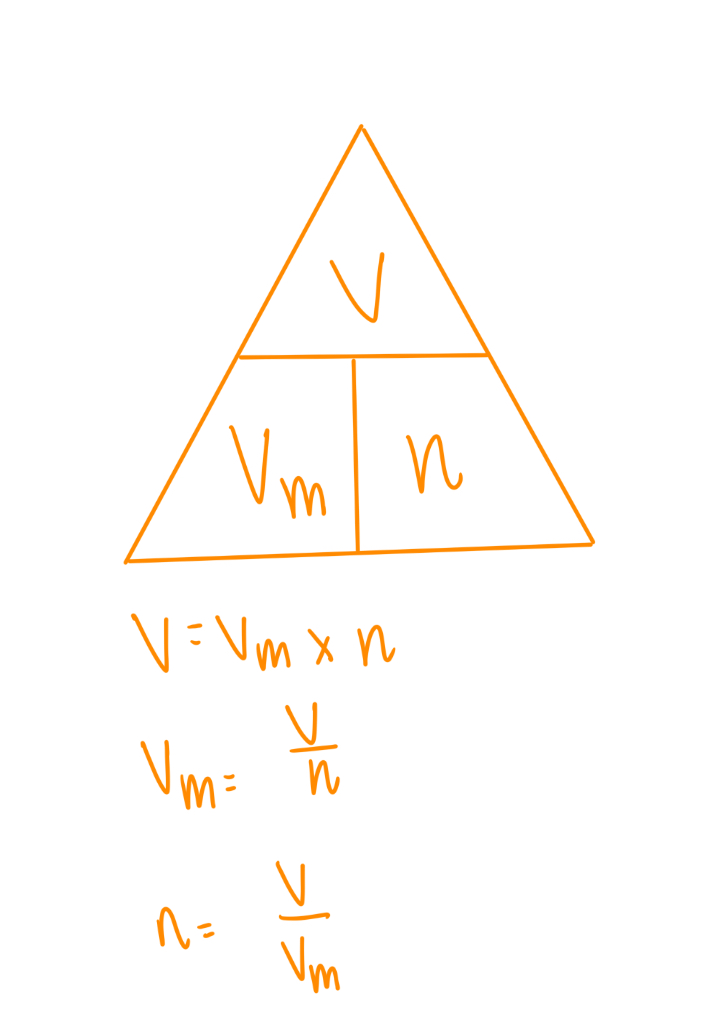3.1: getting the most from reactants
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Industrial processes and various calculations
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What must be considered when making industrial processes?
Cost and efficiency must be considered when making industrial processes to maximize profit and minimise environmental impact
Feedstock
The reactants in a process
What must be considered when choosing feedstock?
Many factors are considered when choosing feedstock, such as: availability, cost (including the cost of transport), sustainability (including when storing feedstock), and risks to humans/the planet
The recycle loop
Byproducts of a process can be recycled as feedstock in other processes or sold, and excess reactants can be reused. This reduces cost, maximises profit, and limits waste
Energy requirements
You must consider if heat produced can be used elsewhere, you should also consider if a catalyst can be used to lower energy requirements
Byproducts
Unwanted or extra products made in an industrial process
How can byproducts be used and what about byproducts must be considered?
Byproducts can be sold or used as feedstock in other processes, if a byproduct is toxic then worker safety and environmental protection laws must be considered
Product yield
The gain of the desired product, you must consider if this is high enough to make a profit
Health and safety considerations for workers, the public, and the environment
You should minimise waste and its toxicity
You should avoid the use of toxic substances as feedstock
You should design biodegradable products/byproducts wherever appropriate
Considerations when analysing flowcharts
Can alternative, cheaper feedstock be used?
Can unreacted reactants be separated and reused?
Can byproducts be used in different processes or sold?
Can energy inputs be lowered?
Moles
The unit of measurement of a substance based on particles. 1mol = avogrado’s constant = 6.02×1023 particles
What factors is the volume of a gas dependent on?
Pressure and temperature
As pressure increases, the volume of a gas…
As pressure increases, the volume of a gas decreases
As temperature increases, the volume of a gas….
As temperature increases, the volume of a gas increases
TRUE OR FALSE: the volume of 1mol of CO2 at 150°C and 150Pa is different to the volume of 1mol of CO2 at 40°C and 150Pa
True
TRUE OR FALSE: the volume of 1mol of CO2 at 40° and 150Pa is different to the volume of 1mol of H2 at 40° and 150Pa
False
Molar volume
The volume occupied by any gas at a specific temperature and pressure
As temperature increases, molar volume…
As temperature increases, molar volume increases
As pressure increases, molar volume…
As pressure increases, molar volume decreases
Formula for molar volume
l mol-1
Consider the equation:
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
If 100cm3 of nitrogen is used, how much hydrogen is used and how much ammonia is produced?
300cm3 of hydrogen is used and 200cm3 of ammonia is produced
Excess reactants
When more of a reactant is used than necessary so that all of the limiting reactant is used up
Why is a reactant used in excess?
So that the limiting reactant is used up completely as it may be expensive or toxic
Steps to calculate limiting and excess reactants
Find the molar ratio of reactants
Find the mass used of each reactant
Find the GFM of each reactant
Calculate the moles of each reactant used and
Percentage yield
Percentage yield compares how much of s product is actually made to what the equation predicts
Why can percentage yield never be 100%?
Impurities in chemicals
Products escaping the system
Unfinished reactants
Side reactions created by by-products
Why can percentage yield sometimes exceed 100%?
Byproducts reacting to form products
Impurities
Solvents
Steps to calculate percentage yield
Write the balanced equation
Find the limiting and excess reactants
Calculate the theoretical yield of the product using a balanced equation and the limiting reactant
Calculate the percentage yield
Atom economy
Atom economy measures the proportion of reactants that have been turned into useful products (theoretical)
Desirable reactions have a high…
Desirable reactions have a high atom economy
What is the atom economy of reactions with one product?
100%
What are the benefits of efficient processes with high atom economies?
They conserve natural resources and reduce waste
Steps to calculate atom economy
Write the balanced equation
Find the total mass of reactants and the mass of the desired product
Calculate the atom economy
Magic triangle for molar volume