System Analysis and Design
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
preparation for the long quiz 2 in SISBUSI
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Systems
organized set of related components
collection of subsystems that are interrelated and interdependent, working together to accomplish predetermined goals and objectives.
EX:
Computer systme
Human body
System Analysis
process of studying an existing system to determine how it works and how it meets client and user needs
Clients
contract to have the systems analysis done
Users
people who will have contact with the system
employees and customers
System Design
process of developing a plan for an improved system
System Analyst
performers both analysis and design
sometimes a programmer is also involved in the analysis
person who systematically assess how business function by examining the inputting and processing of data and the outputting of information with the intent of improving organizational processes.
Key person in the SDLC
who analyzes the business situation, identifies opportunities for improvements, and designs an information system that adds value to the organizations to implement the improvements
Change
must be an impetus for change
related authority for change before an analysis and design project is under taken
Change Agent
system analyst is a catalyst to overcome the natural reluctance to change within an organization
Coordination
Communication
Planning and Design
A system analyst has 3 principal functions
Coordination
an analyst must coordinate schedules and system-related tasks with a number of people.
Communication
The analyst may need to make oral presentations and write reports for clients, users, and others involved with the system.
Planning and Design
The systems analyst, along with the client organization, plans and designs the new system.
This includes all the activities from beginning of the project until its final implementation
analytical mind
self-discipline
self-direction
ability to work without tangible results
Qualities of a System Analyst
Preliminary investigation
System Analysis
System Design
System Development
Implementation
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) has 5 distinct phases
Preliminary Investigation
1st phase in the SDLC
The goal of this phase is to determine the problem and is sometimes called the feasibility study or system survey.
Tools of Preliminary Investigation
system analyst will develop an organizational chart
determine whether to proceed with the project
Nature of the Problem
The systems analyst and the users must agree on the (answer)
Scope of the problem
Determining the (answer) sets limitations on the eventual budget and schedules of the project.
Objectives
Determining the (answer) means to express what the user thinks the system should be able to do.
System Analysis
2nd phase in the SDLC
systems analyst must:
Gather data
Analyze data
Determine system requirements
Report to management
Gathering Data
The thing that system analyst do
The systems analyst relies on the following sources when (answer):
Written documents
Interviews
Questionnaires
Observations
Sampling
Written Documents
Gathering documents includes procedures manuals, forms, and any kind of material that might have bearing on the problems in the organization.
Interviews
Structured include only preplanned questions.
Unstructured allow the systems analyst to digress from the formal line of questioning.
questionnaires
ideal for gathering information from a group too large to interview.
Observation
Systems analysts must observe the flow of information in and out of an organization.
Sometimes this requires them to be a temporary participant in the organization
Sampling
collection of data about quantities, costs, time periods, and other factors relevant to the system.
Analyze Data
the thing that system analyst do
The systems analyst uses charts and diagrams
Data flow diagrams
Decision Tables
Data flow Diagrams
use in Analyzing data
serve as a map of how data flows in and out of an organization and reveal procedures used.
Decision Tables
use in analyzing data
represents the logical decisions that must be made regarding potential conditions in a given system.
System Requirements
in the system analysis phase
a list of the things the system must be able to do
This list of (answer) will determine the design of the new system
Report Management
part of System Analysis
Problems identified in the current system
Requirements for the new system
Cost analysis
Recommendations for future action
System Design
3rd phase of the SDLC
the phase in which the systems analyst actually plans the new system
Preliminary Design
one of the two sub-phases of the system design
systems analyst will review system requirements and consider whether the system should be:
centralized or decentralized
networked or not
run with purchased or custom software
outsourced or in-house
Prototyping
A (answer) of the new system is a limited working system that is developed quickly to produce output that looks like the output the finalized system will produce.
Detail Design
one of the two sub-phases of system design
systems analyst must now develop (answer) specifications, such as:
Output requirements
Input requirements
Files and databases
Systems processing
Systems controls and backups
Output requirements
part of the detail design specifications
systems analyst must determine:
what the client wants the system to produce.
the medium of the output.
the type of reports needed.
the contents of the output.
what forms will be used.
input requirements
part of the detail design specifications
The systems analyst must determine what (answer) to give the desired output.
Files and Database
part of the detail design specifications
The systems analyst will determine whether the files should be stored sequentially, directly, or by some other method.
File storage must also be coordinated with the databases used by the client.
System Processing
part of the detail design specification
involves generating a diagram of how the flow of data works in the new system.
System Controls and backup
part of the detail design specification
designed to prevent fraud and tampering.
system files should be (part of the answer) (copied) and the copies stored in a safe manner and location.
System Development
4th phase of the SDLC distinct phrases
the system is actually developed and includes:
Scheduling
Programming
Testing
Scheduling
part of the system development phase
(answer) deadlines and milestones is another task of the systems analyst.
(answer) involves determining the allocation of people and resources, monitoring schedules, and producing status reports.
Programming
part of the system development phase
At this point in systems development, programmers are given program design specifications and they begin to write code.
Testing
part of the system development phase
After the program for the new system has been written, it must be (answer) under a variety of conditions.
Implementation
5th or last phase of the SDLC
for (answer) to be successful, the ff activities are required:
•Training
• Equipment conversion
• File conversion
• System conversion
• Auditing
• Evaluation
• Maintenance
Training
activities in the implementation phase
A system will only be as good as the people who use it. Therefore, (answer) the users is very important.
Equipment Conversion
activities in the implementation phase
Implementing a system requires that consideration has been given to how best to convert to the new system.
Issues of availability of space, accessibility, and cleanliness of the work area cannot be overlooked.
File Conversion
activities in the implementation phase
Converting old file structures to that needed by the new system can take a long time.
Care must be taken to not corrupt old files, lose files, or disrupt normal operations of the client organization during this conversion.
System Conversion
activities in the implementation phase
A systems analyst will need to determine in what way the client organization should convert to the old system.
Auditing
activities in the implementation phase
To guard against deliberate or unintentional violations in security, the systems analyst designs an (answer) trail.
Evaluation
activities in the implementation phase
(answer) is needed to determine if the system is:
working
meeting the organizational requirements
meeting the original budget limitations
Maintenance
activities in the implementation phase
is an ongoing activity and includes monitoring and making revisions throughout the life cycle of the system.
System Analysis and Design
As performed by system analysts, seeks to analyze data input or data flow systematically, processing or transforming data, data storage, information output within the context of a particular business
Is used to analyze, design and implement improvements in the functioning of businesses that can be accomplished through the used of computerized info. systems.
Lends structure to the (answer)
Consultant
roles of the system analyst
May be hired to address information systems issues within a business
Outside (answer) can bring the companies a fresh perspective that other members of an organization do not possess
Support Expert
roles of the system analyst
Draws on professional expertise concerning computer hardware and software and their uses in the business
you are not managing the project, you are merely serving as a resource for those who are.
Agent of Change
roles of the system analyst
defined as a person who serves as a catalyst for change, develops a plan for change, and works with others in facilitating that change
Quliaties of the system analysis
Problem Solver
Systematically tackle the situation at hand through skillful application
Communicator
have computer experience to program
possess strong personal and professional ethics
self-discipline and self-motivated
System Development Life Cycle
Is the process of understanding how an information system (IS) can support business needs, designing the system, building it, and delivering it to users.
Business Analyst
System Analysis Specialization
Analyzing the key business aspects of the system
-Identifying how the system will provide business value
-Designing the new business processes and policies
System Analyst
system analyst specialization
-Identifying new technology can improve business processes
-Designing the new business processes
-Designing the information system
-Ensuring the system conforms to information system standards
Infrastructure Analyst
system analyst specialization
-Ensuring the system conforms to infrastructure standards
-Identifying infrastructure changes needed to support the system
Change Management Analyst
system analyst specialization
-Developing and executing a change management plan
-Developing and executing a user training plan
Project Manager
System Analysis Specialization
-Managing the team of analysts, programmer, technical writers and other specialists
-Developing and monitoring the project plan
-Assigning resources
-Serving as the primary point of contact for the project.
Application Portfolio
prioritized list of both existing and potential IT applications of a company.
Information System Planning Process
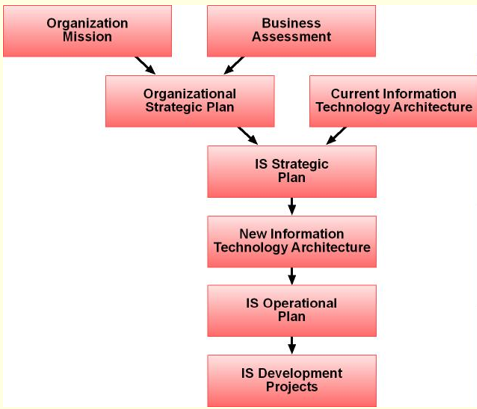
Organizational strategic Plan
part of the Information System Planning Process
it’s in the image, which is the 2nd stage
one of the inputs in developing the IT strategic plan
states the firm’s overall mission, the goals that follow from that mission, and the broad steps necessary to reach these goals.
IT architecture
part of the information system planning process
called “current (answer)” in the chart
one of the inputs in developing the IT strategic plan
delineates the way an organization’s information resources should be used to accomplish its mission.
IT Strategic Plan
part of the information system planning process
a set of long-range goals that
describe the IT infrastructure and major IT initiatives needed to achieve the goals of the organization.
IT Steering Committee
comprised of managers and staff representing various organizational units, establishes IT priorities and ensures that the MIS function meets the needs of the enterprise.
IS Operational Plan
part of the information system planning process
a clear set of projects that the IT department and functional area managers will execute in support of the IT strategic plan
Elements:
Mission
IT environment
Objectives of the IT function
Constraints of the IT function
Application portfolio
Resource allocation and project management
Traditional System Development Life Cycle
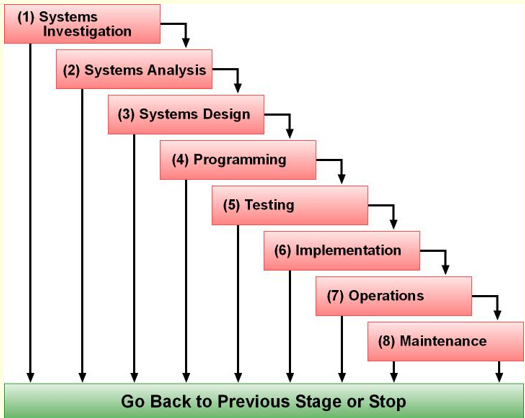
Software Development Life Cycle
another SDLC
the traditional systems development method that organizations use for large-scale IT projects.
SDLC processes are systems investigation, systems analysis, systems design, programming, testing, implementation, operation and maintenance.
Waterfall Approach
when tasks in one phase are completed before the work proceeds to the next stage.
the image of the traditional system development life cycle looks like this
System Investigation
System Analysis
System Design
Programming
Testing
Implementation
Operation
Maintenance
Traditional System Development Life Cycle steps
SDLC - System Investigation
Begins with the business problem (or opportunity) followed by the feasibility analysis.
Feasibility study
Go/No-Go Decision
Feasibility Study
main task of the Systems Investigation phase.
it helps the organization choose between 3 options:
(1) Do nothing and continue to use the existing system unchanged.
(2) Modify or enhance the existing system.
(3) Develop a new system.
SDLC System Analysis
Is the examination of the business problem that the organization plans to solve with an information system.
Main purpose is to gather information about existing system to determine requirements for the new or improved system.
Deliverable is a set of system requirements.
SDLC System Design
Describes how the system will accomplish this task.
Deliverable is the technical design that specifies:
System outputs, inputs, user interfaces.
Hardware, software, databases, telecommunications, personnel & procedures.
Blueprint of how these components are integrated.
SDLC Programming
involves the translation of a system’s design specification into computer code.
SDLC Testing
checks to see if the computer code will produce the expected and desired results under certain conditions.
designed to delete errors (bugs) in the computer code. These errors are of two types:
Syntax errors ( e.g., misspelled word or a misplaced comma)
Logic errors that permit the program to run but result in incorrect output.
SDLC Implementation
or deployment is the process of converting from the old system to the new system
4 major conversion strategies ;
Direct Conversion - old system is cut-off and the new system turned on
Pilot Conversion - that introduces the new system in one part of the organization on a trial basis
Phased Conversion - introduces components of the new system in stages, until the entire new system is operational.
Parallel Conversion - old system and the new system operate simultaneously for a period of time
SDLC Operation and Maintenance
assess the system’s capabilities and to determine if it is being used correctly.
Types of (answer)
Debugging: A process that continues throughout the life of the system.
Updating: Updating the system to accommodate changes in business conditions.
(answer): That adds new functionally to the system –adding new features to the existing system without disturbing its operation.
Joint Application Design
A group-based tool for collecting user requirements and creating system designs.
Computer Assisted Software Engineering
CASE
is a development approach that uses specialized tools to automate many of the tasks in the SDLC; upper CASE tools in SDLC automate the early stages of the SDLC, and lower case tools automate the later stages.
Integrated computed assisted software engineering tools
ICASE
CASE tools that provide links between upper CASE and lower CASE tools
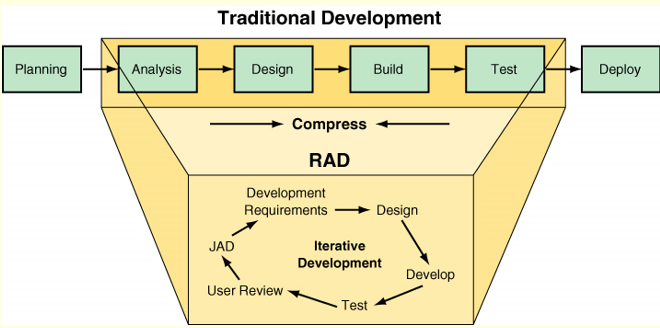
Rapid Application Development
development method that uses special tools and an iterative approach to rapidly produce a high-quality system.
Agile Development
Development method that delivers functionality in rapid iterations requiring frequent communication, development, testing, and delivery.
End User Development
development method that has the actually user develop their own application(s) for use.
Component Based Development
that uses standard components to build applications.
RAD vs SDLC
Outsourcing
when an organization acquires IT applications or services from outside contractors or external organizations
Application Service Provider
is an agent or vendor who assembles the software needed by enterprises and packages the software with services such as development, operations and maintenance.