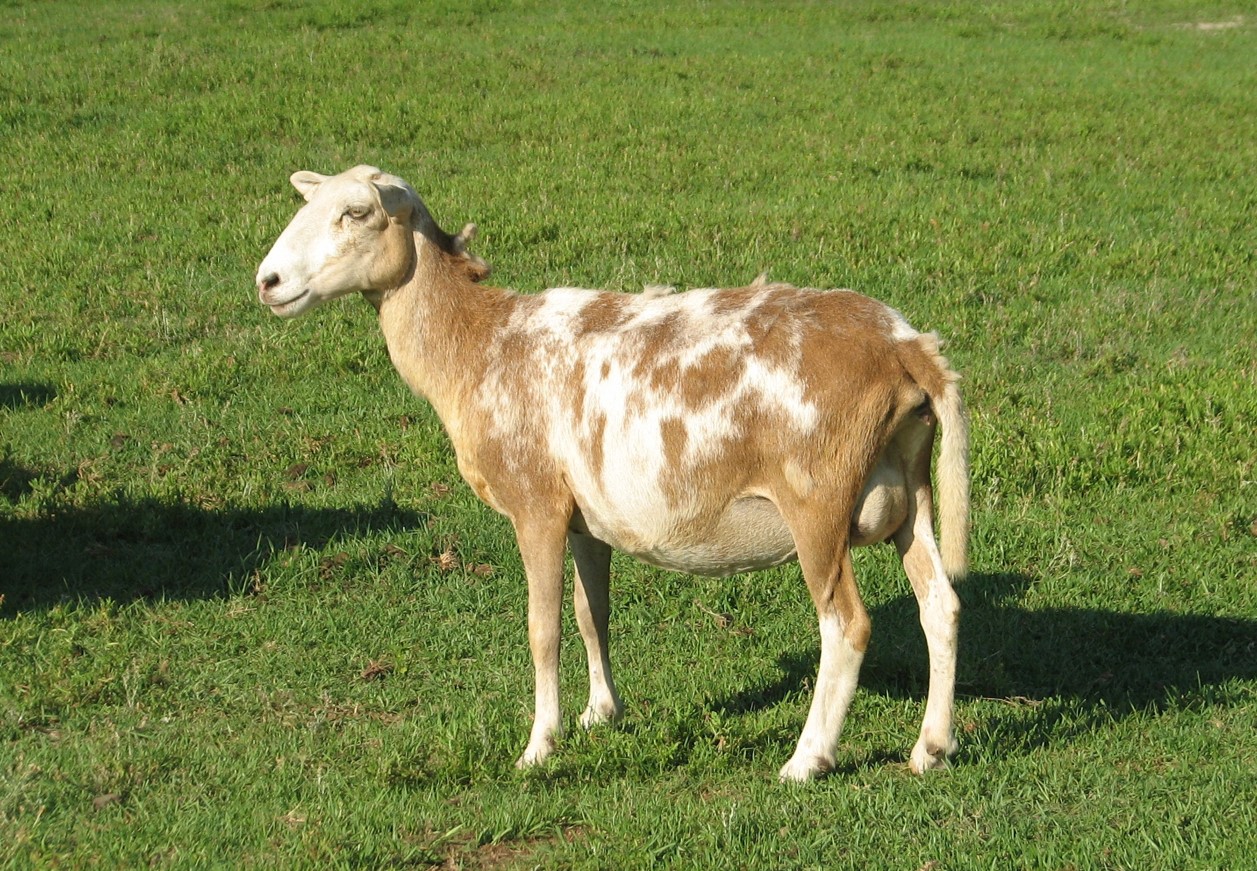

52
New cards
(sheep)hampshire
breed?
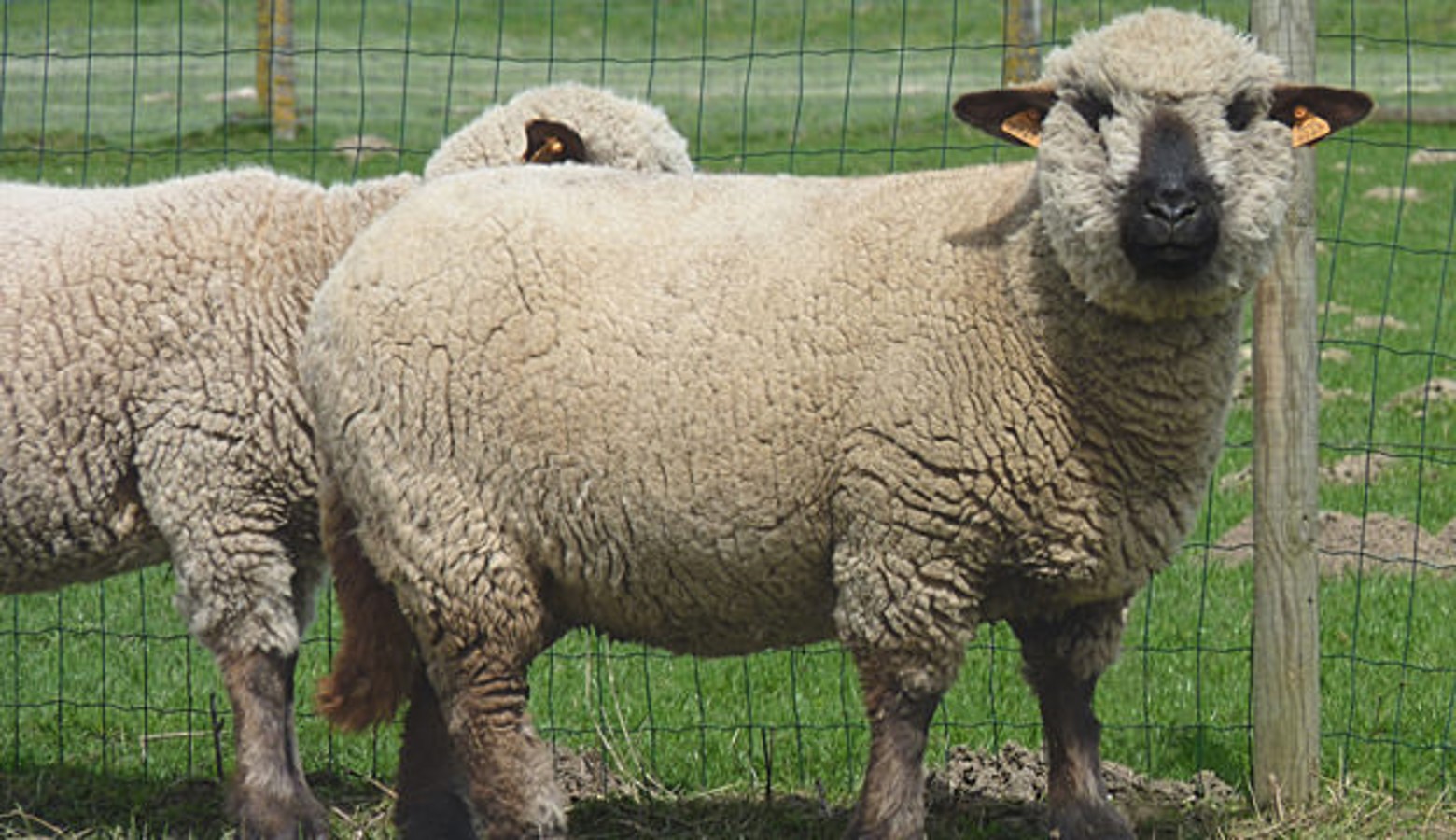

53
New cards
suffolfk (sheep)
breed?
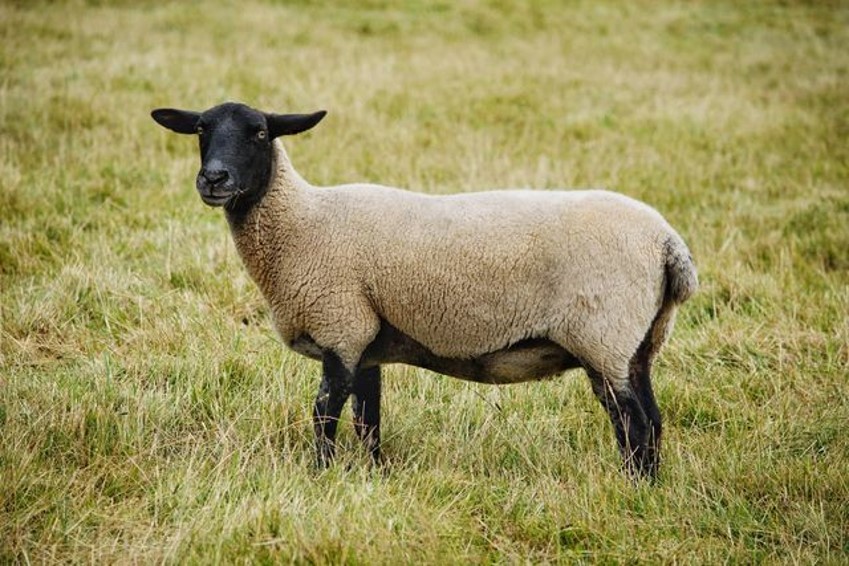

54
New cards
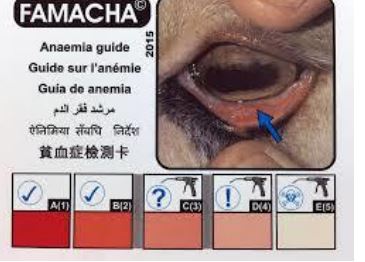
* used to test if sheeps/goats need to be treated for internal parasites by looking at color of eyelid
* dark red=good
* light red or pale pink = parasites
* only ones w parasites are treated instead of all since parasites can build up a resistance
* dark red=good
* light red or pale pink = parasites
* only ones w parasites are treated instead of all since parasites can build up a resistance
Famacha score
55
New cards
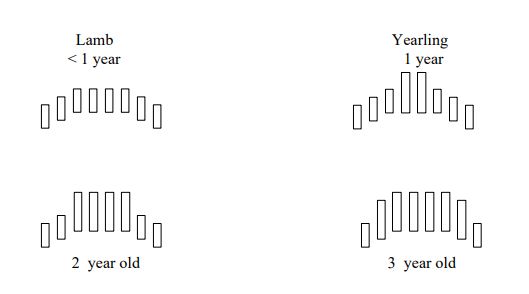
* when lamb is born it has 4 pairs (8 teeth) of temp incisors in lower jaw (similar to baby teeth in humans)
* each year one pair of these temp incisors are replaced w permanent incisors (adult teeth) beginning w pair in center
* so the more adult teeth pairs = the older it is
* each year one pair of these temp incisors are replaced w permanent incisors (adult teeth) beginning w pair in center
* so the more adult teeth pairs = the older it is
how to check the teeth of sheep to estimate age
56
New cards
to prevent foot rot
why do we trim goat/sheep hoofs?
57
New cards
goats they tend to be a bit more curious and approach humans sometimes while sheep are more nervous
between sheep and goats, which are less gregarious (“flock together”)
58
New cards
let head down, grab onto dock and push
If you are leading/moving sheep, what do you do to get them to move?
59
New cards
* All sheep have a characteristic “flight zone” and “flight distance”.
* The flight zone is the minimum zone of comfort or security that sheep maintain between themselves and other animals, especially people or sheep dogs. If this area is penetrated by a person or a dog, then the sheep will likely run away or “flight” will occur.
* How far the sheep runs away before it stops is referred to as the “flight distance”. Both genetics and previous experiences (environment) have a profound effect on an animal’s flight zone and distance
* The flight zone is the minimum zone of comfort or security that sheep maintain between themselves and other animals, especially people or sheep dogs. If this area is penetrated by a person or a dog, then the sheep will likely run away or “flight” will occur.
* How far the sheep runs away before it stops is referred to as the “flight distance”. Both genetics and previous experiences (environment) have a profound effect on an animal’s flight zone and distance
sheep characteristics
60
New cards
Holstein; dairy
breed? type of cow?

61
New cards
Red and white holstein; dairy
breed? type of cow?

62
New cards
jersey; dairy cow breed
breed? type of cow breed?

63
New cards
guernsey; dairy; light brown and white ( dont get confused w red and white that one is darker color)
breed? type of cow?

64
New cards
brown swiss; dairy
breed? type of dairy?

65
New cards
ayrshire; dairy; darker brown and white; head shape slightly differs
breed? type of cow?

66
New cards
milking shorthorn; dairy
breed? type?

67
New cards
7 to 8 wks
How long are dairy calves kept in hutches?
68
New cards
almost as soon as they are born; colostrum
When are dairy calves removed from their mother and what is the essential first but of milk that provides immunity called
69
New cards
cows are far enough to help prevent spread of diseases but can still be social
Why are dairy calves kept in hutches?
70
New cards
twice a day at NCSU but in production it usually 3
How often are cows milked at the NCSU dairy?
71
New cards
temperature and for antibiotics
* freezing point also measured to make sure milk is not watered down
* freezing point also measured to make sure milk is not watered down
● What are two things a milk tank trucker will check for prior to accepting the milk?
72
New cards
\
* to help cool the milk quickly to prevent bacteria and increase of lactic acid; prevents hot spots or areas of warm milk by mixing it with already cool milk
* The cooling process is accomplished by keeping the bulk tank at the desired temperature. In addition, new milk enters most bulk tanks from the bottom of the tank and is constantly mixed with stored milk via the action of an agitator or stirring device. These actions help cool milk quickly and prevent “hot spots” which are pockets or areas of warm milk
* minimizes seperation of milk fat
* to help cool the milk quickly to prevent bacteria and increase of lactic acid; prevents hot spots or areas of warm milk by mixing it with already cool milk
* The cooling process is accomplished by keeping the bulk tank at the desired temperature. In addition, new milk enters most bulk tanks from the bottom of the tank and is constantly mixed with stored milk via the action of an agitator or stirring device. These actions help cool milk quickly and prevent “hot spots” which are pockets or areas of warm milk
* minimizes seperation of milk fat
Why does milk enter the bulk tank from the bottom and not the top?
73
New cards
* helps prevent injury and germs from getting inside teat by closing up teat
● Why does a milker need to ‘strip’ the teat and clean it with iodine prior to and directly after milking?
74
New cards
* lactating requires very high metabolic needs so most of the food goes to that not to fat storage
● Why are dairy cows’ hook and pin bones (hooks) easily visible?
75
New cards
* made of fermented plants; kept in big white bags; bunker or upright silos
* they use the whole plant not just the grain
* they use the whole plant not just the grain
● What is silage?
76
New cards
weight divided by age
Weight/ age= average weight per day
Weight/ age= average weight per day
how to calculate weight per day of age for beef cows?
77
New cards
female who has not calved yet
Heifer-
78
New cards
\- female that has been bred, but has not yet calved
bred hiefer
79
New cards
female who has calved
cow
80
New cards
castrated male, purpose = meat
steer
81
New cards
intact male , purpose=breeding
bull
82
New cards
a calf the has been weaned, usually > 7 months old to 1 year
weaned calf –
83
New cards
– cattle that have been sent to a feedlot, usually they weigh about 700 lbs
feeder cattle
84
New cards
cattle that have been sent to a backgrounding operation, usually they weight about 500 lbs.
stocker cattle
85
New cards
– cattle that are in feedlots that are close to reaching their desired market weight.
fat cattle
86
New cards
* Many cattle have ear tag # of things similar to 04E
* E= year=2017
* 04=number identifies order in which calf was born= 4th calf born
* no years are labeled w I O Q Z
* Relative birthday – 01 would be born near the first of January while 40 would be born near the end of February. 41 would be born near the first of September and 80 would be born near the end of October( to 40 =hereford; 41 to 80=angus)
A 2013
B 2014
C 2015
D 2016
E 2017
F 2018
G 2019
H 2020
J 2021
K 2022
L 2023
* E= year=2017
* 04=number identifies order in which calf was born= 4th calf born
* no years are labeled w I O Q Z
* Relative birthday – 01 would be born near the first of January while 40 would be born near the end of February. 41 would be born near the first of September and 80 would be born near the end of October( to 40 =hereford; 41 to 80=angus)
A 2013
B 2014
C 2015
D 2016
E 2017
F 2018
G 2019
H 2020
J 2021
K 2022
L 2023
how to read nametag and estimate day of birth
87
New cards
sep and oct
when are angus calves born?
88
New cards
jan and feb
when are hereford calves born?
89
New cards
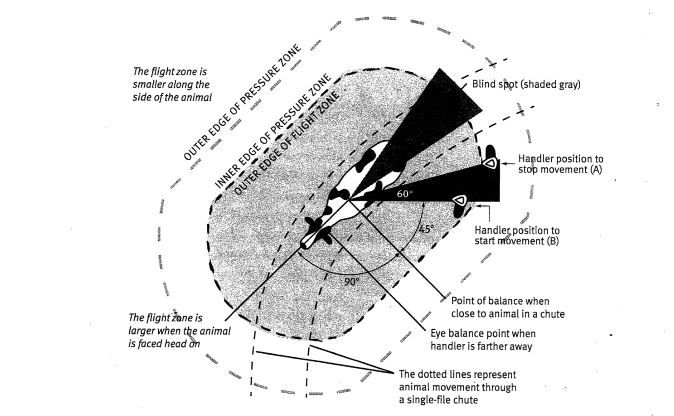
* flight zone is an area where if someone enters it the livestock will flee
* The point of balance is usually at the animal's shoulder and it is determined by the animal's wide angle vision. All species of livestock will move forward if the handler stands behind the point of balance. They will back up if the handler stands in front of the point of balance.
* The point of balance is usually at the animal's shoulder and it is determined by the animal's wide angle vision. All species of livestock will move forward if the handler stands behind the point of balance. They will back up if the handler stands in front of the point of balance.
point of balance/ flight zone
90
New cards
Black angus; beef
breed? type?

91
New cards
hereford; beef
breed? type?

92
New cards
gelbvieh; beef
breed? type?

93
New cards
charolais; beef
breed? type?

94
New cards
beef; simmental
type? breed?

95
New cards
beef; limousin
type? breed?

96
New cards
brangus; beef
breed?type?

97
New cards
brahman; beef
breed? type?

98
New cards
Species: beef cattle
Function: changes color when animal is mounted-detects animals are in heat
Kamar Heat Detection Patch
Function: changes color when animal is mounted-detects animals are in heat
Kamar Heat Detection Patch
Species used on? what is it? what is it used for?

99
New cards
**Species: Beef cattle**
**Function:** Used to manually pull calves during parturition if the cow is experiencing birthing problems
OB Chains and Handle
Species? Function? Name?

100
New cards
**Species: Beef cattle**
**Function:** Used to synchronize estrus by administering the hormone, progesterone
CIDR and inserter
Species? Function? Name?
