Electrical Symbols & series vs parrallel Cirtcuts and formulas
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Symbos and current, voltage, resistance in series and parallel
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Cell
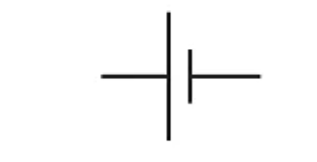
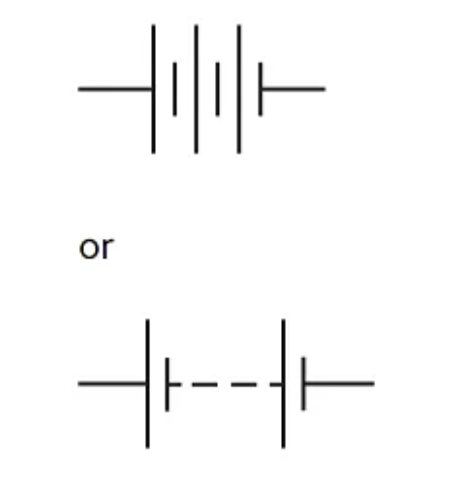
Battery of cells
Power Supply
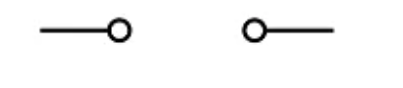
d.c Power supply
a.c power supply

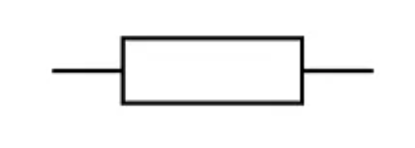
Fixed resistor
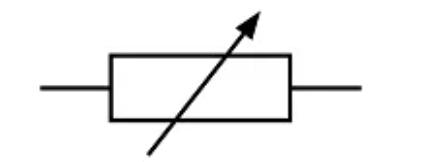
Variable Resistor
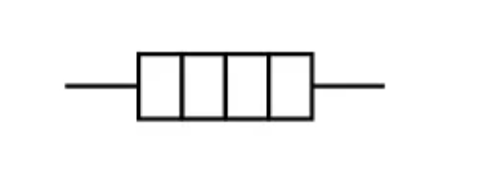
Heater
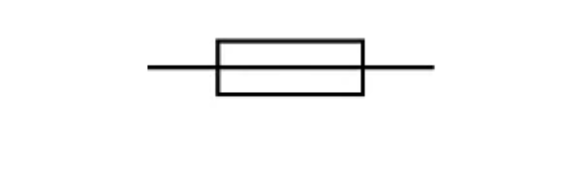
Fuse
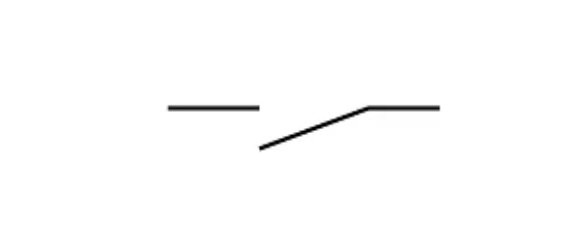
Switch
Earth or ground
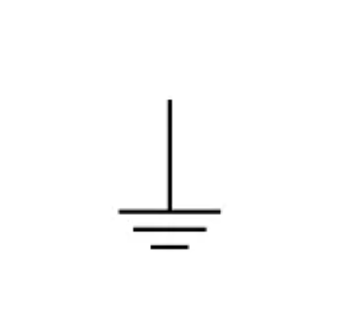
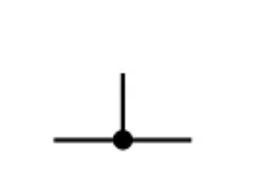
Junction or conductors
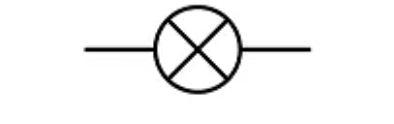
Lamp
Generator
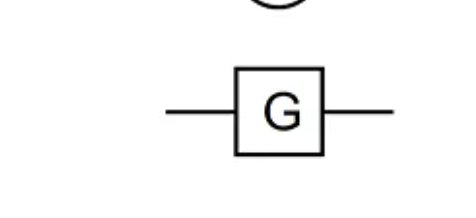
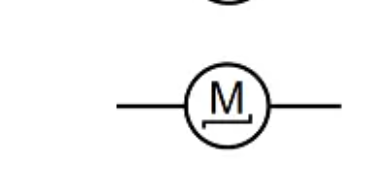
Motor
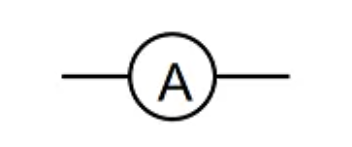
Ammeter
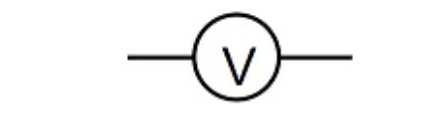
Voltmeter
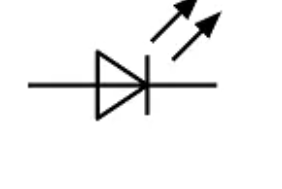
Light-emiting diode
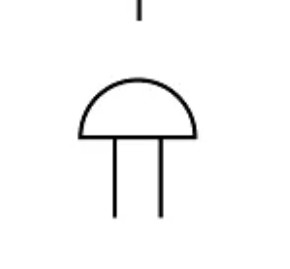
Electric bell
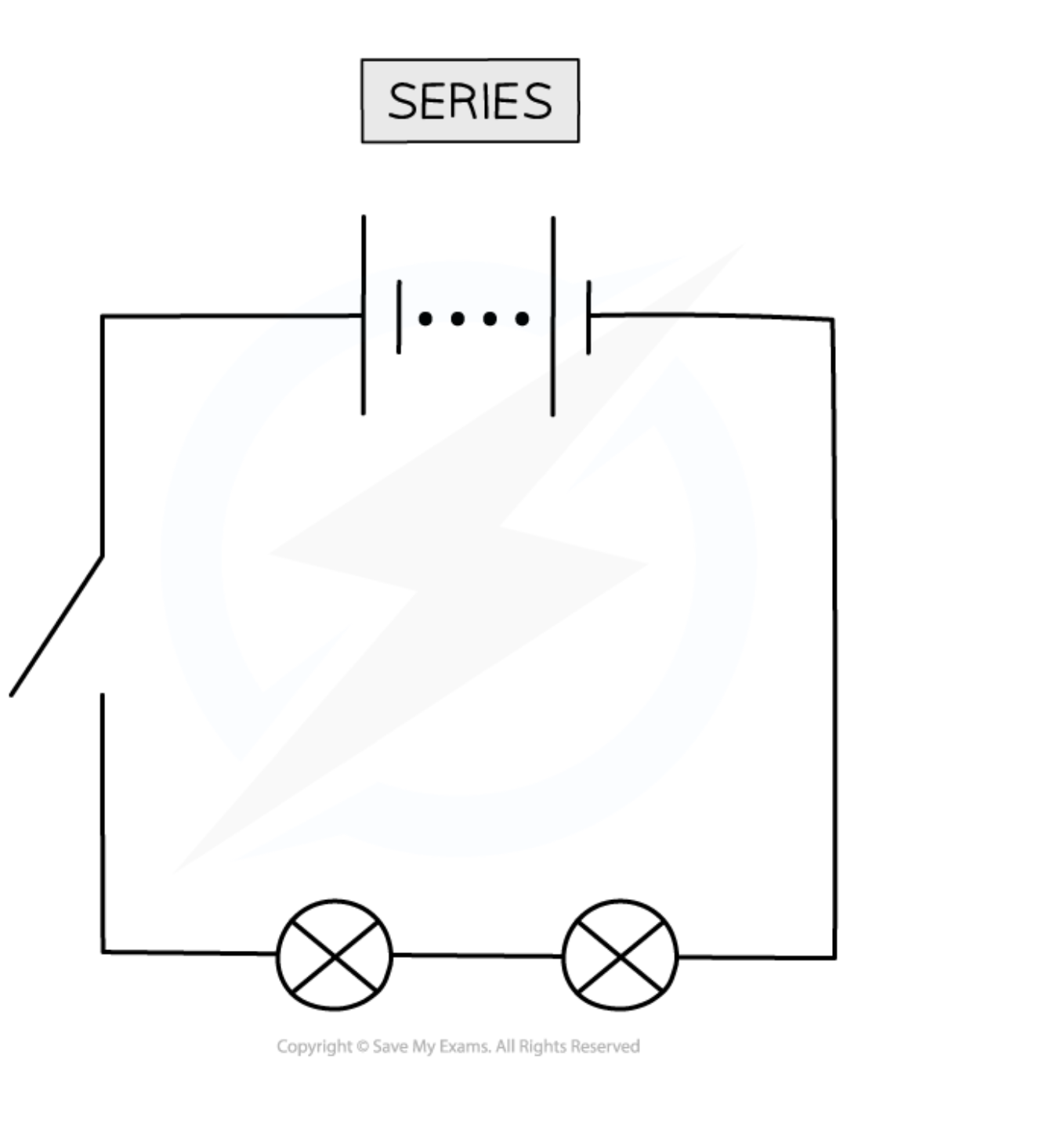
Series Circuts
A series circuit is a circuit in which components are arranged in a single path.
Current in a series circut
The current is the same through each component in a series circuit.
I=I1=I2
Resistance in a series circut
The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of all individual resistances: Rtotal= R1 + R2 +R3
Voltage in series circut
The sum of the voltage drops across each component is equal to the total voltage supplied by the source.
Vtotal=V1+V2+V3
Parallel Circuts
A parallel circuit is a circuit in which the components are arranged so that there is more than one path for the current.
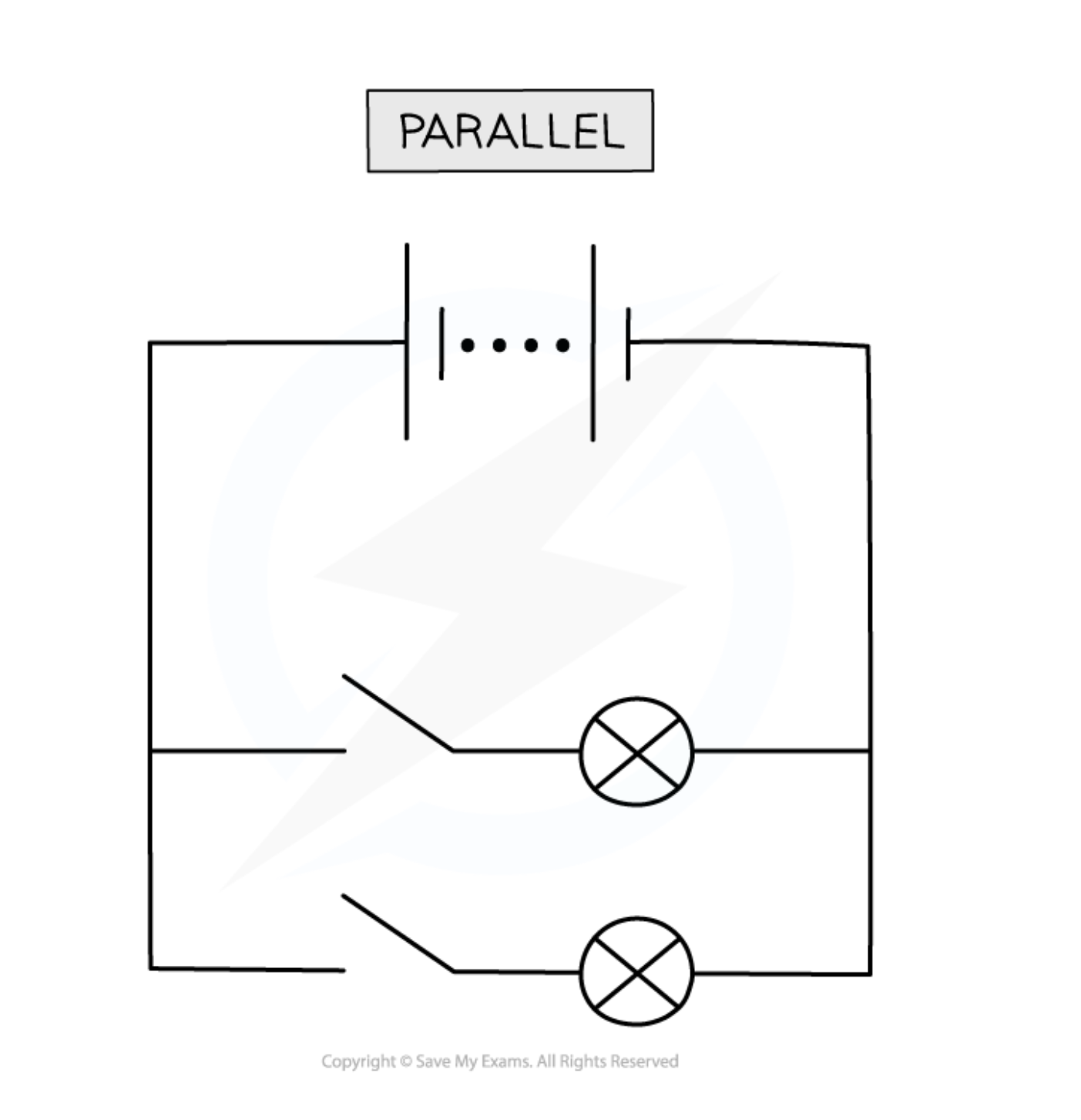
current in a parallel circuts
I=I1+I2
Resistance in a parallel circut
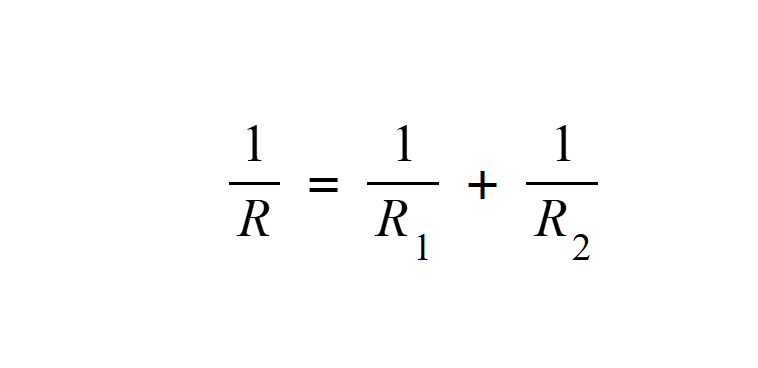
Voltage in a parrallel circut
V=V1=V2
positive + positve= repel
negative + negative= repel
Conductors: The process of electrical current flowing through a wire is called conduction
.silver
.alluminium
.graphite
Insulators: Most non-metals do not allow electrical current to flow through them easily.
rubber
plastic
.glass
a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force in an electric field.
Is meaured in coulombs (C)
d.c an electrical current that flows only in one direction
a.c= an electrical current that changes direction at regular intervals
-Current=Charge/Time
or
-I=Q/T
voltage
use a voltmeter
voltmerers are always connected in parallel
Is the electrical work done by a source in moving a unit of charge around in a complete circuit
is measured in volts
Resistance=Voltage/Current (R=V/I)
Current Voltage/Resistance
Voltage Current X Resistance (V=IxR)
power = Current x voltage (P=I x V)
power is mesaured in Watts