Anatomy 1 Exams + Quizzes
1/259
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
Brachy
Which of the following root words means "short". Select all that apply.
Brady
Brachi
Brachy
Branchi
Blast
Transverse
Which plane divides the limbs and tail into proximal and distal parts?
Parasagittal
Dorsal
Transverse
Median
Medial
Plantar
Which term is used to describe the surface of the pes on which the foot pads are located?
Caudal
Plantar
Cranial
Dorsal
Palmar
Carpal, metacarpal, and digital bones
A dog presents to your clinic with a complex fracture in the manus region, and the radiographs show fractures in multiple bones. Which of the following combinations of bones could be involved in the fracture?
Carpal and metacarpal bones only
Metacarpal and digital bones only
Metatarsal and digital bones only
Tarsal, metatarsal, and digital bones
Tarsal and metatarsal bones only
Carpal, metacarpal, and digital bones
Flexion of both humeral and cubital joints
Contraction of a muscle simultaneously crossing over the caudal aspect of the gleno-humeral joint and cranial aspect of the cubital joint would result in which of the following?
Flexion of the humeral joint only
Extension of the cubital joint only
Flexion of both humeral and cubital joints
Flexion of humeral joint and extension of cubital joint
Moving the thoracic limb away from the median plane
Which of the following motions is an example of abduction?
Movement of the paw so that the palmar surface is rotated medially
Moving the thoracic limb away from the median plane
Moving the pelvic limb towards the median plane
Movement of the paw so that the plantar surface is rotated laterally
Endochondral
A long bone grows in length by which of the following ossification process?
Appositional
Endochondral
Intramembranous
Nutrient artery
Which of the following blood vessels is the largest and main source of blood supply to a healthy bone?
Epiphyseal artery
Periosteal artery
Physeal artery
Nutrient artery
Metaphysis
Which of the following is the rapid growing, flared segment of a long bone?
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Physis
Metaphysis
Apophysis
Calcaneus
Which of the following is an example for a short bone?
Calcaneus
Pubis
Patella
Metacarpal
Medial condyle
A dog presents with a fracture of the proximal end of the tibia. Which of the following is the most likely fractured?
Head
Medial condyle
Medial epicondyle
Medial malleolus
Phalanx
Which of the following terms is the least inclusive?
Digit
Phalanx
Manus
Phalanges
4th and 5th metatarsals only
Fourth tarsal bone articulates with which of the following metatarsal bones?
4th metatarsal only
1st metatarsal only
3rd and 4th metatarsals only
4th and 5th metatarsals only
2nd and 3rd metatarsals only
Supratrochlear foramen
Which of the following is present in the dog, but not present in the cat?
Supracondylar foramen
Acromion
Coracoid process
Clavicle
Supratrochlear foramen
Right and left pedicles and laminae come together to form arch
Which of the following statements is TRUE about a typical vertebra?
Thirteenth thoracic vertebra is the anticlinal vertebra.
Right and left pedicles and laminae come together to form arch
Cranial extremity of vertebral body is concave while caudal extremity is convex
Cranial and caudal costal fovea come together to form the intervertebral foramen.
3
In a typical dog, how many vertebrae fuse to form the sacrum?
4
5
3
6
Vertebral canal
The spinal cord (and associated structures) traverses (i.e. passes through) which of the following?
Vertebral canal
Lateral vertebral foramen
Alar notch
Transverse foramen
Intervertebral foramen
L5
Which of the following lumbar vertebra is the ante-penultimate vertebra?
L6
L4
L7
L5
Dolichocephalic
Which of the following types of dogs has the longest facial length?
Dolichocephalic
Mesocephalic
Brachycephalic
Palatine
Which of the following skull bones do not house a bony alveolus for teeth?
Maxilla
Incisive
Palatine
Mandible
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd~20
Which of the following represents the vertebral formula of a typical dog?
C7 T13 L6 S3 Cd~20
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd~20
C7 T13 L6 S5 Cd~20
C7 T18 L6 S5 Cd~20
C7 T14 L7 S4 Cd~20
C7
Which cervical vertebra lacks a transverse foramen in a dog?
C5
C7
C4
C6
C8
Suture, fibrous connective tissue
The joint formed between the frontal and parietal bones in the skull is best described as a __________, and the type of connective tissue that joins these skeletal elements is __________.
Gomphosis, fibrous connective tissue
Suture, fibrous connective tissue
Suture, fibrocartilage
Symphysis, fibrous connective tissue
Symphysis, fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilaginous joint
Pelvic symphysis is an example of what kind of joint?
Synovial joint
Fibrocartilaginous joint
Fibrous joint
Gomphosis, periodontal ligament
What type of joint and connective tissue should be considered when performing a tooth extraction due to periodontal disease?
Syndesmosis, periodontal ligament
Gomphosis, fibrocartilage
Symphysis, fibrocartilage
Suture, fibrous connective tissue
Gomphosis, periodontal ligament
Synovial fluid
Which component of a synovial joint serves to reduce friction between the articular cartilage and is crucial for joint lubrication?
Joint capsule
Ligaments
Synovial membrane
Bursae
Synovial fluid
Synovial membrane
In a canine patient with a suspected joint infection, which part of the synovial joint would be most susceptible to inflammation?
Joint capsule
Articular cartilage
Synovial membrane
Tendons
Ligaments
Humeroradioulnar
Which of the following joints is an example of a compound joint?
Femorotibial
All of the above are examples of a compound joint.
Glenohumeral
Humeroradioulnar
Coxofemoral
Ligament
A dense fibrous connective tissue that connects two bones is called:
Ligament
Aponeuroses
Superficial fascia
Deep fascia
Tendon
Coxofemoral joint (1)
Multiaxial movement of a bone is possible in which of the following joint types?
Femorotibial joint
Coxofemoral joint (1)
Distal interphalangeal joint
Saddle joint
In feline declawing procedures that involve the removal of the distal phalanx, which type of synovial joint is severed?
Pivot joint
Saddle joint
Ball-and-socket joint
Plane joint
Hinge joint
Ball-and-socket joint
Which type of synovial joint is most capable of allowing circumduction, a complex movement that involves a combination of flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction?
Plane joint
Ball-and-socket joint
Pivot joint
Saddle joint
Hinge joint
Subscapularis muscle
In the absence of "true" collateral ligaments, which of the following muscles helps to stabilize the gleno-humeral joint medially?
Infraspinatus muscle
Deltoideus muscle
Supraspinatus muscle
Brachialis muscle
Subscapularis muscle
Cubital joint
The flexor angles of all synovial joints in the thoracic limb are located caudally (or palmarly) except for which of the following joints?
Distal interphalangeal joint
Cubital joint
Glenohumeral joint
Metacarpophalangeal joint
Proximally with the 1st metacarpal bone
With which anatomical structure does the proximal phalanx of the first digit primarily articulate?
Proximally with the middle phalanx
Proximally with the 1st metacarpal bone
Distally with the middle phalanx
Coxofemoral joint
The flexor surface of which of these pelvic limb joints is located cranially or dorsally?
Metatarsophalangeal joint
Coxofemoral joint
Stifle joint
Distal interphalangeal joint
Cranial tibial ligament of medial meniscus
Which of the following ligaments anchor the menisci to the tibia in a genual joint?
Cranial tibial ligament of medial meniscus
Lateral collateral ligament
Meniscofemoral ligament
Cranial cruciate ligament
Meniscofemoral ligament of the stifle
Which of the following is an example of an intracapsular ligament?
Meniscofemoral ligament of the stifle
Medial glenohumeral ligament of the shoulder
Medial collateral ligament of the stifle
Lateral collateral ligament of the elbow
Cranial cruciate ligament
You diagnose a positive cranial drawer and tibial thrust test in the hindlimb of a canine patient. Which structure is most likely injured in this patient??
Caudal cruciate ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Medial collateral ligament
Cranial cruciate ligament
Tibia
The naming of the cruciate ligaments of the genual joint is based on their attachment on which of the following structures?
Menisci
Tibia
Femur
Patella
Ligament of the head of the femur
Which fibrous connective tissue structure joins the femoral head with the acetabular fossa and provides stability to the hip joint?
Transverse acetabular ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Ligament of the head of the femur
Medial collateral ligament
3 (1)
How many intracapsular ligaments of the genual joint attach to the femur? (1)
4
3
5
2
Nucleus pulposus
Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD) is a spinal disorder that results from a herniated intervertebral disc. What is the central soft gelatinous layer of this disc called?
Vertebral body
Nucleus pulposus
Anulus fibrosus
10
In how many synovial articulations is the 9th thoracic vertebra involved? (assume this is a normal dog)
8
10
6
4
12
Tubercle
Which of the following structures of the rib articulates with the transverse process of a thoracic vertebra?
Head
Shaft
Tubercle
All of the above.
What is inaccurate with the following comic?
Dogs cannot talk.
There is no ACL in the dogs.
All of the above.

Metal > Mineral > Soft Tissue > Fat > Gas
Select the correct list of radiographic opacities from MOST to LEAST opaque:
Gas > Fat > Soft Tissue > Mineral > Metal
Gas>Fat>Soft Tissue>Metal>Mineral
Fat > Gas > Soft Tissue > Mineral > Metal
Mineral > Metal > Soft Tissue > Gas > Fat
Metal > Mineral > Soft Tissue > Fat > Gas
Fat
On the radiograph below of a healthy feline patient, what opacity is highlighted by the asterisk (*)?
Soft tissue
Fat
Mineral
Gas
Metal

Summation
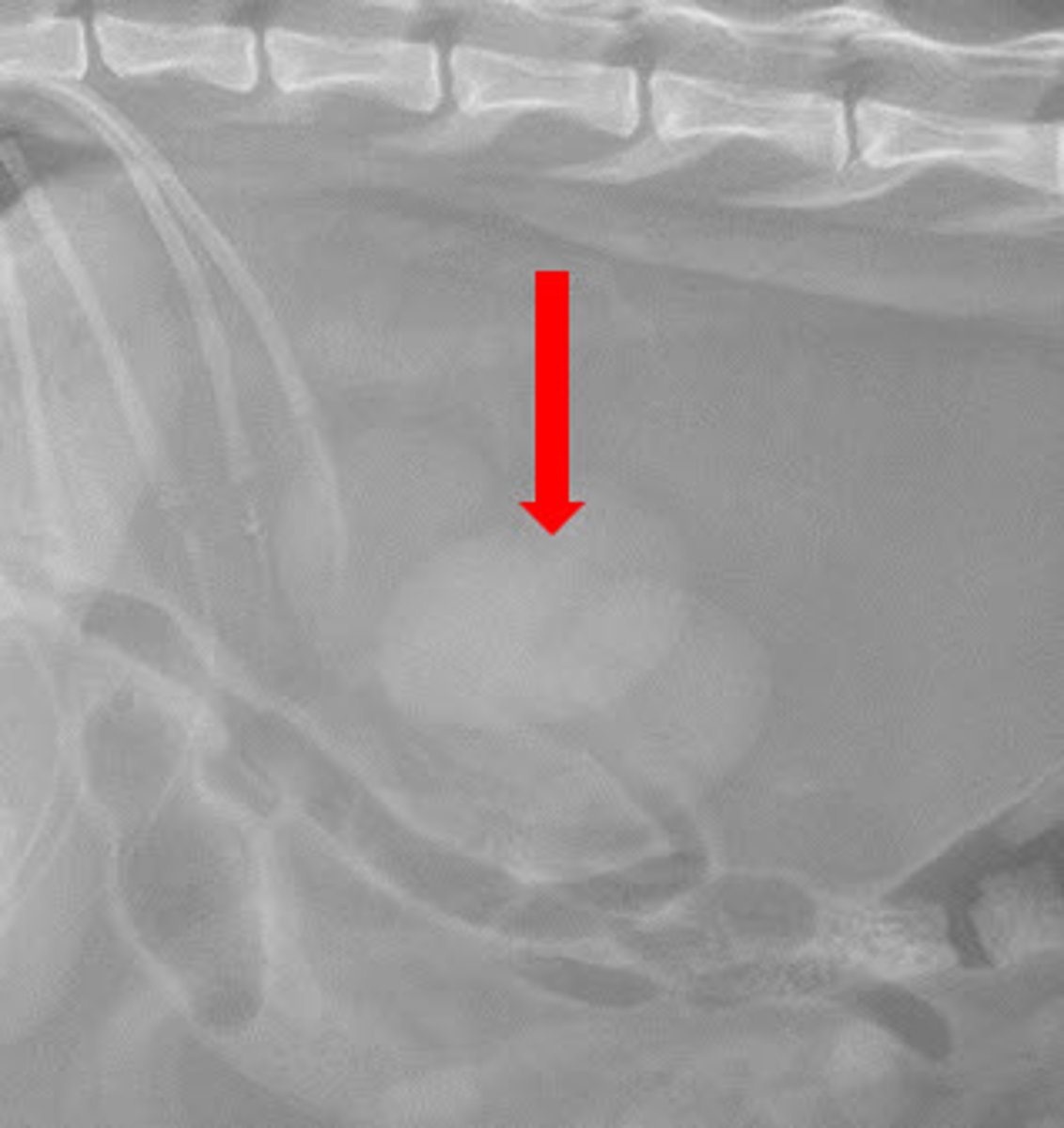
In the radiograph below what radiographic phenomenon is occurring as highlighted by the arrow, which makes the renal silhouettes look more opaque centrally?
Summation
Magnification
Superimposition
Border effacement
Right lateral
A dog is lying on its right side for a thoracic radiograph. The X-ray beam enters the left thoracic wall and exits the right thoracic wall. Which of the following is the correct radiographic position name?
Right lateral
Ventrodorsal
Dorsoventral
Left lateral
Impaired thermoregulation due to sweat gland damage
A patient presents with severe burns covering 35% of their total body surface area, including damage to the epidermis and dermis. Which of the following complications is MOST likely to occur as a result of the burn's impact on the integumentary system?
Increased production of pheromones
Impaired thermoregulation due to sweat gland damage
Enhanced protection against infections due to the exposed tissue
Decreased synthesis of Vitamin A
Dermis
A sub-cutaneous injection is typically given below which layer of the integument?
Dermis
Epidermis
Hypodermis
Caudal superficial epigastric artery
Caudal abdominal mammae in typical dog receive blood supply from which of the following blood vessel(s)?
Internal thoracic artery
Caudal superficial epigastric artery
Cranial superficial epigastric artery
Tarsal pads
Which of the following footpads are ABSENT in the dog?
Metacarpal pads
Metatarsal pads
Digital pads
Carpal pads
Tarsal pads
Left axillary l.n.
A bitch presents with mastitis localized to the left cranial abdominal mammary gland. Which lymph node (l.n.) is MOST likely to show reactive enlargement during clinical examination?
Right superficial inguinal l.n.
Right axillary l.n
Left superficial inguinal l.n
Left axillary l.n.
Thick, highly keratinized epidermis with underlying adipose cushion
A Greyhound presents with ulcerated footpads after training on rough concrete. Which feature of digital pads BEST explains their usual ability to resist such injury?
Thin epidermis with sparse keratinization
Abundant sebaceous glands secreting lubricants
Thick, highly keratinized epidermis with underlying adipose cushion
Dense distribution of vibrissae providing tactile protection
Ceruminous glands are modified sebaceous glands located in the external ear canal.
Which of the following statements about skin glands in the dog is TRUE?
Eccrine sweat glands are widely distributed across the entire body surface for thermoregulation.
Apocrine sweat glands primarily open into hair follicles and contribute to individual scent.
Sebaceous glands secrete primarily watery sweat to cool the body during exercise.
Ceruminous glands are modified sebaceous glands located in the external ear canal.
Wool hairs
Which of the following hair types form the “undercoat” in a dog?
Guard hairs
Wool hairs
Tactile hairs
Storage of information
Which of the following is NOT a function of the muscles?
Generation of body heat
Maintenance of the posture
Storage of information
Movement of the body
Diaphragm
Smooth muscle is NOT found in which of the following locations?
Diaphragm
Walls of blood vessels
Hair follicles of skin
Walls of gastrointestinal tract
Tendon
The triceps brachii attaching to the olecranon of the ulna is an example of which of the following types of muscle attachment to the bone?
Fleshy
Aponeurosis
Tendon
Epitenon
Which connective tissue layer directly surrounds the entire tendon?
Epitenon
Endotenon
Epimysium
Perimysium
Mesotendon
During dissection, you observe a tendon encased by two layers of synovial sheath. The inner visceral layer and outer parietal layer are connected by which structure that also provides vascular supply?
Retinaculum
Paratenon
Endotenon
Mesotendon
False (1)
In the limb, the origin of a muscle is always considered to be distal.
True
False (1)
Biceps brachii m.
Which of the following muscles decreases the angle of flexor surface on the cranial aspect of the thoracic limb?
Biceps brachii m.
Deltoideus m.
Triceps brachii m.
Tensor fascia latae m.
Which of the following muscles is an antagonist to the action of biceps femoris m. at the coxal joint?
Semitendinosus m.
Triceps brachii m.
Middle gluteal m.
Tensor fascia latae m.
Infraspinatus m.
An example for a bipennate type of muscle in a dog is:
Infraspinatus m.
Deep digital flexor m.
Biceps brachii m.
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates.
Which of the following best describes a motor unit in skeletal muscle?
A single muscle fiber and its surrounding capillaries.
A group of muscle fibers that contract in unison but are innervated by different motor neurons.
A single sarcomere and its associated myofibrils.
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates.
Golgi tendon organ
Which of the following sensory receptors provide feedback to the central nervous system on muscle tension?
Pacinian corpuscle
Golgi tendon organ
Muscle spindle
Middle gluteal m.
Which of the following muscles is an agonist to the action of the semitendinosus muscle at the coxal joint?
Middle gluteal m.
Quadriceps femoris m.
Iliopsoas m.
Supraspinatus m.
Which of the following muscles (including any of its heads if applicable) does NOT have a flexor action on any joint?
Ulnaris lateralis m.
Quadriceps femoris m.
Supraspinatus m.
Long digital extensor m.
None of the above
Which of the following muscles has three heads in the dog?
All of the above
Quadriceps femoris muscle
Biceps brachii muscle
None of the above
Triceps brachii muscle
Coracobrachialis m.
Which of the following muscle is a medial stabilizer of the shoulder joint?
Infraspinatus m.
Supraspinatus m.
Coracobrachialis m.
Transversospinalis muscle system
Which of the following muscle group would most likely be dissected during a laminectomy to access the spinous processes of the vertebrae?
Longissimus muscle system
Iliocostalis muscle system
Transversospinalis muscle system
Epaxial muscles lie dorsal to the transverse processes and are innervated by dorsal branches of spinal nerves.
Which of the following correctly distinguishes epaxial from hypaxial trunk muscles?
Epaxial muscles lie ventral to the transverse processes and are innervated by ventral branches of spinal nerves.
Epaxial muscles lie dorsal to the transverse processes and are innervated by dorsal branches of spinal nerves.
Hypaxial muscles lie dorsal to the transverse processes and produce lateral bending of the spine.
Hypaxial muscles lie dorsal to the transverse processes and extend the vertebral column.
Diaphragm (1)
During quiet inspiration, inspiratory muscles enlarge the thoracic cavity by rotating the ribs craniolaterally. Which muscle is primarily responsible for this action?
Serratus dorsalis caudalis
Diaphragm (1)
External abdominal oblique
Internal intercostals
4
A typical dog has how many pairs of asternal ribs?
5
3
4
1
Vagal trunks
A surgeon notes a mass compressing the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm in a dog. Which of the following structures would be most directly affected?
Sympathetic trunk
Vagal trunks
Thoracic duct
Caudal vena cava
Diaphragm
The caudal boundary of the thoracic cavity in a dog is formed by which structure?
Costal arch
Diaphragm
Manubrium
13th rib
The middle of the last rib, curving cranially to the 12th intercostal space
During thoracocentesis in a dog, the veterinarian must avoid puncturing the abdominal cavity. Which landmark corresponds to the caudal extent of the line of pleural reflection?
The cranial border of the 6th rib at the costochondral junction
The middle of the last rib, curving cranially to the 12th intercostal space
The 2nd rib at the manubrium
The costal arch formed by ribs 10–12
Thoracic cavity
The right caudal lung lobe is contained inside which of the following?
Thoracic cavity
Right pleural cavity
Pericardial cavity
Pulmonary pleura
Which of the following layers is a visceral serous membrane?
Costal pleura
None of these
Diaphragmatic pleura
All of these
Mediastinal pleura
Pulmonary pleura
Right cranial and middle
In a typical dog, cardiac notch is present between what two lobes of lungs?
Left caudal part and caudal lobe
Left cranial part and caudal part
Right cranial and middle
Right middle and caudal
Fibrous pericardium prevents significant acute distension of the pericardial cavity
A dog presents with acute cardiac tamponade following trauma. Which structural property of the pericardium explains why even a small accumulation of fluid can rapidly impair cardiac filling?
Pericardial sac communicates with pleural cavities, limiting pressure buildup
Fibrous pericardium prevents significant acute distension of the pericardial cavity
Parietal layer of the serous pericardium promotes fluid absorption
Elasticity of the visceral pericardium allows immediate expansion
Yes
Dwight Schrute from 'The Office' says, "The chest (thoracic) cavity is where the heart is." Is he correct?
No
Yes

Left ventricular free wall and interventricular septum
Occlusion of the paraconal interventricular branch in the dog would MOST directly compromise blood supply to which region of the heart?
Right atrial wall and coronary sinus
Left ventricular free wall and interventricular septum
Interatrial septum
Right ventricular outflow tract (conus arteriosus)
Intervenous tubercle
A catheter is advanced from the cranial vena cava into the right atrium of a dog. Which internal feature helps divert the incoming blood flow toward the right atrioventricular orifice?
Coronary sinus
Intervenous tubercle
Pectinate muscles
Chordae tendineae
Great cardiac vein and middle cardiac vein
A blockage at the coronary sinus would impair venous return from which vessels?
Cranial and caudal venae cavae
Pulmonary veins
Great cardiac vein and middle cardiac vein
Azygous vein and thoracic duct
Visceral serous pericardium
You are performing a partial pericardiectomy (surgical removal of a section of the “clinical” / “surgeon’s” pericardial sac) through an intercostal thoracotomy (opening the thoracic and pleural cavities through an intercostal incision) in order to extend the survival time of a dog with a heart-based tumor by creating an opening in the pericardial sac and allowing excessive fluid to drain from the pericardial cavity. Which of the following structures/layers would NOT be cut during this procedure?
Visceral serous pericardium
Costal pleura
Fibrous pericardium
Pericardial mediastinal pleura
Right ventricle from left ventricle on the right side.
Subsinuosal interventricular groove separates what two chambers of the heart?
Left atrium from right atrium on the left side.
Right ventricle from left ventricle on the right side.
Right atrium from right ventricle on the right side.
Left ventricle from left ventricle on the left side.
Outflow area of the right ventricle
The conus arteriosus is which of the following?
Inflow area of the left ventricle
Outflow area of the left ventricle
Outflow area of the right ventricle
Inflow area of the right ventricle
Aortic arch
Left subclavian artery in a typical dog is a direct branch of which of the following vessel?
Brachiocephalic trunk
Descending aorta
Aortic arch
Ascending aorta
Left ventricle
The systemic circulation of the body is dependent on the contractile force of the __________.
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Right atrium
Left side, low 5th
Mitral (left atrioventricular) valve can best be auscultated at which of the following intercostal spaces?
Right side, high 5th
Right side, low 4th
Left side, high 5th
Left side, low 5th
Opening of aortic valve
Contraction of ventricles
Closure of atrioventricular valves
During the systolic phase of a healthy dog's cardiac cycle, which of the following events are likely to occur? (Select all that apply)
Closure of aortic valve
Opening of aortic valve
Contraction of ventricles
Contraction of atria
Opening of atrioventricular valves
Closure of atrioventricular valves
Umbilical vein
Which of the following blood vessels in the fetus have the highest concentration of oxygen in the blood flowing through them?
Cranial venacava
Pulmonary vein
Umbilical artery
Umbilical vein
Aorta and pulmonary trunk
Ductus arteriosus in the fetus connects what two structures?
Umbilical artery with placenta
Aorta and pulmonary trunk
Umbilical vein and caudal venacava
Right atrium with left
Left atrium
Which heart chamber does not contribute to the margin of the cardiac silhouette on DV/VD projection?
Left auricle
Left atrium
Right atrium
Main pulmonary artery
Thymus
All of these structures are generally seen only in diseased states except:
Thymus
Caudal vena cava
Thoracic lymph nodes
Esophagus
The stomach contains gas in the body on DV projection and contains gas in the fundus and pylorus on VD projection
All of these can be used to differentiate a VD from a DV projection except:
The cardiac silhouette is usually more elongate in VD projection
In VD projection, the diaphragm may have 3 domes visible, while on DV, the diaphragm will only have one dome
Caudal lobar vessels are more conspicuous in DV projection
The stomach contains gas in the body on DV projection and contains gas in the fundus and pylorus on VD projection