MCB 104 Final Exam Review Flashcards
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
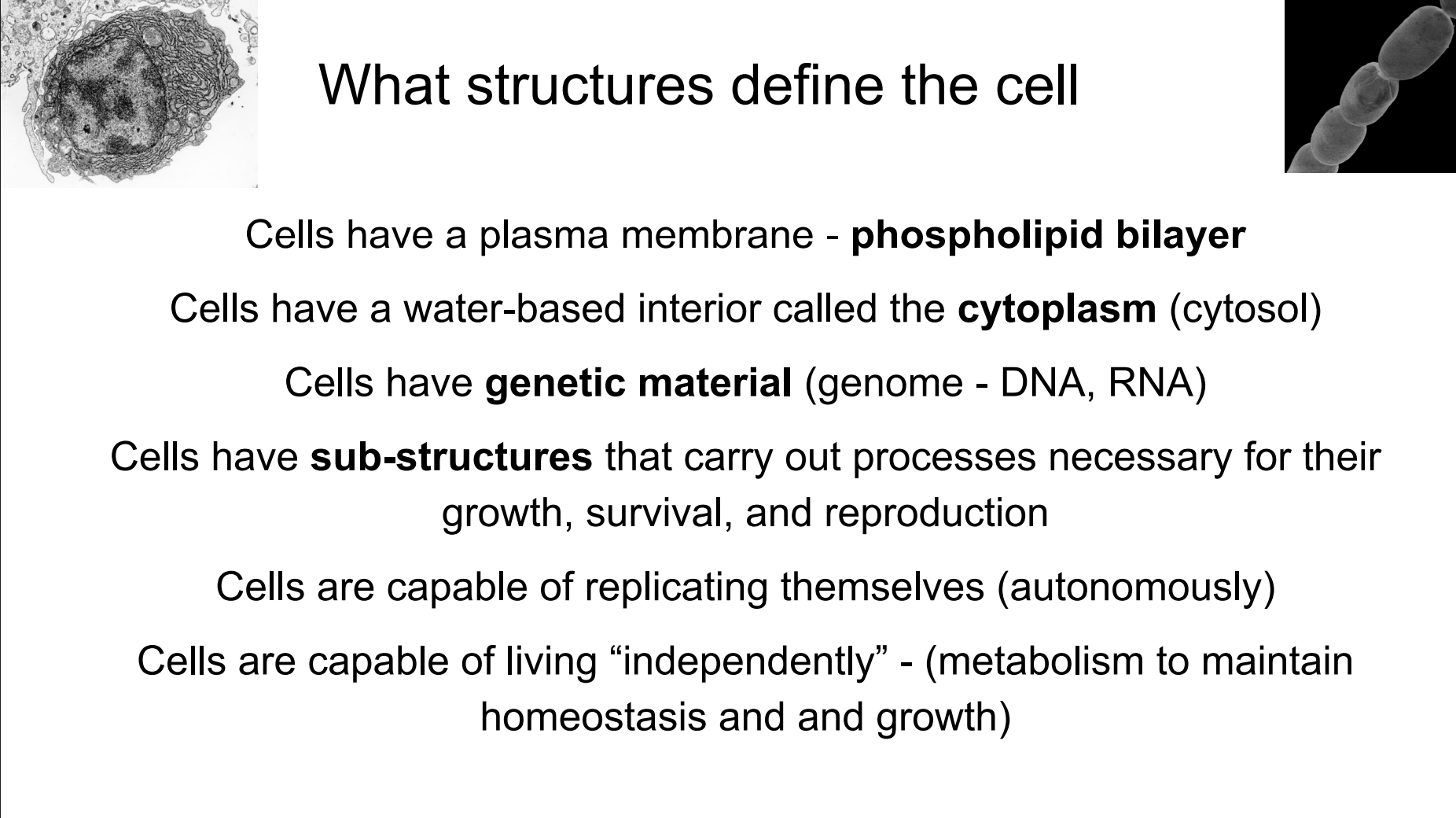
What structures define the cell
Cells are extremely crowded…
This space is taken up by macromolecules (nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates)
The close proximity of macromolecules and subcellular structures allows more random collisions and interactions
The crowded nature of the cell encourages several things: (1) cell compartmentalization and organization (organelles or condensates) (2) increases the effective concentration of certain reacting molecules (3) promotes increased reaction rates due to the closeness of reacting molecules
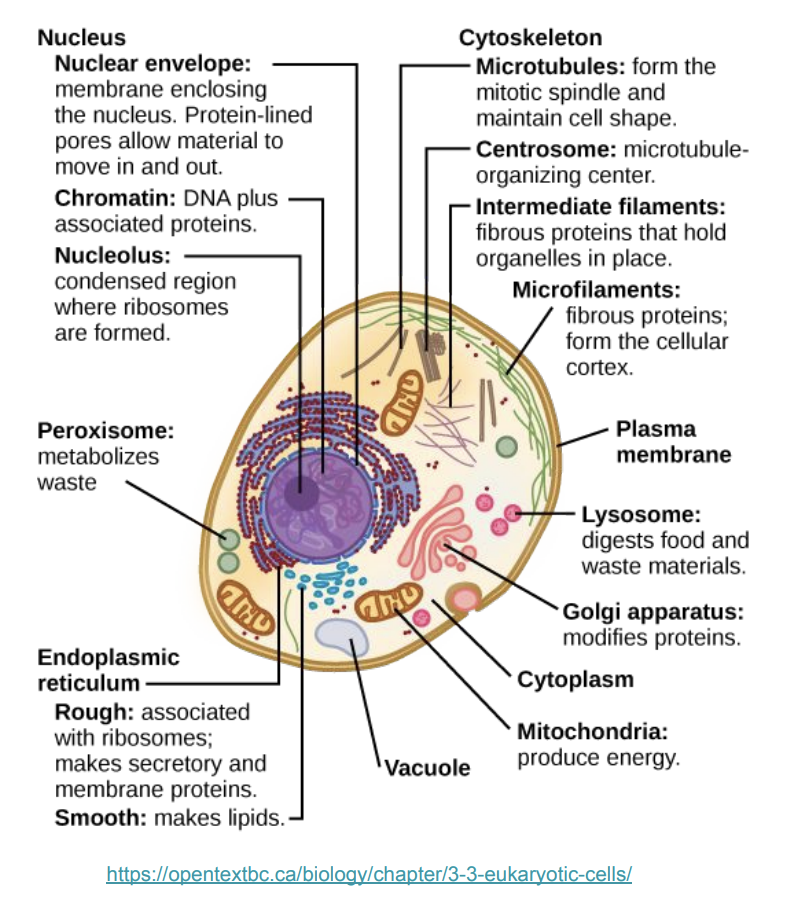
Know your organelles…
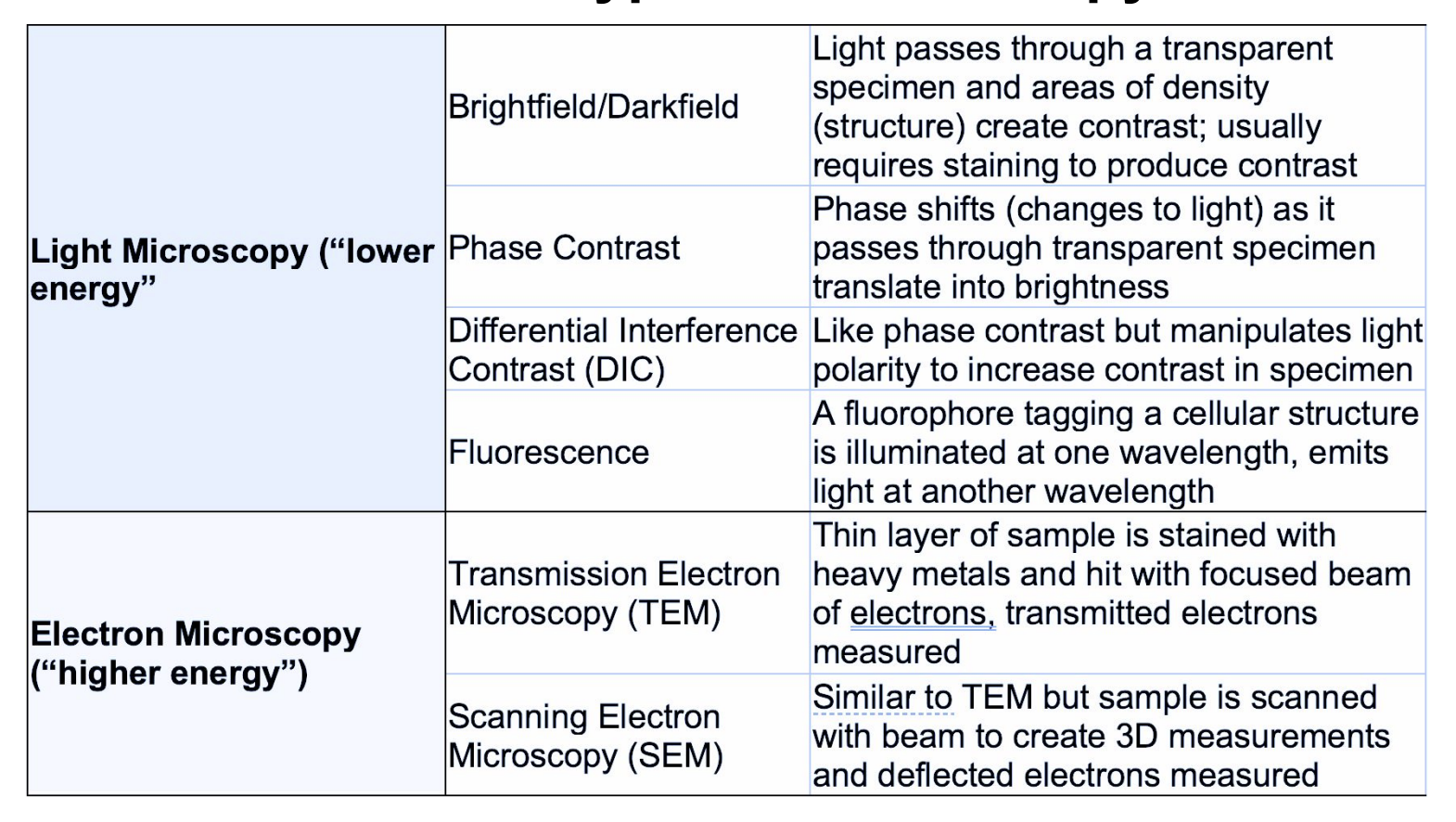
Microscopy basics

Different Types of Microscopy
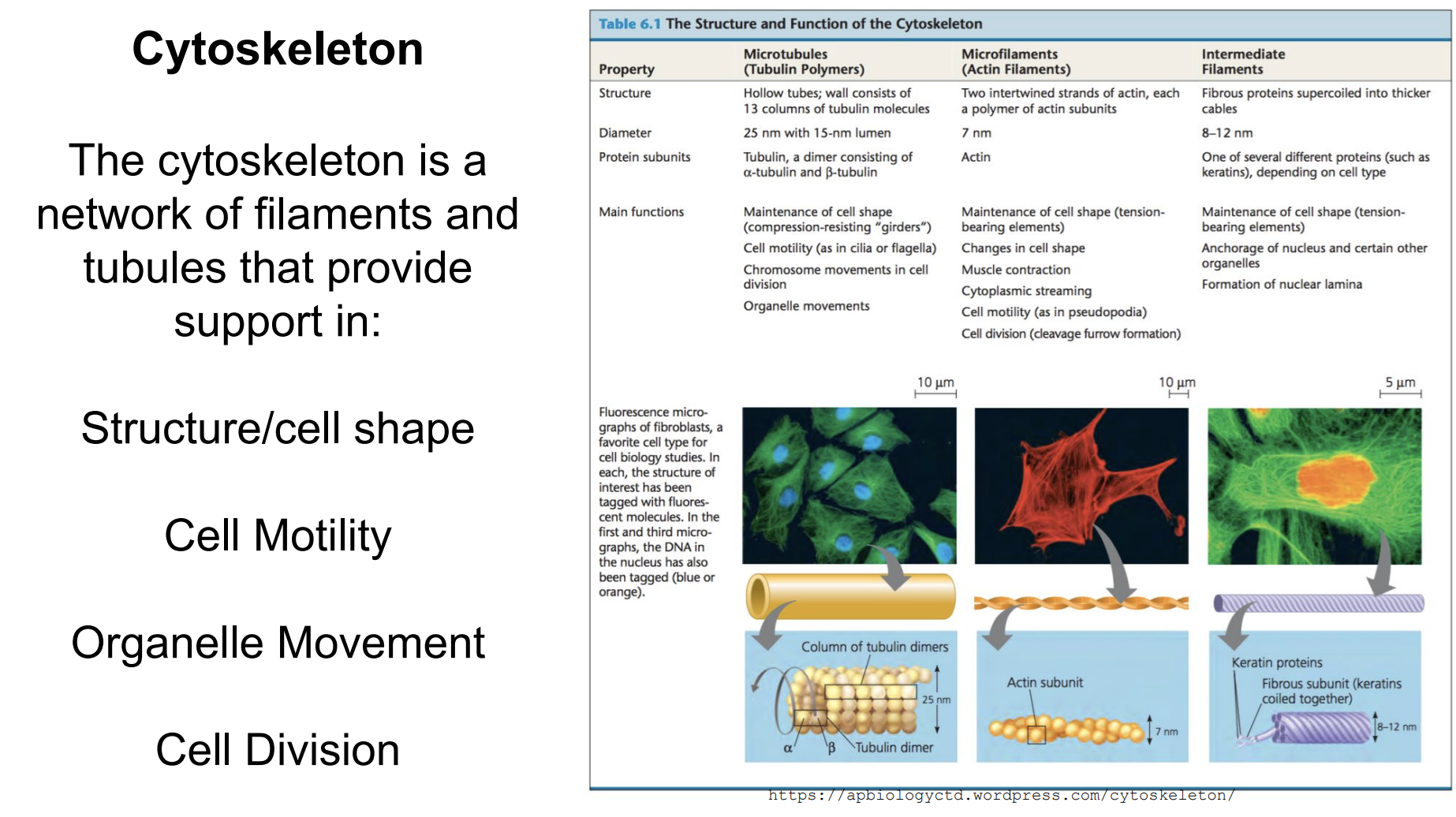
Cytoskeleton
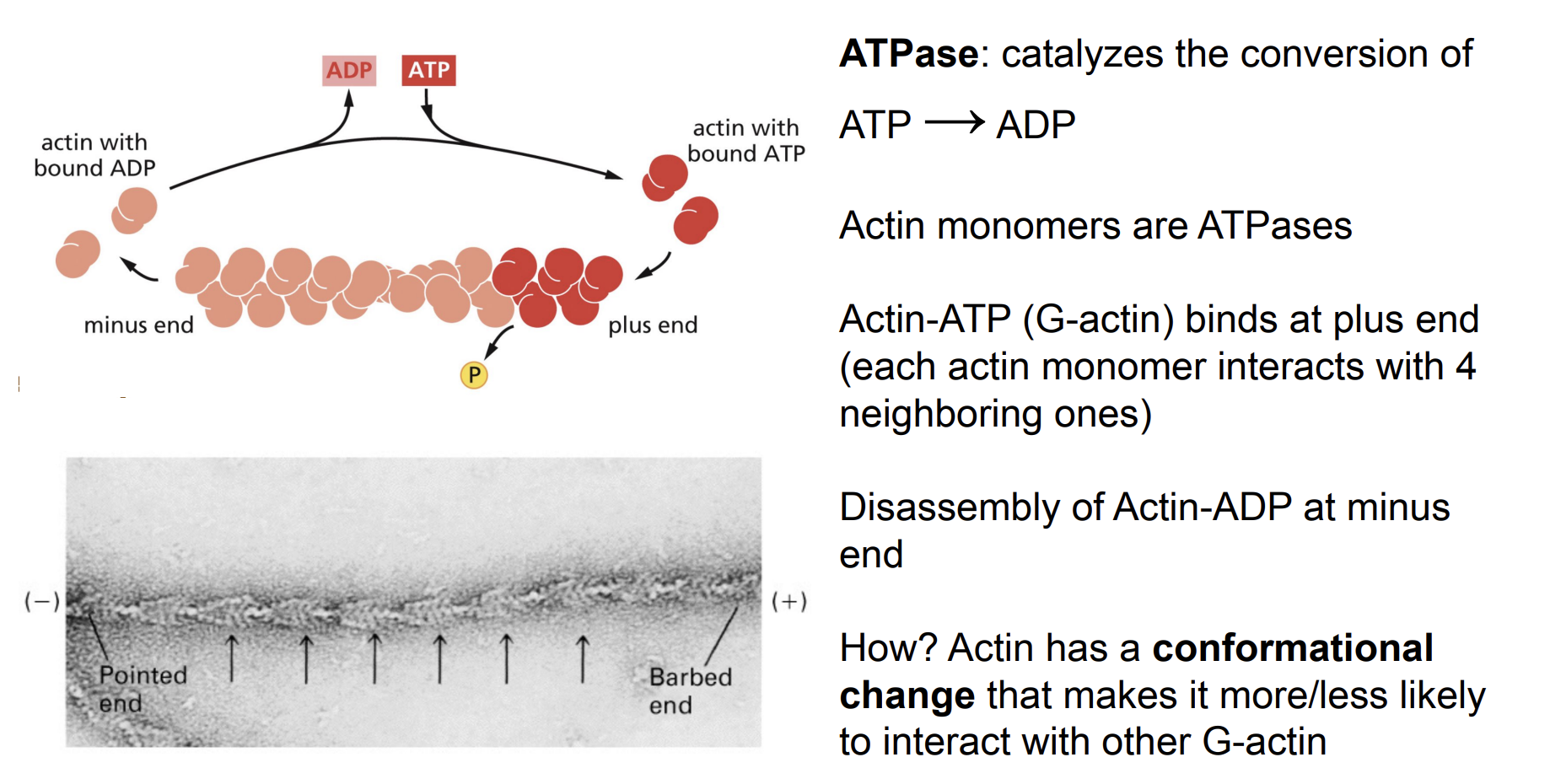
Actin as an ATPase
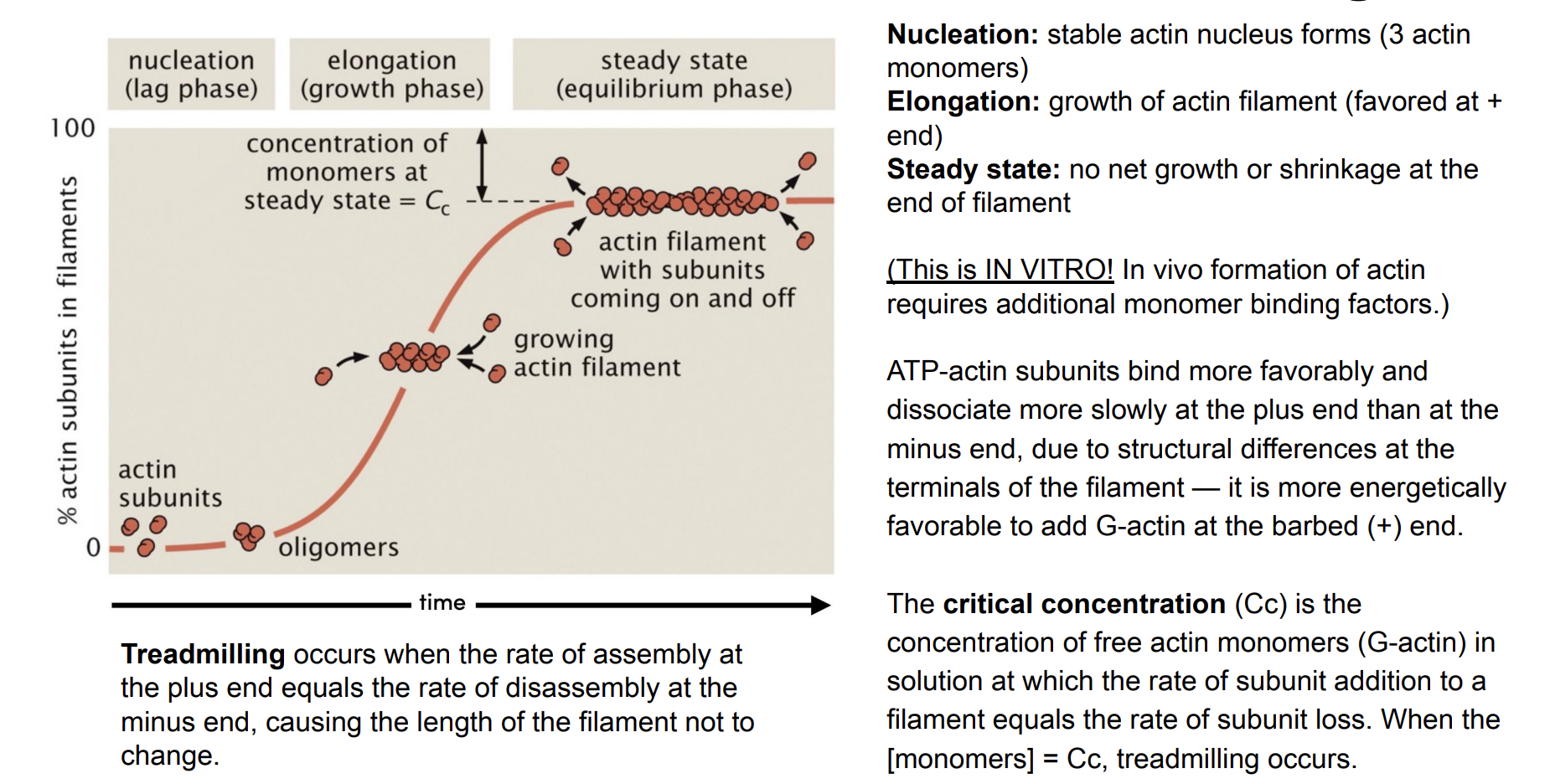
Critical Concentration and Treadmilling
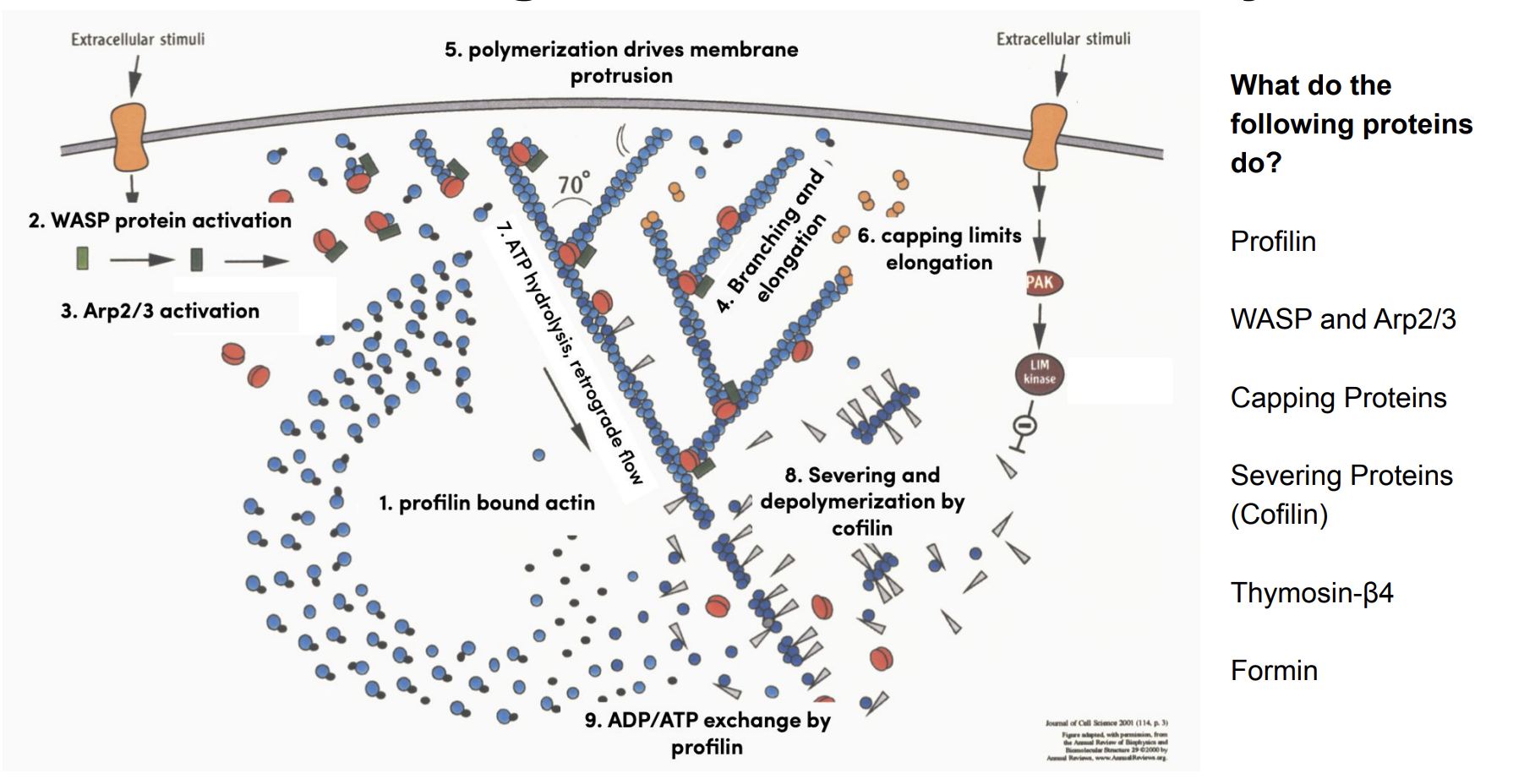
Actin Regulation and Cell Motility
Profilin → Speeds filament elongation at the barbed (+) end
WASP + Arp2/3 → Drive branched actin growth at the leading edge
Capping proteins → Stop filament elongation
Severing proteins (Cofilin) → Cut filaments and accelerate actin turnover
Thymosin-β4 → Prevent actin assembly by sequestering monomers
Formin → Drive linear (unbranched) actin filament growth
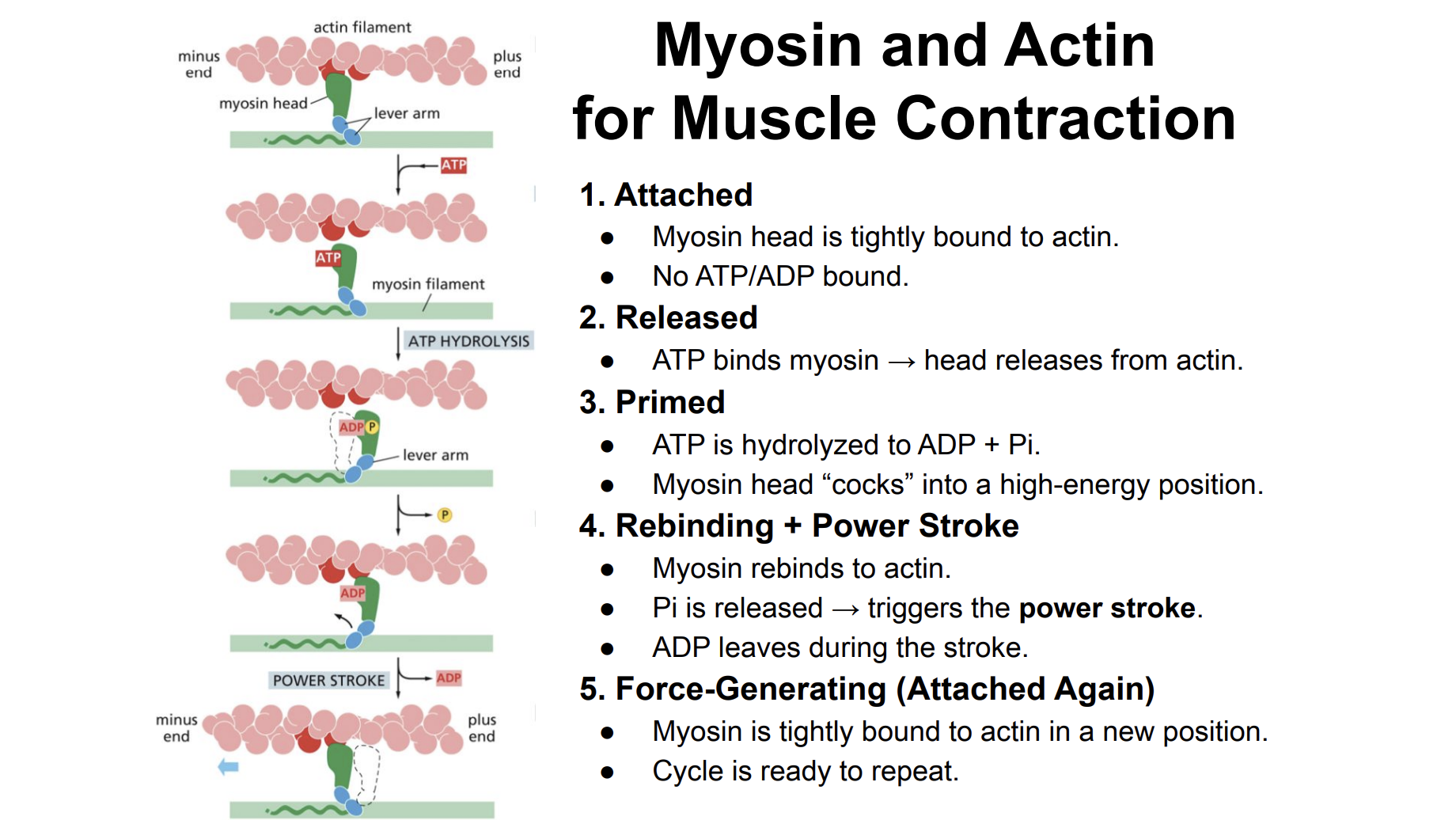
Myosin and Actin for Muscle Contraction
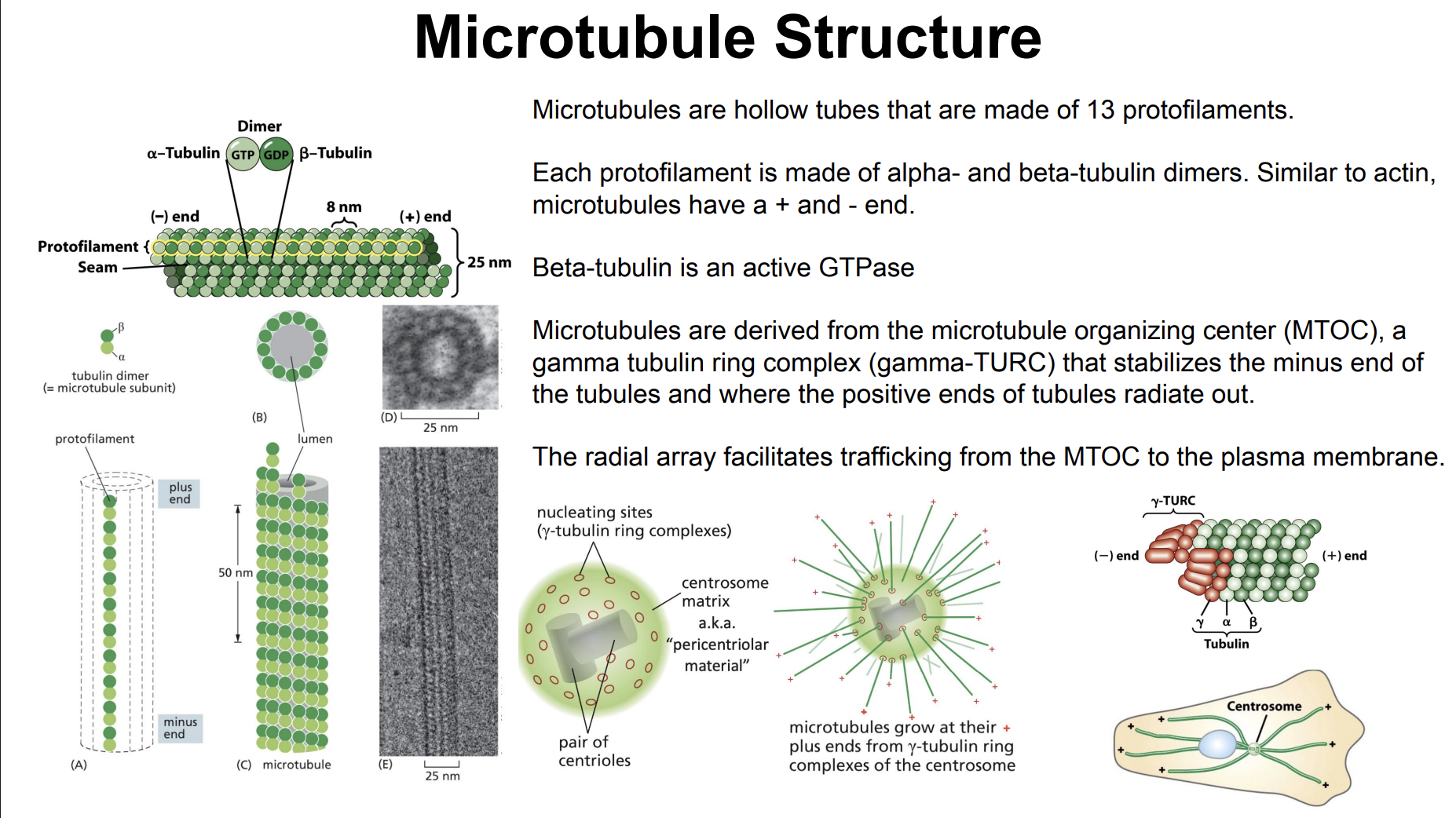
Microtubule Structure
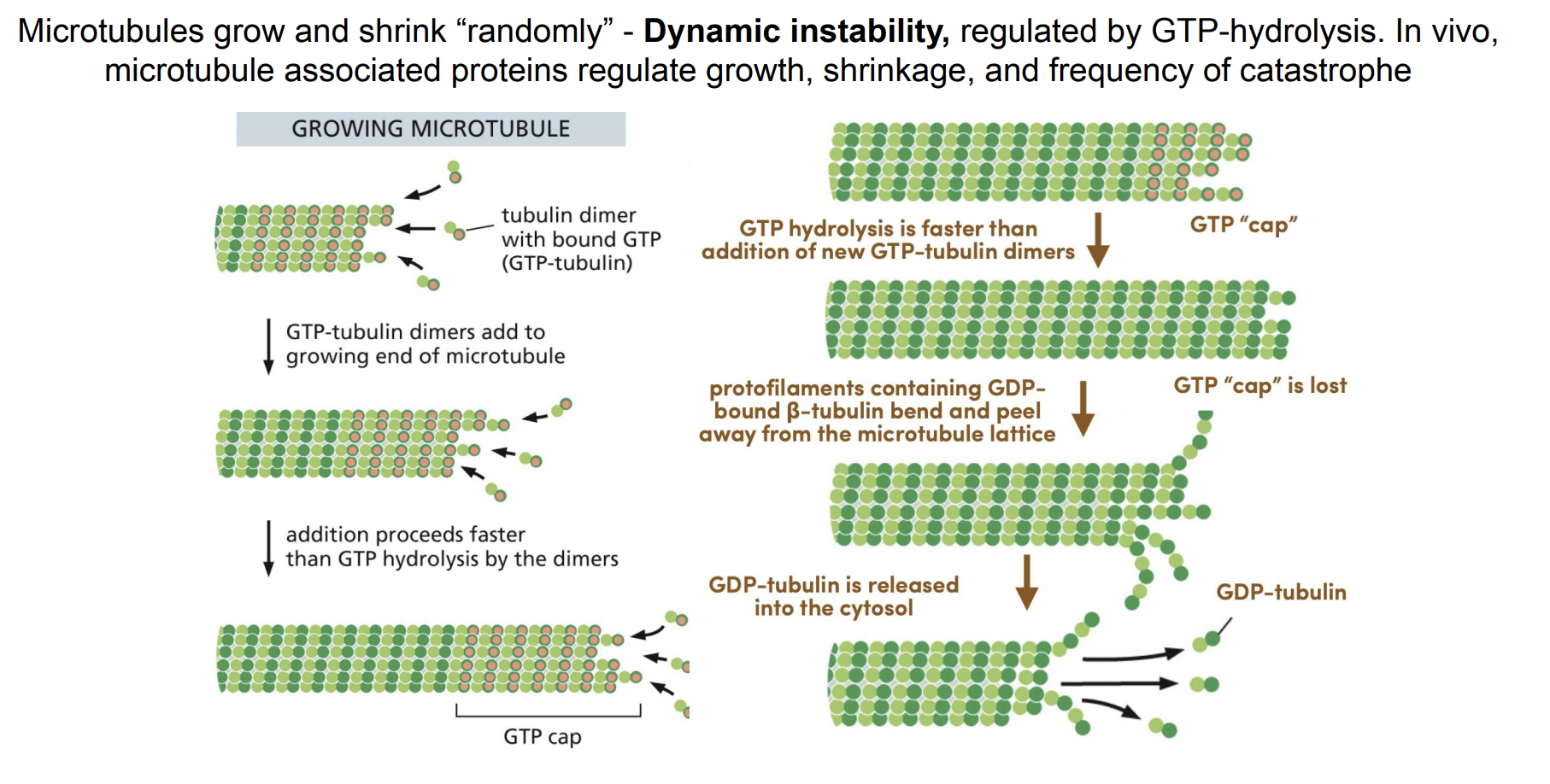
Dynamic Instability
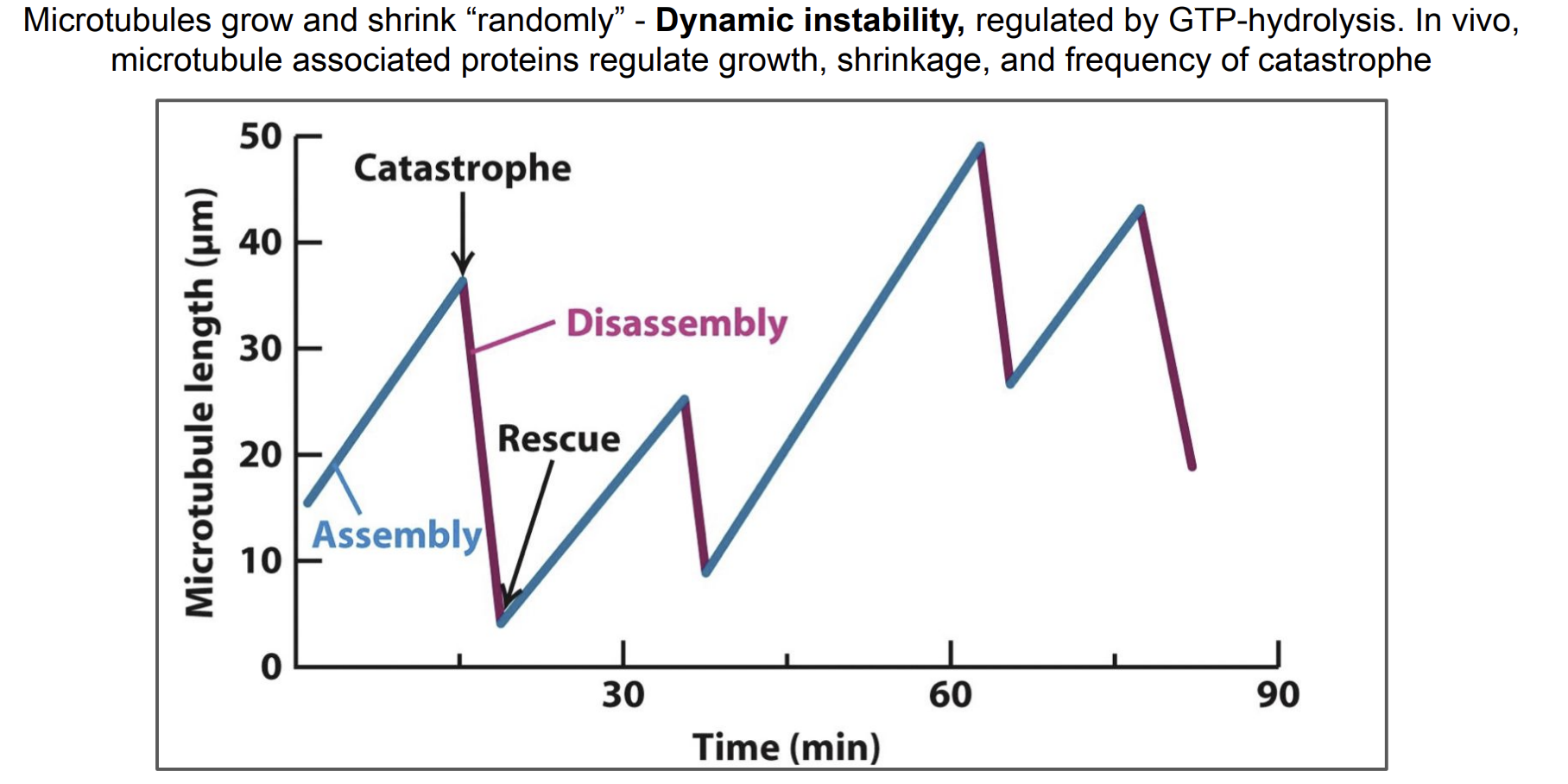
Dynamic Instability (Catastrophe and Rescue)
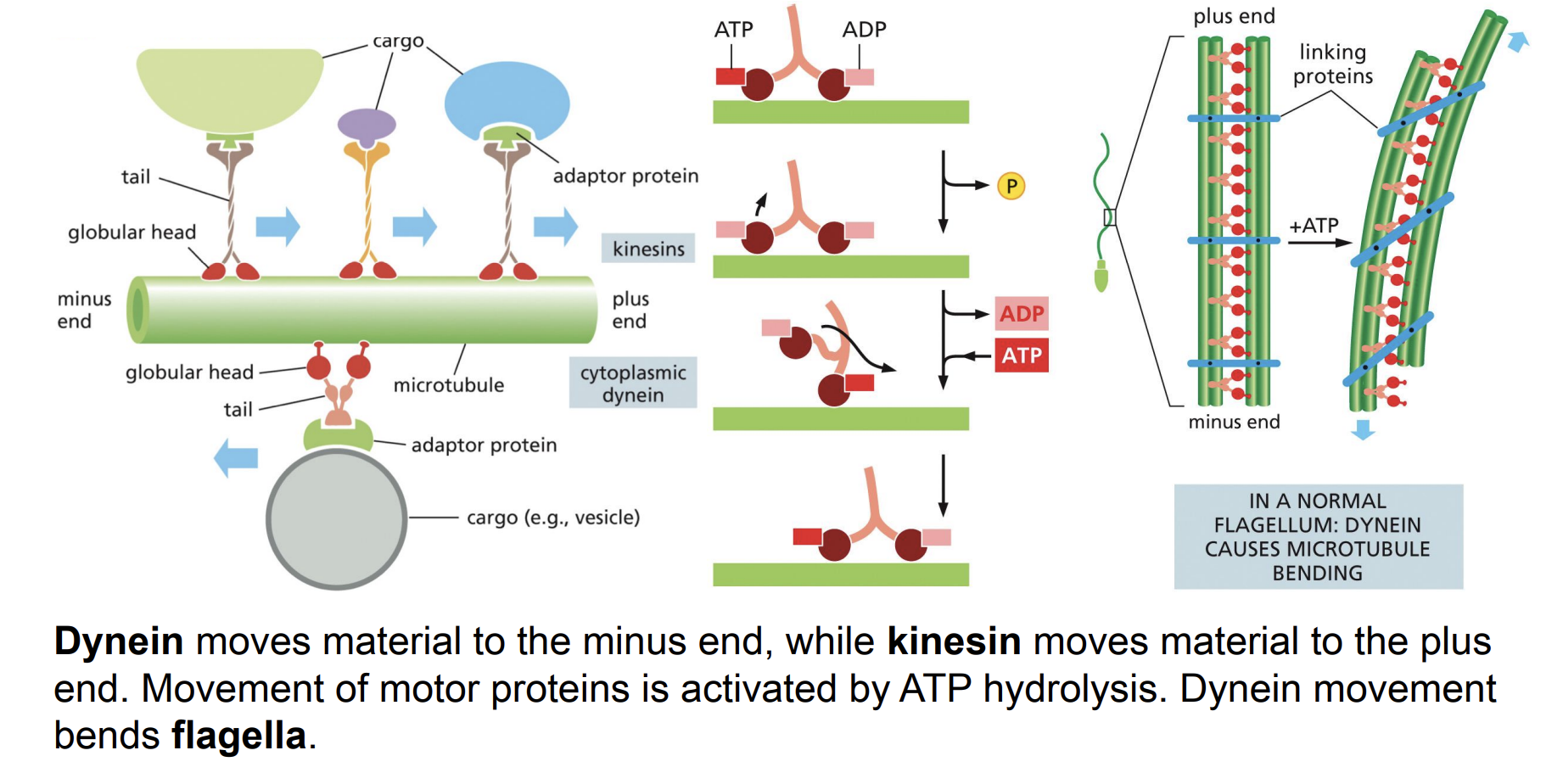
Motor Proteins
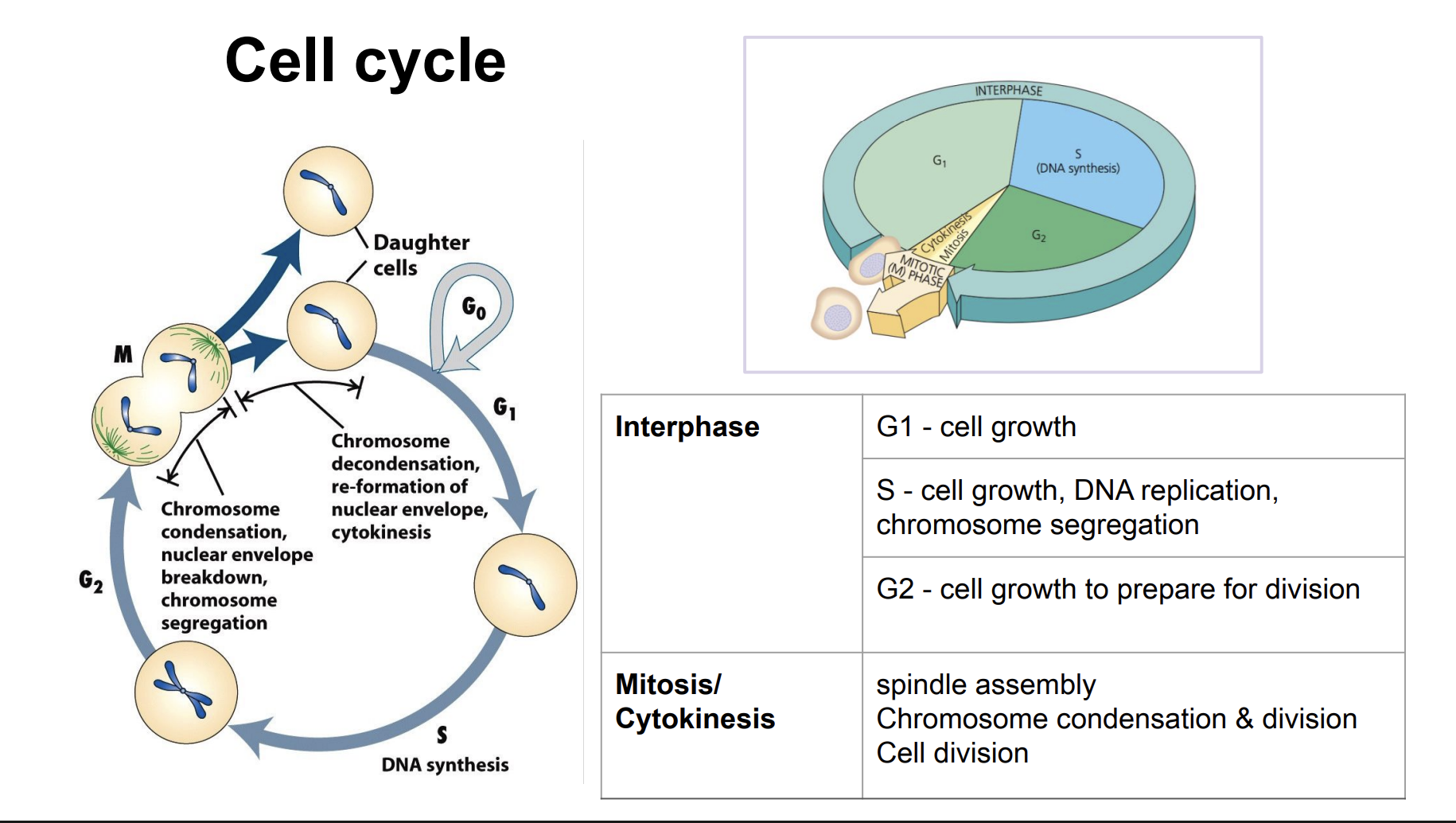
Cell cycle
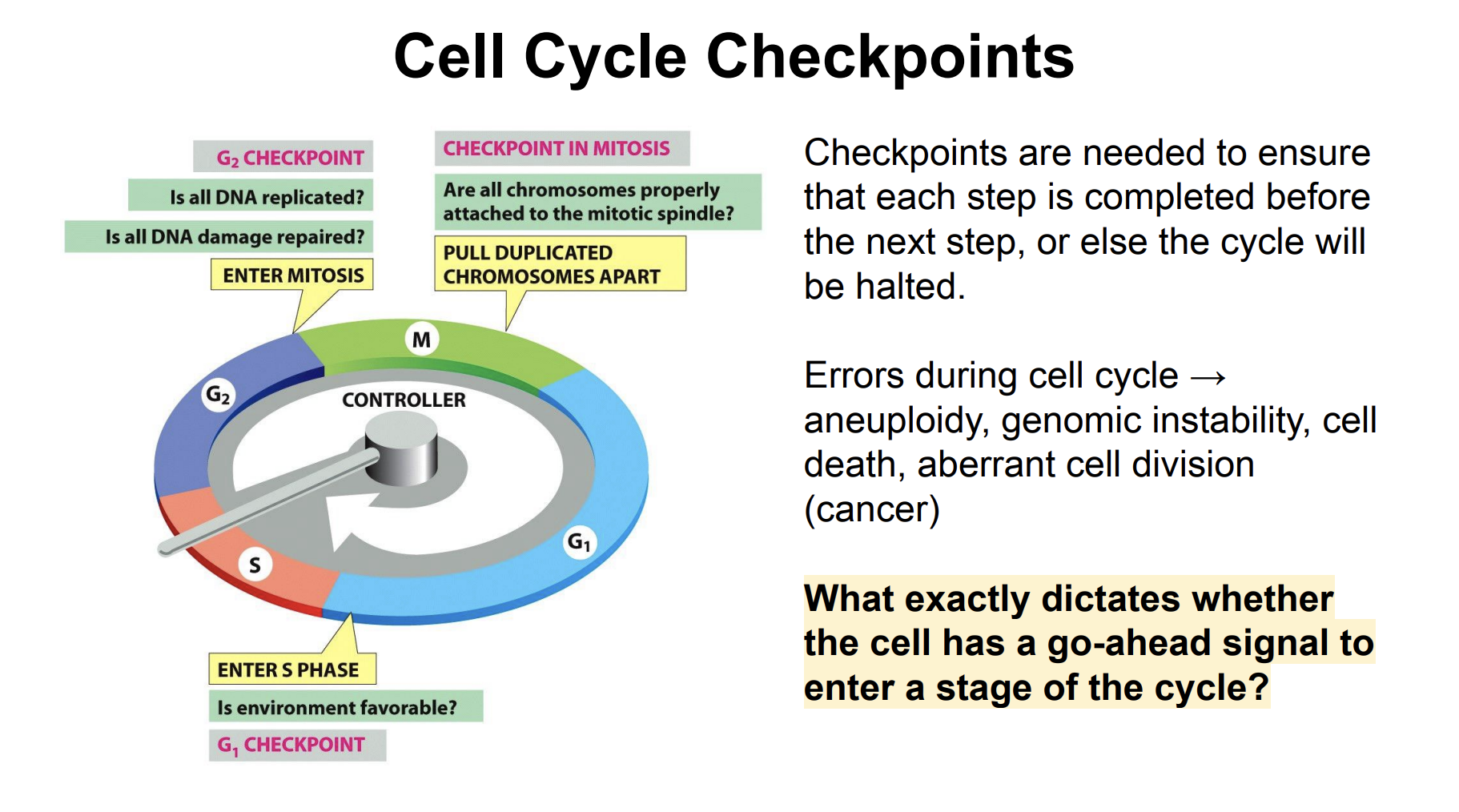
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
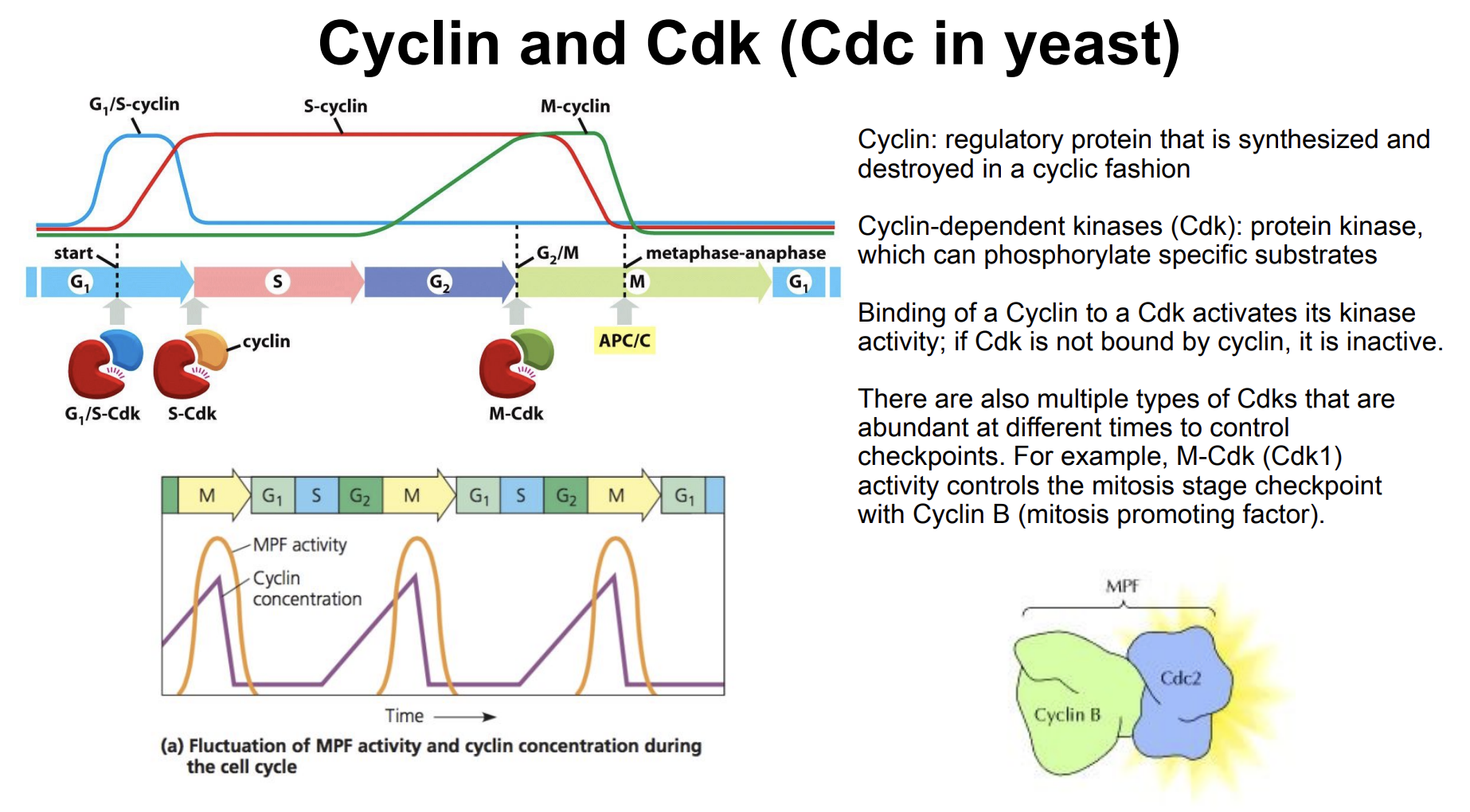
Cyclin and Cdk (Cdc in yeast)
Cyclin B and Cdk1 cycle
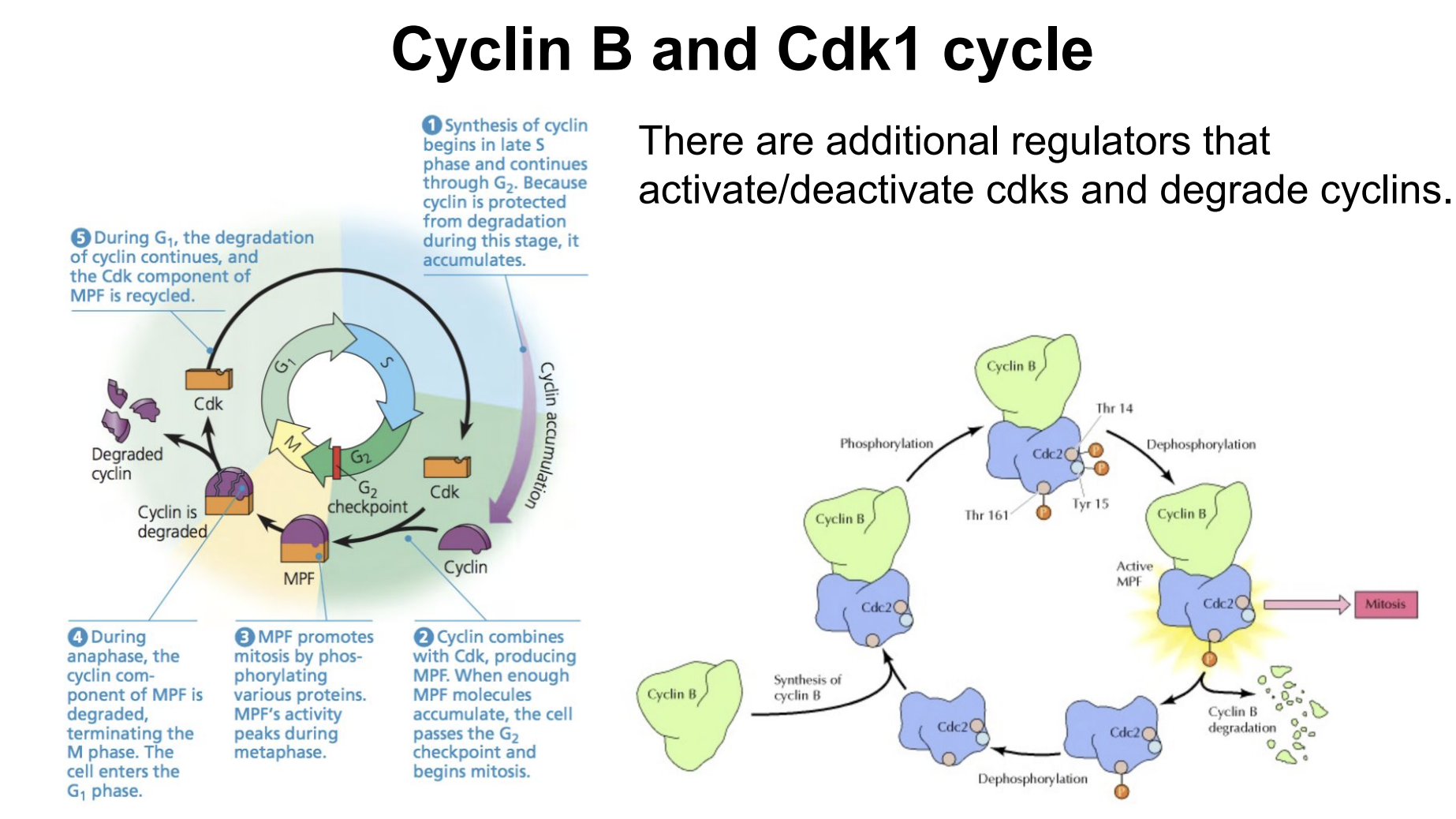
Regulators of MPF
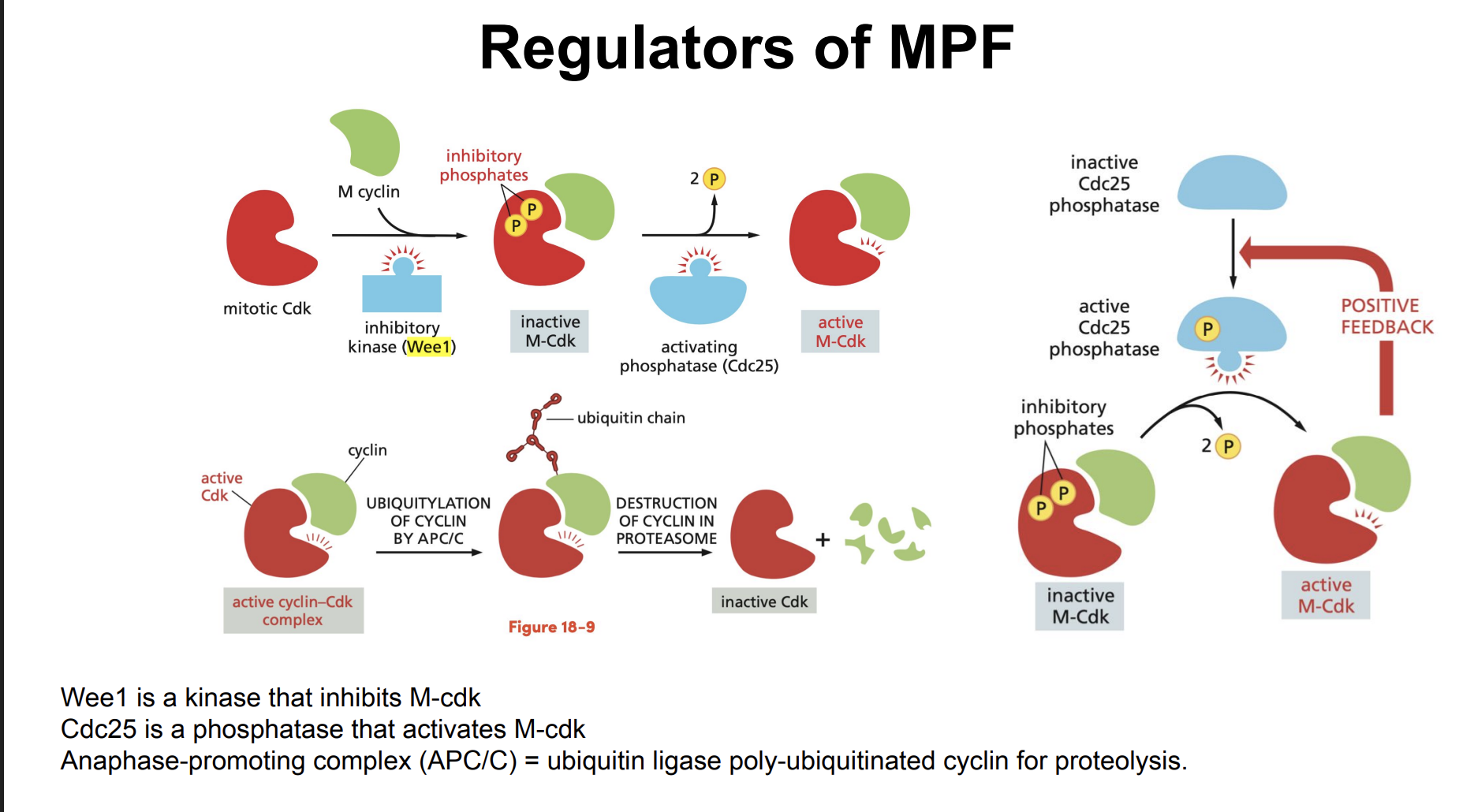
Chromosome Condensation (between prophase and prometaphase)
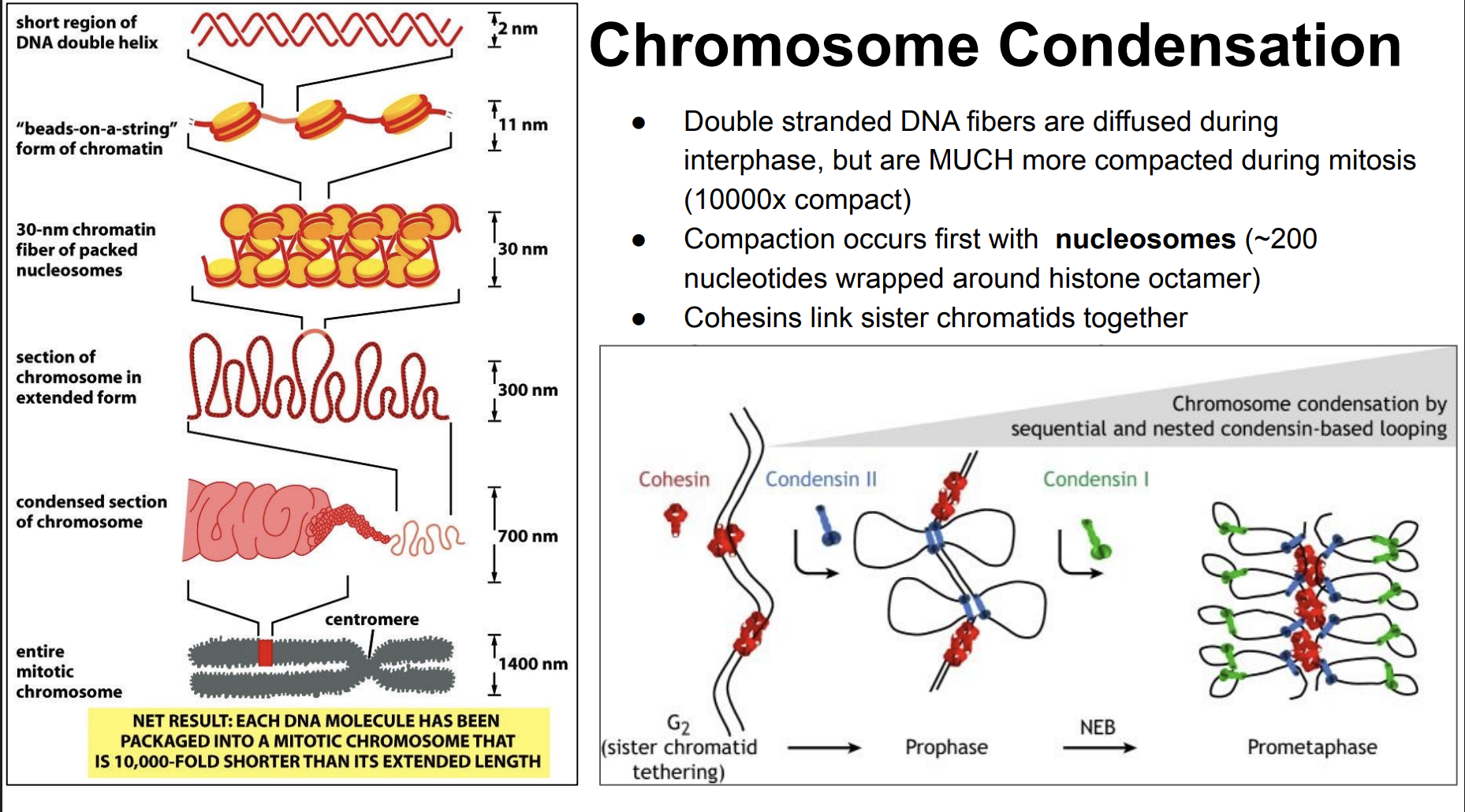
Metaphase-Anaphase Transition
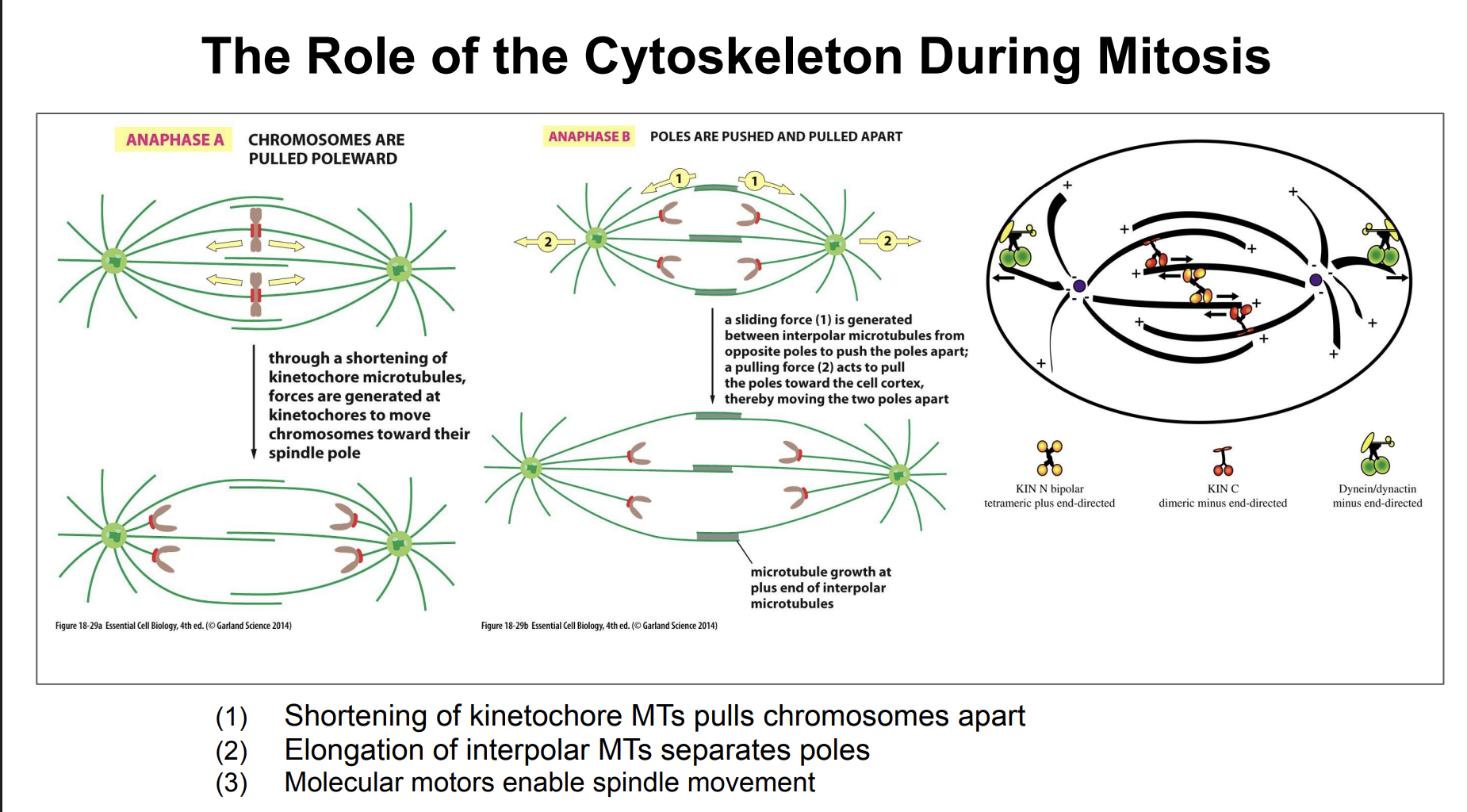
The Role of the Cytoskeleton During Mitosis

The Role of the Cytoskeleton During Mitosis (diagram)
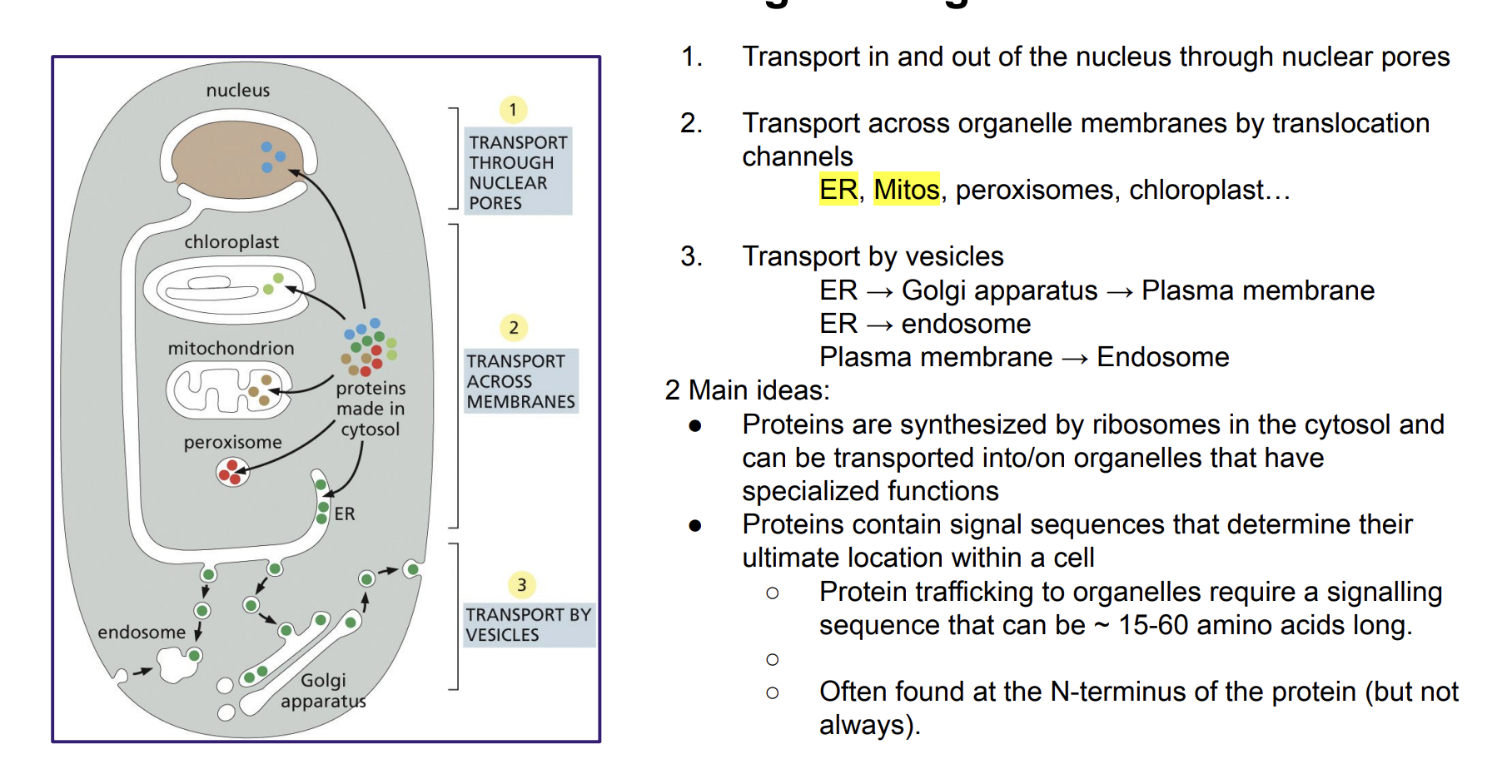
Protein sorting into organelles
Necessary vs. Sufficient
Necessary - A condition is necessary if it must be true or must be present for something else to occur. Without it, the outcome cannot happen. If the outcome occurs, then the condition had to be present.
Sufficient - A condition is sufficient if its presence guarantees the outcome. Whenever the condition is present, the outcome will occur. If the condition occurs, then the outcome definitely happens.
In the case of protein signal sequences:
‘Necessary’ means the signal sequence is required for sorting.
‘Sufficiency’ means the signal sequence alone can specify sorting.
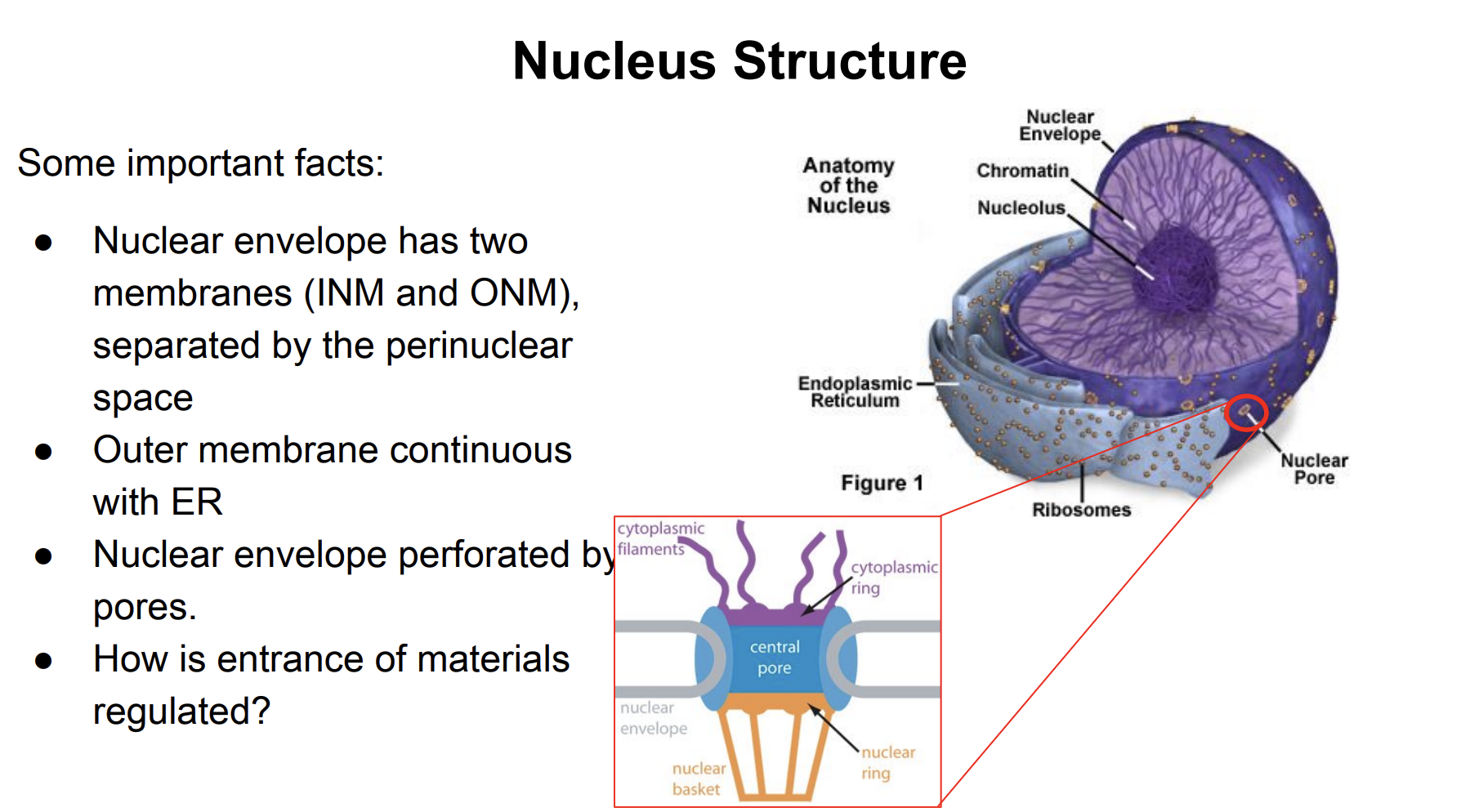
Nucleus Structure
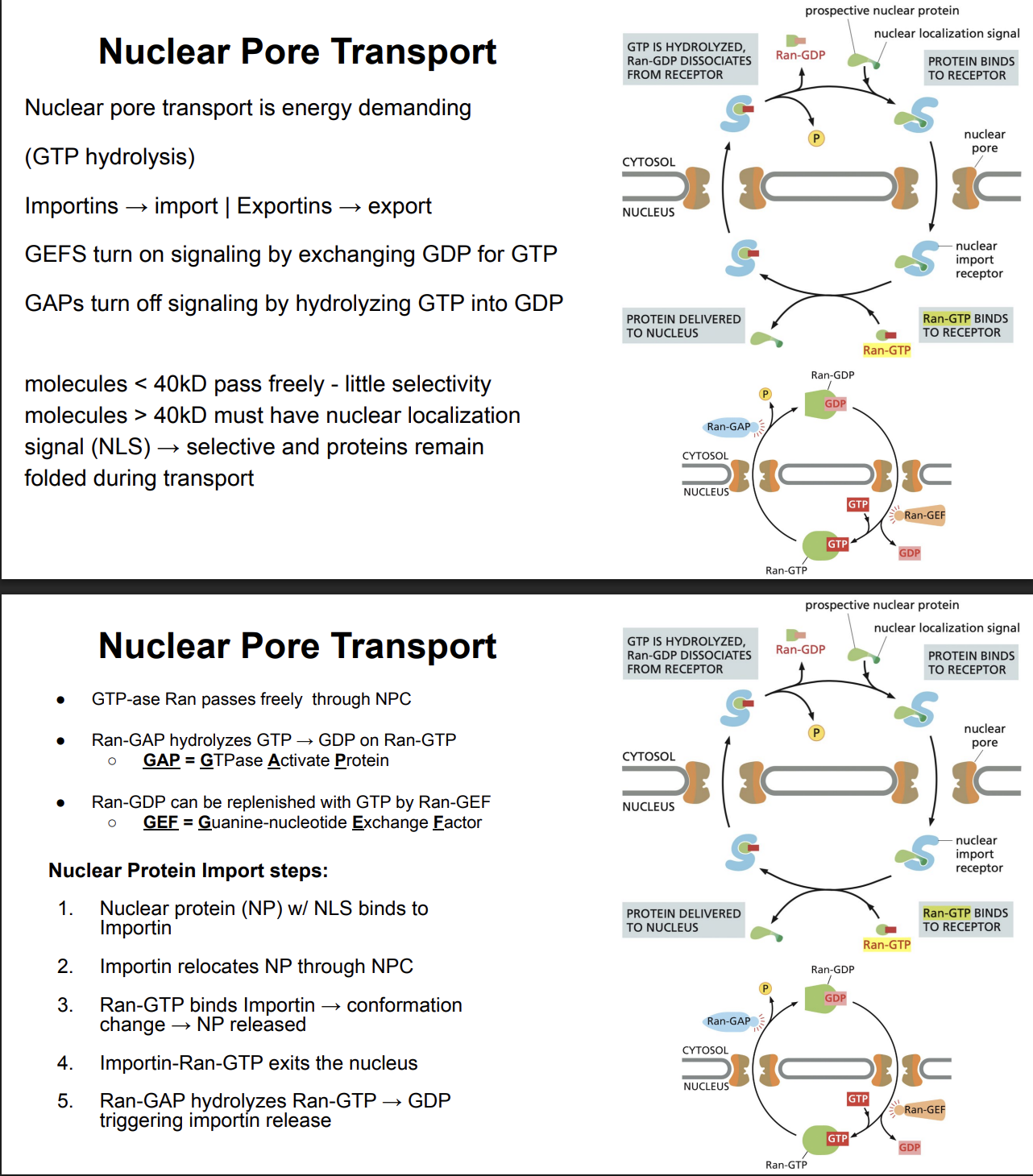
Nuclear Pore Transport
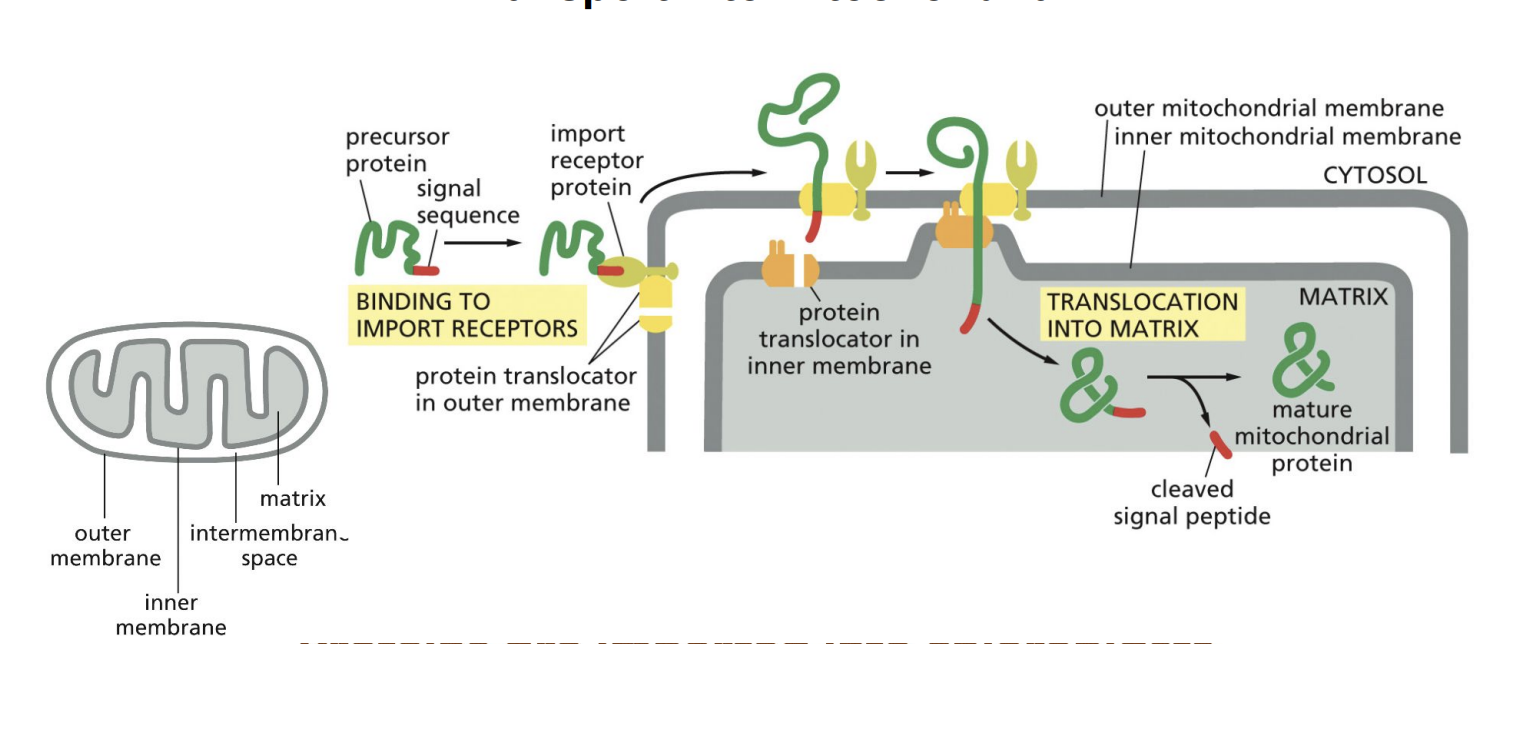
Transport into Mitochondria
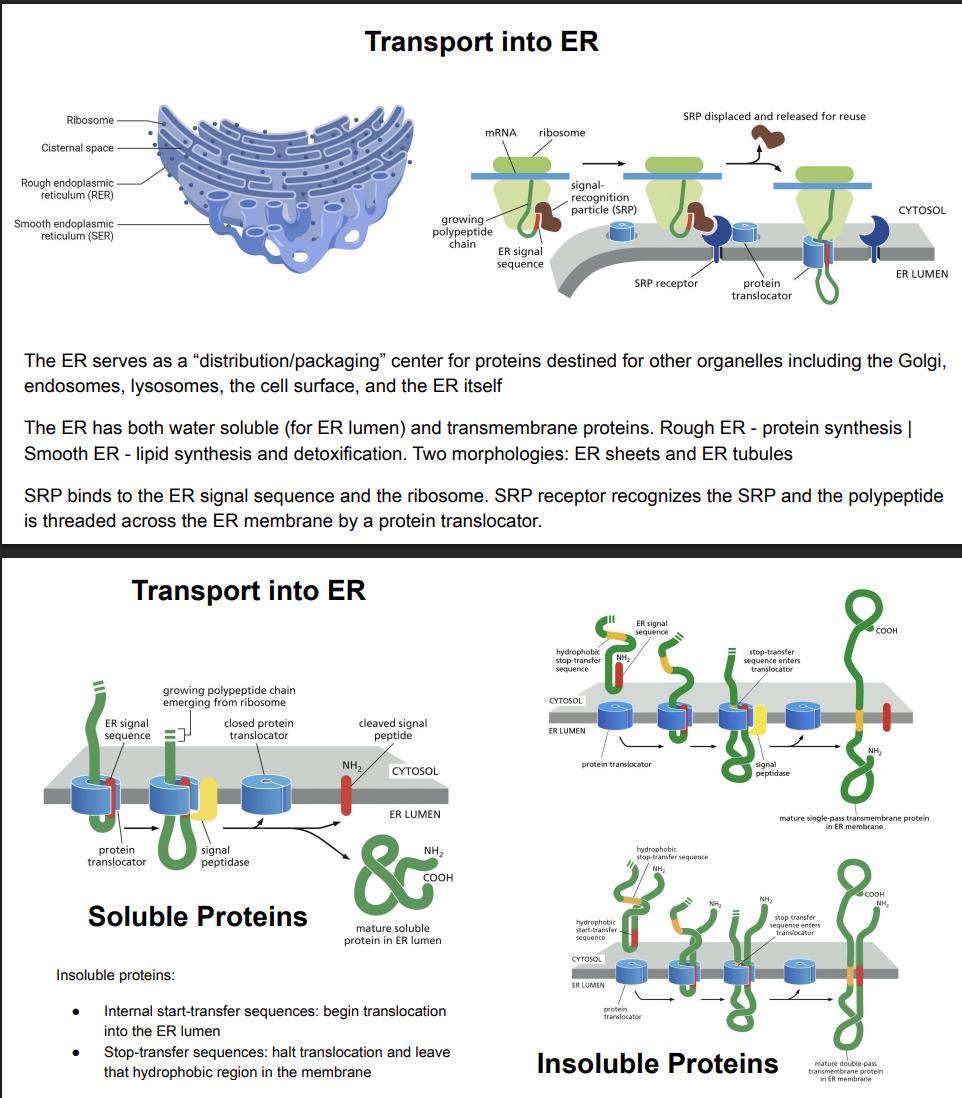
Transport into ER
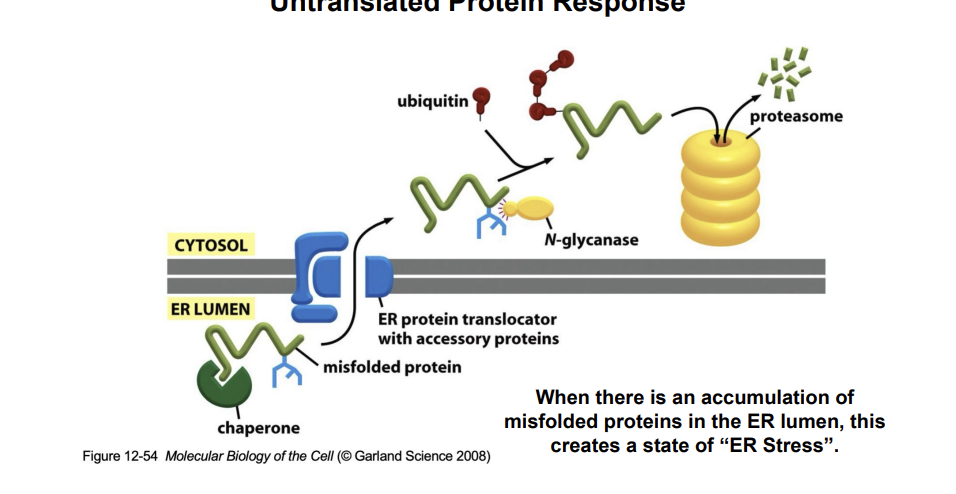
Untranslated Protein Response
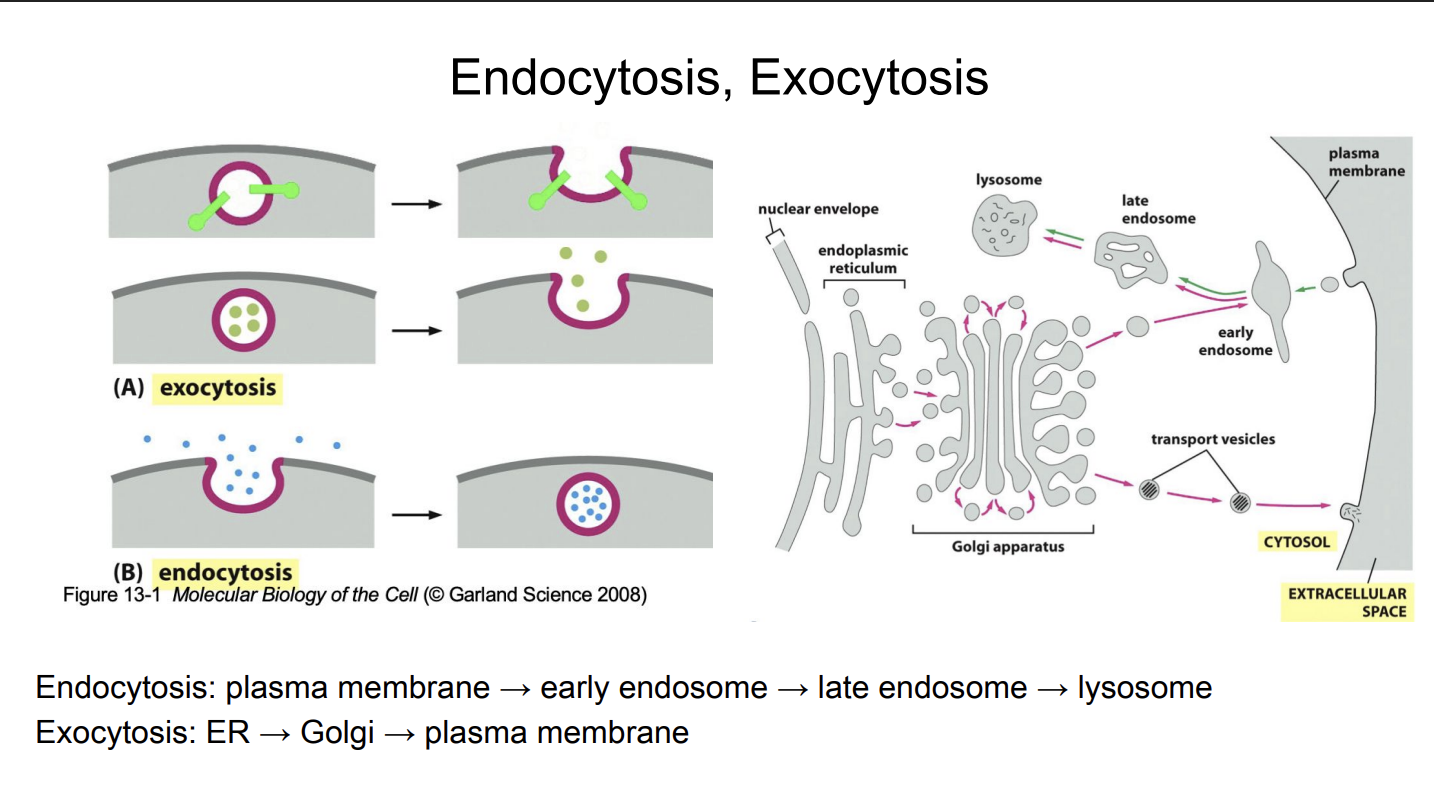
Endocytosis, Exocytosis
Vesicular Transport
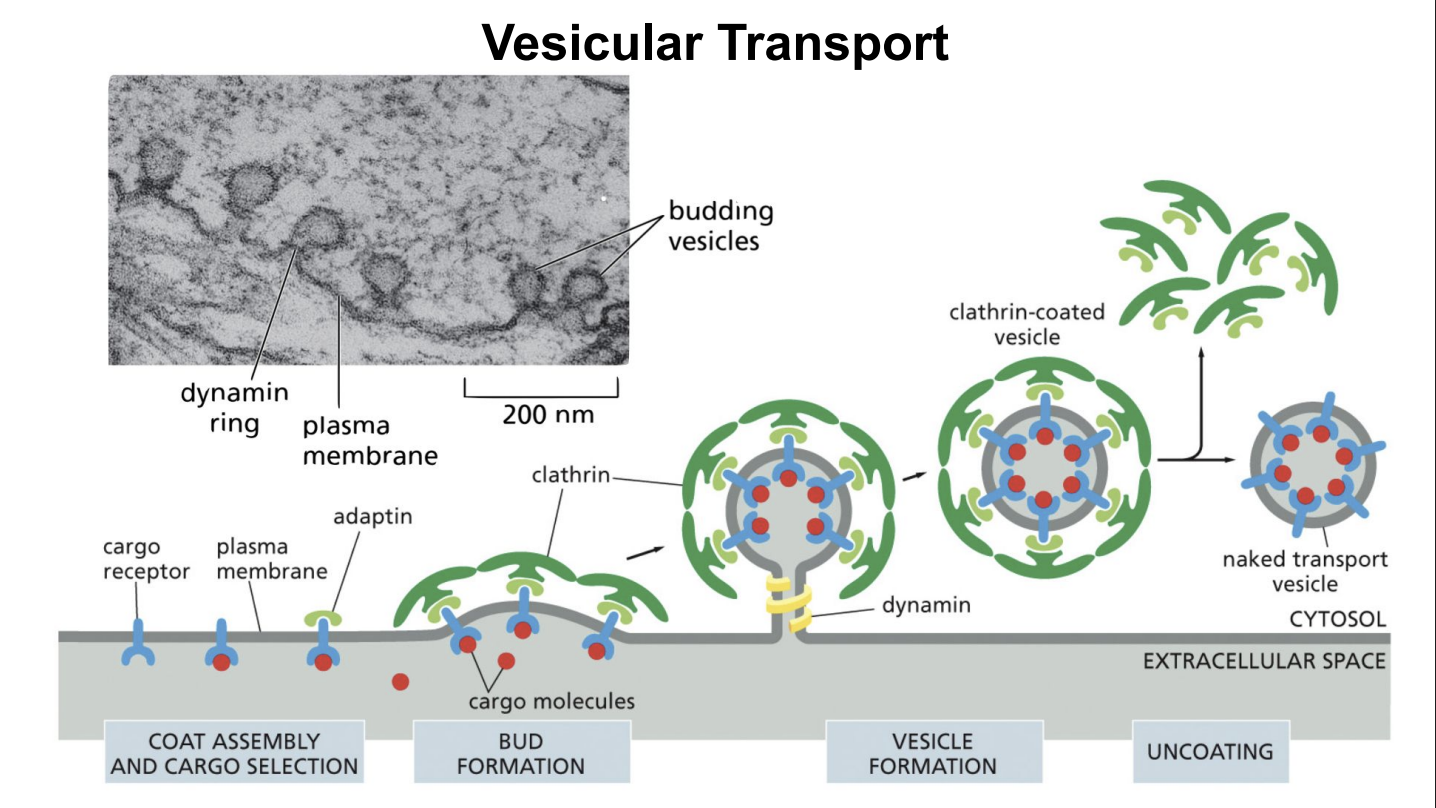
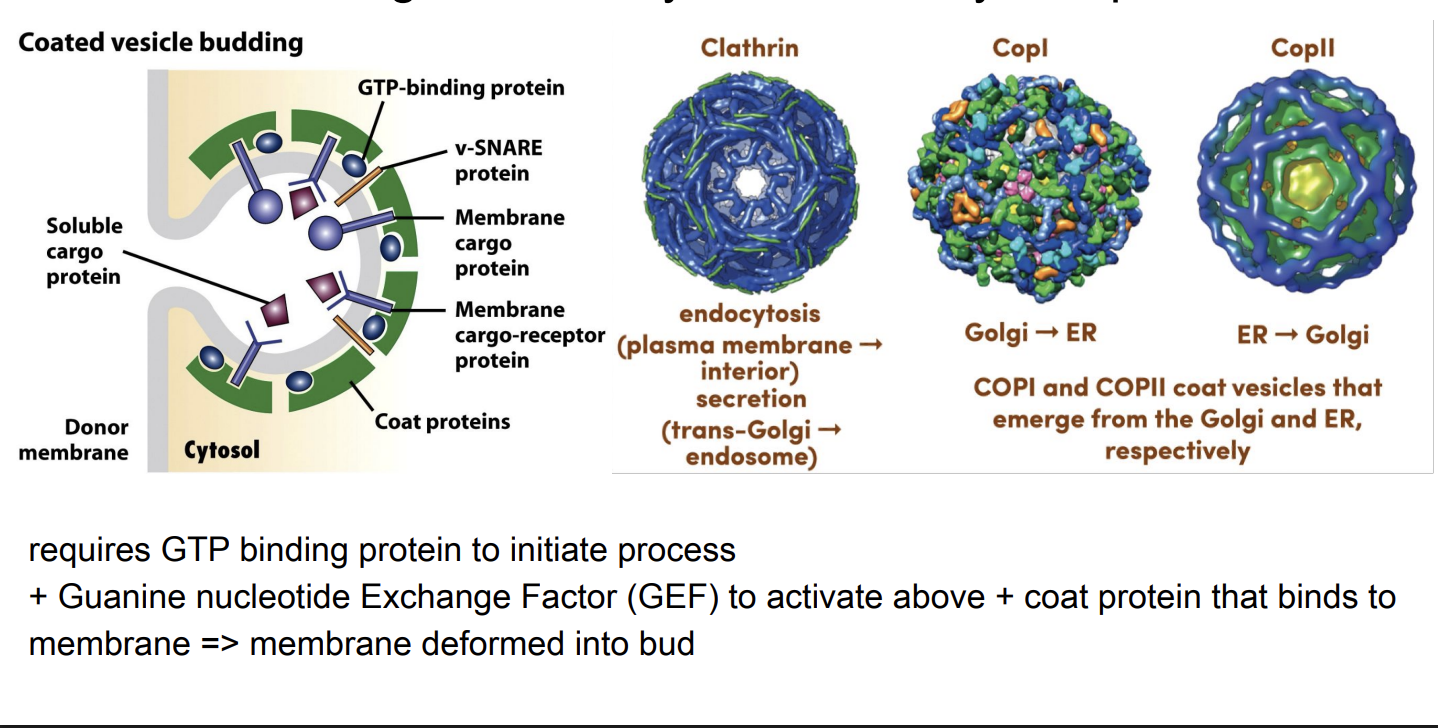
Vesicle budding is driven by the assembly of a protein coat
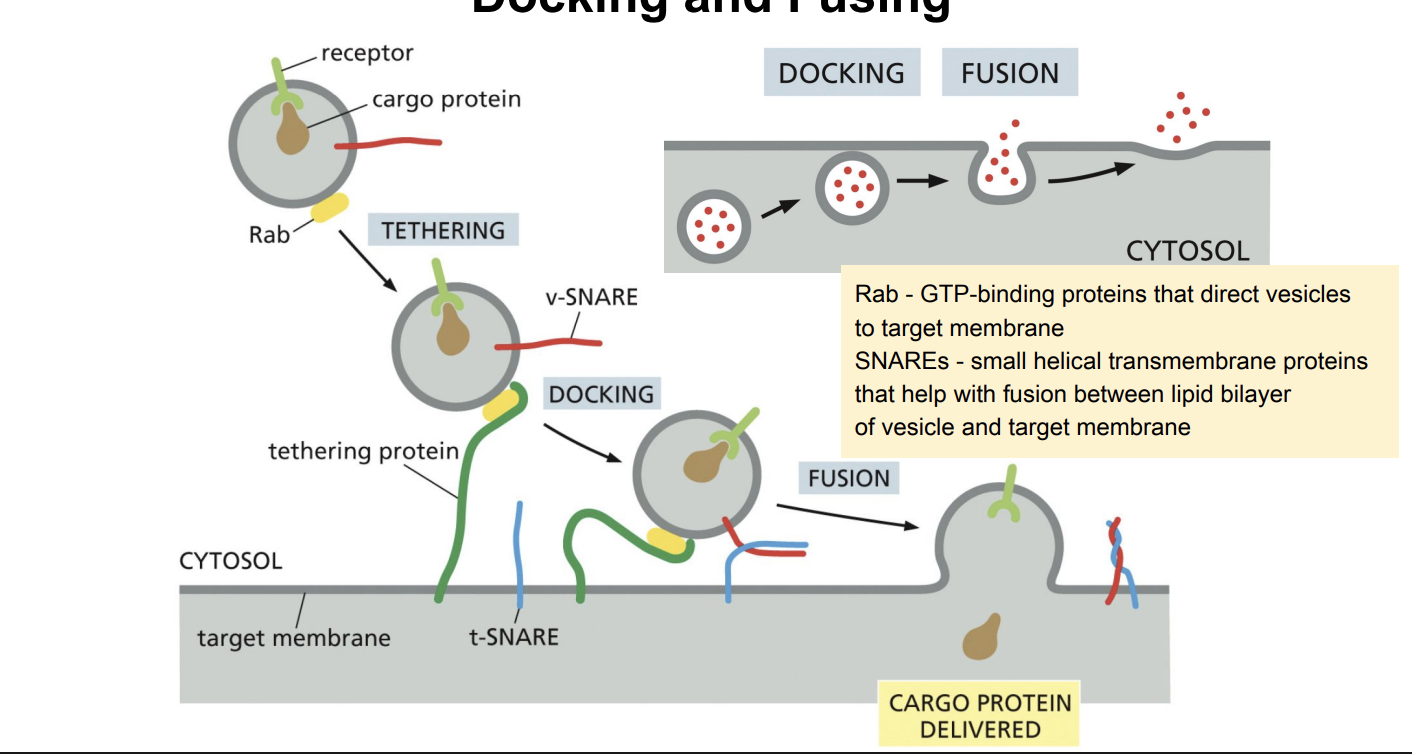
Docking and Fusing
Cell Signaling
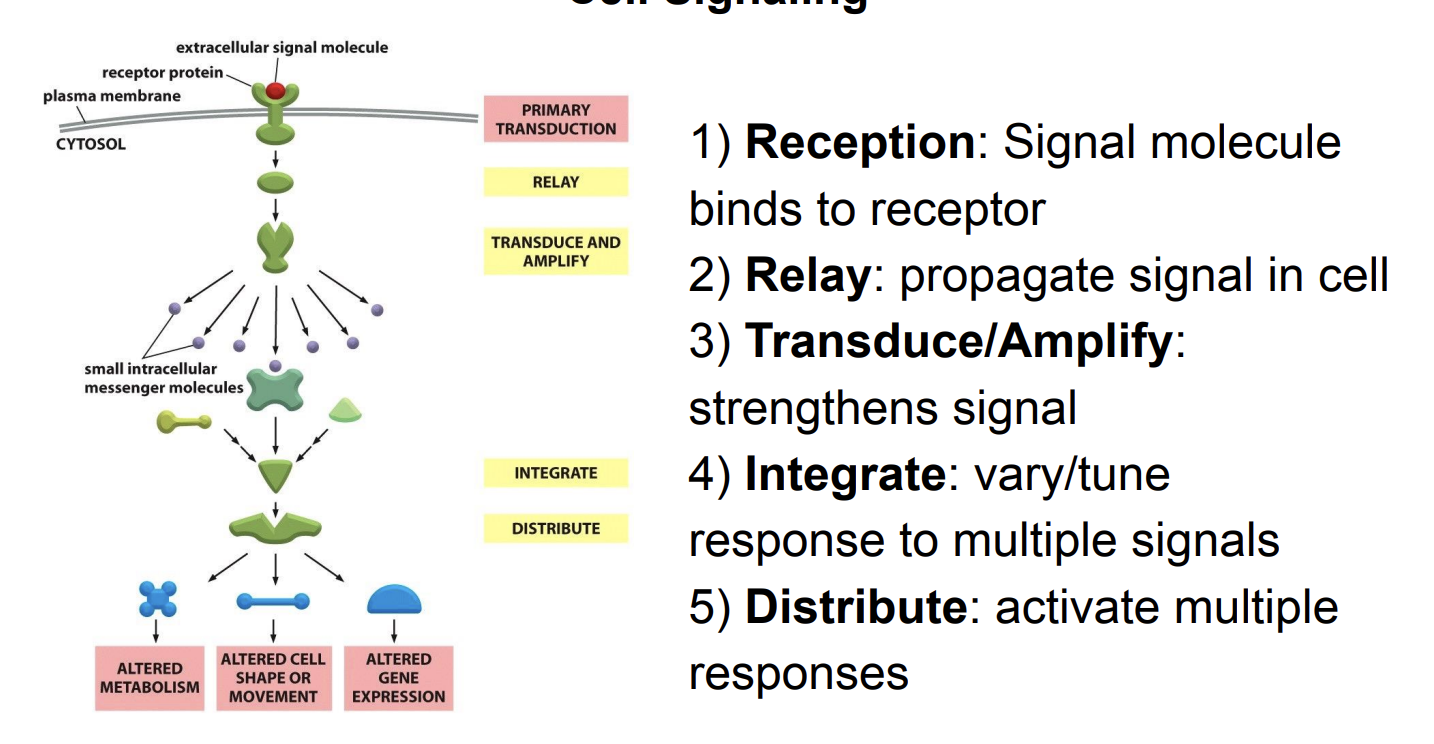
Cell Signaling - Like a relay race

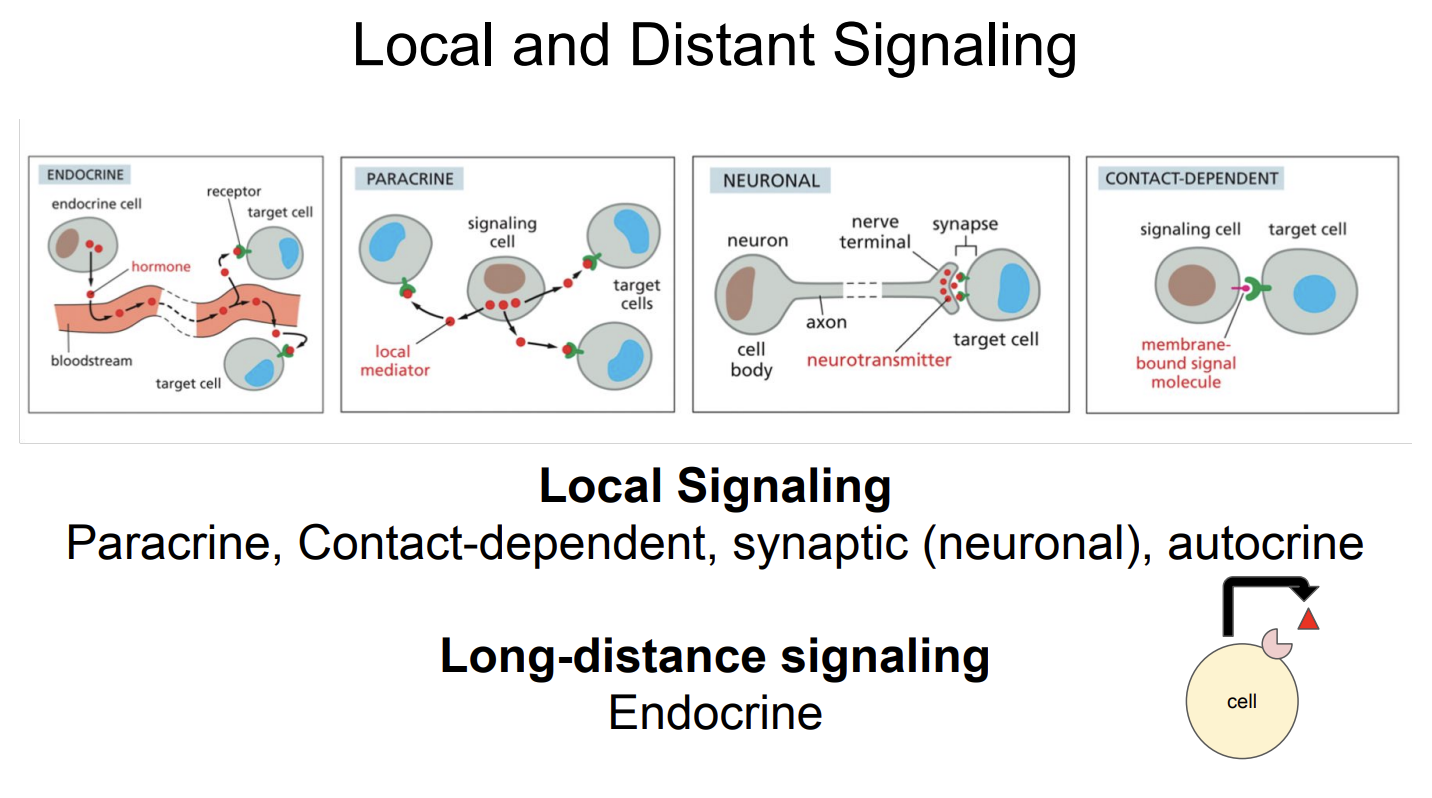
Local and Distant Signaling
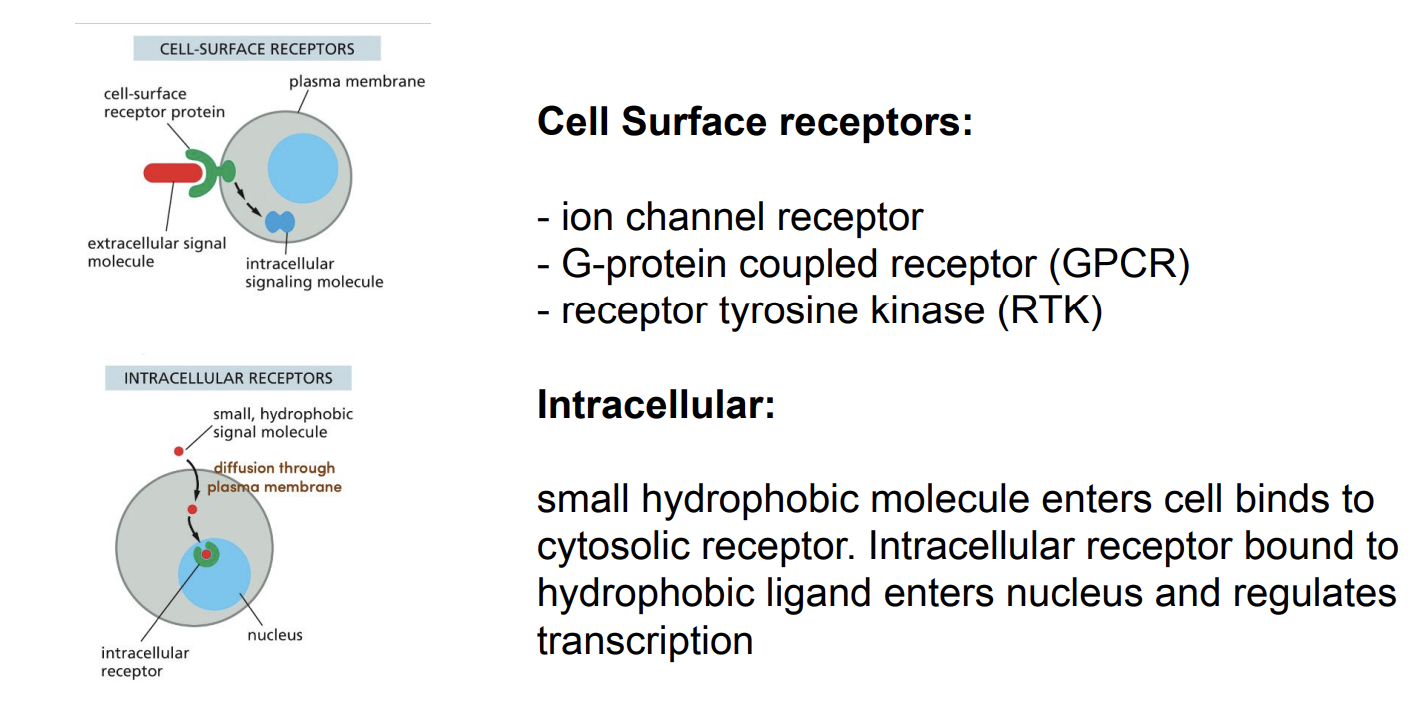
2 Different Types of Receptors
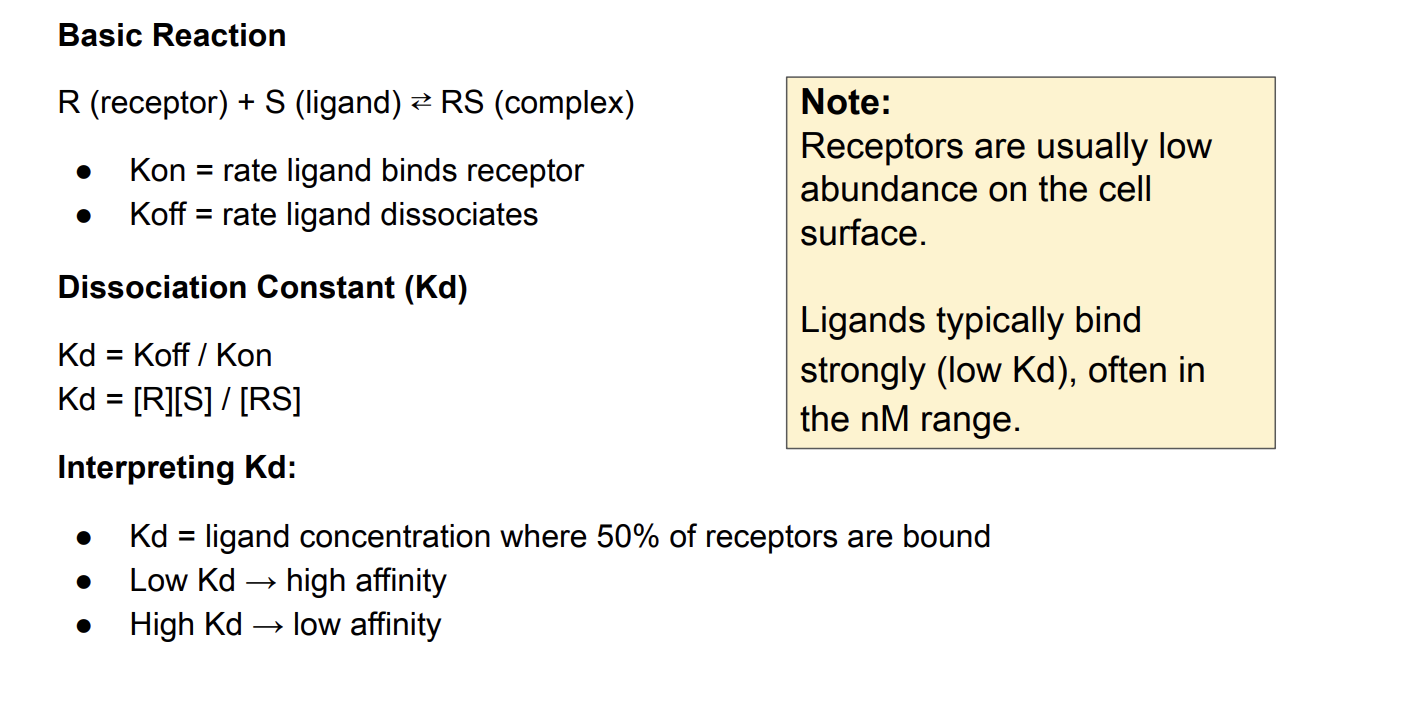
Receptor-Ligand Binding Affinity
Signaling Basics
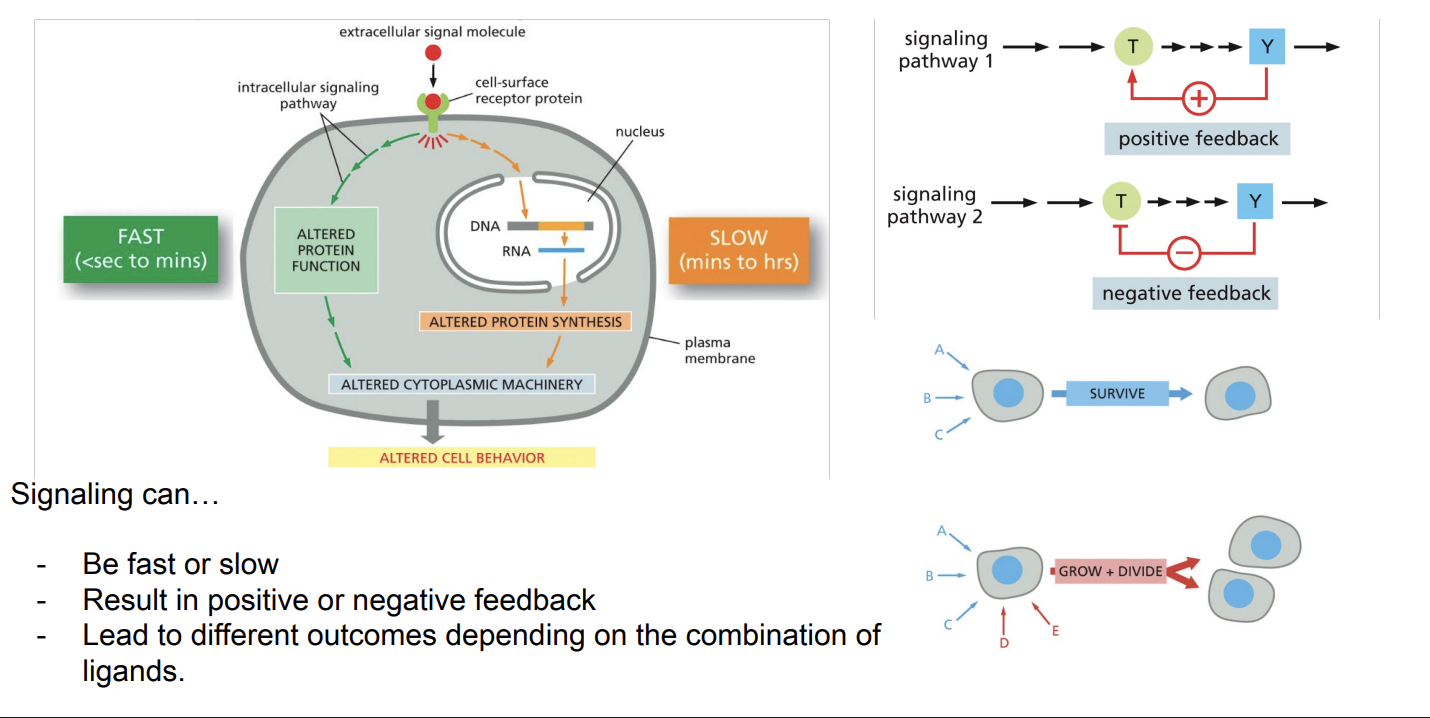
Molecular Switches
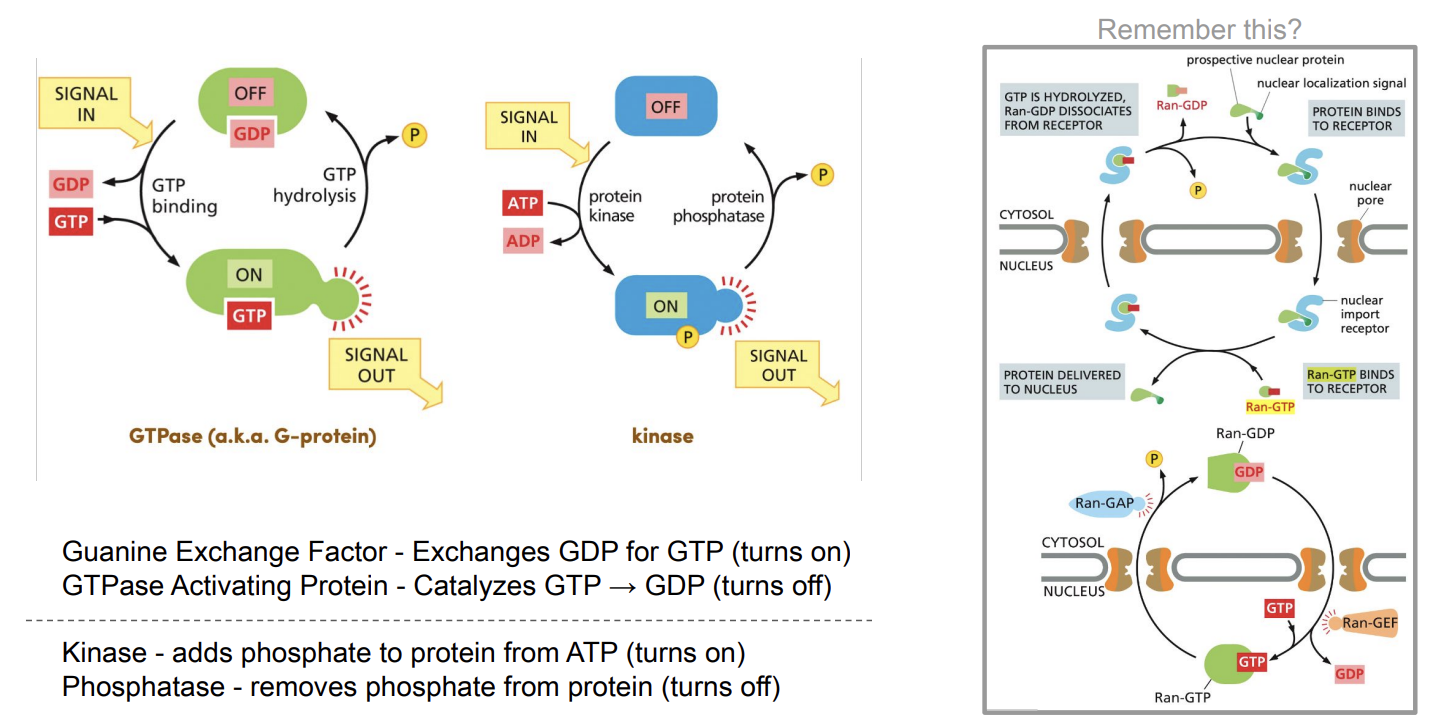
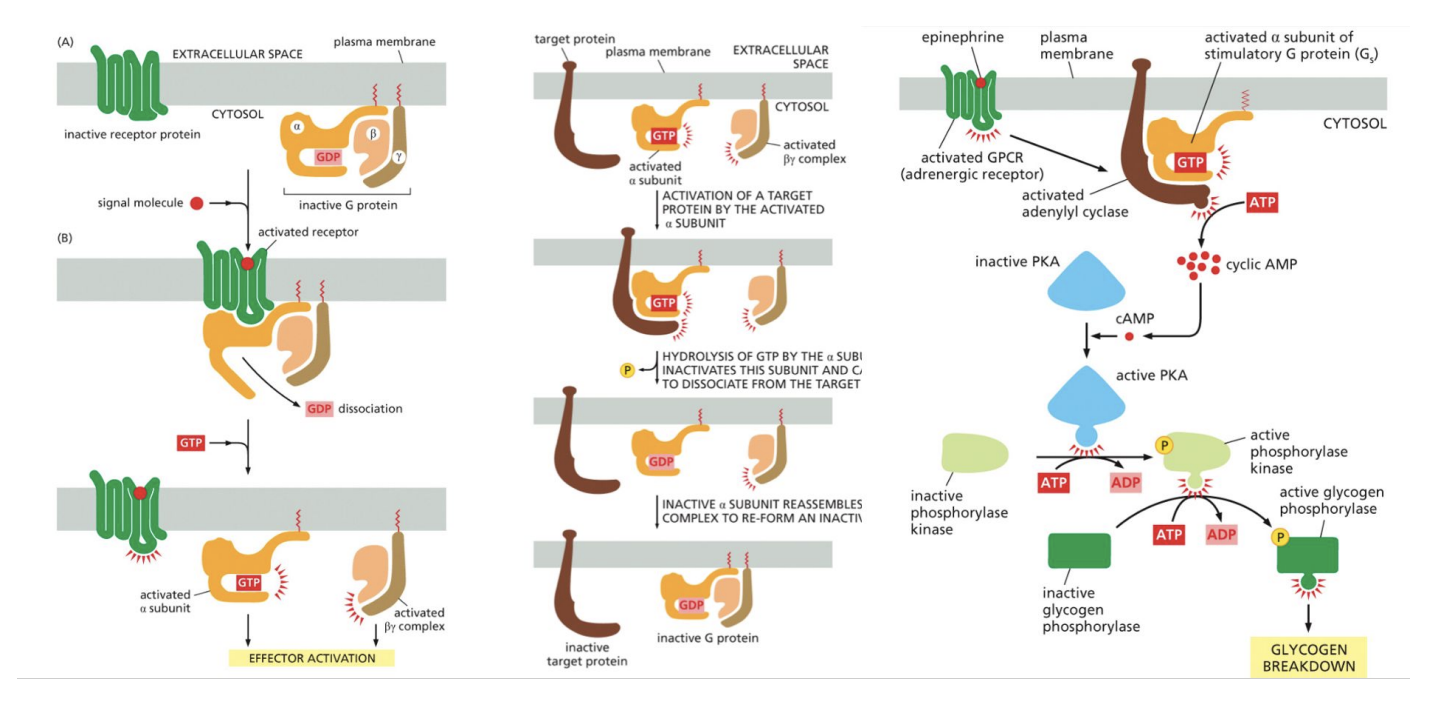
Surface Receptor - G-protein Coupled
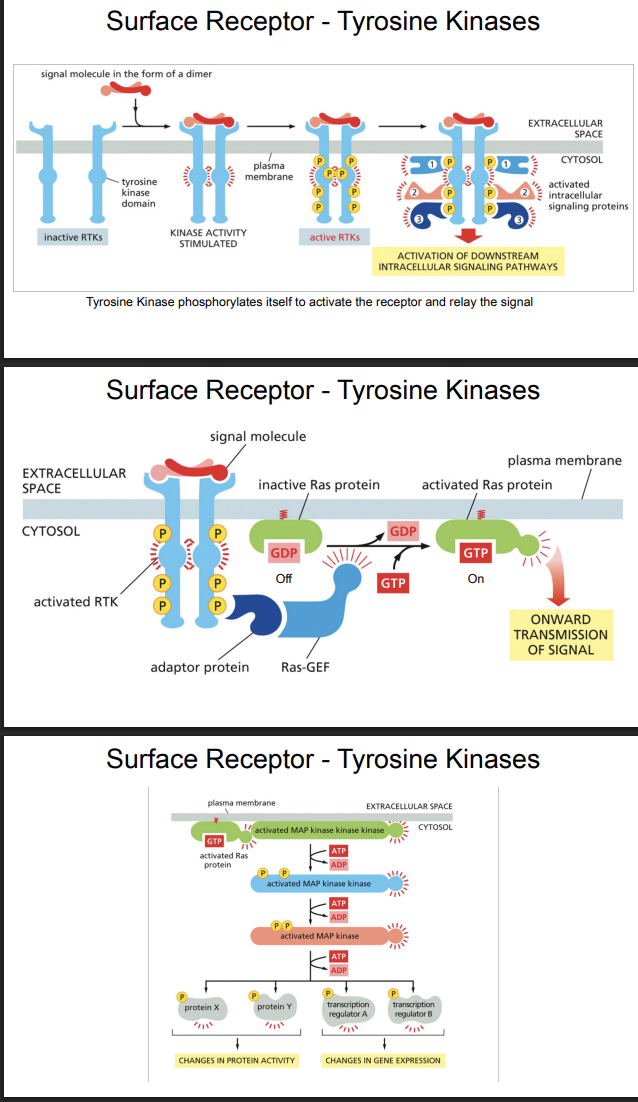
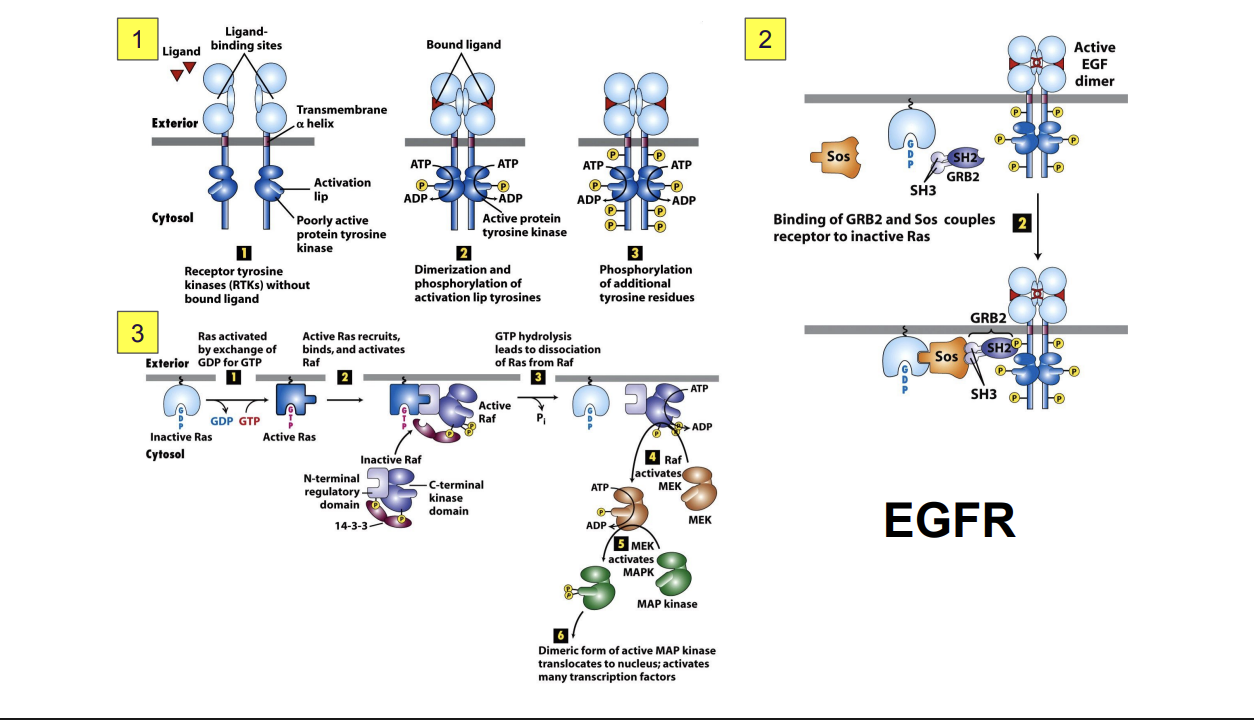
Surface Receptor - Tyrosine Kinases
EGFR
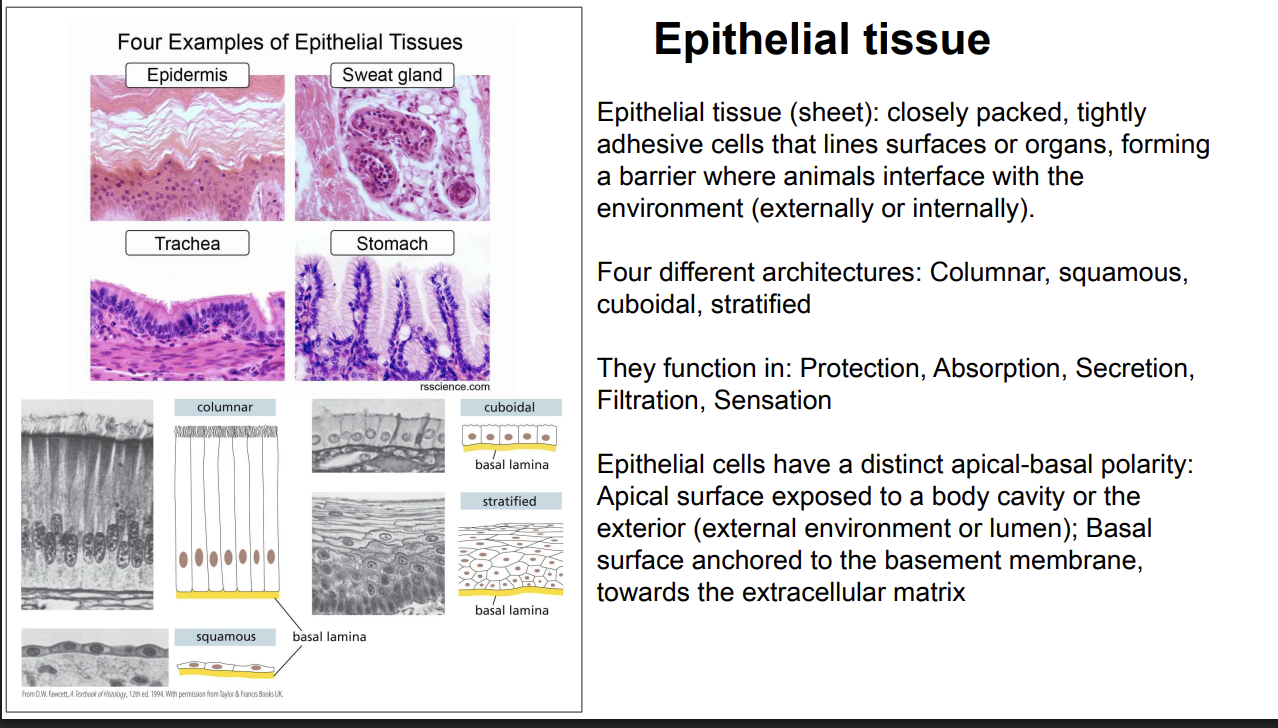
Epithelial tissue
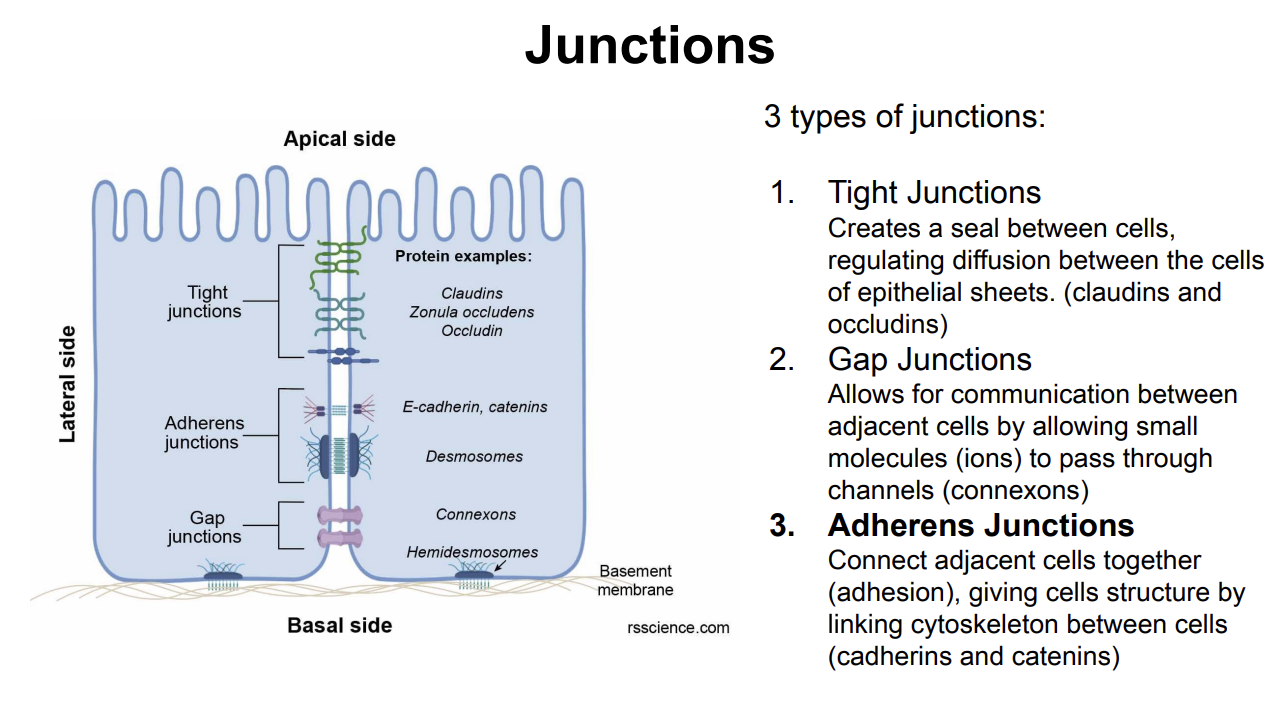
Junctions
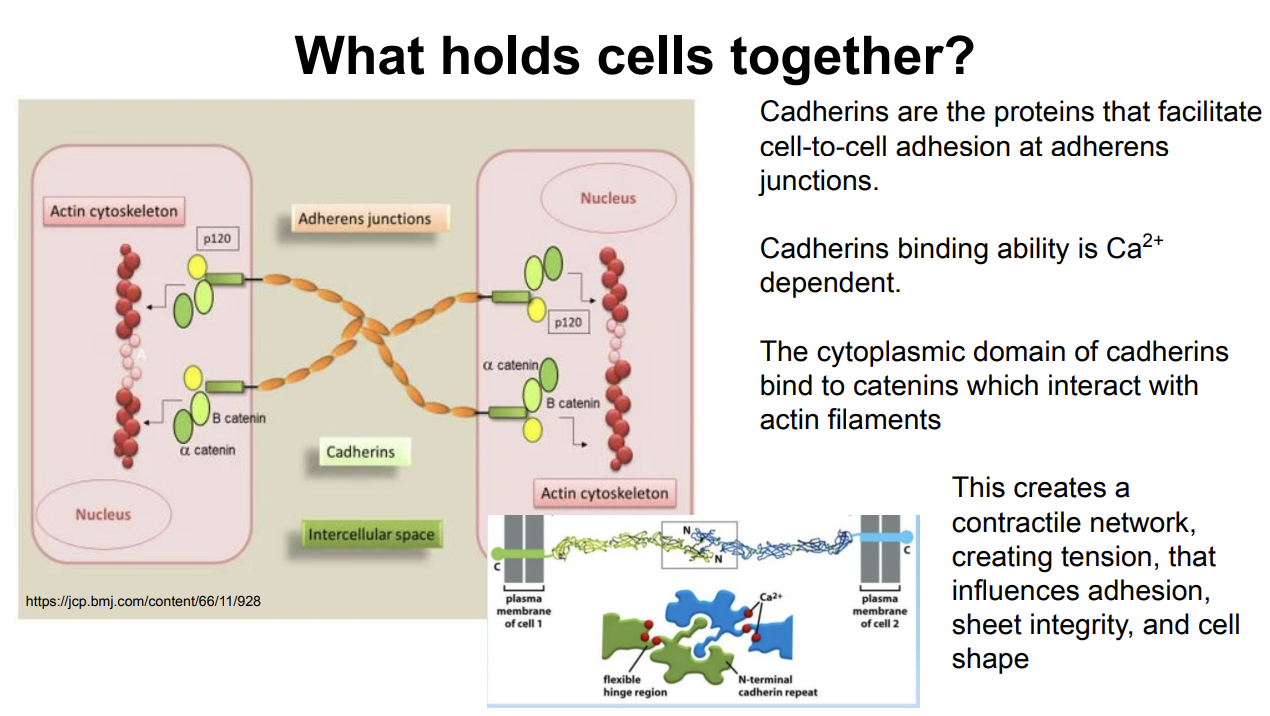
What holds cells together?
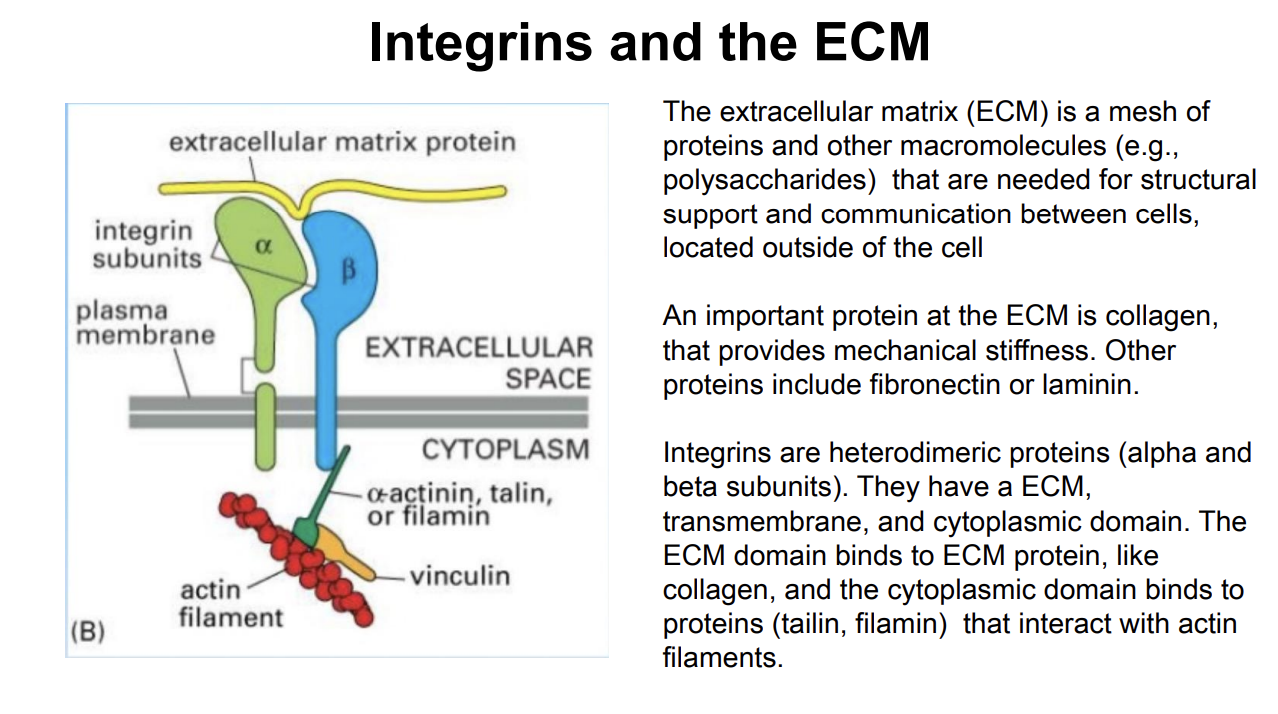
Integrins and the ECM
Cancer v Tumor

five basic principles of cancer
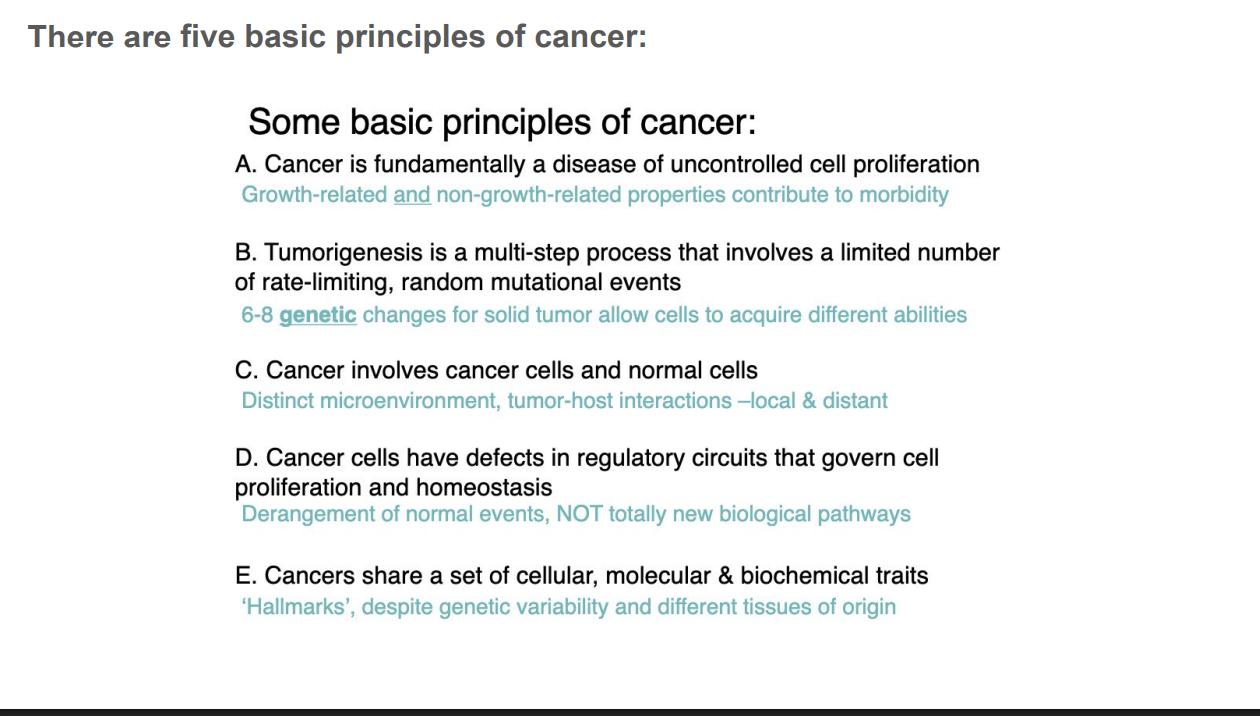
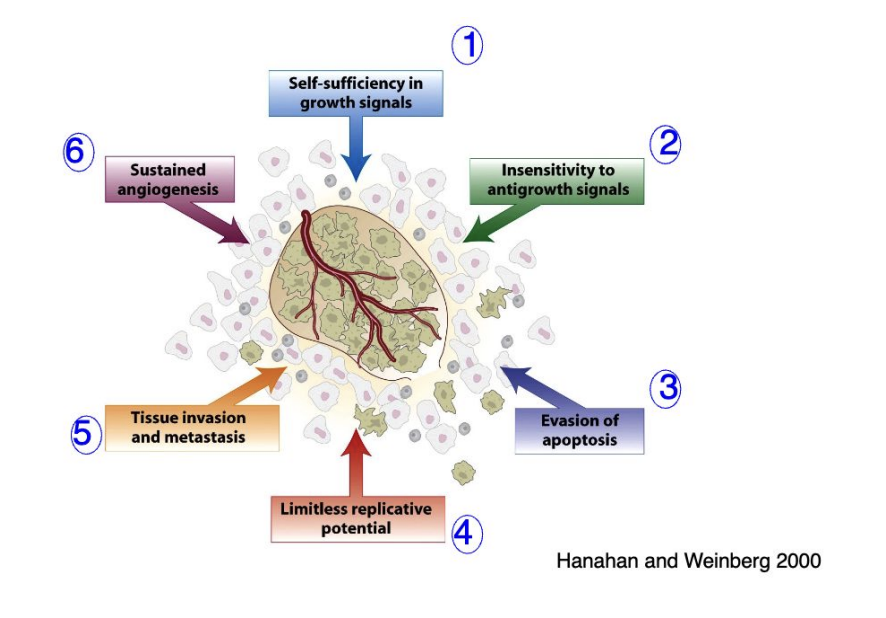
six hallmarks of cancer
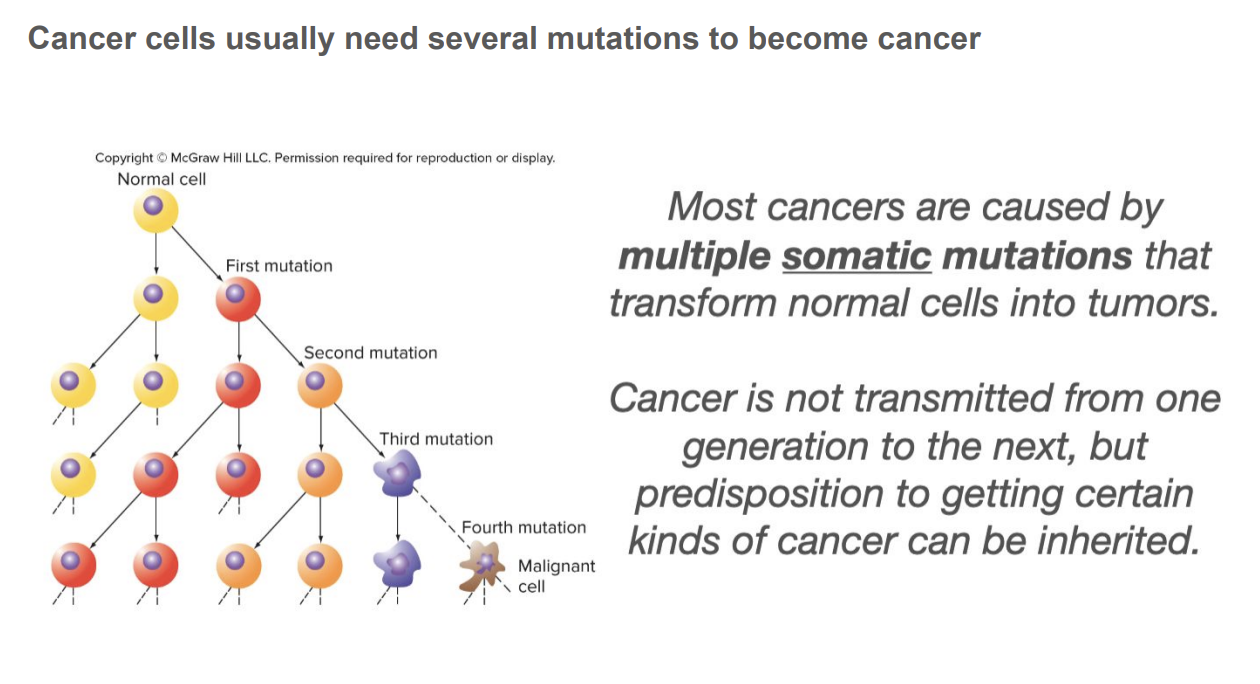
Cancer cells usually need several mutations to become cancer
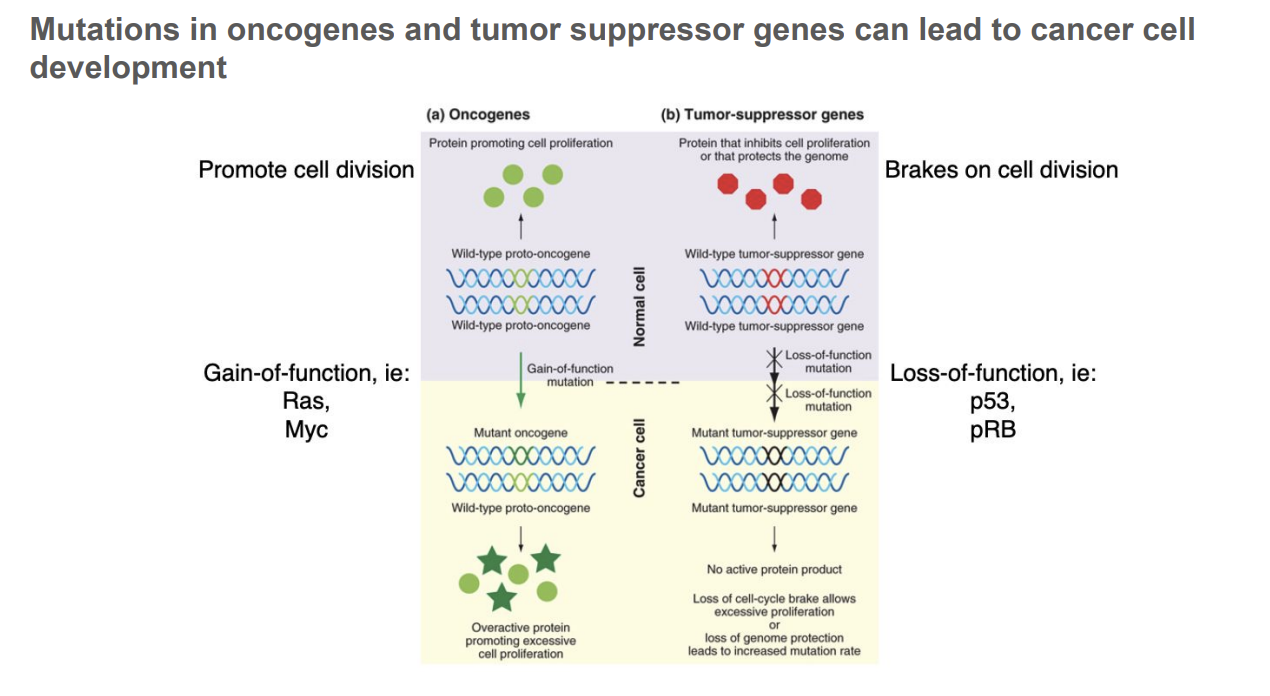
Mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes can lead to cancer cell development
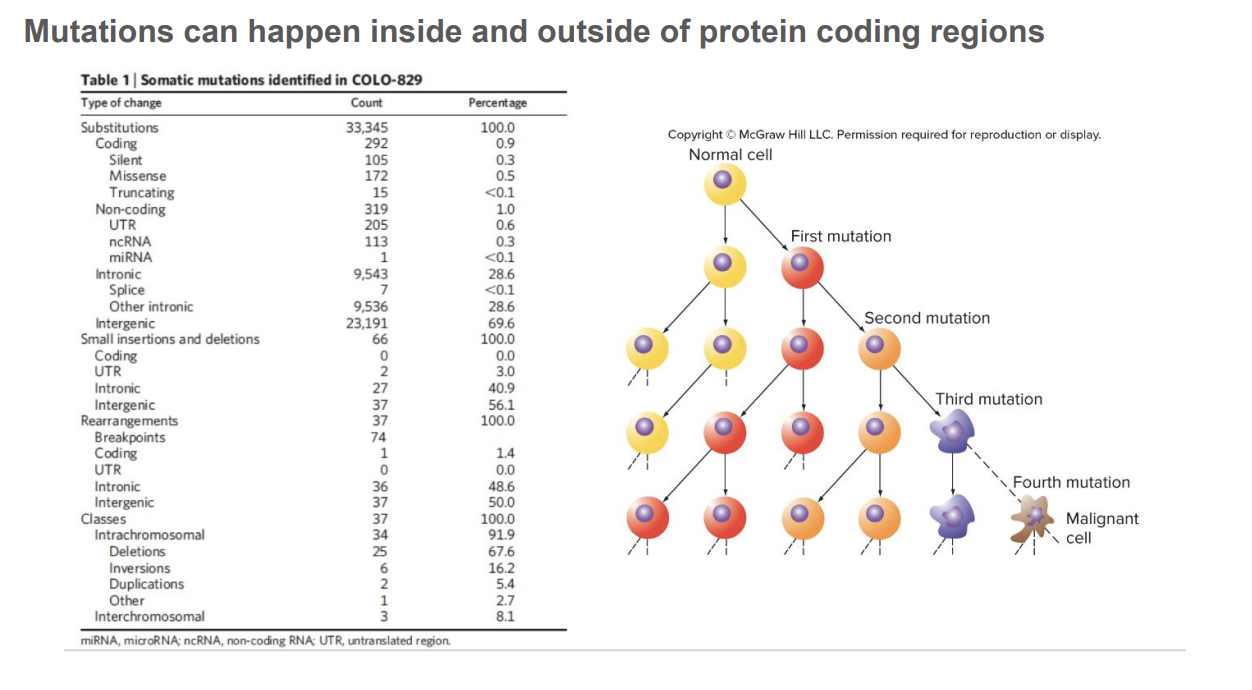
Mutations can happen inside and outside of protein coding regions
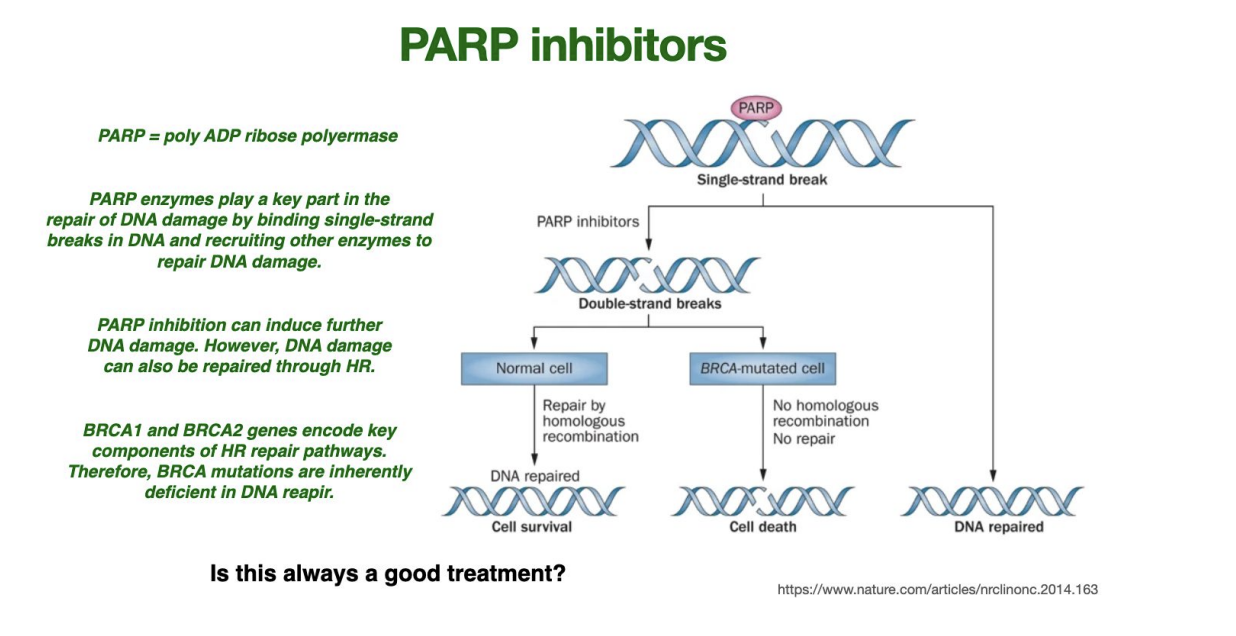
PARP inhibitors
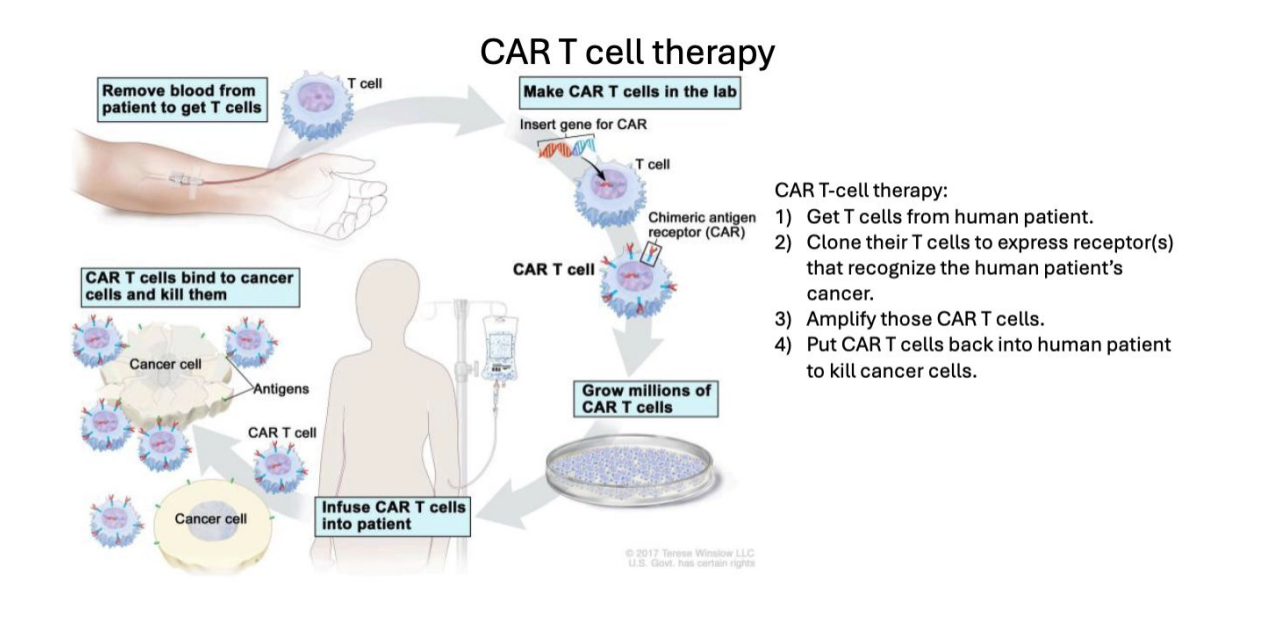
CAR T-cell therapy
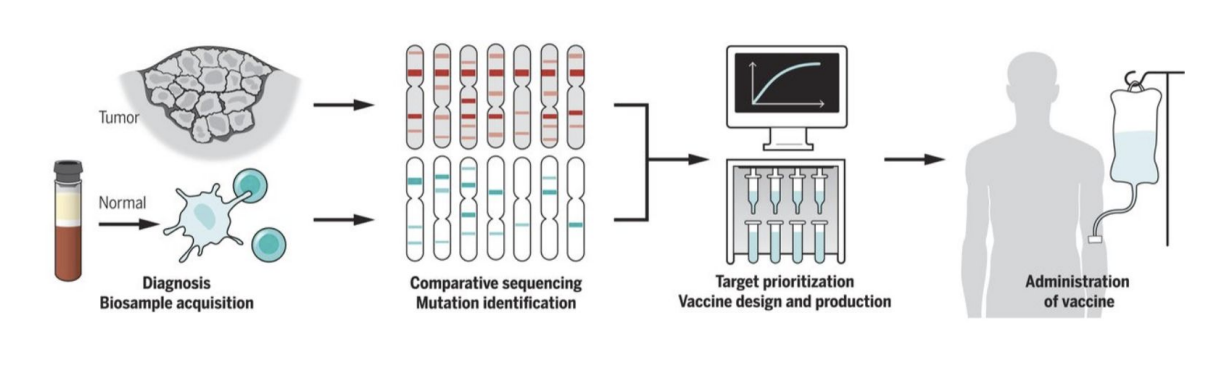
mRNA vaccines/personalized medicine