Unifying Concepts in Animal Structure, Function, and Homeostasis
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the relationship between anatomy and physiology?
Anatomy is the study of structure, while physiology is the study of how body structures function.
What is the initial stage of human development?
Humans start as zygotes.
How many mitotic divisions occur between the zygote and newborn stages in humans?
41 mitotic divisions result in approximately 2.2 trillion cells.
What is the significance of cell differentiation in human development?
It results in over 100 different cell types that interact to form tissues, organs, and organ systems.
List the levels of organization found in an individual human.
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ systems, Organism.
What are emergent properties in biological systems?
Emergent properties are traits that arise at a higher level of organization from the interactions of lower levels.
How does the structure of hemoglobin relate to its function?
Hemoglobin's structure allows it to effectively bind and transport oxygen in the blood.
What is an example of an emergent property of red blood cells?
The ability to transport oxygen, which is related to their biconcave shape that increases surface area.
How does a bird's wing structure facilitate flight?
Feathers provide broad shape without excess weight, and muscles are positioned to maximize power while minimizing weight.
What reflects an animal's phenotype?
An animal's phenotype reflects the observable traits that result from the relationship between structure and function.
What are the four major categories of animal tissue?
Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue, Nervous tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
To cover body surfaces, line internal organs and cavities, and act as a barrier to injury and fluid loss.
How are epithelial tissues categorized?
By the shape of surface cells (cuboidal, columnar, squamous) and the number of cell layers (simple, stratified).
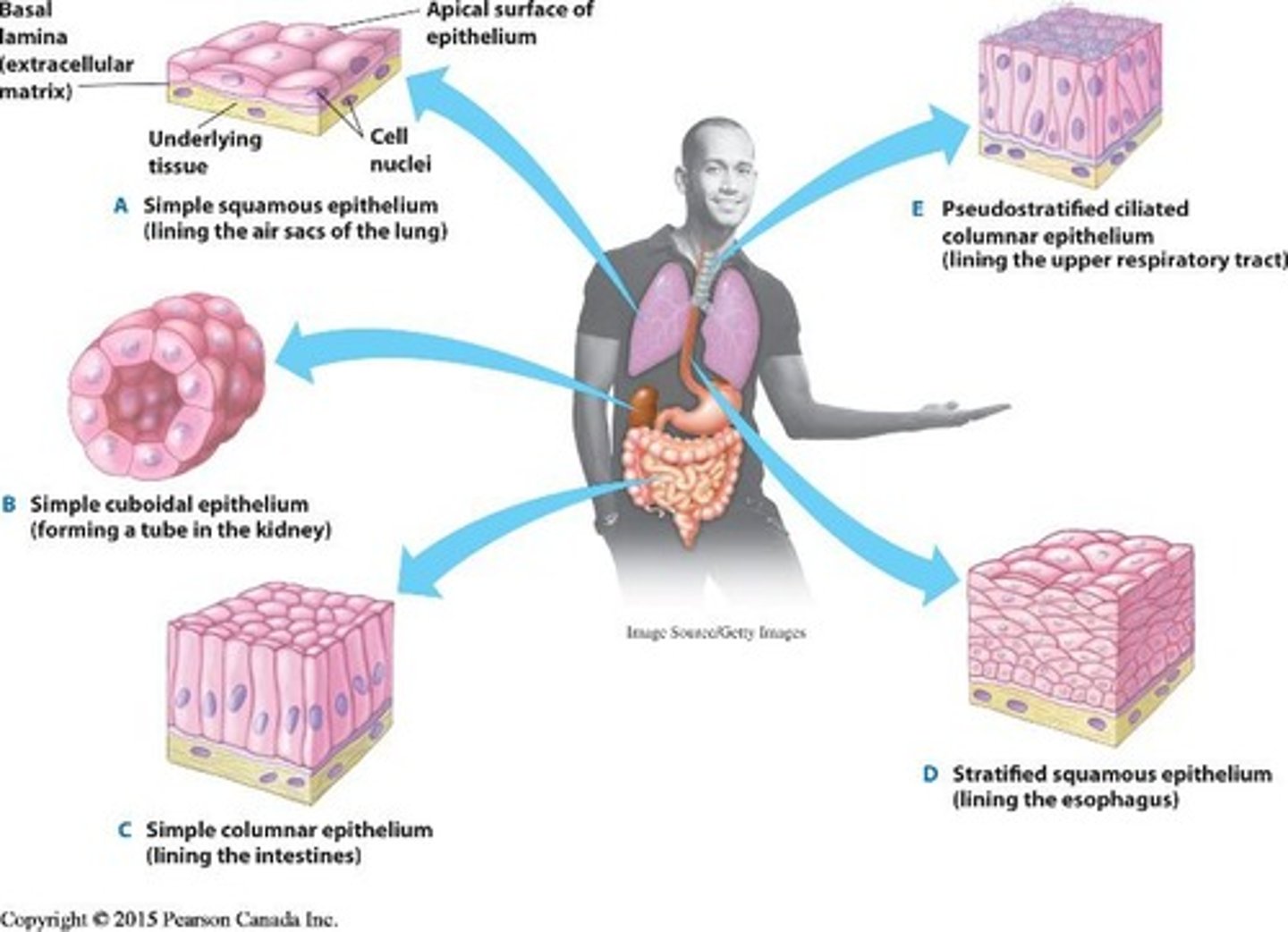
What characterizes connective tissue?
It has a sparse number of cells and an extensive extracellular matrix that provides support and connects other tissues.
What is the function of loose connective tissue?
It serves as binding and packing material that holds other tissues and organs in place.
What is the role of fibrous connective tissue?
To provide great tensile strength, found in tendons and ligaments.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
To store fat for insulation and energy reserves.
What is cartilage tissue and where is it found?
Cartilage is composed of collagen fibers in a rubbery matrix, found in joints, nose, ears, and trachea.
Why does cartilage heal poorly?
Because it is not vascularized.
What is the primary function of bone tissue?
To provide support and protection for the vertebrate body and its organs.
What components make up the matrix of bone tissue?
Collagen fibers embedded in calcium salts.
How does the combination of collagen and calcium salts affect bone?
It makes bone hard but not brittle.
Why are bones vascularized?
So they can heal rapidly.
What is the liquid extracellular matrix of blood called?
Plasma.
What are the three main cellular components of blood?
Leukocytes (white blood cells), erythrocytes (red blood cells), and platelets.
Where are blood cells produced?
In the red marrow of long bones.
What are the primary functions of muscle tissue?
Body movement, posture, respiration, constriction of organs and blood vessels, heartbeat, and body heat production.
What are the four properties of muscle tissue?
Contractility, excitability, extensibility, and elasticity.
What type of muscle is responsible for voluntary movements?
Skeletal muscle.
What is the role of cardiac muscle?
To pump blood involuntarily.
What does smooth muscle do?
Moves the walls of internal organs involuntarily.
What is the primary function of nervous tissue?
To form a communication network that senses stimuli and transmits signals.
What is a neuron?
The major cell of nervous tissue that carries signals by conducting electrical impulses.
What are the four major types of organ systems in animals?
Integumentary, muscular, skeletal, nervous, endocrine, circulatory/cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary/excretory, reproductive, and immune.
What does the integumentary system consist of?
Skin, hair, and nails.
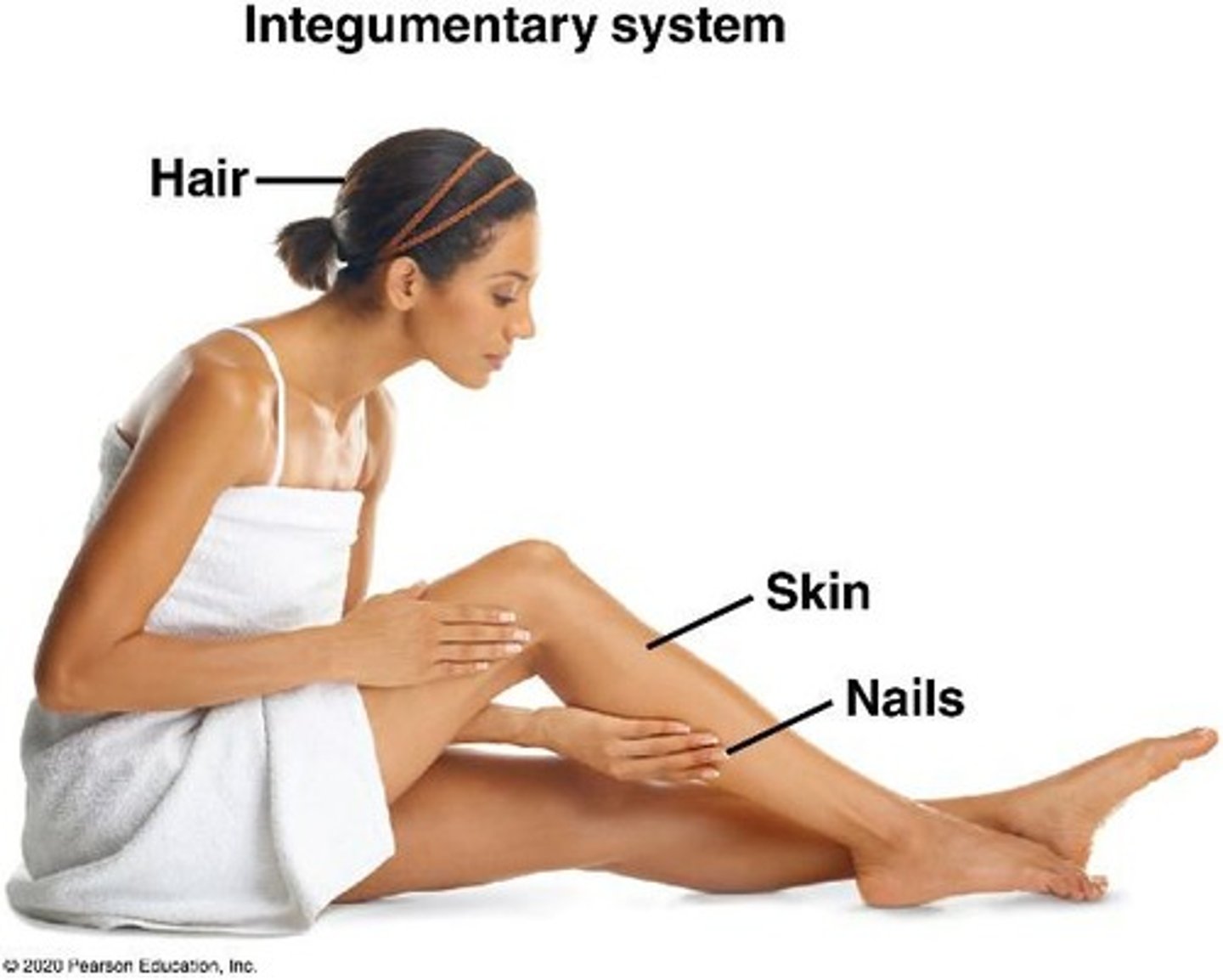
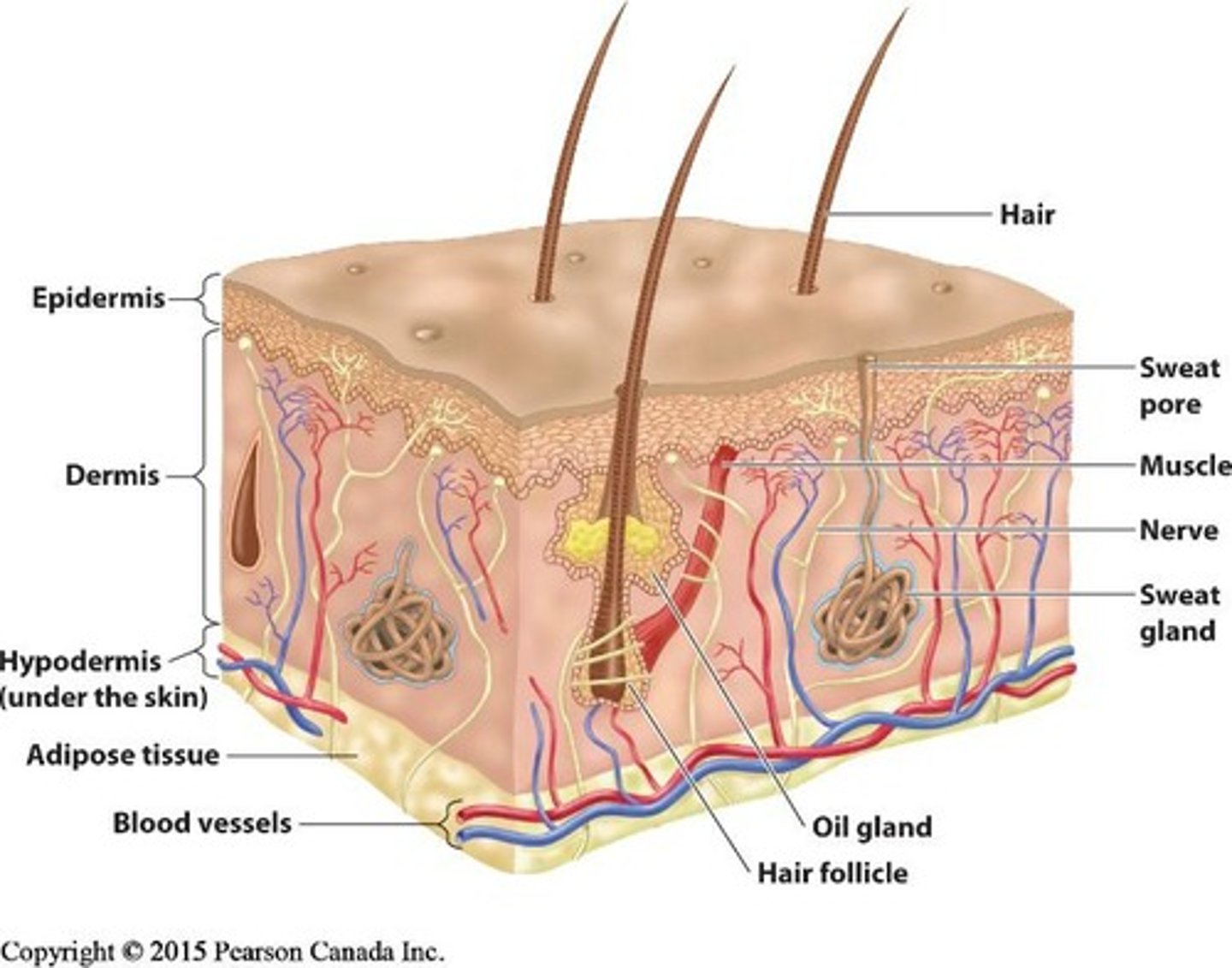
What are the layers of the skin?
Epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
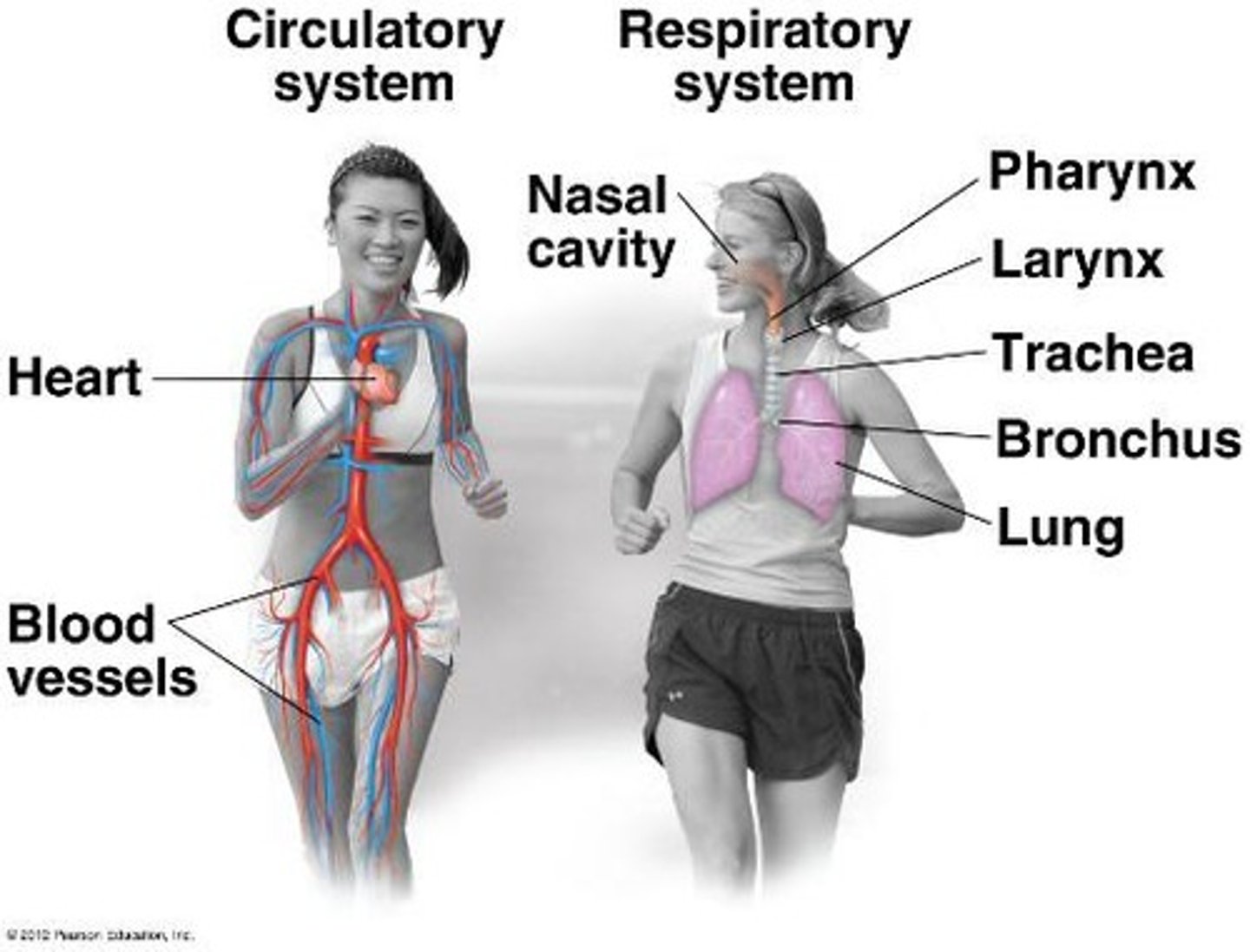
What is the function of the circulatory system?
To pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing wastes.
What is the role of the lymphatic system?
To filter body fluids and work closely with the immune system.
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
To exchange gases with the environment, supplying oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide.
What is the main function of the digestive system?
Ingestion and digestion of food, with nutrients absorbed into the bloodstream.
What do the kidneys do in the urinary system?
Remove wastes produced by cellular metabolism and regulate blood water balance.
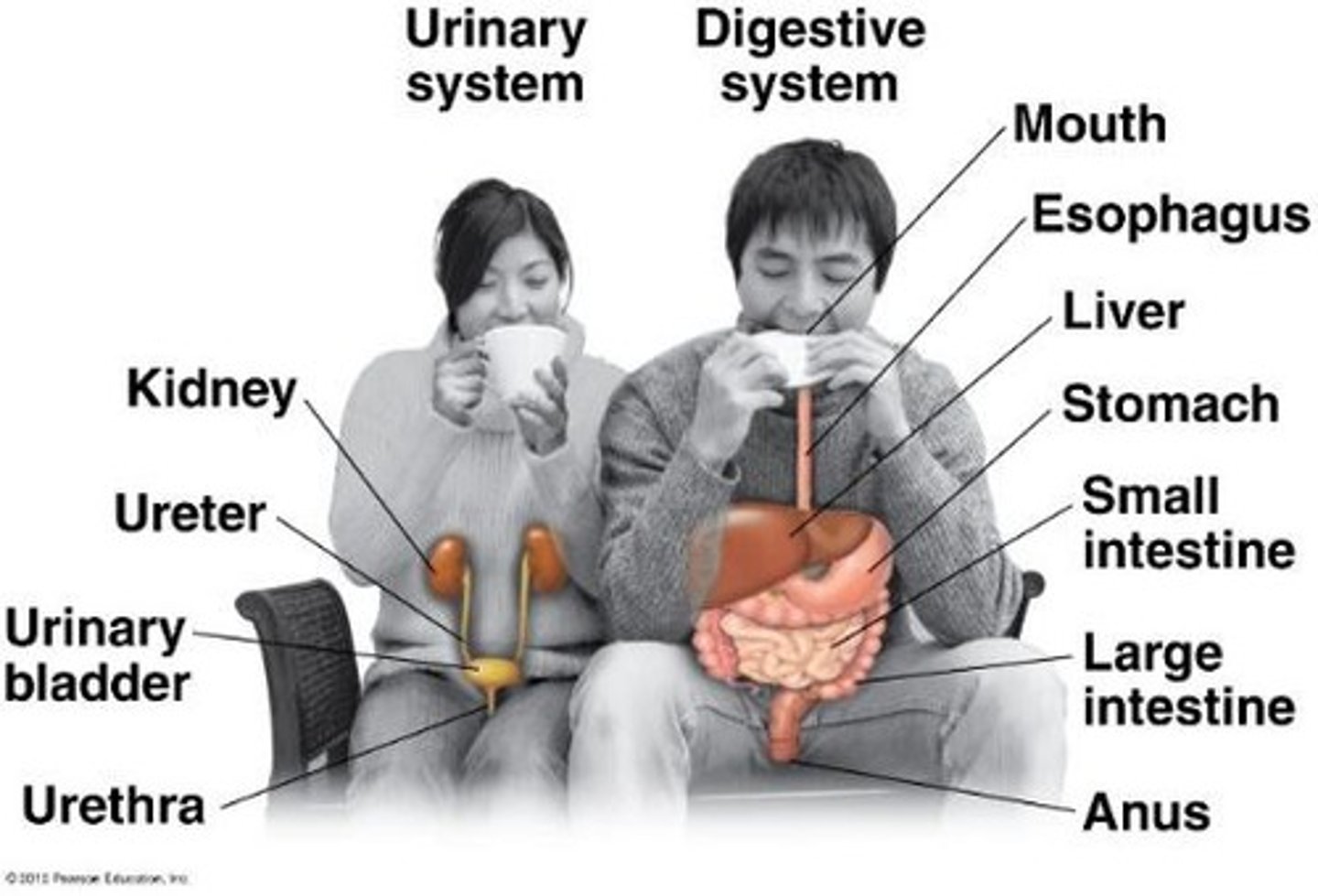
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a steady internal state despite external environmental fluctuations.
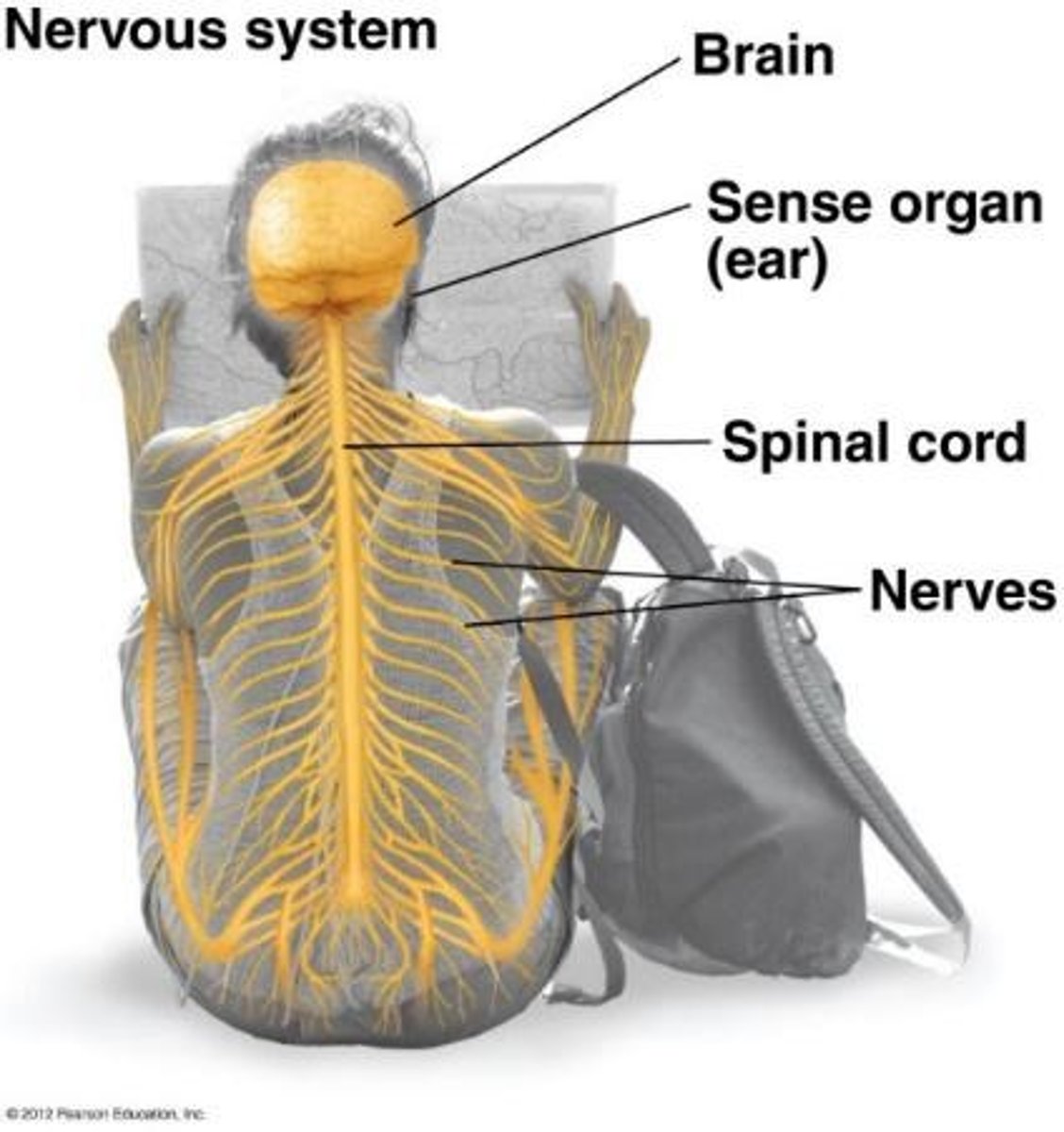
Which systems regulate homeostasis?
The nervous system and endocrine system.
What is a feedback loop in the context of homeostasis?
A mechanism that maintains homeostasis by detecting changes and initiating responses to counteract them.
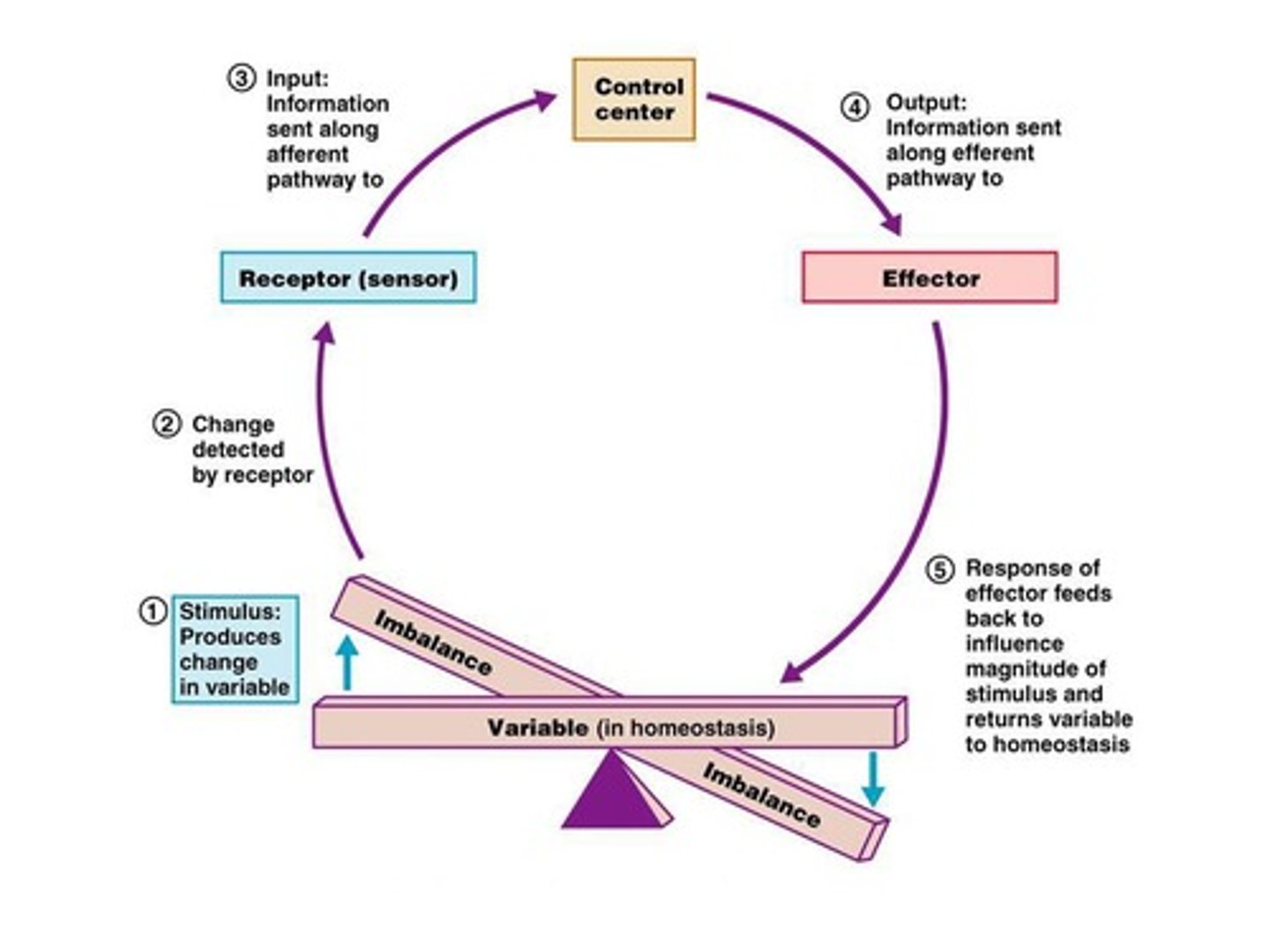
What happens when homeostasis falters?
It can lead to disease or death.
What regulates blood glucose levels?
Insulin decreases blood glucose, while glucagon increases it.
What can happen if blood glucose regulatory mechanisms fail?
High blood glucose can lead to diabetes, while low blood glucose can cause confusion or seizures.
What is the role of regulatory immune cells?
To attack foreign cells while preventing damage to the body's own healthy cells.
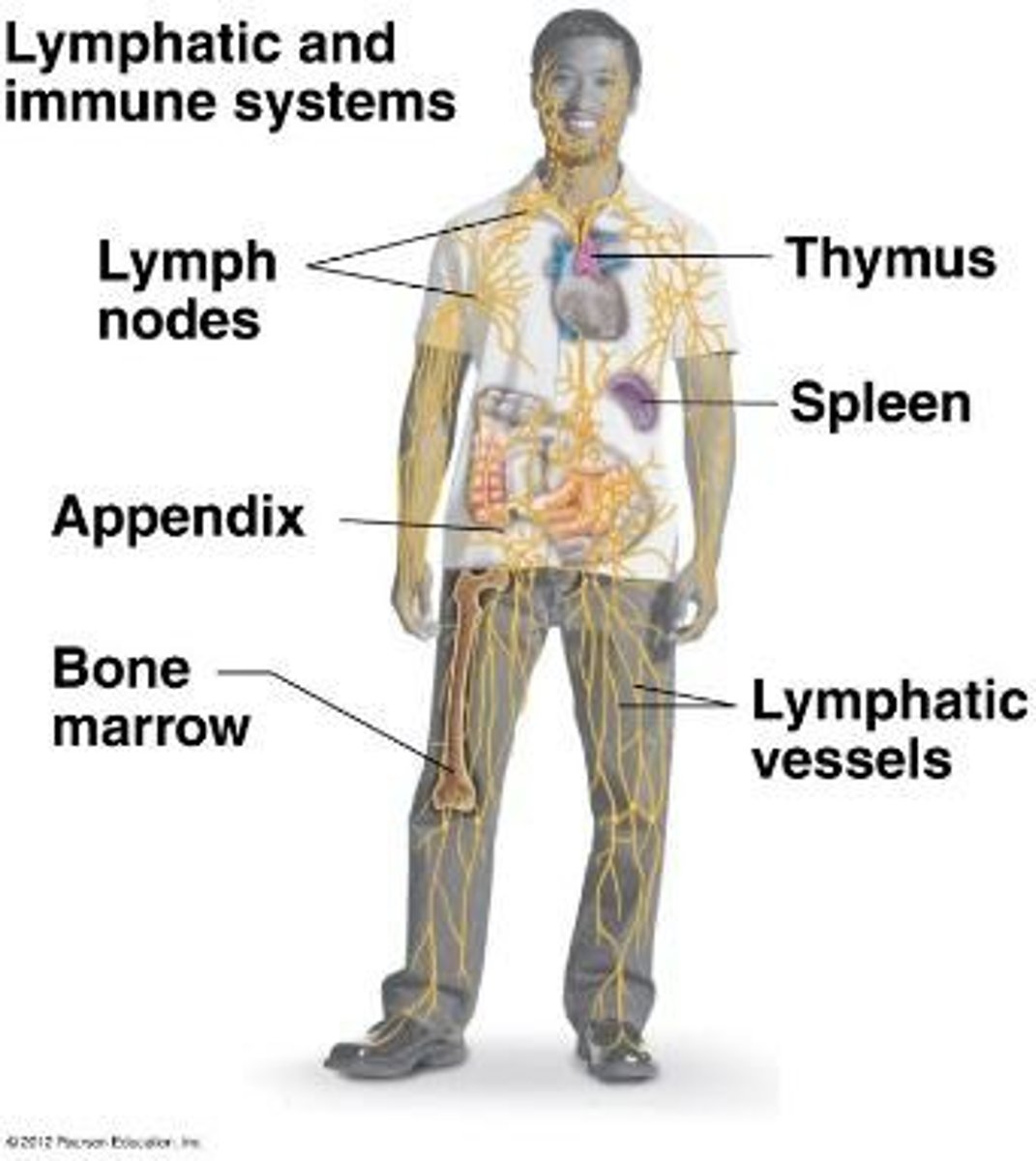
What can occur with too many regulatory immune cells?
Autoimmune diseases can develop, attacking healthy parts of the body.
What can happen with too few regulatory immune cells?
Increased susceptibility to infections.