Tectonic Forces and Natural Disasters I
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3rd lecture (9/9)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Plate Tectonics
Movement of lithospheric plates driven by heat from Earth’s core
Earthquake activity reveals plate boundary locations
Ridge Push
The force of hot magma rising to the surface beneath the ridge
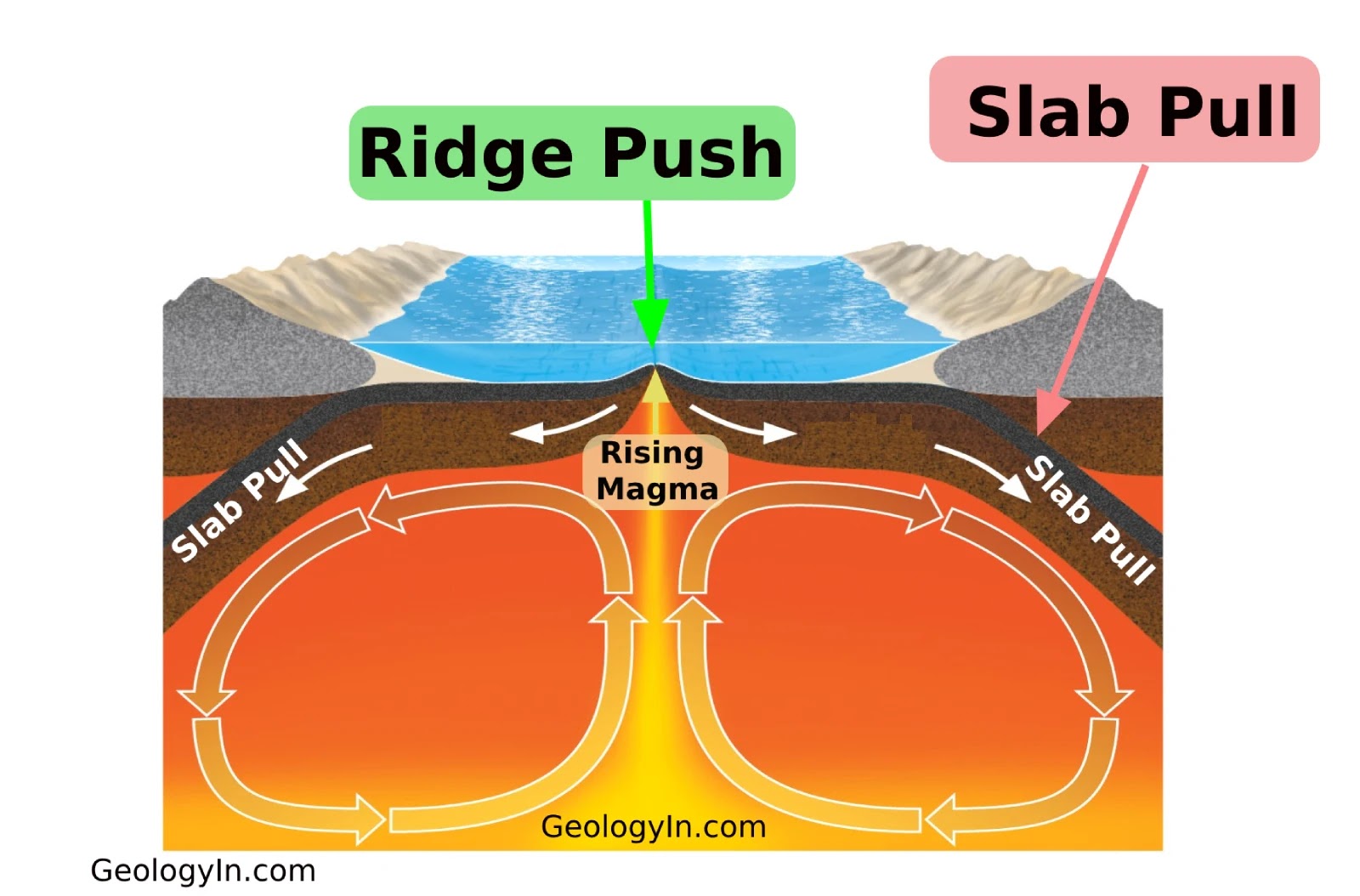
Slab Pull
The slab portion of a plate accelerates plate movement by pulling the plate deeper into the mantle
Mantle Drag
Movement of a plate caused by friction between moving asthenosphere and the lithosphere
Moving Plates Cons (2)
Cause earthquakes which cause tsunamis
Creates volcanoes
Moving Plates Pros (3)
Resulting volcanic ash creates fertile soil
Builds land
Cycles carbon from the asthenosphere and the lithosphere
Faults
A break in the earth’s crust
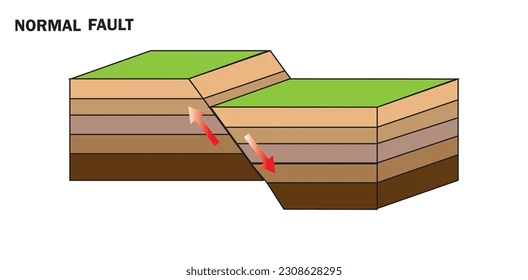
Normal Faults
The block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below
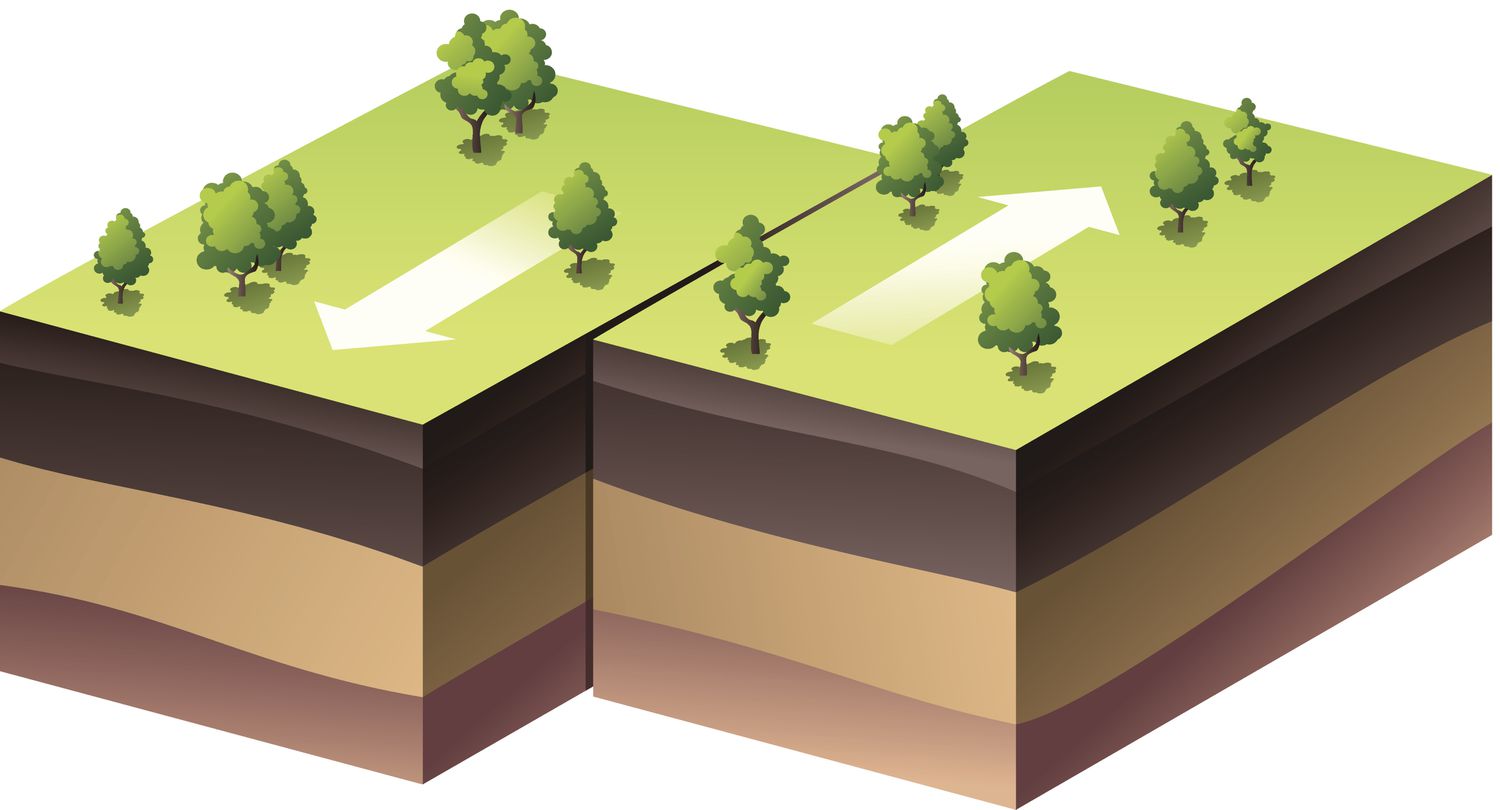
Strike-strip Faults
When tectonic plates move past each other horizontally.
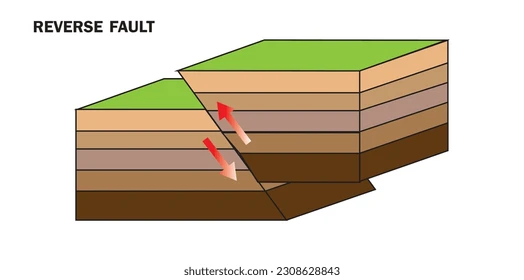
Reverse Faults
The upper block, above the fault plane, moves up and over the lower block
Overthrust Faults
A thrust fault with a low dip and large slip
a thrust fault in which the hanging wall was the one that moved (underthrust)
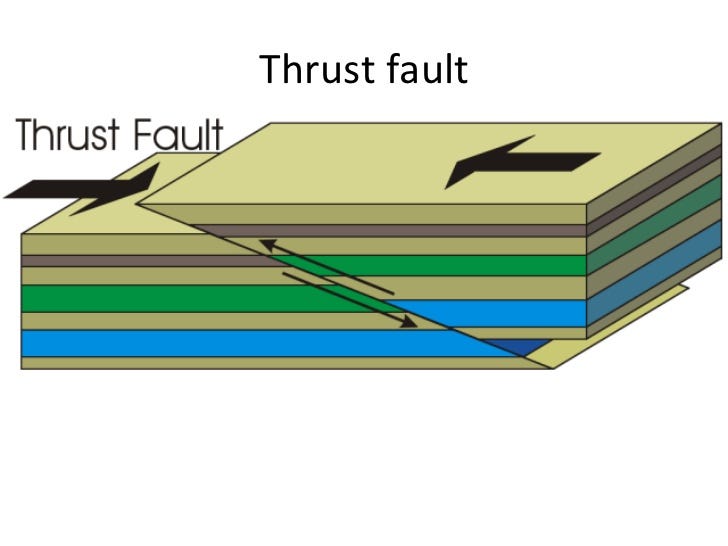
Grabens
A crustal block dropped down between two normal faults
Horst
A crustal block pushed up between two normal faults
Fault Scarps
small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved up
How can earthquakes be helpful?
Earthquake activity reveals plate boundary locations
Magnitude
The amount of energy released by an earthquake
Focus
Location where a fault slipped
Epicenter
Directly above where a fault slipped to produce an earthquake
How are epicenters calculated?
Triangulating readings from three different reading centers across the country (A, B, and C) & using the difference in travel times for P and S heat waves
Human Induced Earthquakes occurr by…(2)
Petroleum (oil) is found w/ sedimentary rocks
Drilling & fracking at shale (rock) oil fields create earthquakes
“Tsunami” translates to...
Harbor Wave
How do tsunamis form?
Underwater earthquakes.
Volcanic eruptions.
Landslides.
Asteroids
How are volcanoes formed?
Lava-Magma that spills onto the surface of Earth’s crust
Volcanic gasses include…
Water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), & hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
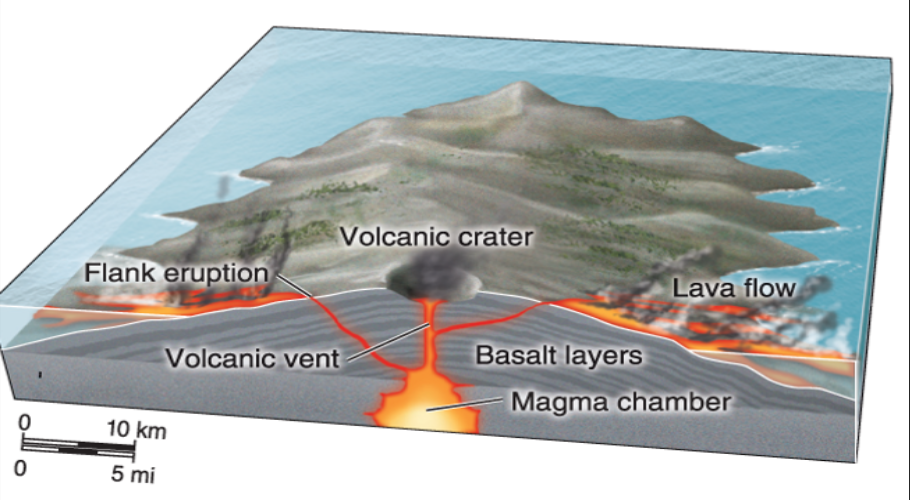
Shield Volcanoes
Broad & domed; LARGEST VOLCANOES
Built as magma travels up from the magma chamber and through the volcanic vent
Stratovolcanoes
AKA composite volcanoes; Cone shaped; Steep; Made of lava & pyroclasts
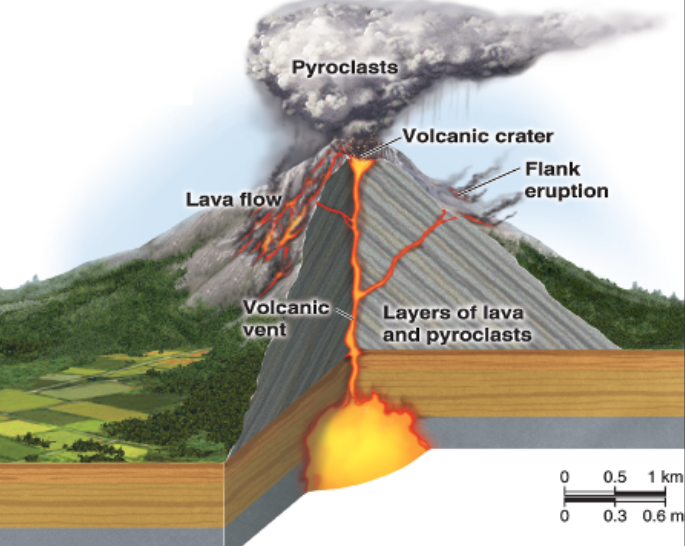
Pyroclasts
Any fragmented solid material that is ejected from a volcano
Ash
Pulvarized rock + solidifed lava
Cinder Cone
Small, cone shaped w/ pyroclasts; Symmetrical, small
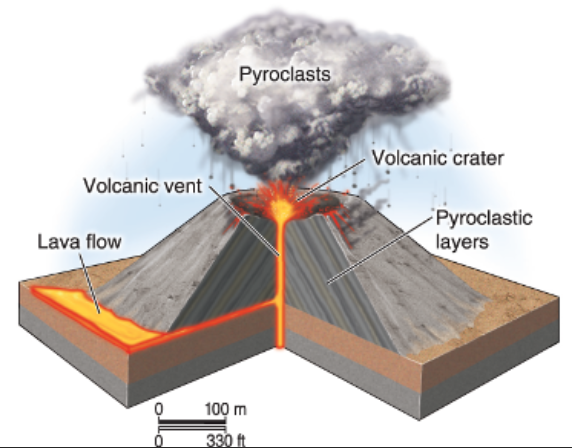
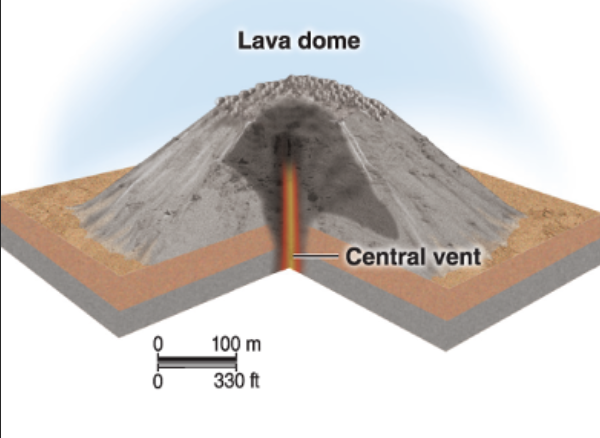
Lava Dome
Dome shaped; thick lava that piles around a volcanic vent & solidifies
REALLY small; Can form on or cap shield and stratovolcanoes
Mafic Lava (temp, vicosity, forms…)
1800-2200 degrees; low viscosity and gas content; forms basalt
Intermediate Lava (temp, vicosity, forms…)
1500-1800 degrees; intermediate viscosity & gas content; forms andesite
Felsic Lava
1200-1500 degrees; high viscosity & gas content; forms rhyolite
Mt. Vesuvius (AD 79)
Stratovolcano; rich volcanic soil good for growing grapes
Named for Herules aka Ves
What caused Mt. Vesuvius & the 3,000+ deaths thereafter
Caused by the collision of the African & European plates
Poisonous gases carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) escaped from the volcanic vent