Human development
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biol- L 112 IU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Fertilization
The fusion of egg and sperm cells that forms a zygote, happens in the fallopian tubes b4 implantation
Polyspermy
is the fertilization of an egg by multiple sperm cells, which can lead to abnormal development.
Prevented after the first sperm fertilizes the egg
Zygote
(Day 1-4) Ball of cells that divides after fertilization and begins the process of cleavage as it travels toward the uterus for implantation.
A stage of embryonic development
Morula
(Day 4-5) A solid ball of 16-32 cells formed from the zygote that undergoes further division before developing into a blastocyst.
A stage of embryonic development
Blastocyte
(Day 5-6) A hollow ball of cells with an inner cell mass eventually develops into the embryo and an outer layer that becomes the placenta.
Implants in the endometrium, around 100 cells
A stage of embryonic development
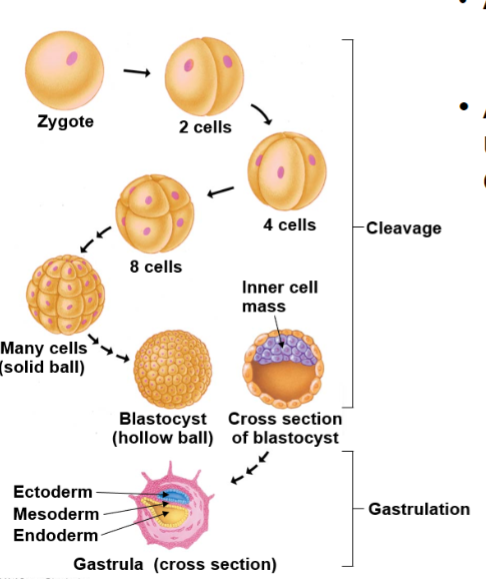
Cleavage
The series of rapid cell divisions that occur immediately following fertilization, resulting in the formation of a multicellular embryo without significant growth.
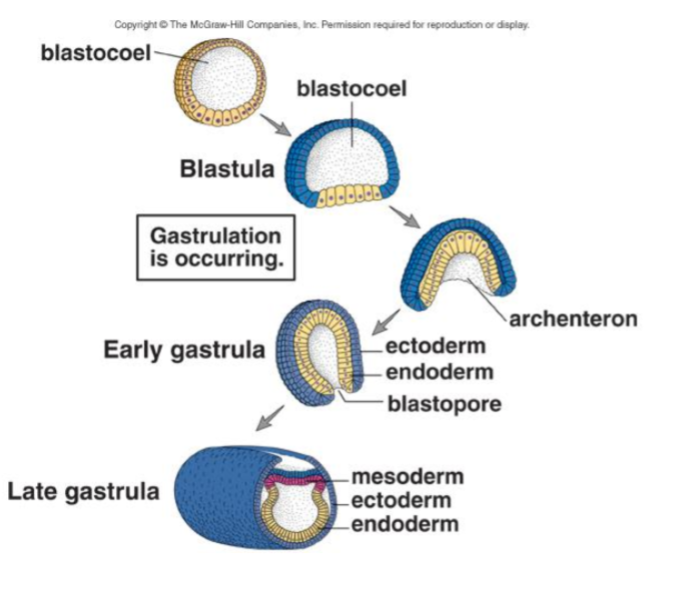
Gastrula
(forms ~ day 9) A stage of embryonic development characterized by the formation of three distinct germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which later give rise to all body tissues.
Ectoderm
(stage of gastrula) The outer layer that forms the nervous system and retinas, as well as skin and hair.
Mesoderm
(stage of gastrula) The middle layer that develops the heart, kidneys, and muscles, as well as blood and connective tissues.
Endoderm
(stage of gastrula) The inner layer that forms the lining of the digestive tract and associated organs, such as the liver and pancreas.
Embryo
from week 2 - ~ week 8
The developing human organism from the blastocyst stage until the end of the eighth week of pregnancy, during which major organs and structures begin to form.
Fetus
from week 8 until birth The developing human organism from the end of the eighth week until birth, characterized by continued growth and maturation of organs and systems.
First trimester (8-9 weeks after fertilization)
embryonic
embryo (called a fetus) has all its major organs, and its limb buds develop into tiny arms and legs with fingers and toes
genitals are rapidly developing
secondary sex determination characteristics like breast, hair, body types, and voice begin to appear. (determined by testosterone/ estrogen)
SRY
(8-9 weeks) protein on the Y gene initiates male sex differentiation
Embryos develop sperm production testies
DAX1
a gene that produces an anti-testis factor (maleness inhibitor factor) that developed ovaries and eggs.
present when SRY is absent
First trimester (week 10)
embryonic
placenta is fully formed producing estrogen and progesterone
Antibody (IgG) crosses the placenta
Second trimester
(week 13-27)
14 weeks: fetus is ~6cm (2.4 inches) long and starting to look distinctly human
20 weeks: fetus is ~19cm (7.6 inches) long and weighs roughly 1lb (half a kilogram) and has the face of an infant
Months 5-7:
12in and 3lb
Langugo - body covered by “downy hair”
kicking
eyes open
Venix caseosa - white cheesy substance
28 weeks (7 months): fetus can survive outside the womb (age of viability)
Third trimester
(week 28-40) The fetus continues to grow rapidly, gaining weight and maturing organs and systems. By the end, the fetus averages around 20 inches and 7.5 pounds, preparing for birth.
Oxytocin
A hormone produced by the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland
stimulates the smooth muscle walls in the uterus, which is important for inducing labor,
Returns the uterus to normal size
forces breast tissue to contract and forces milk to the ducts
used for the treatment of anxiety, schizophrenia, and social bonding
Low levels of Oxytocin
the cervix does not dilate during labor, C-section will be recommended
little breast milk is produced
Prostaglandins
produced by the placenta
induces labor- contraction of the uterine smooth muscles and cervical ripening. 12-16 hours of contractions getting closer, stronger, and more painful
Dilation
stage 1 of labor
Longest stage of labor, increases the opening of the cervix to 10 cm
Amniotic sac ruptures, expulsion of mucus plug, and contractions become more intense and frequent
Expulsion
stage 2 of labor
the baby is delivered through the birth canal.
Delivery
the final stage of labor
the placenta is expelled after the baby has been born.
~15 minutes after birth
Estrogen and Progesterone in lactation
contribute to the growth of mammary glands and ducts in the breast and regulate milk production after childbirth.
Secrets prolactin and oxytocin
Prolactin
a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates milk production in breastfeeding mothers.
Colostrum
the first form of milk produced by mammals after giving birth, rich in antibodies and nutrients for newborns.
Low fat, high IgA, anti-microbial factors, growth factors, protein rich
what happens when a Rh- mother has a Rh+ fetus
The mother's immune system may produce antibodies against the Rh factor, leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn in future pregnancies.