KIN 216 Angular Kinematics
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
linear motion includes
translation, change in position, move in the same direction
angular motion includes
rotation, change orientation, spin around the same fixed axis
most movement is
a combination of linear and angular movement
a combination of linear and angular movement
general motion
angular motion occurs when
a body moves along a circular path, revolving around a central line or point
It’s also referred to as ‘rotation’
Three types of angular movements or rotations
Yaw: rotating to the left or right
Pitch: rotating up and down
Roll: tilting to the left or right
unlike translation, angular motion
keeps a fixed point called axis of rotation
types of axis of rotation
external and internal
external axis of rotation
imaginary/actual line found outside of the body. system moves in a circular path around the axis
internal axis of rotation
imaginary line found inside the body. system moves in a circular path around the axis
common reference system for human body
Anatomical position
Body is erect
Facing forward
Feet parallel to each other
Toes forward
Arms hanging below shoulders
Fingers extended
Palms facing forward
what is anatomical position used for
Standard reference position for the body to describe how it moves
e.g. if we’re lying down top of body is still head
anatomical position is
the standard reference position for the body when we describe locations, positions, or movements of the body
cardinal planes
a plane that passes through the midpoint or centre of gravity of the body
Movements occurs in a plane, and axis of rotation is perpendicular to that plane
how many cardinal planes
3
the planes are useful for
locating anatomical structures. also describing limb movements.
How do movements occur? And how does rotation occur in relation to it
Movement occurs as rotations of the limbs.
Rotations occur around an axis and within specific planes
Yaw (AOR, POM, e.g.)
●Yaw (Rotation around a Vertical Axis)
•Axis of rotation: Vertical (superior-inferior)
•Plane of motion: Transverse plane
•Example: Turning your head left or right
Pitch (AOR, POM, e.g.)
●Pitch (Rotation around a Mediolateral Axis)
•Axis of rotation: Mediolateral (left-right)
•Plane of motion: Sagittal plane
•Example: Nodding your head up and down (like saying “yes”)
roll (AOR, POM, e.g.)
●Roll (Rotation around an Anteroposterior Axis)
•Axis of rotation: Anteroposterior (front-back)
•Plane of motion: Frontal plane
•Example: Tilting your head toward your shoulder (ear moving toward the same side shoulder)
direction of axis of rotation is
perpendicular to plane of motion
Examples of movement in sagittal, frontal, transverse
Sagittal: flexion, extension
Frontal: ad/abduction
Transverse: horizontal ab/adduction
how do you identify an angle on the body
Identify 3 joint centers of rotation (instant center)
Identify the orientation of the two longitudinal segments
3 joint centers and 2 longitudinal segments will give you 1 angle
relative angle
space between the longitudinal axes of adjacent segments
ie the angle at a joint

angle formed inside joint (relative)
internal angle
angle closing the spaces
e.g. (anterior forearm is closing)
external angle
angle formed outside of joint (relative)
absolute angle
Absolute angle is the space between a body segment and a fixed line of reference usually the global x or y axis.
It is used to find the orientation of a single body segment in relation to the env.
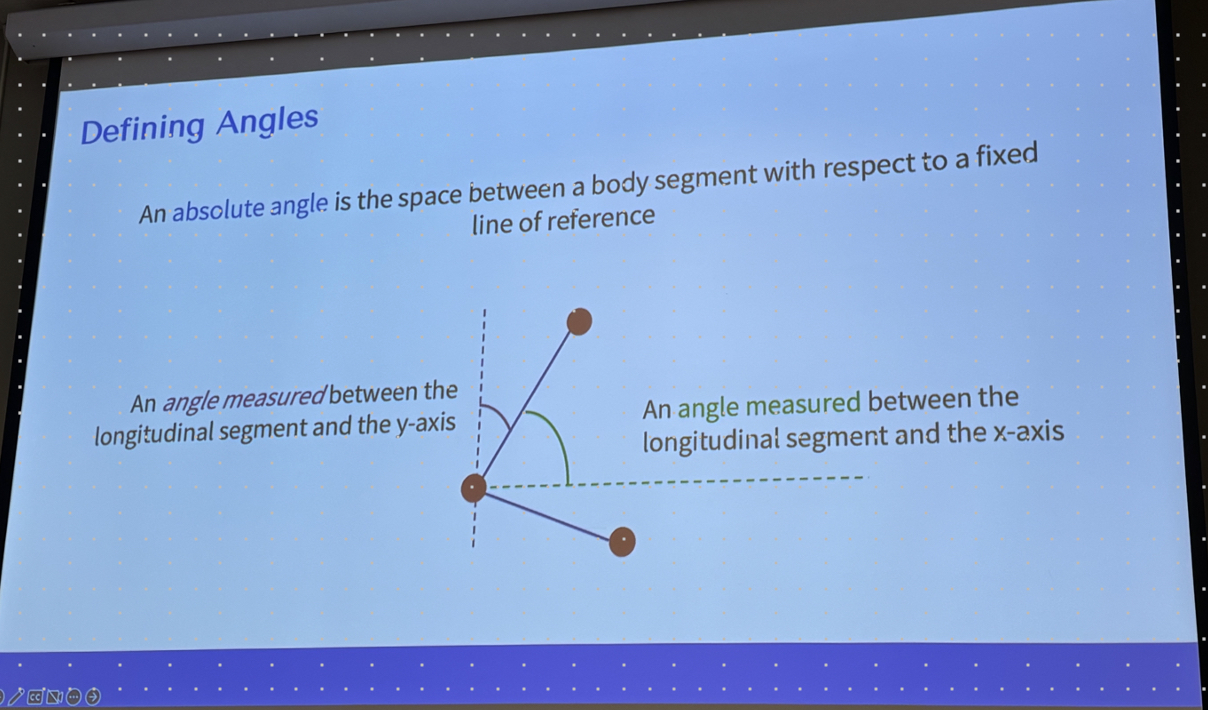
absolute angle can be between
longitudinal and x axis or longitudinal and y axis
Exam Q: which is better for measuring angles. relative or absolute
Doesn’t matter. All that matters is that the measurements are consistent
Which is better: degree or revolutions?
Better to use revolutions
what is a revolution (rev)? how many degree is 1 rev?
simple and natural measurement around a circle. 1 full turn
360 degree = 1 revolution
what is a radian (rad or unitless)
A ratio between the angle inside a circle and the length of the arc where the radius = length of the arc
It is a dimensionless, unit-less number that explores relationship between linear and angular variables
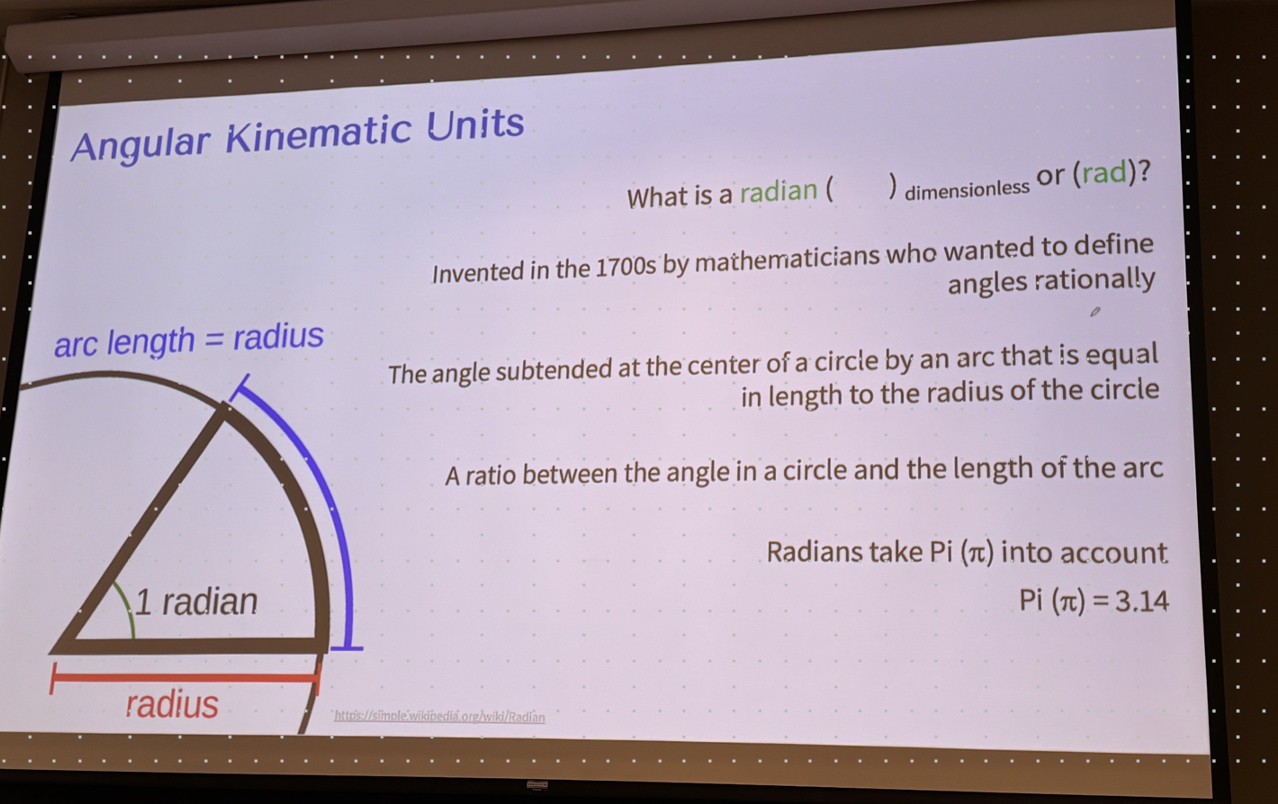
radians take ___ into account
pi (3.14)
radians is based on
when radius and arc length are equal (57.3 degrees)
1 rad = 57.3 degrees
1 revolution or 360 degrees in rad
2 pi rad
1 revolution is how many radians
2 pi rads
2 pi rad is how many degrees
360 degrees
1 radian is how many degrees
57.3
Which of the following is the standard unit of measure for angular variables when measuring human movement?
●degrees
a)Radians
●
b)Revolutions
●
c)All the above are acceptable units of measure
No standard default unit of measure for angular movement so all of the above are acceptable units of measure
●Degrees to revolutions?
●Revolutions to radians?
●Radians to degrees?
●Degrees to radians?
360° = 1 revolution
1 revolution = 2𝜋 rad
2𝜋 rad = 360°
57.3° = 1 rad
If a wheel rotates 7.25 revolutions, how many radians did it complete?
45.5 radians
what is used to measure angle
goniometer
basic goniometer (protractor)
Useful for measuring angles in pictures
Static analysis
electrogoniometer
taking measurements during movement, dynamic analysis
e.g. of electrogoniometer
strain gauge
goniometers are widely used in
physiotherapy to assess range of motion before and after intervention (tracking progress over time)
Do we know axis of rot for joints?
No, we don’t so we just estimate the axis of rot at a joint
instant center
precisely located center of rotation at a joint at a given instant in time
when analyzing human movements, how do we find the axis of rot?
we estimate the position of the axis of rotation
angular distance or displacement describes what?
describes the object's angular position or location in space
angular distance symbol
Φ = Phi
angular distance is?
what kind of quantity?
Possible UoM
the total amount of rotation
Scalar
UoM: degrees, revolutions, radians
angular displacement symbol
θ = theta
angular displacement is?
Type of quantity
UoM:
the change in angular position, change in orientation.
Vector quantity
UoM: degrees, revolutions, radians (rad)
what kind of quantity is angular displacement
vector
units of angular displacement
degree, rev, rad
angular speed is
symbol
quant type
UoM
change in angular distance over time
σ = Sigma
scalar
UoM: deg/s, rev/s, rad/s
Angular velocity is
symbol
quant type
UoM
change in angular displacement over time
ω = omega
Vector quant
UoM: deg/s, rev/s, rad/s
angular velocity is
change in angular displacement over time
the sign for angular displacement represents
direction
+ = counter clockwise
— = clockwise
the sign for angular velocity represents
direction
Describe dynamic motion
Acceleration. dynamic motions is characterized by change in angular velocity
what produces change in angular velocity
torques
Angular acceleration
angular acceleration symbol
Quant type
UoM
change in angular velocity over time
α = alpha
Vector
deg/s2 , rev/s2 , rad/s2
sign for angular acceleration represents
direction
Sign reflects direction of torque and change in angular velocity
To know if speeding up or down, we’d need to know the sign for angular velocity.
If ang vel and ang acc both same sign = speeding up
If ang vel and ang acc diff signs = slowing down
a clock's second hand angular acceleration after one revolution
0 degrees/s^2 (no displacement, no velocity, no acceleration)
angular kinematics tells us
how far you rotate, at what speed, and what state (dynamic or static)
+ sign for angular displacement and velocity means
- sign for angular displacement and velocity means
counter clockwise
clockwise
example of + direction
example of - direction
Positive sign means CCW movement.
The degree numbers get larger
From 200 to 270 degrees = +70 displacement
Negative sign means clockwise movement
The degree numbers get smaller
From 270 to 200 degrees = -70 displacement
●What do positive values tell us about direction of rotation?
●What do negative values tell us about direction of rotation?
●Pos values: rotating counterclockwise
●Those numbers as we move around circle get bigger and bigger.
●Neg values: rotating clockwise.
●Those numbers as we move around circle get smaller.
a bike spins at a rate of +2500 degrees/s^2. what does this mean
either turning counterclockwise and speeding up or turning clockwise and speeding down
object rotates at -3.5 rev/s^2. what does this mean
either rotating counterclockwise and slow down or turning clockwise and speeding up
An angular acceleration of −3.5 rev/s² indicates a clockwise torque and a negative change in angular velocity. Without knowing the angular velocity, the object could be rotating clockwise and speeding up or rotating counterclockwise and slowing down.
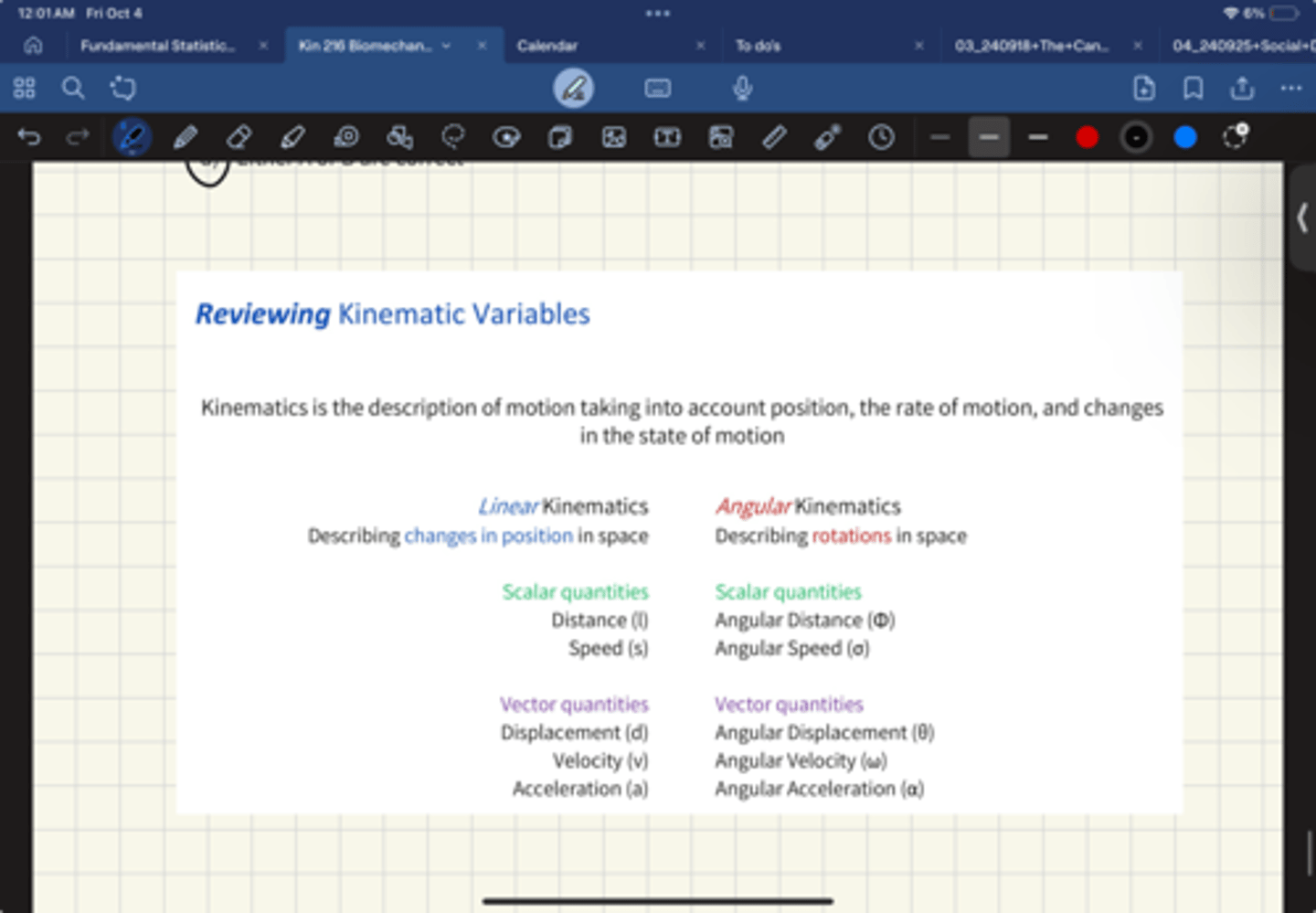
Linear Kinematics
Describing changes in position in space
Scalar quantities
Distance (l)
Speed (s)
Vector quantities
Displacement (d)
Velocity (v)
Acceleration (a
Angular kinematics
Describing rotations in space
Scalar quantities
Angular distance = Phi
Angular speed = sigma
Vector Quantities
Ang displacement = Theta
Ang Velocity = omega
Ang accerlation = alpha
key takeaways
...

Q6: what challenges exist when studying angular movements of the human body?
Axis of rot of a joint is not fixed. The longitudinal segment shifts position bc the axis migrates thus, it is hard to determine the axis of rot (the precisie origin of movement).
Instead we just estimate it because you can’t be certain of the “Instant center” of the origin of the movement
Q5: Which two Greek letters represent angular speed and velocity?
Angular speed = sigma
Angular velocity = omega
●What is the angular acceleration of the second hand on a clock after one complete revolution?
a)60°/s2
b)6°/s2
c)0°/s2
d)Need more information
No change in angular position.
No change in velocity-> no acceleration present
Answer: c)
So maybe scalar quantity is more appropriate or measuring over diff time frame to actually get smth meaningful
●If an object is rotating at -3.5 rev/s2, what is happening?
a)The object is rotating clockwise AND speeding up
b)The object is rotating counterclockwise and slowing down
c)Neither A nor B is correct
d)Either A or B are correct
Answer; d), either a or b are correct because both scenarios are possible depending on the initial direction of rotation.
Bc in absence of context, sign can reflect change in velocity or direction of rotation of the torque.
Torque produces the change in angular velocity.
It matters which direction velocity and direction of torque is going in.
Sign in acceler reflects impact on system.
So without context, you can say either
But most likely, he will give you those details and you’ll know what is happening and what the sign in the acceleration value reflects.
1. The direction of the torque applied (which influences how the object’s rotation changes).
2. The direction of the change in angular velocity (which determines whether the object speeds up or slows down).
Since angular acceleration (α) is the rate of change of angular velocity (ω), its effect depends on the initial direction of ω:
If ω and α have the same sign, the object speeds up.
If ω and α have opposite signs, the object slows down.
This dual interpretation explains why both option A (clockwise + speeding up) and option B (counterclockwise + slowing down) can be correct!
The sign on the acceleration value just means the direction of change (if neg, clockwise; if pos, counterclockwise)