Anatomy and Physology Bones
1/534
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
535 Terms
Fibrous joint pic

cartilaginous joint pic

synovial joint pic
ball and socket joint pic

hinge joint pic
condylar joint pic
saddle joint pic

gliding/plane joint pic

pivot joint pic
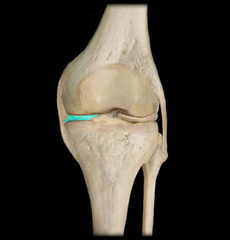
anterior cruicate ligament
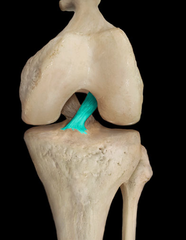
posterior cruciate ligament

fibular collateral ligament
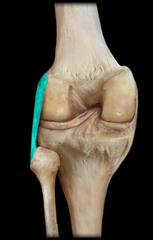
tibular collateral ligament
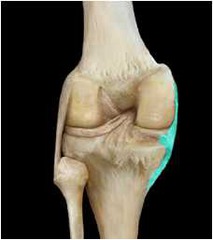
lateral meniscus
away
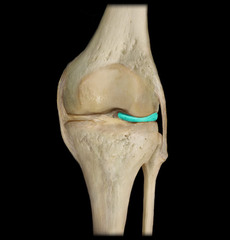
medial meniscus
near
Functions of Skeletal System
Support, movement, storage, blood cell production, protection
Support Function
Provides framework for attachment of other tissues and organs
Movement Function
Serve as levers that are pulled by muscles in movement
Storage Function
Stores calcium and phosphate ions within the bone tissue and fat within yellow marrow
Blood Cell Production Function
Red blood cell production inside of red marrow
Protection Function
Protect soft tissues and organs
Epiphysis
Rounded end of a long bone, where it forms a joint
Articular Cartilage
Covers epiphysis to form a smooth surface
Proximal
Closest to main mass of body
Distal
Farthest from main mass of body
Compact Bone
Densest part of the bone
Spongy Bone
Has many spaces in between bony rods or struts
Red Bone Marrow
Inside of spongy bone, holds stem cells that differentiate into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
Epiphyseal Plate
Made of hyaline cartilage, separates the epiphysis from rest of the bone, called growth plate, cartilage is replaced by bone in adults
Diaphysis bone
The middle shaft of the bone
Periosteum bone
A layer of dense tissues that contains blood vessels and sensory nerves.
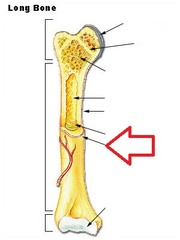
Medullary Cavity
A hollow area inside the diaphysis
Yellow Marrow
Mostly contains fat cells
Endosteum
Innermost layer of tissue
Osteocytes
Mineral structure of compact and spongy bone maintained in cells
Osteoclasts
Dissolve and reshape bone
Osteoblasts
Lay down new bone
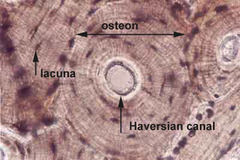
Osteons
Circular units that bone tissue is divided in
Lamella
Thin calcified sheets that form ring shapes
Lacuna
Pits found in each layer of lamella
Osteocyte
Bone cells found inside each of lacunae
Central Canal
Hollow center that contains blood vessels
Canalicuili
Tiny channels that connect osteocytes back to central canal
Ossification
process of bone formation
Composition of Embryonic Bone
Osteoblasts that form spongy bones within center of shaft
Direction of Bony Tissue Growth
Bone continues to lengthen as growth plate produces more hyaline cartilage
Epiphyseal Growth Plate
Eventually growth plate becomes fully ossified and forms epiphyseal line; the bone doesn't grow further at this point
Epiphyseal Line
Formed when growth plate is fully ossified
Axial Skeleton
Includes everything around the longitudinal (vertical) center plane of the body
Appendicular Skeleton
Includes appendages (arms and legs)
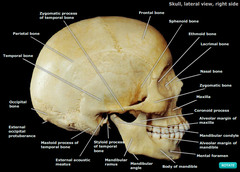
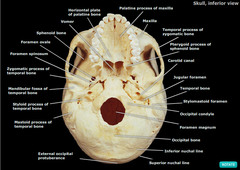
Skull Bones
Bones are flat and designed to be protective
Sutures
Joins bones together; a joint made of dense fibrous tissue
Fontanels
Few sutures that are much wider in fetal skull; allows skull to alter its shape during birth, close within first two years of life
Sinuses
Hollow bones with thin plates between them which are designed to drain fluids
Sinus Headaches
Happen when sinus gets blocked and fluids overflow into nasal cavity
Hyoid Bone
Only bone in entire body that does not form joint with any other bone; base of tongue attaches to this bone and aids in swallowing and speech
Ossicles
Make up the middle ear; malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup); transmit vibrations from sound to the cochlea of inner ear
Vertebral Column
Named based on their location
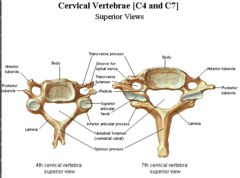
Cervical Vertebrae in Neck
C1-C7
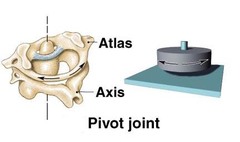
Atlas
C1
Axis
C2
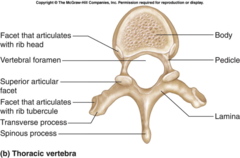
Thoracic Vertebrae in Upper Back
T1-T12
Sacrum and Coccyx
Two bones below lumbar region made from nine fused vertebrae
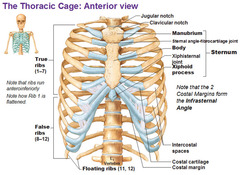
Functions of Rib and Sternum
Ribs articulate with sternum and thoracic vertebrae to protect the heart and lungs
True Ribs
Pairs 1-7; connected directly to sternum
False Ribs
Pairs 8-12; connected to the sternum through cartilage or not at all
Floating Ribs
Pairs 11-12; false ribs connected to thoracic vertebrae
Long Bones
Longer than they are wide with heads at each end (ex. Femur, humerus, metatarsals, phalanges
Short Bones
Cube shaped bones which contain higher amounts of spongy bones (ex. Carpals and tarsals
Flat Bones
Thinner, flattened, and often curved; made of thin layers of compact and spongy bone (ex. Skull bones, pelvic bones, ribs, sternum
Sesamoid Bones
Embedded with a tendon (ex. Patella)
Irregular Bones
Do not fit into any of the other categories due to unusual shape (ex. Vertebrae)
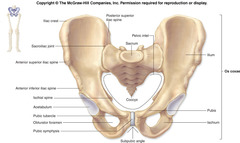
Pelvis (Anterior View)
Appendicular Skeleton (Bottom)
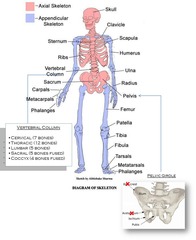
Axial Skeleton (Top)

Sternum and Ribs
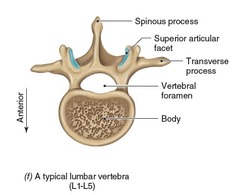
Lumbar Vertebrae Photo
Thoracic Vertebrae Photo
Cervical Vertebrae Photo
Vertebral Column Photo

Skull (lateral view)
Skull (inferior view)
Bone Inside Labeled

Bone Anatomy
Articulations
Joints, exist wherever two bones meet; classified by range of motion
Fibrous Joints
Contain dense fibrous tissue and are immoveable (ex. small cranial structures)
Cartilaginous Joints
Connected entirely with fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage and allow limited movement (ex. symphysis pubis and fibrocartilage between vertebrae
Synovial Joints
Have a space called a synovial cavity filled with fluid that separates the bone, allowing free movement (ex. knee, elbow, shoulder, fingers, etc.) have many structures designed to minimize bone to bone contact.
common class of _ that includes the ankle, elbow, and knee joints.
Synovial Joint- Fibrous Capsule
Continuous with periosteum of each bone
Synovial Joint-Synovial Fluid
Fills space in between bones
Synovial Joint- Synovial Membrane
Seals the synovial fluid
Synovial Joint- Bursa
Fluid filled sac that cushions the area
Synovial Joint- Aspiration
Drain fluid from synovial joints due to swelling or inflammation following an injury or surgery
Synovial Joint- Joint "cracking"
Caused by stretching of a synovial membrane causing air to quickly escape
Ligaments
Join bones together and contain dense regular connective tissue
Menisci
Shock absorbing fibrocartilage pads
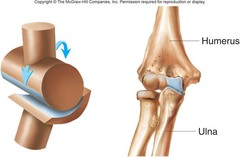
Ball and Socket Joint
Head of one bone rests in a depression of another, greatest range of motion- 360 (ex. shoulder and hip)
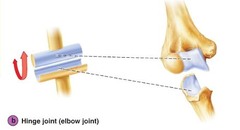
Hinge Joint
Allows movement along a single plane- flexing and extending (ex. elbow, knee, between phalanges)
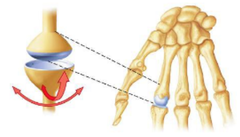
Condylar Joint
Allow angular movement in two planes (ex. radius and carpal bones, phalanges and metacarpals/metatarsals)
Saddle Joint
Allow circular movement and angular movement in two planes (ex. between carpal and metacarpal at base of the thumb)