Ch 16 special senses
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
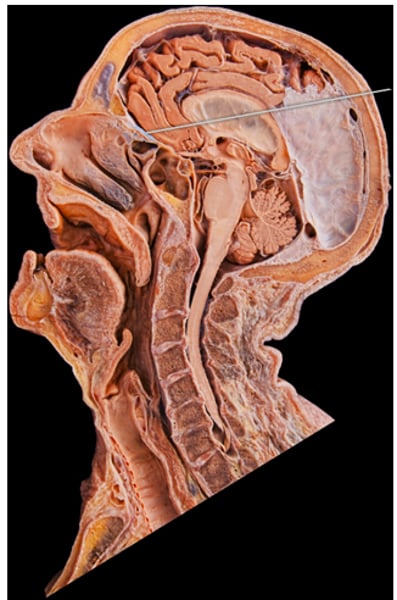
Study this diagram
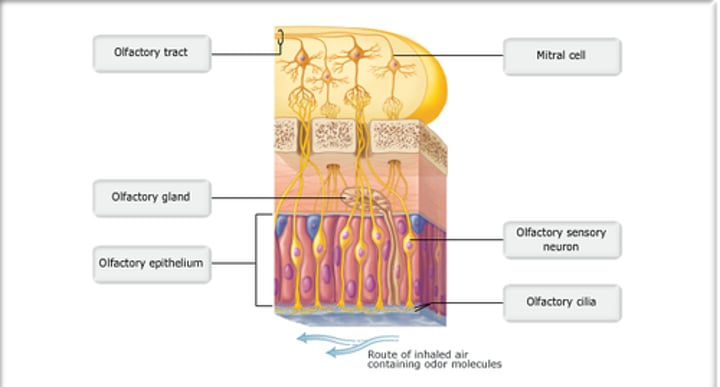
study this diagram
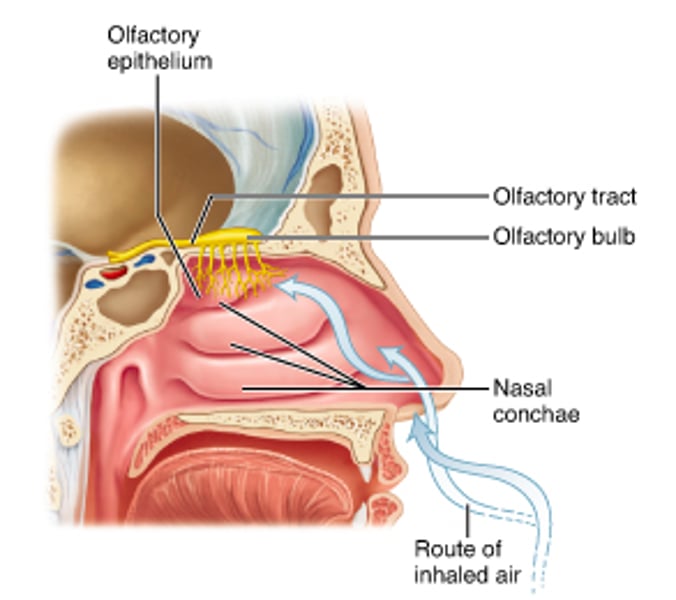
ethmoid
Through which cranial bone do the nerve fibers of the olfactory nerve pass?
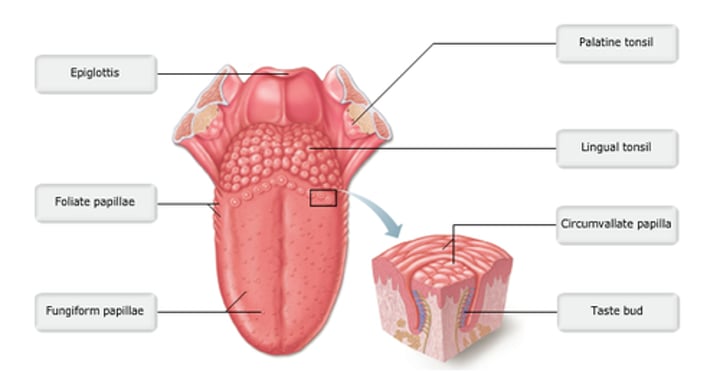
basal epithelial cells
Which cells divide to replace the gustatory cells that are routinely damaged during eating?
cranial nerve IX
Which cranial nerve conveys sensory gustatory impulses from the posterior one-third of the tongue?
taste/gustation
The sensory pathway that passes from the facial nerve to the solitary nucleus in the medulla oblongata to the ventral posterormedial nucleus in the thalamus to a specific sensory interpretation area in the cerebral cortex is __________.
olfactory bulb
Region of the forebrain overlying the cribriform plate of the ethmoid.
chemicals binding to microvilli
The sensation of taste involves _________.
facial
The nerve carrying taste information from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is the________.
false
true or false
Most of the special sensory receptors are free nerve endings.
true
true or false
Taste sensation is carried by the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves.
olfactory tract
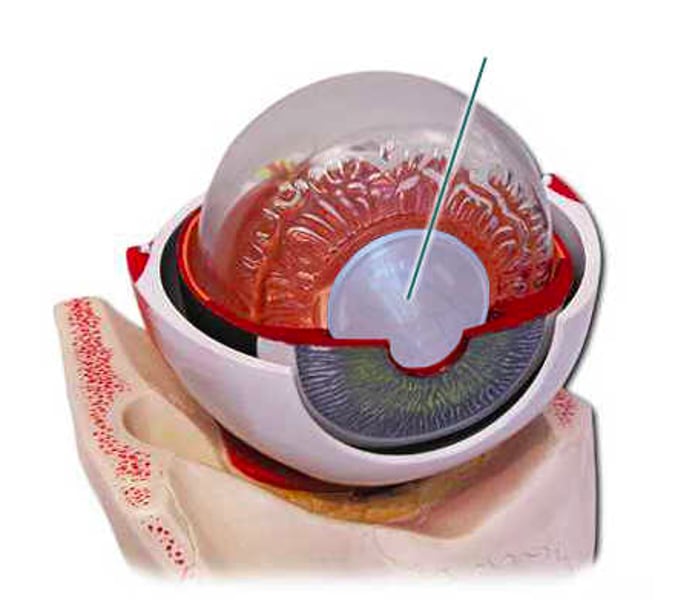
Which structure is highlighted?
lens
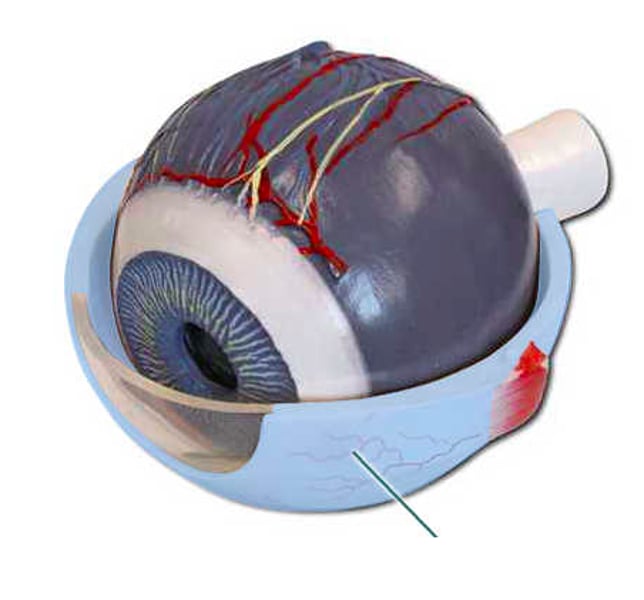
Which structure is highlighted?
sclera
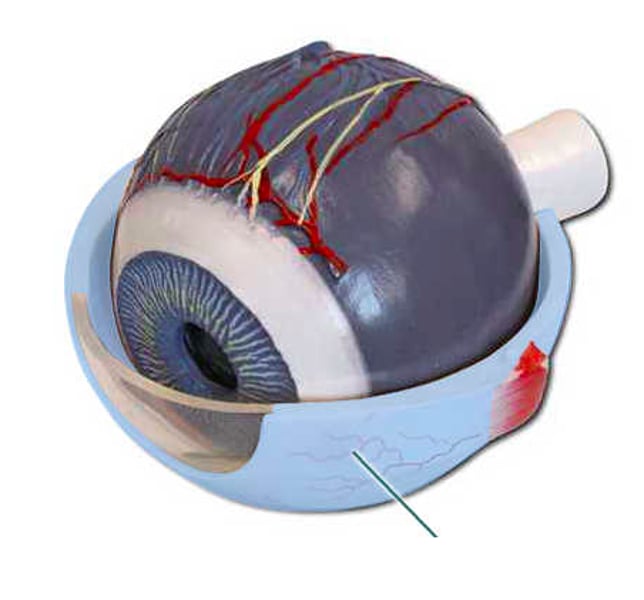
Which structure is highlighted?
protects the eyeball
Which of the following is a function of the highlighted region?
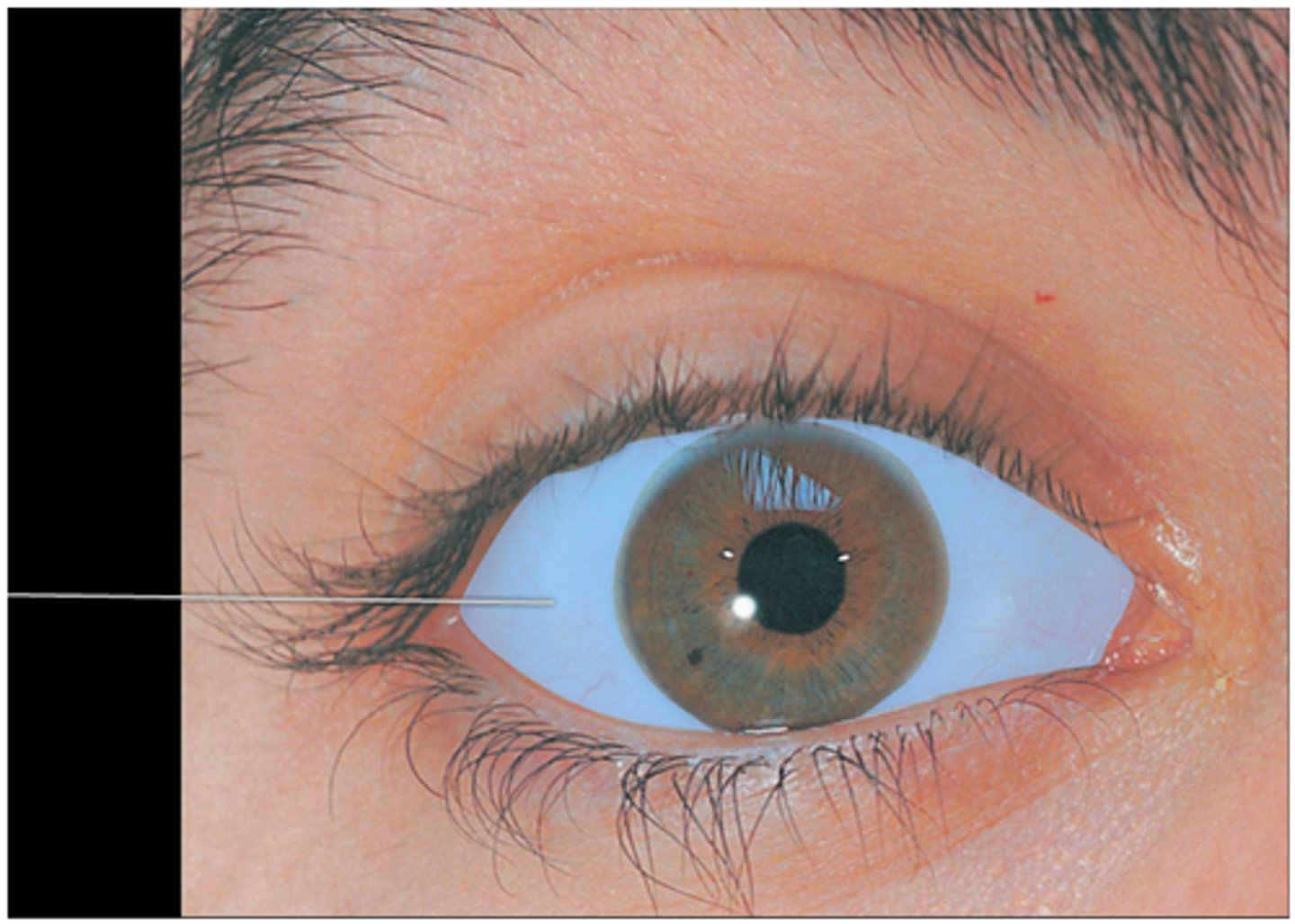
cornea
which structure is highlighted?
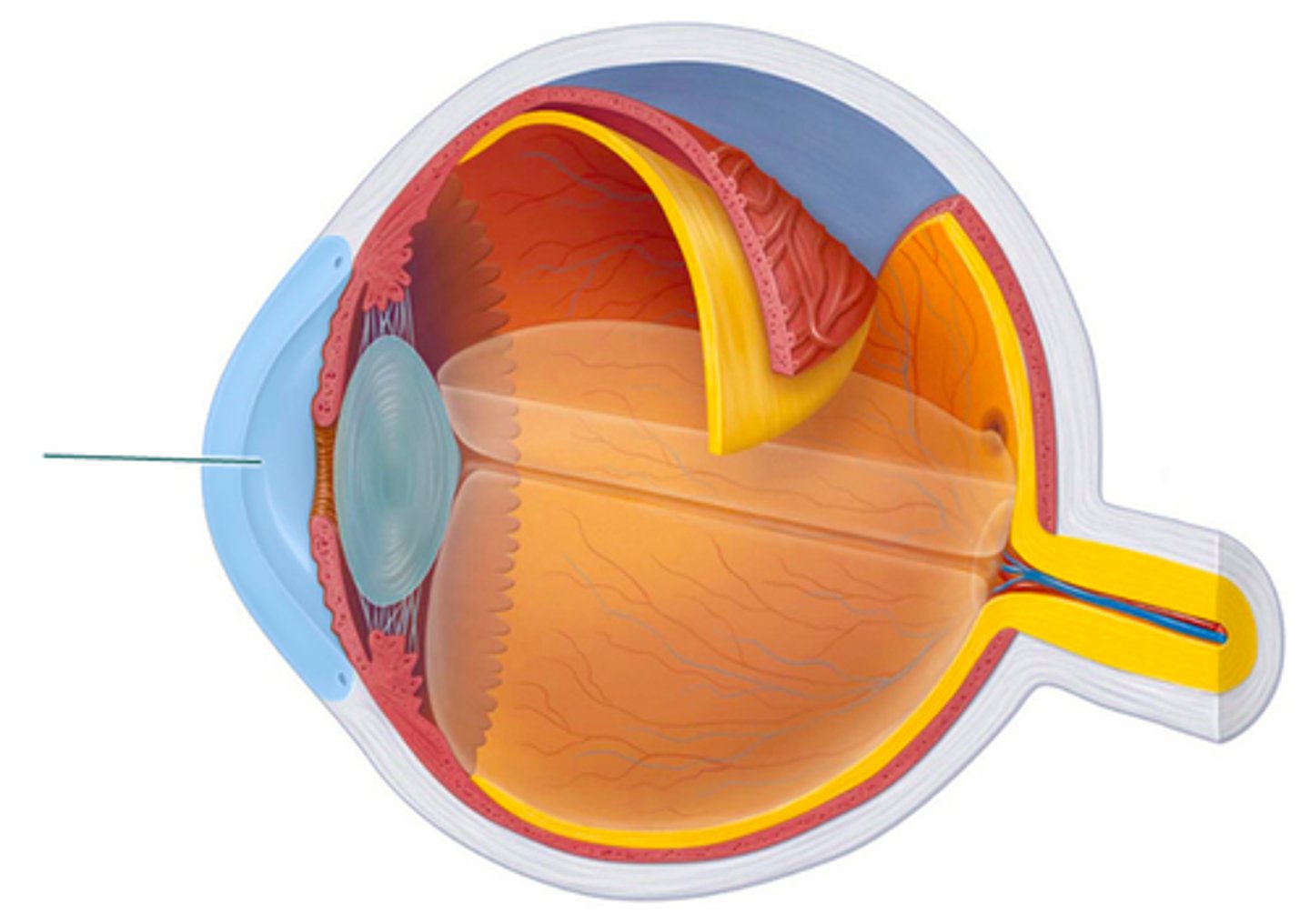
retina
Which structure is highlighted?
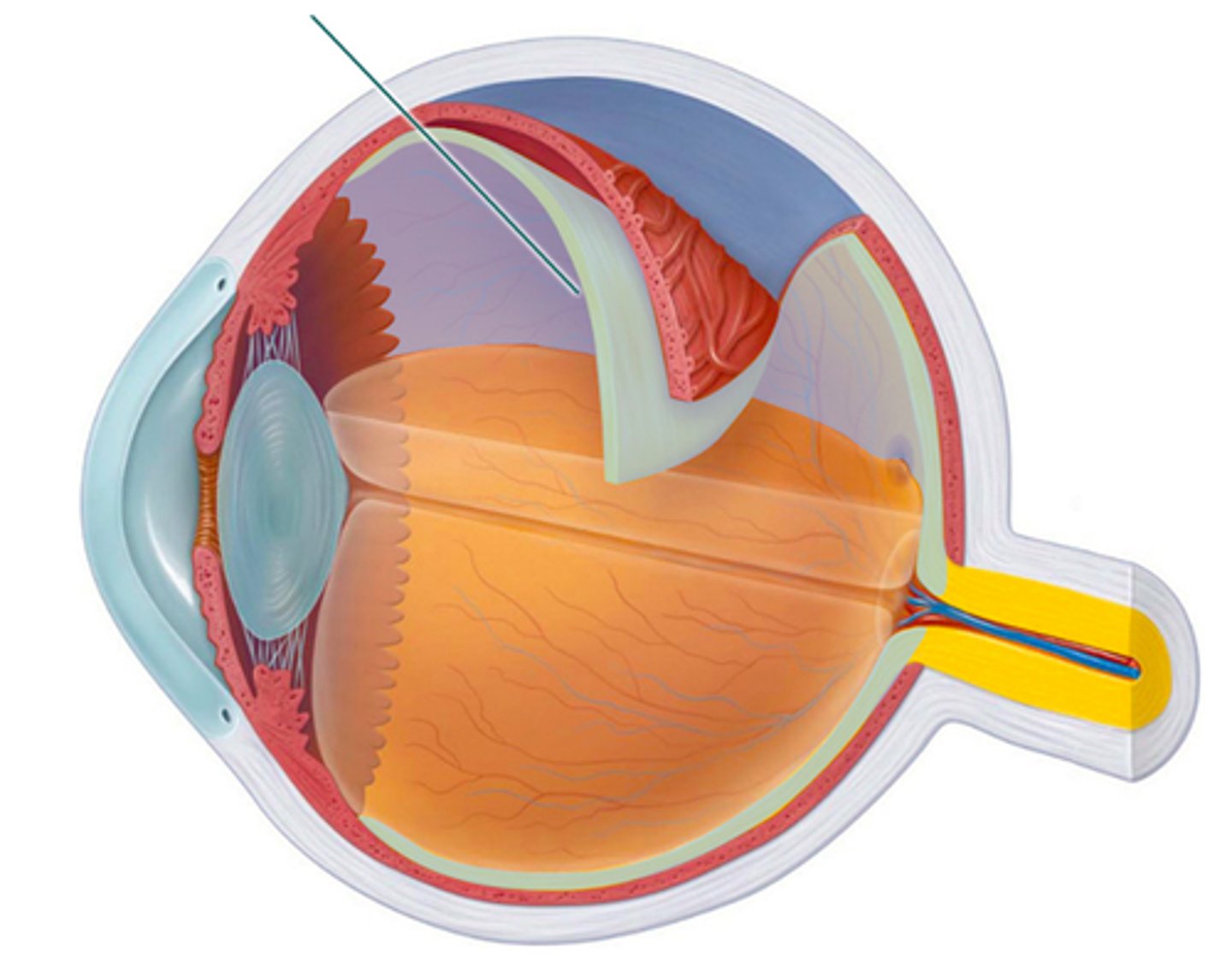
sclera
Which structure is highlighted?
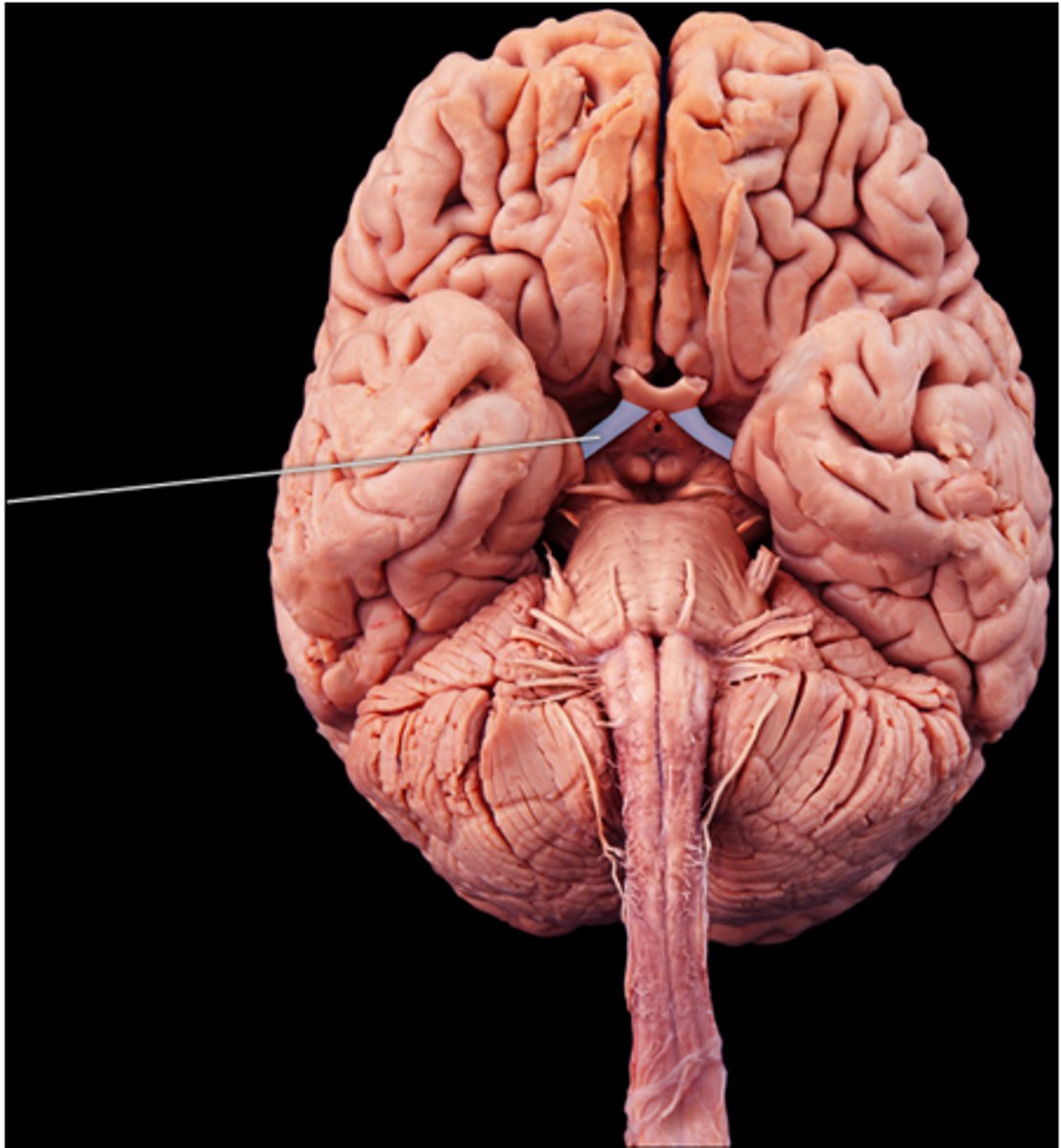
optic tract
Which structure is highlighted?
Study this diagram
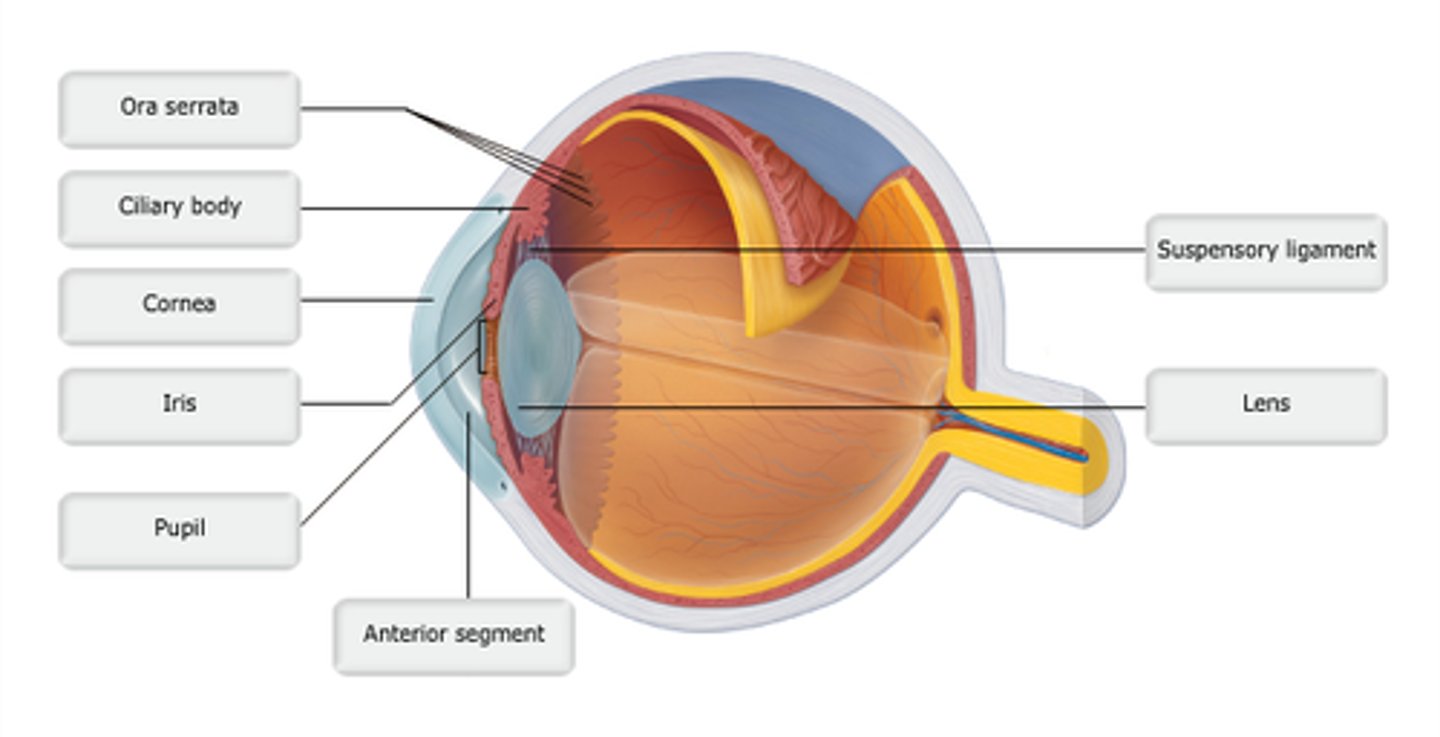
Study this diagram
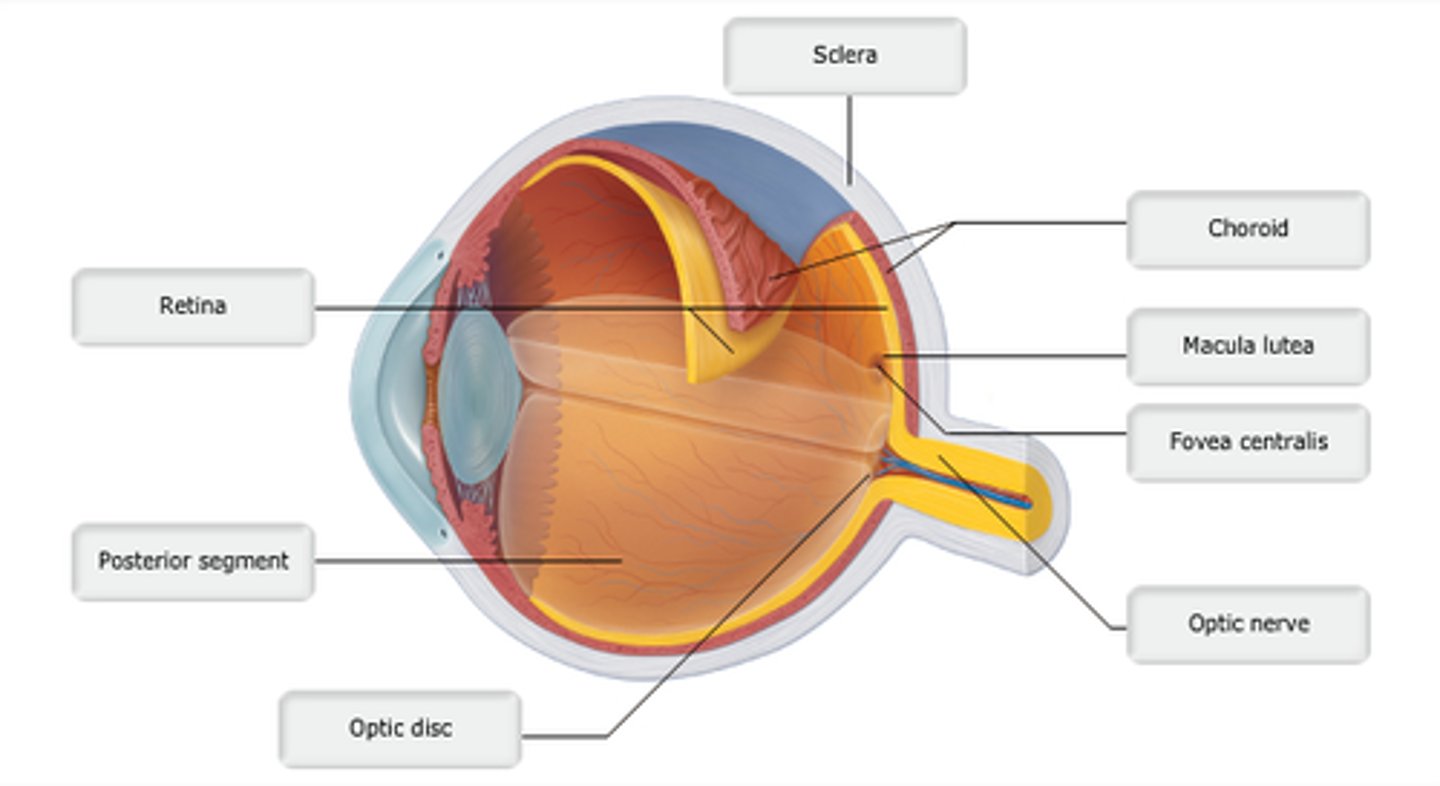
Study this diagram
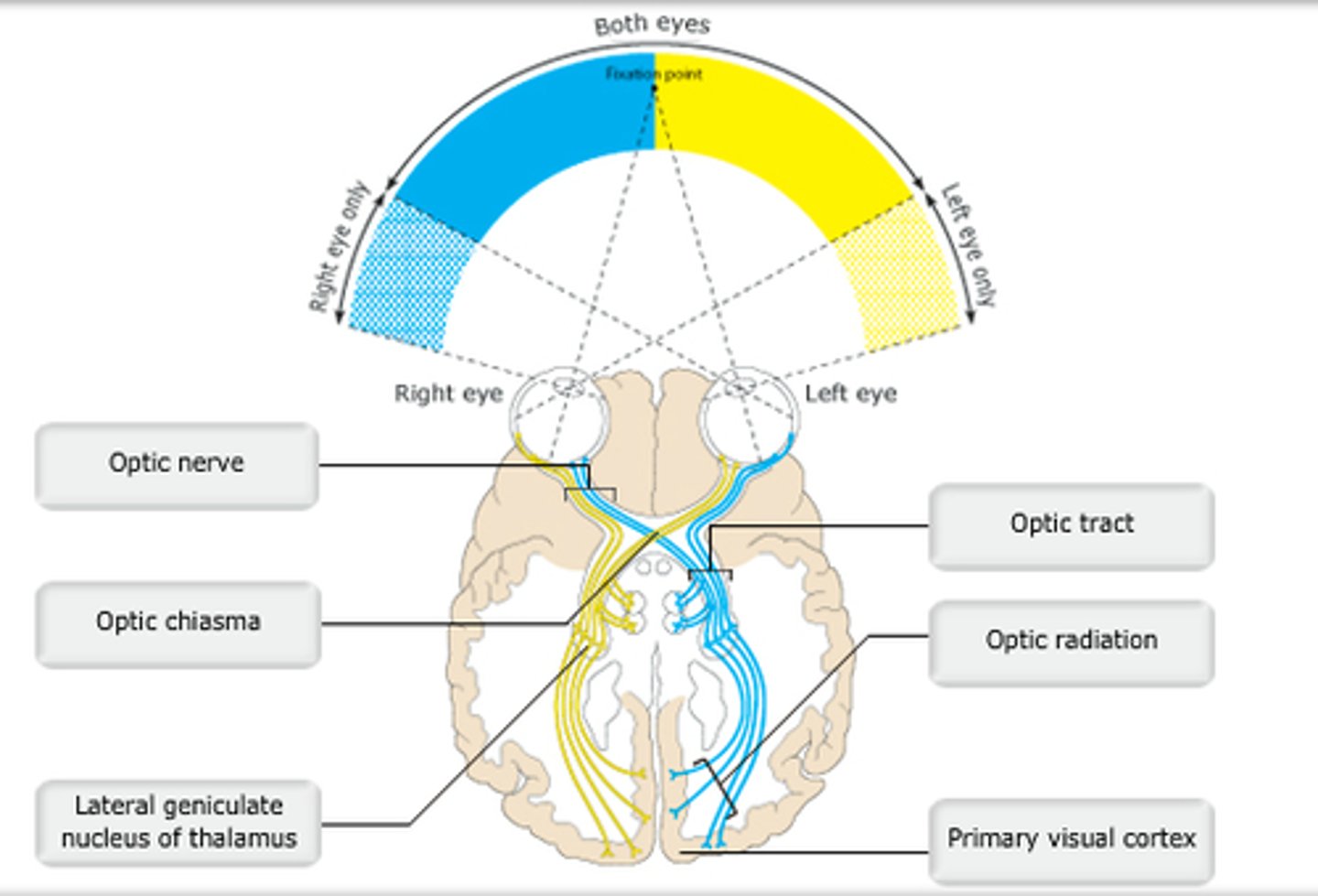
sclera
Which portion of the eye is covered by conjunctiva?
thalamus
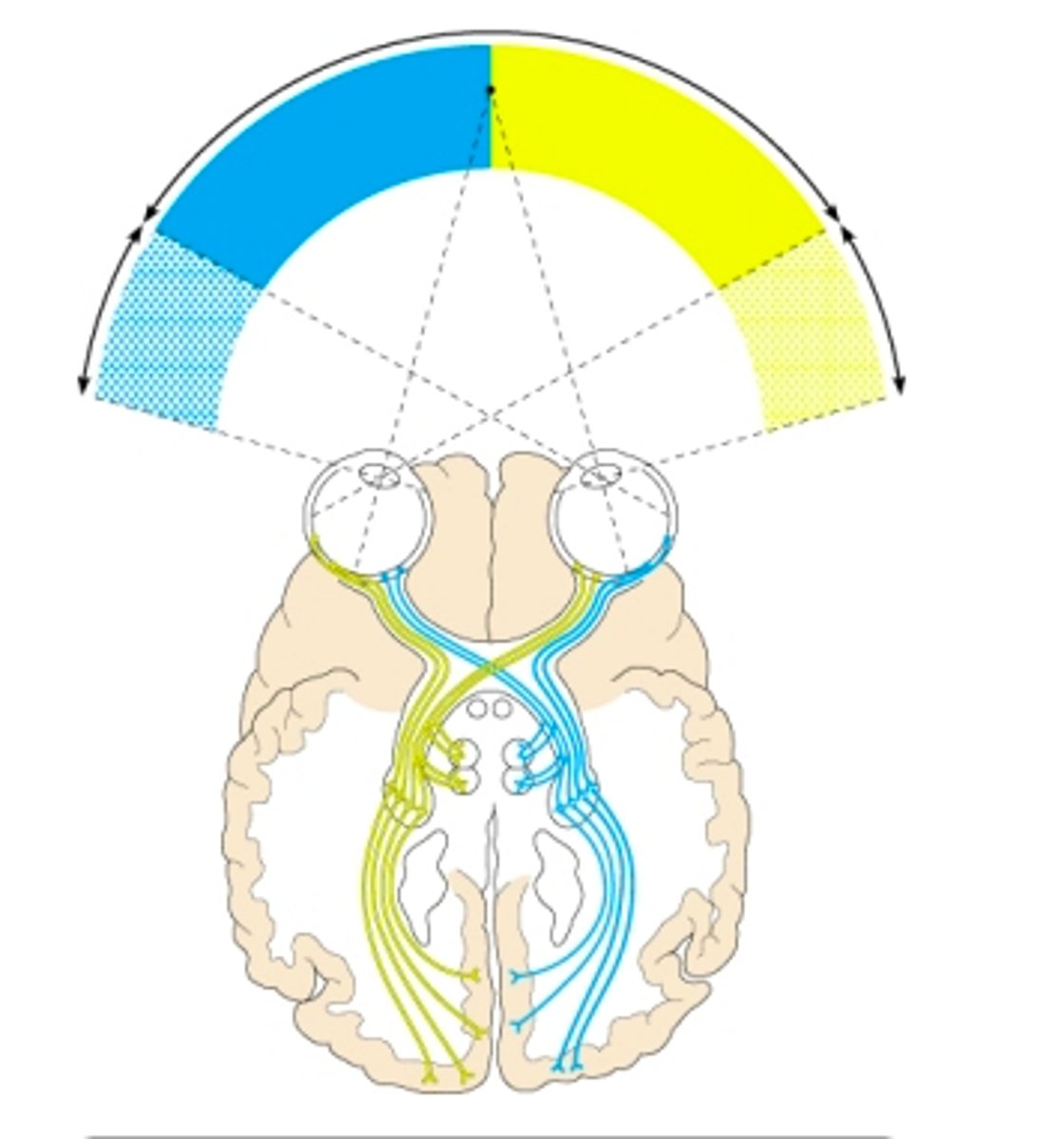
In which region of the brain do the axons of the optic tract synapse?
behind the retina / nearby
In hyperopic (farsighted) eyes, diverging light rays from nearby objects cause the focal point to occur __________, resulting in __________ objects to appear blurry.
C. It is renewed continuously
Which of these statements concerning vitreous humor is FALSE?
A. Vitreous humor transmits light.
B. It supports the posterior surface of the lens.
C. It is renewed continuously.
D. It helps maintain intraocular pressure.
E. It holds the neural retina firmly against the pigmented layer of the retina.
suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus to regulate daily biorhythms
In addition to sending visual information to the primary visual cortex, some axons from the optic tracts go to the __________.
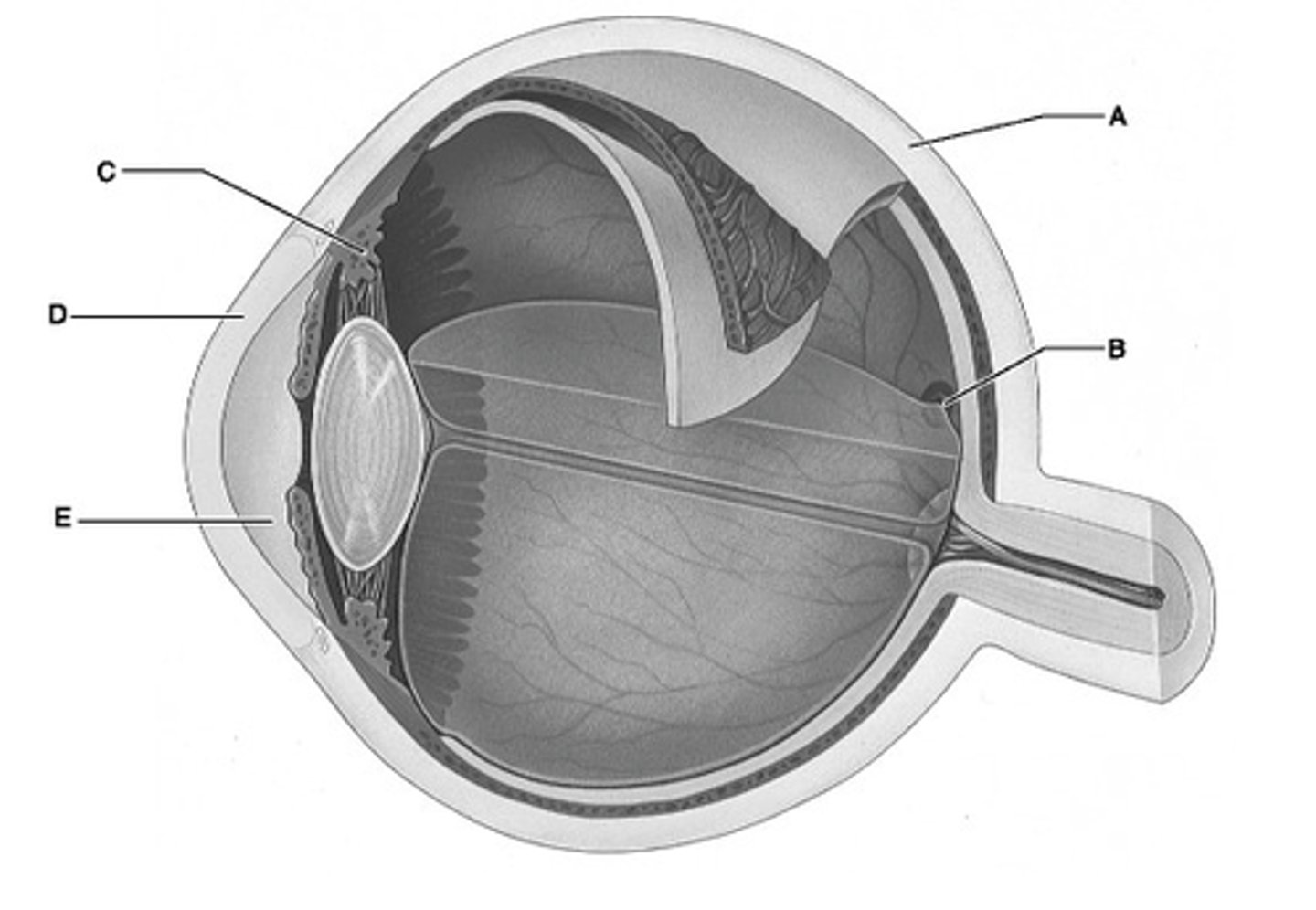
D
Identify the letter that indicates the transparent portion of the fibrous layer.
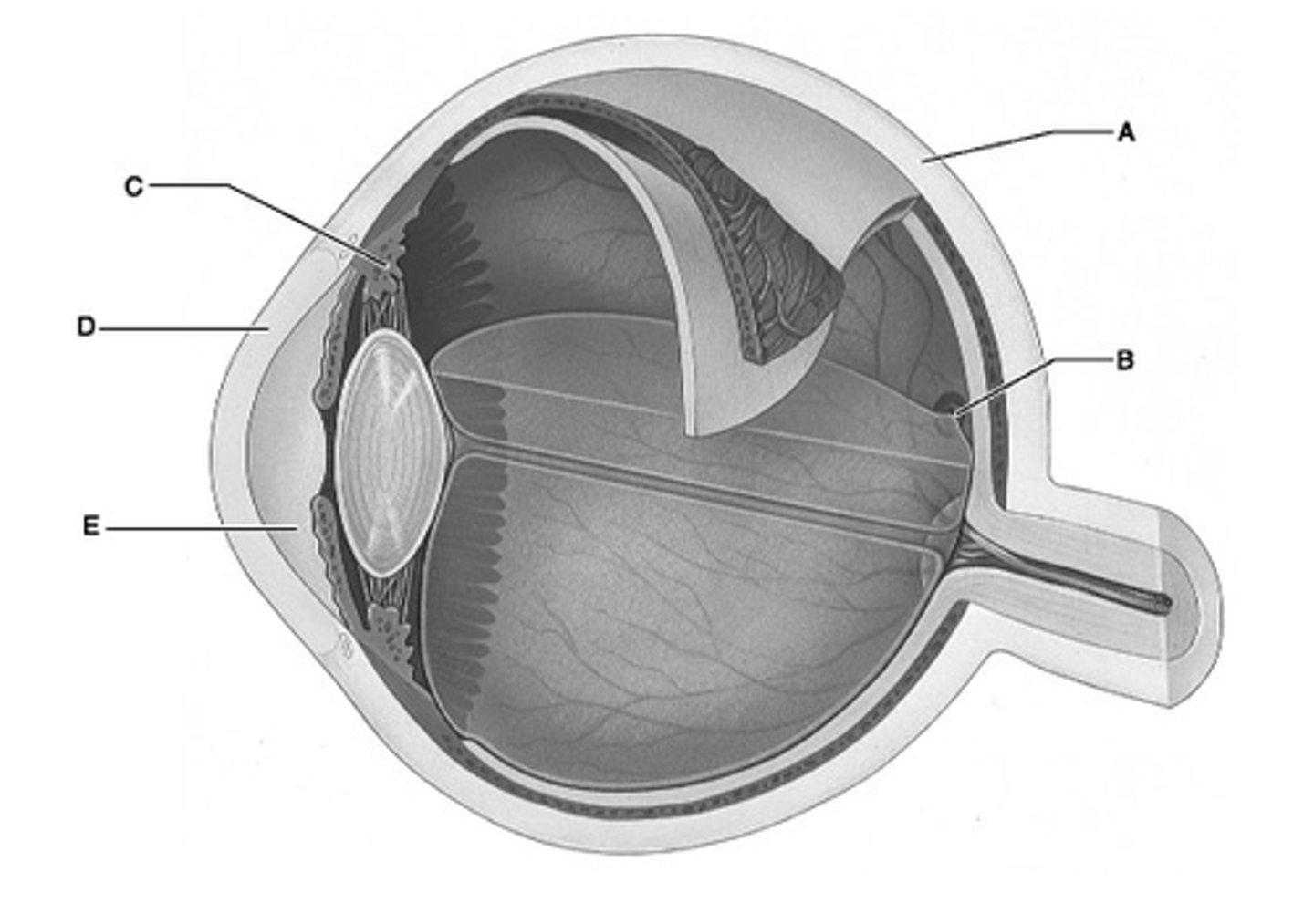
A
Identify the letter that indicates the portion of the fibrous layer known as the sclera.
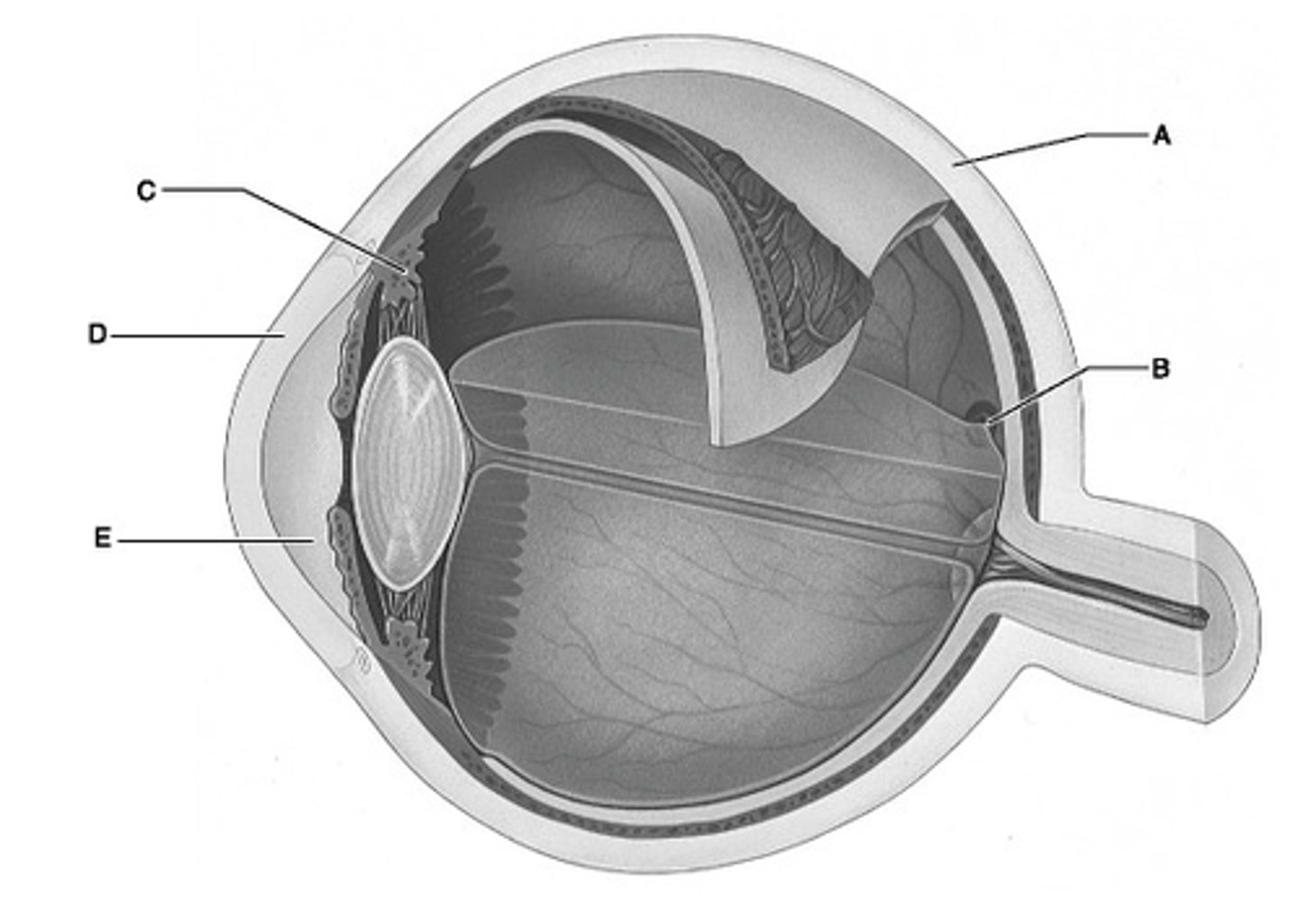
E
Identify the letter that indicates the anterior segment, which is filled with aqueous humor.
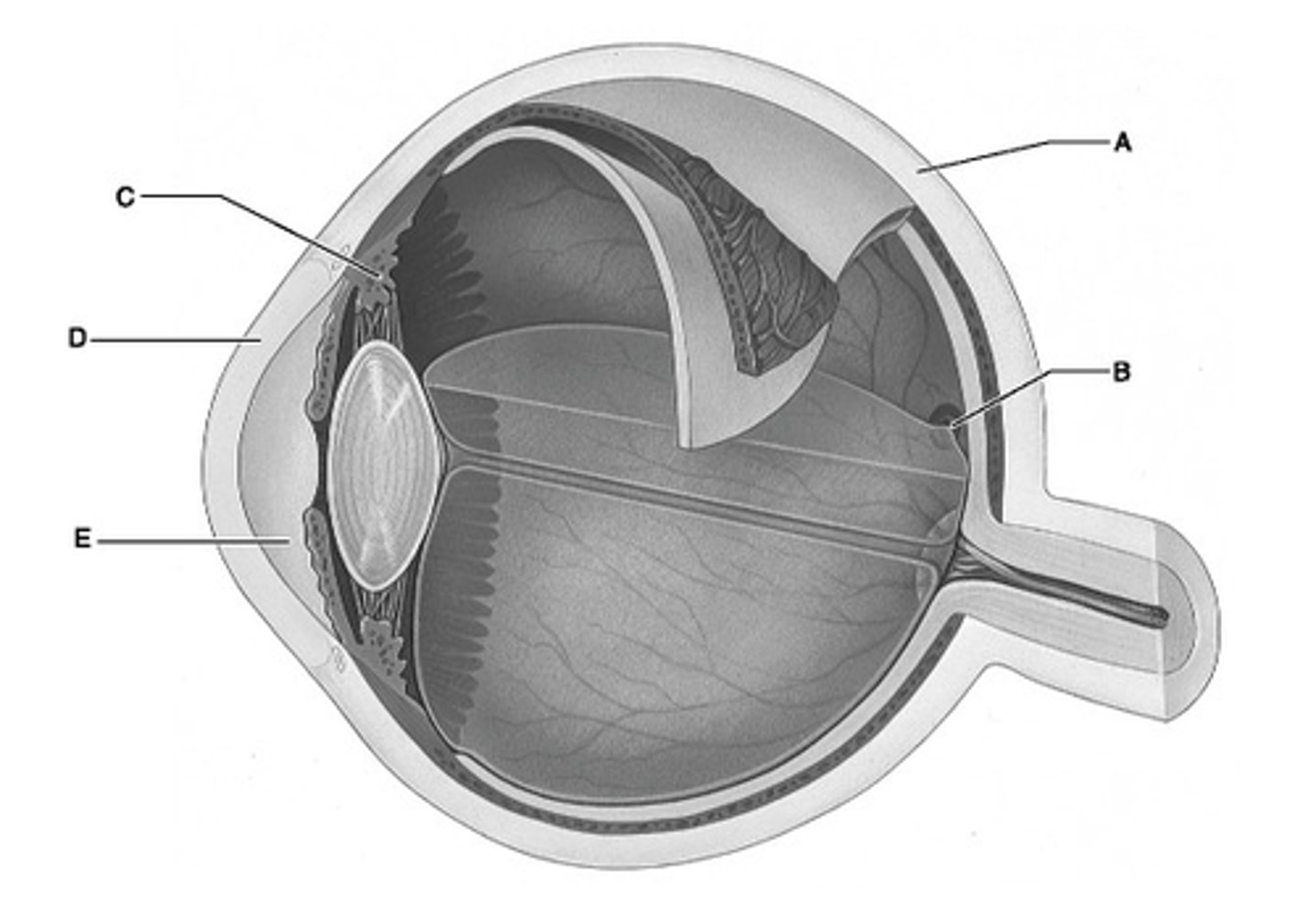
C
Identify the letter that indicates the ciliary body.
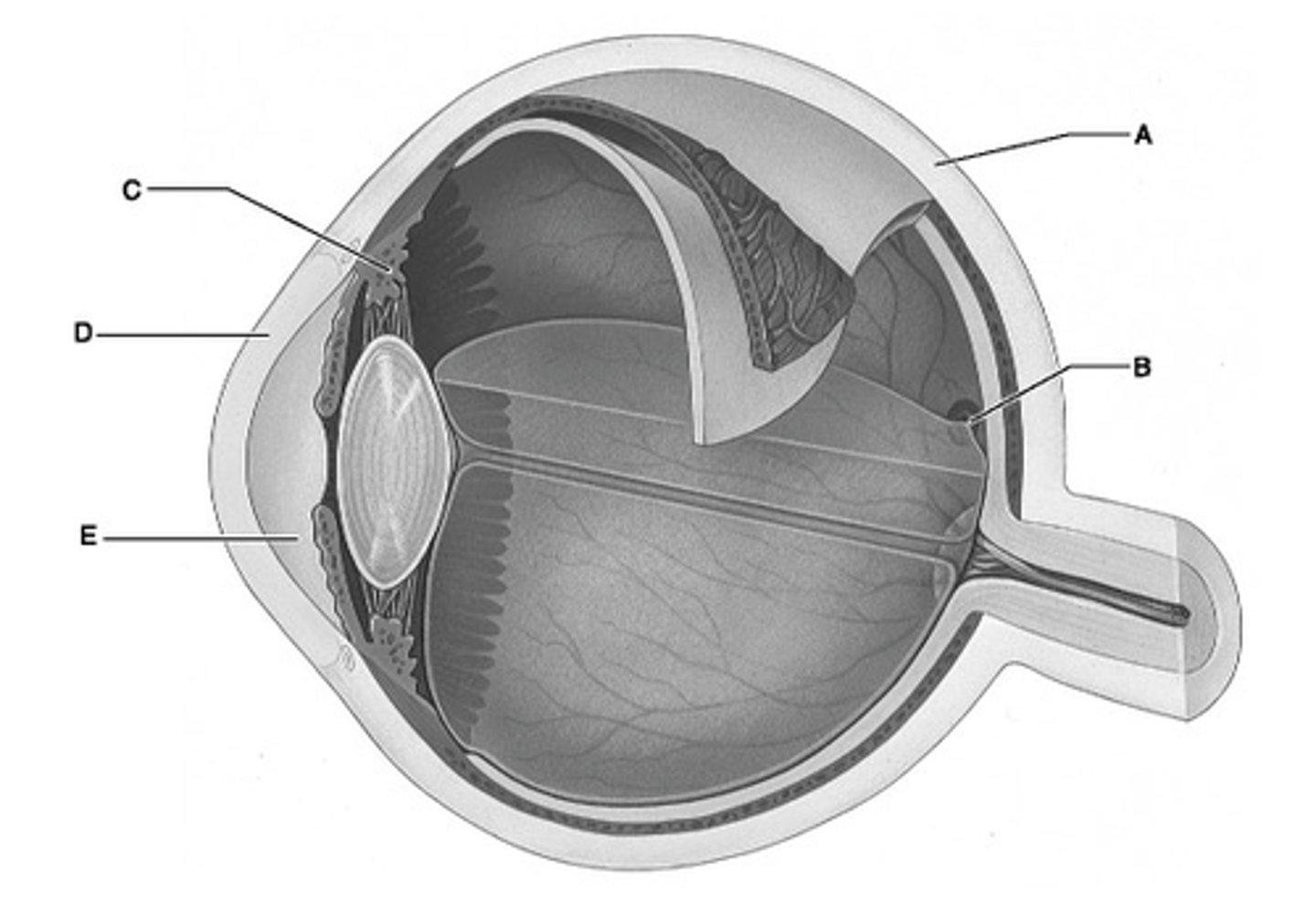
B
Identify the letter that indicates the region of the retina that contains only cones and provides maximal visual acuity.
choroid
Melanin-containing layer of the eye's vascular tunic.
vitreous humor
Fluid filling the posterior segment of the eye.
lens
Clouding of which of the following structures would lead to a clinical condition known as a cataract?
center of the cornea
Which of the following lies closest to the anterior pole of the eye?
dilator/sphincter pupillae muscles
Which of the following controls the amount of light entering the eye?
A. iris
Each of the following structures participates in bending of light entering the eye except the __________.
A. iris.
B. lens.
C. cornea.
D. vitreous humo
pupil
What structure regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye?
A. optic chiasma
Which of the following could not be seen as one looks into the eye with an ophthalmoscope?
A. optic chiasma
B. fovea centralis
C. macula lutea
D. optic disc
occipital lobe
The center for vision in the cerebral cortex is located in the _________.
study this diagram
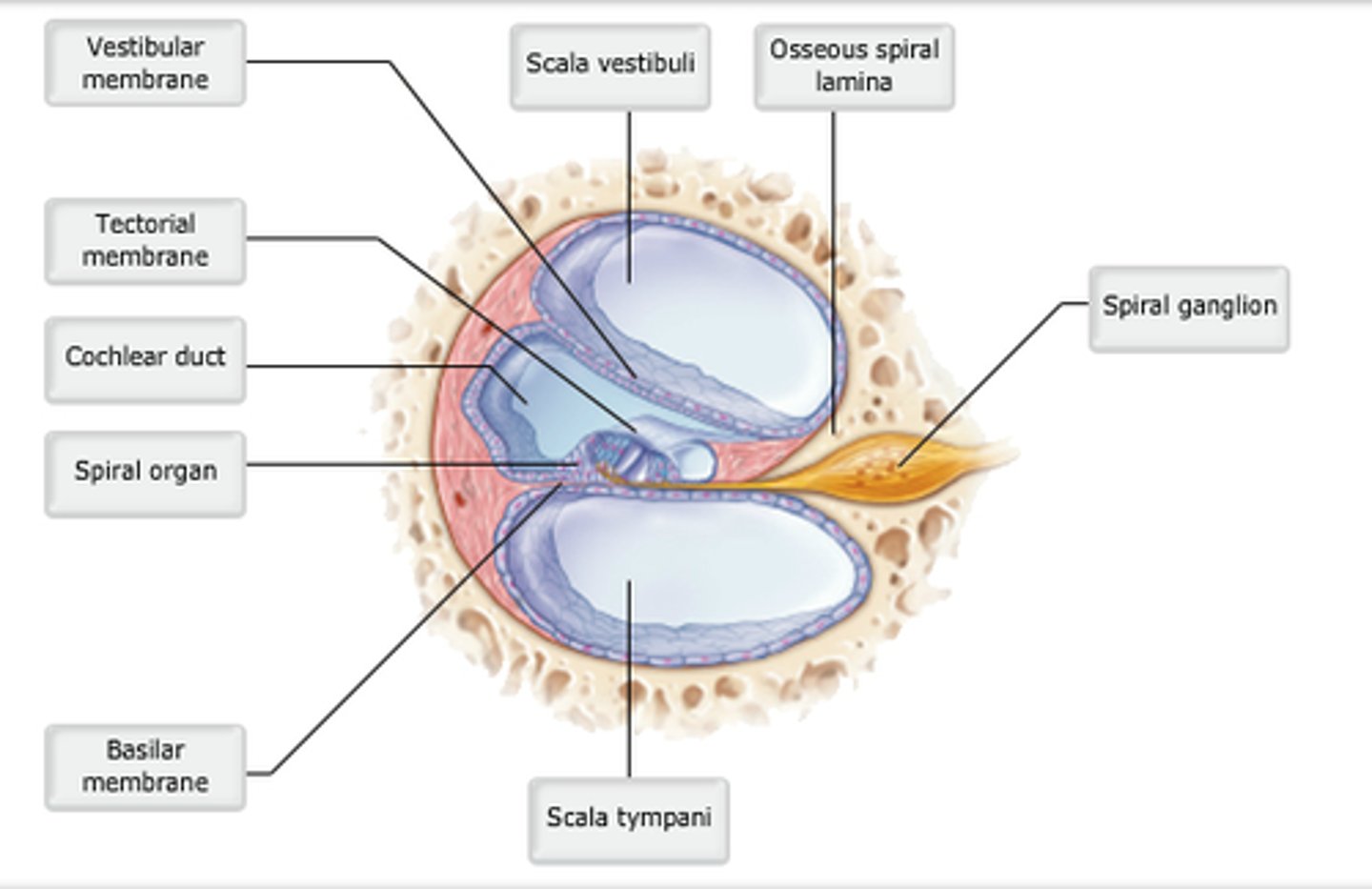
study this diagram
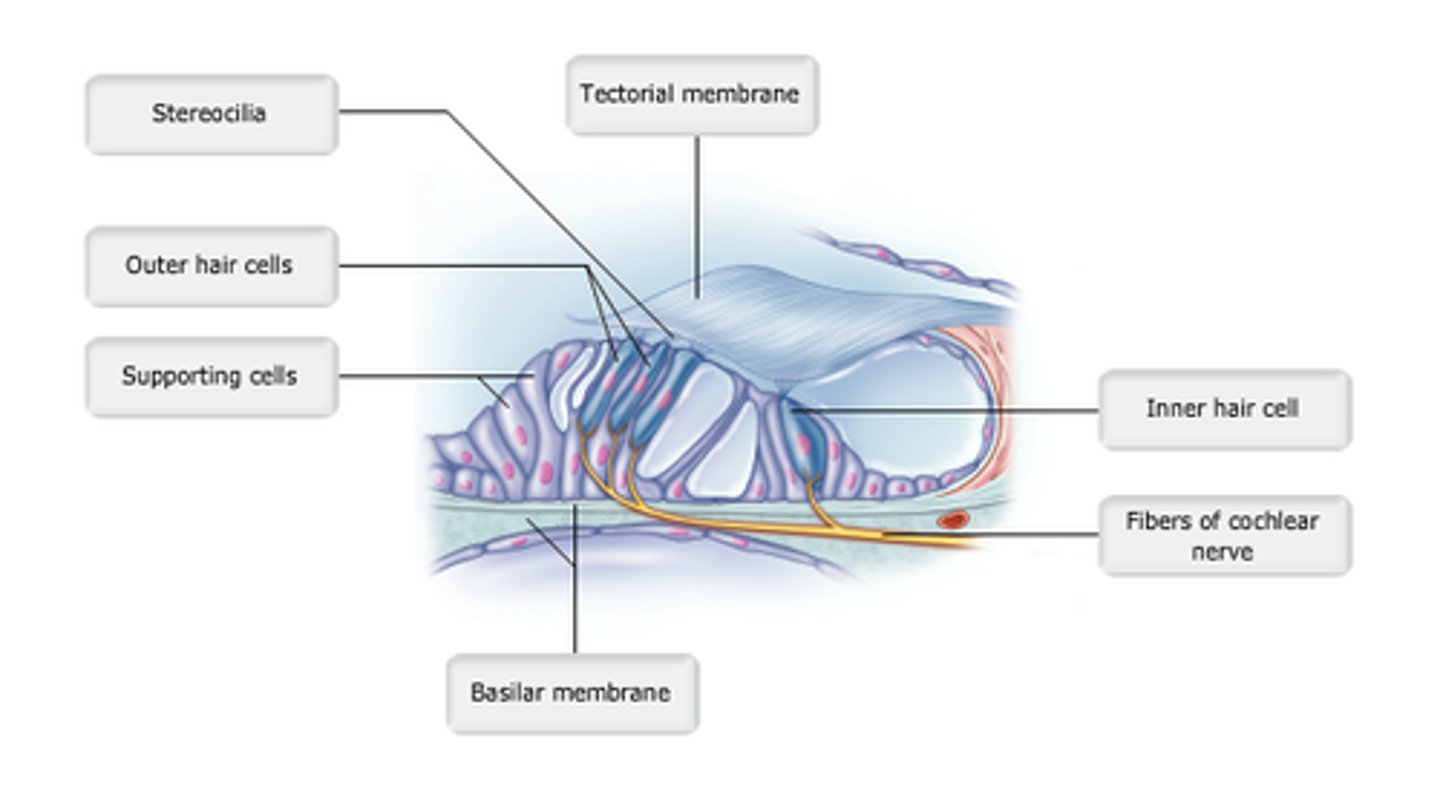
study this diagram
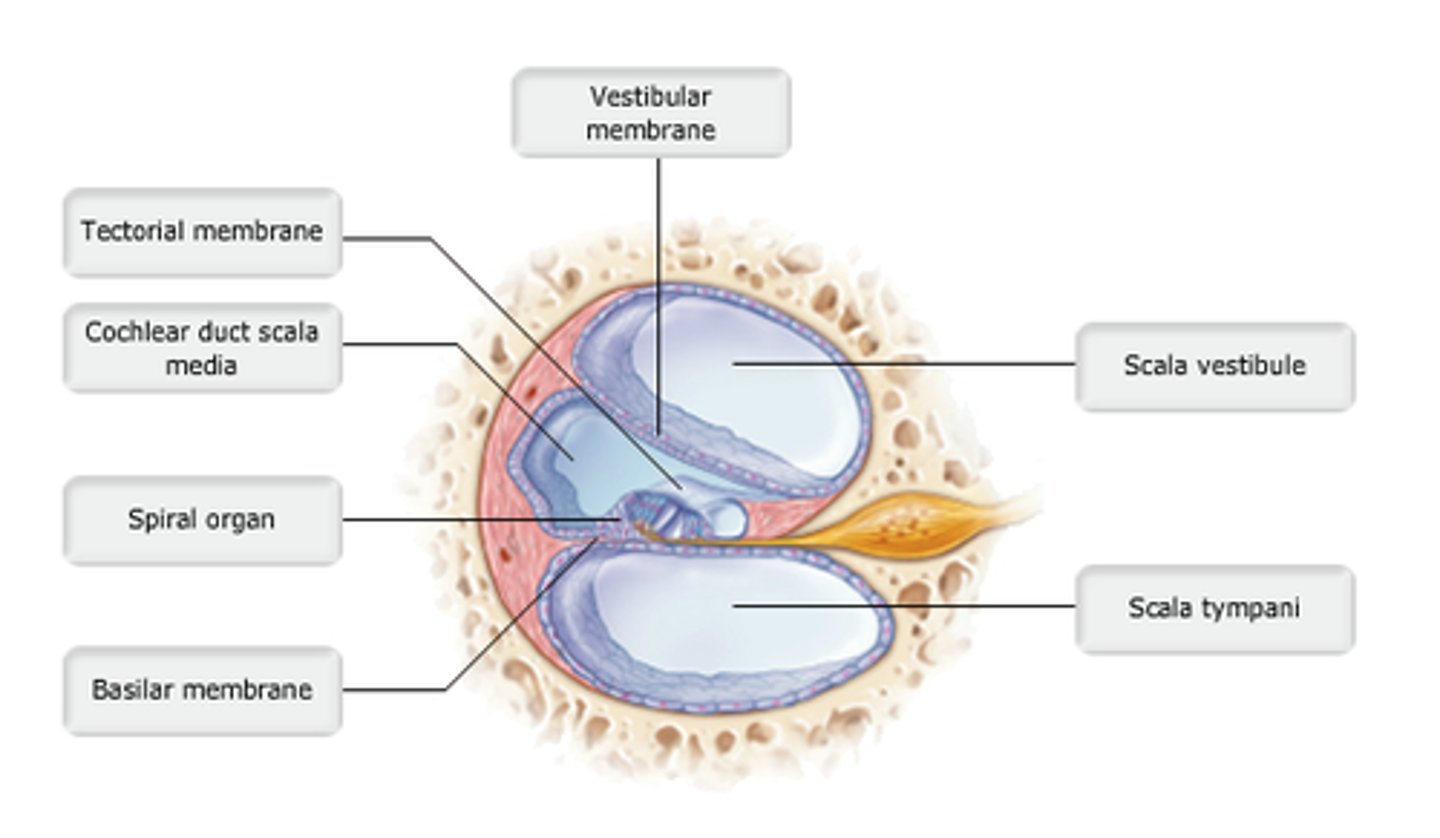
study this diagram
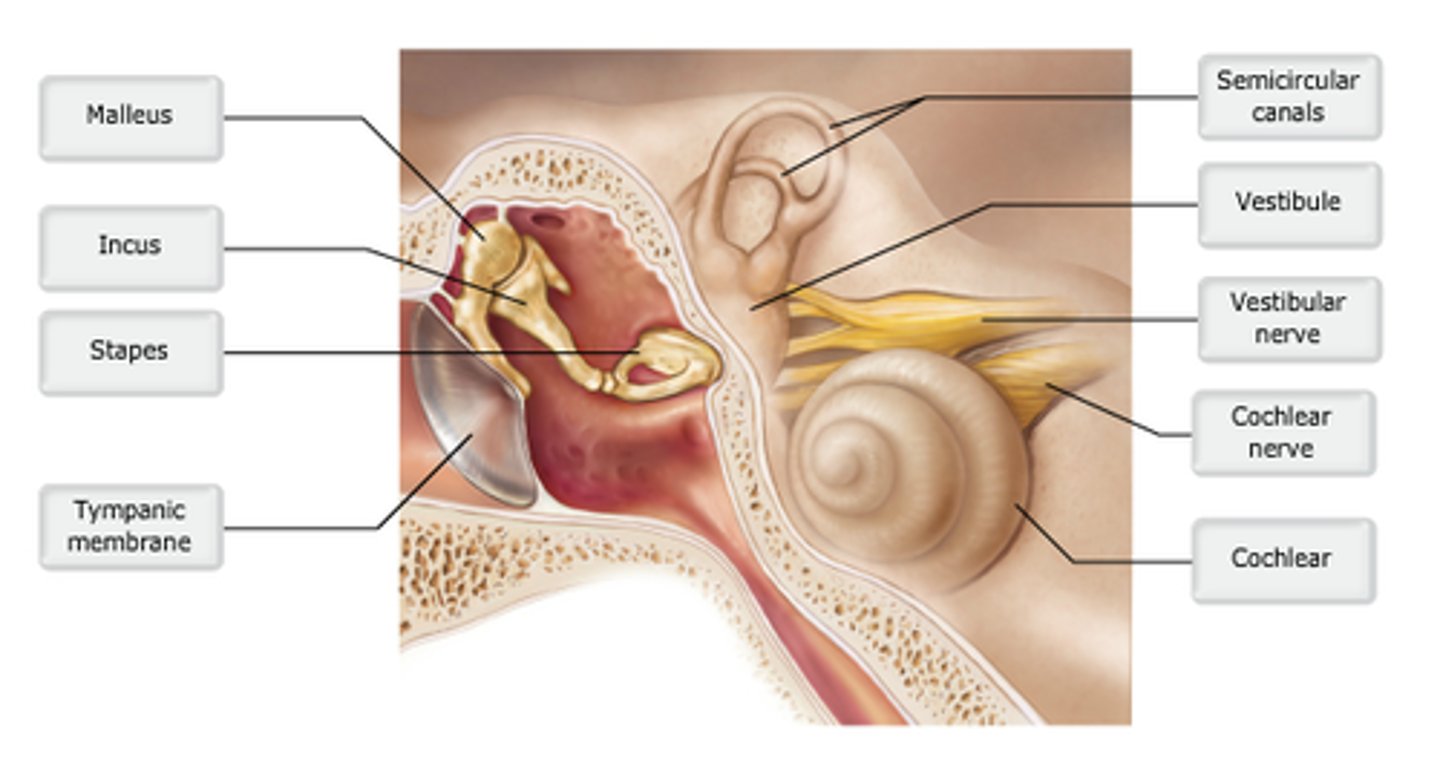
study this diagram
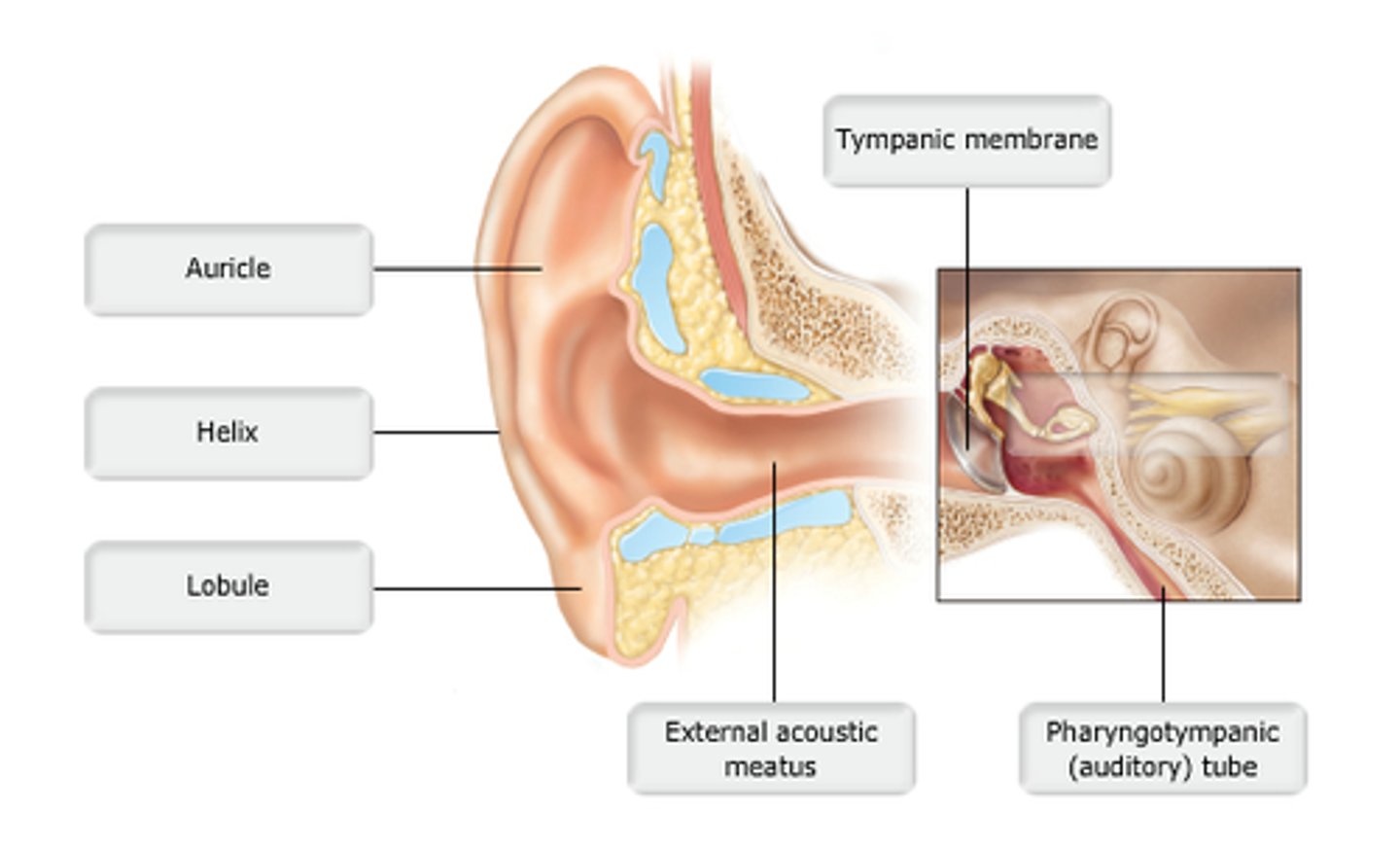
study this diagram
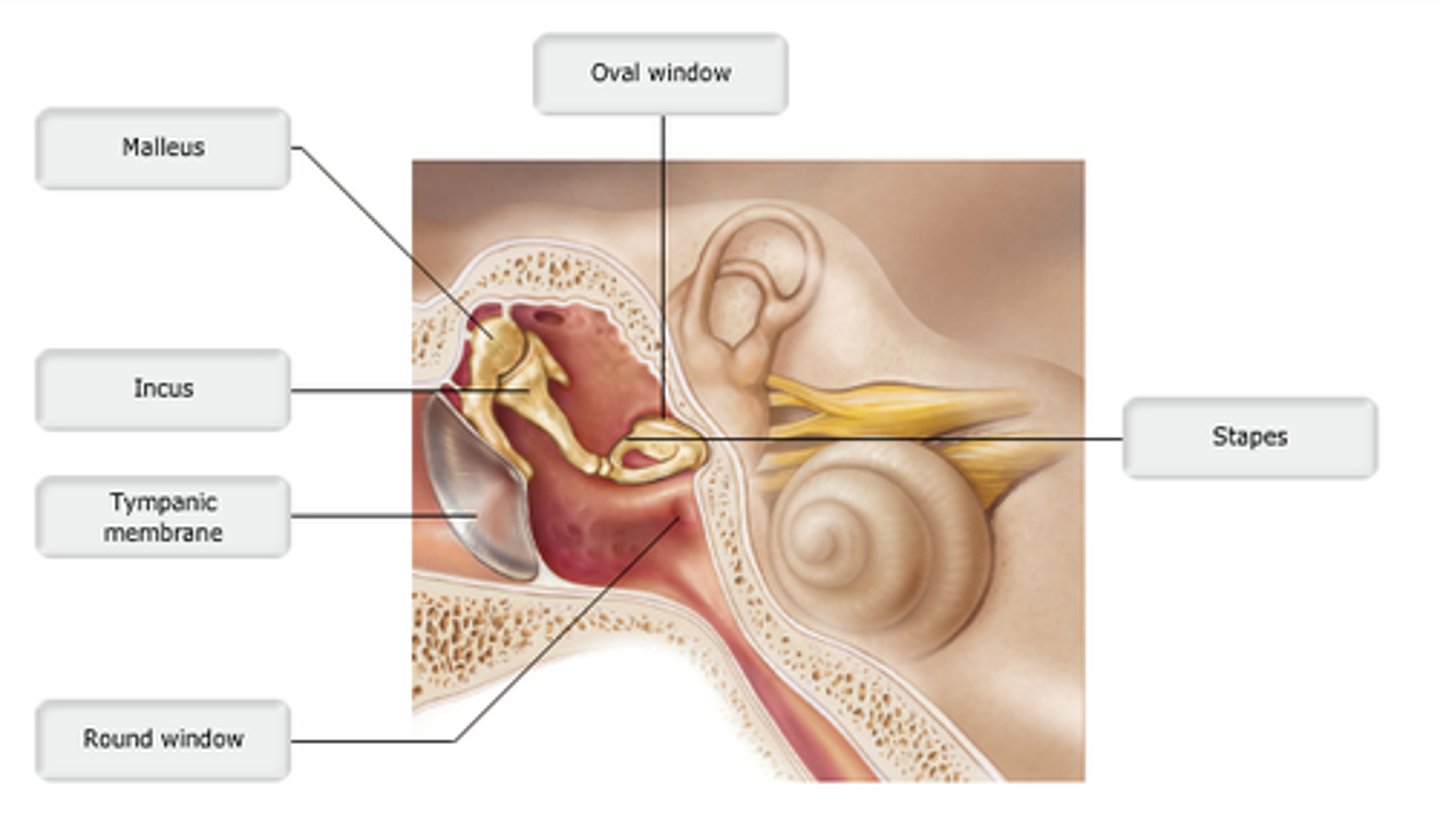
study this diagram
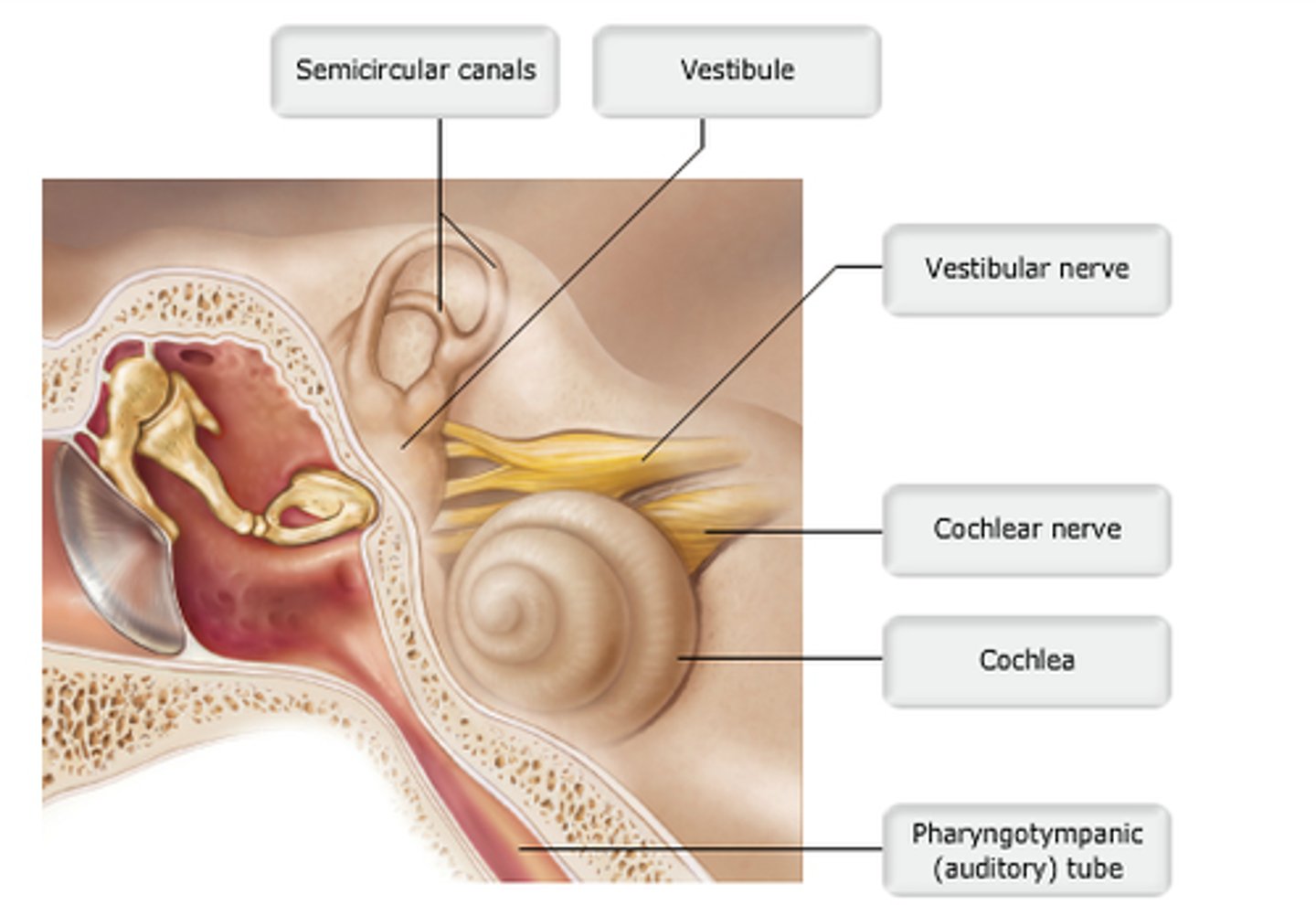
study this diagram
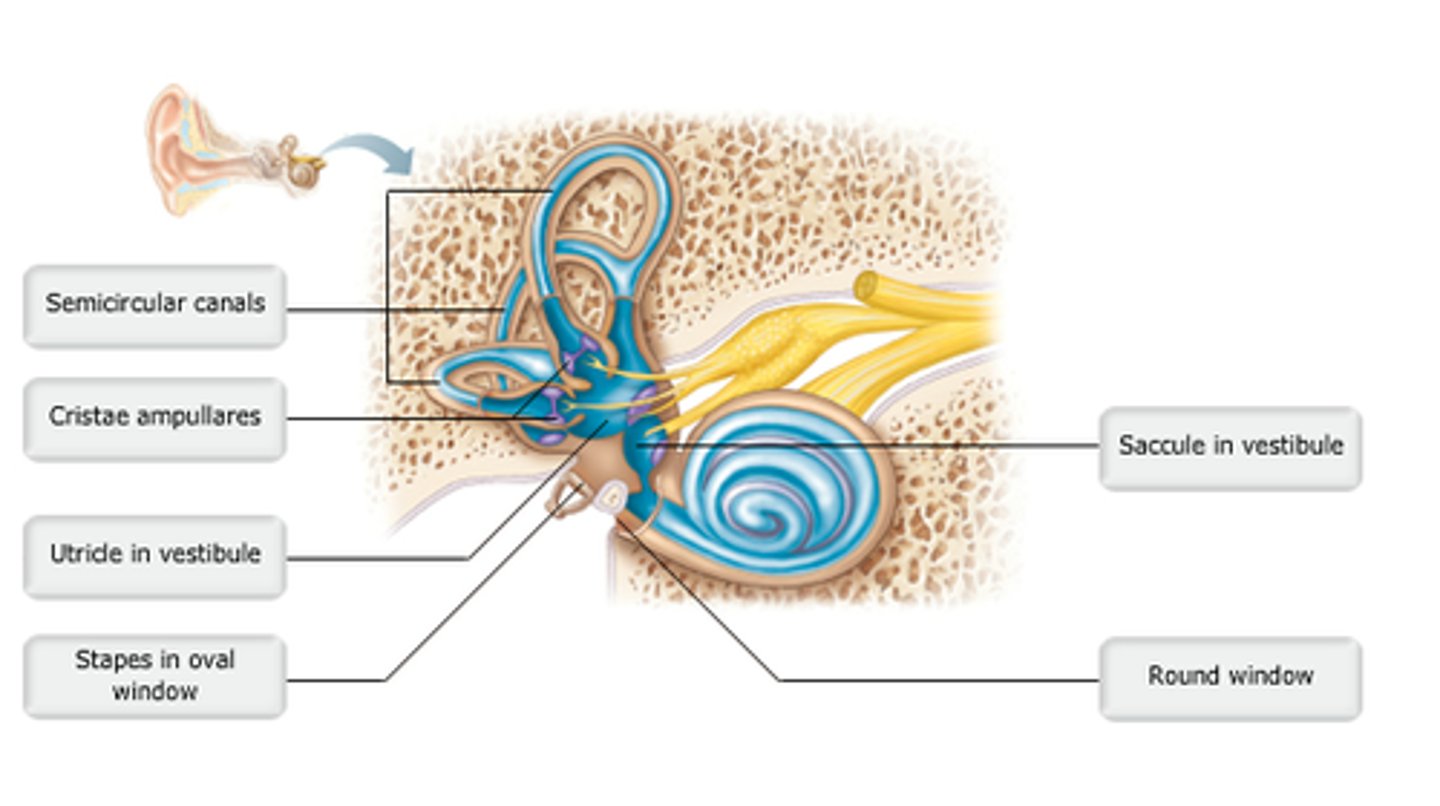
middle
Which portion of ear contains ear ossicles?
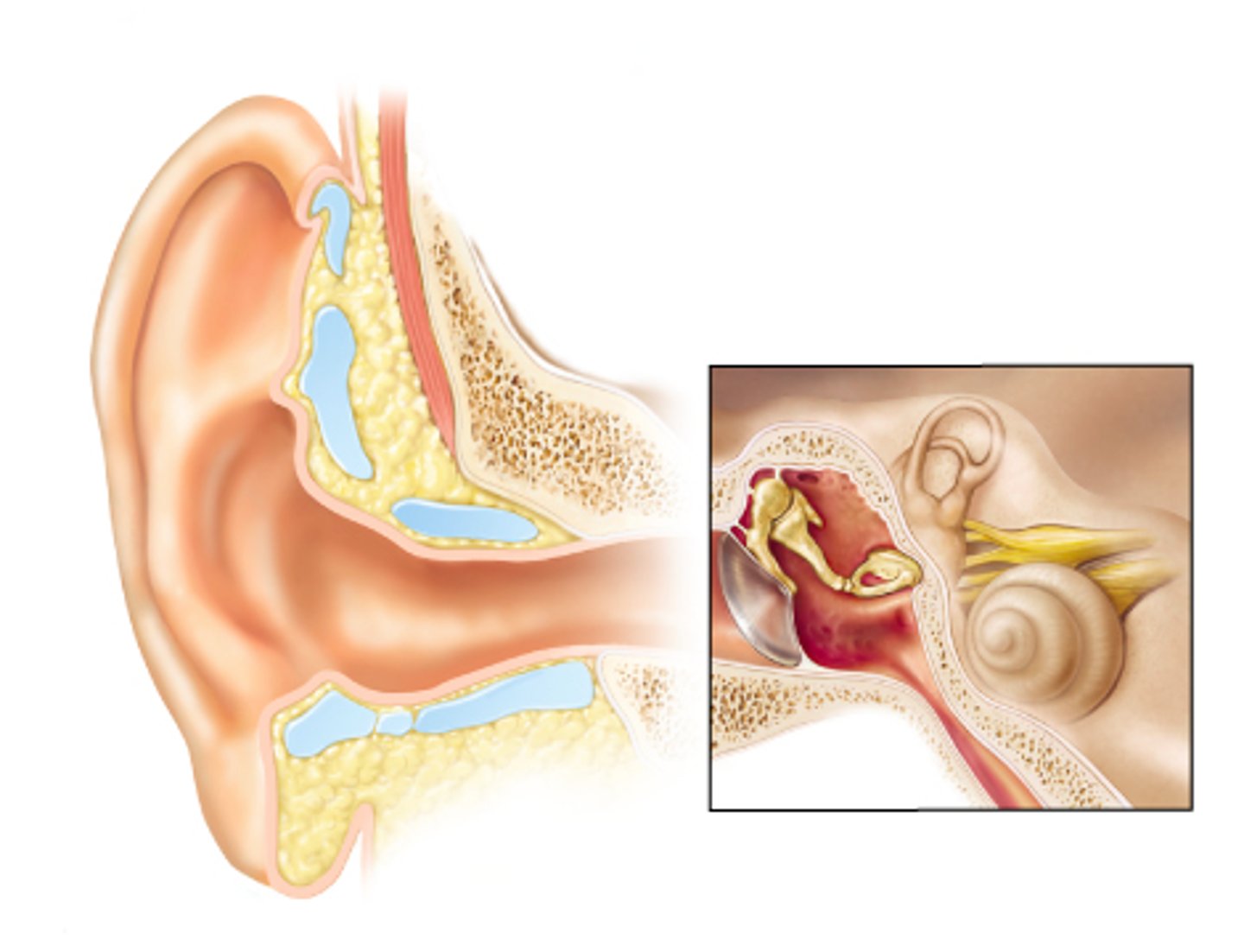
The tensor tympani and stapedius muscles contract reflexively.
You are listening to music on your iPod at a very loud volume. What happens in your middle ear to protect the hearing receptors in your inner ear?
pathway responds to loss of balance and must be rapid and reflexive to prevent injury
The equilibrium pathway transmits most of its information to lower brain centers because the __________.
oval window
The stapes vibrates against the __________.
E
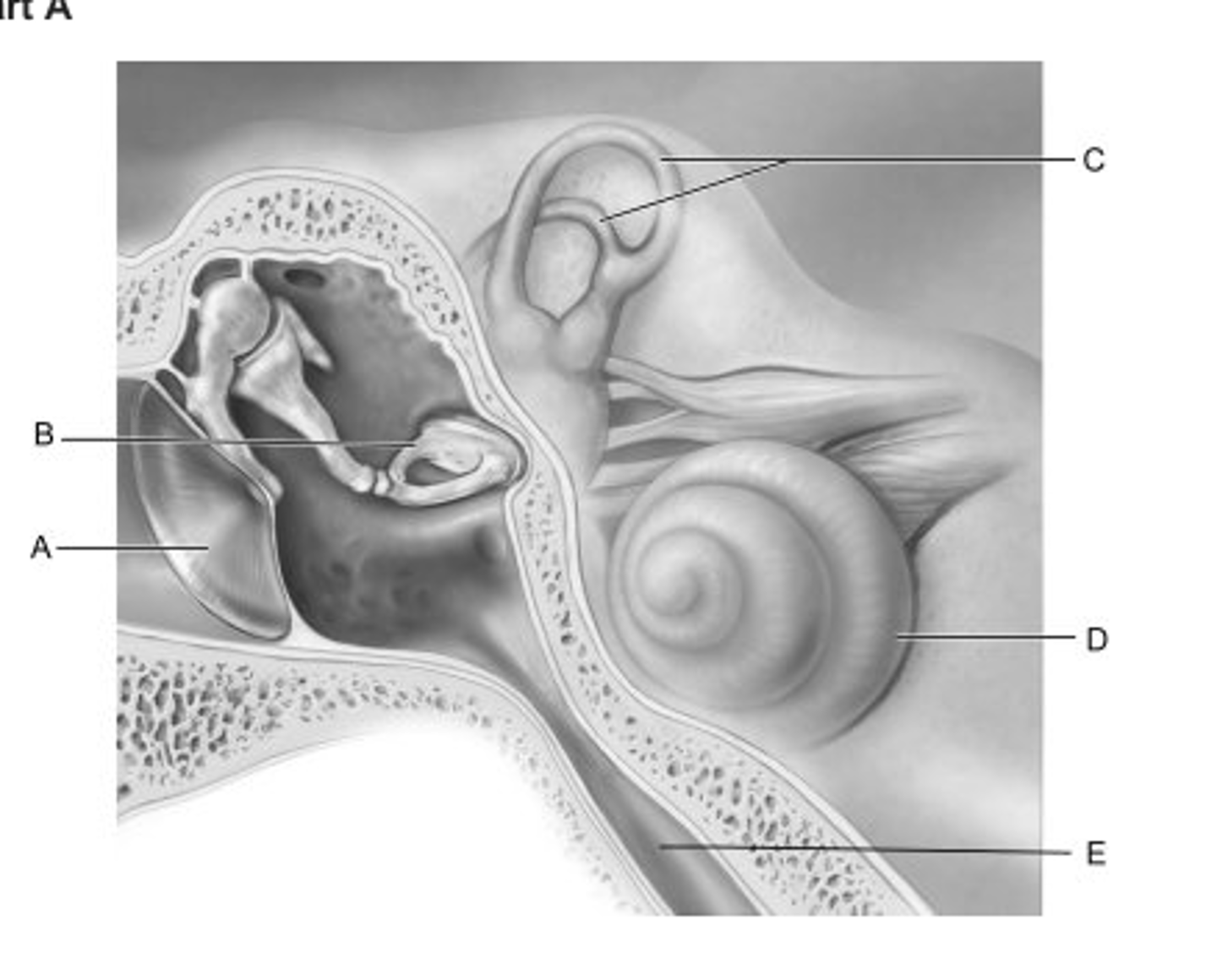
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is important in equalizing air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
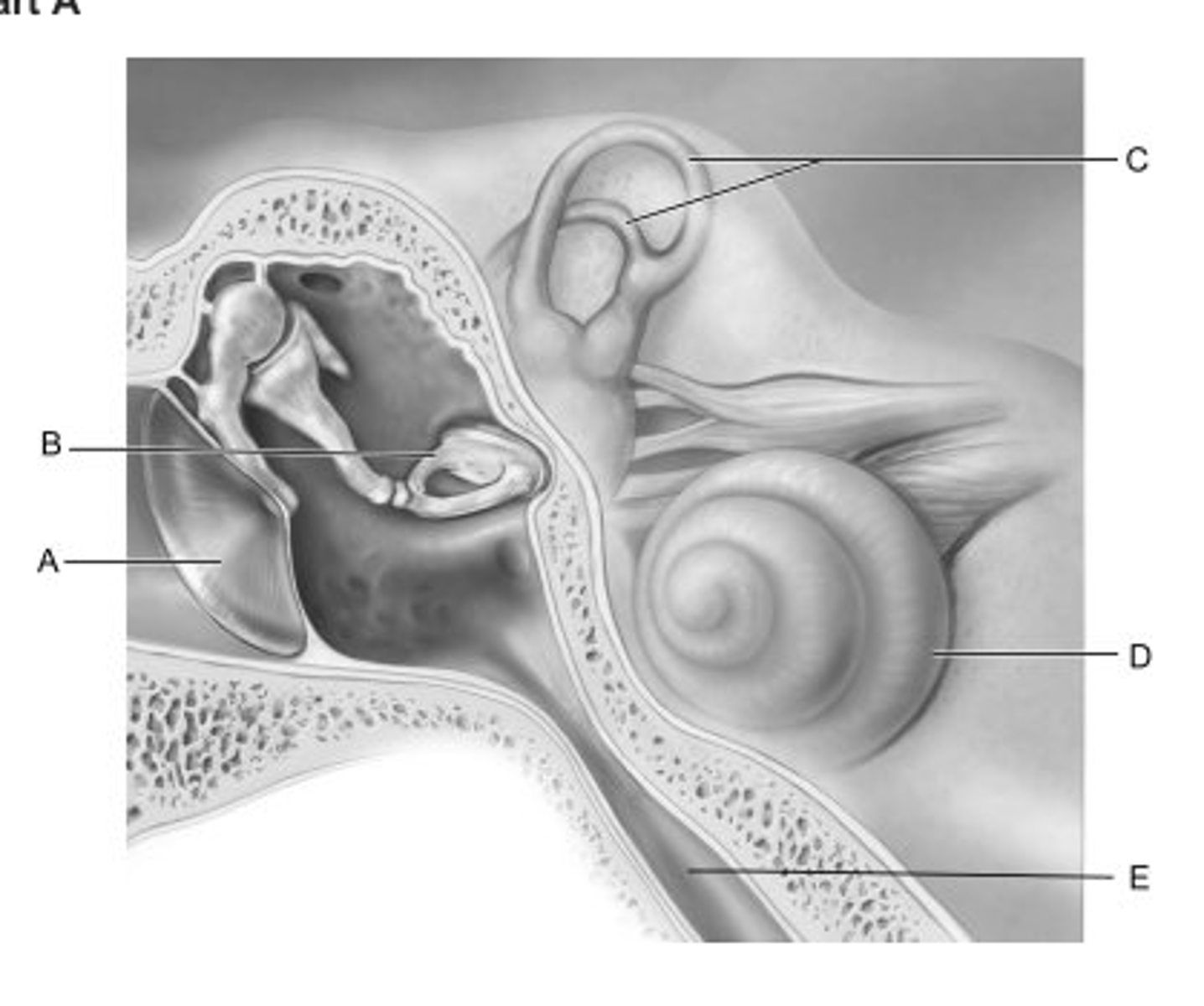
A
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is the boundary between the external and middle ear.
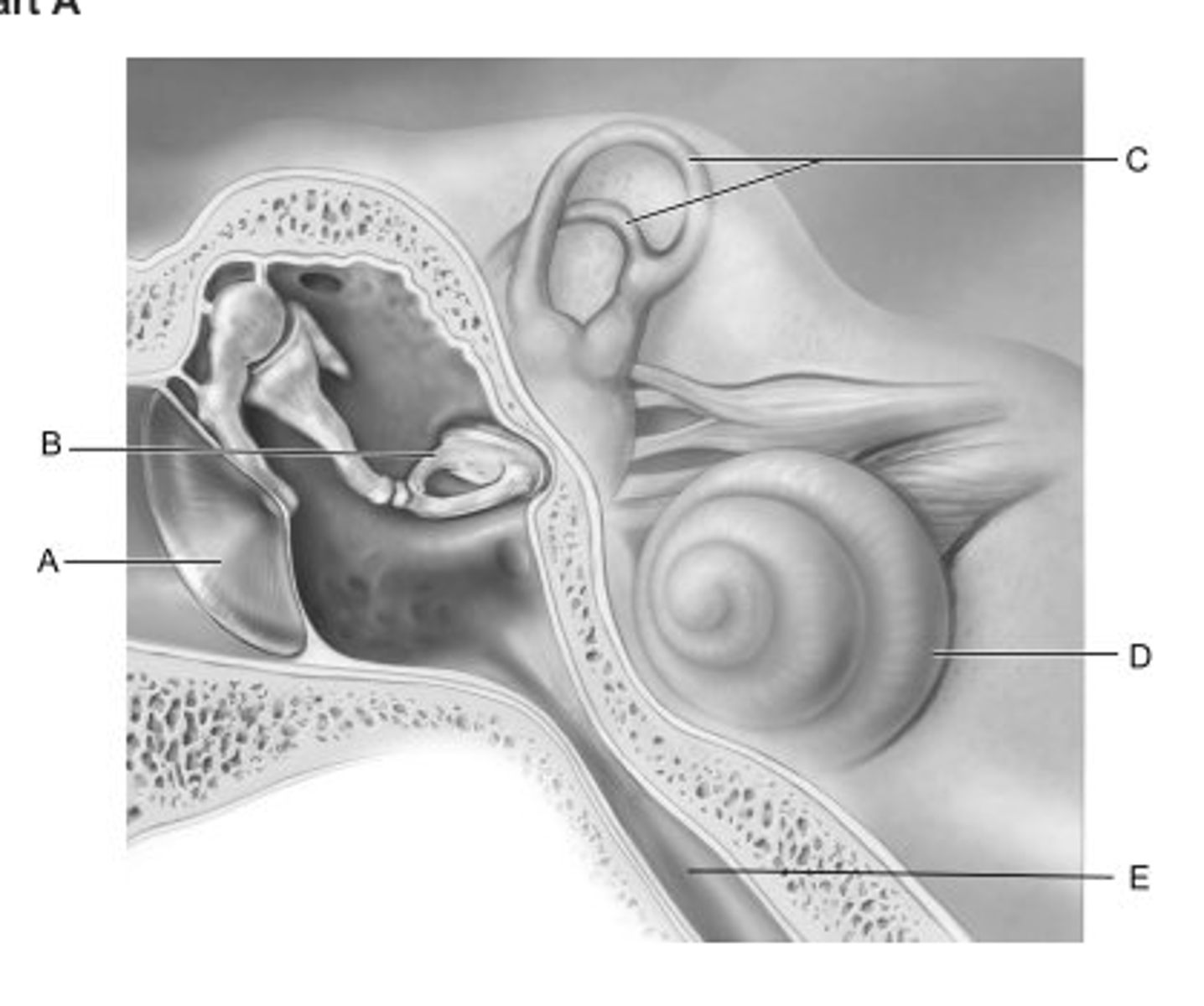
B
Identify the letter that indicates the middle ear ossicle that is known as the stirrup.
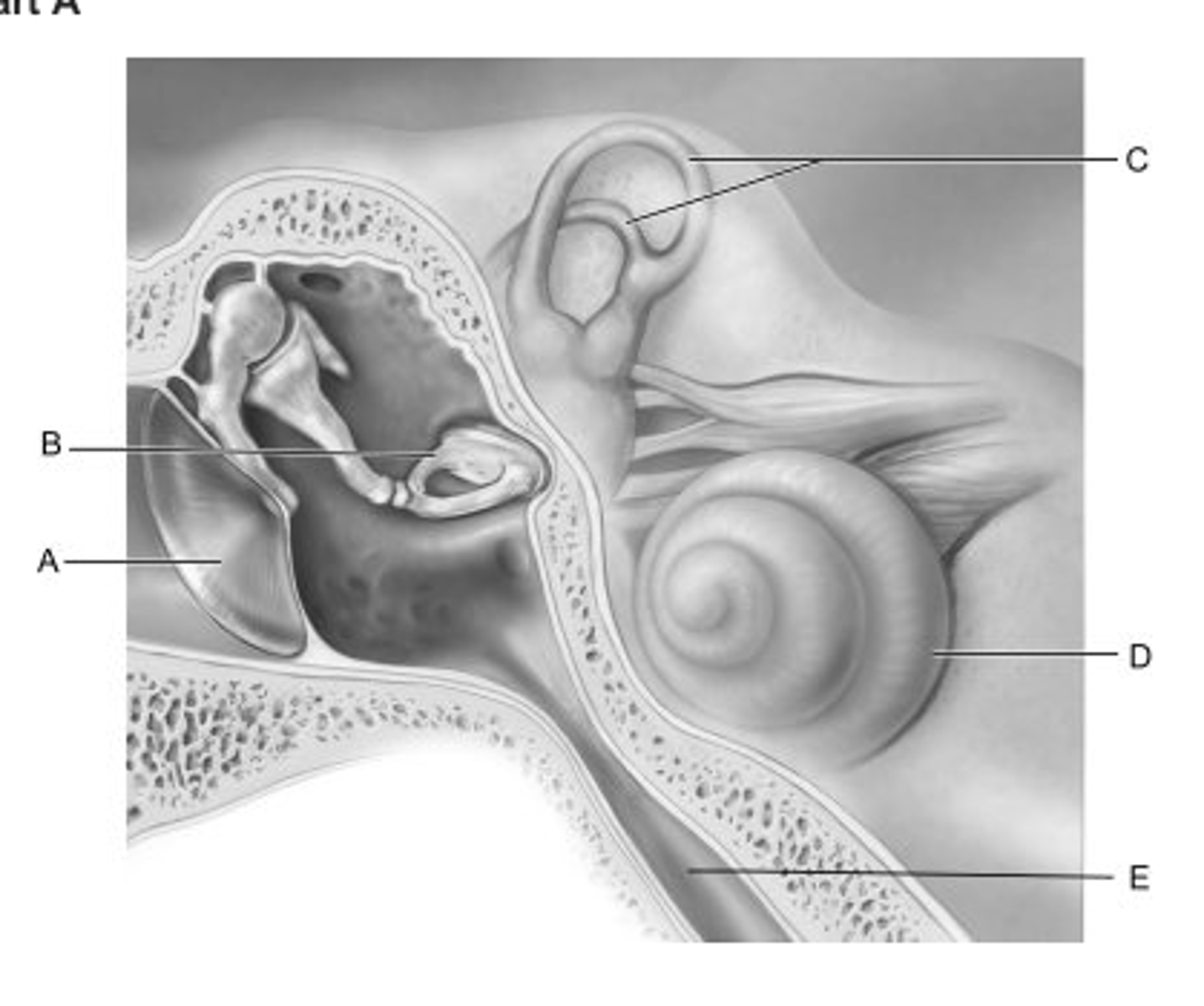
C
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that contains receptors for rotational acceleration.
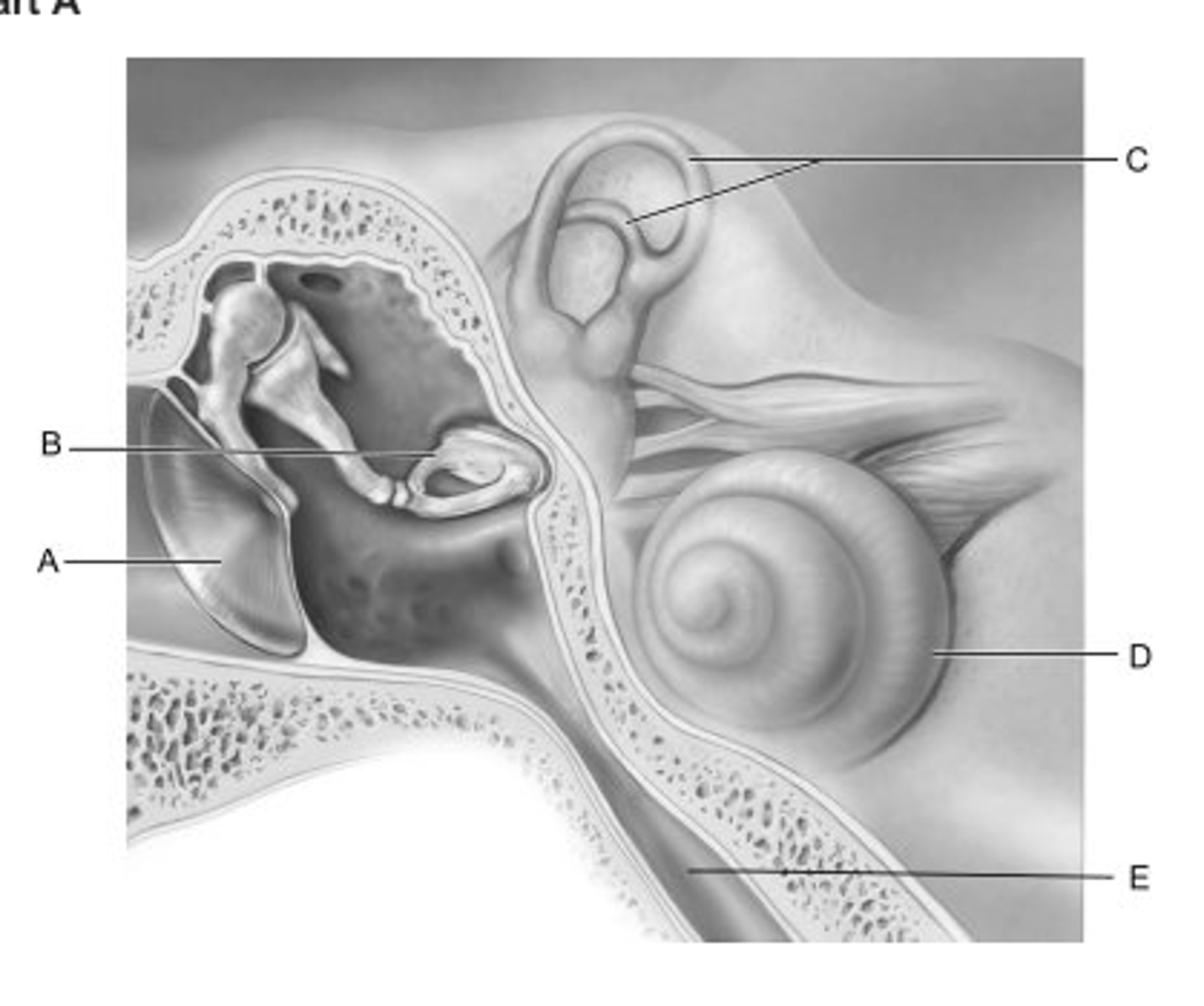
D
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is called the cochlea.
oval window
Membrane attached to the stapes.
vestibule
Bony labyrinth structure containing the utricle and saccule.
otoliths
Calcium carbonate crystals of the macula.
cochlear duct
Endolymph-filled structure containing receptors for hearing.
spiral organ.
The basilar membrane supports the______.
utricle
Along with the saccule, this structure senses linear acceleration.
both hearing and equilibrium.
Hair cells are receptor cells for________.
air
The middle ear cavity is normally filled with______.
cochlear duct.
Receptors for hearing are located in the_______.
B. vestibule
The external ear consists of each of the following structures except the______.
A. lobule.
B. vestibule.
C. auricle.
D. helix.
otoliths.
An essential part of the maculae involved in static equilibrium is/are the _________.
petrous
The bony labyrinth is located in which portion of the temporal bone?
air
The transmission of sound vibrations through the external acoustic meatus occurs chiefly through________.
stapes
The ossicle that is shaped like the stirrup of a saddle is the _________.
semicircular ducts.
The cristae ampullares in the inner ear are located in the __________.
true
true or false
The incus bridges the gap between the stapes connected to the oval window and the malleus connected to the tympanic membrane.
auricle
which structure is highlighted?
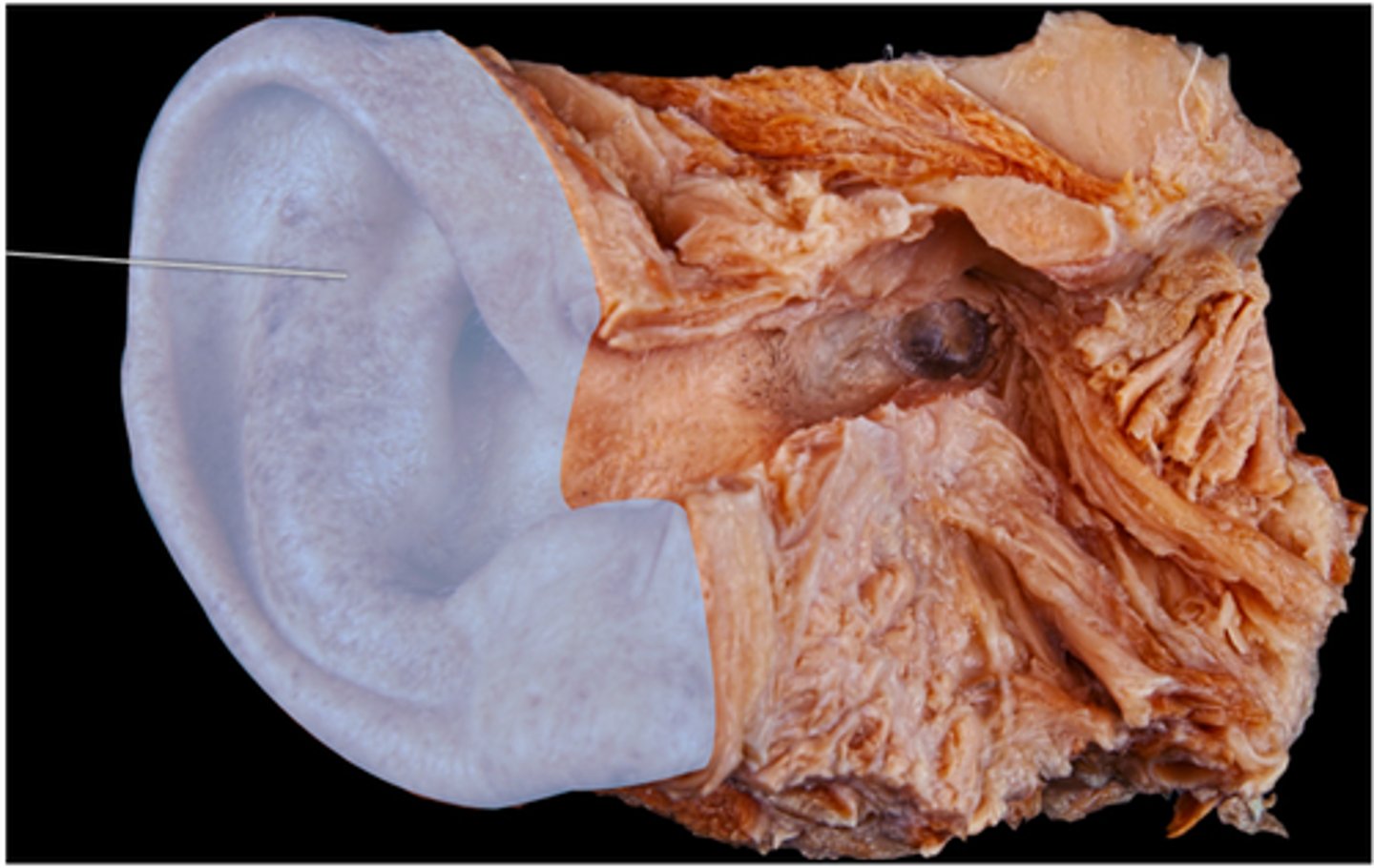
incus
which structure is highlighted?
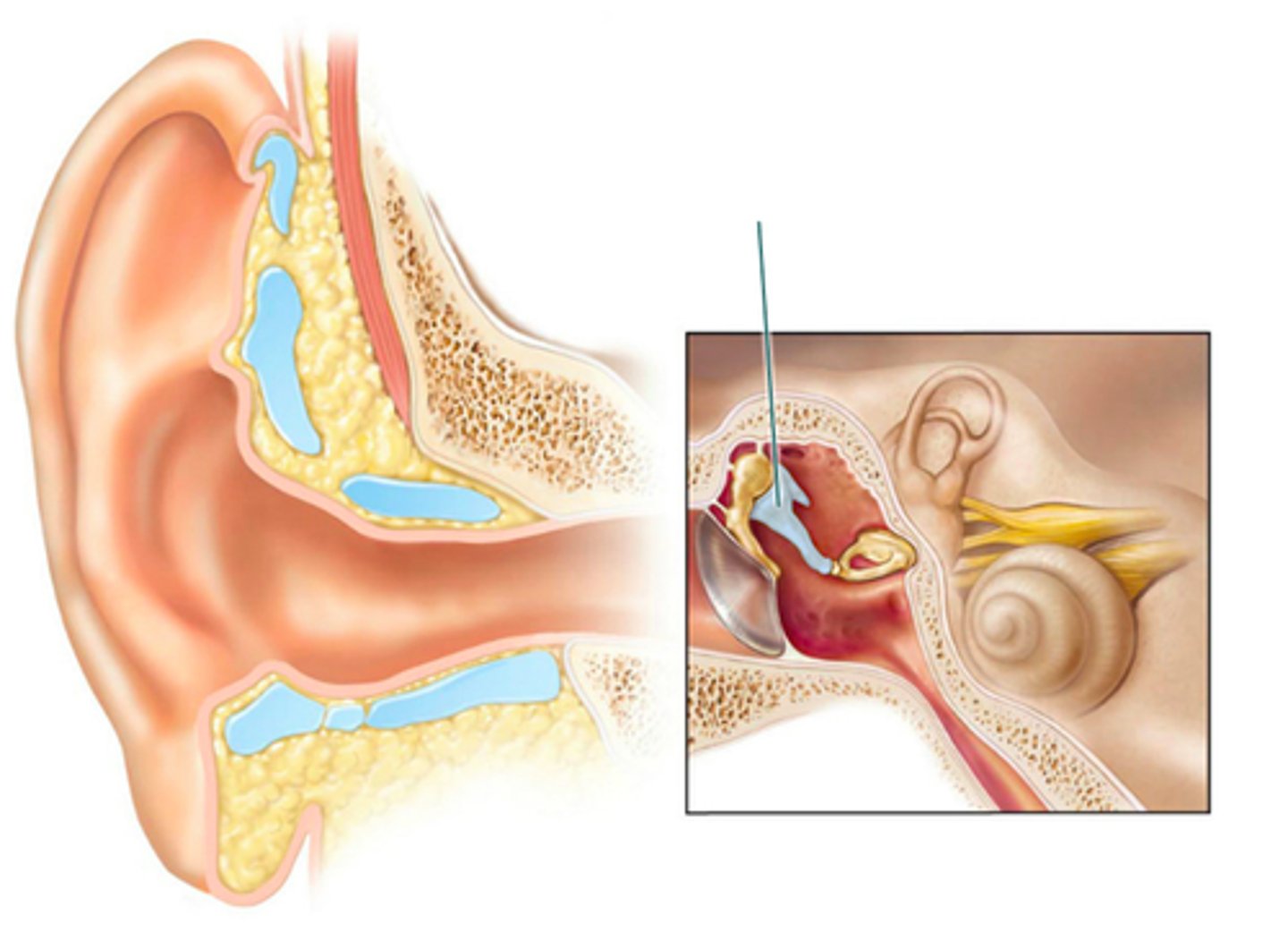
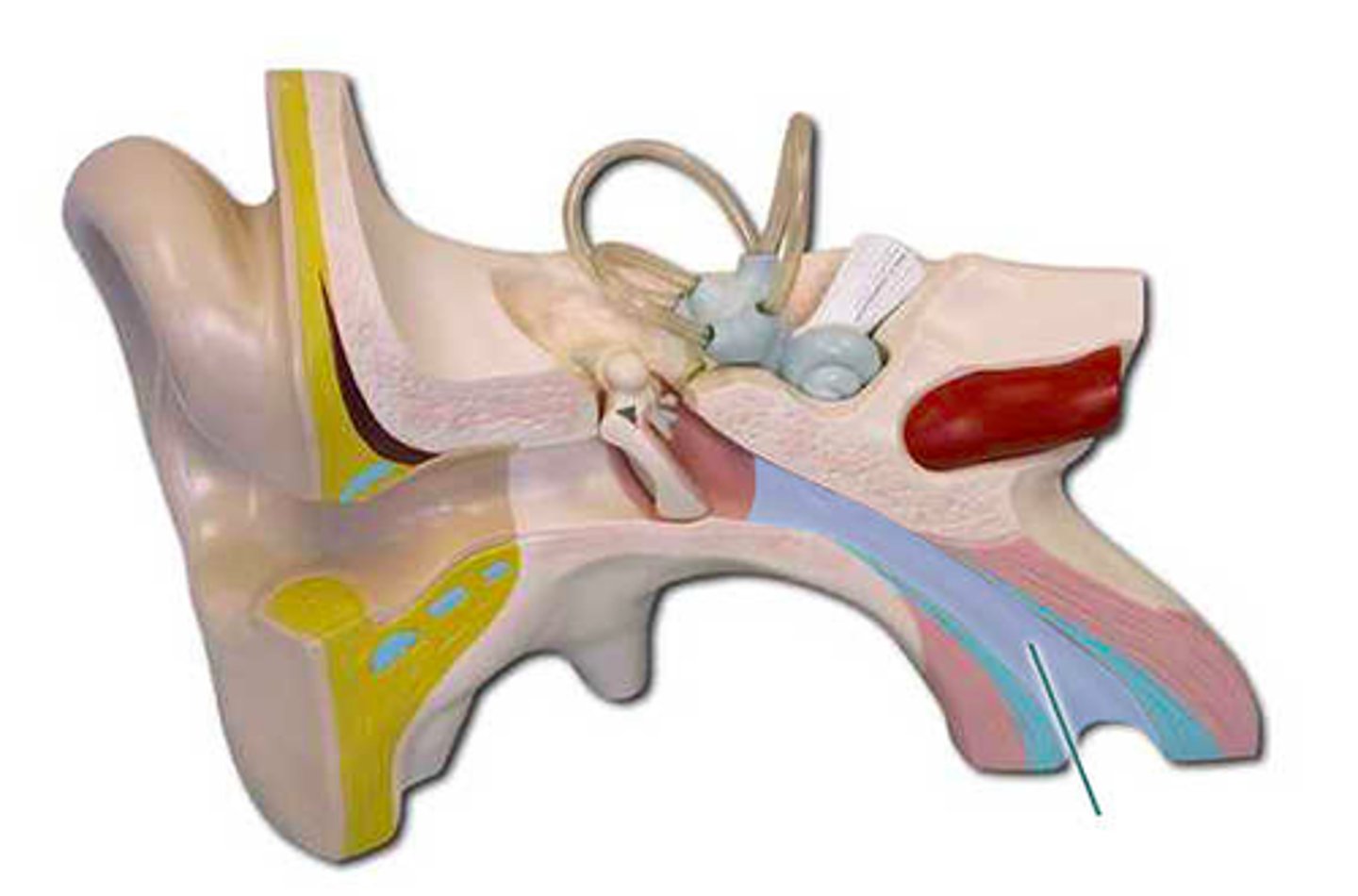
pharyngotympanic tube
which structure is highlighted?
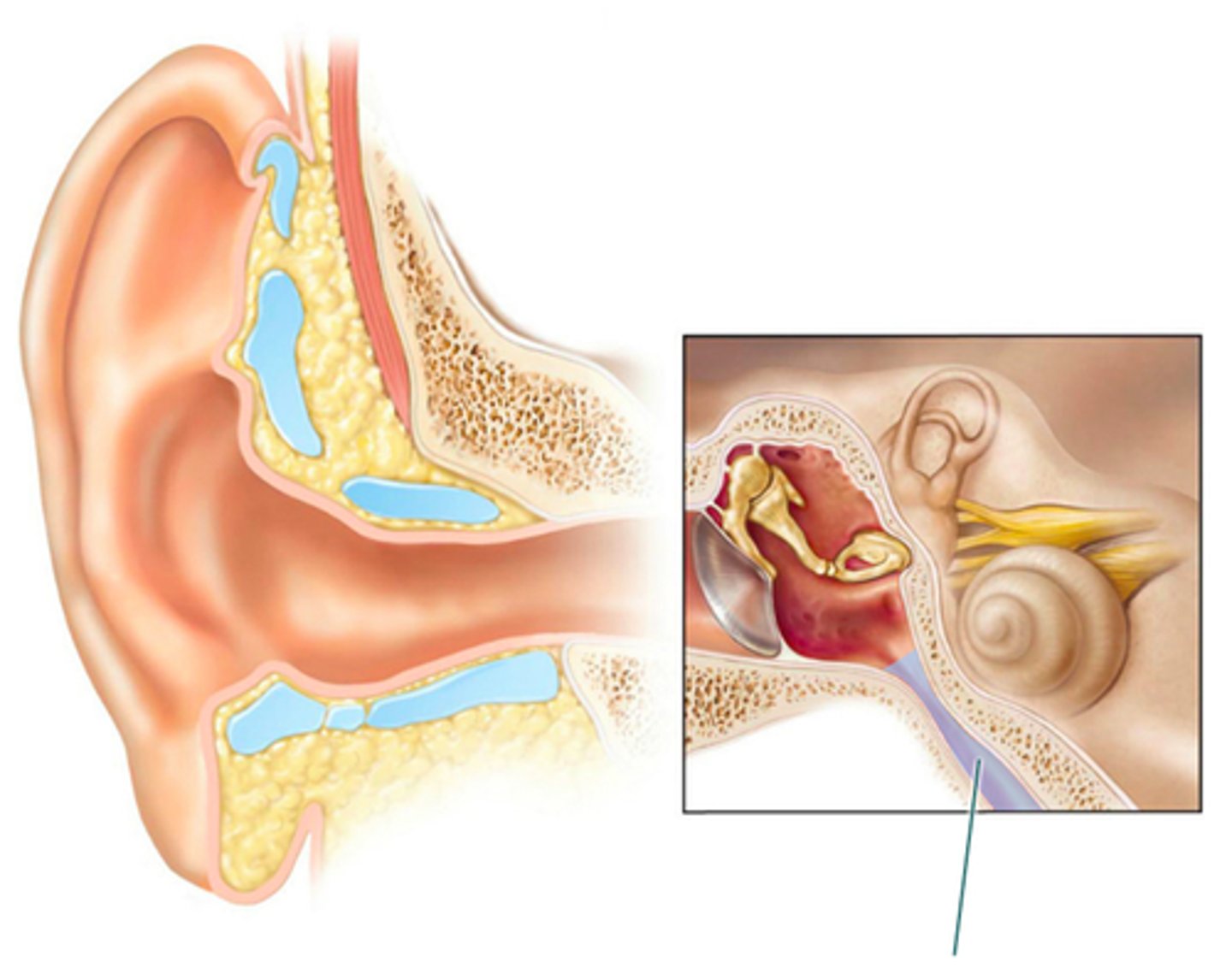
semicircular canals
which structure is highlighted?
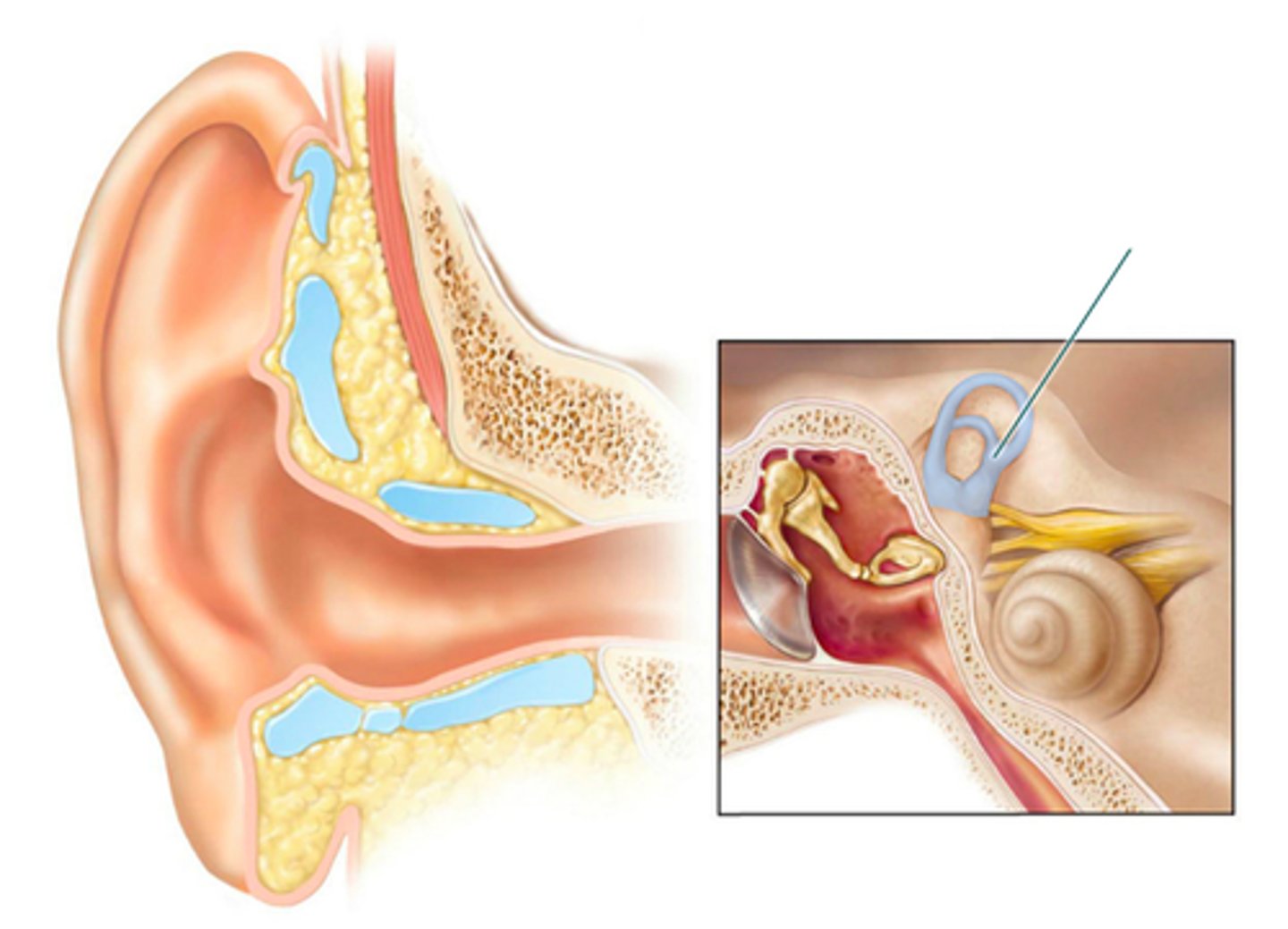
static equilibrium and linear acceleration
The maculae located within the highlighted structure contain the receptors that monitor ________.
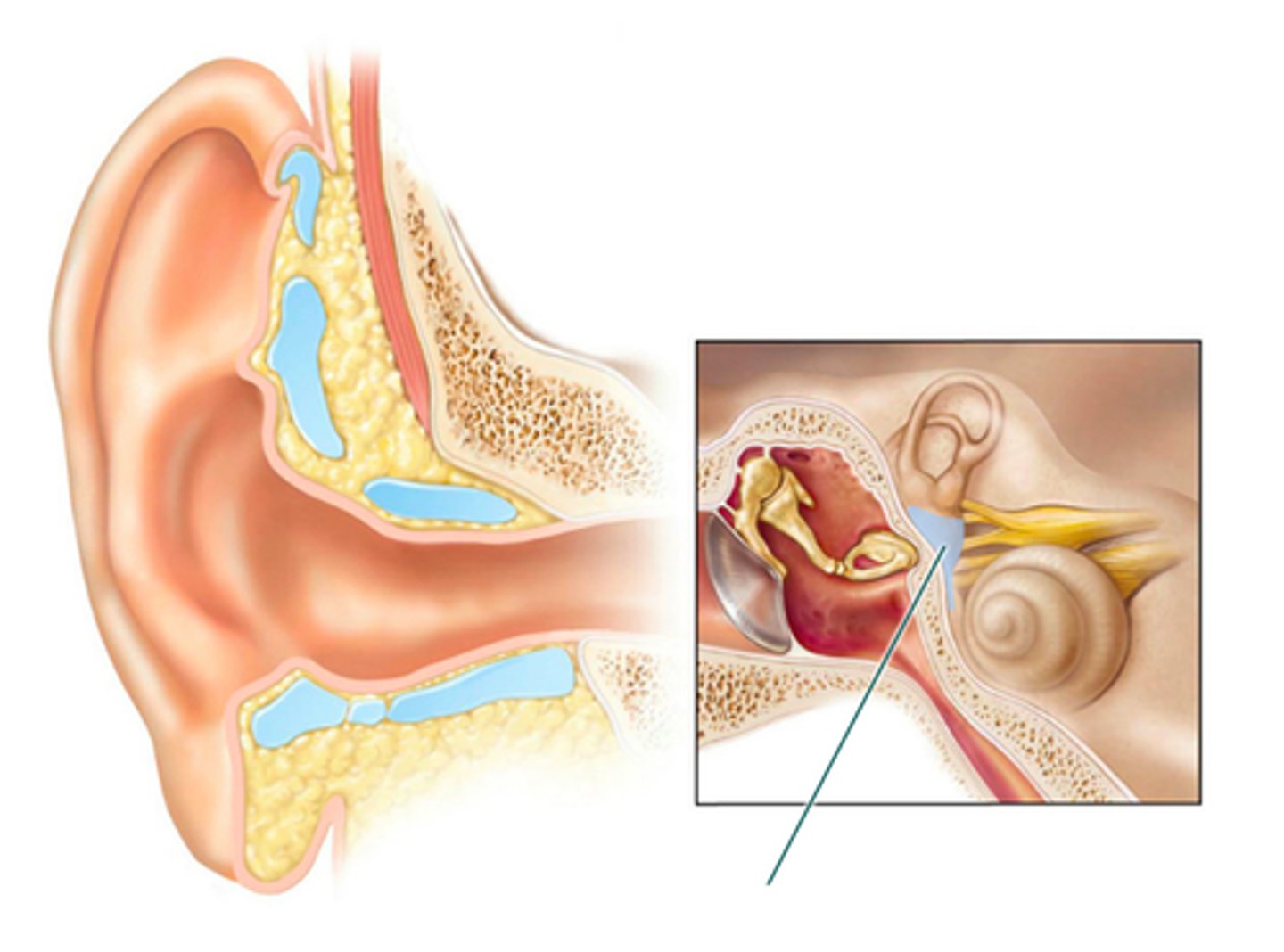
auricle
which structure is highlighted?
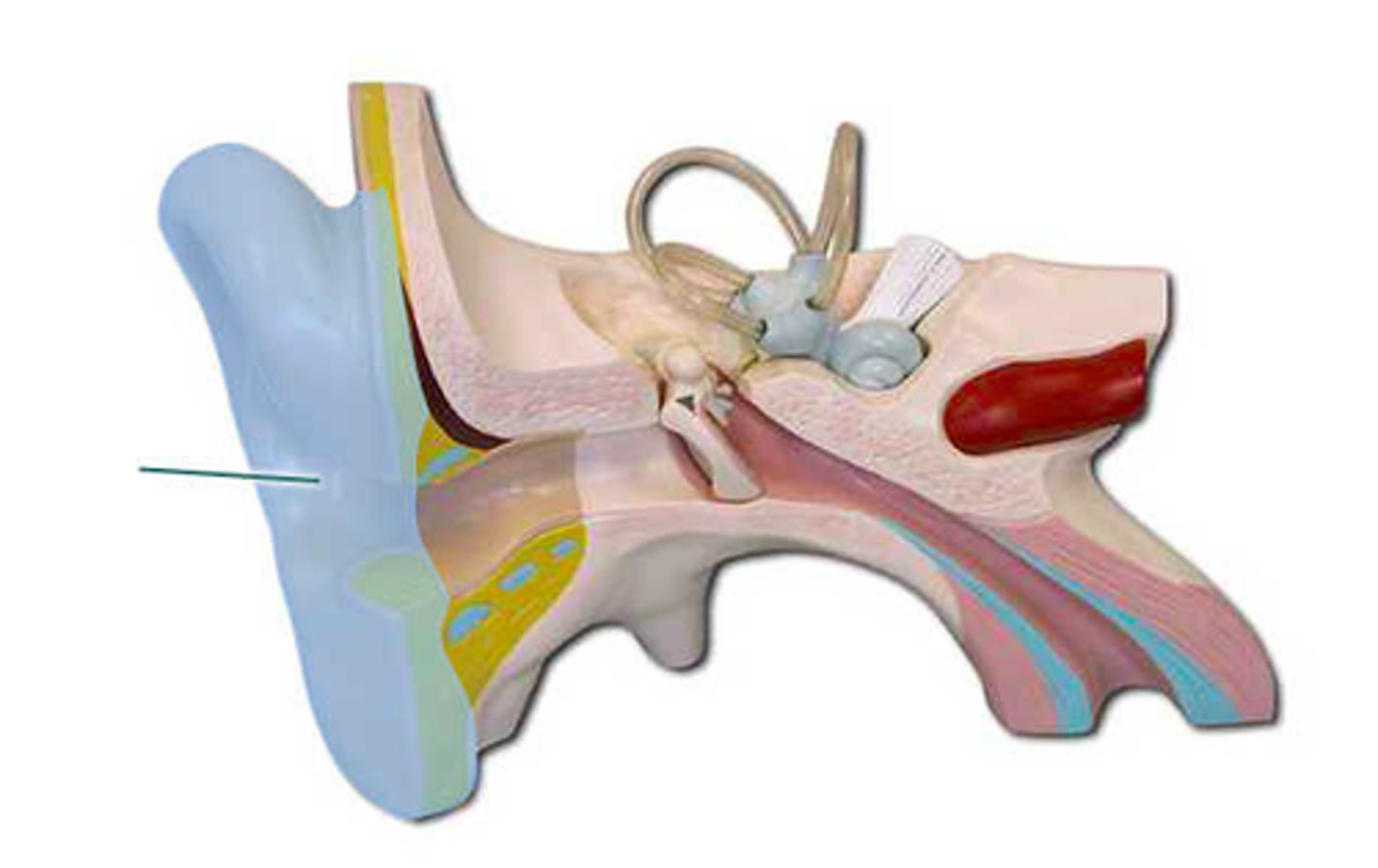
basilar membrane
which structure is highlighted?
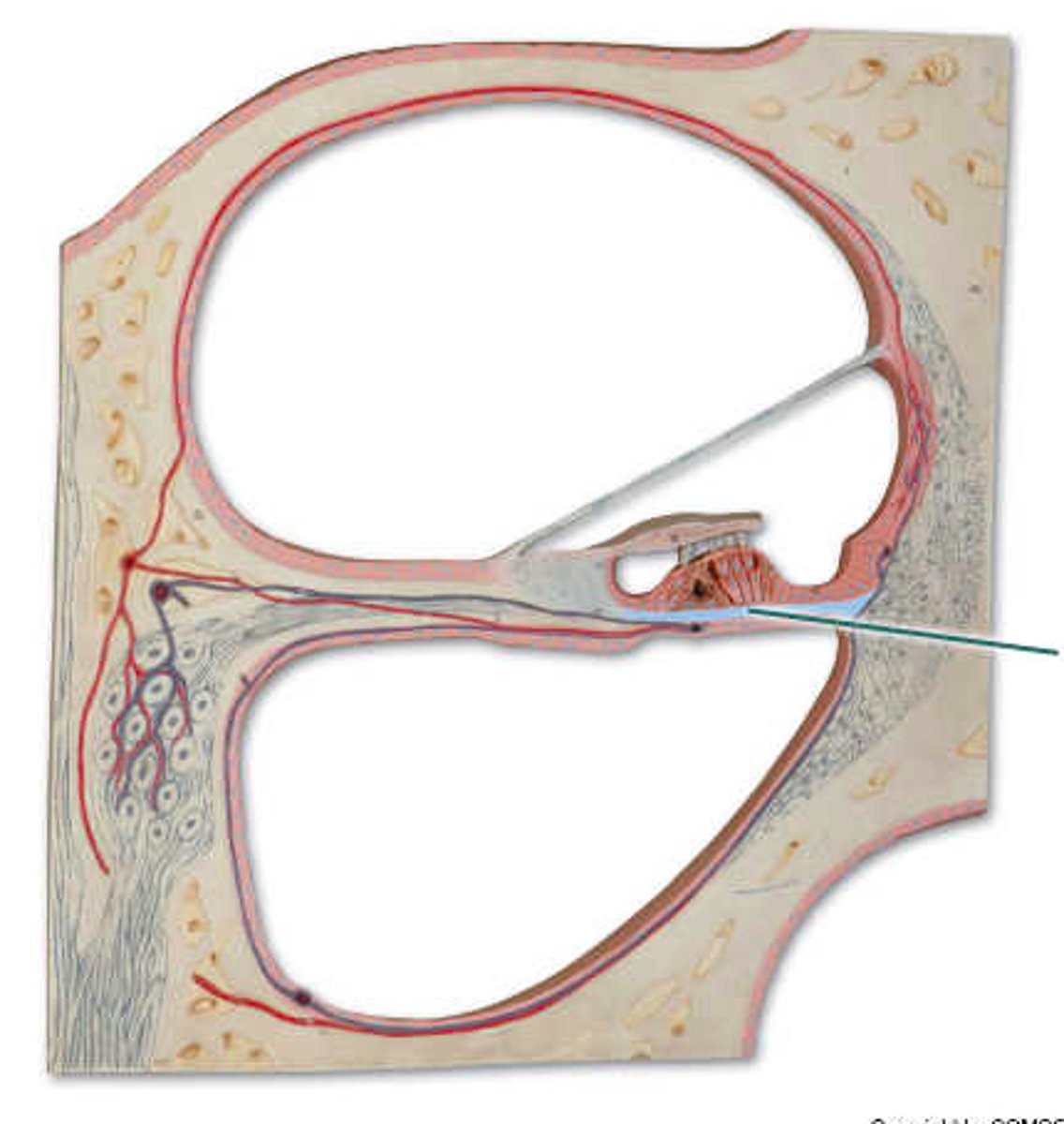
hearing
Receptors within the highlighted structure provide the sense of ___.
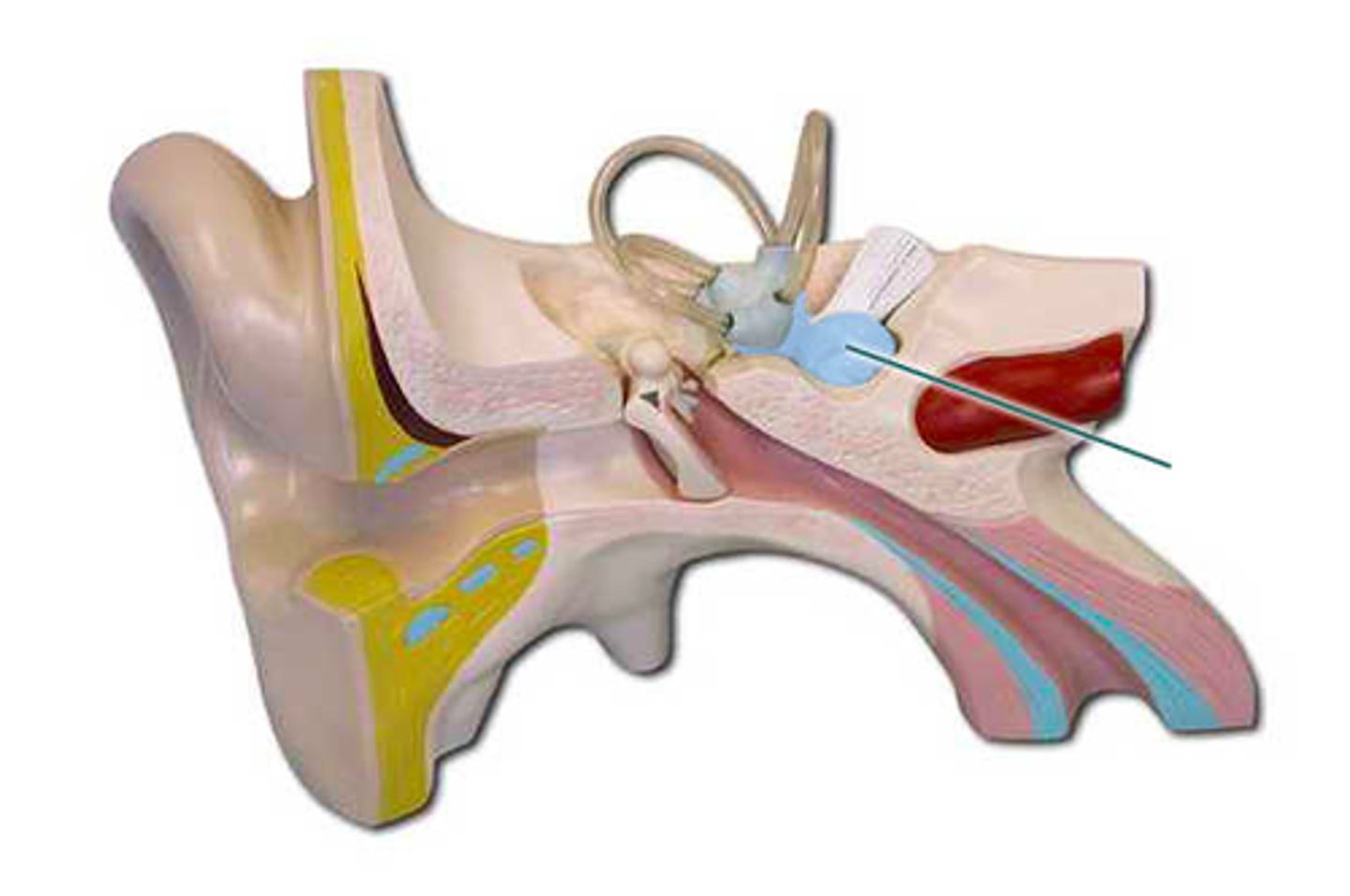
cochlear nerve
which structure is highlighted?
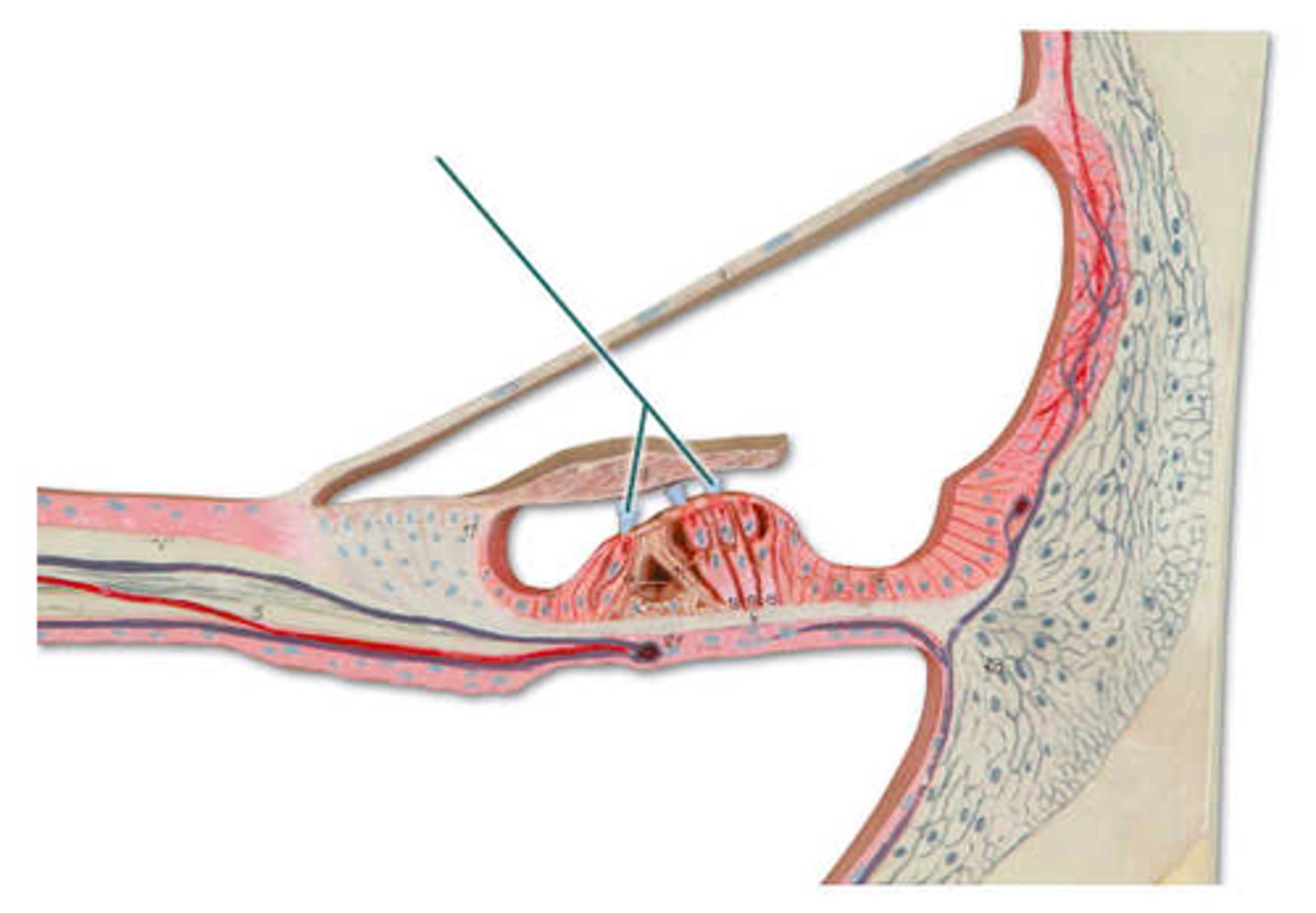
hair (stereocili)
which structure is highlighted?
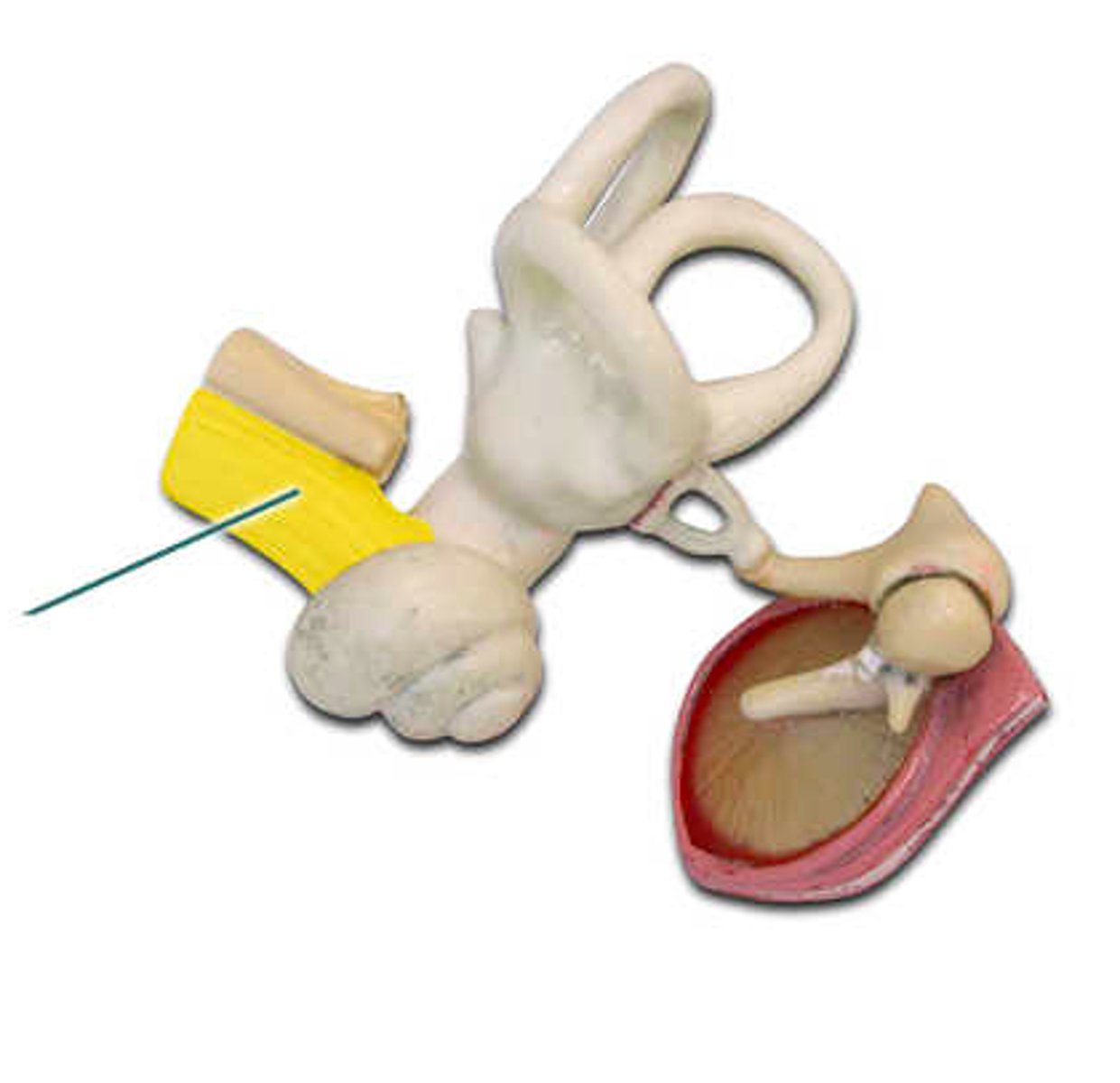
malleus
which structure is highlighted?
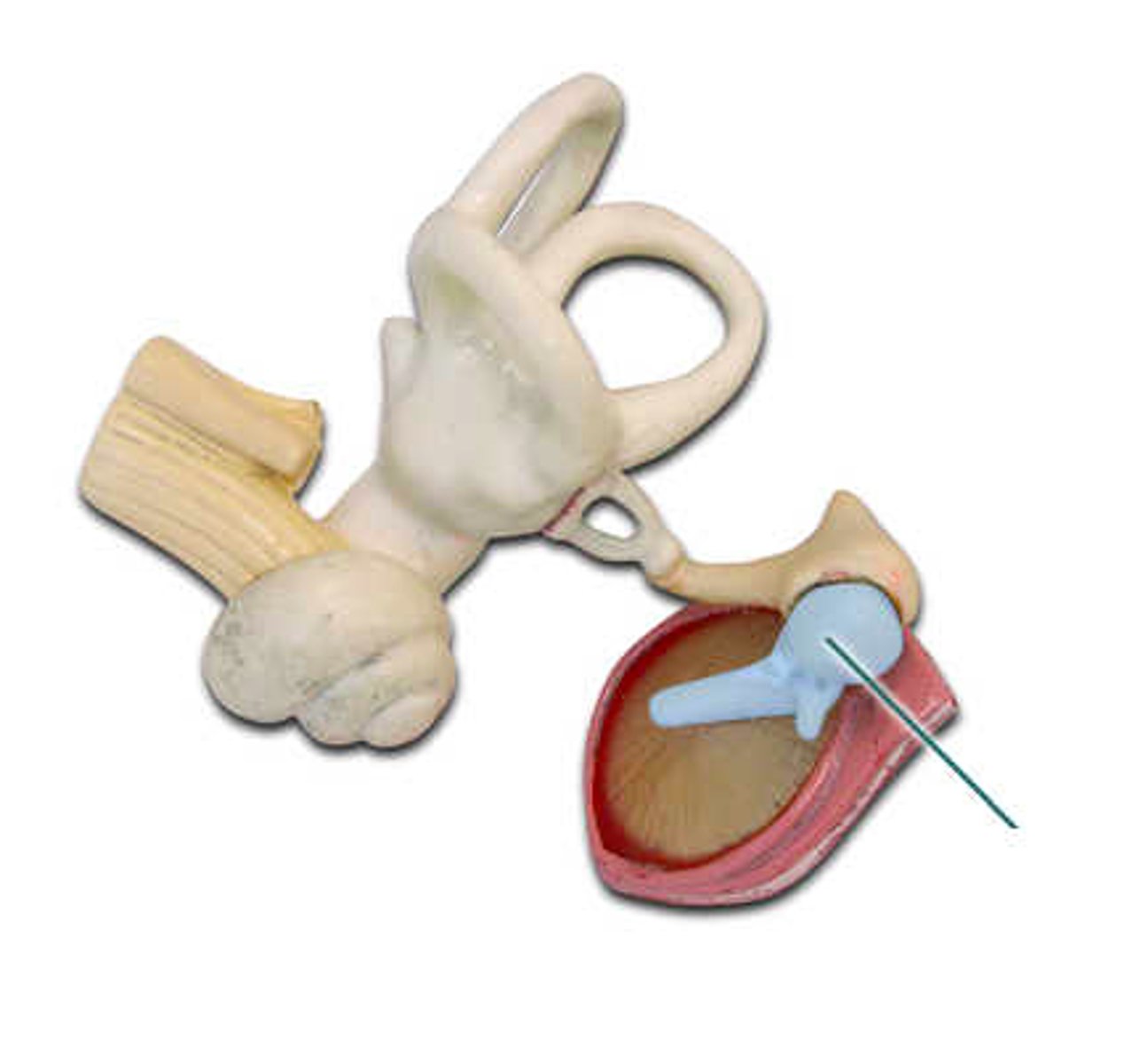
organ of Corti
which structure is highlighted?
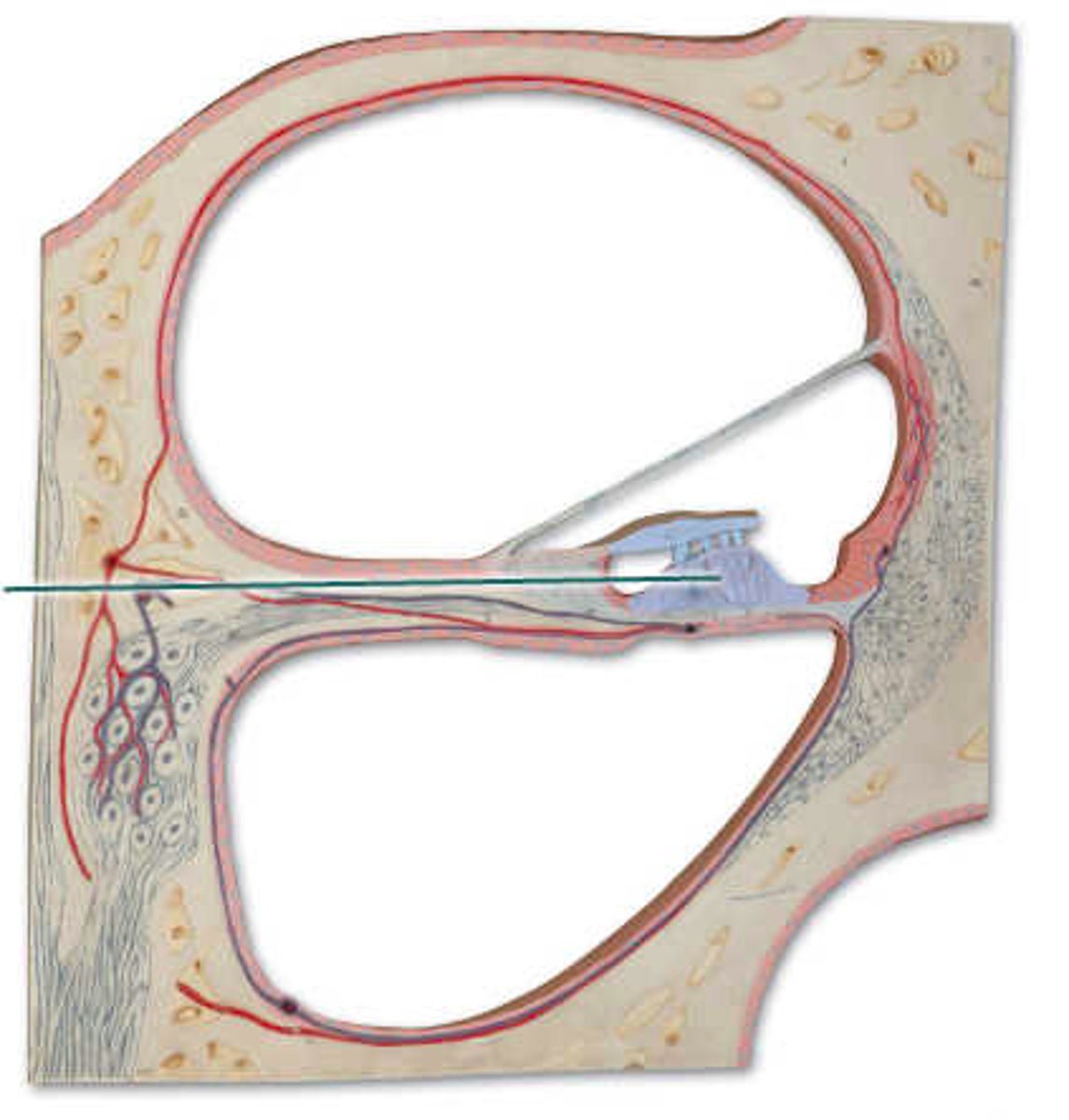
pharyngotympanic tube
which structure is highlighted?