Genetics Year 10 What You Actually Need
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Phenotype
The trait shown: What you see\ observable characteristics or traits It’s the result of genotype + environment. e.g. Eye colour, Hair type, Height, Blood type. Usually visual.
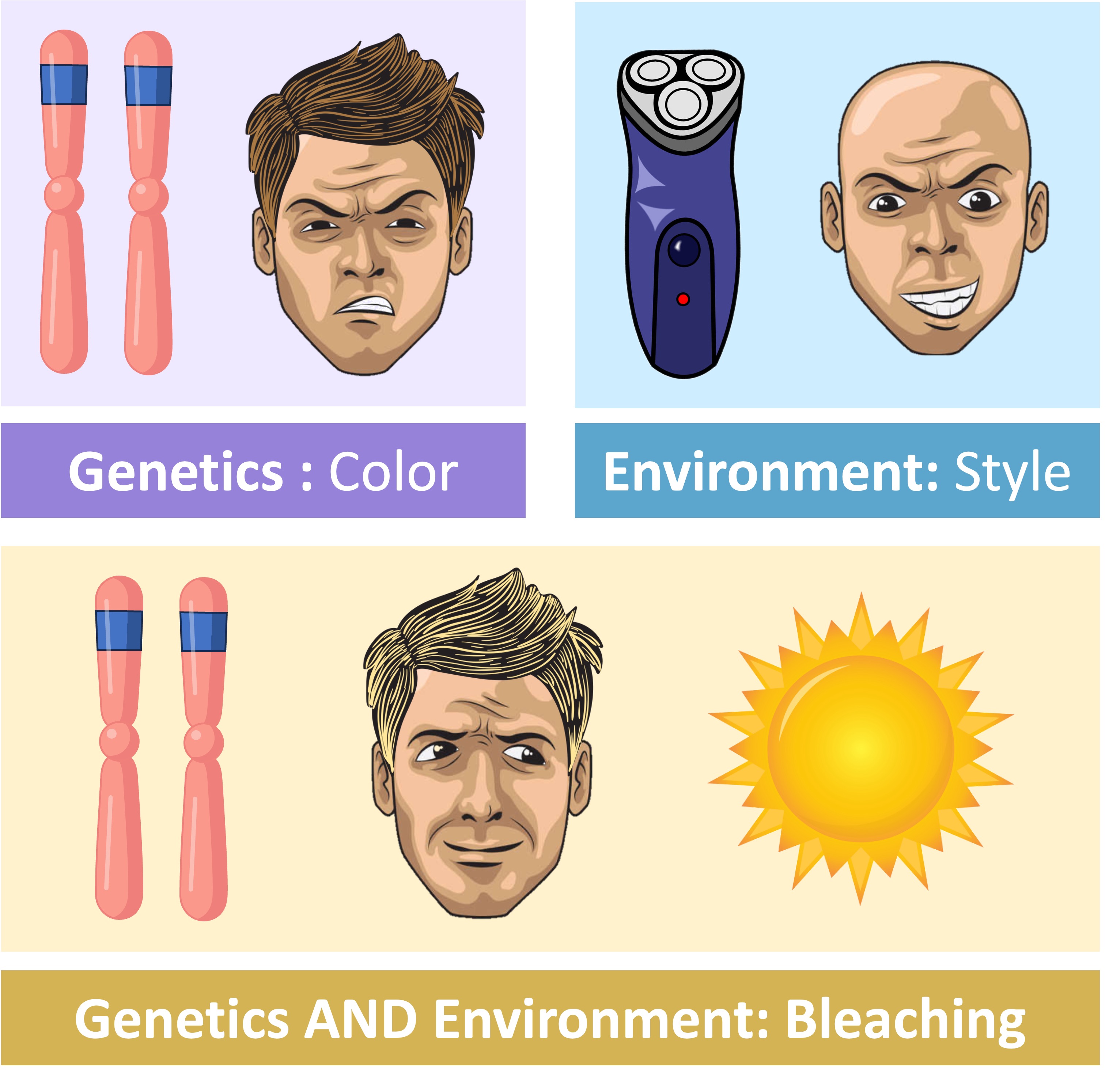
Genotype
Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism (BB). E.g. looking at eye colour Brown eyes: B blue eyes: b the Genotypes could be BB bB bb the trait shown would be brown eyes (that a phenotypes)
Allele
a different version of the same gene. eg: if the trait is eye colour the alleles could be blue eyes: b brown eyes: B green eyes: g etc.
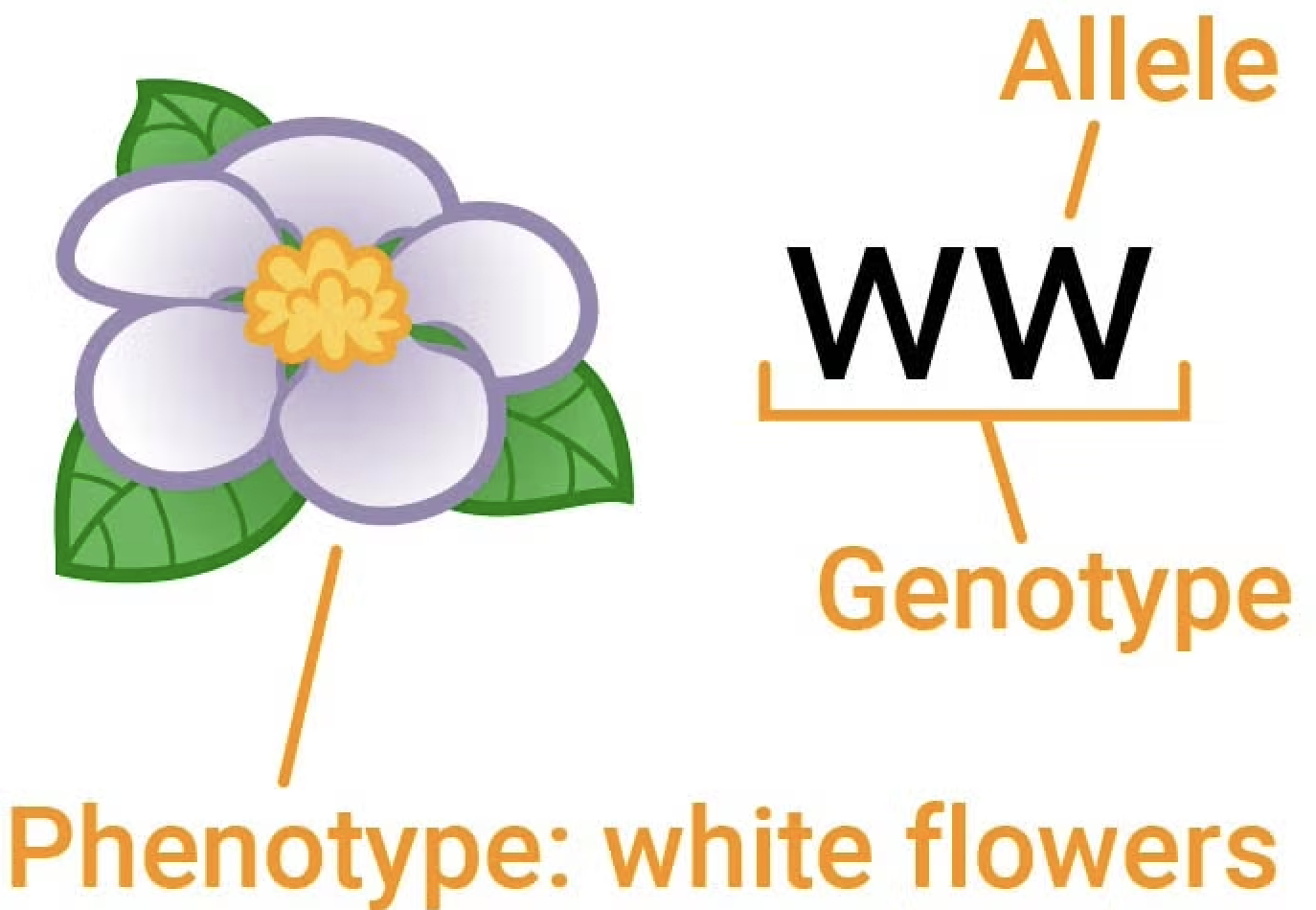
Gamete
A gamete is a sex cell — the special kind of cell used in sexual reproduction.
Male gamete = sperm, Female gamete = egg. they only carry one allele so they need to combine to make the combo.
Somatic cells
Somatic cells are all the body cells except the gametes (sperm and egg) eg. the skin cells, eye cells, brain cells. Somatic cells = all body cells except sex cells. They have a full set of chromosomes (2 alleles per gene) They don’t get passed on to offspring
haploid vs diploid
Haploid (n):
Has 23 chromosomes
No pairs, just one set
Found in sperm and egg cells
Made by meiosis
Diploid (2n):
Has 46 chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes (23 pairs)
Found in regular body cells
Made by mitosis
Created when sperm and egg join
Breakdown of that: Haploid cells combine to restore the diploid number in offspring. This cycle keeps chromosome numbers stable over generations. Haploid cells allow for mixing of genes, increasing variation.
Complimentary bases for DNA and RNA
DNA: T-A, G-C
RNA: U-A, G-C (replace the T with U)
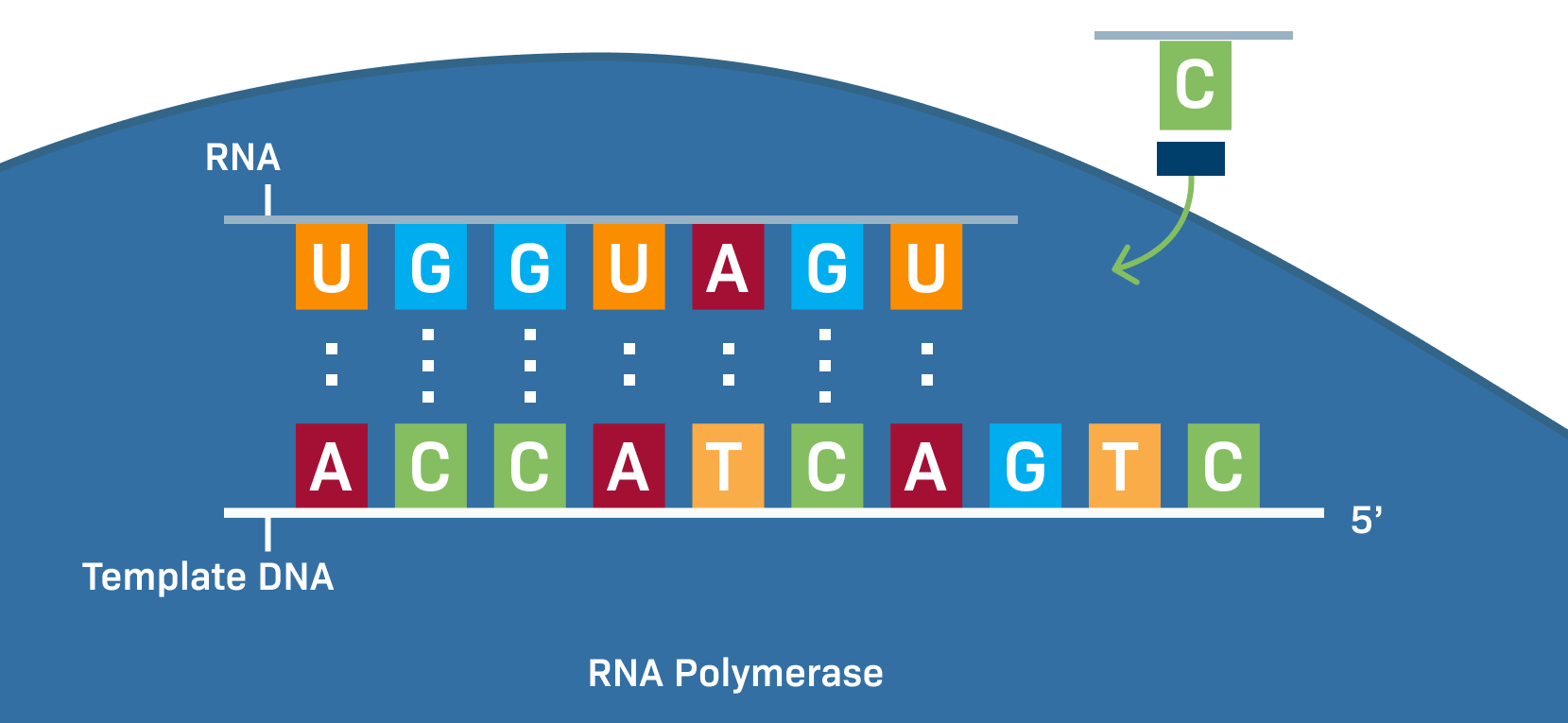
DNA vs RNA
DNA vs RNA (thymine ➡ uracil) DNA is like the master blueprint — it’s double-stranded and has thymine (T) as one of its bases. RNA is like a working copy — it’s single-stranded and instead of thymine, it uses uracil (U). Both have adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA moves out to help make proteins. Basically, RNA replaces thymine (T) with uracil (U) but does the same job reading the code.
Gene
A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions to make a specific protein or control a particular trait. Each gene tells your cells how to make something important, like eye colour or blood type. Genes are made up of sequences of nucleotides (A, T, C, G). Different versions of a gene are called alleles. Genes are the BB, bB and the A, T, C, G.
Dominant allele vs Recessive allele
a dominant allele overpowers the recessive allele and can be expressed in these combos BB, Bb whereas a recessive allele can only be expressed when its bb because it is overpowered by the Dominant allele.
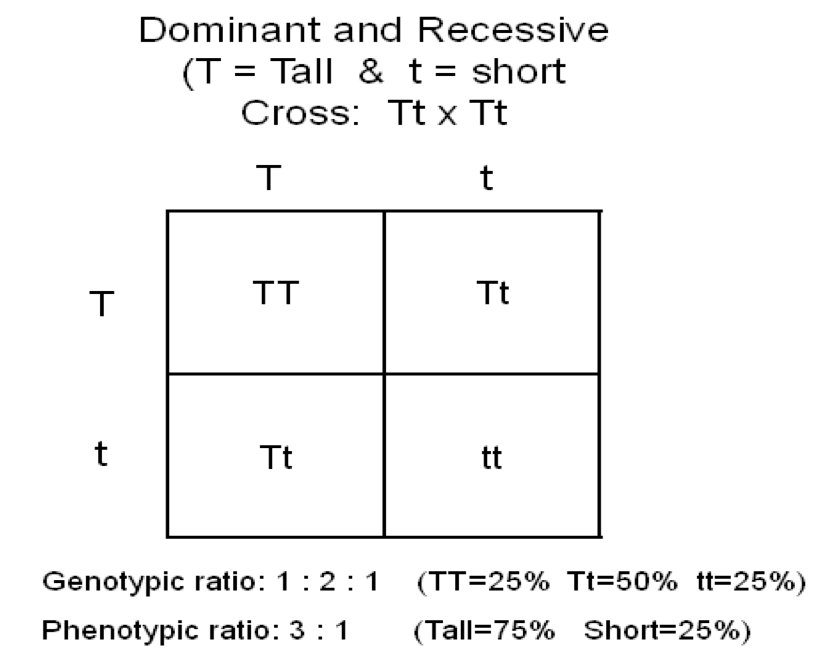
Punnet squares and ratios
if its 2 and 2 ratio is 1:1
X and Y
XX-female, XY-male are the sex chromosomes related to the male and females
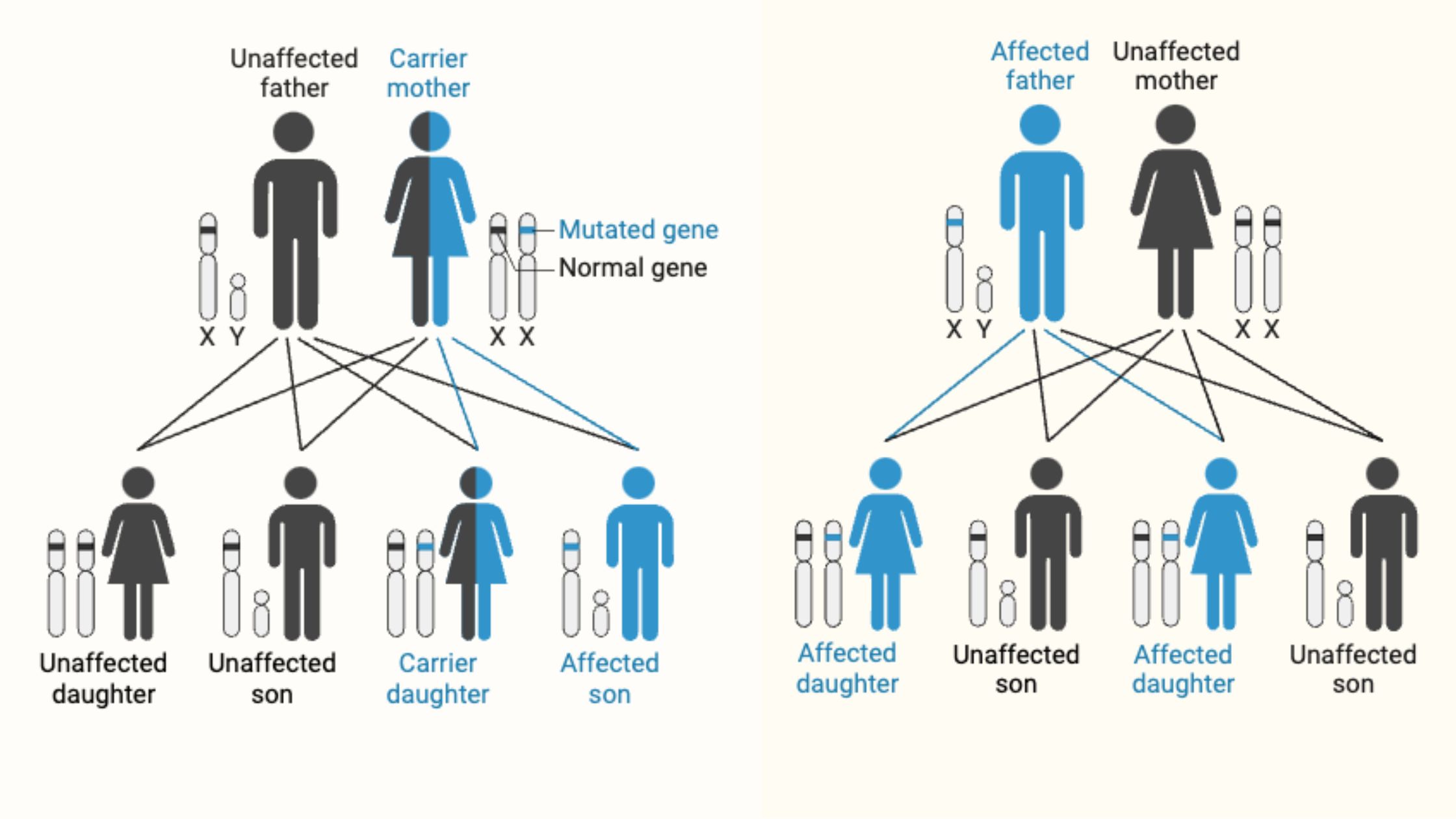
Sex-linked inheritance
Sex-linked inheritance means a gene is on the sex chromosomes (usually the X). Boys (XY) only have one X, so if they get a faulty gene there, they show the trait. Girls (XX) have two Xs, so they usually need two faulty genes to show it. That’s why some traits, like color blindness, happen more in boys.
Heterozygous and heterozygous
Heterozygous: Heterozygous means having two different alleles for a gene eg. Bb is heterozygous. And the phenotype would be B
Homozygous: Homozygous means having two identical alleles for a gene eg. BB or bb is Homozygous. And the phenotype would be B or b
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process where a cell divides to make two identical cells. It happens in several phases. (me too sis, splits into 2 identical ones)
Mitosis is important because it helps your body grow, heal cuts, and replace old or damaged cells. It makes sure that each new cell has the exact same DNA as the original one
Prophase
The chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear membrane starts to break down.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
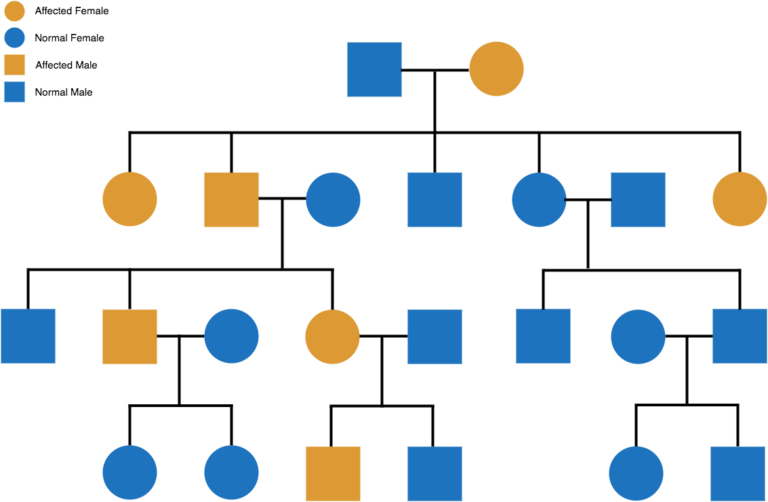
Pedigree
Pedigree: males are squares females are circles: the coloured in one is the trait shown

Anaphase
The chromosome pairs separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase
New nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
The cell splits into two identical cells.
Meiosis
Mitosis: Meiosis is how your body makes sperm and egg cells. It splits the cells twice to make four cells with half the normal number of chromosomes. This helps babies have the right number of chromosomes and makes each baby unique.
Mitosis
Mitosis is important because it helps your body grow, heal cuts, and replace old or damaged cells. It makes sure that each new cell has the exact same DNA as the original one
Karyotyping
Karyotyping is a picture that looks at all the chromosomes in a cell. It arranges the chromosomes in pairs from largest to smallest, ending with the sex chromosomes (XX or XY).
Its function is to check for problems like missing, extra, or damaged chromosomes. Doctors use karyotyping to find genetic disorders, like Down syndrome (which has an extra chromosome 21).
DNA
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It’s the genetic code that tells your body how to grow, work, and look. DNA is like an instruction book inside your cells. It’s shaped like a twisted ladder (called a double helix), and it’s made of smaller parts called nucleotides. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of bases: A with T, C with G Your DNA is stored in your chromosomes, and it carries all your genes — the instructions for your traits.
RNA
RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid.
It’s like a copy of DNA that helps the cell make proteins. While DNA stays safe in the nucleus, RNA goes out to the rest of the cell to tell it what to build.
How its different
Here’s how it’s different from DNA: RNA is single-stranded (DNA is double). RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). RNA is shorter and used as a messenger or helper in making proteins. So, DNA is the full instruction book, and RNA is like a quick note copied from it to do one job.
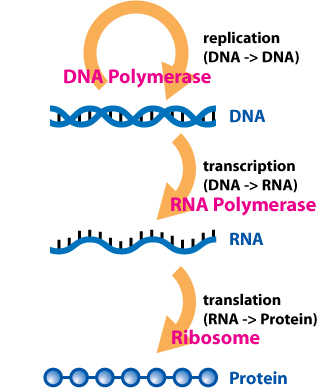
RNA process: Transcription – A copy of DNA is made as mRNA (messenger RNA). RNA uses U instead of T.
Translation – The mRNA (messenger RNA) goes to a ribosome, which reads it and builds a protein using amino acids.
DNA → mRNA → Protein
Nucleotides (structure)
a Nucleotides is the base, the A,T,C and G (and U for RNA) A nucleotide is the building block of DNA and RNA. It has three parts: A sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA) A phosphate group. A nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G in DNA; A, U, C, or G in RNA) These parts join together to form the long chains of DNA or RNA.