CAPE Chemistry Module 3: Industrial Plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:45 PM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Factors Influencing Location of an Industrial Plant
• Suitability of terrain
• Vulnerability of an area to weather/natural disaster events
• Availability and Proximity of building materials • Availability of safe disposal systems
• Availability of commodities like water
• Access to sufficient electrical power
• Proximity of skilled workers
• Effect on nearby community- providing employment versus using up productive farmland.
• Vulnerability of an area to weather/natural disaster events
• Availability and Proximity of building materials • Availability of safe disposal systems
• Availability of commodities like water
• Access to sufficient electrical power
• Proximity of skilled workers
• Effect on nearby community- providing employment versus using up productive farmland.
2
New cards
Health and Safety requirements
• Choosing processes and tools which are inherently safe
• Identifying hazards which cannot be eliminated, and instituting training on how to cope with it
• Having plans for coping with large-scale emergencies like hurricanes and ensuring staff has had chance for training and practice
• Ensuring that emergency exits are clearly marked
• Training staff in proper procedures including use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
• Having some staff qualified in first aid
• Identifying hazards which cannot be eliminated, and instituting training on how to cope with it
• Having plans for coping with large-scale emergencies like hurricanes and ensuring staff has had chance for training and practice
• Ensuring that emergency exits are clearly marked
• Training staff in proper procedures including use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
• Having some staff qualified in first aid
3
New cards
Name the proces of Aluminium Ore Purification
Bayer Process
4
New cards
Main constituent of bauxite
Aluminium Oxide
5
New cards
Name impurities of Bauxite
Iron(iii) Oxide, Silicon Dioxide, Titanium Oxide
6
New cards
State steps of Bayer Process
Digestion, Filtration, Precipitation, Filtration, Calcination
7
New cards
Digestion process in Bayer process
ground bauxite mixed with hot sodium hydroxide.
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2NaAlO2(aq) + H2O(l)
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 2NaAl(OH)4(aq)
SiO2(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SiO3(aq) + H2O(l)
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2NaAlO2(aq) + H2O(l)
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 2NaAl(OH)4(aq)
SiO2(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SiO3(aq) + H2O(l)
8
New cards
First filtration of Bayer process
The insoluble impurities like the iron oxide are filtered out as red mud, and only the soluble products remain
9
New cards
Precipitation of Bayer process
The heated filtrate is stirred and cooled, causing the precipitation of aluminium hydroxide crystals.
NaAlO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → NaOH(aq) + Al(OH)3(s)
A crystal of aluminium hydroxide is usually used to seed the mixture and jumpstart precipitation.
\
Carbon dioxide is pumped to trigger precipitation
2\[Al(OH)4\]-(aq) + CO2(g) → 2Al(OH)3(s) + CO32-(aq) + H2O(l) \n
NaAlO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → NaOH(aq) + Al(OH)3(s)
A crystal of aluminium hydroxide is usually used to seed the mixture and jumpstart precipitation.
\
Carbon dioxide is pumped to trigger precipitation
2\[Al(OH)4\]-(aq) + CO2(g) → 2Al(OH)3(s) + CO32-(aq) + H2O(l) \n
10
New cards
Second Filtration of Bayer process
The silicates remain in solution, leaving aluminium hydroxide crystals
11
New cards
Calcination in Bayer process
The filter residue is heated in a rotary kiln at 1100-1300 degrees Celsius
\- drives off water
\- leaving near pure aluminium oxide (alumina)
\
\- 2Al(OH)3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2O(l) \n
\- drives off water
\- leaving near pure aluminium oxide (alumina)
\
\- 2Al(OH)3(s) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2O(l) \n
12
New cards
Process of Production of Aluminium
Hall-Heroult Process
13
New cards
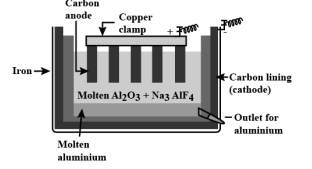
Explain Hall-Heroult Process. give equations
hydrolysis of molten alumina
alumina melts at 2050C (much energy required)
melting point decreased to 960C, molten cryolite (NaAlF6) also increases conductivity. \n
At the cathode (carbon lining), the half \n equation is: O2-(l) + C(s) → CO(g) + 2e-
\
At the anode (carbon rods): Al3+(l) + 3e- → Al(l)
alumina melts at 2050C (much energy required)
melting point decreased to 960C, molten cryolite (NaAlF6) also increases conductivity. \n
At the cathode (carbon lining), the half \n equation is: O2-(l) + C(s) → CO(g) + 2e-
\
At the anode (carbon rods): Al3+(l) + 3e- → Al(l)
14
New cards
List uses of Aluminium and why?
cans & food packaging; non-toxic
kitchen utensils; resistant to corrosion
pots & pans; thermal conductivity
alloys in spacecraft; ligtweight
kitchen utensils; resistant to corrosion
pots & pans; thermal conductivity
alloys in spacecraft; ligtweight
15
New cards
List environmental effects of Aluminium Industry
caustic red mud from extraction seep into ground water; increase pH
\
fluoride gases from Hall-Heroult process escape affecting plans.
\
global warming by gases: PFCs, SO2, CO2, CO
\
mining destroys green areas; reduce aesthetic appeal
\
disposals of used Carbon cell linings containing alkaline solutions.
\
fluoride gases from Hall-Heroult process escape affecting plans.
\
global warming by gases: PFCs, SO2, CO2, CO
\
mining destroys green areas; reduce aesthetic appeal
\
disposals of used Carbon cell linings containing alkaline solutions.
16
New cards
separation of crude oil process called ___________
fractional distillation
17
New cards
Quick overview of Fractional Distillation of Crude oil
heat oil with long carbon chains in fractional column to 300C
\
unboiled liquid (heaviest fraction) piped off as residues
\
vapor rises through the fractionating column, where there is a temperature gradient with the coolest part at the top.
\
When a hydrocarbon compound reaches a part of the column that is cooler than its boiling point, it will condense, be collected, and piped off.
\
vapours which don’t condense are piped off at the top as refinery gases. This is the lightest fraction.
\
unboiled liquid (heaviest fraction) piped off as residues
\
vapor rises through the fractionating column, where there is a temperature gradient with the coolest part at the top.
\
When a hydrocarbon compound reaches a part of the column that is cooler than its boiling point, it will condense, be collected, and piped off.
\
vapours which don’t condense are piped off at the top as refinery gases. This is the lightest fraction.
18
New cards
define reforming in crude oil industry
straight-chain hydrocarbons are broken up and then reassembled into aromatic and highly branched-chain hydrocarbons
19
New cards
why does the industry do reforming?
These ‘higher octane ratings’ (meaning more highly branched compounds) are more resistant to knocking, or the premature combustion of fuels in an engine implicated in engine damage and overheating.
20
New cards
List environmental impacts of crude oil pollution
*Exploration:*
Seismic surveys are used to determine underground oil deposits. These surveys require shock waves which are usually generated using explosions in the ocean or \n underground; destroy ecosystem and wildlife.
\
*Extraction*
The surrounding land is cleared and leveled; destroys flora, fauna and habitats.
Well drilling expels brine and oil into surrounding soil and water; damages plant and aquatic life.
\
*Transportation*
Oil tanker spills kill marine life and contribute to reduce air quality if they catch ablaze; affecting birds, coral reefs, polar bears.
\
*Refining*
releases toxic and hazardous air pollutants (many of which are greenhouse gases) CO, oxides of Nitrogen etc
\
*Use*
fuels releases compounds like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the environment.
Seismic surveys are used to determine underground oil deposits. These surveys require shock waves which are usually generated using explosions in the ocean or \n underground; destroy ecosystem and wildlife.
\
*Extraction*
The surrounding land is cleared and leveled; destroys flora, fauna and habitats.
Well drilling expels brine and oil into surrounding soil and water; damages plant and aquatic life.
\
*Transportation*
Oil tanker spills kill marine life and contribute to reduce air quality if they catch ablaze; affecting birds, coral reefs, polar bears.
\
*Refining*
releases toxic and hazardous air pollutants (many of which are greenhouse gases) CO, oxides of Nitrogen etc
\
*Use*
fuels releases compounds like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the environment.
21
New cards
Name to process of Ammonia production
Haber process
22
New cards
State the major equation for the Haber process. (include conditions)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) H = -92kJ/mol
CONDITIONS: iron catalyst, 400C, 150-250atm
CONDITIONS: iron catalyst, 400C, 150-250atm
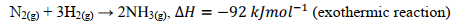
23
New cards
Where is Hydrogen obtained in the Haber process?(state equation and conditions)
steam reforming; reaction of methane with steam
Equation: CH4(g) + H2O(g) →CO(g) + 3H2(g)
Conditions: Ni catalyst, 700-1100C, 20atm
Equation: CH4(g) + H2O(g) →CO(g) + 3H2(g)
Conditions: Ni catalyst, 700-1100C, 20atm
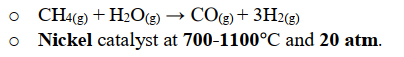
24
New cards
Quickly explain the water gas shift reaction. Include equation and conditions
Additional hydrogen is recovered from the steam through the water gas shift reaction. \n
EQUATION: CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2 + H2(g)
CONDITIONS: Nickel Oxide catalyst, 130C
EQUATION: CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2 + H2(g)
CONDITIONS: Nickel Oxide catalyst, 130C
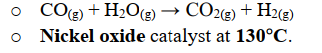
25
New cards
How is Nitrogen procured in Haber process?
fractional distillation of liquefied air
26
New cards
List uses of Ammonia
*Agriculture*
production of nirtogen-based fertilizers
\
*Chemical Industry*
manufacture nitric acid, plastics, pharmaceuticals
\
*Food*
nitrogen source for yeast
refrigerant gas
production of nirtogen-based fertilizers
\
*Chemical Industry*
manufacture nitric acid, plastics, pharmaceuticals
\
*Food*
nitrogen source for yeast
refrigerant gas
27
New cards
State impacts of Ammonia industry of environment
CO2 from the steam-reforming process is emitted
\
Excess fertilizers entering natural waters results in eutrophication; death of aquatic organisms \n
Fertilizer runoff can enter domestic water supply, polluting drinking water.
\
Soil acidification results when ammonium ions in the soil are nitrified by bacteria, releasing hydrogen ions; acidity can affect plant growth.
\
Excess fertilizers entering natural waters results in eutrophication; death of aquatic organisms \n
Fertilizer runoff can enter domestic water supply, polluting drinking water.
\
Soil acidification results when ammonium ions in the soil are nitrified by bacteria, releasing hydrogen ions; acidity can affect plant growth.
28
New cards
Procces of ethanol production?
fermentation
29
New cards
define fermentation
process where sugars are oxidized by living organisms in the absence of oxygen to release energy
30
New cards
why is fractional distillation important in ethanol production
When ethanol concentration reaches 12-15% however, the activity of the yeast stops as the enzymes are denatured by the toxic ethanol.
\
To increase the concentration of alcohol in the solution to the wonderfully deleterious levels found in spirits (even up to 40% alcohol by volume), fractional distillation must be carried out.
\
Close boiling points
\
To increase the concentration of alcohol in the solution to the wonderfully deleterious levels found in spirits (even up to 40% alcohol by volume), fractional distillation must be carried out.
\
Close boiling points
31
New cards
Uses of ethanol
*Fuel*
Ethanol has a very clean (non-smoky) and exothermic combustion. As such, it is used as a fuel additive.
\
*Beverage*
\
*Solvents*
disinfectants
organic solvent
Ethanol has a very clean (non-smoky) and exothermic combustion. As such, it is used as a fuel additive.
\
*Beverage*
\
*Solvents*
disinfectants
organic solvent
32
New cards
Social/Economic Impact of Alcohol Consumption
depressant on nervous system, euphoria, relaxant
\
slurred speech, memory loss, liver cirrhosis, cardiovascular diseases etc.
\
death
\
fetal alcohol disorder
\
slurred speech, memory loss, liver cirrhosis, cardiovascular diseases etc.
\
death
\
fetal alcohol disorder
33
New cards
Name the process of chlorine production
electrolysis of brine in diaphragm cell
34
New cards
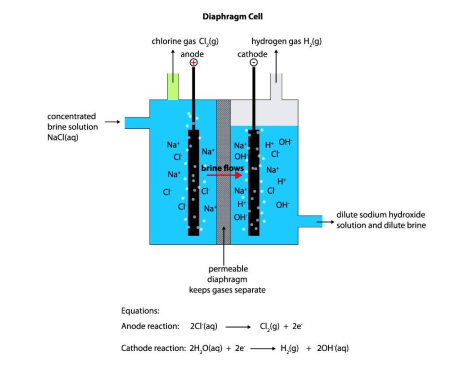
Explain the chemical process at anode and cathode of diaphragm cell in Chlorine production
*At the anode*
2Cl-(aq) →Cl2(g) + 2e- (preferably discharged)
4OH-(aq) →2H2O + O2(g) +4e-
\
*At cathode*
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) (preferably discharged)
2Cl-(aq) →Cl2(g) + 2e- (preferably discharged)
4OH-(aq) →2H2O + O2(g) +4e-
\
*At cathode*
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) (preferably discharged)
35
New cards
Why is separation of gases important in Chlorine production
This separation of gases is necessary because a mixture of hydrogen and chlorine gas can react explosively to form hydrogen chloride in the presence of sunlight or UV radiation.
36
New cards
State economic advantage of using diaphragm cell
Operates at a lower voltage than mercury cell.
\
Brine can be low purity.
\
Asbestos is chemically stable, relatively inexpensive and abundant.
\
Brine can be low purity.
\
Asbestos is chemically stable, relatively inexpensive and abundant.
37
New cards
Industrial importance of Chlorine
bleaches
PVC
organic solvent
aerosols and refrigerants(CFCs)
anesthetics like halothane
PVC
organic solvent
aerosols and refrigerants(CFCs)
anesthetics like halothane
38
New cards
impact of chlorine industry on environment
release of asbestos; lung cancer
PVC is non-biodegradable; burning PVC releases toxins
PVC is non-biodegradable; burning PVC releases toxins
39
New cards
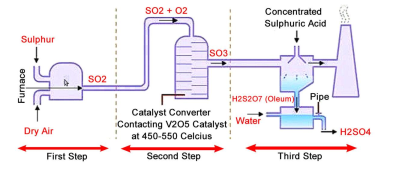
name the process of sulphuric acid production
Contact Process
40
New cards
State the main stages of Contact Process
***Production*** of Sulphur Dioxide
***Oxidation*** of Sulphur Dioxide to Trioxide
***Hydration*** of trioxide to oleum
***Dilution*** of oleum to H2SO4
***Oxidation*** of Sulphur Dioxide to Trioxide
***Hydration*** of trioxide to oleum
***Dilution*** of oleum to H2SO4
41
New cards
State two ways to product Sulphur Dioxide. Include equation and condition
*Burning Sulphur in excess air*
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
\
*Combustion of Sulphur Ores*
4FeS2(s) + 11O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s) + 8SO2(g)
\
CONDITIONS: 1000C
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
\
*Combustion of Sulphur Ores*
4FeS2(s) + 11O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s) + 8SO2(g)
\
CONDITIONS: 1000C
42
New cards
Quickly explain Oxidation of Sulphur Dioxide to Sulphur Trioxide in Contact Process
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) H =-197kJ/mol
\
CONDITIONS: vanadium (V) oxide in silica gel catalyst, 450C
\
CONDITIONS: vanadium (V) oxide in silica gel catalyst, 450C
43
New cards
Explain Hydration of Sulphur Trioxide in Contact Process
The uncontrollable hydration of sulphur trioxide produces sulphuric acid (as SO3, its acid anhydride)
\
formation of intermediate oleum (fuming H2SO4)
The SO3 gas is dissolved in a concentrated sulphuric acid solution to form oleum.
\
H2SO4(l) + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
\
formation of intermediate oleum (fuming H2SO4)
The SO3 gas is dissolved in a concentrated sulphuric acid solution to form oleum.
\
H2SO4(l) + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
44
New cards
Explain the dilution of Oleum
The oleum is slowly diluted with water with continuous cooling to form concentrated sulfuric acid.
\
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
\
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
45
New cards
industrial importance of Sulphur
SO2 as bleaching agent & preservative
H2SO4 in fertilizers, dyes, explosices, car batteries
Sulphate salts: magnesium suplhate as laxative, sodium sulphate as drying agent
H2SO4 in fertilizers, dyes, explosices, car batteries
Sulphate salts: magnesium suplhate as laxative, sodium sulphate as drying agent
46
New cards
Impact of Sulphuric Acid Industry
SO2 emission contribute to acid rain
H2SO4 spills on metal to explosively produce Hydrogen class
used as recyclable catalyst
H2SO4 spills on metal to explosively produce Hydrogen class
used as recyclable catalyst