Anatomy and Kinesiology exam 1
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
bone and connective tissue injuries often cause _____
joint stiffness
kinesiology
study of movement
kinematics
study of motion w/o cause
osteokinematics
looking at bones and how they move
arthrokinematics
joint and how they move
kinetics
forces that cause motion and effect
rotary/rotational
movement around an axis
ex: elbow
translatory
linear motion, or compression and distraction
ex: scapula gliding on thorax /ribs
saggital plane
left vs. right
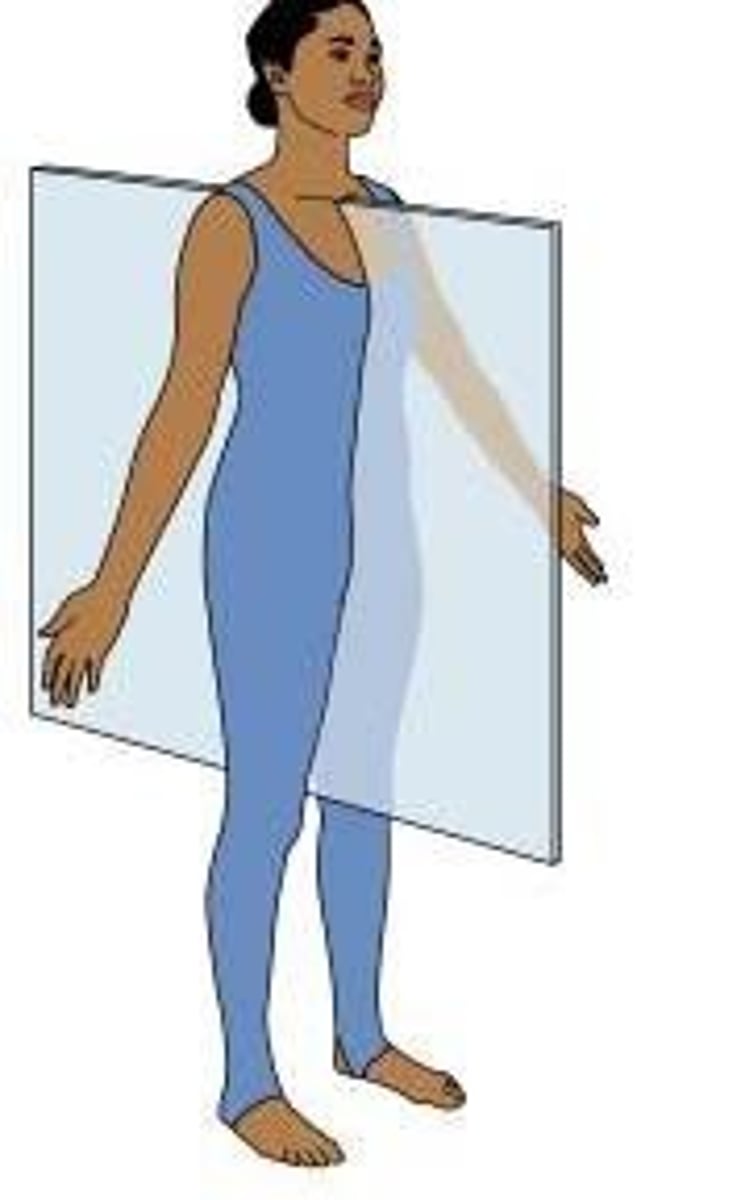
frontal/coronal plane
front vs. back
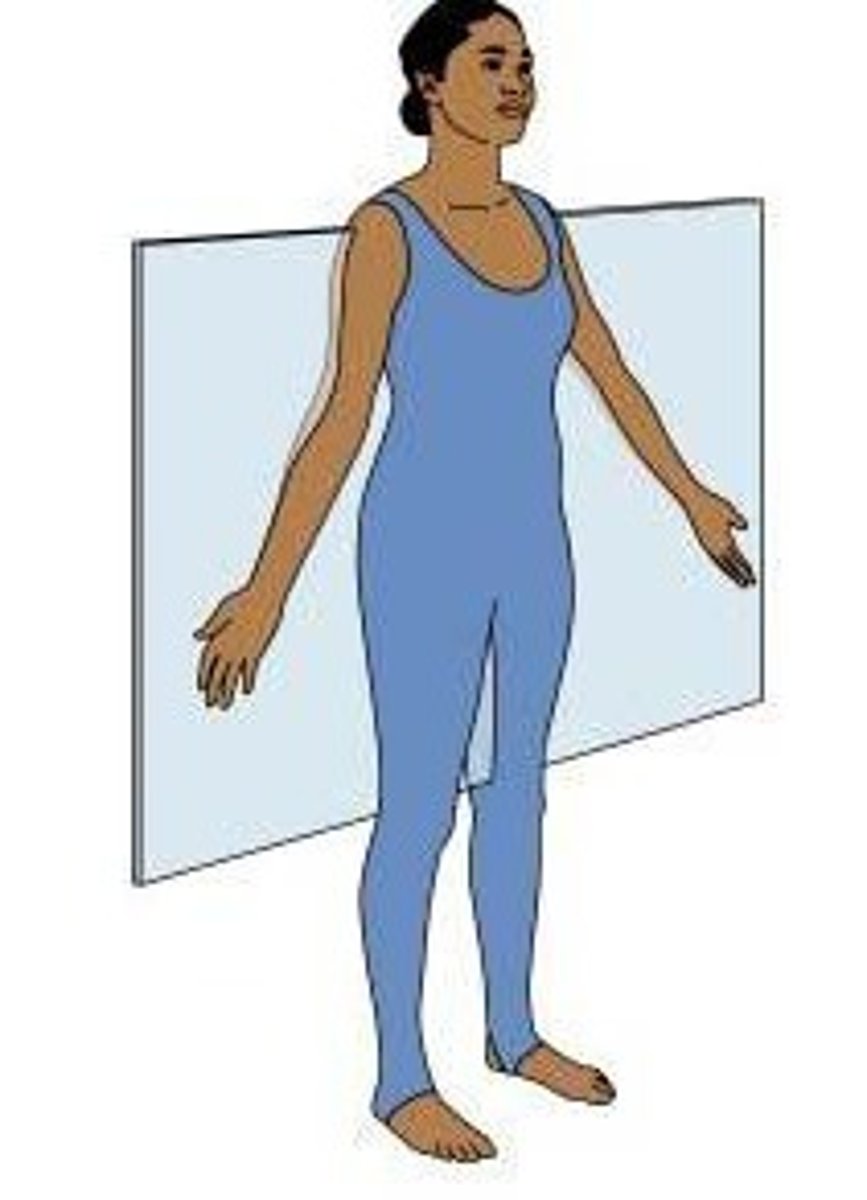
horizontal/transverse
top vs. bottom
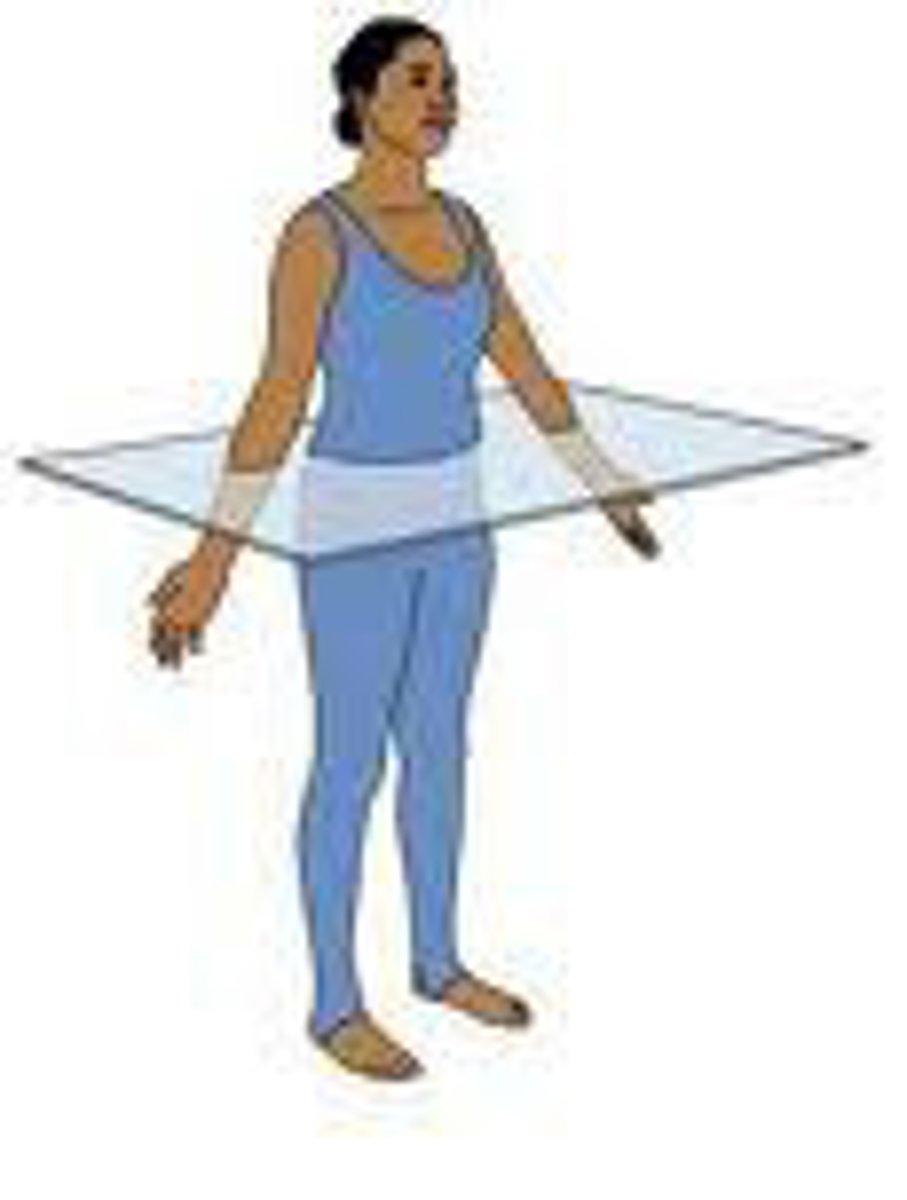
axis of rotation
imaginary line perpendicular to the plane of rotation and passing through the center of rotation
medial-lateral axis of rotation
saggital plane
anterior-posterior axis of rotation
frontal plane
vertical axis
transverse
goniometry
Measurement of joint motion
1 degree of freedom
joint can only move in one plane
ex: flexion and extension of elbow, supination and pronation of forearm
2 degrees of freedom
joint can move in two planes
ex: knuckles of fingers, flexion and extension, abduction and adduction
3 degrees of freedom
joint can move in all 3 planes
ex: flexion and extension, adduction and abduction, medial and lateral rotation
open chain
distal or end segment that's free to move, often upper extremities
closed chain
distal or end segment that is NOT free to move, often lower exttremities
synarthrosis
rigid connection between 2 bones of body held together by dense fibrous connective tissue
ex: sutures of skull
amphiarthrosis
junction of bones that's formed w/ fibrocartilage which allow minimal movement and distribute forces
ex: intervertebral discs of spinal cord
diarthrosis
fluid filled joint cavity between bones; majority UE and LE joints. Also called synovial joints
ex: glenohumeral
axial shifting
axes are not stationary.
force
push or pull with or without motion
internal force
force from inside the body
ex: ligaments
active internal forces
muscles
passive internal forces
tension in muscles, connective tissue, ligaments, joint capsule
external forces
produced by forces outside the body
ex: gravity, people, book bags, etc.
1st law- law of inertia
An object at rest tends to stay at rest; an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an external force
2nd law- law of acceleration
Acceleration of the body is
directly proportional to the force causing it, takes place in the same direction in which the force acts,
and is inversely proportional to the
mass of the body.
• F=ma
• Work is equal to the product of the
force applied to an object and the distance the object moves.
3rd law- law of action-reaction
every action has an equal AND opposite reaction
magnitude
amount of force, measure in newtons or pounds
direction
plane the force moves in
resultant force
-sum/combination of two or more forces.
-integrates direction and magnitude of both forces.
-OVERALL MOTION of object is determined by the RESULTANT FORCE acting on that force.
concurrent forces
-same point of application
-pulls in diff. directions
parallel forces
forces occurring in the same plane or direction but with a counterforce in the opposite direction
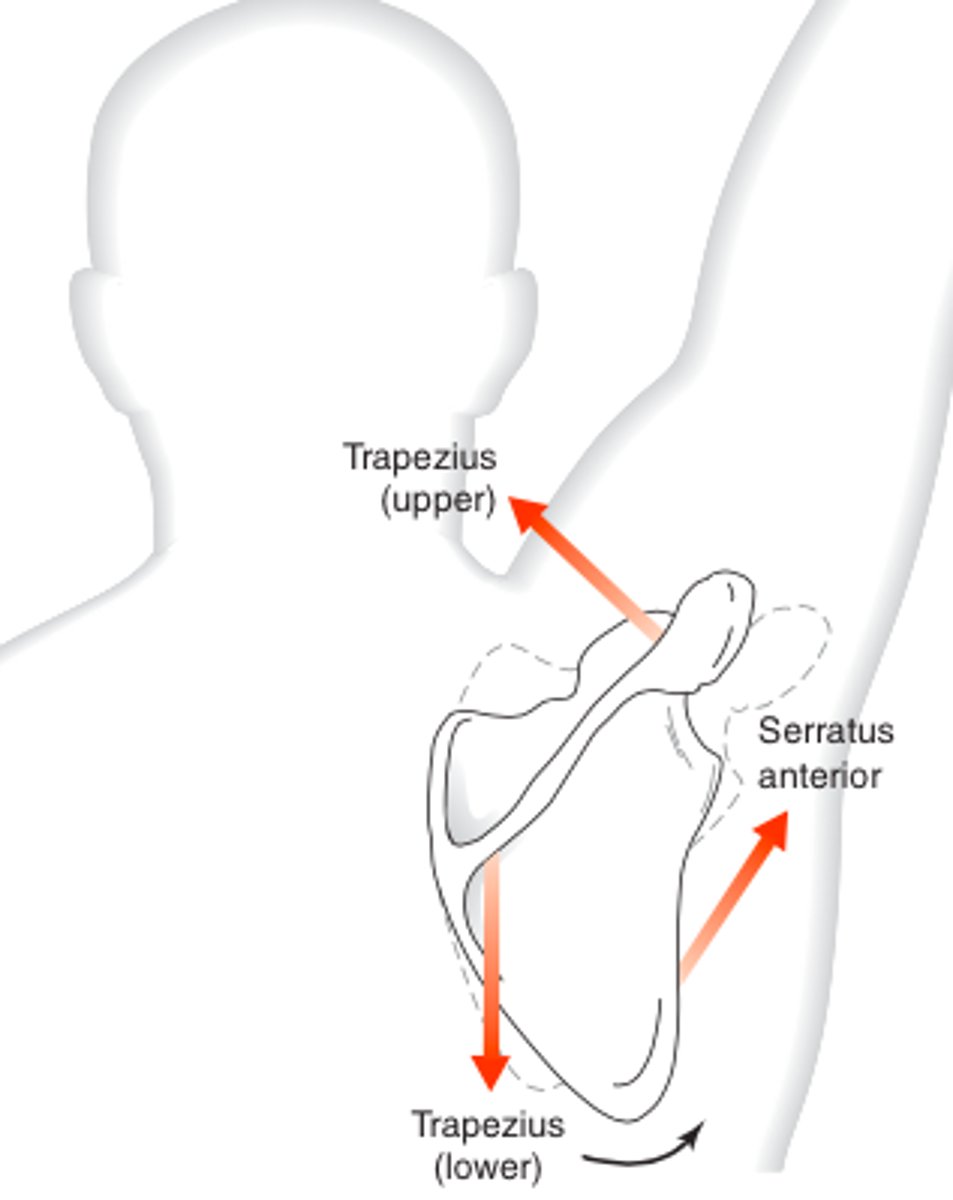
force couple
-2 or more forces involved
-acting with equal magnitude but opposite direction, creates rotary effect
-creates a moment: tendency of a force to cause rotation around an axis
gravity and resistance
-external forces
-center of gravity = balance point of an object
line of gravity
a vertical line that passes through the center of gravity
base of support
the space between the feet that bears the weight of the body
ways to increase stability
- increase body mass
- increase base of support
- vertically position the cg as low as possible
- increase friction between body and surface
- horizontally position the cg near edge of base of support towards the oncoming external force
compression
A force that pushes on or squeezes a material.
tension
stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object
bending
a combination of stretching and compression
shear
force directed parallel to a surface; sliding
torsion
a twisting force
torque
ability of a force to cause rotation at an axis
internal torque
product of internal force and internal moment arm (effort force)
external torque
product of an external force and its external moment arm (resistance force)
moment
another name for torque
moment arm
The perpendicular distance from a reference point to the line of action of the force.
levers
a rigid bar that rotates around an axis
first class levers
effort force, axis, resistance force
second class levers
axis, resistance force, effort force
third class lever
axis, effort force, resistance force
mechanical advantage
efficiency of a lever
- E MoA divided by R MoA
-greater than 1 --> powerful lever
-equal to 1 --> balanced lever
-less than 1 --> able to cause more rotation
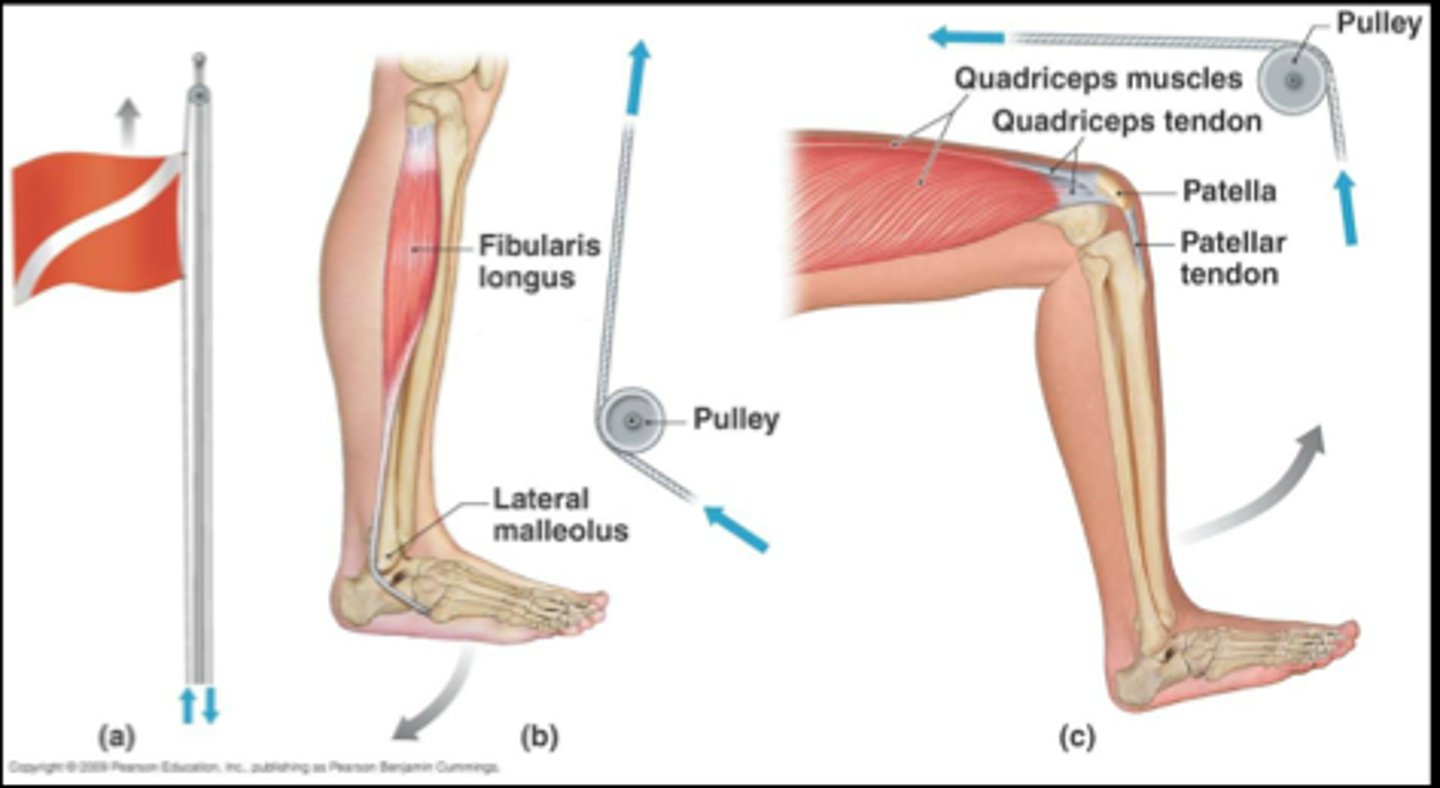
pulleys
-change the direction of a force
-increase or decrease the magnitude of a force
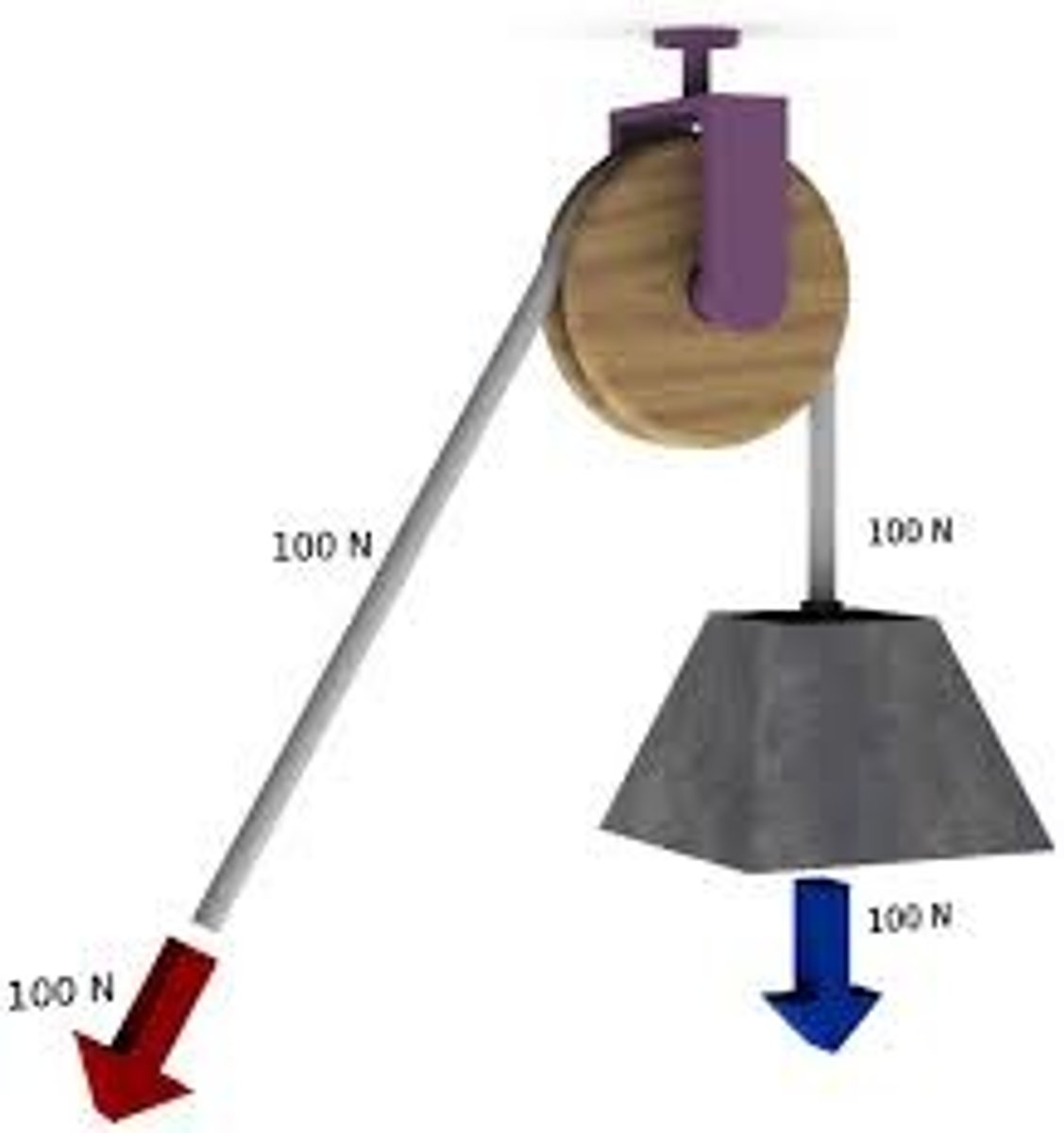
anatomical pulleys
boney structures that change the direction of applied forces
stiated voluntary muscle
skeletal muscle
-movers of the body
muscle names are based on
- location
- shape
- action
- attachment
- #of heads
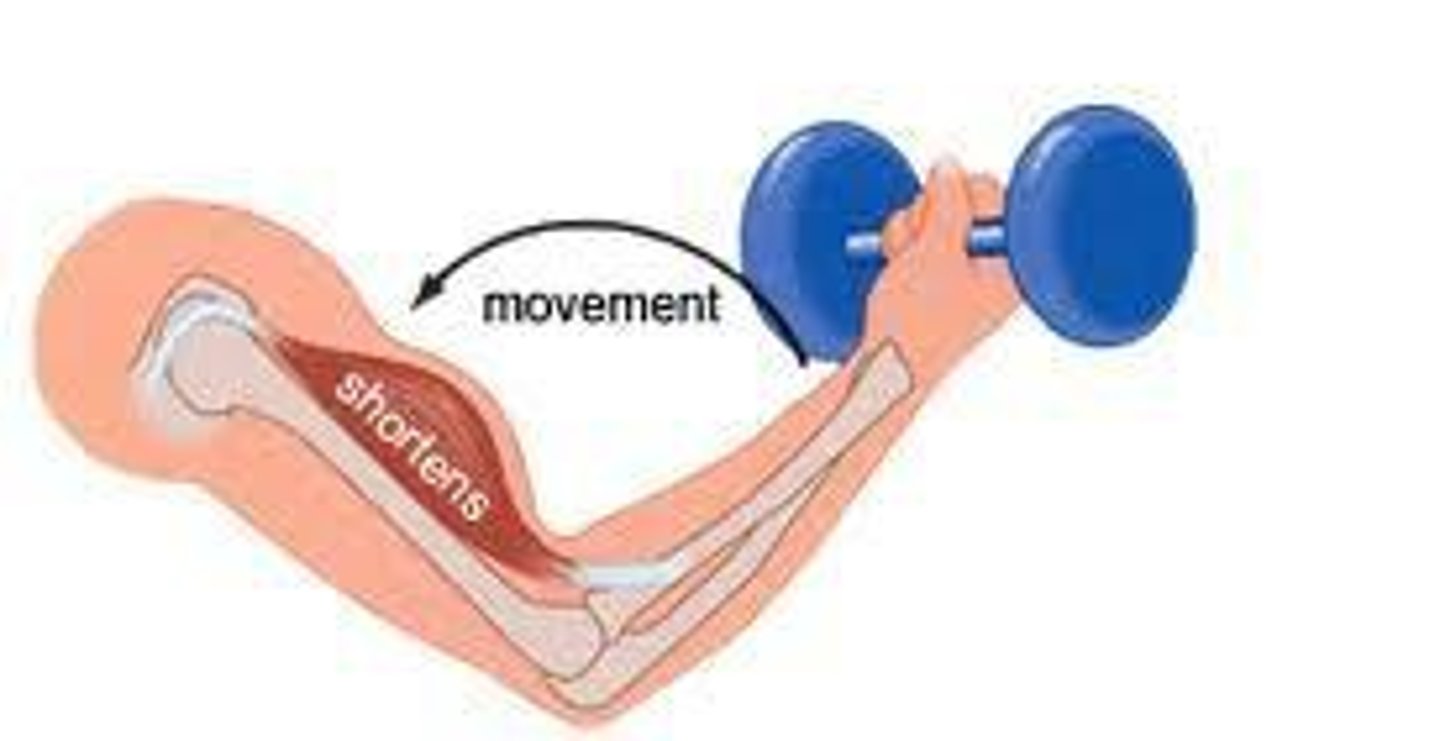
concentric activation
muscle shortens
- muscle exerts more internal torque than external torque
- muscles are winning
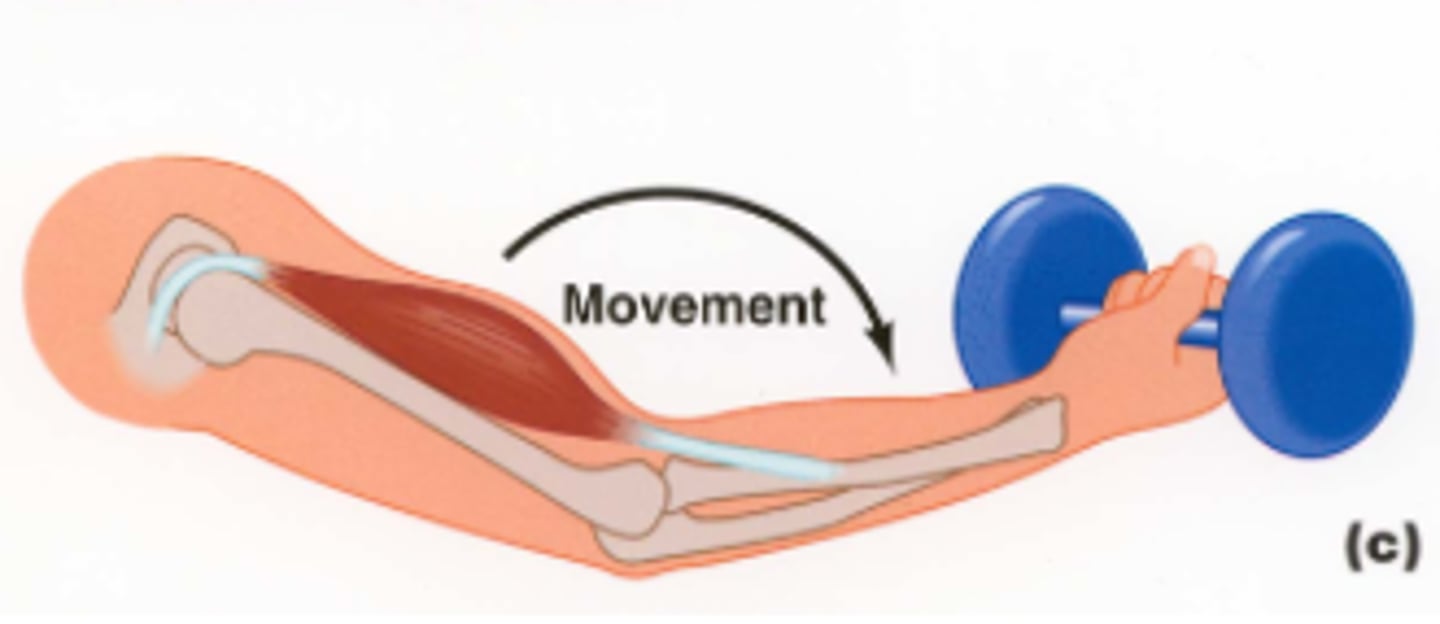
eccentric activation
occurs when external torque is greater than the internal torque
isometric activation
the internal torques are equal
- no change of muscle length, but still contracting.

agonist
prime mover
antagonist
muscle opposite to prime mover
synergist
muscle that helps prime mover
extensibility
the ability to stretch
elasticity
the ability to return to starting point
irritability
ability to respond to a stimulus
contractility
the ability to shorten
viscosity
the muscles resistance to external forces (heat, ice)
muscle stength and force production is influenced by
- age and sex
- moment arm
- size
- arrangement of muscle fibers
- passive components
- speed of activation
- length-tension of muscle
speed of activation
speed = rate of motion
slower concentric activation
greater forces --> greater actin-myosin bonds are able to form
faster concentric activation
less force, less actin-myosin bonds able to form
muscle strength in men
men anatomically have more muscle bulk and fiber than women
parallel "fusiform"
Fibers are arranged in the same direction along the long axis of the muscle. Spindle-shaped with a central, large belly.
- ex: biceps brachii
pennate "oblique"
Short fibers arranged diagonally along the length of a central tendon. This diagonal arrangement allows for greater strength, but shorter ROM.
msucle fibers influence strength by
more muscle fibers the greater the force potential
what determines strength of muscle activation?
physiological cross-sectional area of fibers
length-tension relationship
The resting length of a muscle and the tension the muscle can produce at this resting length.
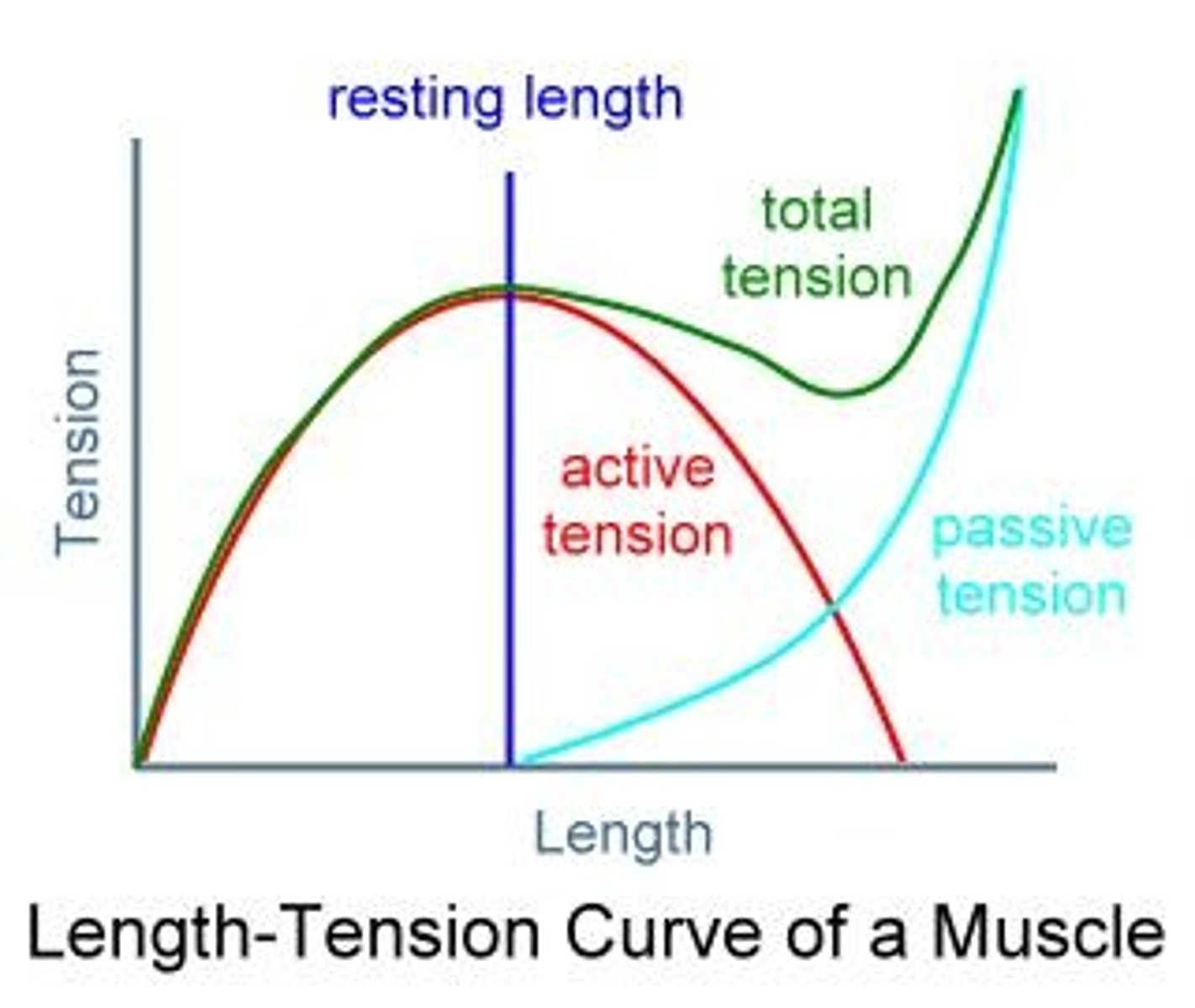
active tension
occurs during activation of muscle tissue
passive tension
occurs during the elongation or the lengthening of muscle tissue
-can be stimulated by brain
active insufficiency
when multi-joint muscle can't produce any more force due to SHORTENED length
passive insufficiency
when multi-joint muscles can't be elongated further without damager
tenodesis
occurs in muscles or tendons that cross multiple joints
-ex: wrist in extension --> fingers flex
wrist in flexion --> fingers extend
shoulder complex involves
-scapula
-clavicle
-humerus
articulation of shoulder
scapulothoracic, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and glenohumeral
scapulothoaric joint
NOT A TRUE JOINT
- glides along rib cage
- stabilized by muscles and ligaments
motions of scapulothoracic joint
elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, upward rotation/downward rotation
acromioclavicular joint
-plane
-joint formed from acromion and lateral end of clavicle
motions of AC joint
small amount of movement
-anterior/posterior translation
-superior/inferior translation
sternoclavicular joint
- complex saddle joint
- 3 df
motions of sternoclavicular joint
elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, axial rotation
fibrocartilage (articular discs)
Pads between vertebrae that are shock absorbers
glenohumeral joint
-ball and socket joint
-3 df
-sacrifices stability for mobility
GH motions
-Flexion/Extension
-Abduction/Adduction
-Internal Rotation/External Rotation
-Horizontal Abduction/Horizontal Adduction
static stabilizers of GH
-capsular ligament
-coracohumeral ligament
-glenoid labrum