Lecture 3: Mycology 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
sterols/ergosterol
in the phospholipid bilayer membrane of fungi
Chitin and a form of glucan polymer
In the cell walls of fungi
Fungi are unaffected by
antibacterial pharmaceuticals
Fungi more closely related to
Animals than they to plants
Hyphae
Long, thread-like chains of cells that make thin filaments making up the fungus
Mycelium
mass of hyphae and grow at the tips and branch
septum
the wall that divides cells (internal cross- walls)
Function of ergosterol as the membrane sterol
provides a unique membrane surface, and a unique biosynthetic pathway
Azoles
Inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis
– Itraconazole, fluconazole, voriconazole, ketoconazole
Polyenes
a class of antifungal drugs used to treat fungal infections by binding to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane which causes pores leading to fungi cell death
– Amphotericin B and Liposomal
Allylamines
Inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis (early)
– Terbinafine
Echinocandins
Disrupt cell wall glucan synthesis
– Caspofungin
Fungi reproduce
either asexually or by sexual reproduction
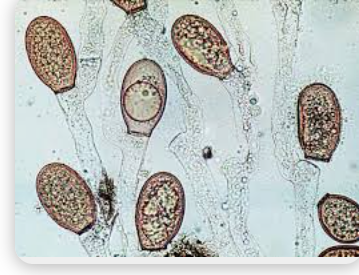
Chytridiomycota
Chytrids

Zygomycota
Common Molds
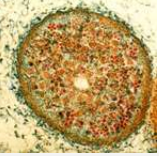
Ascomycota
Sac Fungi
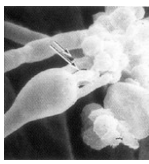
Basidiomycota
Club Fungi

Deuteromycota
Imperfect Fungi (produces no sexual spores)
Microscopic Analysis based on:
Yeast cells, pseudohyphae, hyphae, and thermal dimorphism
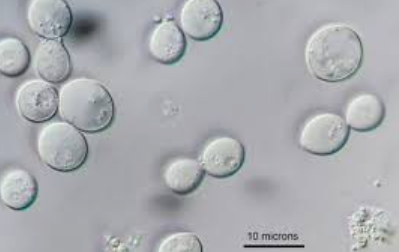
Yeast cells
round or ovoid cells that produce daughters by budding
Pseudohyphae
chains of elongated yeast cells, have indentations in the wall where cells meet
Mycobiome
the fungi that are resident on the human body, can become opportunistic pathogens
Dermatophyte Fungi
Keratinolytic and causes ringworm
-Species: microsporum spp, epidermophyton spp, trichophyton spp
Keratinolytic
Can utilize keratin as a nutrient source
ex: dermatophyte Fungi
Ringworm aka Tinea
Infections of keratinized tissues and named by location
Tinae examples
–Tinea capitis: Scalp
–Tinea corporis: Body
–Tinea cruris: Groin (jock itch)
–Tinea pedis: Foot (athlete’s foot)
Pityriasis Versicolor
superficial infection of the epidermis and caused by Malassezia spp and is treated by antifungals
Malassezia spp
causes Pityriasis Versicolor, dimorphic, lipophilic fungus, commensals on skin, and 90-100% of colonization rate
Onychomycosis
Fungal infection of the nails and is treated by nail lacquers (ciclopirox and amorolfine) or oral antifungals (terbinafine)
Onychomycosis Predisposing factors:
Tinea pedis, family history, age, male gender, trauma, diabetes, immunosuppression, poor peripheral circulation and smoking
Onychomycosis caused by
Dermatophytes: Tinea Unguium. Mainly on toenalis like Trichophyton rubrum
Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis – Mainly fingernails
Opportunistic Fungal Pathogens:
Candida sp., aspergillus fumigatus, and cryptococcus neoformans
Primary Fungal Pathogens
Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Coccidioides immitis
Why are fungi pathogens are emerging b/c
A new susceptible population b/c of HIV, transplantation, and cancer patients
Candida Species Morphology
Form yeast-like cells (blastoconidia), pseudohyphae and true hyphae in tissue
– Yeast cells form germ tubes in response to serum
Candida species are part of
the normal flora of most individuals of GI and GU
Candida is the cause of two major classes of disease:
Muco-cutaneous candidiasis and Disseminated candidiasis
Muco-cutaneous candidiasis
Superficial infection of overgrowth of normal flora limited to lining surfaces such as skin, oropharynx, GU tract, GI tract and respiratory tract
-Becomes invasive in sick people
Disseminated candidiasis
Occurs when Candida enters the bloodstream from the gut “leaky gut”, colonizes vein catheters and forms biofilms
Disseminated candidiasis Epidemiology
Candida bloodstream infections are the fourth most common behind coag-Staph, S. aureus and Enterococcus
Invasive candidiasis can occur
Disseminated candidiasis treatment
High risk patients will often be placed on antifungal prophylaxis and removal of contaminated indwelling catheters
Candida auris
emerging fungal pathogen thats multi drug resistant that causes systemic infections in hospitalized patients and nursing home residents