Biomed Final Flash Cards
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Focus on the heart, brain and DNA.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Biomedical Science
A broad field that incorporates biology to understand human and animal diseases. |
Control Group
A baseline for comparison against an experimental group that is exposed to the variable being tested. |
Dependent Variable
The factor that is measured and is affected by changes in the independent variable. Depending on another
Experiment
A procedure taken to make a discovery, hypothesis, or demonstrate a known fact. |
Forensic Science
the application of scientific principles to solve crimes and analyze evidence.
Hypothesis
a proposed explanation for a phenomenon, often tested through experimentation.
Independent Variable
A variable that is manipulated in an experiment to observe its effects on the dependent variable.
Negative Control
No change or effect is expected.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Clothing and equipment designed to protect users from health or safety risks at work. i.e. gloves, safety goggles.
Positive Control
A positive result.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a genetic autoimmune disorder which causes your body to attack insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is when the body becomes immune to or not producing enough insulin.
How do you deal with diabetes
Monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking insulin or other medications if prescribed.
What is Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite internal and external changes.
What does a feedback loop for diabetes look like?
Increased sugar consumption leads to elevated blood glucose, triggering insulin release, which helps lower blood sugar levels. This process may be impaired in diabetes.
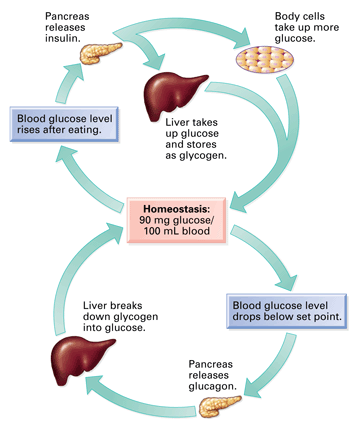
How does the body regulate glucose
Through hormones, insulin and glucagon, and coordinated actions from the liver and other organs.
Hyperglycemia
When the body has too much glucose in the bloodstream.
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution.
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution.
Isotonic
A solution that has an equal concentration of solutes compared to another solution.
Hypoglycemia
A condition when blood-glucose levels drop low. |
Osmosis
When water molecules move through a membrane from an area of lower to an area of higher solute concentration.
Livor Mortis
The pooling of blood in the lower parts of the body after death, causing skin discoloration. |
Rigor Mortis
A postmortem condition characterized by the muscles stiffening because of the chemical changes in the muscle fibers. |
Postmortem
Events that occur after death.
Autopsy
An examination used to determine the cause of death.
Mechanism of death |
The specific physiological disruption or change in the body that ultimately leads to death. Cause, mechanism, manner.
Carbohydrates
Function: Main source of energy, providing the body fuel.
Structure: A chain of carbon atoms
Building block: monosaccharides
Proteins
Function: Required structure for tissues, hormones, enzymes and organs.
Structure: Linear sequence of amino acids to complex 3D shapes
Building Block: Amino Acids
Lipids
Function: Energy storage, structural components of cell membranes, hormone production, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Structure: Glycerol and fatty acids.
Building Block: Glycerol and fatty acids.
Plasma
The liquid part of your blood. Carries red and white blood cells and platelets through the body.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells, responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to tissues, carrying carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
Leukocytes
White blood cells, defends the body against infections, foreign invaders, and diseases.
Thrombocytes
Platelets, form clots to prevent and stop bleeding.
Hematocrit
The percentage of red blood cells in your blood, measured as a percentage of the total blood volume
Amino Acid
Molecules that combine to form proteins
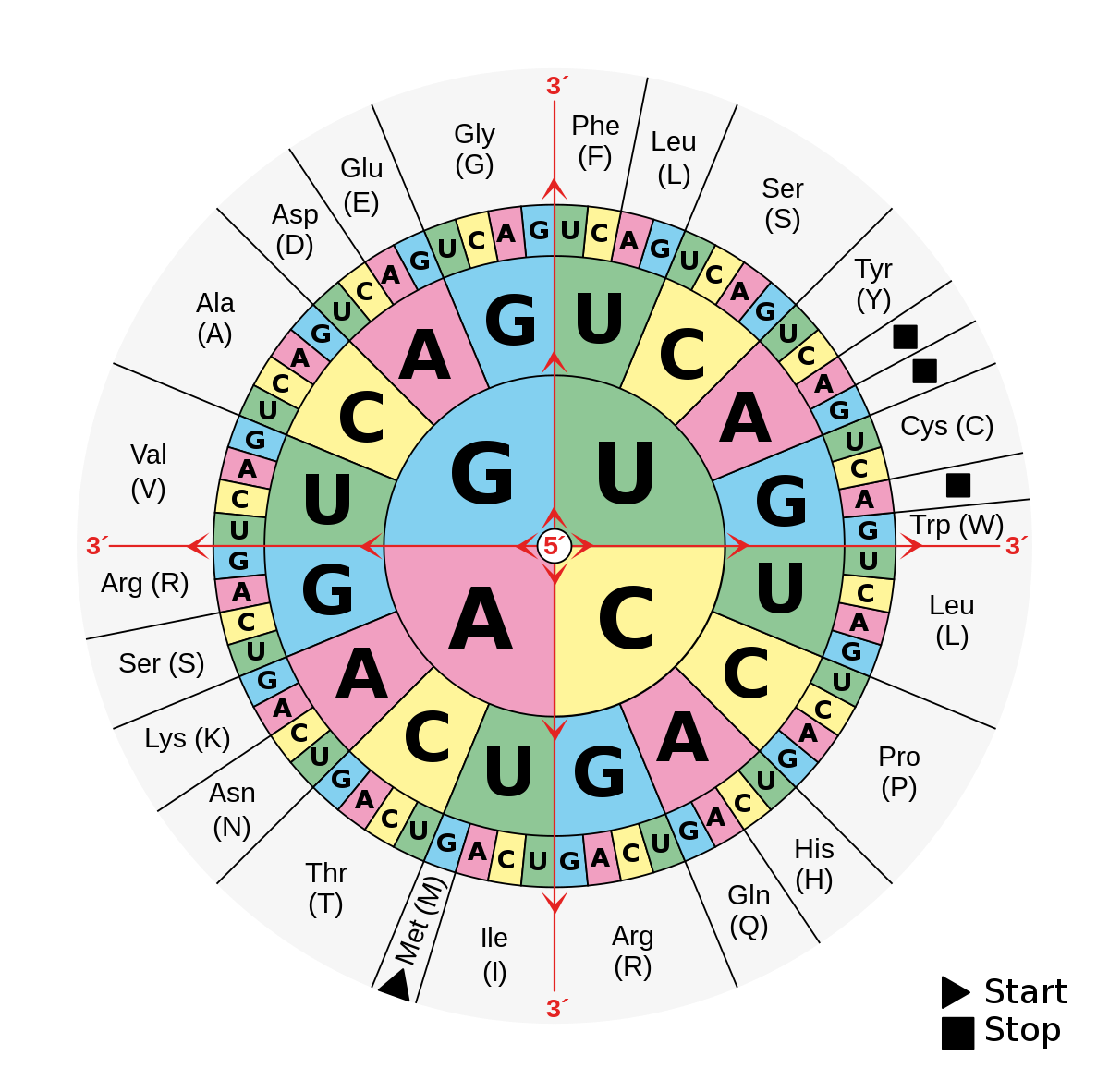
Codon
a sequence of 3 consecutive nucleotide bases in DNA or RNA that specifies a particular amino acid or indicates the start or stop of translation during protein synthesis.
Anticodon
A sequence of 3 nucleotide bases in DNA or RNA that specifies a particular amino acid or indicates the start/stop of translation during protein synthesis.
mRNA
A type of single stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis.
Neucleotide
The building block of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
Protein Synthesis
The process by which cells create proteins, essential for various bodily functions
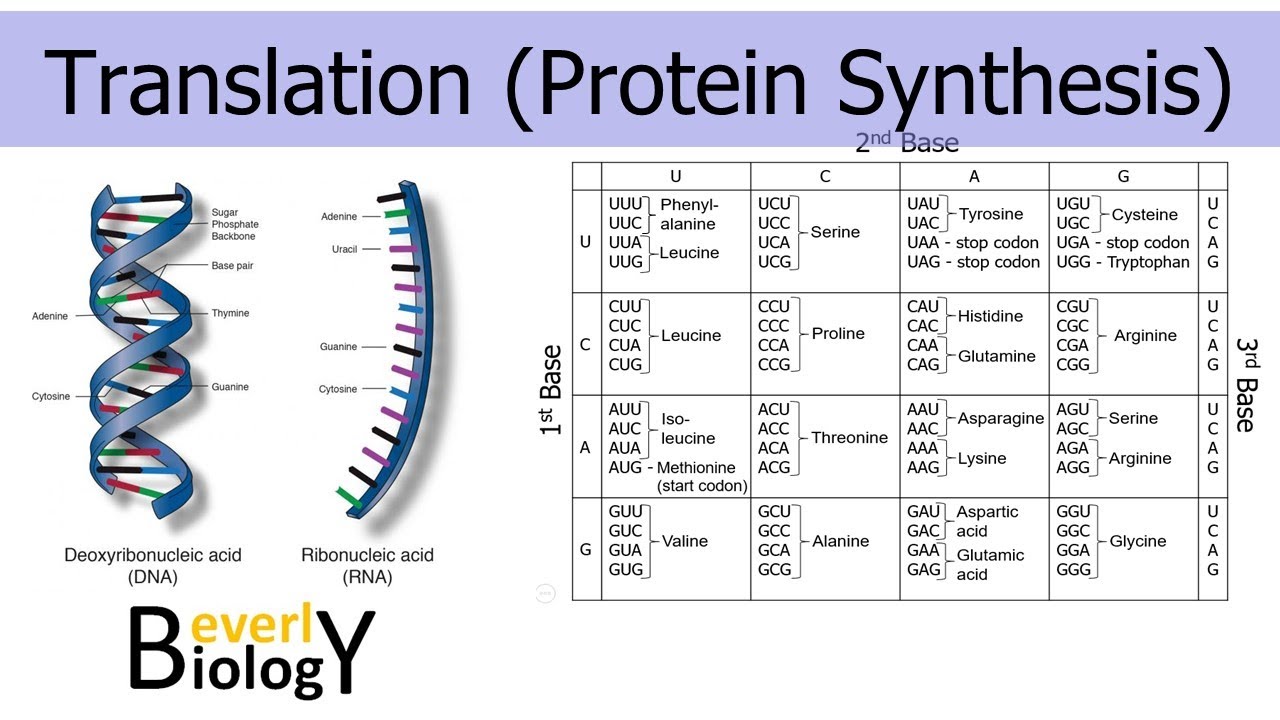
RNA
A molecule found in all living organisms and some viruses. A nucleic acid.
Ribosome
Essential cellular structures responsible for synthesizing proteins.
Transcription
the process by which a cell makes an RNA copy of a piece of DNA.
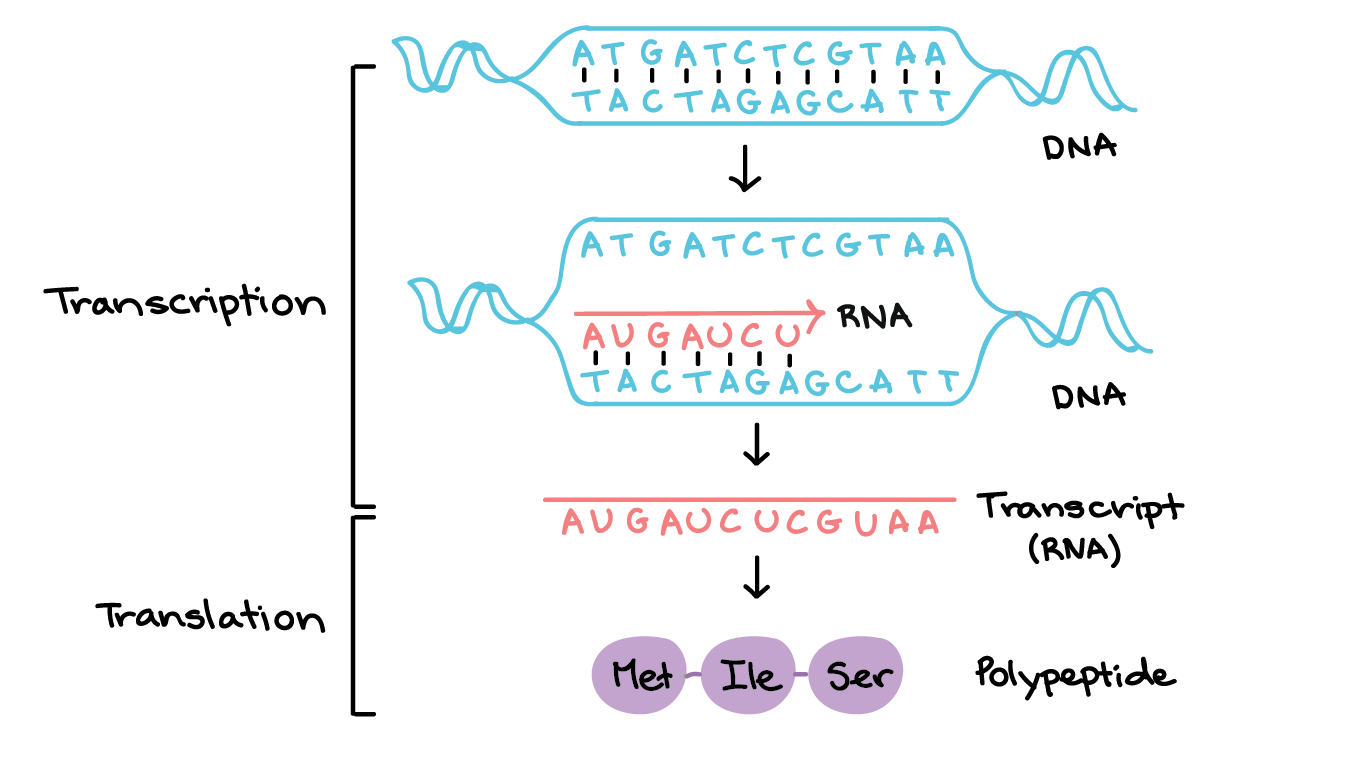
Translation
The process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA).
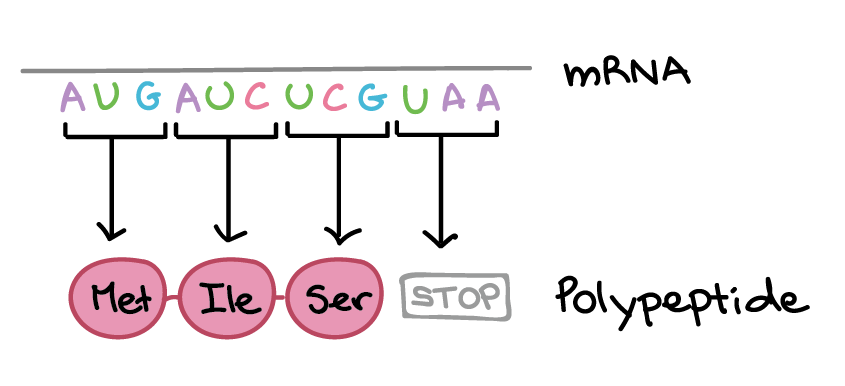
Autosome
any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome.
Dominant Trait
Only one copy of the relevant allele is needed to express the trait
Recessive Trait
A characteristic that is only expressed when an individual has two copies of the recessive allele for that trait, one from each parent
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, specifically the combination of alleles (different forms of a gene) for a particular trait
Phenotype
The observable characteristics or traits of an individual, determined by their genetic makeup and potentially influenced by environmental factors
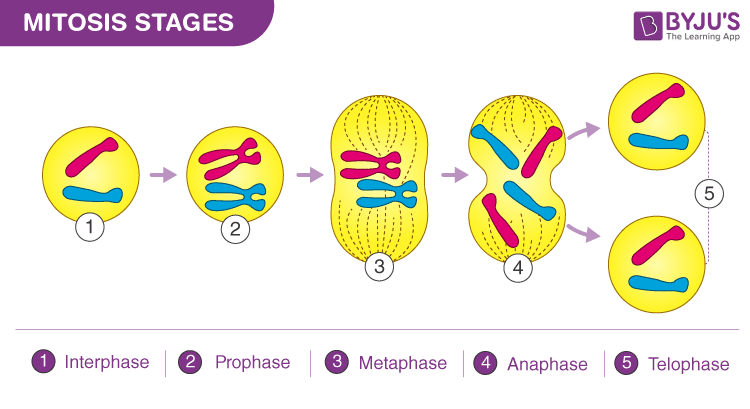
Mitosis
A cell division process in eukaryotic cells where one cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase (PMAT)
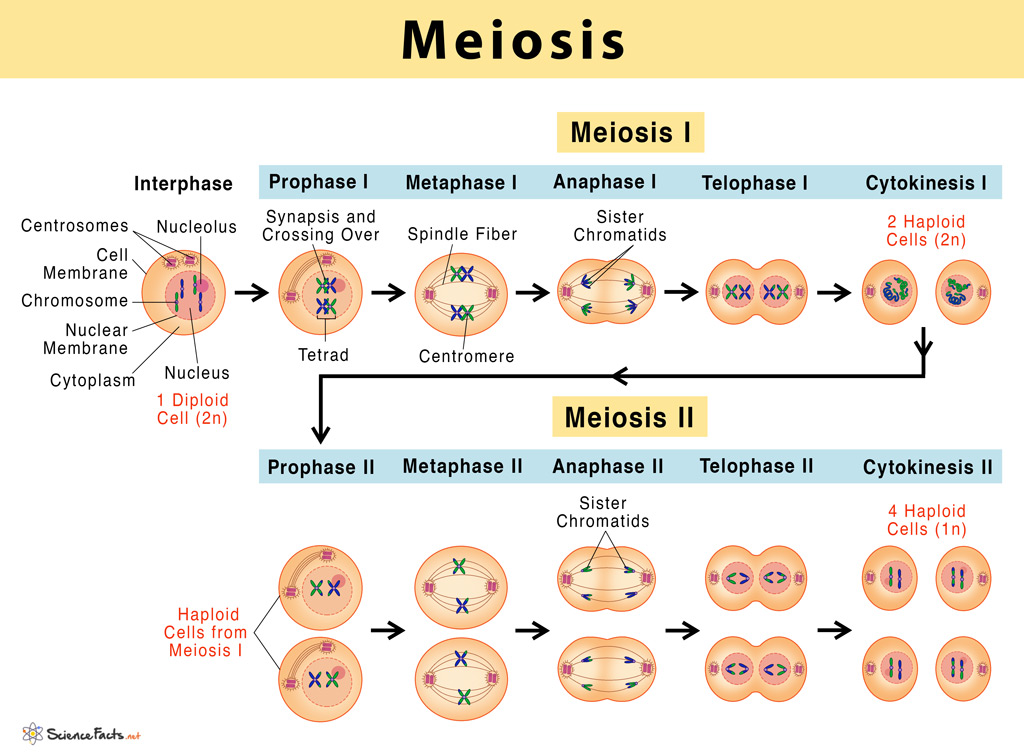
Meiosis
A type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells)
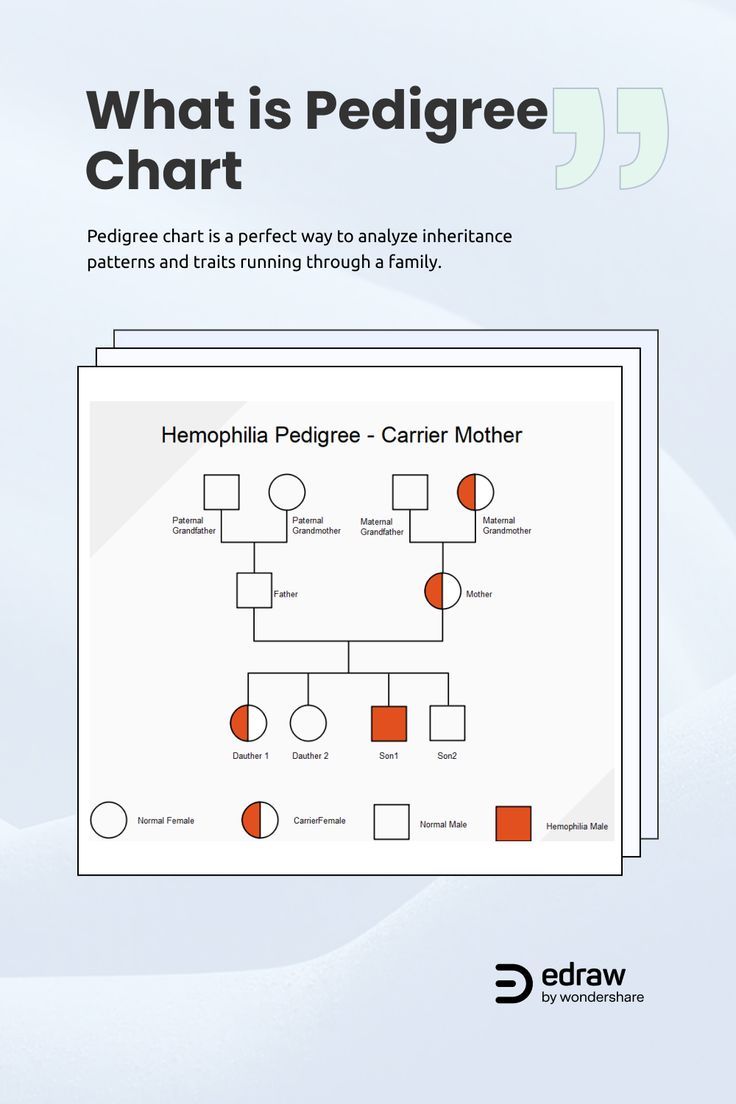
Pedigree Chart
A diagram that visually represents the family history of individuals, particularly to understand the inheritance of genetic traits or conditions
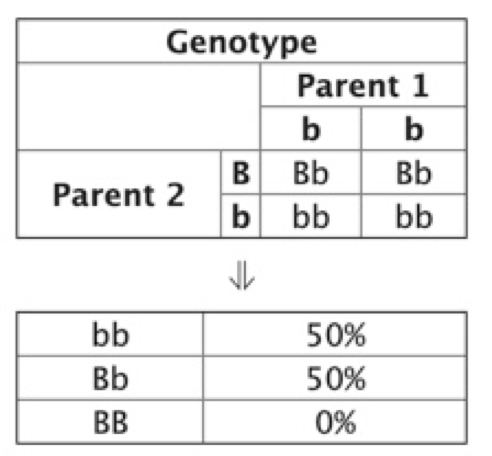
Punnett Square
A diagram used in genetics to predict the possible genotypes of offspring in a cross between two parents
Allele
One of two or more alternative versions of a gene that occur at the same place on a chromosome
Aorta
The main blood vessel through which oxygen and nutrients travel from the heart to organs throughout your body.
Artery
Blood vessels that distribute oxygen-rich blood to your entire body.
Atrium
The two upper chambers of the heart, responsible for receiving blood from the body and lungs
Inferior Vena Cava
The largest vein in the human body, carrying deoxygenated blood from the lower body back to the heart
Mitral Valve
Opens up enough so that blood can flow from the upper chamber of your heart (left atrium) to the lower chamber (left ventricle). It then closes, keeping blood from flowing backwards.
Superior Vena Cava
A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body back to the heart
Tricuspid Valve
One of four heart valves, located between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Ventricle
One of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart
Vein
Any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood toward the heart.
Blood Pressure
The force of your blood pushing against the walls of your arteries
Diastole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood.
Sytole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood.
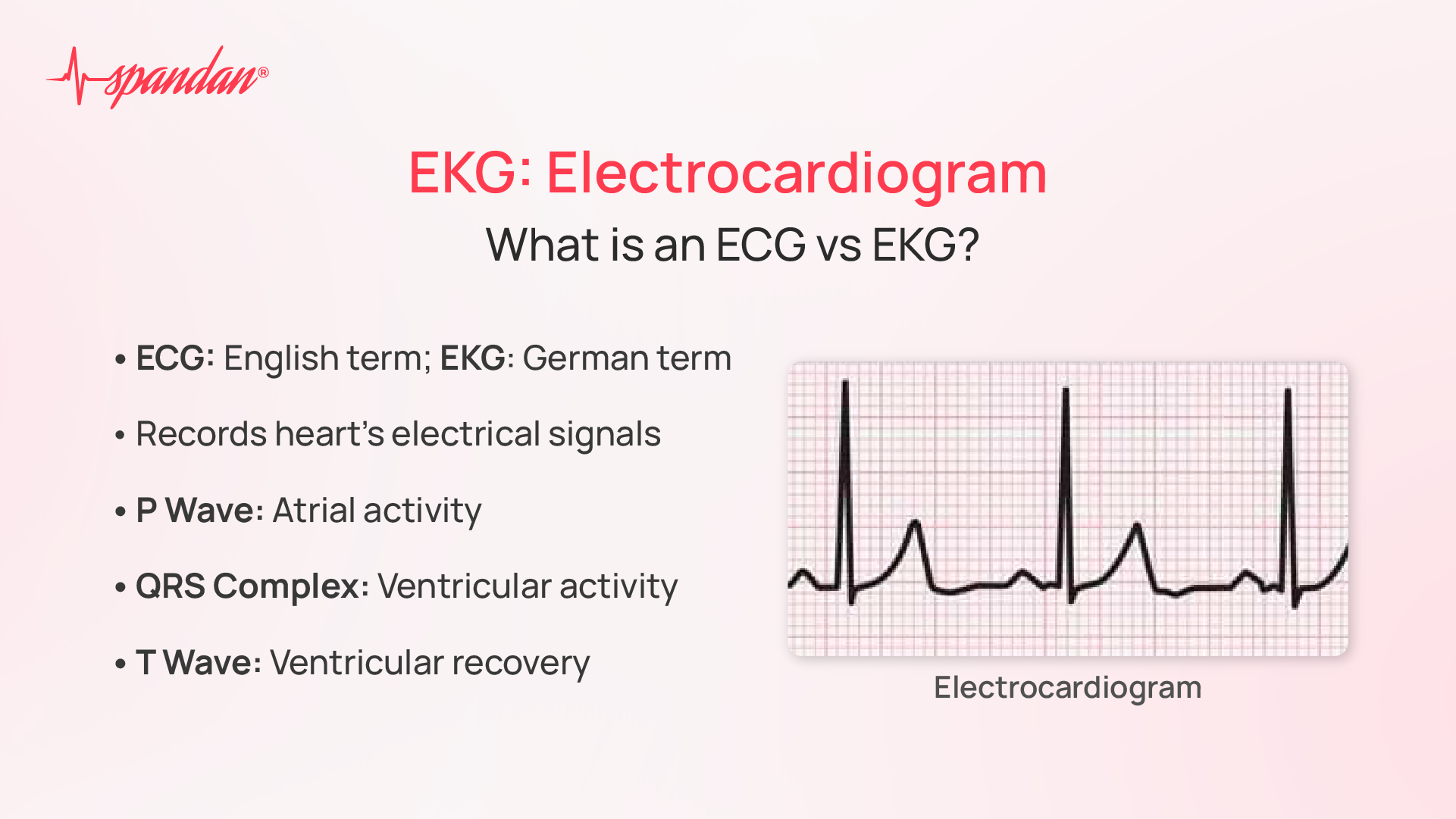
EKG or ECG
EKG and ECG are interchangeable terms for the same medical test: an electrocardiogram
Hypertension
A condition where the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high
Sphygmomanometer
An instrument for measuring blood pressure
Cardiology
The branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the heart and blood vessels
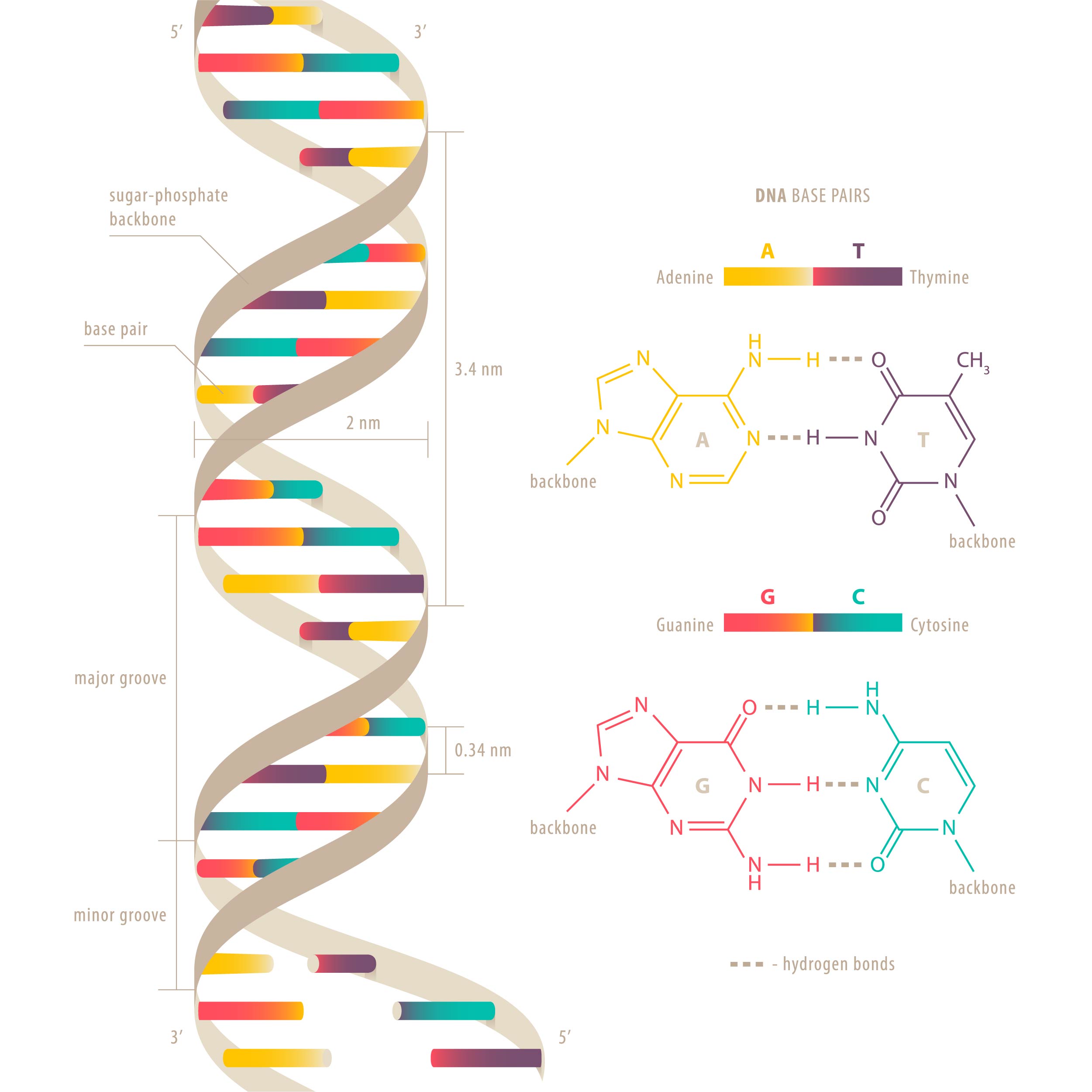
DNA
A molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and functioning of all living organisms
How do scientists isolate DNA to study it and how does it differ from person to person?
Scientists isolate DNA by extracting it from cells and then purifying it. It is different due to variations in base pair sequences, specifically in areas called alleles, which create individual DNA profiles
How can tools of molecular biology be used to compare DNA of two individuals?
Molecular biology tools like restriction enzymes, gel electrophoresis, and PCR can be used to compare DNA from two individuals.
Restriction Enzymes
Proteins produced by bacteria that cut DNA at specific sites
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
A technique that analyzes variations in DNA fragment sizes produced by restriction enzymes
Gel Electrophoresis
A laboratory technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or protein fragments based on their size and charge
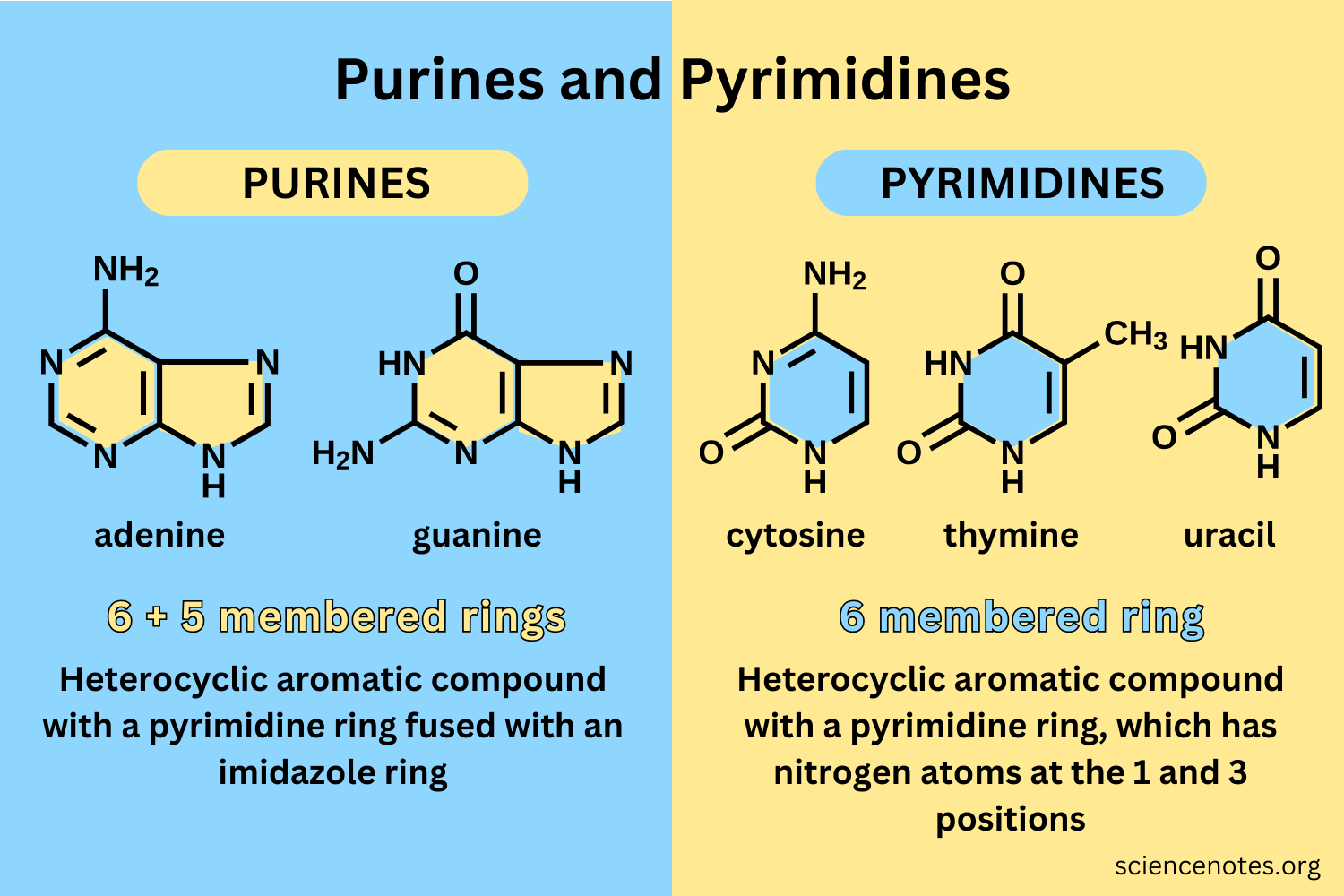
Purines & Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases that are the building blocks of nucleic acids
Sugars & Phosphates
Augars and phosphates work together to form the structural backbone of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA
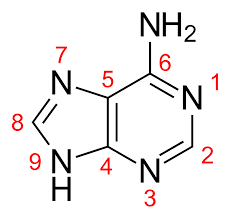
Adenine
One of the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA
Chromosome
Structures within cells that contain genetic information in the form of DNA
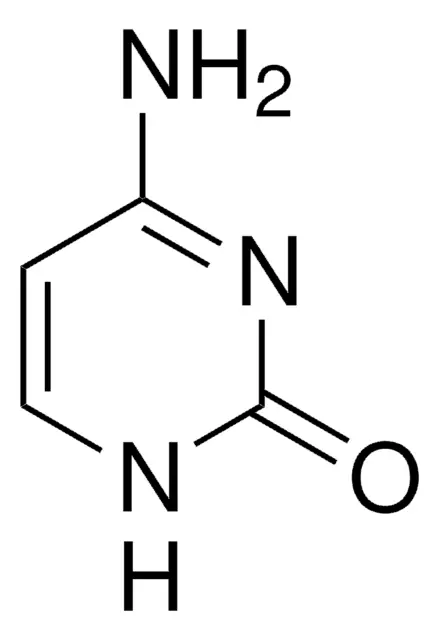
Cystosine
One of the four main nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA

Guanine
One of the four main nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA
Gene
The basic unit of heredity, carrying instructions for building specific proteins or other functional RNA molecules
Helix
Refers to a spiral or coiled structure
Nucleotide
The fundamental building block of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA
Thymine
One of the four main nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA

Model
Various representations used to understand complex biological systems, often by simplifying them into more manageable forms
Human Body Systems
Integumentary System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Cardiovascular System, Lymphatic System, Respiratory System, Digestive System, Urinary System, and Reproductive System
LDL & HDL
Two types of lipoproteins (fat and protein combinations) that carry cholesterol in the blood.
LDL: Low density lipoprotein
HDL: High density lipoprotein
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
A genetic condition that causes high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol
Heart Disease
A broad term encompassing various conditions that affect the heart's structure and function, impacting its ability to pump blood efficiently
What happens inside the heart during a heart attack?
Blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to a clot in a coronary artery
How do doctors treat a blocked blood vessel
Angioplasty and stenting, atherectomy, bypass surgery, and medication
Risk factors for developing heart disease
Lifestyle choices like smoking, unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and excessive alcohol consumption
How can you decrease your risk for heart disease?
Prioritize a heart-healthy lifestyle
Angioplasty
A medical procedure that opens narrowed or blocked arteries, improving blood flow
Stent
A small mesh tube, often made of metal, used to keep a passageway in the body open, particularly in blood vessels
Bypass Surgery
A procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscle when the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked
Stroke
Occurs when something disrupts blood flow to the brain, leading to brain cell damage or death