NCEA Level 3 - Organic
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Optical isomer (enantiomers)
a compound which have the same structure but are mirror images of each other and typically differ in optical activity.
Chiral Compound
a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image
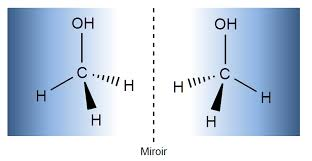
What does a chiral compound require
It requires four different groups bonded to a carbon
Chiral compound chemical properties
They have the same chemical properties because they have the same functional group
Optical isomers differences
they will rotate plane polarised light in opposite directions by the same amount
Addition reaction
involve 2 (or more in the case of polymers) molecules combining to make one molecule. Occurs when double bonds are broken to form a single c-c bond, and 2 new covalent bonds
Markovnikov’s rule
When adding HX or H20 to an asymmetric alkene, the H will form a bond with the carbon of the double bond with the greatest number of H’s already attached
Substitution reaction
Where one group/atom is exchanged for another atom/group
Elimination reaction
A molecule goes from saturated to unsaturated by removing the functional group and H from an adjacent atom (will always yield an alkene)
Zaitsev’s rule
With an asymmetric haloalkane or alcohol, the H is preferentially lost from the adjacent Carbon with the fewest H’s attached.
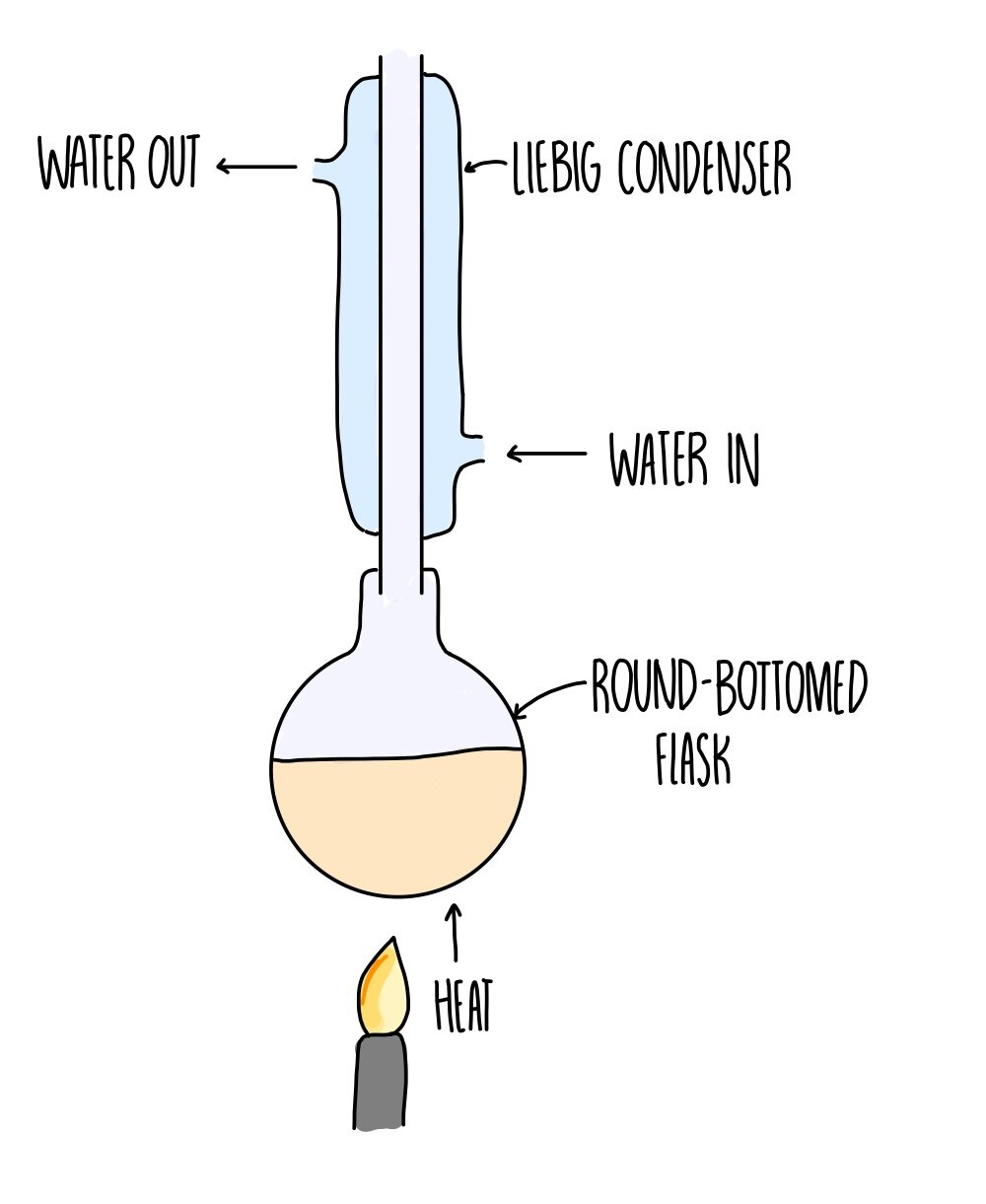
Reflux
As many organic compounds have a low b.p, they are volatile and will evaporate before a reaction can occur. The condenser will condense the vapour and return it to the reaction vessel. This ensures the reaction can occur under heating with out losing product or reactants (keep yield high)
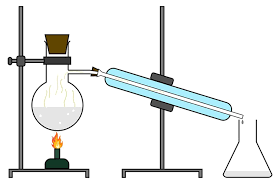
Distillation
Used to seperate organic molecules which have different b.p. The lower b.p substance will be removed first as it boils off. It then cools in a condenser and reverts to a liqud where it is collected.
What happens to a primary alcohol when oxidised
it becomes an aldehyde, then a carboxylic acid
What happens to a secondary alcohol when oxidised
it becomes a ketone
What happens to a tertiary alcohol when oxidised
nothing
Hydrolysis
breaking of a molecule using water. Involves the addition of water with an acid or base