6.3 - Photochemical Smog
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Photochemical Smog
Has significant impacts on societies and living systems. It can reduced by decreasing human reliance on fossil fuel.
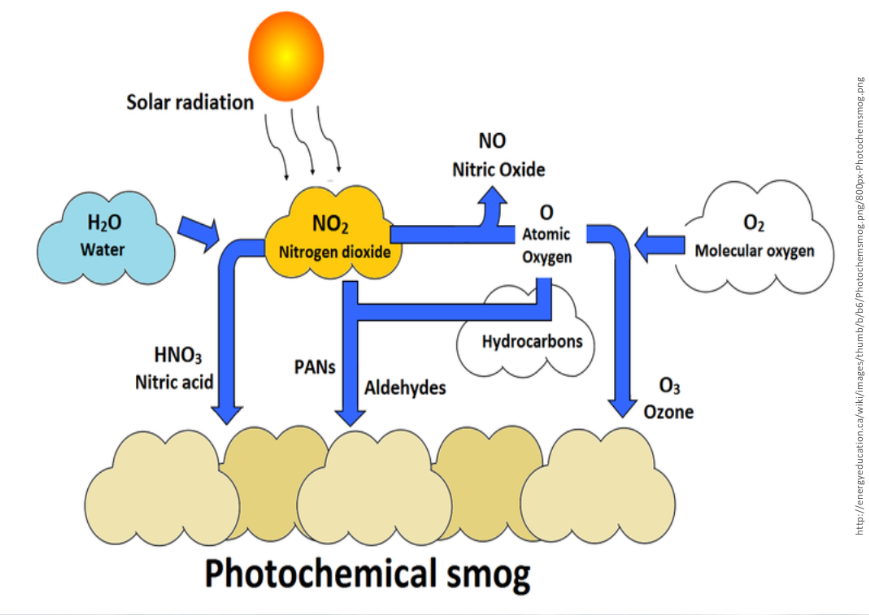
It’s mainly nitrogen dioxide and ozone. The biggest contributor to this is motor vehicle exhausts in cities. It is formed when ozone, nitrogen oxides, and gaseous hydrocarbons from vehicle exhausts interact with strong sunlight.
Primary Pollutants
Emitted directly from a process. The process may be natural like volcanic eruptions or anthropogenic (human-made) from moto vehicle exhausts.
Ex:
Carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
Carbon dioxide
Unburned hydrocarbons
other sources of this include: building sites, forest fires
Secondary Pollutants
Formed when primary pollutants undergo a variety of reactions with other chemicals already present in the atmosphere. Sometimes this is a photochemical reaction in the presence of sunlight.
Ex:
Tropospheric ozone
peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN)
What forms nitrogen dioxide?
When NO reacts with O2 in the atmosphere, which causes the brown haze over many cities like Shanghai and Los Angeles
What forms tropospheric or ground-level ozone (O3)
When NO2 reacts with sunlight to release single, reactive oxygen atoms (O1), which combines with (O2)
What is the bad ozone?
Tropospheric ozone
What is the good ozone?
Stratospheric Ozone
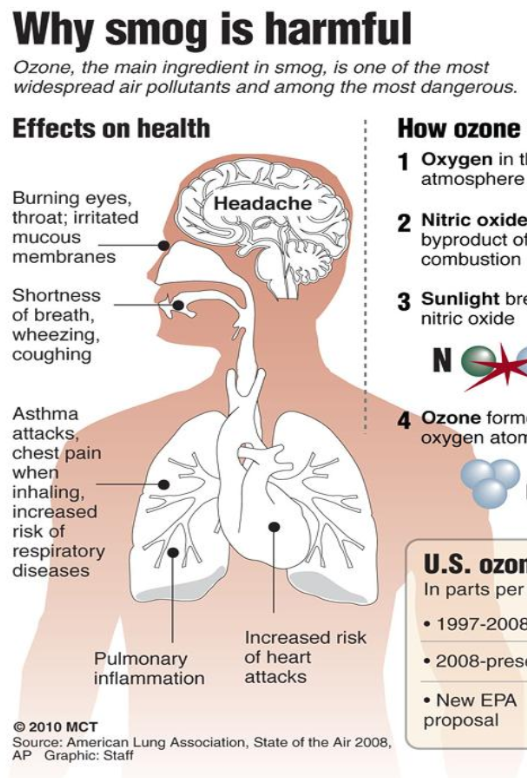
Why is smog harmful?
Burning eyes, throat
Shortness of breath - coughing and wheezing
Asthma attacks - chest pain
Increased risk of respiratory diseases
Factors that affect photochemical smog
Topography
Climate
Population Density
Fossil Fuel Use
Topography as a factor for photochemical smog
Acts as barriers to air movement, trapping pollutants. It increases the likelihood of thermal inversion
Climate as a factor for photochemical smog
Higher temperatures increase frequency and severity since it will occur at a faster rate. Low winds cause less movement of particles
Population density as a factor for photochemical smog
Higher population density increases frequency and severity since more people leads to more cars/more electricity
Fossil fuel use as a factor for photochemical smog
Higher fossil fuel use increases frequency and severity since it produces more primary pollutants which would create more secondary pollutants
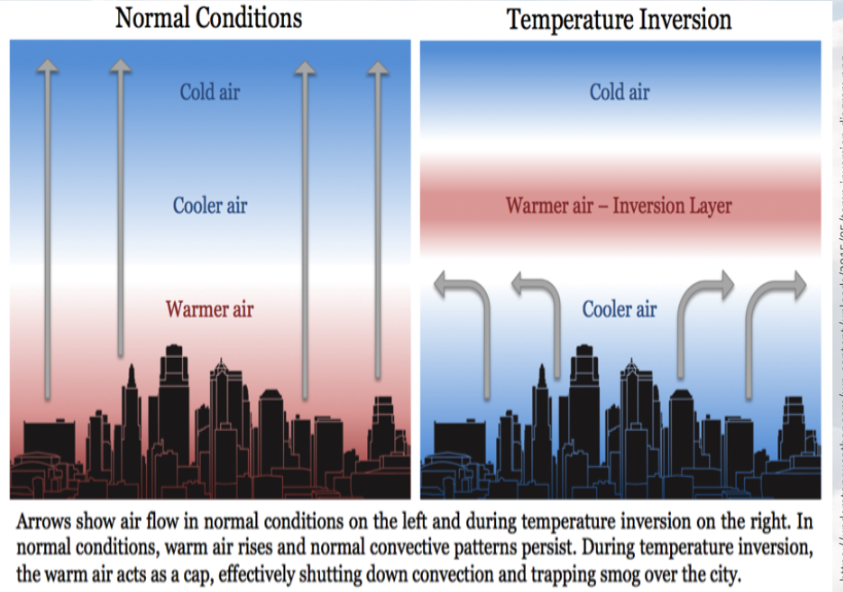
Horizontal Winds
These normally disperse pollutants from urban areas (up and out). But thermal inversions trap pollutants at ground level, usually until a storm system moves in to disrupt the inversion layer
Tropospheric Ozone
An example of a secondary pollutant, formed when oxygen molecules react with oxygen atoms that are released from nitrogen dioxide in the presence of sunlight.
It’s highly reactive and damages crops/forests/plants, irritates eyes, creates respiratory illnesses and damages fabrics and rubber materials
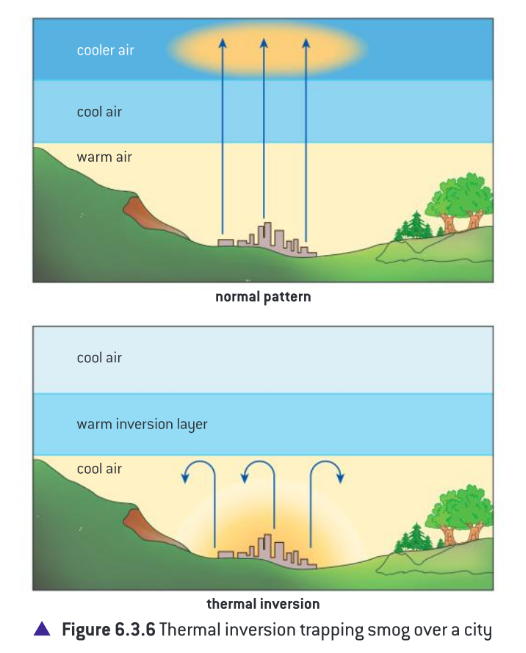
Thermal Inversions
Occur due to lack of air movement when a layer of dense, cool air is trapped beneath a layer of less dense, warm air.
This causes concentrations of air pollutants to build up near the ground instead of being dissipated by “normal” air movements
Possible effects of Ozone
Damage to plants
tropospheric ozone is absorbed by plant leaves where the ozone degrades chlorophyll so photosynthesis and productivity are reduced.
Damage to humans - smog (see other flashcard)
Damage to materials and products
Ozone attacks natural rubber, cellulose, and some plastics
It reduces the lifetime of car tyres
It bleaches fabrics
How are particulates formed?
Through burning almost any organic material or fossil fuel releases small particles of carbon and other substances referred to as _______________.
Poorly maintained diesel engines release large amounts of ______ in exhaust fumes
Dangers of particulates:
Our respiratory fillers the nose and hairs lining the passages of the bronchi and lungs, cannot filter them out, so they enter our bodies and stay there
causing asthma, lung cancer, respiratory problems, premature death
They are carcinogenic (cancer-causing)
In areas close to industrial/dense urban areas, crops become covered with particulates, which reduce their productivity because less sunlight reaches the leaf.
Strategy for reducing urban air pollution
(Altering the human activity producing pollution)
Consume less, burn less fossil fuel - especially in the internal combustion engine
Act as informed consumers for the purchase of energy-efficient technologies
Lobby governments to increase renewable energy use
Strategy for reducing urban air pollution
(Regulating and reducing the pollutants at the point of emission)
Government regulation/taxation
Catalytic converters to clean exhaust of primary pollutants from car exhaust
Fuel quality may be regulated by government
Strategy for reducing urban air pollution
(Clean up and restoration)
Afforestation to increase carbon sinks and filter air (but this does not reduce emissions)
Re-greening of cities - more trees, more parks - absorbs more carbon dioxide