Cell Division
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Each cell contains the same no. of chromosomes with identical genes.
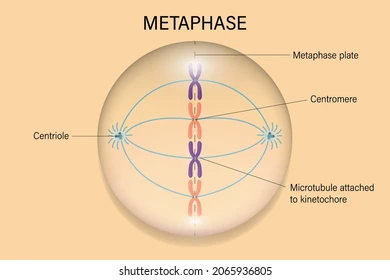
2\.Metaphase
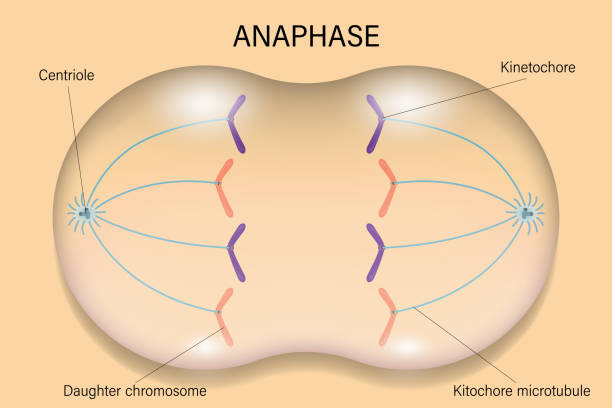
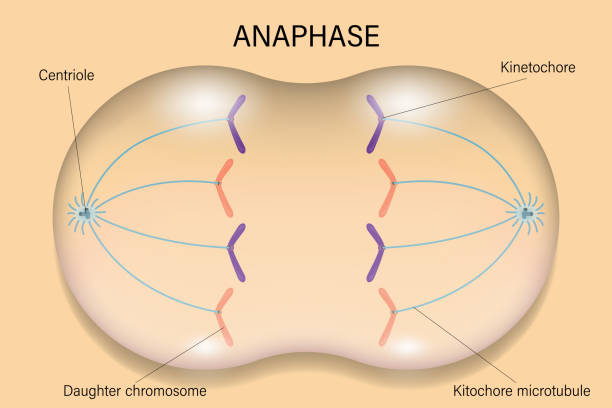
3\.Anaphase
4\.Telophase
* Nuclear membrane breaks down
* Spindle fibres form in the cytoplasm
* ex. in diagram. The diploid number is 4
Name human cell not produced by mitosis
Red blood cells or gut lining cells cannot undergo mitosis, egg, sperm
1. Nuclear membrane breaks down
2. Chromosomes become visible double structures
1. animal- cleavage furrow
2. plant- cell plate
Define meiosis
Form of nuclear division in which the daughter nuclei contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent nucleus.
Meiosis occurs during formation of egg and sperm cells in mammals.
1. __Two__ daughter cells produced
2. __Identical__ to parent cell
3. __Same number__ of chromosomes produced as the parent cell.
\
__Meiosis__
1. Four daughter cells produced
2. Variations to parent cell
3. Daughter cells will be haploid (half the no. of chromosomes of parent) Think: Meiosis is the process by which a haploid cell is formed from a diploid cell.
1. single celled organisms
2. multi-celled organisms
1. in single-celled organisms, the act of mitosis is asexual __reproduction__. Single-celled organisms use mitosis to reproduce and distribute their DNA
2. multicellular organisms because it provides new cells for __growth and for replacement__ of worn-out cells, such as skin cells.
1. Nuclear membrane is gone
2. Chromosomes line up at the equator of cell
3. Spindle fibres attach to chromosomes
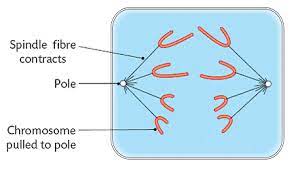
1. Shortest phase
2. Spindle fibres contract, causing the centromeres to split
3. Chromosomes are pulled to either side of the cell
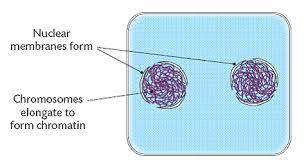
1. Chromosomes elongate and form chromatin
2. Nuclear membranes reform around each clump of chromatin
3. Mitosis is complete
\-Now cell begins to split:
Animal cells=cleavage furrow
Plant cells= cell plate (cell wall is too though to form c.f)
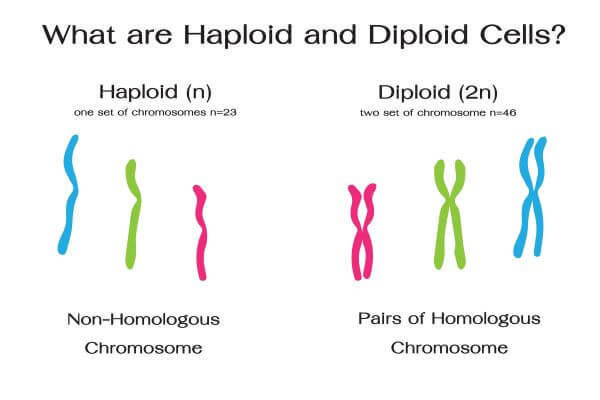
* __diploid__ cells contain __two__ complete sets of chromosomes.
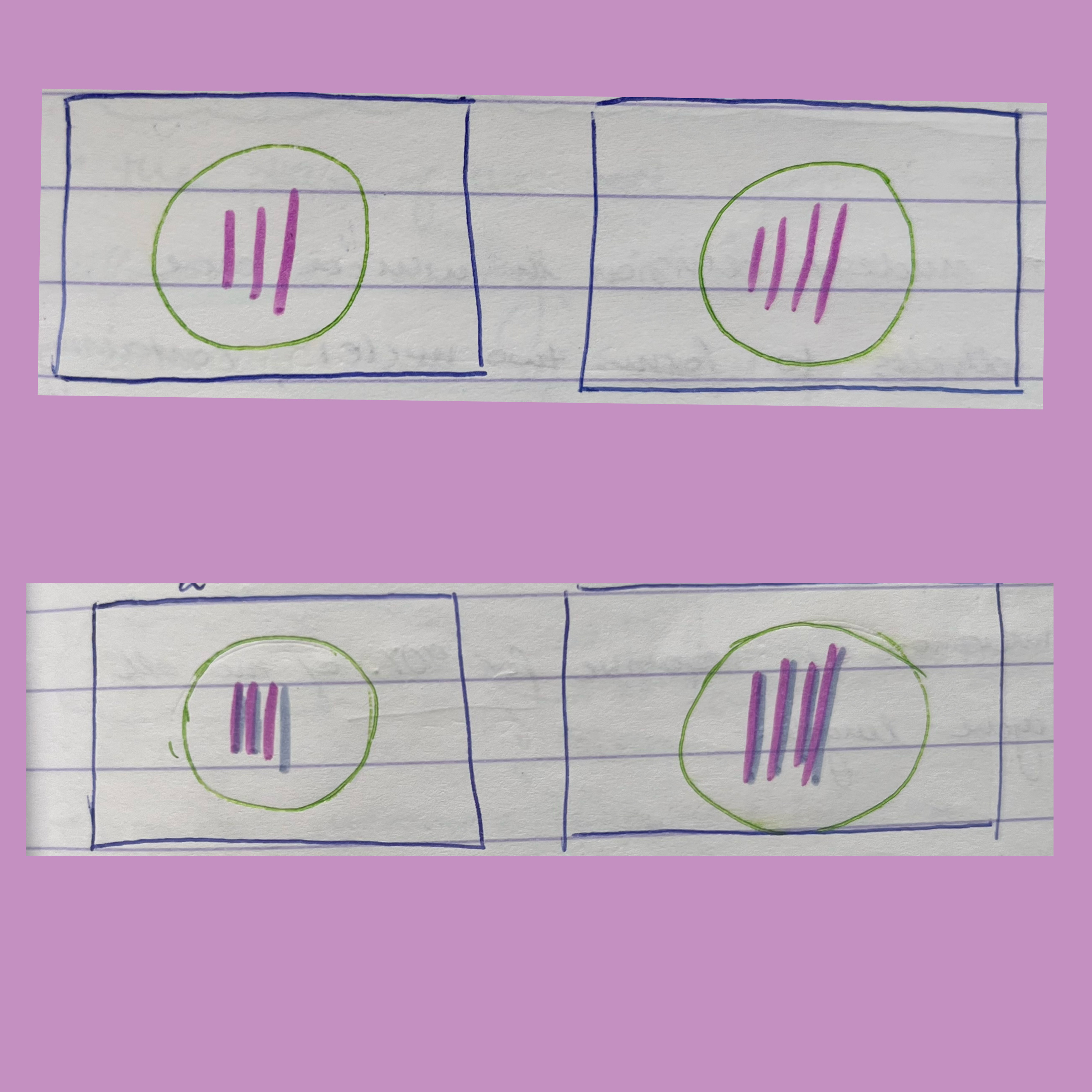
1. Diploid cells are present
2. Haploid cells are present
1. Diploid 2n=4
2. Haploid n=8
* It is __not__ however involved in sexual reproduction.
* Meiosis does not occur during asexual reproduction. Meiosis is the process of producing gametes (eggs and sperm). Mitosis, on the other hand, is simply the process of cell division.
Are gametes and zygotes haploids?
* the sperm and egg are haploid cells, they each contain 23 chromosomes
* fertilisation causes these two haploid cell to form 46 chromosomes
* Hence, a Zygote is diploid. Each chromosome is present in two homologous, or comparable, copies in almost all human body cells. Due to the presence of both of its parents' genes, the zygote is diploid (carrying two sets of chromosomes).
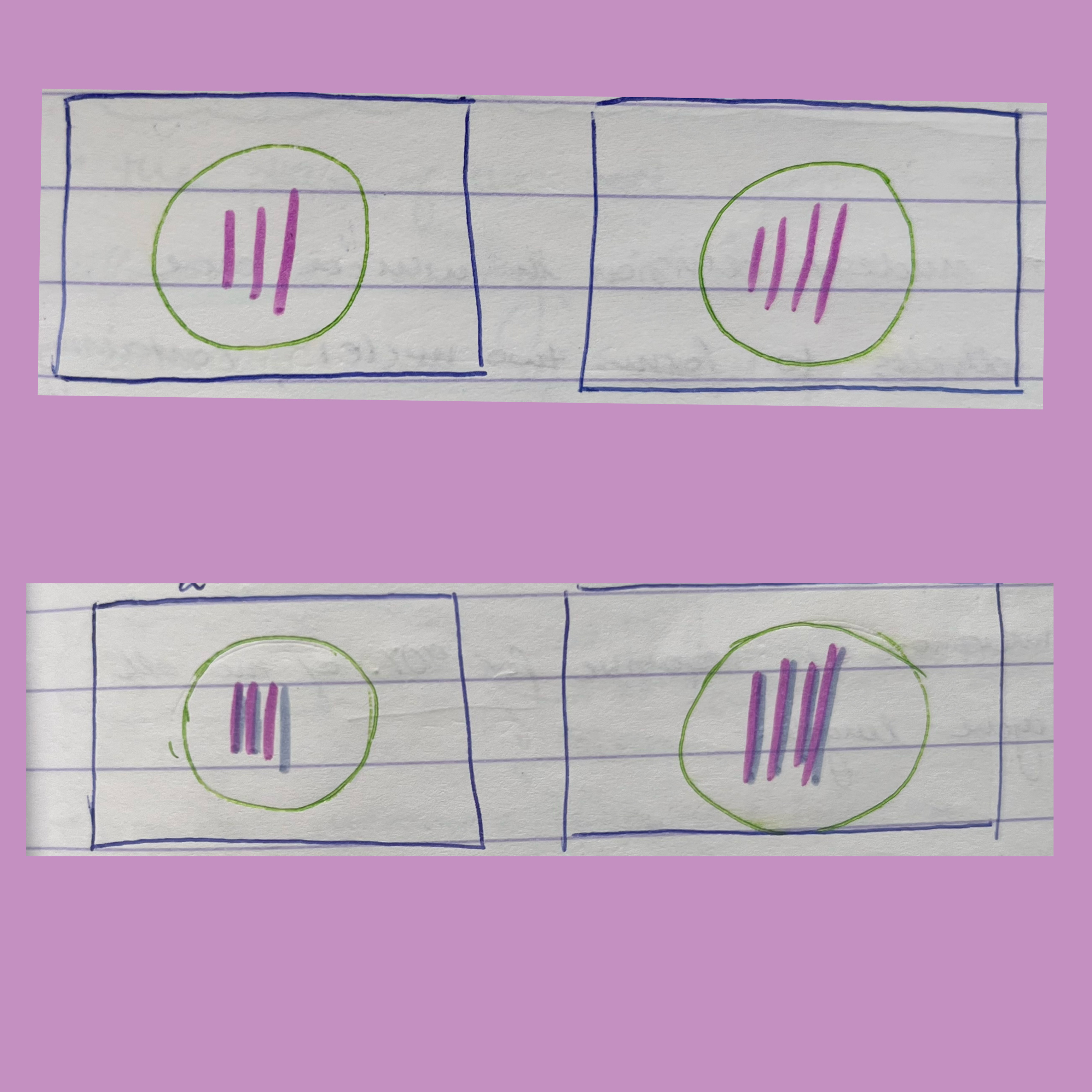
1. haploid cells
2. diploid cells
Also state the ‘n’ or ‘2n’
Bottom is diploid- 2n=6 and 2n=8
* Remember: n represents haploid cells, 2n represents diploid
* 90% of cell cycle
* Function:
1. Chromosome duplication
2. Cell organelle replication (mitochondria, chloroplasts etc.)
3. Production of enzymes
4. Transcription and uncoiling
5. Biomolecules produced; protein, fats, carbs
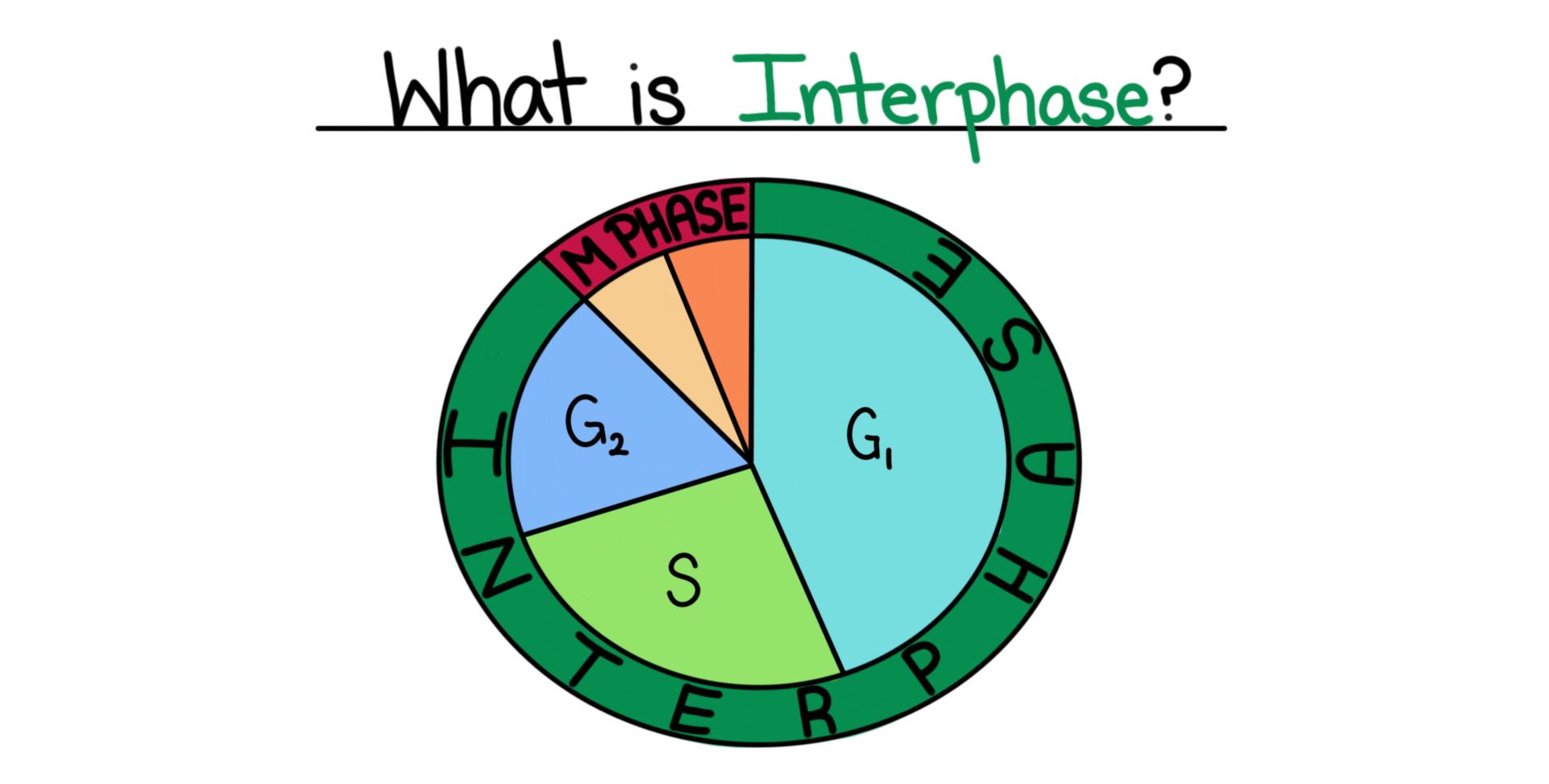
° Cell continuity is useful for the following reasons:
* It produces all needed materials
* It allows organisms to grow larger
* It replaces new cells
* A cell isn’t dividing
* Chromosomes appear as thin threads called chromatin
* Cell is producing new organelles and enzymes
* Chromosomes duplicate and become double stranded
Define ‘oncogenes’
a mutated gene that has the potential to cause cancer
(T/F) In plants, a cell plate forms during telophase of mitosis
T
(T/F) The human zygote divides by meiosis
False
Name two types biomolecules that are produced during interphase
protein
fats
or nucleic acid (RNA/DNA) or carbs
Name one organelle that is replicated during interphase
ribosome/mitochondria/chloroplast
Give any two changes that will have occurred in the cell by the end of interphase, a stage of the cell cycle
Chromosomes visible
Nuclear membrane disappears
End of Interphase is the start of Prophase
Suggest why mature human red blood cells do not undergo cell division
they don’t have a nucleus
Give a cellular process that occurs when the cell is in interphase
protein synthesis
photosynthesis
respiration
growth
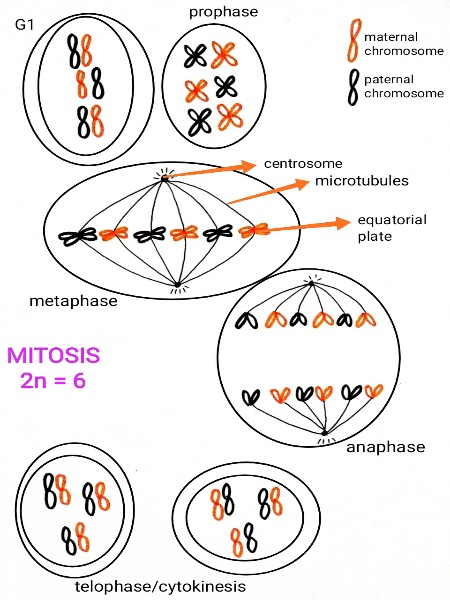
Draw a diagram of a 2n=6 nucleus during metaphase
2n=6, so 6 chromosomes
Give one location where mitosis occurs in flowering plants
buds/ovule/embryo/sac/pollen
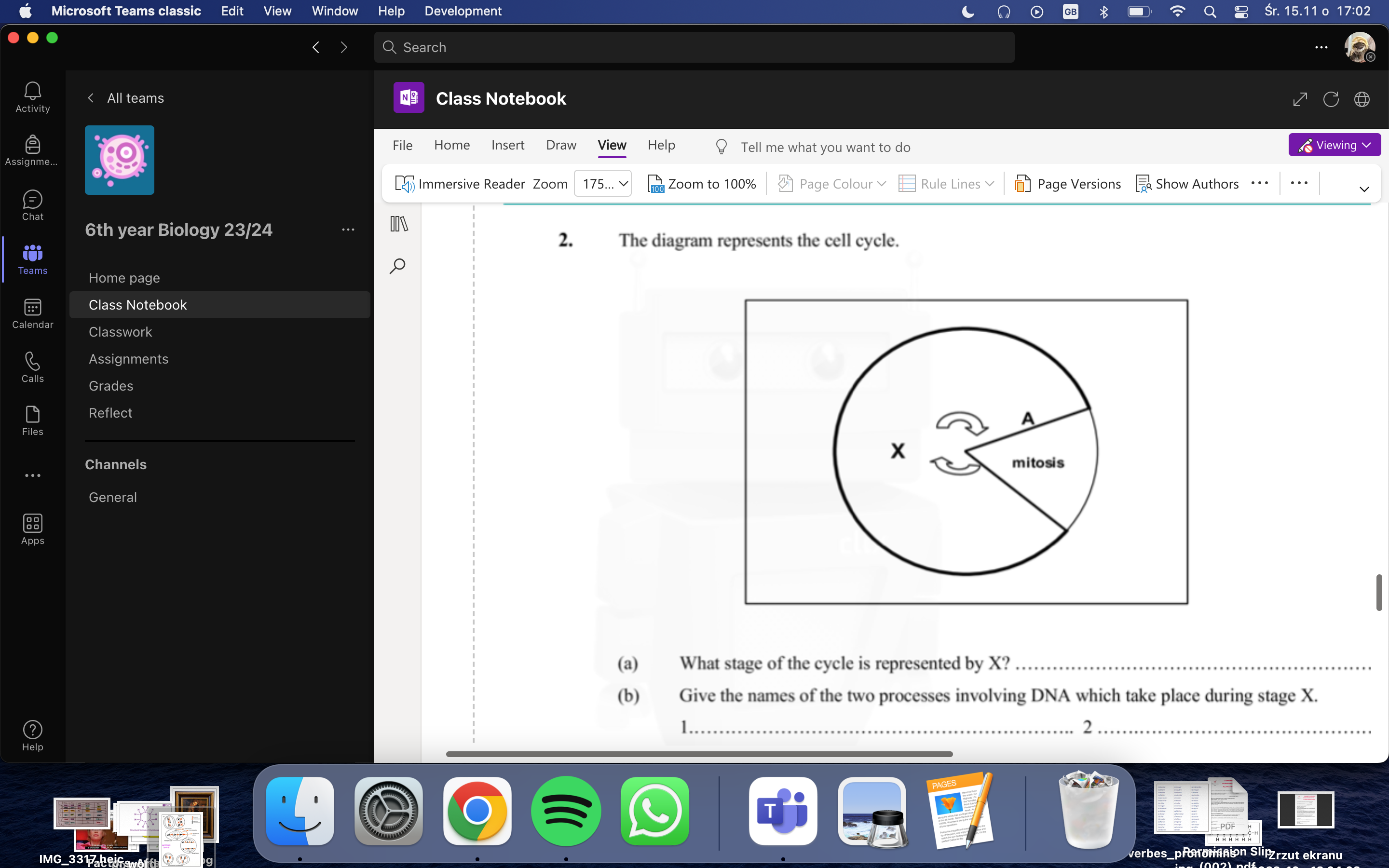
For the convenience of study, mitosis is divided into 4 stages. List these starting at A.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
by start at A they didn’t meant start at Anaphase
Give the names of the two processes involving DNA which take place during interphase
uncoiling
transcription
What is the role of chromosomes?
Carry genetic material, code for protein
Some cells in the body undergo meiosis. Give one function of meiosis
to produce gametes