transport in humans
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
why do multicellular animals need transport systems?
long diffusion distance, cells that need oxygen x get it easily,
larger organisms are more active, therefore cells are respiring quicker
higher metabolic rate
low surface area to vol ratio
what are the different types of circulatory systems?
open - blood flows freely through the body cavity
closed - blood enclosed inside blood vessels
double - blood only passes through the heart once for each complete circuit e.g. mammals
single - blood only passes through the heart twice for each complete circuit of the body e.g. fish
what are the pulmonary and seismic systems?
pulmonary - blood to the heart
seismic - rest of the body
advantage of double circulatory system
heart can give the blood an extra push, travelling faster and is delivered to the tissues quicker
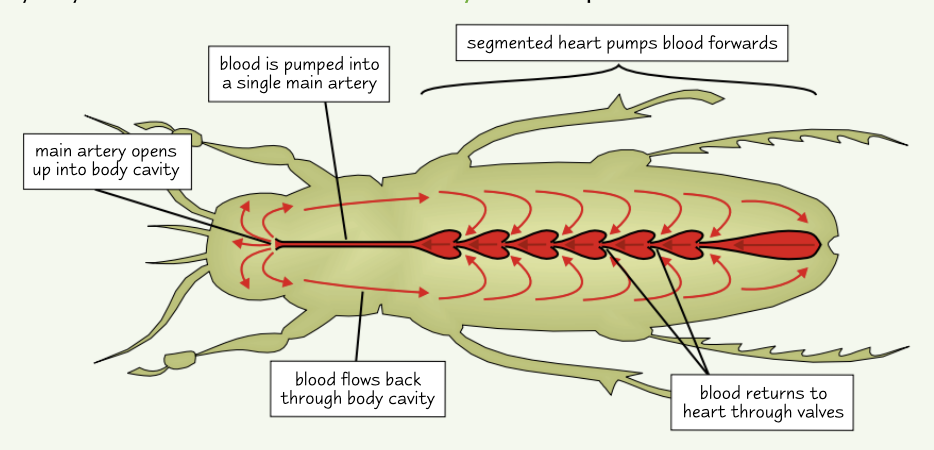
how does an insects circulatory system work?
heart is segmented - contracts in a wave starting from the back
pumps the haemolymph (insect blood) into a single main artery (the dorsal vessel)
the artery opens up into the body cavity
the blood bathes the organs
fluid returns to the heart via valves
transports hormones and nutrients,
no oxygen supplied through circulation
delivered directly via tracheae
structure and function of arteries + arterioles
arteries -
carry blood away from the heart
small lumen - to allow for a high pressure
folded inner wall - lumen to expand with increased blood blow
wall layers
thin layer of elastic tissue
thick layer of smooth muscle
thick layer of elastic tissue and collagen
arterioles
branch into narrower blood vessels - arterioles, transporting blood into capilliaries
elastic tissue purpose
allows walls to stretch and recoil
help maintain blood pressure
structure of capilliaries .
structure of venules and veins